
14 December 2022 | ESMA74-362-2281
Final Report
https://sherpa.esma.europa.eu/sites/
MKT/MDP/Groups/Forms/Group%20
MDP%20Document%20Set/docseth
omepage.aspx?ID=1339&FolderCTI
D=0x0120D52000F338AB8D4718AC
4980888518131BE828020300A279A
C6D96CED64DAC96DA6F4F9AE96B
&List=36f5f926-0ad5-4293-81ad-
0f20a20c29cf&RootFolder=%2Fsites
%2FMKT%2FMDP%2FGroups%2FR
TF%20Meeting%2020210506&RecSr
c=%2Fsites%2FMKT%2FMDP%2FGr
oups%2FRTF%20Meeting%2020210
506paper
Guidelines for reporting under EMIR

1

2
Table of Contents
1 Legislative references, abbreviations and definitions ...................................................... 7
2 Executive Summary ......................................................................................................10
3 Summary of feedback received to public consultation ...................................................11
3.1 General Principles ..................................................................................................11
3.1.1 Transition to reporting under the RTS and ITS on reporting ............................11
3.1.2 Determining the number of reportable derivatives ...........................................14
3.1.3 Intragroup exemption from reporting ...............................................................18
3.1.4 Allocation of responsibility for reporting ...........................................................19
3.1.5 Delegation of reporting ....................................................................................23
3.1.6 Reporting of lifecycle events ............................................................................24
3.1.7 Reporting at position level ...............................................................................31
3.1.8 Reporting of on-venue derivatives ...................................................................33
3.1.9 Timely reporting of conclusion, modification and termination of a derivative ....34
3.1.10 Mapping business events to action types and levels .......................................36
3.1.11 UTI generation ................................................................................................37
3.1.12 Determining counterparty side .........................................................................39
3.1.13 Identification of counterparties .........................................................................40
3.1.14 Procedure when a counterparty undergoes a corporate action ........................41
3.1.15 Identification and classification of products ......................................................43
3.1.16 Identification of underlying ...............................................................................45
3.1.17 Price, notional and quantity fields ....................................................................45
3.1.18 Reporting of valuations ....................................................................................47
3.1.19 Reporting of margins .......................................................................................50
3.1.20 Identification of the trading venue ....................................................................52
3.1.21 Fields related to clearing .................................................................................53
3.1.22 Fields related to confirmation ..........................................................................54
3.1.23 Fields related to settlement .............................................................................55
3.1.24 Reporting of regular payments ........................................................................55
3.1.25 Reporting of other payments ...........................................................................56
3.1.26 Dates and timestamps fields ...........................................................................57
3.1.27 Reporting of derivatives on crypto assets ........................................................57
3.1.28 Reporting of complex products ........................................................................59
3.1.29 Ensuring data quality by counterparties ...........................................................59

3
3.2 Reporting per product type .....................................................................................63
3.2.1 Reporting of IRS ..............................................................................................63
3.2.2 Reporting of swaptions ....................................................................................64
3.2.3 Reporting of other IR products ........................................................................64
3.2.4 Reporting of FX swaps and forwards ...............................................................65
3.2.5 Reporting of NDFs ..........................................................................................66
3.2.6 Reporting of CFDs ..........................................................................................66
3.2.7 Reporting of equity derivatives ........................................................................67
3.2.8 Reporting of credit derivatives .........................................................................68
3.2.9 Reporting of commodity derivatives .................................................................69
3.3 EMIR Tables of fields .............................................................................................70
3.3.1 Table 1 Counterparty data ...............................................................................70
3.3.2 Table 2 Common data .....................................................................................71
3.3.3 Table 3 Margin data ........................................................................................73
3.4 Guidelines on derivatives data management ..........................................................74
3.4.1 Trade State Report ..........................................................................................74
3.4.2 Reconciliation ..................................................................................................78
3.4.3 Data Quality feedback .....................................................................................82
3.4.4 Data access ....................................................................................................88
4 Cost-benefit analysis .....................................................................................................88
5 Advice of the Securities and Markets Stakeholders Group ............................................89
Annex: Guidelines for reporting under EMIR ........................................................................90
1 Legislative references, abbreviations and definitions .....................................................90
2 Scope ............................................................................................................................93
3 Purpose .........................................................................................................................94
4 General Principles .........................................................................................................95
4.1 Transition to reporting under the RTS and ITS on reporting ...................................95
4.2 Determining the number of reportable derivatives ..................................................96
4.2.1 Reportable products ........................................................................................96
4.2.2 Reporting obligation with regards to the parties involved in the trade ..............99
4.2.3 Reportability in specific scenarios.................................................................. 101
4.3 Intragroup exemption from reporting .................................................................... 103
4.4 Allocation of responsibility for reporting ................................................................ 108
4.4.1 General clarifications ..................................................................................... 108
4.4.2 FC trading with NFC ...................................................................................... 108

4
4.4.3 CCP .............................................................................................................. 114
4.4.4 Funds (UCITS, AIF and IORP that, in accordance with national law, does not
have legal personality)................................................................................................. 115
4.5 Delegation of reporting ......................................................................................... 117
4.6 Reporting of lifecycle events ................................................................................. 119
4.6.1 Action types .................................................................................................. 119
4.6.2 Action types and event types combinations ................................................... 122
4.6.3 Lifecycle events and use of linking IDs (Prior UTI, PTRR ID, Subsequent position
UTI) 128
4.7 Reporting at position level .................................................................................... 128
4.8 Reporting of on-venue derivatives ........................................................................ 132
4.9 Timely reporting of conclusion, modification and termination of a derivative ......... 138
4.9.1 Conclusion of a derivative ............................................................................. 138
4.9.2 Modification or correction of a derivative ....................................................... 139
4.9.3 Reporting of margin and valuation updates ................................................... 139
4.9.4 Termination of a derivative ............................................................................ 139
4.10 Mapping business events to action types and levels ............................................ 141
4.11 UTI generation ..................................................................................................... 149
4.12 Determining counterparty side .............................................................................. 153
4.13 Identification of counterparties .............................................................................. 155
4.14 Procedure when a counterparty undergoes a corporate action ............................. 157
4.15 Identification and classification of products ........................................................... 159
4.16 Identification of underlying .................................................................................... 160
4.17 Price, notional and quantity fields ......................................................................... 161
4.18 Reporting of valuations ......................................................................................... 164
4.19 Reporting of margins ............................................................................................ 168
4.20 Identification of the trading venue ......................................................................... 174
4.21 Fields related to clearing ...................................................................................... 175
4.22 Fields related to confirmation ............................................................................... 176
4.23 Fields related to settlement .................................................................................. 177
4.24 Reporting of regular payments ............................................................................. 177
4.25 Reporting of other payments ................................................................................ 178
4.26 Dates and timestamps fields ................................................................................ 179
4.27 Reporting of derivatives on crypto-assets ............................................................. 180
4.28 Reporting of complex products ............................................................................. 181

5
4.29 Ensuring data quality by counterparties ................................................................ 183
5 Reporting per product type .......................................................................................... 189
5.1 Reporting of IRS ................................................................................................... 189
5.2 Reporting of swaptions ......................................................................................... 191
5.2.1 Swaption on a fixed-to-floating IRS ............................................................... 191
5.3 Reporting of other IR products ............................................................................. 196
5.4 Reporting of FX swaps and forwards .................................................................... 197
5.4.1 FX swaps (spot-forward and forward-forward) ............................................... 197
5.4.2 Compression of the near leg of the FX swap ................................................. 204
5.4.3 FX option ....................................................................................................... 213
5.4.4 Additional considerations on the reporting of currencies ................................ 216
5.5 Reporting of NDFs................................................................................................ 216
5.5.1 NDF .............................................................................................................. 216
5.6 Reporting of CFDs................................................................................................ 218
5.6.1 CFD .............................................................................................................. 219
5.7 Reporting of equity derivatives ............................................................................. 221
5.7.1 Dividend swap ............................................................................................... 222
5.8 Reporting of credit derivatives .............................................................................. 226
5.8.1 CDS .............................................................................................................. 228
5.9 Reporting of commodity derivatives ...................................................................... 232
5.9.1 Electricity future ............................................................................................. 233
6 EMIR Tables of fields .................................................................................................. 235
6.1 Table 1 Counterparty data .................................................................................... 236
6.1.1 Cleared Option between FCs (ETD) .............................................................. 236
6.1.2 Cleared Option between FCs with voluntary delegation agreement (ETD) .... 238
6.1.3 Non-Cleared Option between FCs ................................................................. 240
6.1.4 OTC Option between NFC - and FC .............................................................. 242
6.1.5 OTC Option between NFC - and NFC + ........................................................ 243
6.1.6 OTC Contract type which requires the population of fields ‘Direction of Leg 1’ and
‘Direction of Leg 2’ between FCs ................................................................................. 245
6.2 Table 2 Common data .......................................................................................... 247
6.2.1 Reporting of action types at trade and position level...................................... 247
6.2.2 Other reportable details ................................................................................. 262
6.3 Table 3 Margin data ............................................................................................. 281
6.3.1 Reporting of margin update for a new uncollateralised derivative .................. 281

6
6.3.2 Reporting of margin for a new derivative collateralized at portfolio level ........ 282
6.3.3 Reporting of margin update at an individual transaction level for an uncleared
derivative ..................................................................................................................... 285
7 Guidelines on derivatives data management ............................................................... 288
7.1 Trade State Report ............................................................................................... 288
7.1.1 Introduction ................................................................................................... 288
7.1.2 Treatment of event date ................................................................................ 289
7.1.3 Uniqueness of derivatives and special fields ................................................. 295
7.1.4 Treatment of action type ‘Revive’. ................................................................. 296
7.1.5 Reporting with action type ‘EROR‘ and ‘REVI’ ............................................... 297
7.1.6 Inclusion in the TSR of schedule information ................................................. 298
7.1.7 Dead derivatives ........................................................................................... 299
7.2 Reconciliation ....................................................................................................... 300
7.2.1 Scope of data subject to reconciliation .......................................................... 300
7.2.2 Position-level vs trade-level reconciliation ..................................................... 300
7.2.3 Reconciliation of valuation ............................................................................. 302
7.2.4 Derivatives with two legs ............................................................................... 302
7.2.5 Reconciliation of schedule information .......................................................... 302
7.3 Data Quality feedback .......................................................................................... 303
7.3.1 Rejection feedback ........................................................................................ 303
7.3.2 Warnings feedback ....................................................................................... 308
7.3.3 Reconciliation feedback ................................................................................ 315
7.4 Data access ......................................................................................................... 319
7.4.1 Operational aspects ...................................................................................... 319
7.4.2 Template form for data access ...................................................................... 321
7.4.3 EMIR fields for data filtering .......................................................................... 326

7
1 Legislative references, abbreviations and definitions
Legislative references
EMIR
Regulation (EU) 648/2012 of the European Parliament and
Council on OTC derivatives, central counterparties and trade
repositories -European Market Infrastructures Regulation
1
SFTR
Regulation (EU) 2015/2365 of the European Parliament and
of the Council of 25 November 2015 on transparency of
securities financing transactions and of reuse and amending
Regulation (EU) No 648/2012
2
– Securities Financing
Transactions Regulation
RTS on reporting
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) No 2022/1855 of 10
June 2022 supplementing Regulation (EU) No 648/2012 of the
European Parliament and of the Council on OTC derivatives,
central counterparties and trade repositories with regard to
regulatory technical standards specifying the minimum details
of the data to be reported to trade repositories and the type of
reports to be used
3
ITS on reporting
Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) No 2022/1860 of
10 June 2022 laying down implementing technical standards for
the application of Regulation (EU) No 648/2012 of the European
Parliament and of the Council on OTC derivatives, central
counterparties and trade repositories, with regard to the
standards, formats, frequency and methods and arrangements
for reporting and repealing Implementing Regulation (EU) No
1247/2012
4
1
OJ L 201, 27.7.2012, p.1
2
OJ L 337, 23.12.2015, p.1
3
OJ L 262, 7.10.2022, p. 1
4
OJ L 262, 7.10.2022, p.68.

8
RTS on registration
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) No 150/2013 of 19
December 2012 supplementing Regulation (EU) No 648/2012
of the European Parliament and of the Council on OTC
derivatives, central counterparties and trade repositories with
regard to regulatory technical standards specifying the details
of the application for registration as a trade repository, as
amended by Commission Delegated Regulation (EU)
2019/362 of 13 December 2018
5
and by Commission
Delegated Regulation (EU) 2022/1857
6
RTS on data quality
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) No 2022/1858 of 10
June 2022 supplementing Regulation (EU) No 648/2012 of the
European Parliament and of the Council on OTC derivatives,
central counterparties and trade repositories, with regard to
regulatory technical standards specifying the procedures for
the reconciliation of data between trade repositories and the
procedures to be applied by the trade repository to verify the
compliance by the reporting counterparty or submitting entity
with the reporting requirements and to verify the completeness
and correctness of the data reported
7
.
RTS on data access
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) No 151/2013 of 19
December 2012 supplementing Regulation (EU) No
648/2012 of the European Parliament and of the Council on
OTC derivatives, central counterparties and trade
repositories, with regard to regulatory technical standards
specifying the data to be published and made available by
trade repositories and operational standards for aggregating,
comparing and accessing the data, as amended by
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2017/1800 and by
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2019/361, as
amended by the Commission Delegated Regulation (EU)
2022/1856
8
.
5
OJ L 52, 23.2.2013, p. 25
6
OJ L 262, 7.10.2022, p.41
7
OJ L 262, 7.10.2022, p.46.
8
OJ L 262, 7.10.2022, p.34.

9
RTS on organisation
requirements
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2017/565 of 25 April
2016 supplementing Directive 2014/65/EU of the European
Parliament and of the Council as regards organisational
requirements and operating conditions for investment firms
and defined terms for the purposes of that Directive
Abbreviations
CFI code Classification of Financial Instruments code
CM Clearing Member
CCP Central Counterparty
CP Consultation paper on Guidelines on Reporting under EMIR
CP on RTS/ITS Consultation paper on the technical standards on reporting, data
quality, data access and registration of TRs under EMIR REFIT
9
FR on RTS/ITS Final report on the technical standards on reporting, data quality,
data access and registration of TRs under EMIR REFIT
10
CPMI Committee on Payments and Market Infrastructures
EC European Commission
ECB European Central Bank
EEA European Economic Area
ERR Entity responsible for reporting
ESCB European System of Central Banks
ESMA European Securities and Markets Authority
9
https://www.esma.europa.eu/sites/default/files/library/esma74-362-
47_cp_on_the_ts_on_reporting_data_quality_data_access_and_registration_of_trs_under_emir_refit.pdf
10
https://www.esma.europa.eu/sites/default/files/library/esma74-362-
824_fr_on_the_ts_on_reporting_data_quality_data_access_and_registration_of_trs_under_emir_refit_0.pdf

10
EU European Union
FIRDS Financial Instruments Reference Data System
FSB Financial Stability Board
IOSCO International Organisation of Securities Commissions
ISIN International Securities Identification Number
ISO International Organization for Standardization
ITS Implementing Technical Standards
LEI Legal entity identifier
MIC Market identifier code
NCA National Competent Authority
OJ The Official Journal of the European Union
OTC Over-the-counter
Q&A Questions and Answers
RSE Report submitting entity
RTS Regulatory Technical Standards
SWIFT Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication
TR Trade repository
UTI Unique Transaction Identifier
XML Extensible Mark-up Language
XSD XML Schema Definition
2 Executive Summary
Reasons for publication
This Final report on Guidelines on reporting under EMIR REFIT contains the assessment of
the feedback received from stakeholders on key elements of ESMA Guidelines on reporting
under EMIR REFIT. The Guidelines provide clarification regarding the compliance with the

11
EMIR technical standards and ensure the consistent implementation of the revised rules on
reporting under EMIR.
Contents
The Final report is split into different sections. The sections contain a brief explanation of the
proposals in the consultation paper and the assessment of the feedback that is taken on board
and the one that is not taken on board together with the reasons for it. Section 3.1 contains the
assessment of the feedback to the general principles that apply to derivatives reporting,
including how the derivatives reports should be constructed as well as in what circumstances
and how many derivatives reports should be sent. In particular, this section discusses the
feedback relating to the transitional provisions, number of reportable derivatives, exemptions
from reporting, allocation of responsibility for reporting and delegation of reporting, reporting
of lifecycle events, the timeliness of reporting, population of different sections of fields in the
reports, reporting of complex products and ensuring data quality by the counterparties. Section
3.2 refers to the feedback on the reporting of specific types of derivatives, whereas section 3.3
summarises the feedback on the use cases relating to the population of the tables of fields to
be reported under EMIR, explaining how the relevant fields for particular topics should be
reported. For each example in the Guidelines there is a corresponding table of relevant fields
and the expected XML-text rendering. Section 3.4 details the assessment of the feedback on
the clarifications relating to the data management, including the constructions of the Trade
State Report by TRs, reconciliation of derivatives, data quality feedback to be provided by the
TRs and rules on granting authorities’ access to data. Finally, section 4 contains the cost-
benefit analysis of the proposals that are included in the Guidelines and section 5 refers to the
request for advice of the Securities and Markets Stakeholders Group.
Next Steps
ESMA will publish the final report and the Guidelines on the ESMA’s website.
3 Summary of feedback received to public consultation
3.1 General Principles
3.1.1 Transition to reporting under the RTS and ITS on reporting
Q1: Are there any other clarifications that should be provided with regards to the
transition to reporting under the revised technical standards?
1. In the Consultation Paper on the Guidelines (CP), ESMA clarified the aspects
concerning the transition to reporting according to the revised RTS and ITS on
reporting.
2. The approach proposed in the CP has been broadly supported, however several
respondents asked for additional explanations.
3. In the CP ESMA explained how the counterparties should update all their
outstanding derivatives both at a trade and at a position level in the course of the

12
transition period, and the relevant action types that should be used. ESMA also
clarified that the transition period does not impact in any way the obligation under
Article 9 of EMIR to report the relevant events by T+1 and that all the reports
submitted after the start of reporting under the revised technical standards will have
to comply with the amended requirements.
4. One respondent expressed concerns over the ability of NFC- to comply with the
revised rules and suggested to extend the 180 days transition period to lifecycle
events on bilateral OTC transactions between NFCs-. With reference to this point,
ESMA would like to clarify that the length of the implementation period and of the
transition period has already been specified in the Final Report on the RTS and ITS
on reporting (FR on RTS/ITS) where input from the consultation on the standards
was taken into consideration.
5. One respondent asked what actions a TR should take for trades that are not
updated at the end of the transition period. In this respect, ESMA will be monitoring
the situation during the transition period and may suggest any actions deemed
necessary. However, the expectation is that all counterparties comply with the 180-
day deadline.
6. One respondent recommended to specifically mention that backlogging of
terminated trades is not expected under the new reporting standards. ESMA does
not expect entities to update and re-report the terminated trades; this is of course
without prejudice to send modifications, corrections, etc for past dates, where
relevant. ESMA has clarified this aspect in the Guidelines.
7. One respondent made reference to the paragraph in the CP where ESMA clarifies
that “In the case where a derivative has two or more legs […] all legs of the contract
should be reported in one report, where the combination of fields allows for this”
and inquired whether ESMA expects that the existing trades are to be closed, and
a new single report sent during the transition period. For the avoidance of any
doubt, there is no need to submit any update if the derivatives were reported
correctly. As a matter of fact, the requirement to include the details and information
of derivatives within a single report has already been enshrined in the previous RTS
on reporting
11
.
8. One respondent asked what happens in case trades are required to be ported but
they are not updated to the new RTS on reporting, during and after the transition
period. ESMA expects Trade Repositories to continue applying the Guidelines on
transfer of data between TRs after the entry into force of the revised standards.
According to the Guidelines, prior to the data transfer TRs should ensure that TR
participants upgrade the outstanding derivatives that are subject to data transfer to
the most up to date reporting requirement. ESMA will be monitoring the situation
during and at the end of the transition period and will suggest any actions deemed
necessary.
9. In the CP, ESMA clarified that TRs should include all outstanding derivatives in the
reconciliation process, irrespective of whether they have been updated or not.
11
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2017/104

13
Several queries were submitted regarding the reconciliation process. One
respondent asked if trades not updated to the latest RTS on reporting should be
part of the reconciliation process after the transition period. Two respondents
suggested an ease period on reconciliation for the transition period. One responded
suggested that during the transition period only new fields would be subject to
reconciliation. One respondent suggested to require TRs to temporarily suspend,
for the transition period the transmission of the reconciliation breaks’ notifications
for the outstanding contracts (not for the new contracts), to avoid production of
inflated statistics on reconciliation breaks.
10. For the avoidance of any doubt, TRs should include all derivatives in the
reconciliation process as of the reporting start date irrespective of whether they
have been updated or not. As already clarified in the FR on RTS/ITS, a different
reconciliation process for the transition period would create additional
implementation efforts. It is recognised that there will be reconciliation breaks and
reconciliation may be hampered in this period due to counterparties updating the
derivatives at different points in time, but the long-term benefits out-weigh this
temporary risk. It is expected that the fields required under the revised technical
standards are subject to reconciliation as specified in the Annex to the RTS on data
quality; however fields that were reported in the past but are no longer required
under the revised technical standards will not be reconciled. For the sake of clarity,
also fields that have been amended in the RTS and ITS on reporting should be
subject to reconciliation as specified in the Annex to the RTS on data quality.
11. In the CP, ESMA clarified that the counterparties should not create a new UTI for
outstanding derivatives, even if the original UTI is not fully compliant with e.g. new
format requirements under the revised technical standards. Similarly, the TRs
should follow the validation rules in this regard and should not reject reports due to
UTIs that are not fully compliant with the new requirements for those derivatives
that were concluded before the reporting start date of the revised technical
standards.
12. With reference to the fact that counterparties should not create a new UTI for
outstanding derivatives in order to comply with the revised format requirements for
the UTI, two respondents asked if this refers also to field 2.3 ‘Prior UTI’ and field
2.4 ‘Subsequent position UTI’. ESMA confirms that for both fields the counterparties
should not create a new UTI for outstanding derivatives but rather to report the UTIs
that already were generated.
13. One respondent asked if for outstanding trades the client code should be updated
to the new requirements during the transition period. As any other update to
outstanding derivatives – except for UTI – also updates to the client code should
occur before the end of the transition period.
14. In the CP, ESMA clarified that during the transition period the TRs should provide
the Trade State Report to the authorities using a relaxed version of that XML
schema (i.e. a version with fewer restrictions and validations) which accommodates
for the non-updated derivatives. One respondent asked if the concept of relaxed
XML schemas during the transition period could be adopted also by TR participants.
The XML schema should be relaxed (to accommodate for non-updated derivatives

14
and legacy trades) for the Trade State Report provided by the TRs both to
authorities and reporting entities. For the avoidance of doubt, the reporting entities
will need to report to the TRs using the restricted schema with a view to ensure high
quality of the data reported to the TRs and compliance with the revised standards.
15. Finally, one respondent asked if it is possible to start reporting in line with the new
standards before the deadline in order to facilitate the transition to the new
standards. The date of application of the revised standard is set in the RTS on
reporting; until that date the previous technical standards apply.
3.1.2 Determining the number of reportable derivatives
3.1.2.1 Reportable products
16. ESMA provided in the CP some additional clarifications on the reportability of
contracts based on the definition of derivative contract under Article 2(5) of EMIR
which relates to the Section C of the Annex I to MiFID. Specific consultation was
carried out on various types of derivative contracts.
Currency derivatives
Q2: Are there any additional aspects to be considered with regards to the eligibility to
reporting of currency derivatives?
Q3: Are there any aspects to be clarified with regards to the rest of contract types of
currency derivatives? Please provide the relevant examples.
17. Some respondents welcomed the proposed clarifications while other expected
some additional clarifications.
18. A respondent requested a clarification on the situation of banking holidays for the
T+2 rule. The RTS on organisational requirements for investment firms refers to 2
trading days. Therefore, it is ESMA’s understanding that banking holidays are to be
taken into account as these are in general not trading days in the specific
jurisdictions. The Guidelines have been amended in order to specify that trading
days are to be considered.
19. A respondent suggested to include explicitly in the Guidelines the provisions on
spot and forward currency contracts as per Article 7(2), 2
nd
sub-paragraph of the
RTS on organisational requirements for investment firms. The Guidelines have
been amended in accordance with the similar provision of the Article 10(2) of the
RTS on organisational requirements for investment firms.
20. A respondent raised the situation of FX strategies meaning the simultaneous
execution of two or more FX transactions that are priced as a single unit and where
the execution of each component is contingent on the execution of all other
components. While the reportability is not questioned here, the reporting of complex
derivatives is addressed in section 4.28 of these Guidelines. In particular, ESMA
wants to remind that in accordance with the CDE technical guidance, each

15
component should be valued individually. ESMA reminds as well that FX swaps
should be reported as a single transaction.
21. A respondent asked whether physical precious metals with a dedicated FX ISO
code (XAU, XAG, XPT, XPD, XRH) are to be considered as currency or commodity
derivatives. ESMA considers that derivatives based on precious metals are
commodity derivatives.
22. A respondent considered that the interpretation of whether a contract is a spot or a
forward depends on the fund accountant. ESMA did not retain this comment as
there is a clear legal reference.
Derivatives on crypto-assets
Q4: Are there any additional aspects to be considered with regards to the eligibility for
reporting of the derivatives on crypto-assets? Please provide the relevant examples.
23. Most respondents confirmed that there is no need for further clarification on the
reportability of derivatives on crypto assets. Some questions were more related to
reporting of crypto-assets which are addressed in the section 4.27 of the
Guidelines.
Total return swaps, liquidity swaps or collateral swaps (in relation to SFTR)
Q5: Are there any additional aspects to be considered with regards to the eligibility for
reporting of Total Return Swaps, liquidity swaps, collateral swaps or any other
uncertainty with regards to potential overlap between SFTR and EMIR? Please provide
the relevant examples.
24. Overall respondents welcomed the clarifications.
25. One respondent raised that there is no clear definition of what constitutes a
collateral swap or liquidity swap by reference to SFTR. ESMA is of the opinion that
the notion of liquidity swap is detailed in the SFTR recital 7.
Complex contracts
Q6: Are there any additional aspects to be considered with regards to the eligibility for
reporting of complex derivative contracts? Please provide the relevant examples.
26. Most of the feedback on reportability for complex contracts were more related to
how such contracts are to be reported which is clarified in section 4.28 of the
Guidelines.
27. One respondent asked whether options on a future, where the result is an FX spot,
the FX spot is considered reportable or not under EMIR. The Guidelines have been
completed in order to confirm that there is no requirement to report the FX spot
under EMIR.
Market transactions that do not fall under the definition of a derivative

16
Q7: Are there other situations where a clarification is required whether a derivative
should be reported?
Q8: Do you agree with the above understanding?
28. ESMA provided a non-exhaustive list of transactions that do not fall under the
definition of a derivative under EMIR based on MiFID in the CP.
29. Respondents welcomed these clarifications. Some respondents asked questions
on qualification of certain transaction types under MiFID such as “weather
derivatives” or “Voluntary Emission Reduction (VER) certificates”. ESMA invites
respondents to review on a case-by-case basis these instruments in light with
MiFID and its evolutions. In case the qualification of a specific product remains
unanswered, the related counterparty(ies) are invited to submit a dedicated
question with the details of the specific instrument.
3.1.2.2 Reporting obligation with regards to the parties involved in the trade
Q9: Are there other situations where a clarification is required whether a derivative
involving a specific category of party should be reported?
Q10: Do you agree with the above understanding?
30. Respondents were in favour of the details provided with regards to the reporting
obligation of the parties involved in the trade.
31. A respondent asked to clarify how to report the broker in particular in the case where
the broker is a counterparty to the trade. A specific paragraph has been added in
the Guidelines.
32. Another respondent asked for details on reporting obligation for funds in case either
the AIFM or the fund are not located in the Union.
33. If a fund manager in the EU has funds domiciled outside the EU, the reporting
obligation applies to counterparties in general and more particularly to FC,
regardless of the country of establishment of the FC. Based on the definition of an
FC, derivative contracts entered into by AIFs established in a third country and
where the AIFM is authorised or registered in the Union are subject to the reporting
obligations.
34. If a trade is allocated to multiple funds in various jurisdictions, likewise to the above
point, the country of establishment of the AIFM is to be considered in order to
determine if the funds are FCs.
35. Where there is cross-jurisdiction fund management (for example, an AIFM based
in the UK and the Fund/AIF based in the EU, or vice-versa), the respondent
considered that ideally the transaction should not be reported to both ESMA and
FCA under EMIR. There is currently no agreement to avoid duplicate reporting with
UK, thus ESMA cannot confirm that transactions should not be reported to both
ESMA and FCA. With regards to EMIR and its application in the Union, the country

17
of establishment of the both the AIF and the AIFM trigger or not the reporting
obligation.
36. The Guidelines have been amended in order to clarify that the status of the fund
determines whether it is subject to the reporting obligation.
37. One respondent asked whether CCPs are expected to populate field 2.37
‘Intragroup’ with ‘True’ in the situation where a clearing member defaults and the
CCP temporarily assumes both side of the outstanding derivative contracts. ESMA
considers that the field should not be populated as ‘True’ as this is only a temporary
situation and that these derivative contracts are not meant to be intragroup
contracts.
3.1.2.3 Reportability in specific scenarios
Q11: Are there other specific scenarios where a clarification is required?
Q12: Do you agree with the above understanding?
38. ESMA included in the consultation paper some specific scenarios where the
reportability might be questionable. Overall respondents were favourable and
agreed with ESMA’s understanding. Nevertheless a few proposals for additional
clarifications were made by respondents.
39. A few respondents suggested some minor amendments on the paragraph related
to novations. These were integrated in the Guidelines.
40. A counterparty considered that the statement “the details of the reported derivative
should be consistent across both reports” should only concern the details that are
included in the pairing and matching process. ESMA considers that this statement
is to be kept as it refers to the requirement for dual reporting and ESMA expects
that both counterparties should have agreed on the details of the derivative and
thus report them consistently even though the details are not subject to pairing and
matching.
41. One respondent requested to change the wording from ’termination‘ to ’early
termination; in paragraph 47 of the CP. ESMA did not retain the proposal as it relies
on wording from EMIR.
42. A respondent expected ESMA to clarify the notion of ’several days‘ in the paragraph
47 of the CP. As this comment was only raised by one respondent ESMA considers
that the notion was clear for most respondents and that adding another specific
detailed requirement is not beneficial for the Guidelines.
43. One respondent raised that there is a risk of dual reporting in the case of porting.
ESMA considers that this comment is rather related to the Guidelines on transfer
of data between TRs rather than to the Guidelines on reporting.

18
3.1.3 Intragroup exemption from reporting
Q13: Are there any other clarifications required with regards to the IGT exemption from
reporting?
44. In accordance with Article 9(1) of EMIR, as amended by Regulation 2019/834,
counterparties can benefit from an intragroup (IGT) exemption from reporting for
the derivative contracts within the same group where at least one of the
counterparties is a non-financial counterparty or would be qualified as a non-
financial counterparty if it were established in the Union and when the following
conditions are met: “ (a) both counterparties are included in the same consolidation
on a full basis; (b) both counterparties are subject to appropriate centralised risk
evaluation, measurement and control procedures; and (c) the parent undertaking
is not a financial counterparty”.
45. ESMA detailed in the CP some elements regarding the process to be followed in
order to submit a notification to benefit from the exemption.
46. In addition, ESMA provided clarifications with regards to the eligibility of
counterparties to the exemption, including a guidance provided by the European
Commission.
47. In general respondents considered that no further clarifications are required.
However, some respondents asked to complete the Guidelines with regards to
some elements and a few respondents challenged the eligibility to the exemption
for certain group structures.
48. In particular, respondents stated that the notion of ultimate parent undertaking is
not sufficiently clear or raises legal uncertainty and that ESMA should consider that
exemptions should be granted to counterparties which are part of a sub-
consolidation at the level of the Union (at an intermediate parent level) even if the
ultimate parent undertaking is located outside of the Union, in particular if the
intermediate parent at Union level is relevant for centralised risk evaluation,
measurements and control procedures with regard to the counterparties. One
respondent considered that the interpretation underlying the Commission’s
guidance could disincentivize investment from non-EU jurisdictions as it would very
likely result in a situation that an industrial group ultimately owned by an EU parent
undertaking would be subject to different market conditions than the groups owned
by a third country parent undertaking which would clearly mean there would be an
unlevel playing field among the businesses. Overall, as per this respondent, it could
negatively impact the competitiveness of the EU manufacturing and industrial
groups which are in any way connected to the commodity markets. ESMA
considers that the Commission’s interpretation is clear, legally sound and thus is
literally applicable. Nevertheless, ESMA completed the Guidelines with some
illustrative examples in order to reduce the doubt of potential misinterpretations of
the notion of ultimate parent undertaking in this context.
49. In a similar context, ESMA understands that the notion of parent undertaking in the
context of a submission of notifications on behalf of the group, might lead to

19
unnecessary burdens. Therefore, ESMA updated the wording in the Guidelines in
order to allow for a greater flexibility for the submission.
50. A respondent suggested that the opportunity to submit anticipated notification
should be considered in the Guidelines. ESMA agreed with this proposal and has
added a paragraph in the Guidelines to allow counterparties to submit a notification
even if the counterparties are not required to report at the time the notification is
submitted but will be required to do so in the future (for example, because they do
not engage in derivatives trading at all on the date of notification but plan to do so
in the future) as long as all conditions to benefit from the exemption are met. As an
example, ESMA considers the case where an NFC is acquired by a group during
the financial year (i.e. between two annual reports), following the acquisition the
NFC might be included in the consolidation on a full basis. Therefore, the
notification for the IGT exemption from reporting can be submitted after the
acquisition has been finalised, even if the new consolidated annual report has not
yet been published and no derivative transactions have been concluded yet.
51. A respondent considered that, in the case where two NCAs are involved, linking the
NCAs decision to each other conflicts with EMIR. The respondent considered that
each NCA will only grant the exemption (actively or by omission of a reaction)
limited to its national jurisdiction. ESMA does not agree with this statement as the
reporting obligation under Article 9 of EMIR applies to derivative contracts and thus
the exemption applies to contracts rather than counterparties. Therefore, the
intragroup exemption from reporting can only be granted if none of the NCAs object
within 3 months after the notification has been received by the respective NCAs.
52. A respondent suggested that in case an initially granted exemption ceases to be
valid, the objection should only be applicable once the counterparty has received
its notification rather than when the NCA objects. In addition, the respondent
considers that once objected, counterparties should get enough time to implement
the reporting structure, which could be a complex and time-consuming process.
ESMA considers the process detailed in the CP is consistent with EMIR and this
process should therefore be applied.
53. A respondent considered the notion of outstanding derivative should be clarified.
ESMA used another wording in the Guidelines.
54. One respondent considered that ESMA should focus on the big players in EMIR
reporting and at a later stage extend it to the smaller players. The regulation is
applicable to all counterparties and the Guidelines should therefore cover all
situations. ESMA therefore did not consider this comment in the Guidelines.
3.1.4 Allocation of responsibility for reporting
3.1.4.1 FC trading with NFC
Q14. Are there any other clarifications required for the handling of derivatives between
NFC- and FC?

20
55. In the CP, ESMA highlighted the Article 9(1a) of EMIR which introduces the
principle that “Financial counterparties shall be solely responsible, and legally
liable, for reporting on behalf of both counterparties, the details of OTC derivative
contracts” concluded with an NFC-. Nevertheless, the 3
rd
subparagraph of that
Article allows NFC- to continue to report the details of those OTC derivative
contracts to a trade repository.
56. The Article 9(2) of the ITS on reporting specifies the requirements related to the
arrangements to be put in place with regards to the transfer of responsibility and
legal liability:
a. Timely provision of details by the NFC- to the FC with regards to information the
“FC cannot be reasonably expected to possess”, indicating a list of fields for
which the details should be provided by the NFC- to the FC.
b. Timely information of the change in the reporting responsibility, i.e. when the
NFC- becomes NFC+ or vice versa.
c. Requirements for the NFC- to renew its LEI so that the status of the LEI is
’Issued’.
d. Timely notification by the NFC- if it decides to cease the “opt-out” so that the FC
becomes responsible for reporting on its behalf.
57. In the CP ESMA provided some clarifications regarding the expectations with
regards to the requirements introduced in the ITS on reporting and summarized
here above as well as some general clarifications.
58. Most respondents considered that no more clarifications are required. A few
respondents asked for specific clarifications or proposed some modifications to the
proposals in the CP.
59. A respondent considered that the LEI of an NFC- should be renewed, not only when
a transaction is concluded but as well for each reporting event. ESMA confirmed
that an NFC-, as well as any other counterparty, should ensure the duly renewal of
its LEI in accordance with the terms of any of the accredited Local Operating Units
of the Global LEI System during the whole period when a derivative contract is
outstanding in accordance with the Article 9(2) of the ITS on reporting.
60. Several respondents reminded that the responsibility for renewal of their LEIs lies
with the NFC- and consider that there should not be an additional requirement put
towards the FC in this context with regards to the paragraph 72 of the CP. ESMA
has no intention to shift the responsibility or to set an additional requirement.
Nevertheless, ESMA considers, that the FC would benefit from supporting the NFC-
in the process of LEI renewal as it would help reduce the risk of rejection and
resubmission caused by outdated LEI of NFC-. There is no question of
responsibility or even specific requirement towards the FC in this paragraph, but it
merely refers to considerations that could be included in the arrangement between
the FC and the NFC-. Therefore, ESMA will not consider these comments in the
Guidelines.

21
61. Some respondents challenged the proposal raised by ESMA in the paragraph 73
of the CP relating to the possibility for FCs to provide NFC- on a regular basis with
the information concerning the contracts that are outstanding at the TRs. Similarly,
to the considerations here above with regards to LEI renewal, this paragraph is
merely a suggestion rather than a requirement towards the FC. ESMA
acknowledges that nothing prevents NFC- to onboard directly to a TR and have
access to the data that has been reported on their behalf as per Article 18 of RTS
150/2013, nevertheless ESMA does not expect that the majority of NFC- will use
this opportunity. Therefore, ESMA invites FCs to consider whether they would be
willing and able to provide support to NFC- that are their clients in fulfilling their
EMIR obligations and NFC- to consider such opportunity when agreeing on the
arrangements required under the Article 9(2) of the ITS on reporting.
62. A respondent requested ESMA to clarify the responsibility of reporting when a NFC-
traded with EU FC and the EU FC became TC FC (e.g. Brexit) or when an ETD
contract becomes an OTC contract or vice versa. ESMA acknowledges that such
situations have occurred in the past and might occur again in the future and
considers that in such cases the Level 1 and 2 provisions should be strictly followed,
i.e. the reporting obligation will depend on the situation as it stands on the event
date. ESMA has integrated these scenarios in the Guidelines.
63. A respondent suggested that the responsibility for reporting of ETDs should be
transferred to “Clearing Banks or CCPs”. As this is not consistent with Level 1,
ESMA did not take this proposal into consideration.
64. A respondent asks who is required to update reports submitted to the TR that have
been concluded before EMIR Refit entered into force and that do not meet the
requirements of the latest technical standards during the transition period of 180
days. ESMA considers that a limited number of trades should be impacted as all
trades concluded after 1/11/2017 or subject to a reporting event since that date
should be aligned with the current reporting standards. Furthermore, ESMA
considers that the arrangements between the NFC- and the FC should take into
account such situations in order to ensure the continuity of the reporting and avoid
duplication.
65. A respondent asked for clarification on the term used in paragraph 66 of the CP
“predefined standard values”, in particular to clarify if the CP refers to specific
transaction attributes that are supposed to be populated by the FC by default.
ESMA referred to the fields that are specified in the Article 9(2) of the ITS on
reporting, in relation to the details of the derivative contracts the FC cannot be
reasonably expected to possess and are unknown to the FC. ESMA has included
an example in the Guidelines.
66. A respondent recommended ESMA to consider "mirrored trades" by TRs for trades
under the allocation of responsibility for reporting. Similarly another respondent
considered that when a trade is submitted on behalf of both counterparties, then
only the leg related to the NFC- that has not renewed its LEI should be rejected and
not the leg related to the FC. While ESMA is aware that it is currently possible to
submit a single trade with both legs at some TRs and the TR then generates the

22
’mirrored trade‘, ESMA considers that the principles of such reports are not in line
with the new requirements laid down in the Article 1(4) of the RTS on reporting.
Q15. Are the current illustrative examples providing clarity and are there other examples
that should be incorporated in the guidelines?
67. In the CP, ESMA included a table with illustrative examples on how the major fields
related to the parties involved in the reporting are expected to be populated.
68. While most respondents considered Table 1 with examples as sufficient, some
respondents suggested to add several other scenarios:
a. Where the other counterparty is not eligible for an LEI, i.e. there is
no leg 2 report.
b. Example where the traded derivative is an ETD.
c. NFC+ not delegating to an FC.
d. A complex example with changes in responsibility and delegations.
69. ESMA has updated the table accordingly.
3.1.4.2 CCP
Q16. Are there any other clarifications required for the reporting obligation related to
CCPs?
70. ESMA reminded in the CP that the CCPs are not impacted by the changes in the
allocation of responsibilities introduced under EMIR Refit.
71. Most respondents did not express the need for more clarifications.
72. One respondent suggested that CCPs should have a particular responsibility in
ensuring that the information they report is consistent with the information reported
by their clearing members. As there is no legal basis in Level 1 nor Level 2 to add
such requirement, ESMA did not consider this suggestion in the Guidelines.
3.1.4.3 Funds (UCITS, AIF and IORP that, in accordance with national law, does not
have legal personality)
Q17. Are there any other clarifications required for the reporting obligation related to
investment funds i.e. UCITS, AIF and IORP that, in accordance with national law, does
not have legal personality?
73. ESMA provided some clarifications and examples with regards to the allocation of
responsibility impacting funds.
74. Most respondents did not express the need for more clarifications.

23
75. One respondent suggested that, in the case of a fund trading with an NFC- (Table
3), the fund should voluntarily delegate the reporting to its manager. As this
suggestion is not compliant with Level 1, ESMA did not retain the suggestions.
76. Two respondents suggested to add examples where the investment fund manager
subdelegates the reporting to a third party RSE. In particular, one respondent would
like that in this case intermediaries should have access to the reports as well, while
these are not identified in the report. ESMA did not retain this suggestion, as it is
already foreseen in Article 78(7) of EMIR and Article 4 of RTS on data quality that
the counterparty or the entity responsible for reporting might allow for 3
rd
parties to
have access to TR data. In case this does not allow to address the issue raised
(e.g. multiple managers to a single fund) the provisions relating to voluntary
delegation should apply between the intermediate and the RSE or the counterparty.
3.1.5 Delegation of reporting
Q18. Do you see any other challenges with the delegation of reporting which should be
addressed?
77. In the CP, ESMA summarized the legal background of voluntary delegation of
reporting and addressed the need for further details on several aspects.
Respondents to the CP did not raise any objections to this proposal and mostly
supported it. Several respondents asked for more clarity regarding certain aspects.
78. A respondent requested to specify in the Guidelines an expectation of the ERR to
on-board the relevant TR in order for this entity to most efficiently be able to monitor
compliance. However, such a requirement cannot be stipulated at the level of
ESMA guidelines. Another respondent pointed out that if the party providing the
delegated reporting service is required to provide regular reports of outstanding
contracts, it could introduce additional processing requirements for the delegating
party, and it could be easier and less challenging for the delegating entity to on-
board to the TR used by the party providing the delegation service. ESMA confirms
that no restrictions are introduced for the delegating parties to on-board the TR as
they seem fit.
79. Another respondent raised a question whether field 1.2 ‘Report submitting entity ID’
should be populated with the LEI of the entity ultimately submitting the report to the
TR in a scenario where there is a chain of intermediary agents used as data
providers. ESMA confirms that the ultimate entity submitting the data to the TR
should be identified in field 1.2. ESMA is aware that the intermediaries will not be
identified in the report, thus providing only limited visibility of the chain.
80. One respondent argued that where the RSE is a third party, the TR may not be able
to provide all of the information to third party due to client data privacy concerns,
particularly around reconciliation breaks and other data quality issues. For example,
if RSE would receive rejections, which would then be passed on to the reporting
entities, the RSE would not receive the transaction reports or other pertinent
information from the TR. ESMA does not see a need for the TRs to provide the RSE
with the transaction data, the RSE which submitted the data to the TR should

24
already have all the relevant data to which the data quality feedback pertains at
their disposal.
81. Further confirmation was sought that the information about the relevant reporting
and data quality issues will be mandatory only in the presence of voluntary
delegation agreements. ESMA expects that the establishment of delegation of
reporting according to EMIR Art. 9(1f) is governed by an agreement between
delegating and delegated entity, and the relevant requirements arise as a
consequence of existence of such agreement.
82. Several respondents also requested ESMA to clarify that
e. the delegation of reporting is a different process from the allocation of
responsibility for reporting according to section 3.1.4,
f. any task (individually and separately) related to the reporting of data can be
delegated to a report submitting entity.
83. These clarifications were included in the Guidelines.
84. Two respondents asked ESMA to provide further clarifications on the process of
authorization / permissioning of a report submitting entity as per Article 1(1)(c) of
the RTS on data quality. These requests are addressed in section 3.4.3.1.
3.1.6 Reporting of lifecycle events
3.1.6.1 Action types
Q19. Do you agree that only action types ‘Margin Update’ and ‘Correct’ should be used
to report collateral?
85. In the CP ESMA proposed that only two action types, ‘Margin Update’ and ‘Correct’
are used to report collateral.
86. This proposal was fully supported by the respondents, who argued that this solution
will simplify reporting with no detriment to the reported information. Two
respondents brought to ESMA attention a few instances where the CP was
inconsistent and suggested reporting collateral for the first time with action type
‘New’. These parts of the Guidelines were amended accordingly. Similarly, ESMA
corrected typos where the action type was incorrectly referred to as ‘Market update’
or ‘Collateral update’.
87. One respondent asked what would be the expected behaviour in case a margin
update report is submitted to a TR by mistake, e.g. in case of counterparties without
obligation to report collateral on a daily basis, and whether the counterparties
should, instead of submitting a margin message with action type ‘Error’, use action
type ‘Correct and update field 3.11 ‘Collateralisation category’ to ‘UNCL’. Reporting
of a collateralised trade as uncollateralised would provide false information to the
regulators. If an entity without obligation to report collateral has send a margin
update by mistake and does not wish to continue reporting collateral information, it
should instead not submit any further margin updates.

25
88. Following a question from a respondent, it has also been clarified how to report a
change in the collateral portfolio code.
89. One respondent stated that the collateral information should be reported for a first
time as a derivative report with action type ‘New’. ESMA confirms that this is indeed
a possibility when reporting collateral for a given derivative (not at portfolio level).
However, counterparties are also free to choose to report collateral for a first time
with action type ‘Margin update’.
90. One respondent flagged that correction of historic data on collateral will be
burdensome but bring very little value. ESMA reiterates that EMIR sets out an
obligation to report correctly, thus when a counterparty identifies a mistake in its old
reports, it should send a report correcting such mistake.
91. A question has been posed how historical corrections of collateral should be
displayed back to the clients, i.e. whether this is displayed as trade activity only or
whether (and how) margin updates should be displayed in the Trade State Report.
This aspect has been covered in the Guidelines in the section 7.1.
Q20. Are there any other clarifications required with regards to the use of the action
types in general (other than specific aspects covered in the sections below)?
92. While the guidance on the use of action types was considered overall clear and
helpful, some additional clarifications were requested.
93. ESMA confirms that amendments to the terms of the derivative should be made
with action type ‘Modify’, unless such amendments are correction of a previously
reported erroneous information, in which case action type ‘Correct’ should be used.
This distinction was already included in the CP and is maintained in the Guidelines.
94. ESMA also confirms that a separate margin report is expected to report collateral
at portfolio level, instead of reporting such collateral multiples times for each
derivative in a portfolio.
95. One respondent asked whether it is permissible to use ‘Position component’ to
cancel trades which are netted to a position, e.g. in the scenario where the trades
net to a zero position, hence there should not be any subsequent position to be
reported. ESMA reiterates that the report at position level should be made in such
case, however the counterparty can subsequently decide whether to terminate the
position or not.
96. Following a question raised by a respondent, ESMA confirms that action type
'Revive' can be used to re-open derivatives cancelled (with action type 'Error'),
terminated by mistake (with action type 'Terminate') and to reopen derivatives that
reached (incorrectly reported) maturity date.
97. ESMA also confirms that ‘Revive’ can be used after the action type ‘Position
component’, if the latter was reported by mistake. The revived derivative at the trade
level will be perceived as outstanding (subject to the expiration date), which will
allow to preserve the same UTI. If the counterparty reported new/modification of a
position, it would need to be reverted separately.

26
98. With regards to the action type ‘Correct’, counterparties should be able to correct
the derivative data or the derivative and valuation data or margin data. Validation
rules specify which fields are required for this action type.
99. One respondent asked how to correct information in the field ‘Event type’ given that
this field is not applicable for action types ‘Correct’ and ‘Revive’. ESMA added a
clarification that it is not possible to correct the field ‘Event type’. Counterparties
should simply send an appropriate ‘Event type’ in the next report.
3.1.6.2 Sequences of action types
Q21. Do you agree with the sequences proposed? Please detail the reasons for your
response.
Q22. Are there any specific scenarios in which the expected sequence of action types
is unclear?
100. The main feedback received from the respondents concerned the lack of
possibility to use action type ‘Revive’ after 30 days from the cancellation,
termination or expiration of the derivative. The respondents raised a number of
concerns, linked mainly to the costs and complexity of having two different
solutions, lack of procedures for re-generating the UTIs in such scenario,
inconsistency with the global UTI guidance and lack of traceability of reopened
trades from the data user perspective. The 30-day limit was proposed by ESMA to
minimise the negative incentives for not having procedures in place by the
counterparties to control the proper use of action types as well as to avoid the
situations where a derivative - following 30 days in non-outstanding status - is
removed from the reconciliation process and needs to be reinserted afterwards.
However, upon careful analysis of the arguments presented by the respondents
ESMA decided to remove the 30-day limit. Notwithstanding, ESMA highlights that
counterparties should strive to report correctly cancellations and terminations,
rather than rely on the possibility to use action type ‘Revive’. Proper use of the
action types is one of the aspects that can be examined by the supervisors to
ensure high data quality.
101. Furthermore, some respondents commented that the requirement to report in
sequence all missing lifecycle events until the date of revival is too onerous and/or
redundant, particularly with regards to reporting of corrections. ESMA reiterates that
this requirement stems from the provision in EMIR to report each conclusion,
modification and termination. Importantly, this requirement is to ensure that
authorities have complete trade activity information and to avoid wrong incentives
for counterparties to use ‘Revive’ instead of reporting correctly during the lifetime
of a derivative.
102. Notwithstanding the above, it is not necessary to submit a correction message
if the only correction was to update the derivative to outstanding status, given that
this can be inferred from the ‘Revive’ report itself. ESMA added this clarification to
the Guidelines.

27
103. ESMA has taken on board drafting suggestions made by a respondent to better
clarify that counterparties are not expected to report expiration of a derivative upon
reaching a scheduled expiration date.
104. One respondent commented that action type ‘Margin update’ should be included
in the graph showing the allowable sequences. ESMA clarifies that it’s already
included and simply referred to as ‘Collateral’.
105. One respondent suggested also to remove from that graph indication that a
derivative is non-outstanding in the box referring to errored derivatives. ESMA
maintained this indication with a view to clearly indicate in the graph in all
circumstances which derivatives are considered outstanding and which not.
106. One respondent suggested that additional clarification, e.g. in the form of matrix
of allowable sequences would be helpful. ESMA recalls that such format was used
in SFTR guidelines but it was considered confusing by some respondents as it was
not clear if it shows only the possible direct sequences or possible sequences
where other events could be reported in the meantime. The flow diagram was
considered more precise in this regard as it clearly shows which action types are
allowed immediately after a given action type.
107. Respondents raised also a number of questions related to the validations of
events and of the event date by the TRs. Such questions were addressed by
updating the validation rules.
108. One respondent commented that late reporting of a derivative that is no longer
outstanding would follow the same pattern in the chart as report with action type
‘Position component’. ESMA added a clarification in this regard.
109. One respondent commented that the chart allows for late reporting of collateral,
however the validation rules require that at least one derivative to which collateral
pertains is outstanding. ESMA confirms that late reporting of collateral is possible
and updated the validation rules accordingly.
110. One respondent suggested to clarify that TRs should validate that report with
action type ‘Revive’ does not change any of the previously reported details. ESMA
reiterates that, as specified in the CP, ‘Revive’ should contain all details as of the
time of revival, therefore any such detail may be different from the derivative
characteristics as of the date it was cancelled/terminated by mistake.
111. One respondent asked if there would be any restrictions on the ordering of how
lifecycle events and ’Revive’ messages are submitted. ESMA does not envisage
such restrictions, other than the allowable sequences illustrated in the chart.
112. One respondent asked which action type should be used to modify incorrect
expiration date of a terminated trade, and the new correct expiration date is also in
the past. ESMA considers it to be an example of a correction (to be reported with
action type ‘Correct’) and does not see a need to address it specifically in the
Guidelines.
113. Following a question from respondent, ESMA added a clarification concerning
sending a correction for a derivative reported with action type ‘POSC’.

28
114. One respondent asked if same rules on permitted sequence of action types
would apply for pre-Refit data, both for outstanding and non-outstanding derivative
contracts. ESMA confirms that having a different set of sequencing rules specifically
for pre-Refit derivatives was not considered, therefore no change has been made
to the Guidelines in this regard.
115. Finally, respondents raised a number of questions related to the reporting and
validation of reports in the context of 30-day limit for sending ‘Revive’. Given that
the limit was removed, the questions are no longer pertinent.
3.1.6.3 Action types and event types combinations
Q23. Are any further clarifications needed with regards to the action type - event type
combinations or their applicability?
116. The respondents overall welcomed the clarifications.
117. Two respondents suggested that more examples should be provided in the
table. ESMA clarifies that the more comprehensive list of examples of business
events is provided in the section on mapping of business events. The main purpose
of the table in this section is to clarify the applicability of different combinations of
events. Nevertheless, ESMA added to the examples a few clarifications to address
the questions raised explicitly by the respondents.
118. A few respondents expressed concern that market participants do not have a
clear data source to determine the appropriate event type for a particular action and
encouraged ESMA to provide input as to how event types should be approached
from a data sourcing and implementation perspective. ESMA acknowledges the
request, however such guidance would necessarily be firm-specific and thus is not
appropriate for the Guidelines.
119. A few respondents asked also about dependencies between event type and
other reportable fields. ESMA clarifies that some of these dependencies may be
verified in the validation rules (in which case will be clearly specified therein).
120. One respondent flagged a potential inconsistency between the table in this
section and the validation rules, however in ESMA’s understanding the comment
pertained to different fields (field ‘Event type’ with value ‘PTRR’ and the field ‘PTRR’
which is a boolean flag). ESMA highlights that these are 2 separate fields.
121. One respondent stated that the action type ‘New’ should be able to be reported
without an event type at a position level, the same as the action type ‘Modify’, since
there could be more than one type of business events that occurred intraday, which
lead to a new position. ESMA has not included such clarification in the Guidelines
because a new position should be reported with the event that led to its creation,
and only then any other intraday events can be reflected in the end-of-day report
with no event type.
122. Some respondents asked about a clear delineation between events ‘Step-in’
and ‘Allocation’ inquiring in particular which event should be used in the case of
deal novation. ESMA confirms that event type 'Step-in' should be used in the case

29
of novations, whereas ‘Allocation’ is expected to be used in the case of block trades.
The relevant example was already included in the Guidelines section on the
mapping of business events.
123. One respondent argued that the proposed way to report termination of a trade
‘in advance’ (with an action type ‘Modify’ and event type ‘Early termination’) is taken
from SFTR framework where it is used to report settlement fails and that it should
not be applied under EMIR. ESMA highlights that this way of reporting terminations
agreed in advance is already in place under the current technical standards and will
be maintained under the amended technical standards.
124. One respondent asked if it will be possible to limit the content of the correction
report to the valuation data only. ESMA clarifies that entities will be able to send the
derivative data only or the derivative and valuation data, which is reflected in the
validation rules and XSD schemas. Furthermore, the respondents asked how many
reports should be sent to correct previously submitted incorrect valuation updates.
ESMA included a relevant clarification in the Guidelines in the section 7.1.
125. A question has also been raised whether the combination of ‘Modify’ and ‘Step-
in’ would only be used for a partial novation and whether this is consistent with
footnote 15 in the CP which stated that “The term ‘Step-in’ is used, as novation may
refer also to updates to the terms of the trade that do not transfer the derivative to
a different counterparty”. ESMA confirms the understanding regarding the
applicability of the combination of ‘Modify’ and ‘Step-in’ and clarifies that the
footnote was included merely to make clear that ‘Step-in’ should not be used to
report novations when only some trade details are amended, but no transfer to
another counterparty takes place.
126. One respondent asked how TRs should update the field ‘Event type’ in the TSR
after a counterparty reported an event for which ‘Event type’ is not applicable. The
respective clarification is provided in the section 7.1.
127. One respondent flagged that reporting of field ‘Event type’ at position level is
not mandatory, but it is required by the draft validation rules. ESMA updated the
validation rules accordingly.
128. One respondent asked if it is necessary to submit multiple modification
messages with different event types for modifications on trade level, where multiple
events could occur on the same day just like for positions. ESMA clarifies that this
is expected and flags that in the case of position-level reporting the relevant events
are in most cases reported separately at trade level (e.g. all conclusions and
terminations of derivatives at trade level that lead to modifications of a position).
3.1.6.4 Lifecycle events and use of linking IDs (Prior UTI, PTRR ID, Subsequent position
UTI)
Q24. Is it clear when the linking IDs should be used, and in which reports they should
be provided? Do you agree that the linking IDs should be reported only in the reports
pertaining to a given lifecycle event and should not be included in all subsequent

30
reports submitted for a given derivative? Are any further clarifications on linking IDs
required?
129. The respondents overall supported the guidance on the use of linking IDs. They
also supported that the linking IDs should be reported only in the reports pertaining
to a given lifecycle event arguing that this gives a clearer overview of the current
state of the outstanding contract.
130. Some respondents flagged however that reporting of subsequent position UTI
is technically challenging and that for ETDs, one execution may ultimately end up
in multiple positions, e.g. in the case of a split or cascading. The case of cascading
has been addressed in the section on mapping of business events where it is
clarified that counterparties should report termination of the original trade and report
the resulting trades with action type ‘New’. In the case of a split, understood as
dividing a trade and allocating it to multiple positions, the counterparties should
report termination of an original trade and the new positions / modifications of
existing positions, as appropriate. The event type which should be used in this case
is ‘Allocation’ and counterparties should populate field ‘Prior UTI’ when sending a
report with action type ‘New’ or ‘Modify’. The relevant use case was added to the
section on mapping of business events.
131. One respondent asked also whether a prior UTI would be required in the case
of a transfer of an ETD position (using event type ‘Step-in’), flagging that for ETD
positions multiple transfers can occur in the course of a day and they would be
reported at the end of the day as a single modification of an existing position. ESMA
reiterates that intraday reporting of changes to a position is not necessary and flags
that in the case of modification at position level, the indication of the event type is
not mandatory, thus the prior UTI would also not be mandatory as the population
of the field ‘Prior UTI’ is verified only for certain events.
132. Two respondents suggested to align EMIR with SFTR and clarify that CCPs are
not expected to report the prior UTI of the bilateral derivative that is cleared. This
suggestion however is not in line with the RTS on data quality which list the field
‘Prior UTI’ as reconcilable field. Furthermore, in the case of derivatives, the field
‘Prior UTI’ forms part of a globally agreed guidance on critical data elements.
133. Respondents requested also a clarification whether the linking ID values should
persist in the TSR if no subsequent submission updating these fields was received.
The relevant clarifications were included in the section 7.1.
134. Two respondents asked also how multiple choices for events need to be
handled in terms of priority as there may be instances in which an action is driven
by more than one event type. ESMA considers that in principle it should be feasible
to determine and report a single event type for each reported lifecycle events,
except for modification reports at position level for which event type is not required.
135. ESMA updated the paragraph 122 (numbering as per the CP) to correct a typo
and include an additional precision requested by the respondents.

31
3.1.7 Reporting at position level
Q25: Do you agree with the ESMA´s approach related to leaving the ‘Event type’ blank
in the case of multiple events impacting the same position on a given day? How often
multiple events/single events impact the same position on a given day? Have you
assessed the single versus multiple events impacting positions on a given day? Do you
have systems or methods to distinguish between one or multiple events impacting the
positions on a given day?
136. In the CP, ESMA included a proposal related to leaving the field ‘Event type’
blank in the case of multiple events impacting the same position on a given day.
137. In general, most respondents were in favour of or not against this proposal.
138. Some additional proposals made by the respondents were as follows:
a. Event type should be left blank when reporting positions in general, not only in
the case of multiple events impacting the same position.
b. To design a methodology to logically derive event types based on certain
criteria.
c. In case that multiple events impact a position on the same day, at least the last
event type should be populated.
139. Furthermore, some respondents commented that there is not a large number of
events impacting a position on a same date. On the other hand some respondents
flagged that it is burdensome to identify the events impacting positions as well as
to distinguish whether a given position was impacted by one or multiple events.
140. Therefore, considering the respondents´ answers, ESMA retained its proposal
to leave the field ‘Event type’ blank in the case of multiple events impacting the
same position on a given day. As well as, and because reporting of field ‘Event
type’ at position level for action type ‘Modify’ is not mandatory, ESMA has updated
the validation rules accordingly.
Q26. Do you agree with the proposed clarifications concerning population of certain
fields at position level?
141. With regards to this question, the most common suggestions made by
respondents were the following:
a. Reporting of flat/net zero positions: Most of the respondents considered that the
reporting of daily zero contract values for flat ETD positions is burdensome and
unnecessary, as it does not provide any added value and it reduces oversight
capabilities due to the increased number of submissions.
b. ‘Maturity date’: Many CCPs report the settlement date as the maturity date given
that the contract remains on the CCP’s books and records until settlement. The
respondents flagged also a discrepancy in the naming of field ‘Expiration date’
between the validation rules (‘Expiration date’) and the CP (‘Maturity date’).

32
c. ‘Execution timestamp’ and ‘Clearing timestamp’: The respondents suggested to
leave these fields empty for all ETD positions as an alternative to the proposals
made in the CP which were considered burdensome.
d. ‘Notional’: In general, the respondents communicated that populating the field
’Notional‘ with the product of two fields which are included in the reporting record
was redundant as well as highlighted insufficient guidance on the reporting of
field ‘Total Notional Quantity’. Some of them expressed the idea of using the
reference amount of the underlying instead.
142. Concerning the reporting of flat/net zero positions, ESMA retained the
clarification provided in the CP, stating that once a position becomes zero, the
counterparties can report in one of the following ways:
a. Termination of the position and, if new trades are concluded at a later stage,
reporting of a new position using a different UTI.
b. Maintaining the position open and reporting a zero contract value on a daily
basis.
143. Maturity date is commonly and generally defined as the date at which
obligations under a derivative transaction stop being effective. Therefore, the
practice developed by CCPs when they report maturity date as settlement date
should be avoided.
144. The discrepancy with regards to the naming of the expiration date will be
amended, so that the term applied in the RTS on reporting (‘expiration date’) is
used consistently also in the Guidelines and the validation rules.
145. To avoid inconsistent reporting, ESMA further clarified and updated in the
Guidelines how to report ‘Execution timestamp’, ‘Clearing timestamp’ and ‘Effective
date’, aligning them better with the definitions included in the RTS on reporting.
146. Computation of notionals at trade level is specified in the Article 5 of the RTS
on reporting. However, taking into consideration that a position comprises several
trades, ESMA decided to retain in the Guidelines further clarification concerning the
calculation of notional at position level to ensure that the systemic risks pertaining
to the outstanding exposures are correctly reflected in the reports. It should also be
noted that fields ‘Quantity’ and ‘Price multiplier’ were removed from the revised RTS
on reporting, reducing in this way redundancies in the reportable details related to
the notional.
Q27: Do you need any other clarification with regards to the position level reporting?
147. Most of the respondents expressed concerns about the optionality of reporting
ETD positions. They were of the opinion that the best manner of reflecting the
systemic risk of these trades is reporting always at position level. Only one
respondent was in favour of reporting ETD trades at both position and trade level.
In this regard, ESMA reiterates that reporting at position level is not mandatory
because all the conditions stated in the Article 3 of the RTS on reporting must be
fulfilled for the position-level reporting to be allowed. Furthermore, one of the

33
conditions is that the counterparties to the derivative agree that the derivative
should be reported at position level. ESMA would like to stress the importance of
the general obligation according to which the counterparties need to agree the
report's contents before submitting it to TRs. This obligation stems from the
requirement of Article 9(1) of EMIR.
148. Some respondents communicated the difficulty of reaching an agreement
between the counterparties when reporting at position level because of the volume
of transactions and the burdensome task associated with it.
149. One respondent asked for clarification about the reporting of lifecycle events at
position level. ESMA reiterated that when a trade is terminated and included in a
position, all the subsequent updates, including valuation updates, collateral
updates and other modifications and lifecycle events, should be reported at position
level and they should not be reported for the original derivative at trade level (Article
3(3) of the RTS on reporting).
150. Although the reporting of the field ‘Venue of execution’ is optional at position
level, one respondent communicated that this field at this level could be considered
as useless because the different trades which constitute a position could be
executed on different trading venues. This same respondent raised concern about
the optionality of this field at this level and the inclusion of this field in the scope of
reconciliation. ESMA clarified that at position level, the ‘Venue of execution’ field,
should be populated with the MIC code (defined by ISO 10383) of the venue where
the highest number of derivatives that are included in the reported position were
executed. Given that trades included in a position could be executed in different
trading venues, the field ‘Venue of execution’ is optional at position level in the
validation rules. However, the condition of agreement of the counterparties involved
still applies and counterparties are expected to report consistently.
3.1.8 Reporting of on-venue derivatives
Q28: Are there any other aspects that should be clarified with regards to reporting of
on-venue derivatives?
151. Several respondents asked for clarifications with regards to the Report Tracking
Number (RTN). In particular, they asked if there is a link between the RTN and the
Trading Venue Transaction Identification Code (TVTIC). Furthermore, respondents
asked if RTN is required for trades concluded on a SI (Systematic Internaliser).
Many respondents asked also for more clarification about the format, the
methodology to develop, the features for different counterparties involved and the
dissemination among entities when reporting the RTN. Finally, some respondents
asked for clarification about what should be populated in this field for a CFD that is
included in a position. ESMA included the relevant clarifications about the RTN in
the Guidelines.
152. Some respondents requested also a clarification with regards to reporting of a
transaction opened and then closed during the same day. ESMA further clarified in
the Guidelines the reporting of intraday derivatives.

34
153. In relation to when the process of collateralisation takes place through direct
arrangements between the client and the clearing member, one respondent asked
clarification whether in the case where a clearing member delegates reporting to
the CCP, the latter would need to submit any report on the value of the collateral
as well as any subsequent modification or termination. ESMA confirmed that in this
case the CCP would submit relevant reports as the submitting entity on behalf of
the clearing member. Only in the particular case when an investment firm is not
involved in the process of receiving and/or posting any collateral for the client
because of the direct arrangements between the client and the clearing member,
the investment firm is not expected to submit any report.
154. Regarding the reporting of a derivative concluded on a trading venue and then
cleared on the next day, some respondents asked about the logic of the reporting
and the identification of the counterparties involved when the trade has been filled
via an anonymous order book. The relevant clarifications were included in the
Guidelines.
155. One respondent asked for a clarification about the execution on regulated
markets (RMs) and the concept of ETD. Given that OTC derivatives, as defined
under EMIR, can be executed on trading venues such as MTFs and OTFs, there
could be confusion with regards to delineation between ETD and OTC. For the
purpose of clarifying the reporting for derivatives concluded on RMs, MTFs and
OTFs, ESMA refers in the Guidelines to ‘on-venue derivatives’. The relevant
guidance applies to all on-venue derivatives, irrespective of whether they were
executed in any kind of trading venue as defined in MiFID II.
3.1.9 Timely reporting of conclusion, modification and termination of a derivative
Q29. Do you agree with the proposal for reporting conclusion of derivatives? Please
detail the reasons for your response
Q30. Do you agree with the proposal for reporting modifications and corrections to
derivatives? Please detail the reasons for your response.
Q31. Do you agree with the specification of the ‘Event date’ for different action types?
156. A majority of the respondents welcomed the clarifications related to the timely
reporting, however a number of questions have been raised.
157. A few respondents expressed concerns regarding the requirement to report
modifications when they become effective, rather than when they are agreed.
Those respondents argued that delaying the reporting of future dated events is
likely to add additional cost and complexity for reporting systems and it will require
all market participants to develop and implement processes that are able to identify
when reporting should be delayed and on what future date to report. According to
the feedback, most of the booking systems used on the market will be updated with
the modified data on the day of agreement. Furthermore, the respondents
expressed a view that delaying the reporting of modifications hinders the
transparency. ESMA took note of these concerns, however the initial proposal was
maintained, as this way of reporting ensures that the reported derivative
characteristics reflect accurately at all stages the economic reality. For example,

35
reporting of a reduced notional where such reduction was agreed only for a future
date, would result in an underestimation of the outstanding exposure.
158. However, it should be noted that in the specific case of early terminations
agreed in advance, the counterparties are expected (by the end of the working day
following the date of such agreement) to report a modification amending the field
‘Expiration date’. There is no contradiction between this requirement and the
general expectation to report modifications when they become effective, because
the amended ‘Expiration date’ forms part of the updated terms of the contract (is
‘effective’) following to the agreement. Therefore, the regulators would have at all
stages the most accurate information concerning the outstanding duration of the
derivative. This specific case was already covered by the CP in the section 5.6 and
corresponds to how early terminations agreed in advance were already reported
under previous EMIR technical standards. Only one respondent opposed such way
of reporting of the early terminations agreed in advance.
159. Two respondents asked which event date should be reported in case of
modifications messages to be sent for the reporting of an early termination agreed
in advance. ESMA added a relevant clarification in the Guidelines.
160. One respondent suggested to clarify that trades and positions are automatically
considered to be exited once the reported expiration date has passed. Such
clarification was already included in the CP and is maintained in the Guidelines.
161. One respondent asked whether the warnings feedback on late reports should
consider local calendars and local time given that the counterparties report in UTC,
flagging that TRACE functional specifications indicate that ‘All late reports’ query
should return late reports based on the difference between the reporting timestamp
and execution timestamp. In this regard ESMA clarifies that late reports are not
covered in the scope of warnings reports under the RTS on data quality (section
7.3.2 of the Guidelines).
162. Two respondents found the paragraph 179 (numbering as per the CP) confusing
and potentially redundant. ESMA clarifies that this explanation, while may seem
evident, was included to address a doubt raised by a respondent to the Consultation
of Guidelines on SFTR reporting in his feedback on the equivalent section. ESMA
redrafted the paragraph to avoid any confusion.
163. One respondent asked whether TRs should include modifications in
reconciliation process even when they refer to future dates. ESMA reiterates that
reporting of future-dated modifications is not expected therefore this question is not
relevant.
164. One respondent stated that it is understood that whenever a lifecycle event is
submitted for a derivative contract, TRs should persist in the TSR values previously
reported whenever such fields are not applicable in the lifecycle event that is being
submitted and should update to value blank whenever the field is
optional/conditional and the entity decides not to report it. A clarification in this
regard was included in the section 7.1.

36
165. One respondent stated that field ‘Event date’ is redundant and it could be
inferred from the field ‘Reporting timestamp’. ESMA disagrees with this statement,
given that the counterparties are free to choose between reporting on T+0 or T+1.
Furthermore, such approximation would not work in case of late reports.
166. One respondent asked if paragraph 183 (numbering as per CP) implies that
there would be no possibility to report/correct historical margins, after the trade has
been terminated. ESMA confirms that this is not the intention and the relevant
paragraph was updated.
167. Furthermore, several respondents provided comments on the two alternatives
in relation to the treatment of the field ‘Event date’ by the TRs for the construction
of the TSR. These comments were analysed and addressed together with the
feedback received to the questions in the section of the Guidelines dedicated to the
TSR.
3.1.10 Mapping business events to action types and levels
Q32. Do you agree with the interpretation of the business events and the suggested
action and event types?
Q33. Are there other business events that would require clarification? If so, please
describe the nature of such events and explain how in your view they should be
reported under EMIR (i.e. which action type and event type should be used).
168. ESMA provided a table for mapping of business events to the reportable action
and event types. Feedback was sought to understand if there are further events
that needed clarification.
169. While respondents mostly deemed the table useful and adequate, some events
were highlighted where more clarity is needed.
170. Two respondents raised the scenario of cascading ETDs, which is understood
here as the event where, e.g. a yearly futures contract transforms into four
outstanding quarterly contracts spanning the same year. The respondents
suggested to terminate the existing contract with action type ‘Terminate’ and report
the new contracts with action type ‘New’. ESMA agrees with the interpretation and
has added the event to the table. Furthermore, it is clarified that event type ‘Trade’
should be used.
171. One respondent asked for clarification on the details on how and when the
changes in price of position level reports should be reported. This is covered in the
dedicated section on position level reporting.
172. One respondent pointed out the ISO 20022 table
12
for corporate action codes
and asked if the events in that table could be included in the mapping table. While
ESMA in general supports the usage of standards, the ISO 20022 table seems to
mostly contain events that are clearly not reportable (as clarified by the overall
principles of reportability). However, ESMA has added an item ‘Other corporate
12
https://www.iso20022.org/standardsrepository/type/CorporateActionOption5Code

37
actions’ to the table. ESMA believes that many corporate action events can be
unique in nature. Hence, giving more detailed guidance on universal level is
challenging.
173. Two respondents highlighted the lack of guidance on the action and event types
of the new trades resulting from an allocation. ESMA has added this to the table.
Finally, ESMA has made some further minor additions and corrections to the
mapping table.
3.1.11 UTI generation
Q34. Which approach do you prefer to determine the entity with the soonest reporting
deadline? Please clarify the advantages and challenges related to each of the
approaches.
Q35. Are there any other aspects that need to be clarified on UTI generation?
174. With regards to the UTI, ESMA consulted on aspects related to the UTI
generation, in particular on the approach to determining the counterparty with the
sooner reporting deadline.
175. ESMA proposed to consider 3 alternative approaches: (i) execution clock
approach, where each counterparty should assess the reporting deadline according
to its own time zone, (ii) semantic approach, where a T+1 end-of-day reporting
deadline is equivalent to any other T+1 end-of-day reporting deadline and (iii) follow
the sun approach, whereby there would be a static order of jurisdictions, based e.g.
on the timezones.
176. Overall, majority of respondents that answered on this aspect supported the
semantic approach, a few respondents supported the follow-the-sun and no
support was expressed for the execution clock approach. The respondents who
supported the follow-the-sun approach, argued that it would be easier to implement
than the execution clock approach, but would make more sense than the semantic
approach where timezones are not considered at all. On the other hand, the
respondents who preferred the semantic approach, flagged that the follow-the-sun
approach based on timezones would put a burden on counterparties in the East
and that this extra step of the waterfall seems to be unnecessary as there should
be enough time for the UTI generation, independently from the timezones.
177. Given that the guidance on determining the sooner reporting deadline will need
to be coordinated globally with other jurisdictions, ESMA refrains at this stage from
including this aspect in the Guidelines. The feedback from respondents will feed
into the discussion at international level.
178. Furthermore, respondents pointed out to additional aspects that may require a
clarification.
179. Regarding the determination of the sooner reporting deadline, one respondent
flagged that it will be challenging under any approach given the need to determine
it on a trade-by-trade basis depending on the location of the trader or salesperson.
In this regard it is important to note that the determination of the sooner reporting
deadline refers to the counterparties only and any nexus reporting deadline should

38
not be considered in this context. A relevant clarification has been added to the
Guidelines.
180. Several respondents suggested that the step in the UTI generation waterfall that
includes the TR generating the UTI should be removed. This step however, even if
in principle not expected to materialise for the EU counterparties, follows the global
UTI Technical Guidance and as such should be retained. It has also been included
in the ITS on reporting.
181. It has also been suggested to refer to the ISDA logic for using buyer/seller
convention as counterparties agreement method. Requiring the counterparties to
use such logic would be inconsistent with the global guidance and the ITS on
reporting, however the Guidelines clarify that where the counterparties reach the
counterparties’ agreement step in the UTI generation waterfall, they can bilaterally
agree on using a specific logic, such as the ISDA convention.
182. A few respondents made further proposals regarding the specific steps of the
UTI generation flowchart and the timeline for provision of the UTI. Such comments
were not taken on board, as the UTI generation logic and timeline for sharing the
UTI are enshrined in the ITS on reporting and cannot be altered by the Guidelines.
183. A few respondents also suggested to allow the UTI receiving counterparty to
generate the UTI itself, past a certain “cut-off” time, for example 09:00 T+1, which
would ensure the receiving counterparty still meets the regulatory reporting
deadline. This would be however inconsistent with the ITS on reporting. As clarified
in the Guidelines, in such cases the receiving party should contact the generating
party and enquire about the process instead of reporting using a UTI generated on
its own. Only if the other counterparty is not EU-based (and thus not subject to the
supervision in the EU), the reporting counterparty could generate an UTI on its own
in order to meet the reporting deadline.
184. One respondent has also commented on clearing members and CCPs having
a different view on what constitutes the reportable position, e.g. where a CCP may
report a position at account level, whereas a clearing member at treasury desk
level. In this regard ESMA recalls that as a principle the CCP is responsible for the
UTI generation and as such should provide the clearing member with the UTIs for
the relevant positions, which should be then used by the clearing member for the
purpose of reporting.
185. A respondent flagged issues with possibility to validate by the TR the UTI
generated within a regime that has differing UTI rules. In this regard ESMA recalls
that the same UTI requirements should apply in all jurisdictions implementing the
UTI Technical Guidance. i.e. if the UTI generation hierarchy is followed, the
formatting requirements should be as well.
186. One respondent also noted that ESMA should consider UTI implementation
timeline across different jurisdictions. ESMA acknowledges that the differences in
the implementation timelines may cause temporary issues with the UTI generation,
however it is not feasible to fully coordinate the timeline at the global level.

39
187. One respondent enquired about any specific requirements with regards to the
methods and formats for sharing the UTI. ESMA included in the Guidelines a
clarification on best practices to ensure the efficient communication, however
ESMA acknowledges that no new requirements should be introduced in the
Guidelines. Furthermore, ESMA is cautious that too specific requirements in this
regard could favour specific technical solutions or service providers.
188. Following to the questions received in the feedback to the CP, ESMA has also
included in the Guidelines a clarification on the applicability of the 10:00 a.m.
deadline for UTI communication to the reports at position level as well as a
clarification on the possibility to delegate the generation of the UTI.
3.1.12 Determining counterparty side
Q36. Are there any other types of contracts for which the determination of the
counterparty side needs more clarity?
Q37. Are there any other clarifications required with regard to the determination of the
counterparty side (other than specific aspects covered in other sections)?
189. In the CP, following the Article 4 of the ITS on reporting, ESMA provided that
the counterparty side to the derivative contract should be determined at the time of
the conclusion of the derivative on the basis of the type of contract concluded.
190. Under this provision, the counterparties should determine the counterparty side
at the time of the conclusion of the derivative and report either ‘Buyer’/‘Seller’ in
field ‘Direction’ or ‘Payer’/‘Receiver’ in fields ‘Direction of Leg 1’ and ‘Direction of
Leg 2’ depending on the type of contract concluded.
191. The vast majority of respondents have not raised any issue with the
determination of the counterparty side and declared that the guidance is sufficiently
clear and complete.
192. However, some of the respondents requested some clarifications regarding the
determination of the counterparty side for FX forwards and Non-Deliverable
Forwards (NDFs). On this aspect, while the FX forwards are classified in the table
provided in the CP under the currency forward type of contract category, NDFs type
of contract and their determination of direction were added as an additional
reference to the table provided in the CP.
193. Furthermore, in relation to the determination of the counterparty side using the
most recent trade for the reporting of a position when it is the result of netting of the
position to 0, many respondents argued that the practice is inconsistent and leads
to reconciliation breaks as counterparties might book or close down positions in
different orders. In addition, they argued that the value zero is mathematically
neither positive nor negative, therefore it is problematic assigning what is effectively
a sign in the form of side for netted positions where the quantity by definition is zero.
On this aspect some of them proposed to remove from the reconciliation the
counterparty side fields when a position is netted to 0. Alternatively, they proposed
to leave this field blank when a position is netted to 0.

40
194. Considering that the fields related to directions cannot be left blank and should
always be reported as per the RTS on reporting, ESMA decided that the most
practical way forward is to remove from the reconciliation fields related to directions
when the positions are netted to zero.
3.1.13 Identification of counterparties
Q38. Are there any other clarifications requested with regards to the identification of
counterparties?
195. The CP provided that the counterparty 1 to a derivative and the entity
responsible for reporting should ensure for the purpose of reporting the conclusion
or modification of a derivative that the reference data related to its ISO 17442 LEI
code is renewed in accordance with the terms of any of the accredited Local
Operating Units of the Global LEI System.
196. On this aspect, some respondents argued that action type ‘Revive’ should be
included as one of the action types where a lapsed LEI is permitted because where
the reporting counterparty or the ERR with a lapsed LEI report action types
‘Termination’ or ‘Error’ by mistake and move a trade to a non-outstanding status, it
should be possible to revive the trade without having to re-new the LEI first.
However, this comment could not be taken into consideration because if an entity
needs to revive a trade it should be required to have a valid LEI, as per the Article
3 of the ITS on reporting, as in principle it would have open trades.
197. Some other respondent asked for some clarification regarding the point in time
in which the LEI status should be validated by the TRs. ESMA assessed pros and
cons of different options, such as validating as of the event date or as of the day of
reporting and clarified that TRs should check the validity of the LEI as of the day of
reporting. The exact validation comprising specific rules for different action types is
set out in the validation rules.
198. One respondent asked for a clear guidance on whether for action types ‘Error’
and ‘Termination’ TRs should check that the LEI is included in the GLEIF database
maintained by the Central Operating Unit, irrespective of the registration status of
that LEI, or just check it is a 20-character code. In this context, ESMA clarified that
the TRs are expected to check whether the LEI is included in the GLEIF database
for these action types.
199. Another respondent argued that in the case where the field ’Counterparty 2
identifier type‘ is populated with ’True’, i.e. the counterparty 2 is identified with a LEI
code, the population of field ’Country of the counterparty 2‘ seems redundant since
the information can be derived from GLEIF reference data. The comment has been
taken onboard and the Guidelines have been amended accordingly.
200. The CP also provided that the client codes should be composed of LEI of
counterparty 1 and an internal identifier of individuals, where such identifier should
be unique at the level of the given reporting counterparty (counterparty 1). One
respondent asked whether the TRs should implement a validation check on client
codes in order to verify that client codes contain the LEI of the counterparty 1 and

41
that the internal identifier of individuals is unique. ESMA confirms that TRs should
implement a validation check on client codes to verify if the client code contains the
LEI of the counterparty 1, however such validation should be restricted only to
reports of new derivatives (action types ‘New’ and ‘Position component’) to account
for e.g. changes of LEI of the reporting counterparty due to the corporate event.
With regards to the uniqueness of the internal identifier of individuals, TRs are not
in the position to verify that and therefore are not required to check the uniqueness
of the internal identifier.
3.1.14 Procedure when a counterparty undergoes a corporate action
Q39. Are there any other aspects to clarify in the LEI update procedure when a
counterparty undergoes a corporate action?
Q40. Are there any other aspects to be considered in the procedure to update from BIC
to LEI?
201. In the CP ESMA, following the provisions of RTS and ITS on reporting and RTS
on data quality, clarified the procedure and the timelines to be applied to ensure a
correct update of derivatives reports when a counterparty undergoes a corporate
action resulting in the change of its LEI.
202. ESMA has included in the Guidelines a section on the procedure to be applied
by both TRs and counterparties to ensure a correct update of the derivatives.
203. Considering that the procedure provides that the LEI update should occur on
the date of the corporate restructuring event, one respondent proposed to postpone
the update to the first non-working day following the corporate restructuring event.
However, this proposal could not be considered since it would not be in line with
Article 2 of the ITS on reporting.
204. Considering that some respondents raised concerns over the timelines of the
update, ESMA clarifies that an interim period should not occur since the TRs are
bounded by the ITS on reporting to perform the LEI update on the date of the
corporate event. However, in case of delay in the application of the corporate
action, the TRs should perform the update as soon as possible and no later than
30 calendar days from receiving the request.
205. Furthermore, one respondent proposed to assign the ERR, rather than RSE,
the responsibility for the communication of the LEI change to the TRs in order to
avoid that third parties used for reporting services should be responsible for
communicating the LEI changes. This proposal could not be accommodated
considering that reporting counterparties and ERR might not have any contractual
relationship with the TRs unlike the RSEs which always have a contractual
relationship with the TRs.
206. Another aspect to be clarified, according to one respondent, is related to the
rationale behind the broadcast of the information about a LEI update from the
receiver TR (i.e. the TR that receives a request for an update from the RSE) to their
clients and to other TRs. Clarifying that the communication from the receiver TR of

42
the corporate action to other TRs is sufficient for the adjustments and that no
additional steps are required by other TRs to verify the circumstances, the rationale
behind the communication from the receiver TR to their clients and other TRs is
that all the stakeholders in the process should be informed about a corporate action
in order to make any adjustment in their reporting to avoid rejection/reconciliation
breaks.
207. Paragraph 238 of the CP specified that in case of corporate event affecting only
a subset of derivatives (e.g. spin offs), TRs should put in place common procedures
for updating LEI data on those derivative contracts that could be affected by partial
changes of the LEIs. In this regard, one respondent asked whether TRs only need
one counterparty or ERR to indicate what UTIs are affected or both counterparties
or entities need to agree. On this, ESMA clarifies that both counterparties affected
by the spin-off should agree on the derivatives which took part in the corporate
action and both counterparties should communicate their TRs the change.
208. Some other respondents asked for clarifications in case the corporate event
affects NFC-. In this regards the respondents asked whether the FCs are required
to notify TRs in case the NFC- is affected by a corporate event. In this regard, ESMA
included a relevant use case in the table in the section 4.4.2.
209. In relation to paragraph 239-241 of the CP, some respondents complained
about the process of reviving trades errored or terminated by mistake prior to the
corporate event. The reason behind this provision is that the notice of a corporate
event represents the moment in which the reporting counterparty or ERR, as
applicable, should, in principle, assess the entire perimeter of outstanding
derivatives to be affected by the event and the moment in which the counterparties
affected by the change could realize that one or more derivatives have been
terminated or errored by mistake. In this regard, ESMA reiterates the importance of
the assessment by counterparties or ERRs of the perimeter of outstanding
derivatives affected by a corporate event before such event occurs.
210. Many other respondents to the consultation needed clarification on the
expectations of machine-readable format, i.e. on the format to be used, on how it
would be communicated, etc. ESMA clarified that the information about the update
of the LEI, as specified in paragraph 3 (b) of Article 2 of RTS on data quality, should
be readable in an automatized form and provided in accordance with the procedure
put in place by the TRs.
211. With reference to paragraph 237 of the CP, one respondent outlined that the
procedure described is not clear enough. For the sake of clarity, it should be noted
that the procedure in paragraph 237 of the CP applies to reports pertaining to
affected entities in which the affected entities are neither the reporting counterparty
nor the other counterparty of the derivative (for example the entity affected by the
change is the entity reported in ‘Broker ID’ or ‘Clearing member’ fields). In this case
the TR should wait for a confirmation by the affected entities for these reports in
due time (i.e. before the corporate action). However, this communication does not
impact per se the procedure for updating the LEI due to corporate actions because
the fields other than ‘Counterparty 1’ and ‘Counterparty 2’ could always be

43
amended through the action type ‘Modify’, even after the corporate event takes
place.
3.1.15 Identification and classification of products
Q41: Do you require any further clarification on the use of UPI, ISIN or CFI for
derivatives?
Q42: Do you require any further clarification with regards to the reporting of fields
covered by the UPI reference data? Which fields in the future should /should not be
sourced exclusively from the UPI reference data rather than being reported to the TRs?
212. In the CP ESMA clarified when a derivative should be identified with a UPI or
an ISIN, how to report classification of a derivative and what are the regulatory
expectations with regards to reporting of the product reference data. While overall
the proposal was deemed clear, several respondents raised points requiring further
clarifications.
213. A few respondents suggested alternative proposals with regards to when a
derivative should be identified with an ISIN or UPI, however the way of identification
of the derivative has been set out in the technical standards (following also a
consultation on this matter) and cannot be altered by the Guidelines.
214. Some respondents inquired how to report in case UPI will not be available yet.
ESMA highlights that the UPI system is expected to go-live prior to the reporting
start date under ITS and RTS on reporting, thus UPIs will be available. Furthermore,
ESMA confirms that the requirement to provide UPI will apply also to relevant
derivatives outstanding on the reporting start date, even if previously they were
identified with an OTC ISIN (e.g. on a voluntary basis) but will be in the scope of
derivatives to be identified with UPI under RTS and ITS on reporting.
Counterparties will be able to obtain the respective UPIs given that UPI is expected
to be available for each OTC ISIN record.
215. Furthermore, a potential misalignment between EMIR and MiFIR requirements
has been brought to ESMA’s attention with regards to the identification of product
traded on SIs. In this regard, ESMA confirms that indeed following to the feedback
received in the consultation on the technical standards, the objective was to align
the scope of derivatives identified with ISIN with MiFIR. The text of the Guidelines
was therefore updated accordingly.
216. Some respondents asked if there is any prioritisation between the fields 2.7
‘ISIN’ and 2.8 ‘UPI’, as well as flagged potential reconciliation issues when the two
counterparties use a different identification method. It should be noted though that
the ITS on reporting clearly specifies that counterparties should provide only one
identifier as well as which type of identifier should be used for a given derivative.
Therefore, if counterparties follow the ITS on reporting, the reconciliation breaks
caused by a different identification method will not occur. Additionally, to prevent
reconciliation breaks, validation rules were updated to specify that UPI cannot be
provided for derivatives identified with ISIN. Two respondents suggested also that
the validation rules should specify that UPI must be reported when venue is not
populated with a MIC of an EU trading venue, however this comment was not taken

44
on board, given that UPI may not be available in case of certain derivatives traded
on third country exchanges.
217. A few respondents asked about the expected validation of the UPI codes to be
performed by the TRs. ESMA considered this feedback and updated the validation
rules to clarify that the TRs should not only check the conformity of the format of
the reported code, but also whether the code corresponds to a valid UPI issued by
ANNA DSB. However, at this stage ESMA does not propose consistency checks
between the UPI, CFI and other relevant fields (‘Asset class’, ’Product type’ etc.),
given that in the future ESMA may cease to require reporting of some of these fields
to the TRs.
218. With regards to the classification of a derivative, a few respondents suggested
not to require a CFI given that it does not bring additional value on top of UPI. ESMA
considers CFI useful for analytical purposes, as it provides a straightforward way
of classifying the instruments. However, as noted in the Guidelines, ESMA will
consider in the future which of the reference data could potentially cease to be
required once the UPI system is fully in place.
219. A few respondents expressed concerns about the requirement to agree on the
CFI in case it is not available for certain derivatives. ESMA considered this
feedback and updated the Guidelines. In particular, ESMA highlights that CFI forms
part of UPI reference data and therefore should always be available for derivatives
identified with UPI. In case of derivatives outside of the scope of the UPI for which
CFI has not been yet assigned, the counterparties should request it to the relevant
NNA.
220. Finally, one respondent asked if CFI must be updated in the case of outstanding
derivatives upon the entry into force of the ITS and RTS on reporting. This is indeed
the case, in line with the requirement to update as necessary all the reportable
fields (except for the UTI which is not expected to be regenerated).
221. With regards to the reporting of the UPI reference data, several respondents
asked if a possibility to remove the need to report reference data fields could be
extended also to the products identified with an ISIN. ESMA acknowledges that the
relevant data could be obtained both from the DSB and FIRDS databases, thus the
intention would be to remove the obligation to report same set of reference data
fields irrespective of whether the product is identified with the UPI or with the ISIN.
Furthermore, ESMA confirms that removing of this obligation will only be
considered in the future, after the reporting start date, when the UPI system is fully
in place and once the users got sufficient experience with using it. Advance notice,
indicating clearly the impacted fields, will be given to the market participants ahead
of any changes to the mandatory nature of the fields (as it is usually done in case
of changes to the validation rules).
222. Two respondents asked whether – following to the relaxation of requirements
for reporting of reference data – the fields in question would be not required or not
allowed to be reported for derivatives identified with ISIN/UPI. ESMA has not
identified any clear benefit of reporting of such fields on a voluntary basis. On the
other hand, ESMA acknowledges that leaving the population of the fields to the

45
discretion of the reporting parties would lead to inconsistencies in reporting and
reconciliation breaks. Consequently, ESMA confirms that the fields would not be
allowed to be reported following to the change. Again, the requirements will be
clearly set out in the validation rules.
3.1.16 Identification of underlying
Q43. Do you require any further clarification on the reporting of details of the
underlying?
223. ESMA received some clarification requests in terms of the part stating: “if it is
available”. Furthermore, some respondents asked for clarifications for instances
such as on listed rates index reporting where the underlying has an ISIN code. One
of the issues raised by respondents was that there is reliance on the reporting of
the index name instead on ISIN only, which can be confusing, cumbersome and
may lead to reconciliation breaks. ESMA clarified in the Guidelines that in case of
indices the counterparties should report always the name of the index as it is
currently the only way of identifying indices that is always available. Counterparties
should report as well the relevant ISIN and 4-letter indicator, to the extent that those
are available, i.e. have been assigned to a given index.
224. Clarification was requested regarding the definition of field 2.18 ‘Identifier of the
basket’s constituents’, notably whether indeed the constituents not traded on a
trading venue should not be identified. ESMA confirms that only the constituents
traded on trading venues are expected to be reported, as only those would always
be identifiable with ISIN.
225. ESMA was encouraged to provide more guidance on how index or basket
composition could be shared. This request was considered outside of the scope of
the Guidelines on reporting.
226. Finally, one respondent asked when to report the underlying and when the
reference entity. This clarification was added to the Guidelines.
227. Another respondent asked if ESMA would allow for reporting of other identifiers
where ISIN is not available. ESMA clarifies that this proposal is not compliant with
the ITS on reporting.
3.1.17 Price, notional and quantity fields
Q44. Is any further guidance required in relation to the population of the ‘Notional’ field?
Q45. Is any further guidance required in relation to the population of the ‘Total
notional quantity’ field? How should the ‘Total notional quantity’ field be populated,
distinguishing between ETD and OTC and asset class?
Q46. Are there other instances when we would expect to see a zero notional for
position reports? Please provide examples. Are there any instances when we would
expect to see a notional of zero for trade level reports? Please provide examples.

46
228. The CDE guidance provided detailed instructions regarding the reporting of
notional for different OTC products. ESMA leveraged on the content of that
guidance and included it in the RTS on reporting.
229. The ‘Notional’ is a key field and it is crucial that this field is populated correctly.
’Notional’ and ‘Notional amount’ fields should be populated in accordance with
Article 5 of the RTS on reporting.
230. It was highlighted that while the RTS on reporting provides a general framework
for calculation, it does not cover non-standard commodity derivatives. The relevant
clarifications regarding the calculation of notional for non-standard commodity
derivatives and updates of such notional during the duration of the derivative were
included in the Guidelines.
231. Some respondents requested further clarification on the notional amount
schedule fields. In the case of derivatives involving notional amount schedules, the
notional amount input in field 2.55 ‘Notional amount of leg 1’, will also need to be
input in the notional amount schedule fields. The same applies for the field ‘Notional
amount of leg 2’, if applicable.
232. In relation to the inconsistencies between the CPMI IOSCO CDE Technical
Guidance and the EMIR validation rules raised by some respondents in relation to
the notional amount schedule, the validation rules were updated to optional for the
‘end date’ of the schedule. The ‘end date’ is not required if the end date is back-to-
back with the effective date of the subsequent period.
233. Furthermore, ESMA clarified in the Guidelines, that when reporting a notional
amount schedule, the date schedules are to be reported in chronological order. The
same logic applies when reporting a notional quantity schedule.
234. With regards to the quantity fields, following the consultation on the technical
standards, ESMA decided to proceed with the proposal to remove the fields
‘Quantity’ and ‘Price multiplier’ as these fields are not relevant for OTC derivative
contracts. Furthermore, ESMA decided to proceed with the inclusion of the field
‘Total notional quantity’, to ensure alignment with the global guidance on reporting
of OTC derivatives data and to ensure consistency of data reported to TRs.
235. Total notional quantity should be understood as the aggregate notional quantity
of the underlying asset for the term of the derivative. Where the total notional
quantity is not known when a new derivative is reported, the total notional quantity
should be reported with a default value and updated as it becomes available.
236. There was a small number of respondents to question 45 with clarification
requested as to whether field ‘Total notional quantity’ is only applicable for
commodity and equity products.
237. Total notional quantity applies to ETDs more generally. Based on clarification
requested by respondents this field is relevant for equities and commodities. If
applicable, it should also be populated for the other asset classes.
238. In the case where a position is netted (the notional becomes zero) two possible
ways to proceed were proposed in the CP:

47
a. The position can be terminated. If the position is reopened it should be reported
with a new UTI.
b. Counterparties can maintain the open position and report a zero contract value
on a daily basis. If new trades are then incorporated into this position the
notional, and other relevant fields, should be updated accordingly.
239. Based on the small number of responses received as well as the limited details
provided in these responses, ESMA maintained this guidance on reporting of zero
net positions.
240. ESMA also received some feedback to the reporting of price from two
respondents.
241. First, one respondent asked if ‘Price’ field could be applicable in cases other
than the ones listed in Article 6(1) of the RTS on reporting. The respondent gave
commodity and equity futures as potential examples. ESMA has added a
clarification to the Guidelines that the list in Article 6(1) is not exhaustive, and ‘Price’
field can be applicable also in other cases, such as commodity and equity futures.
242. Second, one respondent highlighted the phrasing in paragraph 253(g) about
“floating leg of commodity fixed/float swaps” not requiring the ‘Price’ field to be
populated. ESMA has deleted the mention, as fixed/float commodity swaps are
covered in Article 6(1) of the RTS on reporting, thus requiring the fixed price to be
populated in the ‘Price’ field.
243. In addition, one respondent sought clarification on the way different types of
total return swaps are to be reported. ESMA confirms that equity total return swaps
fall under Article 6(1)(c) of the RTS on reporting, meaning that the initial price of the
underlying is to be reported in the ‘Price’ field. Credit total return swaps, however,
fall under paragraph 253(j) of the Guidelines, meaning that the ‘Price’ field is not
applicable to those products.
244. Finally, ESMA has made some drafting improvements to the price section.
Paragraph 253(d) in the CP was incorrectly formatted as a list item, even though it
should have been a new paragraph and some expressions were changed for the
sake of clarity.
3.1.18 Reporting of valuations
Q47. Are there any other aspects in reporting of valuations that should be clarified?
245. ESMA received constructive feedback and some clarification requests on the
reporting of the contract valuation.
246. One of the major issues raised by some respondents in relation to the valuation
of cleared trades concerned valuation and reporting of the so-called Settle to
Market (STM) model transactions as opposed to the Collateralised to Market (CTM)
valuation approach, the latter being in line with the proposed draft Guidelines.
247. Regarding this point, the respondents stated that the valuation approach of the
draft Guidelines only reflects the reality of CCP valuation for CTM transactions and

48
does not take into account the STM model functioning. Under STM transactions,
the outstanding mark to market (MTM) exposure is settled at the end of the day and
thus the MTM exposure is reset to zero on a daily basis. After the end-of-day
settlement, the exposure is zero and the only available collateral is the initial
margin, which covers the risk of price changes until the next settlement. The
respondents also maintained that reporting the accumulated profit/loss numbers
would not only be wrong (as it would not reflect the outstanding risk) but would also
require CCPs and counterparties to build up a whole new accounting logic.
248. ESMA explored this problem in more detail to better understand the issue that
the approach to valuation reporting needs to be adapted in a way that will provide
regulators with the most accurate view of end-of-day exposures of entities under
the STM methodology while allowing to understand the outstanding risks
associated with the derivatives that remain open. ESMA is of the view that allowing
for a different way of reporting under CTM and STM models would not pose a
problem if data users were able to identify which model was used for a given
derivative based on the reportable fields. It should be noted that such additional
field has not been accounted for during the review of the technical standards, but it
could be considered in the future. ESMA may also explore potential ways to indicate
the model using the existing fields.
249. In light of the above, ESMA changed the Guidelines approach to account for the
STM model and clarify that CCPs and counterparties can report daily change in the
valuation for STM transactions. ESMA recommends that data users pay close
attention when processing the data related to valuation and collateral to keep in
mind the coexistence of the CTM and STM methodologies.
250. Apart from this point, one respondent was of the view that the Guidelines should
be aligned to the CPMI IOSCO CDE guidance. Otherwise, market participants will
need to report two different valuation amounts for the same contract where this
contract is subject to multiple jurisdictions. ESMA would like to clarify that the
reason to report unadjusted value is the fact that the contract value is used to
determine counterparty exposure and that collateralisation and margining are
reported separately for this purpose. In fact, ESMA notes that currently CPMI
IOSCO CDE guidance does not indicate specifically how to report the valuation
amount and leaves room for interpretation with regards to the application of the
valuation adjustments. In this respect, ESMA will maintain its guidance as proposed
in the CP and will liaise with other regulators.
251. As mentioned above, ESMA also received some clarification requests. One
respondent pointed out that contracts reported on T without a valuation should not
appear on the missing valuation report. ESMA confirms that this is the case, i.e.
valuation reporting remains within the T+1 timeline. Furthermore, the warnings
reports for missing valuations are expected to be triggered when valuation that was
reported is dated more than fourteen calendar days earlier than the day for which
the report is generated.
252. Another respondent noted that uncleared OTC derivatives contracts cannot
benefit from a third-party valuation which may lead to different valuations from the
two parties of the contract. The respondent suggested to set the “matching

49
tolerances” at a higher level than that used for cleared OTC derivatives contracts.
In this respect, it should be noted that ESMA is in fact proposing new matching
tolerances (please see section 3.4.2 on reconciliation). In general, ESMA
recommends that counterparties discuss between themselves to ensure that
valuations are consistent and aligned as much as possible and within the tolerance
levels included in the table.
253. Furthermore, ESMA was asked to prescribe its preferred option of reporting the
first valuation of a given derivative from the two alternatives set out in paragraph
274 of the CP. ESMA notes that both solutions are equally acceptable, and the
choice is up to the reporting entities who can design their reporting logic according
to the solution that is easier for them to implement.
254. ESMA was also asked to provide additional clarity and examples on how the
value of the contract should be determined in light of the inconsistencies observed
across CCPs in relation to the methodology they use to calculate valuations. ESMA
would like to highlight that harmonization of the methodologies across the CCPs
remains out of the scope of the technical standards and Guidelines on reporting.
255. In the same vein, to respond to a request to clarify valuation for smart derivative
contracts (SDCs) where CVA and DVA is zero, ESMA notes that the purpose of the
Guidelines is not to provide indications on how to perform derivatives valuations. In
any case, the value of CVA and DVA is irrelevant for uncleared derivatives as they
have to be reported without the relevant adjustments. In addition, the way in which
a derivative is concluded should not have an impact on how it is valued.
256. Lastly, ESMA hereby confirms that the valuation should be reported on a daily
basis even if there is no change or the valuation is zero (see also paragraph 364 of
the FR on ITS/RTS). This is important from the perspective of data quality and
enables the regulators to monitor that reporting parties keep complying with the
valuation reporting requirement.
Q48. Are there any other aspects in reporting of delta that should be clarified? Are there
instrument types (in addition to swaption) where further guidance is needed with
regards to the calculation of delta?
257. ESMA sought input in the CP to potential issues regarding the reporting of delta
that would need further clarification. There were no major objections to the given
guidance, but some respondents asked for additional clarifications.
258. Some respondents raised questions on the process and viability of the
reconciliation of the delta values. ESMA understands that the process and potential
challenges around the reconciliation of this field are similar to those around the
reconciliation of valuations.
259. Two respondents required additional clarification on the way delta is reported.
ESMA confirms that the initial value can be reported with the action type ‘NEWT’ or
’POSC’, that contains the relevant element for delta. For daily delta updates, the
process is similar to valuation update.
260. Some respondents asked clarification on the way in which delta is to be
understood for products that have more than one underlying. First, ESMA clarifies

50
that the reporting of delta is only applicable to options and swaptions (i.e. multi-leg
swaps are not in scope for the reporting of delta). Then, as for basket options ESMA
clarifies that delta is not required.
261. One respondent asked how delta should be reported in cases where its value
is less than -1 or more than 1. ESMA understands that such a value might occur
with options with non-linear payoff, such as digital options or knock-in/out options.
The reporting format is set by the ITS on reporting (derived in this case from CDE
Guidance), limiting the allowed values to between -1 and 1. Hence, ESMA clarifies
that the values of -1 and 1 should be used in cases where delta is below or above
the allowed range, respectively.
262. Finally, two respondents asked whether adjusted or unadjusted delta values
should be reported. ESMA confirms that unadjusted delta should be reported, i.e.
the reported value should not contain adjustments pertaining to, e.g. counterparty
credit risk.
3.1.19 Reporting of margins
Q49. Are there any further clarifications required with regards to the reporting of
margins?
263. Article 4 of the RTS on reporting provides that data on collateral for both cleared
and non-cleared derivatives shall include all posted and received collateral. In
addition, where the counterparties collateralize on a portfolio basis, the reporting
counterparty or ERR shall report collateral posted and received on a portfolio basis
specifying the code identifying the portfolio.
264. In the CP ESMA asked feedback on further clarifications required with regards
to the reporting of margins. Most of the respondents supported and agreed with the
provisions for margins reporting, while requesting some clarifications.
265. One respondent asked which UTI should be used in field 3.10 in case of
collateralization on portfolio basis. As reflected in the validation rules, UTI should
not be reported in a margin update pertaining to collateral provided on portfolio
basis.
266. Three respondents requested clarifications on how to deal with variation
margins reporting in case of Collateralise to Market (CTM) and Settle to Market
model (STM). The respondents, after providing a complete description of the
mentioned models, complained that the term ’variation margin’ as used in EMIR
only covers the CTM model payments, i.e. payments that are provided as margin
for any open exposures resulting from changes in market prices. STM model is not
covered by the EMIR definition of ’variation margin‘ and consequently any
payments that are made to finally settle any outstanding exposure (i.e. STM) could
not be properly reported under EMIR because after the end-of-day settlement,
exposure is zero and the only available end-of-day collateral is the initial margin,
which covers the risk of price changes until the next settlement.

51
267. Taking into consideration the received feedback, ESMA understands that when
STM model is applied, variation margins are paid and settled end-of-day. Therefore,
ESMA considers that reporting of variation margins needs adjustments to better
reflect the specificities on the STM model, while ensuring that authorities receive
the complete information about the margins. For that reason the Guidelines were
amended to clarify that under STM model counterparties should report daily change
in the variation margins.
268. Moreover, in relation to paragraph 284 of the CP, two respondents challenged
the reporting of margin currencies “as long as the base currency chosen is one of
the major currencies which represents the greatest weight in the pool”. In their view,
the margin currency could be bilaterally agreed by counterparties in their relevant
contractual annexes and may not necessarily be the currency with the greatest
weight in the pool. Such reporting would not represent the contractual agreement
between the counterparties. Therefore, following this feedback, ESMA has
amended accordingly the Guidelines providing that the margin currencies to be
reported should be the ones contractually agreed between the counterparties and
maintaining the originally proposed guidance only for the cases where the currency
has not been contractually agreed.
269. In addition, one respondent asked for clarifications on margins updates for
uncollateralised trades considering that collateral information has been included in
Table 3 only as provided by the RTS on reporting. On this aspect ESMA clarifies in
its Guidelines that the reporting entities subject to margin reporting obligation,
would need to submit at least one margin report (field 3.28 populated with action
type ‘New’), even if only to inform that the derivative contract is uncollateralised.
Should ’UNCL‘ be the latest value submitted, no further margin update is expected.
For details regarding the generation of the missing margin information report please
see the section 7.3.2.2.
270. Some other respondents complained about the amendments in the format of
collateral portfolio code which under the ITS on reporting does not allow anymore
the reporting of special characters. This means that any market participants who
previously included special characters in the collateral portfolio codes will need to
re-issue any such codes to meet the new validation requirements. Following this
feedback, ESMA checked the relevance of this issue on the overall data reported
and found that it was negligible. In addition, the removal of special characters from
the reporting of collateral portfolio code aligns with the CDE guidance. For the
reasons above, this feedback was not accommodated.
271. On the same topic, one respondent sought clarification on the uniqueness of
collateral portfolio code on the level of counterparty, since some entities use the
same collateral portfolio code for different pools of collateral (e.g. collateral portfolio
code is unique within, but not across asset classes). On this aspect ESMA clarifies
that the collateral portfolio code should be unique on the level of the counterparty
and consequently, the margins reported for a specific collateral portfolio code
should be equal when reported for different transactions/positions at the same
reference date.

52
272. Another respondent asked for clarifications on how to account for the
independent amount to be reported when exchanged in addition to initial margin.
On this topic, ESMA clarified that in principle, and in compliance with the CDE
guidance, any collateral under the definition of initial margin is to be reported under
the initial margins fields.
273. One respondent sought clarification on how to report penalty payments on
Smart Derivative Contracts (SDC) and whether the margin of an SDC should be
reported as an initial margin or as a variation margin. ESMA noted these
considerations without updating Guidelines at this stage, however further
clarifications may be provided in the future on this topic.
274. Furthermore, one respondent proposed to discard paragraph 289 of the CP
which refers to the consistency in the reporting of margins because this provision
implies some level of reconciliation without providing any additional guidance as to
the reporting requirements of market participants. However, on this aspect ESMA
clarifies that counterparties should always check whether the data reported to TRs
are complete and accurate as referred in Article 1 of the RTS on reporting.
275. Another respondent did not support paragraph 259 of the CP in which it is
provided that ’If counterparties decide to post more collateral than required and this
additional collateral is not posted separately and independently of variation margin
and initial margin, both counterparties need to include this in the initial and or
variation margin reported‘. In their view the margin posted in excess of the required
initial/variation margin should be allocated to excess collateral, independently of
whether it was posted within the initial/variation margin payment or not. However,
ESMA noted that the definition of excess collateral applied in the RTS on reporting
is in line with the CDE guidance thus the proposed approach cannot be
accommodated.
276. Finally, one respondent complained about the fact that reporting of margins
suffers from issues, such as discrepancies in the aggregate margin posted by one
counterparty to another which does not correspond to the respective margin
received by the other counterparty, and discrepancies in the aggregate variation
margin posted and received by some CCPs which differ significantly, although they
should be equal.
277. On this aspect, ESMA remarks that counterparties should report margin in a
consistent way as referred in paragraph 289 of the CP and that counterparties
should always check whether the data reported to TRs are complete and accurate
as referred in Article 1 of the RTS on reporting.
3.1.20 Identification of the trading venue
Q50. Are there any further clarifications required with regards to the reporting of the
trading venue?
278. In the CP, ESMA proposed clarifications for the identification of the trading
venue in the field ’Venue of execution‘ (field 2.41), which were mostly welcomed
while some further clarifications were asked.

53
279. The field ’Venue of execution‘ should be populated in accordance with the type
of conclusion of the derivative, notwithstanding the classification of the derivative
as ETD or OTC. The ISO 10383 segment MIC code should be used. For derivatives
executed on a RM, MTF, OTF or SI, the segment MIC code should be used. For
third country trading venues considered as equivalent to a regulated market and
organised trading platform outside of the Union, where the segment MIC does not
exist, they should use the operating MIC. When traded OTC, the counterparties
should either use the code ‘XOFF’ or ‘XXXX’ depending on the admission of the
financial instrument to trading on a trading venue.
280. Respondents asked for clarification regarding the reporting of derivatives
executed on UK regulated markets, in particular if they are to be reported as OTC
or ETD, given that they are traded on a venue. With regard to the ‘Venue of
execution’ field, ESMA recalls that, notwithstanding the use of the MIC code, the
derivatives contracts traded outside European regulated markets or third country
trading venues considered as equivalent to a regulated market in accordance with
Article 19(6) of Directive 2004/39/EC should be considered OTC as opposed to
ETD, and their reporting should be performed according to such qualification.
281. Respondents to the CP highlighted the need for clarifying that derivatives
executed on or pursuant to the rules of venues should be considered as on venue
trading. For example, derivatives such as bilaterally negotiated or pre-arranged
derivatives formalised pursuant to the rules of a venue, still should be reported with
the relevant platform identifier.
282. Even if some respondents have highlighted the difficulties and reporting
implications to consider derivatives negotiated outside EU or third country
equivalent RMs as OTC, ESMA recalls that the definition of OTC transactions is
included in EMIR therefore OTC derivatives are to be reported consistently with
their qualification.
3.1.21 Fields related to clearing
Q51. Are there any further clarifications required with regards to the reporting of
clearing?
283. The CP provided guidance on the reporting of clearing, particularly the use of
the field ’Cleared‘, the reporting process applicable to bilateral derivatives that are
later accepted for clearing, the reporting process applicable to on-venue derivatives
accepted for clearing on the same day, the execution timestamp for cleared trades,
the fields ’Clearing obligation‘, ’Central counterparty‘ and the disclosure of final
parties to a cleared transaction (paragraph 320 of the CP).
284. Most of the additional clarifications provided were supported, except the
disclosure of the final parties by the trading venues or the clearing house for
anonymously-executed cleared transactions, as proposed in the CP, which raised
numerous concerns due to inconsistency of the disclosure obligation with the
anonymity requirement. ESMA notes however that the exception under which such
disclosure requirement is indeed unnecessary applies only to standardised on-

54
venue derivatives which are cleared in the course of same day by a CCP, which to
a great extent mitigates the risk. The same treatment cannot be applied to
derivatives netted by a clearing house that is not a CCP, therefore ESMA retained
its guidance.
285. Another respondent noticed an inconsistency in the drafting using ’COMP‘ for
position component instead of ’POSC’. The Guidelines were corrected.
286. One respondent has indicated difficulties in the workflow when the derivatives
are traded on a trading venue and cleared on the same day, since it implied a logic
to hold the transaction until notice of acceptance by the CCP. ESMA underlines
that Article 2(2) of the RTS on reporting applies to derivatives that are cleared on
the same day and that, consequently parties should be aware of the clearing
acceptance. Otherwise, the clearing should not be considered as occurring on the
same day.
287. Last, some respondents also wondered whether a validation rule will be applied
to check if the validity of the central Counterparty identifier is representing a valid
CCP according to EMIR. ESMA considers that such validation rule would ensure
better quality of EMIR reporting, however at this stage a list of all CCPs (i.e. not
only those that are authorised or recognised under EMIR) is not available.
3.1.22 Fields related to confirmation
Q52. Are there any further clarifications required with regards to the reporting of
confirmation timestamp and confirmation means?
288. The additional explanation provided in the CP on the reporting of confirmation
timestamp raised some questions regarding novations and derivatives concluded
on venue (not cleared) for which the trading venue rules implies the acceptance of
transaction terms between parties.
289. With regard to novations one respondent asked whether the field ’Confirmed‘
should be updated to its new status and whether the field ’Confirmation timestamp‘
should be updated. Regarding confirmation of a contract after it was reported as
unconfirmed, novation or portfolio compression of such contract, the field
’Confirmed‘ should be updated to its new status, as well as the field ’Confirmation
timestamp’.
290. With regard to derivatives concluded on venue (not cleared) for which the
trading supposes the acceptance of transaction terms between parties, one
respondent argued that they should automatically be regarded as electronically
confirmed. ESMA considers that the trading and the confirmation process on such
venues depends on the venue itself and cannot be regarded as automatically
confirmed for all of them and recommends that careful scrutiny should be used to
determine whether the transactions should be considered as confirmed. ESMA
therefore recommends filling the field ’Confirmed‘ with the appropriate value
’NCNF‘, ’ECNF‘ or ’YCNF‘ depending on the method of confirmation (even if it is
unlikely to be populated with ’YCNF‘, given the level of automation such trading
requires).

55
3.1.23 Fields related to settlement
Q53. Are there any further clarifications required with regards to the reporting of
settlement currencies?
291. The CP included clarification regarding the currency code to be used to populate
the field ’Settlement currency‘. Respondents to the consultation asked for a
clarification of the ISO standard to be used for the currency code and asked for
guidance relating to the code to be used for historical and offshore currencies.
292. ESMA proposes to clarify that ISO 4217 currency codes are to be used for the
field ’Settlement currency’. The validation rules for all currency fields allow for the
use of historical currencies, however those are not expected to be reported as
settlement currency.
293. For the case of offshore currencies, ESMA wishes to recall the position taken in
the RTS on reporting: while the CDE guidance suggests the reporting of a field
’Settlement location‘ for derivatives to cope with the case of offshore currencies and
to keep the field ’Settlement currency‘ expressed in onshore currency, ESMA did
not see at this stage the reporting of this field as necessary and proposed that for
the derivatives traded in off-shore currencies, the counterparties simply report
onshore currency in the relevant currency fields.
294. Questions on reporting of cryptocurrencies are addressed in section 3.1.27.
3.1.24 Reporting of regular payments
Q54: Are there any additional clarifications to be considered related to reporting of
regular payments?
295. In the CP, ESMA clarified that taking into consideration the contract type,
counterparties should report only those fields related to data elements of regular
payments that apply to a given derivative. Furthermore, ESMA stated that the report
should contain information in dedicated fields for each fixed or floating leg of a
derivative and that the same rule applies in the case of data elements describing
the reset frequency and reference period of the floating rates.
296. Also, ESMA proposed to identify floating rates with an ISIN and/or with a 4-letter
standardized code, explicitly included in the ITS on reporting, and that the official
name of the rate, as assigned by the index provider, should be always reported.
297. Half of the respondents argued about the identification logic of floating rates,
requesting clarifications and suggesting rewording proposals based on the
assumption that multiple fields request the reporting of the same information.
298. ESMA confirms there are different purposes (specific identification of the
underlying, or specific identification of the fixed rate/ floating rate) that lead to
subsequent requests for information in the reporting format fields. It was also
clarified that the existing condition linking the fields 2.13 (‘Underlying identification
type’), 2.79 (‘Fixed rate of leg 1 or coupon’), and 2.85 (‘Name of the floating rate of

56
leg 1’) identifies the fields in which information related to fixed or floating rate has
to be found.
299. Two respondents highlighted the necessary harmonization of validation rules
for fields 2.13, 2.79 and 2.85 that should consistently refer to same fields. In this
respect, ESMA updated accordingly the validation rule applied for field 2.13
(‘Underlying identification type’).
300. Regarding the information related to the identification of the underlying two
respondents pointed out that a further clarification will be welcomed, in order to
avoid double reporting of the same information on fields 2.14 (‘Underlying
identification’) and 2.83 (‘Identifier of the floating rate of leg 1’), or at the level of
fields 2.14 and 2.99 (‘Identifier of the floating rate of leg 2’). The same issue has
been observed for the indication of the floating rate index, linked with the reporting
of fields 2.15 (‘Indicator of the underlying index’) and 2.84 (‘Indicator of the floating
rate of leg 1’), or in the case of fields 2.15 and 2.100 (‘Indicator of the floating rate
of leg 2’).
301. Based on the feedback received, ESMA clarifies, at the validation rules level for
fields 2.83 and 2.99 that having the same floating rate reported in both underlying
and floating rate fields should be avoided, by leaving fields 2.83 and 2.99 blank,
when field 2.14 (‘Underlying identification’) is populated. The same rule applies in
the validation rules for fields 2.84 and 2.100, when field 2.15 (‘Indicator of the
underlying index’) is populated.
302. One respondent stated that specific clarification related to the payment
frequency period will help to ensure consistent interpretation of the information that
has to be reported.
303. ESMA, therefore, clarified that the longest time of the period identifier should be
used rather than transforming the value of the payment frequency period into
another payment frequency period (e.g. a year into months).
3.1.25 Reporting of other payments
Q55: Are there any further clarifications needed with regards to the reporting of
other payments?
304. Some respondents asked for clarifications concerning how the initial and final
principal exchange amounts of a cross-currency swap are to be reported as other
payments.
305. ESMA clarifies that the elements related to the ’other payments‘ dataset could
be reported more than once, in the case of multiple payments, and the final principal
exchange amount should be reported once it has been agreed, and not at the time
when the payment will be effective.
306. One respondent requested guidance on whether novation fees are reportable
as other payments. ESMA acknowledges that there might be other instances of
’other payment types‘, currently not covered by the three alternatives, outlined in

57
the respective field, but decided at this stage to limit the list of them to those
proposed in the CDE Technical Guidance and included in the ITS on reporting.
307. Two respondents inquired, in the case that there is a need to send historical
modifications/corrections whether the LEI code of the other payment payer/receiver
should be valid at the time of reporting or on the other payment date. ESMA clarified
this aspect in the validation rules.
308. One respondent mentioned that at the level of the validation rules applicable to
fields 2.77 ‘Other payment payer’ and 2.78 ‘Other payment receiver’, conditioning
is required because they cannot contain the same LEI unless this corresponds to
the LEI of the CCP. Based on the consultation feedback, ESMA updated the
respective validation rules accordingly.
3.1.26 Dates and timestamps fields
Q56. How would you define effective day for novations and cash-settled commodity
derivatives?
Q57. What are reporting scenarios with regards to dates and timestamps which you
would like to be clarified in the guidelines? Are there any other aspects that need to be
clarified with respect to dates and timestamp fields?
309. The respondents agreed generally with ESMAs proposal of effective date.
ESMA clarified in the Guidelines that in case of cash-settled commodity derivatives
and novations the same rule applies, even though other references were made by
market participants, i.e. to calculation and/or delivery period.
310. The respondents agreed generally with the definition of expiration date / early
termination date. One respondent asked for a clarification of “unadjusted”. This
term, referring to dates not adjusted for non-working days, is considered clear and
is used also in the CDE Technical Guidance. The table with an example was
ultimately removed as it was deemed that it did not contribute to the clarification.
3.1.27 Reporting of derivatives on crypto assets
Q58. Are there any other aspects that need to be clarified with respect to the derivatives
on crypto-assets?
311. The main suggestions made by respondents were:
a. To use in the field 2.11 ’Asset class‘ the value ’COMM‘ (commodities) for
derivatives based on crypto-assets, as in their view crypto-assets have similar
aspects to commodities.
b. To approve a new underlying category of assets for derivatives based on crypto-
assets.
c. To clarify how to report the currency fields for derivatives based on crypto-
assets, when there is for example a settlement, valuation, collateralization, etc.

58
They also asked about if it is possible to apply a conversion to an ISO 4217
currency.
312. Because of the ongoing developments in regulation that are currently being
discussed about the crypto-assets, ESMA has decided when drafting the ITS and
RTS on reporting not to include any detailed requirements with regard to the
reporting of derivatives based on crypto-assets until there is further developed and
coherent regulation. This is the reason why ESMA has decided only to include in
the RTS on reporting an additional field ’Derivative based on crypto-assets‘ in order
to be able to assess the trading volumes and outstanding risk as well as to analyse
how these instruments are reported. Therefore, a new underlying category of
assets would not be compliant with the ITS on reporting. Similarly, it would be
erroneous and not future-proofed to e.g. require that all derivatives on crypto-assets
should be reported as commodity derivatives.
313. Regarding on how to report the currency fields for the derivatives based on
crypto-assets, ESMA recalls that the currency fields only allow for currencies listed
on ISO 4217 Currency Codes. Therefore, these fields should not be populated with
so-called crypto-currencies. Under RTS on reporting there is only obligation to
report the field ’Derivative based on crypto-assets‘ with a boolean format for these
derivatives on crypto-assets that fulfil the definition of derivatives under MiFID,
filling in the fields related to currencies with a value converted to one of the listed
ISO 4217 currency codes.
314. Other suggestions made by respondents in response to other questions in the
CP were:
a. To clarify how to report derivative transactions where the underlying is an index
or a basket which includes crypto assets.
b. To include information related to new products based on crypto-assets in the
reference data to avoid potential inconsistency between counterparties when
one counterparty could consider this new product as based on crypto-assets
and the other not.
c. To clarify the case of a physical settlement for derivatives based on crypto-
assets, in particular how the settlement currencies should be reported.
315. With regards to indices and baskets based on crypto-assets, the reporting does
not differ from other types of derivatives. The counterparties should report the name
of the index as well as, if available, its ISIN and/or 4-letter code indicating the index.
In the case of baskets, counterparties should report only those components that
are financial instruments traded on a trading venue.
316. Changes to the content of the instruments reference data under MiFIR are out
of scope of these Guidelines, therefore the suggestion was not considered.
317. Regarding on how to report the settlement currency fields for these new
derivatives, same logic applies as already indicated above. Furthermore, it should
be noted that settlement currency should not be reported in the case of physically-
settled derivatives.

59
3.1.28 Reporting of complex products
Q59. Do you consider any scenarios in which more clarification on the correct
population of the fields related to package transaction is needed?
318. ESMA included proposals for the newly introduced fields related to package
transactions in compliance with the CPMI-IOSCO CDE Guidance in the CP and
asked about scenarios, where more clarification on the correct population of fields
is needed. Several respondents provided their comments on the proposals, mainly
reacting to the fact that the guidance gave the impression that non-EMIR products
would be made reportable through the approach taken for package transactions.
Only one respondent asked for more clarification on the reporting of Roll-Overs in
this context. ESMA would like to clarify that Roll-Overs are not considered as
complex products as such.
319. Regarding the concerns raised by the majority of respondents that non-
reportable products could be brought into the scope through the definition of
package transactions, ESMA clarifies that the misunderstanding resulted from
using a swap as an example in the CP. When a package transaction includes
reportable and non-reportable contracts (e.g. an FX spot contract and FX forward,
that are executed as such rather than as an FX swap) only those contracts that are
in the scope of Article 9 of EMIR need to be reported (in this case only the FX
forward). The relevant fields for package transactions (e.g. field ‘Package price’)
should nevertheless be populated corresponding to the entire package negotiated,
rather than only to the reportable part of the package transaction. It is also worth
noting that in the case of an FX swap which is executed as such, the entire
derivative should be reported (as an FX swap, in a single report).
320. As there were uncertainties when the reporting field 2.6 ’Package identifier’
should be used, it is highlighted that this field is relevant when a complex derivative
cannot be reported by using only one single report (e.g. as the fields would not
allow for it; please see also Recital 3 of the RTS on reporting) or it is traded as part
of a package transaction (e.g. negotiated not as single, individual, trades but in its
entirety).
3.1.29 Ensuring data quality by counterparties
Q60. Which of the proposed alternatives with regard to significance assessment method
do you prefer? Should ESMA consider different metrics and thresholds for assessing
the scope of notifications sent to the NCAs?
Please elaborate on the reasons for your response.
Q61. Do you prefer Option 1 or Option 2 with regard to the number of affected reports
notified to the NCAs? Please elaborate on the reasons for your response.
Q62. Should significance of a reporting issue under Article 9(1)(c) of the draft ITS on
reporting also be assessed against a quantitative threshold or the qualitative
specification only is appropriate? In case threshold should be also applied, would you
agree to use the same as under Alternative A or B? Is another metric or method more
appropriate for these types of issues? Please elaborate on your response.

60
Q63. Are there any other aspects or scenarios that need to be clarified with respect to
ensuring data quality by counterparties? Please elaborate on the reasons for your
response.
321. In the CP, ESMA summarized the legal background of ensuring data quality by
counterparties and addressed the need for further specification of the key metrics
and thresholds to assess the scope of data quality issues notifications, mainly:
a. which data quality issues are considered as significant and
b. what is a significant number of affected reports.
322. ESMA proposed two alternatives to calculate a significant number of reports
together with an example of thresholds to be used for the assessment. First
alternative (Alternative A) was based on a ratio of the number of affected reports
over monthly average of the number of submissions. The second (Alternative B)
was based on a ratio of number of affected reports over the number of submissions
during the period when misreporting existed.
323. Nearly all respondents expressed their preference for Alternative A appreciating
its robustness and efficiency. This metric will capture systematic errors and will be
less susceptible to issues that are resolved within a short period of time, while it will
be easier to implement and more practical to use. One respondent advocated for
full reporting of all data quality issues, however ESMA considers such proposal as
too burdensome and unnecessary.
324. Several respondents suggested that TRs should be requested to share the
monthly number of submissions and/or daily number of submissions with ERRs or
RSEs. For this purpose a daily number of submissions provided by the TRs in the
end-of–day reports can be used.
325. Overall, respondents did not object to the proposed thresholds, although some
respondents highlighted the need to set a minimum threshold in order to ascertain
that small reporting entities are not obliged to submit notifications to the NCAs.
Such minimum threshold was already included in the CP and as no alternative
value for this threshold was proposed it will be kept, together with other proposed
thresholds, as a starting point for the calibration of the requirement. One respondent
proposed that small and non-complex institutions (SNCIs) within the meaning of
Article 4(1) No 145 of the CRR
13
should be carved out of the requirement altogether.
Such an explicit exception however cannot be introduced at the level of these
Guidelines, moreover the proposed minimal threshold ensures to alleviate the
burden of minor reporting entities.
326. Respondents to the CP also did not object to ESMA’s proposal to use other
means than these Guidelines for publication of the relevant thresholds so that
flexibility and optimal calibration of the requirement was ensured.
327. One respondent requested clarification whether the proposed thresholds apply
to all the categories of reports. In the CP ESMA envisaged only one set of
13
Regulation (EU) No 575/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 26 June 2013 on prudential requirements for
credit institutions and investment firms and amending Regulation (EU) No 648/2012

61
thresholds applicable to all the categories, however if deemed necessary for
optimal calibration of the requirement, it might be considered in the future to set
different thresholds for different categories.
328. Another respondent asked whether a RSE is expected to notify the
counterparty's NCA of any significant issues impacting reporting on the other
counterparty’s behalf. The ITS on reporting requires the entity responsible for
reporting to notify its competent authority and, if different, also the competent
authority of the reporting counterparty. Hence, RSE is expected to send the
notification to NCAs only if it is ERR for some or all of the counterparties on whose
behalf it reports.
329. As pointed out by one respondent to the CP, this set-up of the notification
requirement implies that in case of a market-wide issue pertaining to data quality
such an event is likely to be reported to NCAs multiple times by multiple ERRs.
However, ESMA considers that setting up a finer and more clean-cut process would
become overly complex and more burdensome to implement and operate by the
ERRs.
330. An alternative approach has been proposed by one respondent suggesting that
the responsibility to notify the NCAs of certain data quality issues should be
transferred to the TRs. This proposal however is not in line with the
abovementioned requirement stipulated in the ITS on reporting.
331. This respondent also commented that NCAs should focus on large players first,
and only after a certain milestone in data quality is reached, the regulators should
target the smaller entities, and also to prioritize the significance of risk setting at the
position level reports. Even though a risk-based approach is often used by the
NCAs, no further guidance will be provided in the Guidelines since the supervisory
practices of NCAs are not in scope of these Guidelines.
332. ESMA also noted a comment on substantially different levels of internal controls
pertaining to data quality implemented by various reporting entities, and the
suggestion for ESMA to issue guidance on best practice controls to prevent or
detect errors and omissions and principles for effective prioritization of reporting
risks. ESMA will not issue guidance on best practices in the near future, but it might
be considered further along when sufficient experience is gathered with the revised
reporting regime.
333. The respondent also incorrectly pointed out that for misreporting due to errors,
the use of the ‘Error’ action type signals to the regulators the identification and
rectification of errors in reporting. ESMA reminds again that action type ‘Error’
should only be used in scenarios allowed by the Guidelines, especially to cancel a
report that should never have been reported in the first place. Action type ‘Error’
should never be used as a correction measure for misreported information.
334. In the CP ESMA included several examples of scenarios describing the
assessment of requirement to notify NCAs under different circumstances. One of
the scenarios included case where the RSE submits reports on behalf of several
counterparties, but at the same time it is an ERR for only one of them. At the level
of RSE the data quality issue is assessed as significant, but at the counterparty

62
level the issue is significant only for the counterparty for which the RSE is ERR.
With regards to the number of affected reports to be reported to the NCAs, ESMA
sought respondents view on two options. Under Option 1 the RSE would notify to
the NCAs only the number of reports pertaining to the counterparty for which it is
ERR, under Option 2 the RSE would include in the notification affected reports of
all the counterparties.
335. Majority of respondents expressed their preference for Option 1, pointing out
that the effort to report all reports would be disproportionate to the benefit of NCAs
and arguing that it is best to focus on the reporting of ERR. ESMA therefore adapted
the example in the Guidelines to reflect Option 1.
336. With regard to data quality issues to be notified under Article 9(1)(c) of ITS on
reporting ESMA provided in the CP qualitative criteria to assess which issues are
considered as significant. Views of the industry were sought on whether also
quantitative criteria should be applied and whether different metrics and thresholds
than those already proposed should be introduced.
337. Almost every respondent provided an opinion that the quantitative criteria
should be also applied and that proposed metrics and thresholds are appropriate
also for the assessment of issues under Article 9(1)(c) of ITS on reporting. One
respondent suggested that a number of affected UTIs should be used as a metric,
however ESMA is of the view that such a metric would heavily downplay the
significance of data quality issues, especially for example for valuations or collateral
data. ESMA took note of the expressed views and amended the Guidelines to
reflect the majority opinion.
338. As a follow up to the requirement of Article 9(1)(c) of ITS on reporting a
respondent asked for an exhaustive list of errors that would cause a rejection by a
TR. ESMA confirms that such list will be available in the form of validation rules
which will be applied by the TRs on the submitted data.
339. Some respondents perceived as conflicting the guidance not to notify every
single reconciliation break and the guidance to notify misreporting caused by
incorrect or inconsistent interpretation of the content of the fields. Generally,
reconciliation break can be caused by various reasons, for example it can happen
due to misreporting of the field due to a technical issue or fat-finger error and swift
correction rectifies the issue. On the other hand, it can be caused by long-lasting
diverging interpretation between counterparties of how to populate the field. This
case is of special interest to the regulators as it provides an opportunity to analyse
the inconsistencies and issue further guidance if considered useful. However, since
the quantitative criteria were introduced also for data quality issues under Article
9(1)(c) of ITS on reporting, it should now be clear that not every single reconciliation
break should be notified, and ESMA removed the confusing sentence from the
Guidelines.
340. In addition, respondents to the CP requested following further clarifications:
a. when to report errors to authorities and whether the notifications are to be
provided on a regular basis,

63
b. what is the difference between Article 9(1)(a) and Article 9(1)(b) of the ITS on
reporting with respect of omitted reports,
c. if historical errors are expected to be corrected.
341. ESMA included relevant clarifications in the Guidelines.
342. Further guidance was requested as to the format and possible harmonized
template of the notifications. ESMA noted the suggestion and further examined the
appetite for such guidance. It was determined that common harmonized template
is mainly supported as it will ease the burden and provide certainty for many entities
which need to provide notifications to multiple NCAs. On the basis of this feedback
ESMA introduced additional guidance on the data quality notification template into
the Guidelines.
3.2 Reporting per product type
3.2.1 Reporting of IRS
Q64. Are there any other aspects in reporting of IRS that should be clarified?
343. In the CP, ESMA proposed that, when reporting IRS, counterparties should
describe the underlying fixed or floating rates in the dedicated rate fields for leg 1
and leg 2 (fields 2.79-2.110), rather than e.g. providing the floating rate in the
underlying index field.
344. The feedback received was generally supportive and included few clarification
requests.
345. To clarify, ESMA proposes that counterparties should populate the following
three distinct fields to describe a floating rate:
a. to the extent that they are available for a given rate, the identifier (fields 2.83
and 2.99), which should be populated with ISIN, and/or the indicator (fields 2.84
and 2.100), which should be populated with a standardised 4-letter code; and
b. in all cases, the name (fields 2.85 and 2.101), which should be populated with
the full name of the rate.
346. ESMA notes that, in the drafting of the ITS on reporting, the provision of the
official name was considered important as this is the way in which the rates are
referred to in the register for clearing obligation.
347. ESMA would also like to clarify that the greying of the fields 2.109 and 2.110 in
the example set out in Table 29 of the CP was because in that particular example
the IRS had no additional spread. As correctly pointed out by the respondent,
however, the spread is indeed conditionally mandatory in the draft validation rules
(i.e. it must be populated when floating rate is populated). Therefore, ESMA clarifies
that, where no spread exists, counterparties should populate the field with zero (the
relevant example was updated in the Guidelines).
348. Finally, in response to a request that ESMA should provide an example with all
relevant fields (including counterparty data such as direction), ESMA would like to

64
refer to the example set out in the section 6.1.6 (“OTC Contract type between FCs
which requires the population of fields ‘Direction of Leg 1’ and ‘Direction of Leg 2’”)
and confirm that it covers also IRS reporting.
14
3.2.2 Reporting of swaptions
Q65. Are there any other aspects in reporting of swaptions that should be clarified?
349. In the CP, ESMA proposed that, when reporting swaptions, the counterparties
should provide both the fields related to options (fields 2.132-2.142) as well as the
fields characterising the underlying swap (fields 2.79-2.110).
350. ESMA proposed that the execution of the swaption should be reported with
action type ‘Terminate’ and event type ‘Exercise’. The resulting swap should be
reported with action type ‘New’ and event type ‘Exercise’. The swaption and the
resulting swap should have each its own UTI. Moreover, when reporting the
resulting swap, the ‘Prior UTI’ field (field 2.3) should be populated with the UTI of
the swaption.
351. Like the IRS reporting above, ESMA received general support on its proposal
while some clarification requests were made.
352. ESMA’s feedback in the section above (regarding fields 2.109 and 2.110 of
Table 29 of the CP) is also applicable to Tables 30 and 32, i.e. there is no additional
spread for the swaption in the example. The respondent further noted that no value
is provided in the ‘Example’ column for field 2.138 ’Strike price currency / currency
pair‘ though a value would be expected to be reported based on the draft validation
rules and a value does seem to have been included in the XML message. ESMA
would like to clarify that the greying of field 2.138 is because the strike price is
expressed in percentage and to confirm the erroneous existence of ‘EUR’ in the
XML message (the relevant example is correctly updated in the final Guidelines).
353. Finally, ESMA would like to confirm the existence of a mistake in the example
of Table 31 of the CP which illustrates the termination of a swaption due to the
exercise, i.e. the UTI should be the same with that used in Table 30, and the ‘Prior
UTI’ field should be empty (the relevant example is correctly updated in the final
Guidelines).
3.2.3 Reporting of other IR products
Q66. Are there any other aspects in reporting of FRAs, cross-currency swaps, caps and
floors or other IR derivatives that should be clarified?
354. In the CP, ESMA proposed that when reporting Forward Rate Agreements
(FRAs), the counterparties should report the underlying rate in the fields pertaining
14
Section 6.1.6 should be read together with the table in section 4.12 , in which it is summarized how to determine the counterparty
side for every product, including the IRS. It should be clear from that table that for OTC FX Swap and IRS, the counterparty side
should be determined accordingly by the counterparties and that the reportable fields should be ’direction of leg 1‘ and ’direction
of leg 2‘ only.

65
to the underlying section (fields 2.13-2.16). Furthermore, ESMA clarified how to
correctly report the fields ’Execution timestamp‘, ’Effective date‘, ’Maturity date‘ and
’Settlement date’.
355. ESMA received general support on its proposal.
356. Two respondents provided an example of a FRA using commonly agreed
industry terms for the different dates and asked if: i) the effective date could be
interpreted as the future date on which the obligation between the parties arises;
and ii) the maturity date for the purpose of reporting can be interpreted as the fixing
date of the FRA. To ensure full clarity ESMA included an example in the Guidelines
in order to clarify what is expected to be reported for these dates.
357. In the CP ESMA clarified that other instruments that should be classified as
interest rate derivatives are cross-currency swaps as well as caps and floors.
358. In the case of caps and floors, the counterparties should populate both the fields
relevant for options and fields relevant for interest rate derivatives (similarly to the
example of swaption illustrated in the section 5.2).
359. In the case of cross currency swaps, the counterparties should populate both
the fields relevant for foreign exchange derivatives and fields relevant for interest
rate derivatives.
360. Respondents did not provide specific comments on these additional
clarifications for cross-currency swaps, caps and floors.
3.2.4 Reporting of FX swaps and forwards
Q67. In the case of FX swaps, what is the rate to be used for notional amount of leg 2?
Should it be the forward exchange rate of the far leg as it is in the example provided?
Or the spot exchange rate of the near leg?
Q68. In the case of FX swaps, considering that the ‘Final contractual settlement date’ is
not a repeatable field, should the settlement date of the near leg be reported, for
example using the other payments fields?
Q69. Do you have any questions with regarding to reporting of FX forwards?
Q70. Do you have any questions with regarding to reporting of FX options?
361. In the CP, ESMA explained how reporting of FX swaps and forwards should be
done. Several detailed questions were raised to get industry feedback on the
proposed reporting process and fields.
362. Regarding question 67 of the CP, most respondents stated that the forward
exchange rate of the far leg should be used for notional amount of leg 2, as initially
proposed in the CP.
363. Regarding question 68 of the CP, respondents considered the proposal to report
the settlement of a near leg in other payments fields as inappropriate because it
implies using a field differently from its initial purpose and questions the use of such
data. Since populating fields differently from their original purpose is error-prone
because of the confusion it creates, ESMA discarded the proposal of question 68
of the CP.

66
364. Question 69 of the CP asked whether there were additional questions regarding
the reporting of FX forwards. A respondent asked clarification on the use of the
delivery type ’PHYS‘ for FX swaps and FX Options, since the physical delivery of
those is done in currencies and should therefore be ’CASH‘ instead. ESMA clarifies
that where the delivery involves an exchange of amounts in the original currencies,
the delivery type should be ‘PHYS’. Delivery type ‘CASH’ would be reported e.g. in
the case of NDF. ESMA has adjusted the examples accordingly.
365. Question 70 of the CP asked whether there were additional questions regarding
the reporting of FX options, but only minor comments on the population of fields
were received, which were taken into account in the Guidelines.
3.2.4.1 Additional considerations on the reporting of currencies
Q71. What is the most appropriate way to report direction of the derivative and of the
currencies involved with an objective to achieve successful reconciliation? Please
detail the reasons for your response.
366. Last, the CP requested feedback on the most appropriate way to report direction
of the derivative and of the currencies involved with an objective to achieve
successful reconciliation with different options. Two options were mainly
considered by respondents: the agreement between the parties using a market
convention based on the alphabetical order of the currencies and the use of
reconciliation rules by the TRs to solve the reconciliation challenge. The views were
split on this question, the options that required ex-ante decision between parties
and the use of a convention were logically not supported by respondents except
TRs, while TRs supported the use of a convention. Given the more comprehensive
answers provided in the reconciliation section, where respondents have preferred
the option to require the TRs to manage the reconciliation of the two legs of the
derivative, ESMA has consequently updated the guidance in line with the answers
provided in the reconciliation section. As a consequence, TR should reconcile FX
swaps legs and currencies irrespective of the order of reporting done by the
counterparties.
3.2.5 Reporting of NDFs
Q72. Do you agree with the population of the fields for NDF as illustrated in the above
example? Should other pairs of NDFs be considered? Please provide complete details
and examples if possible.
367. The CP provided example on the population of the fields for NDF and asked for
feedback on those, which were broadly not questioned, but some inconsistencies
were pointed out and were corrected accordingly.
3.2.6 Reporting of CFDs
Q73. Do you agree with the population of the fields for CFD as illustrated in the above
example? Do you require any other clarifications?

67
368. The respondents who commented on the CFD example were overall favourable
of the provided clarifications. A few additional questions were raised.
369. One respondent requested to provide an example with a non-zero price
multiplier. This request was not taken on board, as the price multiplier will no longer
be a reportable field under the new technical standards.
370. One respondent flagged a typo in the ‘Notional’ field, which has been corrected
in the final version of the Guidelines.
371. One respondent asked to clarify that CFDs should always be reported at
position level. Such clarification was not included in the Guidelines, because the
reporting at position level is only a possibility that can be used when certain
conditions are met and when the two counterparties agree to report at position level.
372. Finally, one respondent asked if field 2.46 ’Final contractual settlement date‘
should be populated as it is mandatory for action type ‘NEWT’ as per the validation
rules. ESMA concluded that for contracts with no maturity date the counterparties
may not know the final contractual settlement date and changed the validation rules
accordingly.
3.2.7 Reporting of equity derivatives
Q74. Specifically, in the case of equity swaps, portfolio equity swaps and equity CFDs,
how should the notional and the price be reported in the case of corporate event and in
particular “free” allocations?
373. In the CP, ESMA asked about how the notional and price should be reported in
the case of corporate event and in particular “free” allocations, in the case of equity
swaps, portfolio equity swaps and equity CFDs.
374. One respondent answered that it should be advisable to apply a modification
message keeping the same UTI and adjust any changes to price, notional and
underlying instrument. Should the upstream system trigger a termination followed
by a new trade, counterparties should align with each other’s following best
practices. This respondent added that price for “free allocations” might follow the
MiFIR model of allowing ‘NOAP’ value (No applicable price).
375. One respondent indicated that it is difficult to provide an answer valid for all the
cases mentioned in the question. It considered more appropriate to underline that,
in case of a corporate event, the relevant trade is usually updated within the internal
systems, and this is followed by the exchange of a confirmation between the parties
involved. Accordingly, the reporting should be done consistently to i) the event that
has borne the modification within the position keeping systems and ii) the
confirmation with the relevant counterparty.
376. Having considered the received feedback, ESMA decided not to develop
additional clarifications on this matter.
377. One respondent mentioned that this section made reference to the event type
’Corporate actions‘ that is not known as an event type in the previous chapters.

68
ESMA clarified that the correct term would be ’Corporate event‘ and modified it in
the final Guidelines.
Q75: Are there any other clarifications required with regards to the reporting of equity
derivatives?
378. In the CP, ESMA asked whether any other clarifications were required with
regards to the reporting of equity derivatives.
379. One respondent commented that the notional amount for options should
recognise the asymmetry of risk for a buyer versus a seller of an option. This
proposal was discarded as the notional is defined already in the RTS on reporting.
380. One respondent highlighted the importance to complement the final version of
the Guidelines in this specific scope with further examples on ETDs, both futures
and options on equities. In response to this request, ESMA included an additional
example of ETD future on equity in the section 4.8.
381. One respondent noted that in the example provided in Table 41 of the CP,
neither field 2.17 ’Custom basket code‘, nor field 2.18 ’Identifier of the basket’s
constituents‘ were included even though field 2.13 ’Underlying identification type‘
was reported and so both fields 2.17 and 2.18 would be expected according to the
draft validation rules. It was also noted that, similarly, field 2.19 would also be
expected given that field 2.47 ’Delivery type‘ was populated with ’CASH‘. ESMA
confirmed this interpretation of the draft validation rules and the mentioned fields
should indeed be included. However, in the final Guidelines, ESMA included a
different example.
3.2.8 Reporting of credit derivatives
Q76: Are there any other clarifications required with regards to the reporting of credit
derivatives?
382. In the CP, ESMA asked whether any other clarifications were required with
regards to the reporting of credit derivatives.
383. One respondent highlighted the importance to complement the final version of
the Guidelines with further examples on the reporting of credit derivatives. In
response to this request, ESMA included a new more detailed example with all
relevant fields in section 5.8.
384. One respondent noted that in the example provided in Table 42 of the CP, given
that field 2.41 ’Venue of execution‘ was reported with the value ’XXXX‘, and field
2.31 ’Cleared‘ was reported as ’N‘, it would expect field 2.29 ’Confirmed‘, and
depending on the value of this field, presumably also field 2.28 ’Confirmation
timestamp‘ to have been included in the example. ESMA confirmed this
interpretation of the draft validation rules and included these additional fields in the
example. However, ESMA clarified that the proposed example may not contain all
the required fields, but the most relevant ones.

69
3.2.9 Reporting of commodity derivatives
Q77. Are there any other aspects in reporting of commodity derivatives that should be
clarified?
385. In the CP ESMA clarified several aspects regarding reporting of commodity
derivatives.
386. Furthermore, in the CP ESMA included an example of reporting of a peak load
future on the price of electricity.
387. The approach proposed in the CP has been broadly supported, however some
respondents asked for additional explanations.
388. One respondent proposes that non-standardized OTC derivatives should be
expressly exempt from the obligatory use of UPI, CFI and/or ISIN Codes for NFCs,
considering the difficulties for counterparties to obtain access to such codes. This
point has already been addressed in the ITS on reporting, which set out which
derivatives need to be identified with ISIN (only), and which with UPI (only).
Furthermore, in the FR on RTS/ITS ESMA addressed the most relevant comments
raised by the respondents in relation to the use of ISIN and UPI. Further comments
in this regard are also addressed in section 3.1.15 of this document.
389. Two respondents commented that for energy derivatives it should be sufficient
to report either field 2.119 or field 2.120. ESMA points out that there is no change
compared to the current applicable rules for those fields, which were also consulted
in the past with ACER.
390. One respondent asked a series of clarifications concerning Virtual Power
Purchase Agreements (VPPA).
391. ESMA has analysed the questions received and has determined that they
require interpretation of the Union Law and that similar queries on the nature of
VPPAs and related classification have been previously received by ESMA and
forwarded to the European Commission
15
. Once these have been clarified, ESMA
will update the EMIR Q&As accordingly.
392. One respondent inquired how to report multiple values for the days of the week.
ESMA clarifies that it is possible to report multiple values, e.g. ‘MOND’, ‘TUED’ (Mo-
Tu) or ‘WDAY’, ‘XBHL’ (weekdays excluding bank holidays) or other combinations.
The field 2.127 ’Days of the week‘ is already marked as repeatable and it will be
allowed at the level of the schema to provide multiple values. This has been further
clarified in the Guidelines.
15
The questions are published within a spreadsheet available on the Q&A webpage of the ESMA website

70
3.3 EMIR Tables of fields
3.3.1 Table 1 Counterparty data
Q78: Do you agree with the population of the counterparty data fields? Please detail the
reasons for your response and indicate the table to which your comments refer.
Q79: Is there any other use case related to the population of counterparty data which
requires clarifications or examples? Please detail which one and indicate which aspect
requires clarification.
393. In relation to section related to counterparty data reporting, overall the
respondents welcomed and supported the examples provided and requested some
minor clarifications.
394. In particular, one respondent requested to clarify whether the daily reports to be
reported to TR should be referred to: a) 2 reports per counterparty data and 1 report
per trade data + collateral or b) 2 reports per counterparty data and 2 reports per
trade data + collateral, as provided for SFTR reporting. On this ESMA clarifies that,
as per Article 1(4) of the RTS on reporting, where one report is made on behalf of
both counterparties, it shall contain the details set out in Tables 1, 2 and 3 of the
Annex in relation to each of the counterparties. Therefore, just the solution under
letter b) of this paragraph is acceptable.
395. Another respondent, in relation to the population of field 1.13 (‘Clearing
threshold of the counterparty 2’) proposed that only parties above the clearing
threshold would be required to ask for the “status” of their counterparties and only
in cases where an OTC derivative is actually signed/concluded, limiting the
population of field 1.13 only to cases where field 1.7 (‘Clearing threshold of
counterparty 1’) is ‘True’. In addition, the proposal set out that field 1.17 ’Direction‘
should be restricted only to cases in which the field 2.30 is ‘True’ or ‘False’.
However, this proposal would overcomplicate too much the reporting scenarios.
Furthermore, the conditionality of the direction field is not under discussion since
this field is fundamental to assess the directions of the risk involved in the
derivatives contracts. In addition, fields related to clearing thresholds should be
already part of the KYC information requested by FC to NFCs. Finally, ITS on
reporting requires NFC to timely inform of the change in the reporting responsibility,
i.e. when the NFC- becomes NFC+ or vice versa. So, in all the cases the
information about the clearing threshold should be already assessed by the relevant
parties.
396. One respondent requested clarifications on paragraph 474 of the CP on whether
the separate submissions referred therein are related to the two sides of a
derivative being reported separately or to each side being separated further so that
Table 1 data is reported separately from Tables 2 or 3. On this ESMA clarifies that
the separate submission in para 474 refers to the two sides of a derivative being
reported separately in case of voluntary delegation or allocation of responsibility.

71
397. One respondent requested complex examples along the full clearing chain
(alpha, beta, gamma trades). ESMA does not see further benefits in more examples
as these examples would be nothing different from already included cases.
3.3.2 Table 2 Common data
3.3.2.1 Reporting of action types at trade and position level
Q80. Do you agree with the approach to reporting action types? Please detail the
reasons for your response and include a reference to the specific table.
398. Respondents expressed support for the action types reporting examples, raising
however certain points for clarifications.
399. A few respondents asked how to treat fields that can be left blank in certain
scenarios, such as ‘Event type’ or ‘Prior UTI’. In particular, the respondents were
interested if the previously reported values should persist in the TSR if they are
subsequently reported as blank by the counterparty. The relevant clarifications
were included in the section 7.1.
400. Following to the requests from respondents ESMA added examples of a
modification of a position resulting from multiple events, of a correction of the
valuation and of position-level report of an OTC derivative cleared on the day of its
execution.
401. One respondent asked for which action types the counterparty data section is
mandatory. In this regard ESMA recalls that the mandatory/optional nature of each
field is specified in the validation rules.
402. One respondent asked if the margin update should be rejected if the
corresponding trade(s) are no longer outstanding. ESMA confirms that TRs should
only verify that at least one derivative to which a given collateral pertains has been
reported prior to the margin update.
403. Finally, with regards to margin updates, one respondent asked whether - and if
so, how - it will be possible to link the correction with the original, erroneous report.
ESMA clarifies that it is expected that such link can be established based on the
event date.
3.3.2.2 Other reportable details
3.3.2.2.1 Reporting of cleared / non-cleared trade
404. Respondent spotted typos for the reporting examples in this section at the XML
message level. ESMA considered this feedback and updated the Guidelines
accordingly.

72
3.3.2.2.2 Trading venue
405. One respondent argued that the case of financial instruments admitted to
trading or traded on a trading venue or for which a request for admission was made,
where the derivative on that financial instrument is not executed on a trading venue,
SI or organised trading platform outside of the Union, mentioned in paragraph 512
of the CP is not sufficiently clear. ESMA highlights that this paragraph sets out the
reporting requirement specified in the ITS on reporting and is also aligned with the
reporting of the trading venue field in transaction reporting according to Article 26
of MiFIR.
406. Further clarification was requested for the example of two SIs facing each other,
for reasons of consistency with the reconciliation rules. ESMA clarified in the
Guidelines that the field 2.41 ‘Venue of execution’ should only be populated with
values allowed under the ISO 10383 Market Identifier Code (MIC) standard and, in
this specific scenario, should contain the MIC of the counterparty that acts as the
SI for the given trade. This does not impact the reconciliation rules for this field.
407. One respondent highlighted that the reporting example of post-Brexit derivative
executed on the UK regulated market demonstrates how to populate the fields
‘Clearing obligation’ and ‘Intragroup’ depending on whether the derivative is an ETD
or an OTC derivative and requested details for all impacted fields of the report.
ESMA highlights that this is reflected in the validation rules which set out relevant
dependencies between the fields, specifying e.g. the fields that are mandatory for
OTC derivatives or cleared/uncleared derivatives.
408. Following to the feedback from one respondent, ESMA also included relevant
correction in the XML message example in the Guidelines.
3.3.2.2.3 Reporting of valuations
409. One respondent stated that according to the FR on RTS/ITS for the field ‘Delta’
( "To make this clearer, ESMA will move the field to the valuation section of table
of fields" (paragraph 420)), the field should not still be exemplified in the transaction
data reporting fields, as in the example illustrating the population of the valuation
data when the counterparty submits a daily valuation update for a previously
reported derivative at trade level. ESMA highlights that under the RTS on reporting
all valuation data (including delta) form part of the Table 2.
3.3.2.2.4 Reporting of other payments
Q81. Are there any additional clarifications required with regard to the reporting of
other payments?
410. In the CP, ESMA clarified the reporting logic for upfront, unwind payments and
principal exchange through a set of examples and the presented approach gained
overall support.

73
411. However, one respondent flagged an inconsistency in the XML extract, in the
case of the upfront and unwind payments examples, which has been corrected in
the final version of the Guidelines.
412. Two respondents requested further clarifications, in particular on the example
of the cross-currency swap. They asked whether the final principal exchange
amount of a cross-currency swap, reported as other payment at the start of the
trade, will be included in all future reports due to the payment date at the maturity
of the cross-currency swap. ESMA has already clarified this aspect in section 3.1.25
Reporting of other payments, confirming that the final principal exchange amount
should be reported once agreed, and not when the payment will be effective.
413. With regard to the example of the cross-currency swap, some respondents
commented about the implementation of the validation rules for fields 1.17, 1.18
and 1.19, and highlighted that field 1.17 ’Direction’ should be left blank. ESMA
therefore included relevant correction in the Guidelines.
414. On the same example the respondents sought clarification regarding the values
for field 1.18 ‘Direction of leg 1’ and field 1.19 ‘Direction of leg 2’ that should be
populated the other way round. ESMA considered this feedback and updated the
Guidelines.
415. One respondent flagged a typo related to the number of the field ‘Expiration
date’ which should be 2.44 in the example of the cross-currency swap, and ESMA
implemented the correction accordingly.
416. One respondent raised the idea of a different reporting logic for the exchange
of currencies at maturity date by combining the information related to the derivative
contract (contract type and asset class) with the type of operations and the way
how the currencies are exchanged, rather than using the dedicated fields (2.73-
2.77) of other payments reporting. However, ESMA noted that the utilization of the
other payments fields is in line with the CDE guidance and the RTS on reporting,
and the new proposal for reporting logic cannot be accommodated.
3.3.3 Table 3 Margin data
Q82. Do you agree with the approach to reporting of margin data? Please detail
417. The approach proposed in the CP, related to the examples for reporting of
margin data, has been broadly supported, however some respondents asked for
additional explanations.
418. One respondent requested an additional example within the guidance for
reporting the margin data of a trade for the first time, for a better understanding of
reporting the action type ’MARU‘. ESMA highlights that such example is already
contained in the section 6.2.1.
419. One respondent stated that margin can be reported at a portfolio level without
requiring specific UTI. ESMA has already clarified this aspect in several examples
related to the reporting of margins.

74
420. With regard to the example of reporting of margin update at portfolio level for a
cleared derivative, one respondent highlighted an inconsistency regarding the
delegation of reporting from a clearing member to an NFC. ESMA implemented the
correction accordingly.
421. One respondent asked for a rule to be implemented throughout the guidelines,
regarding the collateralisation at the portfolio level, when at least one derivative
contract in the portfolio must be outstanding. The same idea, according to the
validation rules, should apply when collateralizing at UTI level, and such UTI must
pertain to an outstanding derivative contract. Another respondent suggested to
reconsider the possibility of allowing the submission of margin update reports over
non-outstanding contracts, allowing additional scenarios of late reporting. ESMA
has updated the Guidelines and the validation rules to clarify that the derivative has
to be previously reported but not necessarily still outstanding.
422. In addition, one respondent asked that the applicable fields in Table 2 should
be reviewed to incorporate a boolean field to allow counterparties to identify
whether a contract is collateralized. Only if this field is set to ‘True’, counterparties
would need to submit margin updates on a daily basis, that is also a flag used for
TRs to determine the applicability of the missing margin report end-of-day report.
However, ESMA noted that this request cannot be accommodated at this stage as
it would require an amendment to the RTS and ITS on reporting.
423. One respondent reminded that the reporting rules provided through the
Guidelines are very complex and it has not to be taken for granted the possibility to
retrieve the required information on haircut from the internal position-keeping
systems of the counterparties. ESMA highlights that the margin information,
including the haircuts, was included in the global CDE Technical Guidance as part
of the key derivative data.
424. Following to the request from one respondent ESMA added one example of
reporting of margin data.
425. With regard to the examples of reporting margin update at the portfolio level for
a cleared/uncleared derivative, one respondent spotted an inconsistency at XML
level. ESMA considered this feedback and updated the Guidelines.
3.4 Guidelines on derivatives data management
3.4.1 Trade State Report
3.4.1.1 Introduction
426. Following to the feedback received, this section of the Guidelines was updated
with a clarification concerning the provision of TSR to counterparties and authorities
in cases where e.g. valuation data is submitted by a different report submitting
entity.

75
3.4.1.2 Treatment of event date
Q83. Which of the two approaches provides greater benefits for data reporting and data
record-keeping? Please elaborate on the reasons for your response.
Q84. In case Approach B is followed, should the TRs update the TSR when
counterparties have reported lately the details of derivatives? If so, do you agree with
the time limit ten years for such an update? Please elaborate on the reasons for your
response
427. ESMA proposed two alternative approaches to construct the TSR from the
perspective of the field ’Event date‘. Alternative A would entail sequential
chronological order derived from the interaction between field ’Reporting
timestamp‘ and field ’Event date‘, whereas alternative B would entail chronological
order obtained solely from the field ’Event date’.
428. Most respondents were in favour of alternative B which was thought to provide
greatest benefits for data reporting and data record-keeping. However, a few of the
respondents in favour of alternative B disagreed with the requirement for TRs to
update the historical trade state of a derivative when receiving late reports or
reports with event date in the past. Moreover, updating historical trade states for up
to 10 years following the maturity of contracts was considered as adding
unnecessary complexity and costs on the TRs.
429. Considering some of the technical challenges with the implementation of
alternative B, ESMA further clarified in the Guidelines that updating the state in the
past does not imply that TRs should reproduce and dispatch corrected historical
TSRs on a recurrent basis and in an automated manner every time late reports or
lifecycle events referring to event dates in the past are received. The TSR produced
for a specific date should be considered as a snapshot of all available information
at a certain point in time. However, the expectation is that TRs’ internal databases
should always be updated accordingly when counterparties submit late reports or
lifecycle events referring to event dates in the past. The benefit of using the field
’Event date‘ would otherwise be limited if such logic was discarded.
430. TRs should have in place a process for reproducing and dispatching corrected
historical TSRs only based on ad-hoc requests. Such TSRs, when reproduced,
should include missing information from late submitted reports and lifecycle events
referring to event dates in the past which were not included in the original TSR
produced at a specific point in time in the past.
431. Whereas for non-outstanding derivatives TRs should be in a position to update
their state for up to ten years following their maturity or termination. This limit is
related to the requirement under Article 80(3) of EMIR for TRs to keep records of
derivatives for at least ten years following their maturity or termination.
432. ESMA has added several examples in the Guidelines to illustrate how exactly
the alternative B would work in practice in different reporting scenarios.

76
3.4.1.3 Uniqueness of derivatives and special fields
Q85. Are there any fields that should be taken into account in a special way not allowing
change in values?
433. ESMA proposed in the CP that from the date of application of the RTS on
reporting the uniqueness of derivatives concluded after that date should be ensured
at the level of the UTI. From that date onwards, TRs should therefore use:
a. the triplet (LEI1-LEI2-UTI) to update the state of the derivatives concluded prior
to the application date of the draft RTS on reporting,
b. the UTI to update the state of derivatives concluded after the application date
of the draft RTS on reporting.
434. Following to the feedback and requests for clarifications received from the
respondents, ESMA updated the above guidance to specify separately the fields
that can or should be used to uniquely identify the derivative and the fields that
cannot be modified.
3.4.1.4 Treatment of action type ’Revive’.
Q86. Is the guidance on treatment of action type “Revive” clear? What additional
aspects should be considered? Please detail the reasons for our answer.
435. ESMA has updated the Guidelines to align with the final version of the RTS and
ITS on reporting which allow for submission of a report with action type ‘Revive’
after 30 days from the expiration, termination or cancellation of a derivative.
436. Furthermore, ESMA has simplified the table showing the impact of the reports
with action type ‘Revive’ on the TSR.
3.4.1.5 Reporting with action type ‘EROR’
Q87. Should the TR remove after 30 calendar days the other side of a derivative for
which only one counterparty has reported “Error” and no action type ”Revive”? Please
detail the reasons for your answer.
437. Where a counterparty sends a ’EROR‘ report for its side of the derivative, the
TR that has received such report should remove the derivative reported by that
counterparty from the TSR. The TR should do so even when the other counterparty
reports to the same TR and has not made the same report.
438. A few respondents believe that TRs could remove the other side of a derivative,
but 30 days is too short of a deadline as some issues take longer time to resolve.
One respondent sees the benefits of TRs removing the other side of a derivative if
counterparties are properly notified when it happens.
439. However, most respondents did not find it appropriate for TRs to remove the
other side of a derivative, even if the first leg has been ‘errored‘ and 30 calendar

77
days have lapsed. The responsibility should lie with the counterparties to resolve
reconciliation breaks.
3.4.1.6 Inclusion in the TSR of notional schedules and other payments
Q88. Which alternative relating to the provision of the notional schedules and other
payments data would be more beneficial? Which of the two alternatives has higher
costs? Please detail the reasons for your answer.
440. There were two alternatives considered with regards to the provision of this
information in the TSR:
a. Alternative A would entail the regular update of the TSR based on the schedule
reported. This will reduce the amount of data provided to authorities and would
facilitate the immediate assessment of exposures.
b. Alternative B would entail the provision of the full schedule in the TSR on a daily
basis. While this would provide the highest level of transparency, it would also
require authorities to set-up somehow complex processes to assess the current
exposure, as they would need to process and remove unnecessary information
for non-current data.
441. Most respondents were in favour of Alternative A, which will reduce the amount
of data provided to authorities and would facilitate the immediate assessment of
exposures as opposed to Alternative B.
442. Clarification if approach A is selected, as to whether the TR should include the
details as of the reporting date of the TSR or the day prior to the reporting date,
conscious that either may differ from the event date, was included in the Guidelines.
3.4.1.7 Dead derivatives
Q89. Do you agree with the described process of update of the TSR? What other aspects
should be taken into account? Please elaborate on the reasons for your answer.
443. In the CP ESMA has proposed the following waterfall approach to be followed
where the reporting counterparty has ceased to exist and has not terminated the
outstanding derivatives and the TR becomes aware of this situation:
a. If the ERR is different from the reporting counterparty and that ERR has not
used RSE, the TR should contact the ERR, should request the submission of
reports with action types ’TERM‘ where the termination date is at the latest the
date of the dissolution of the reporting counterparty and, simultaneously, should
raise the issue to the NCA of the reporting counterparty. If the reporting
counterparty or the ERR has used a RSE and that entity is still an active RSE
at the TR, the TR should contact the RSE, should request the submission of
reports with action types ’TERM‘ where the termination date is at the latest the
date of the dissolution of the reporting counterparty and, simultaneously, should
raise the issue to the NCA of the reporting counterparty.

78
b. If the previous step is not applicable, the TR should assess the maturity date of
the outstanding derivatives that should be terminated in order to assess whether
they would naturally expire in the following twelve months. If that is the case, no
further action should be undertaken by the TR.
c. If the second step is not applicable, the TR should contact the other
counterparty/ies to the outstanding derivatives, where those entities report
directly to the TR, and request them to terminate the outstanding derivatives on
behalf of the reporting counterparty while, if possible, raise the issue to the
NCA(s) to follow-up with the other counterparty/ies.
d. Finally, in case none of the above is applicable, the TR, upon confirming with
the NCA and notifying ESMA, should flag the relevant derivatives accordingly
and not take them into consideration for the purposes of TSR, reconciliation
process, or any subsequent aggregations such as position reporting. The
feedback received was generally supportive of the waterfall approach to be
used by TRs and NCAs when dealing with outstanding derivatives that have not
been properly terminated by a reporting counterparty who has ceased to exist.
444. To address the feedback received, ESMA clarified that TRs should also exclude
dead trades from the TSR, reconciliation process and any other subsequent
aggregations.
445. Furthermore, ESMA clarified that no action is required by TRs for excluding
dead trades that would naturally expire within 12 months. This is to alleviate the
work of TRs and minimise the risks associated with the process of excluding trades.
446. The feasibility of implementing step c of the waterfall approach was questioned
by a few respondents. In ESMA’s view, there is no legal impediment for TRs to put
in place the necessary arrangements. Moreover, this is how it has also been
envisaged under the current Q&A 57.
3.4.2 Reconciliation
3.4.2.1 Scope of data subject to reconciliation
Q90. Should only the field 1.14 be used for determining the eligibility of derivative for
reconciliation? Please detail the reasons for your response.
Q91. Is there any additional aspect that should be clarified with regards to the
derivatives subject to reconciliation? Please detail the reasons for your response
447. Most respondents agreed with the proposal to use the conditions to determine
the eligibility of derivatives for reconciliation as proposed in the CP, however some
respondents asked for additional clarifications.
448. Following to the feedback received, ESMA considered that the scope of data
subject to reconciliation with regards to countries joining the EU would need to be
determined in legislation and delegated acts. Hence, ESMA will not include such
clarification in the Guidelines.

79
449. Some respondents requested clarifications on the field(s) that should be used
to determine whether or not a derivative has been outstanding in last 30 calendar
days. The specification of outstanding derivatives is included in delegated act, in
particular Article 2(2) of the ITS on reporting.
450. Respondents asked if, in the case approach B is followed (Q83) and out-of-
sequence reporting is permitted, TRs should include late reported derivatives in the
reconciliation process. ESMA clarified that depending on the action type and if the
late report refers to an outstanding derivative subject to reconciliation, then TRs
should attempt to reconcile the information.
3.4.2.2 Position-level vs trade-level reconciliation
Q92. From reconciliation perspective do you agree with the proposed differentiated
approach for the latest state of derivatives subject to reconciliation depending on the
level at which they are reported? What are the costs of having such a differentiation?
Should the timeline for reconciliation of derivatives at trade level be aligned with the
one for positions? Please detail the reasons for your response.
Q93. From data use perspective, should the information in the TSR and in the
reconciliation report be different? Please detail the reasons for your response.
451. One of the main issues linked to the reconciliation of derivatives relates to the
possibility for counterparties to report with a different time schedule the lifecycle
events relating to the derivative. This is the case for all derivatives, but the impact
is exacerbated in the case of position-level ones.
1. Performing the reconciliation process with a two-day lag would eliminate
reconciliation breaks which are only caused by the timing aspect of
reporting, for example where one counterparty reports at T and the other
counterparty reports at T+1.
452. In fact, most respondents disagreed with the proposed differentiated approach
and would rather see the position- and trade-level reconciliation to be aligned. From
a TR perspective, having two separated processes involves higher maintenance
cost and adds more complexity to their systems.
453. It was further clarified that TRs should reconcile the data in line with the relevant
reconciliation tolerance, as well as the relevant start date as included in Table 2 of
the Annex to the RTS on data quality.
3.4.2.3 Reconciliation of valuation
Q94. Which alternative do you prefer? What are the costs for your organisation of each
alternative? Please elaborate on the reasons for your response.
454. Under the RTS on data quality, ESMA introduced the reconciliation of the
information on valuation of derivatives. Mindful of the need to adjust the reporting
systems, ESMA has included a delayed start of the reconciliation of the data on

80
valuation by two years. To be considered reconciled the valuation data should be
expressed in the same currency as indicated in the RTS on data quality.
455. When one of the counterparties to the derivative is an NFC-, that entity is not
required to report valuation data. ESMA understands that this would not allow for
the performance of the reconciliation process of the valuation data, as one of the
data sets would be missing.
456. The following two alternatives were proposed:
a. Alternative A: the TRs should reconcile all the derivatives for which valuation
data has been reported in the last 14 calendar days.
b. Alternative B: TRs should include all the data in the reconciliation process and
flag the derivatives where one of the counterparties have not reported valuation,
irrespective of the reason, as not reconciled.
457. Mixed feedback was received where 4 respondents preferred alternative A, 8
respondents preferred alternative B, and 6 respondents did not have a clear
preference or are strictly against the requirements for reconciling valuation
information.
458. Main argument presented was that valuation of derivatives, especially OTCs, is
not an exact science. Derivatives pricing models, market data, timing of fixings, and
other parameters that go into the valuation of a derivative may slightly differ
between two parties of a contract. However, ESMA believes that with the right
reconciliation tolerance, valuation information should be subject to reconciliation as
it constitutes an important part of EMIR reporting. Alternative B remained the
preferred one which has been included in the final Guidelines. However, it has been
clarified that the derivatives where one of the counterparties is NFC- and therefore
is not subject to the requirement to report valuation data, should be flagged as ‘Not
applicable’.
3.4.2.4 Derivatives with two legs
Q95. Which alternative do you prefer? What are the costs for your organisation of each
alternative? Please elaborate on the reasons for your response.
459. TRs should reconcile derivatives with two legs by reconciling each of the legs
as reported by the counterparties. It is worth noting that in the case of most types
of derivatives with two legs such as interest-rate swaps, cross-currency swaps and
FX swaps, the order of the legs cannot be unequivocally defined, as there is no
specific prevalence of one leg over the other.
460. The following two alternatives were proposed:
a. Alternative A: Counterparties should agree on the reporting of the respective
legs of the derivative. When counterparties report inconsistently the two legs of
the derivative, the TR might not succeed in matching the details of the
derivative. This will put the burden on the counterparties as it would require
them for the successful reconciliation to agree on a sequence for the reporting
of the different legs. This would be consistent with the current framework.

81
b. Alternative B: When counterparties report inconsistently the two legs of the
derivative, the TR should intend to match the two legs irrespective of the
sequence, taking into account the values reported by the two counterparties
under field ’Direction of leg 1‘ by matching the legs with opposite values. In case
counterparty 1 has reported it with ’payer‘ the TR should reconcile it with the leg
that is identified as ’receiver‘ or with the leg that is not identified, when leg one
is identified with ’payer‘ This would move the burden to the TRs, but it would
also limit the existence of reconciliation breaks, as well as it would facilitate their
resolution.
461. Most respondents representing market participants were in clear favour of
alternative B. Most respondents representing TRs were in favour of alternative A,
apart from one who did not express a clear preference but mentioned that while
option A is the simplest for TRs to implement, option B would ensure the legs are
appropriately reconciled.
462. In order to avoid a situation where TRs and counterparties need to agree on the
best practice, a few respondents suggested that ESMA should be in charge of
providing clear guidance on how to report. ESMA believes that any guidance at this
point would merely be artificial, therefore the two alternatives were proposed.
Alternative B remains the preferred one which will be included in the final
Guidelines.
3.4.2.5 Reconciliation of notional schedules and other payments
Q96. Do you agree with the proposed approach for reconciliation of notional schedules?
Please elaborate on the reasons for your response.
463. With regards to the inclusion of notional schedules and other payments, ESMA
proposes to align this approach with the one taken under section 3.4.1.6 referring
to Q88. ESMA believes that this alignment should ensure consistent application of
the requirements. Therefore the TRs should reconcile the data on notional
schedules and other payments that is included in the TSR as of the date on which
the reconciliation takes place.
464. Feedback received was mainly related to Alternative B proposed under Q88 and
on how TRs should order the information in order to succeed with the reconciliation.
Since alternative A was the preferred one under Q88, TRs will not be required to
reconcile the full notional schedule, but only the one appearing in the TSR.
3.4.2.6 Derivatives between two systematic internalisers
Q97. Do you agree with the proposed approach for reconciliation of venues and the
clarification in case of SIs? Please elaborate on the reasons for your response.
465. ESMA has updated section 4.20 of the Guidelines to clarify that in the case of a
trade between two SIs, the counterparties should populate the field ‘Venue of
execution’ with the MIC of the entity that is acting in the SI capacity for a given
trade. Consequently, both counterparties are expected to populate the field with the

82
same value thus there is no impact on the reconciliation process. The respective
section has been removed from the final Guidelines as no longer relevant.
3.4.3 Data Quality feedback
3.4.3.1 Rejection feedback
Q98. What other aspects need to be considered with regards to the aforementioned
approach to rejection feedback? Please detail the reasons for your response.
466. In the CP, ESMA summarized the requirements pertaining to ensuring data
quality by trade repositories, the relevant processes, timelines and details to be
provided by trade repositories with respect to rejected data. Rejection feedbacks
should be provided by means of immediate rejection response within 60 minutes
after the reception of data and also by means of end-of-day reports made available
by 6:00 UTC on the following working day.
467. One respondent considered given deadlines too strict and advocated for
extension. However, the timelines are specified in the RTS on data quality and
cannot be amended by the Guidelines.
468. With respect to the timelines another respondent asked for clarification whether
the “working day” should be understood as in line with the TARGET 2 calendar or
whether national calendars should be taken into account. ESMA confirmed in the
Guidelines that TARGET 2 calendar should be used for the determination of
working days. ESMA was further asked to specify more precisely the exact moment
from when the 60 minutes start counting. The relevant moment is the minute when
the submitted file entered the IT system of the trade repository, e.g. by being placed
in the SFTP folder.
469. Several respondents to the CP pointed out that under current reporting regime
the provided rejection information does not suffice for effective error handling and
that current proposal of rejection categories is not granular enough to be useful in
investigation or analysis of rejections. ESMA confirms that rejection categories will
not be used for identification of errors, instead specific error codes and error
messages containing xml paths for each validation rule will be provided in the
rejection feedback. ESMA also takes into account a request for publication of the
validation rules, so that all market participants are fully aware of each set of
changes to the validation rules and the applicable effective dates when the TRs
initiate the amended validations.
470. Further suggestions were received from one respondent to include in the
rejection feedback values of some other fields, such as ‘Action type’, ‘Event date’
or ‘Reporting timestamp’ so that counterparties, RSEs or ERRs may more easily
identify the rejected reports. ESMA has considered this feedback and updated the
Guidelines accordingly to facilitate the identification of the rejected reports. This
respondent further inquired whether blank values will be possible for these key
fields in the rejection feedback, e.g. when UTI does not pass format validations. In
case of format errors, submitted file will fail the validation against the XSD schema

83
and the whole file will be rejected. Furthermore ESMA clarified, that information on
errors pertaining to the whole file should be made available to the RSE of the file
and to all ERRs and counterparties populated in fields 1.3 and 1.4 in that rejected
file as applicable, assuming it is possible to read the information from the rejected
file. ESMA also clarified in the Guidelines that where the rejection (other than format
rejection) pertains to field 1.4 ‘Counterparty 1 (Reporting counterparty)’ or field 1.9
‘Counterparty 2’, these fields might not be populated in the rejection report.
471. The respondent proposed specific potential statuses, and related definitions, to
be incorporated into the XSD schema. At file level the statuses were proposed
ACPT (file is correct, schema authorization, filename and file size validations are
passed), RJCT (failure in filename, file size or authorization validations), CRPT
(schema validation fails, thus rejecting the complete file). At the record level
statuses ACPT (logical and business validations are passed), RJCT (either logical
or business validations fail) were proposed. ESMA confirms that relevant statuses
are already included in the XSD schemas.
472. One respondent asked whether the end-of-day reports which should be
provided to the RSE, ERR and the counterparty can be provided only to subset of
these entities and who would ultimately decide upon such limits on file distribution.
For example, if a counterparty can suppress a report being sent to a third-party
vendor that only submits collateral on their behalf. For the distribution of files Article
4(1) of the RTS on data quality specifies that the end-of-day reports shall be made
available to all of these entities. However, the TRs should use all the data they have
collected to determine what information they should provide and to which RSEs,
ERRs and counterparties. Additional clarifications were included in the Guidelines.
473. Two respondents expressed their preference to exclude from the end-of-day
rejection feedback rejected records that have been resubmitted and accepted
within the same day. Those rejections would only be included in the immediate
rejection feedback, while the end-of-day rejection feedback would only contain
information on issues that were not resolved by the end of the day. Even though
ESMA recognizes the benefits of this proposal, it is worth emphasizing that Article
4(1)(c) of the RTS on data quality does not allow the TRs to provide information
only on a subset of derivative reports that have been rejected during that day.
Moreover, in such feedbacks the statistics on accepted, rejected and all daily
submissions would not match with the provided details. This could create some
confusion and it would not be possible to quickly recognize erroneous rejection
feedback. ESMA will keep the current proposal where the total numbers should
match the details of the report.
474. Respondents to the consultation queried whether the rejection feedbacks could,
in addition, be provided in other format than ISO 20022 XML format. Article 1(3)
and Article 4(1) of the RTS on data quality specifies that the rejection feedback
should be provided in an XML format and a template developed in accordance with
the ISO 20022 methodology. ESMA included a clarification that TRs could, in
addition, use another interface to e.g. facilitate access to the information to the
reporting counterparties and entities responsible for reporting that do not report
directly to TRs and have a view-only access. However, rules or best practices

84
concerning any such services that the TRs decide to provide to the report
submitting entities and counterparties are out of scope of these Guidelines.
475. Two respondents asked ESMA to provide further clarifications on the process
of authorization / permissions of a report submitting entity as per Article 1(1)(c) of
the RTS on data quality. ESMA clarifies that it is not necessary for all reporting
counterparties and ERRs to be onboarded to the TR to provide explicit permission
that the RSE is authorized to submit reports on their behalf. Also, it is not necessary
to provide the permission before every trade. The permissioning is expected to be
a one-off action at the start of reporting on behalf of the reporting counterparty or
ERR, as applicable, and the RSE should provide a contact to the reporting
counterparty or ERR so that TR could receive the permission from them.
3.4.3.2 Warnings feedback
Q99. Do you agree with the approach outlined above with regards to the missing
valuations report? Are there any other aspects that need to be considered? Please detail
the reasons for your response.
Q100. Do you agree with the approach outlined above with regards to the missing
margin information report? Are there any other aspects that need to be considered?
Please detail the reasons for your response.
Q101. Do you agree with the approach outlined above with regards to the detection of
abnormal values and the corresponding end-of-day report? Are there any other aspects
that need to be considered? Please detail the reasons for your response.
476. The CP introduced new feedback reports pertaining to warnings on missing
valuations of outstanding derivatives, missing margin information of outstanding
derivatives, and abnormal values reported in notional amount fields. These end-of-
day reports should also be made available to the relevant entities no later than
06:00 UTC on the following working day.
477. With regards to warnings feedbacks, respondents raised again their objections
and comments on strict timelines, format of the files, use of national calendars of
working days and possibility to suppress distribution of the files. For warnings
feedbacks same reasoning and conclusions on these issues apply as outlined for
rejection feedbacks in the section 3.4.3.1.
478. Commenting on missing valuation and margin reports respondents pointed out
that these reports should not be provided to entities who are not required to submit
daily information on valuation and margins. ESMA confirms it is not expected that
entities, e.g. NFC-, who are not required to submit that information would be
receiving warnings feedback on missing valuations and missing margin information.
Similarly, the missing margin information warnings feedbacks are not expected to
be provided for uncollateralized trades. Relevant clarifications were included in the
Guidelines. Excluding trades concluded prior to the application start date of the
margin obligation or intragroup trades was considered too complex to be
implemented by the TRs and therefore this proposal was not taken on board.
479. To easily identify uncollateralized trades it was proposed to add new field
’Collateralised‘ in Table 2, or to include field 3.11 ‘Collateralisation category’ also in

85
Table 2. However, adding a new field is not possible at this stage, therefore ESMA
did not take this suggestion into account. Instead, ESMA clarified in the Guidelines
that counterparties (that are required to report margin information) would need to
send at least one ‘Margin update’ report to notify that the trade is uncollateralised.
480. One respondent asked ESMA to clarify that the number of outstanding
derivatives included in the warnings feedback should be assessed from the
viewpoint of counterparty 1. Clarification was included in the Guidelines.
481. Further clarification was sought whether the TRs are expected to reproduce the
warnings reports for previous days, taking into account submissions to the TR
which may have been accepted in the interim with a valuation timestamp value
which influences the results. ESMA confirms it is not expected that the once
provided warnings feedbacks would be regenerated and redistributed. The
warnings reports should reflect the state of play at the end of the relevant day, and
any further submissions should be reflected in the next day’s warnings feedback.
482. One respondent pointed out an inconsistency in referring to the action type used
for the first margin report submitted for a given UTI. ESMA confirms the first report
should be submitted with Action type ‘MARU’ and amended the Guidelines
accordingly.
483. The respondent also suggested that it should be differentiated in the warnings
report whether the warning was generated because the information was never
reported, or the information was outdated. ESMA confirms that for missing
information the relevant data elements for valuation amount and timestamp or
collateral timestamp will be blank, while for outdated information these data
elements will be populated.
484. Another clarification was requested as to whether the missing margin
information warnings reports will present the data at a collateral portfolio code level
or at a UTI level. Both alternatives are technically possible, however the warnings
are expected to inform about missing or outdated collateral for a derivative,
therefore they are expected to be provided at UTI level.
485. Comments received on the reconciliation of valuations are addressed in section
3.4.2 and suggestions to include more examples on reporting of margins were
reflected in section 3.3.3.
486. With regards to warnings feedbacks on abnormal values most respondents
requested ESMA to provide guidance and workshops on the methods for outlier
detection. However, ESMA does not envisage such guidance or workshops in the
near future, even though it is obvious that with no common guidance a value could
be considered abnormal by one TR and normal by another. ESMA will, however,
monitor the implementation of outlier detection methods and consider possible
further steps, with the ultimate goal to ensure comparable results. This approach
will provide flexibility in order to have the possibility to change the values to adjust
to market conditions. It will also reduce cases where TRs set different threshold
levels resulting in a single trade being considered to be over the threshold level by
one TR, but under the threshold level by another. More generally, the setting of
threshold levels is an area where machine learning and/or AI could potentially be

86
utilised. This should lead to more considered and relevant threshold levels being
established and enable the levels to be modified more easily.
487. A proposal was made to consider using the field 2.11 ‘Asset class’ instead of
2.9 ‘Product classification’ to categorize derivatives for the purpose of abnormal
values detection. Population of ‘Asset class’ field is considered by the respondent
to be of higher data quality than CFI code, therefore the categorization would be
more reliable. ESMA considered this proposal and amended the Guidelines to
reflect the change of fields.
488. A few respondents suggested also to expand the scope of this report to include
other numerical fields linked to valuation, margin, and collateral updates. ESMA
would be willing to consider such request, but it is not possible to change the
technical standards at this point. A gradual implementation can be beneficial for
minimising data quality issues and allow for adaptation.
489. A respondent asked ESMA to align the Guidelines with timelines of Article 4(2)
of the RTS on data quality with respect to the content of the warnings feedback on
abnormal values. ESMA confirms that reports received on the working day (and if
needed also non-working days) preceding the working day when the feedback is
generated should be included and amended the Guidelines accordingly.
490. Further requested clarification was included in the Guidelines on which records,
and abnormal values should be included in the warnings feedback.
491. Respondent deemed inconsistent the list of action types considered for
abnormal values feedback, specifically action type ‘POSC’, and the fact that only
outstanding trades should be considered. However, it is necessary to highlight that
abnormal values warnings feedback does not pertain only to outstanding
derivatives, as specified in Article 4(1)(g) of the RTS on data quality. Non-
outstanding derivatives should also be considered for outlier detection.
3.4.3.3 Reconciliation feedback
Q102. Is there any additional aspect related to the provision of reconciliation feedback
by TRs that should be clarified? Please detail the reasons for your response.
492. In Table 3 to the Annex of the RTS on data quality, ESMA has included different
categories of statuses for a derivative, as follows:
Table 1
Reconciliation categories
Allowable values
Reporting requirement for both counterparties
Yes/No
Reporting type
Single-sided/dual-sided
Pairing
Paired/unpaired
Reconciliation
Reconciled/not reconciled
Valuation reconciliation
Reconciled/not reconciled
Revived
Yes/No

87
Table 1
Reconciliation categories
Allowable values
Further modifications:
Yes/No
493. One respondent suggested adding ’not applicable‘ as a value in the category of
valuation reconciliation to account for reporting features of ETDs. ETD trades
reported with action type ‘Position component’ are considered as non-outstanding.
Subsequent valuation updates are reported at position level, and not at trade level.
Consequently these trades should always be flagged as ‘not applicable’. Moreover,
NFC- are not obliged to submit valuation updates for their derivatives which would
lead to similar behaviour. Based on the feedback, the XML schema was revised to
allow for the categorisation of certain cases as ’not applicable’ rather than ’not
reconciled’.
494. Other respondents to the consultation questioned whether the reconciliation
feedback could, in addition, be provided in another format than ISO 20022 XML
format. Article 1(3) and Article 4(1) of the RTS on data quality specifies that the
rejection feedback should be provided in an XML format and a template developed
in accordance with the ISO 20022 methodology. Any other services that the TRs
decide to provide to the report submitting entities and counterparties are out of
scope of these Guidelines.
495. Another respondent considered the given deadline to provide reconciliation
feedback too strict and advocated for extension. However, the timeline is specified
in the RTS on data quality and cannot be amended by the Guidelines.
496. Furthermore, it was suggested to clarify that field ’Further modifications‘ should
be set to ’Yes‘ by TRs every time that a derivative contract is incorporated in the
Trade Data Details following the reception of a lifecycle event other than ‘NEWT’,
and that such value is kept until the updated contract is reconciled. Similarly, a
clarification was requested on whether ’Revived‘ should be reported as ’True‘ if a
report with action type ’REVI‘ has ever been reported for the derivative or should
only the recent history of the derivative be considered. Relevant clarifications were
provided in the Guidelines.
497. A few respondents noticed also some inconsistencies with Table 91 in the CP.
The information in columns 3 and 4 had been shuffled around and did not
necessary correspond to values in column 2. The table has been reviewed and
amended accordingly.
3.4.3.4 Revive
Q103. Is there any additional aspect related to the rejection of reports with action type
“Revive” by TRs that should be clarified? Please detail the reasons for your response.
498. A few respondents requested additional clarifications on some specific use case
scenarios for action type revive and the 30-days limit. Clarifications were linked to

88
the 30-days limit, but since the limit was revoked, those clarifications were no longer
relevant.
3.4.4 Data access
Q104. Regarding the requirements in the RTS on registration, as amended, and the RTS
on data access, as amended, do you need any further specifications and/or
clarification?
Q105. Are there any specific aspects related to the access to data based on UPI that
need to be clarified? Please detail which ones.
Q106. What access rights would you like to be clarified and/or which access scenarios
examples would you consider to be inserted in the guidelines? Please list them all, if
appropriate.
Q107. Are there any aspects, or procedures you would like to be clarified? If yes, please
describe in detail.
Q108. Is there any other information that should be provided by the entity listed in
Article 81(3) EMIR to facilitate the swift and timely establishment of access to data?
499. Regarding the provision of access based on the UPI and the use of the available
information published by ANNA-DSB one respondent asked ESMA for clarification
with regards to any validation checks TRs will be expected to apply to the UPI.
ESMA enhanced the validation rules with regards to the UPI (see validation rules
for more details).
500. If a counterparty uses a third party to report their transactions, but the
counterparty submits its valuation reports itself, under the current process the
counterparty cannot see the valuation data in the TSR. ESMA clarified that it should
be possible for all the reporting information to be amalgamated in the TSR so the
parties have all the relevant information available. Furthermore, ESMA clarified that
authorities should have access to all information in the TSR.
501. As respondents asked for more clarification, ESMA further elaborated the
wording regarding trading venues, overall transaction data access, overall position
data access and regarding takeover bids. ESMA took into account respondents’
requests for relevant fields and filtering rules for the provision of access to data and
amended the Guidelines accordingly.
502. Although respondents asked ESMA to provide an automated feed of indices
ESMA decided that such automation is not necessary given the expected frequency
and content of the updates.
4 Cost-benefit analysis
ESMA’s choices in the Guidelines are of pure technical nature and do not imply strategic
decisions or policy choices.

89
ESMA’s options are limited to the approach it took to drafting these Guidelines and the need
to ensure clarity, consistency of reporting and uniformity of formats.
The main policy decisions have already been analysed and published by the European
Commission under the primary legislation, i.e. Regulation (EU) No 2019/834 of the European
Parliament and of the Council of 20 May 2019. Similarly, ESMA conducted an assessment of
the proportionality of the policy choices when submitting the draft technical and implementing
standards to the European Commission on 16 December 2020
16
.
5 Advice of the Securities and Markets Stakeholders
Group
In accordance with Article 16 of the ESMA Regulation ESMA requested the opinion of the
ESMA Securities and Markets Stakeholder Group. The SMSG decided not to provide an
opinion.
16
https://www.esma.europa.eu/sites/default/files/library/esma74-362-
824_fr_on_the_ts_on_reporting_data_quality_data_access_and_registration_of_trs_under_emir_refit_0.pdf

90
Annex: Guidelines for reporting under EMIR
1 Legislative references, abbreviations and definitions
Legislative references
EMIR
Regulation (EU) 648/2012 of the European Parliament and
Council on OTC derivatives, central counterparties and trade
repositories - European Market Infrastructures Regulation
17
SFTR
Regulation (EU) 2015/2365 of the European Parliament and
of the Council of 25 November 2015 on transparency of
securities financing transactions and of reuse and amending
Regulation (EU) No 648/2012
18
– Securities Financing
Transactions Regulation
RTS on reporting
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) No 2022/1855 of 10
June 2022 supplementing Regulation (EU) No 648/2012 of the
European Parliament and of the Council on OTC derivatives,
central counterparties and trade repositories with regard to
regulatory technical standards specifying the minimum details
of the data to be reported to trade repositories and the type of
reports to be used
19
ITS on reporting
Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) No 2022/1860 of
10 June 2022 laying down implementing technical standards for
the application of Regulation (EU) No 648/2012 of the European
Parliament and of the Council on OTC derivatives, central
counterparties and trade repositories, with regard to the
standards, formats, frequency and methods and arrangements
for reporting and repealing Implementing Regulation (EU) No
1247/2012
20
17
OJ L 201, 27.7.2012, p.1
18
OJ L 337, 23.12.2015, p.1
19
OJ L 262, 7.10.2022, p. 1
20
OJ L 262, 7.10.2022, p.68.

91
RTS on registration
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) No 150/2013 of 19
December 2012 supplementing Regulation (EU) No 648/2012
of the European Parliament and of the Council on OTC
derivatives, central counterparties and trade repositories with
regard to regulatory technical standards specifying the details
of the application for registration as a trade repository, as
amended by Commission Delegated Regulation (EU)
2019/362 of 13 December 2018
21
and by Commission
Delegated Regulation (EU) 2022/1857
22
RTS on data quality
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) No 2022/1858 of 10
June 2022 supplementing Regulation (EU) No 648/2012 of the
European Parliament and of the Council on OTC derivatives,
central counterparties and trade repositories, with regard to
regulatory technical standards specifying the procedures for
the reconciliation of data between trade repositories and the
procedures to be applied by the trade repository to verify the
compliance by the reporting counterparty or submitting entity
with the reporting requirements and to verify the completeness
and correctness of the data reported
23
RTS on data access
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) No 151/2013 of 19
December 2012 supplementing Regulation (EU) No
648/2012 of the European Parliament and of the Council on
OTC derivatives, central counterparties and trade
repositories, with regard to regulatory technical standards
specifying the data to be published and made available by
trade repositories and operational standards for aggregating,
comparing and accessing the data, as amended by
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2017/1800 and by
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2019/361, as
amended by the Commission Delegated Regulation (EU)
2022/1856
24
21
OJ L 52, 23.2.2013, p. 25
22
OJ L 262, 7.10.2022, p.41
23
OJ L 262, 7.10.2022, p.46.
24
OJ L 262, 7.10.2022, p.34.

92
RTS on organisation
requirements
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2017/565 of 25 April
2016 supplementing Directive 2014/65/EU of the European
Parliament and of the Council as regards organisational
requirements and operating conditions for investment firms
and defined terms for the purposes of that Directive
Abbreviations
CFI code Classification of Financial Instruments code
CM Clearing Member
CCP Central Counterparty
CP Consultation paper on Guidelines on Reporting under EMIR
CP on RTS/ITS Consultation paper on the technical standards on reporting, data
quality, data access and registration of TRs under EMIR REFIT
25
FR on RTS/ITS Final report on the technical standards on reporting, data quality,
data access and registration of TRs under EMIR REFIT
26
CPMI Committee on Payments and Market Infrastructures
EC European Commission
ECB European Central Bank
EEA European Economic Area
ERR Entity responsible for reporting
ESCB European System of Central Banks
ESMA European Securities and Markets Authority
25
https://www.esma.europa.eu/sites/default/files/library/esma74-362-
47_cp_on_the_ts_on_reporting_data_quality_data_access_and_registration_of_trs_under_emir_refit.pdf
26
https://www.esma.europa.eu/sites/default/files/library/esma74-362-
824_fr_on_the_ts_on_reporting_data_quality_data_access_and_registration_of_trs_under_emir_refit_0.pdf

93
EU European Union
FIRDS Financial Instruments Reference Data System
FSB Financial Stability Board
IOSCO International Organisation of Securities Commissions
ISIN International Securities Identification Number
ISO International Organization for Standardization
ITS Implementing Technical Standards
LEI Legal entity identifier
MIC Market identifier code
NCA National Competent Authority
OJ The Official Journal of the European Union
OTC Over-the-counter
Q&A Questions and Answers
RSE Report submitting entity
RTS Regulatory Technical Standards
SWIFT Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication
TR Trade repository
UTI Unique Transaction Identifier
XML Extensible Mark-up Language
XSD XML Schema Definition
2 Scope
Who?
1. These Guidelines will apply to financial and non-financial counterparties to
derivatives as defined in Articles 2(8) and 2(9) of EMIR, to trade repositories (TRs)
as defined in Article 2(2) of EMIR and to competent authorities.

94
What?
2. These Guidelines will apply in relation to the derivatives reporting obligation as
stated in Article 9 of EMIR and the TRs’ obligations under Articles 78 and 81 of
EMIR.
When?
3. These Guidelines will apply from 29 April 2024.
3 Purpose
4. These Guidelines are based on Article 16(1) of ESMA’s Regulation. They fulfil
several purposes with regards to the harmonisation and standardisation of reporting
under EMIR. This is key to ensure high quality of data necessary for the effective
monitoring of the systemic risk. Furthermore, increased harmonisation and
standardisation of reporting allows to contain the costs along the complete reporting
chain - the counterparties that report the data, the TRs which put in place the
procedures to verify the completeness and correctness of data, and the authorities,
defined in Article 81(3) of EMIR which use data for supervisory and regulatory
purposes. The Guidelines provide clarifications on the following aspects:
a. transition to reporting under the new rules,
b. the number of reportable derivatives,
c. intragroup derivatives exemption from reporting,
d. delegation of reporting and allocation of responsibility for reporting,
e. reporting logic and the population of reporting fields,
f. reporting of different types of derivatives,
g. ensuring data quality by the counterparties and the TRs,
h. construction of the Trade State Report and reconciliation of derivatives by the
TRs,
i. data access.

95
4 General Principles
4.1 Transition to reporting under the RTS and ITS on reporting
5. All the reports submitted by the counterparties to the TRs after the start of reporting
under the RTS and ITS on reporting will have to comply with the amended
requirements. This applies to the reports of derivatives concluded after the reporting
start date and to any modifications or terminations reported after that date,
irrespective of when the derivative that is modified or terminated was concluded.
6. In general, any reportable lifecycle event will need to be reported in line with the
revised requirements.
7. In accordance with the Article 10(2) of the ITS on reporting, the counterparties
should update all their outstanding derivatives to conform with the revised reporting
requirements within 180 calendar days of the reporting start date by submitting a
report with event type ‘Update’, unless they have submitted a report with the action
type ‘Modify’ or ‘Correct’ (correcting the details of the trade
27
) for such derivatives
within this period (given that ‘Modify’ and ‘Correct’ will be full messages, thus
reporting of a modification or a correction of the derivative will require provision of
all relevant details of that derivative).
8. If the counterparty does not report within the 180-day transition period any
modification or any correction of the derivative, it should submit a report using
combination of action type ‘Modify’ and event type ‘Update’, populating all the
relevant details in accordance with the RTS and ITS on reporting.
9. Even if a counterparty reports daily collateral and valuation updates, but no
modification or correction was reported during transition period for a given
derivative, the counterparty should update that derivative.
10. If the derivative matures or is terminated during the transition period, counterparties
do not need to send the report with event type ‘Update’ when no reportable
modification took place.
11. All outstanding derivatives, both at a trade and at a position level, should be
updated. The derivatives at trade level that were included in a position are not
outstanding and therefore should not be updated. Only the corresponding
derivative at position level should be updated, to the extent it is outstanding on the
reporting start date.
12. Terminated or matured trades should not be updated and re-reported. This is
without prejudice to sending reports such as modifications and corrections with
regards to past events for terminated or matured trades, where relevant.
27
Action type ‘Correct’ will allow for correcting trade data or trade and valuation data or margin data. Only the report with action
type ‘Correct’ related to trade data or trade and valuation data will ensure update of all relevant fields of a derivative. Valuation
and margin data will be updated in any case by sending the daily valuation and margins reports (action types ‘Valuation’ and
‘Margin update’, respectively)

96
13. If a counterparty reopens a not-updated derivative with action type ‘Revive’, either
during the transition period or afterwards, it should provide all relevant details of the
derivative as of the date of the revival, as in any other ‘Revive’ report.
14. The transition period does not impact in any way the obligation under Article 9 of
EMIR to report the relevant events by T+1. Therefore any conclusion, modification
or termination of a derivative occurring after the reporting start date, should be
reported accordingly by the end of the next working day (T+1), also if it occurs
during the 6-month transition period.
15. During the transition period TRs should include all outstanding derivatives in the
reconciliation process, irrespective of whether they have been updated or not. The
fields required under the RTS and ITS on reporting will be subject to reconciliation
as specified in the Annex to the RTS on data quality. Fields that were reported in
the past but are no longer required under the RTS and ITS on reporting will not be
reconciled.
16. The counterparties should not create a new UTI for outstanding derivatives, even if
the original UTI is not fully compliant with the new format requirements under the
RTS and ITS on reporting. This applies also to field 2.3 ‘Prior UTI’ and field 2.4
‘Subsequent position UTI’.
17. In line with the EMIR validation rules TRs should not reject reports due to UTIs that
are not fully compliant with the new requirements for those derivatives that were
concluded before the reporting start date of the RTS and ITS on reporting.
18. In case of transfer of data between TRs, prior to the data transfer TRs should
ensure that TR participants upgrade the outstanding derivatives that are subject to
data transfer to the most up to date reporting requirement
28
.
4.2 Determining the number of reportable derivatives
4.2.1 Reportable products
19. EMIR Article 9(1) states that “counterparties and CCPs shall ensure that the details
of any derivative contract they have concluded and of any modification or
termination of the contract are reported to a trade repository […]”. A derivative
contract or derivative is defined in EMIR Article 2(5) as a financial instrument as set
out in points (4) to (10) of Section C of Annex I to MiFID. In the last few years
several uncertainties have been raised with regards to the qualification of certain
contracts as derivatives. This section aims to provide clarification to market
participants taking into account the current state of the regulations.
Currency derivatives
28
See Guideline 11 in the ESMA74-362-2351 Guidelines on transfer of data between Trade Repositories under EMIR and SFTR

97
20. MIFID RTS on organisational requirements for investment firms
29
clarifies in Article
10 the characteristics of other derivative contracts relating to currencies which
allows to differentiate between spot contracts that are not derivatives and forward
contracts that are derivative contracts. In principle, and more particularly for major
currency pairs, a FX contract is considered a derivative if the delivery is scheduled
to be made at least 3 trading days after the execution of the contract, while under
some circumstances this limit may be extended based on standard market
practices. Based on the above elements, forward FX contracts are reportable under
EMIR while spot FX contracts are not.
21. As an illustration a FX contract selling X EUR and purchasing Y USD traded on
Monday 4 January 2021 and settling on Thursday 7 January 2021 is a forward
contract and reportable under EMIR. A similar FX contract traded on Monday 4
January 2021 and settling on Wednesday 6 January 2021 is a spot contract and
not reportable under EMIR.
22. A FX contracts selling X EUR and purchasing Z ZAR traded on Monday 4 January
2021 and settling on Wednesday 6 January 2021, for which the transaction is
carried out in order to purchase an equity traded on the JSE
30
with a T+3 settlement
cycle is not a derivative and thus not subject to reporting under EMIR based on the
fact that when a FX contract is linked to the purchase of transferable securities or
units of collective investment undertaking, it is considered as a derivative when the
delivery is made after the delivery period of the market where the transferable
securities or units in an undertaking for collective investment in transferable
securities (UCITS) are traded or after 5 days, whichever is the shorter.
23. Furthermore, Article 10 provides that “a contract shall not be considered a spot
contract where, irrespective of its explicit terms, there is an understanding between
the parties to the contract that delivery of the underlying is to be postponed and not
to be performed within” the period referred to in the above paragraphs.
24. For swaps, at first cross currency swaps and FX swaps are to be distinguished.
Cross currency swaps are contracts that contain both an interest rate factor and a
currency factor. They are considered as interest rate derivatives and should be
reported as such under EMIR. FX swaps to the contrary only entail a FX factor (i.e.
in general no interim payments occur). FX swap is a derivative composed of 2 legs,
a near leg and a far leg. Regardless of whether the near leg is a spot or a forward,
the FX swap should be reported as a single derivative rather than as a combination
of derivatives. Further details on how these derivatives should be reported are
contained in section 5.4.
Derivatives on crypto-assets
25. Only derivatives on crypto-assets that fulfil the definition of ‘derivative’ or ‘derivative
contract’ under EMIR are expected to be reported.
29
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2017/565 of 25 April 2016 supplementing Directive 2014/65/EU of the European
Parliament and of the Council as regards organisational requirements and operating conditions for investment firms and defined
terms for the purposes of that Directive (Text with EEA relevance)
30
Equity Market Risk Management | Johannesburg Stock Exchange (jse.co.za)

98
26. For the reporting of the details of derivatives, counterparties should rely on the
regulatory framework that is applicable. Therefore, if the derivative on a
crypto-asset is considered as a financial instrument under MiFID, it should be
reported in accordance with its features.
27. In case where a counterparty enters a derivative contract with a crypto-asset as the
underlying, it should populate the field 2.12 ’Derivative based on crypto-assets‘ with
’True’.
Total return swaps, liquidity swaps or collateral swaps (in relation to SFTR)
28. Some obligations related to total return swaps (TRS) are included in SFTR, notably
in Chapter IV relating to Transparency towards investors. Nevertheless, TRS are
derivatives and thus are reportable under EMIR and not under SFTR. The definition
in Article 3(18) of SFTR clearly states that a TRS “means a derivative contract as
defined in point (7) of Article 2 of Regulation (EU) No 648/2012 in which one
counterparty transfers the total economic performance, including income from
interest and fees, gains and losses from price movements, and credit losses, of a
reference obligation to another counterparty.” It is to be noted that depending on
the underlying, TRS are to be reported either as credit derivatives or as equity
derivatives. Details on how these are to be reported can be found in sections 5.7
and 5.8.
29. Furthermore, Recital 7 of SFTR clarifies that some transactions that are commonly
referred to as liquidity swaps and collateral swaps, which do not fall under the
definition of ’derivative contracts‘ under EMIR, are included in the scope of SFTR.
These contracts are not reportable under EMIR.
Complex contracts
30. In the case of contracts stemming from another contract (e.g. option on a future),
the first contract ceases to exist before giving rise to the second one which is
materially different from the first one. The two contracts should be reported
separately, i.e. the second one should only be reported once the first contract is
terminated. Therefore, even though the two contracts are connected in the way they
come into existence, they should be reported in two separate reports. In case where
the resulting contract does not qualify as a ‘derivative’ or ‘derivative contract’ as
defined in EMIR Article 2(5), the resulting contract should not be reported.
31. In the case where a derivative has two or more legs (e.g. a single derivative contract
representing a strategy that has the features of several contracts), all legs of the
contract should be reported in one report, where the combination of fields allows
for this. Otherwise, a report per leg should be submitted and those reports should
be linked by using the same package identifier in field 2.6.
Market transactions that do not fall under the definition of a derivative
32. The following transactions do not fall under the definition of a derivative under EMIR
and thus should not be reported under EMIR:

99
a. Financial instruments with embedded derivatives (e.g. convertible bonds): some
financial instruments are issued with features that could be considered as
derivatives embedded in the structure of the instrument itself. This is for
instance the case of convertible bonds which according to Table 2.2 of Annex
III of RTS 2017/583 “means an instrument consisting of a bond or a securitised
debt instrument with an embedded derivative, such as an option to buy the
underlying equity”.
b. Structured finance products or structured products are defined in Article
2(1)(28) of MiFIR as “those securities created to securitise and transfer credit
risk associated with a pool of financial assets entitling the security holder to
receive regular payments that depend on the cash flow from the underlying
assets”.
c. Securitised derivatives are defined in Table 4.1 of Annex of RTS 2017/583 as
“a transferable security as defined in Article 4(1)(44)(c) of Directive 2014/65/EU
different from structured finance products”. These include at least:
• plain vanilla covered warrants;
• leverage certificates;
• exotic covered warrants;
• negotiable rights;
• investment certificates.
4.2.2 Reporting obligation with regards to the parties involved in the trade
33. Intragroup derivatives, not eligible for exemption, should be reported as any other
derivatives and the corresponding field 2.37 ’Intragroup‘ should be populated as
’True‘. However, Article 9(1) EMIR provides for an exemption of intragroup
derivatives from the reporting obligation where the relevant conditions are met. In
these cases, both counterparties should continue to report until the conditions for
applying the exemption can be met and the exemption is granted (further
clarifications on the exemption are provided in the section 4.3).
34. Derivatives within the same legal entity (e.g. between two desks or between two
branches of the same entity) should not be reported under EMIR as they do not
involve two counterparties. The only exception is the situation in which a Clearing
Member defaults and the CCP temporarily assumes both sides of the outstanding
derivative contracts.
35. Similarly, non-EU subsidiaries of a group for which the parent undertaking is
established in the Union are not required to report their derivatives under EMIR. In
the case of contracts between an EU counterparty and a non-EU counterparty, the
EU counterparty will need to report such contracts.
36. EMIR requires counterparties and CCPs to report. CCPs are defined in EMIR
Article 2(1) and counterparties are defined either as FC if the entity falls under any
of the categories of financial counterparties defined in EMIR or as an NFC if it is an

100
undertaking established in the Union other than a CCP or a FC. The concept of an
undertaking is not defined in EMIR. However, the European Commission provides
in its FAQ
31
, question II.14 a rationale leading to the consideration that the “concept
of undertaking is broader than that of 'companies or firms' and thus, is not restricted
to entities with legal personality or with for-profit-making (Article 54 TFEU)”. It is
worth noting that individuals not carrying out an economic activity are consequently
not considered as undertakings and thus are not subject to the reporting obligation
under EMIR.
37. As a consequence, if the activity performed by the entity with a charitable nature or
otherwise a non-profit profile falls under the definition of an economic activity that
qualifies it as a charity or non-profit entity, it would be subject to the obligations
applicable to non-financial counterparties for the derivatives concluded, including
the reporting obligation.
38. With regards to investment funds (e.g. UCITS, AIF, unincorporated funds, IORP),
the counterparty to the derivative is generally the fund (or in case of umbrella funds,
the sub-fund). When a fund manager executes a contract for different funds at the
same time (e.g. block trade), it should immediately allocate the relevant part of that
contract to the relevant funds and report accordingly. As a consequence, the
counterparty ID should be the ID of the fund, not the ID of the fund manager.
According to Articles 9(1b) to (1d) EMIR, the fund manager shall report the OTC
derivatives on behalf of the funds. The ID of the fund manager should be included
as the entity responsible for reporting and where it reports directly as the report
submitting entity. It should be noted that in rare circumstances, the fund manager
executes trades on its own account and not on behalf of the funds it manages. In
such case the counterparty would be the fund manager.
39. Non-EU AIFs that are set up exclusively for the purpose of serving one or more
employee share purchase plans, or that are securitisation special purpose entities
as referred to in point (g) of Article 2(3) of Directive 2011/61/EU, do not qualify
either as FCs under Article 2 (8) nor as NFCs under Article 2(9). As such, these
AIFs are not subject to the reporting obligation and therefore, they should not report
derivatives under EMIR. However, if the other counterparty is subject to the
reporting obligation under EMIR, that counterparty should report derivatives
concluded with such non-EU AIFs.
40. More generally, with regards to funds and in particular when an AIFM is managing
AIFs domiciled in the Union and AIFs domiciled in third countries, fund manager
should establish whether the AIF qualifies as a FC under EMIR Article 2(8). In case
the AIF qualifies as a FC, the AIFM that is authorised or registered under AIFMD
should ensure that the derivative details are reported.
41. Finally, some specific entities are out of scope of EMIR in general in accordance
with EMIR Article 1(4) such as the BIS, central banks or public bodies charged with
or intervening in the management of the public debt for a given list of countries.
However, with regard to Article 1(5) the reporting obligation is the only EMIR
31
emir-faqs-10072014_en.pdf (europa.eu).

101
obligation that applies to multilateral development banks, some public sector
entities, the ESF and ESM.
42. Investment firms that provide investment services (such as execution of orders or
receipt and transmission of orders) without becoming a counterparty to a derivative
by acting as principal do not have an obligation to report under EMIR. Nevertheless,
in case the investment firm acts as an investment fund manager as described in
paragraphs 1b, 1c or 1d of EMIR Article 9, then this investment firm becomes
responsible and legally liable to report on behalf of the counterparty and to report
its own LEI in the field 1.3 ‘Entity responsible for reporting’.
43. Similarly, when a management company provides the service of portfolio
management (as defined in Article 4(8) of MiFID) to a client, and, by doing so,
enters into derivative contracts, the client should be considered as the counterparty
to the derivative, except when the management company bears the risk of the
derivative contract and therefore is considered as a counterparty. The management
company can report to TRs on behalf of its clients without prejudice to the client’s
liability for meeting the reporting obligation. In that situation, the ID of the
management company should be provided as the report submitting entity ID.
44. When a broker is a counterparty to a derivative, it should report the derivative and
identify itself as a counterparty. In line with the RTS on reporting and more
particularly with regard to the details to be reported in the field 1.15, the broker is
then not required to report its LEI in the field ’Broker ID’ Otherwise, if a broker only
acts as an intermediary for counterparty 1, the LEI of the broker should be reported
in the ‘Broker ID’ field.
4.2.3 Reportability in specific scenarios
45. Reporting under EMIR is dual-sided, i.e. both counterparties to derivative contracts
are required to report if they fall under the scope of EMIR. As a consequence, for a
derivative entered into by two counterparties subject to EMIR, the same derivative
is expected to be reported twice, once on behalf of each counterparty, and the
details of the reported derivative should be consistent across both reports.
46. Article 9(1e) stipulates that counterparties and CCPs should ensure that such
details are reported correctly and without duplication. Based on this requirement,
counterparties or other entities responsible for reporting should put in place
processes and controls in order to avoid the risk of duplicate reporting. This is
particularly important (i) in the case of a change of TR (ensure that the reports are
channelled to the right TR), (ii) in the case of a corporate event such as a merger
or an acquisition (avoid reporting the same derivative on behalf of the wrong entity)
or (iii) in the case of changes in delegation (ensure that only one delegated entity
reports a derivative). In case a duplicate report is identified the counterparty should
immediately take corrective actions with diligence in order to resolve the problem.
47. In the event of a novation, where a counterparty (being a CCP or another
counterparty) steps into a derivative and becomes a new counterparty to the
derivative (this paragraph does not cover clearing events), the derivative should be
reported with action type ‘New’ and event type ‘Step-in’ by both counterparties, i.e.

102
the new counterparty stepping-in as well as the counterparty that does not change.
For the original report relating to the existing derivative, both counterparties should
send a report with action type ‘Terminate’ and event type ‘Step-in’, populating the
field 2.45 ’Early termination date’.
48. For block trades, there is a distinction necessary between (i) scenarios where the
block trade was concluded by an investment firm and then allocated to clients and
(ii) those scenarios where the block trade was concluded by a fund manager without
own reporting obligation and then allocated to individual funds.
49. In the first case the block trade should first be reported by the investment firm. The
investment firm should then report the allocations to the individual clients.
50. In the second case, block trades that are subsequently allocated to individual funds
on trade date are not required to be reported. In such cases, the counterparty to
the derivative is the individual fund, therefore the allocations should be reported (a)
specifying the relevant individual fund (on behalf of which the fund manager has
entered into the block trade) as counterparty to the said trade and (b) specifying the
allocation of the relevant part of the trade to the relevant individual fund. Any parts
of a block trade that are not allocated on trade date should be reported with the
fund manager as the counterparty. This reporting logic would only apply where the
allocation post trade date is permitted by the applicable national legislation.
51. In case a collateral agreement allows the covering of exposures in transactions that
are not to be reported under EMIR, the collateral reported should be just the
collateral that covers the exposure related to the derivatives reported under EMIR.
If it is impossible to distinguish within a pool of collateral the amount which relates
to derivatives reportable under EMIR from the amount which relates to other
transactions, the collateral reported can reflect the actual collateral posted /
received covering a wider set of transactions. As a consequence, in case none of
the transactions covered by the report is reportable under EMIR, no collateral
should be reported.
52. Regulation (EU) 2019/834 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 May
2019 amending Regulation (EU) No 648/2012 removed the backloading
requirement from Article 9 of EMIR, therefore derivatives concluded before and no
longer outstanding on 12 February 2014 are not subject to the reporting obligation.
53. Where no contracts are concluded, modified or terminated during several days, no
reports are expected apart from updates to valuations or collateral on outstanding
derivatives, as required. As the obligation to report should be complied with by T+1
(T being the date of conclusion/modification/termination of the contract), there is no
other need to send daily reports if there are no conclusion, modifications to the
contract or termination.
54. Derivatives that are concluded and then netted or terminated for other reasons
during the same day, should be reported to TRs. In case of a termination during the
same day, at least two reports should be sent: a report with action type ‘New’ and
a second report with action type ‘Terminate’ and the relevant event type, unless the
derivative is reported with action type ‘Position component’ in which case it will be

103
netted into the subsequent position (please refer to section 4.7 for position level
reporting specificities).
55. With regards to cleared derivatives, the Article 2 of the RTS on reporting details
how trades that are cleared should be reported. As a consequence, if the derivative
is not cleared on the same day by a CCP or if the derivative is concluded off venue,
the derivative should first be reported in its original state and then, once it is cleared,
the original derivative should be terminated with action type ‘Terminate’ and event
type ‘Clearing’. The subsequent derivative should be reported with action type
‘New’ and event type ‘Clearing’ or, if relevant, with action type ‘Position
Component’.
4.3 Intragroup exemption from reporting
56. The three-month period referred to in Article 9(1) EMIR, as amended by Regulation
2019/834, in which the authorities may disagree with the fulfilment of the above
conditions, starts on the calendar day following receipt of the notification(s) by the
relevant NCA(s).
57. The exemption should be valid from the date when the NCA(s) confirm(s) to the
counterparty(ies) that the conditions to use the exemption are satisfied, or if no
decision is notified by the NCA(s), it will be valid from the end of the three-month
non-objection period. If the conditions, referred to in the third sub-paragraph of
Article 9(1) EMIR, as amended by Regulation 2019/834, may be no longer fulfilled
due to a change in the counterparties characteristics, the counterparties need to
inform the relevant NCA(s). Without prejudice to the existing exemption, the NCA(s)
can object to the use of the exemption if the conditions are no longer met. From the
point in time at which the NCA objects to the use of the exemption the exemption
will not be valid.
58. It should be noted that the counterparties should report derivatives during the three-
month period unless the NCA(s) notify(ies) the counterparty(ies) that they agree
upon fulfilment of the conditions before the three-month period expires.
59. With regards to the reference to the ‘parent undertaking’ for the purpose of the
conditions for the exemption under Article 9(1) EMIR, as amended by Regulation
2019/834, it should be considered that:
a) the ultimate parent undertaking of the group
32
relevant for the consolidation on a full
basis is the parent undertaking for that purpose, and
b) the centralised risk evaluation, measurements and control procedures should be
applicable for the counterparties notifying the exemption from reporting. It is not
32
The European Commission has clarified that the exemption contained in Article 9(1) of EMIR does not cover intragroup
transactions for which the parent undertaking is established in a third country, even if the transaction occurs between two
counterparties which are both established in the EU. (see ESMA EMIR Q&A TR Answer 51 (m).)

104
necessary that they are established at the level of the whole group of the ultimate
undertaking.
60. The notion of ultimate parent undertaking under point a) here above is to be
understood as the highest consolidating entity in the group. Figure 1 illustrates the
general case.
FIGURE 1: EXAMPLE OF A TWO-LAYER GROUP STRUCTURE
61. Some specific use cases are detailed in Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5.
FIGURE 2: FULL CONSOLIDATION BY THE ULTIMATE PARENT UNDERTAKING

105
FIGURE 3: FULL CONSOLIDATION BY THE ULTIMATE PARENT UNDERTAKING WITH ANOTHER
ENTITY HAVING FINAL OWNERSHIP
FIGURE 4: FULL CONSOLIDATION BY THE ULTIMATE PARENT UNDERTAKING WITH AN
INTERMEDIATE PARENT

106
FIGURE 5: FULL CONSOLIDATION BY THE ULTIMATE PARENT UNDERTAKING WITH AN
INTERMEDIATE PARENT AND WITH ANOTHER ENTITY HAVING FINAL OWNERSHIP
62. Counterparties should submit their notifications to their respective NCAs (individual
notifications should be sent to each NCA where counterparties are located) in
accordance with the procedures adopted by those NCAs in each Member State. If
this is acceptable for the respective NCA, the ultimate parent undertaking (as per
paragraph 59 of these Guidelines) or the entity relevant for centralised risk
evaluation, measurements and control procedures with regards to the
counterparties for which the exemption is notified may provide a single notification
identifying each entity of its group situated within that Member State for which
exemption is requested. It is not necessary that the ultimate parent undertaking or
the entity relevant for centralised risk evaluation, measurements and control
procedures with regards to the counterparties for which the exemption is notified,
is a counterparty to a derivative contract, neither that it is located in the Member
State where it submits a notification.
63. When notifying of their intention to apply the exemption from the reporting obligation
in accordance with Article 9(1) EMIR, the notifying counterparty should state that it
fulfils the conditions laid down in the third subparagraph of Article 9(1) EMIR and,
if applicable, should indicate the other NCA(s) that have been notified with regards
to the counterparty(ies) included in the notification. The NCA may ask for additional
information and/or documents to assess the fulfilment of the conditions laid down
in the third subparagraph of Article 9(1) EMIR.
64. Counterparties may notify their intention to apply an intragroup exemption even if
the counterparties have not yet concluded any derivatives and consequently apply
the exemption unless one of the NCAs objects for derivatives concluded after the
exemption has been granted. Nevertheless, the notification should only be
submitted once all the conditions specified in third sub-paragraph of Article 9(1) of
EMIR are fulfilled.
65. When counterparties of the same group established in at least two different Member
States notify their NCAs of their intention to apply a reporting exemption under
Article 9(1) EMIR, each NCA needs to consider whether the conditions laid down

107
in the third subparagraph of Article 9(1) are met. NCAs may disagree on the
fulfilment of these conditions. Where one of the NCAs considers that the conditions
are not fulfilled, it should notify the counterparty in its Member State as well as the
other NCA(s) within the three-month period of the receipt of the notification and
specify the reasons.
66. Where counterparties want to benefit from the exemption from reporting and once
they consider they have addressed the objection(s) raised by the objecting NCA(s),
they should renotify accordingly of their intention to apply the reporting exemption
under Article 9(1) EMIR.
67. A derivative contract between a financial counterparty (FC) and non-financial
counterparty (NFC) where:
a. the FC belongs to both a group of undertakings referred to in Article 3(1) or
Article 80(7) and (8) of Directive 2006/48/EC (CRD), and another group referred
to in Articles 1 and 2 of Directive 83/349/EEC, and
b. the NFC merely belongs to the group under Articles 1 and 2 of Directive
83/349/EEC,
c. may be eligible for an intragroup exemption from reporting. Notably, in
accordance with the definition of ‘group’ in Article 2(16) EMIR, as amended by
Regulation 2019/834, such a contract may be eligible for an intragroup reporting
exemption if the NFC, while not consolidated under the CRD, is part of the same
consolidated non-financial group as the FC.
68. For the avoidance of doubt, if counterparties notify their respective NCAs on
different dates, they should wait until the end of the later of the two three-month
periods before relying on the exemption (provided neither NCA objected) or until all
relevant NCAs agree on the fact that the conditions laid down in the third
subparagraph of Article 9(1) EMIR are met. The reporting exemption for the
derivative contracts concluded by the relevant counterparties is not valid, if one
NCA has objected to it. Therefore, the derivatives concluded between the
counterparties, that are included in the notification, should continue to be reported.
69. Once the reporting exemption is valid, the counterparties that benefit from the
exemption should send reports with action type ‘Error’ for all the derivatives referred
to in paragraphs 2(a) and 2(b) of Article 2 of the ITS on reporting with the
counterparties for which the reporting exemption is valid.
70. If the reporting exemption ceased to be valid due to a non-compliance with any of
the conditions referred to in the third sub-paragraph of Article 9(1) EMIR, the
counterparties concerned should report the derivative contracts that have been
concluded and have not been terminated by the counterparties nor matured on the
date the exemption ceased to be valid using action type ‘New’ and event type
‘Trade’ and provide all the relevant details of those derivatives as they stand on the
date when the exemption ceases to be valid, and report all subsequent lifecycle
events as they occur. It is not necessary to report the lifecycle events to the
derivative that occurred between the date of conclusion of that derivative and the
date when the exemption ceased to be valid. If these derivatives were previously

108
cancelled with action type ‘Error’ at the moment when the exemption was granted,
the counterparties should report such derivatives with action type Revive. Also in
this scenario, it is not necessary to report lifecycle events that occurred during the
period when the exemption from reporting was valid.
4.4 Allocation of responsibility for reporting
4.4.1 General clarifications
71. In accordance with EMIR Article 9(1), counterparties and CCPs are required to
ensure that the details of any derivative that is reportable as described in the section
4.2 are reported to a TR. Therefore, unless an exemption applies or unless a
different party is responsible and legally liable for reporting pursuant to Article 9(1a)
of EMIR, the reporting obligations apply to all counterparties and CCPs established
in the Union as soon as they enter into a derivative contract. This means, that such
a derivative should be reported no later than the working day following its
conclusion, modification or termination.
4.4.2 FC trading with NFC
72. With regard to the provisions under Article 9(2) of the ITS on reporting, ESMA
considers that, in order to fulfil the respective requirements, NFC- and FC should
agree on the way to exchange information in each of these cases. More particularly,
with regard to Article 9(2)(a) of the ITS on reporting, those arrangements should
allow the FC to have the information no later than T+1 after the conclusion or
modification of a contract so that the FC can proceed to the timely reporting. This
can be achieved e.g. by providing a list of predefined standard values to be used
as default by the FC, unless specified otherwise by the NFC-. In any case the NFC-
remains responsible for providing the FC with correct details and the FC is
responsible for using the information provided by the NFC-. As an example of
predefined values, consider the case where an NFC- is entering into derivative
contracts with a credit institution without the use of a broker, not clearing those
contracts and entering into them only to hedge its commercial activity in the sense
of EMIR Article 10(3). In this case, the NFC- could agree that the FC reports the
below pre-defined values in the fields specified in Article 9(2) of the ITS on
reporting, unless the NFC- specifically instructs the FC otherwise:
a. 1.15 ‘Broker ID’: blank.
b. 1.16 ‘Clearing Member’: blank.
c. 1.20 ‘Directly linked to commercial activity or treasury financing’: ‘True’.
73. ESMA takes this opportunity to remind market participants that NFC- are not
required to report data on collateral, mark-to-market, or mark-to-model valuations
of the contracts in accordance with Article 4 of the RTS on reporting. Nevertheless,
should the FC report this information, it should be correct as of the respective
collateral or valuation timestamp.

109
74. A particular situation is where a conclusion of a derivative has been reported or
should have been reported by the NFC- (either because it was executed before the
provisions setting out the reporting responsibility became applicable on 18 June
2020 or because the NFC- opted-out at the time of the execution), and a
modification or termination is to be reported under the provisions assigning the
responsibility and legal liability to the FC. More particularly, this situation might
happen during the transition period, thus under the principles explained in section
4.1 on the transition to the new reporting standards. ESMA considers as well that
the arrangements between the NFC- and the FC should take into account such
situations in order to ensure the continuity of the reporting in terms of content,
timeliness and adequacy. The counterparties should as well ensure that those
contracts are not reported with duplication.
75. For any outstanding OTC derivatives where an FC and an NFC- report to two
different Trade Repositories at the moment the responsibility and legal liability are
transferred, the outstanding OTC derivatives of the NFC- should be ported to the
TR of the FC at that moment, unless the FC decides to become client of the TR of
the NFC- and report the OTC derivatives concluded with the NFC- to that TR.
Similarly, each time when NFC changes its status from NFC- to NFC+, and thus
the responsibility and legal liability is transferred to the NFC, the outstanding OTC
derivatives concluded with the FC should be ported to the TR of the NFC, unless
the NFC decides to become client of the TR of the FC and report the OTC
derivatives concluded with the FC to that TR. Any such transfer of OTC derivatives
between the TRs of any pair of FC-NFC should be performed following the
Guidelines on transfer of data between Trade Repositories
33
(in particular, the
derivatives subject to transfer should not be cancelled and re-reported by the
counterparties, but rather transferred as specified in the Guidelines).
76. With regard to Article 9(2)(b) of the ITS on reporting, the fields 1.7 ‘Clearing
threshold of counterparty 1’ and 1.13 ‘Clearing threshold of counterparty 2’ are part
of the reportable details. To the extent possible, the NFC- should inform the FC of
an anticipated change in its status ahead of the date of the required annual
calculation of its positions pursuant to the Article 10(1) of EMIR to avoid any
disruption in the continuity of reporting. While the status of the NFC is known and
primarily assessed by the NFC itself, the FC should collect the information on a
regular basis in order to be able to perform its own reporting. When the FC becomes
aware of a change from NFC+ to NFC- after the calculation date, it should submit
the missing reports pertaining to the OTC derivatives that were concluded, modified
or terminated after that date without undue delay. Such submissions should be
done, upon having received from the NFC all relevant details (as per Article 9(2)(a)
of the ITS on reporting) pertaining to these derivatives.
77. Similarly, the NFC should take all relevant steps in order to ensure that it is capable
to take over the reporting once it changes its status from NFC- to NFC+ in order to
ensure continuity of the reporting in terms of content, timeliness and adequacy. This
33
https://www.esma.europa.eu/sites/default/files/library/esma74-362-2351_final_report_-
_guidelines_on_data_transfer_between_trade_repositories_emir_sftr.pdf

110
includes as well that the NFC should inform the FC as soon as possible and
therefore, the NFC should ideally anticipate the change.
78. With regard to the Article 9(2)(c) of the ITS on reporting, NFCs are responsible for
ensuring that their LEI is renewed in a timely fashion. In order to avoid disruptions
in the reporting and for the FC to avoid having to manage rejections by the TRs,
ESMA considers that FC can e.g. timely liaise with the NFC- so that the latter
renews its LEI. Nevertheless, if the NFC- has not timely renewed its LEI and
therefore FC was not able to successfully report on behalf of NFC-, the FC should
submit the missing reports without undue delay as soon as the LEI of the NFC- is
renewed.
79. While the obligation to report OTC derivatives is no longer on the NFC-, ESMA
considers that it is of utmost importance that both counterparties, including the
NFC-, are in possession of complete and up-to-date information about the details
of the derivatives that have been reported to a TR. Therefore, ESMA considers that
FCs can e.g. provide its NFC- counterparties on regular basis (e.g. monthly) with
the information concerning the contracts that are outstanding at the TRs. Being able
to compare its own records with the records of derivatives stored at the TRs on a
regular basis would support the NFC- in fulfilling its other obligations as defined
under EMIR and more particularly to EMIR Article 9(2) “Counterparties shall keep
a record of any derivative contract they have concluded and any modification for at
least five years following the termination of the contract” or other relevant
regulations as well as to be aware of the information that is available to the entities
listed in EMIR Article 81(3) on their behalf.
80. For the avoidance of doubt, ESMA stresses again that all the aforementioned
clarifications apply only to OTC derivatives. Thus, for ETDs, i.e. any derivative
contracts that do not qualify as OTC based on the definition of Article 2(7) of EMIR
as amended by Article 32 of SFTR, the counterparty remains responsible and
legally liable for reporting the details to a TR and the provisions related to the
transfer of responsibility and legal liability do not apply. Counterparties cannot
assume that all options and futures traded on venue are ETDs.
81. In very specific cases, external circumstances might lead to a change in the
allocation of responsibility for the reporting e.g.:
a. FC that was established in an EEA country will be established in a third country,
b. Derivative contract changes from OTC to ETD or vice versa.
82. In such cases, ESMA considers that the allocation of responsibility depends on the
situation at each time a reporting requirement arises, e.g. for a derivative contract
that is considered OTC until 30//11 and becomes an ETD as of the 1/12, the FC is
responsible for reporting until 30/11 included while the NFC- will be become
responsible and legally liable for reporting as from the 1/12. All other provisions of
these guidelines will be applicable in accordance with the allocation of
responsibility.

111
83. Another limitation is that the provisions on allocation of responsibility only apply
when the FC is established in the Union or where the conditions laid down in the
fourth sub-paragraph of Article 9(1a) of EMIR are fulfilled.
84. Finally, counterparties should take into account the situation of the implementation
of the amendments to EMIR in EEA countries (Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway).
Until the amendments to EMIR are incorporated into the EEA agreement and
transposed into the national laws of these countries, counterparties should carefully
assess their obligations when trading with EEA counterparties and have
arrangements in place to ensure that reports are made without duplication.
Table 2 - Population of the fields pertaining to counterparties, report submitting entity and entity
responsible for reporting
Scenario
Report
submitting
entity (field 1.2)
Entity
responsible for
reporting (field
1.3)
Counterparty
1 (field 1.4)
Counterparty
2 (field 1.9)
FC reporting
on behalf of
NFC- in
accordance
with Article
9(1a)
Leg 1
FC LEI
FC LEI
FC LEI
NFC- LEI
Leg 2
FC LEI
FC LEI
NFC- LEI
FC LEI
FC reporting
on behalf of
NFC- in
accordance
with Article
9(1a) and FC
delegating to
RSE
Leg 1
RSE LEI
FC LEI
FC LEI
NFC- LEI
Leg 2
RSE LEI
FC LEI
NFC- LEI
FC LEI
NFC- opting
out from FC
reporting on
their behalf in
accordance
with Article
9(1a)
Leg 1
FC LEI
FC LEI
FC LEI
NFC- LEI
Leg 2
NFC- LEI
NFC- LEI
NFC- LEI
FC LEI
NFC- opting
out from FC
reporting on
their behalf in
accordance
Leg 1
RSE LEI
FC LEI
FC LEI
NFC- LEI
Leg 2
RSE2 LEI
NFC- LEI
NFC- LEI
FC LEI

112
Table 2 - Population of the fields pertaining to counterparties, report submitting entity and entity
responsible for reporting
Scenario
Report
submitting
entity (field 1.2)
Entity
responsible for
reporting (field
1.3)
Counterparty
1 (field 1.4)
Counterparty
2 (field 1.9)
with Article
9(1a)
FC delegating
to RSE
NFC-
delegating to
RSE2
NFC+
delegating to
FC
Leg 1
FC LEI
FC LEI
FC LEI
NFC+ LEI
Leg 2
FC LEI
NFC+ LEI
NFC+ LEI
FC LEI
NFC+
delegating to
FC and FC
subdelegating
to RSE
Leg 1
RSE LEI
FC LEI
FC LEI
NFC+ LEI
Leg 2
RSE LEI
NFC+ LEI
NFC+ LEI
FC LEI
NFC+ not
delegating to
FC
Leg 1
FC LEI
34
FC LEI
FC LEI
NFC+ LEI
Leg 2
NFC+ LEI
35
NFC+ LEI
NFC+ LEI
FC LEI
Counterparty
trading with a
natural
person not
eligible for an
LEI delegating
to RSE
Leg 1
RSE LEI
CP 1 LEI
CP 1 LEI
Client code as
specified in ITS
on reporting for
field 1.9
No Leg 2 reporting required
The contract
is an ETD
Leg 1
FC LEI
FC LEI
FC LEI
NFC- LEI
Leg 2
NFC- LEI
NFC- LEI
NFC- LEI
FC LEI
34
If the the FC relies on another entity to submit the reports on its behalf, the field should be populated with the LEI of that RSE.
35
If the the NFC+ relies on another entity to submit the reports on its behalf, the field should be populated with the LEI of that
RSE.

113
Table 2 - Population of the fields pertaining to counterparties, report submitting entity and entity
responsible for reporting
Scenario
Report
submitting
entity (field 1.2)
Entity
responsible for
reporting (field
1.3)
Counterparty
1 (field 1.4)
Counterparty
2 (field 1.9)
(No other
delegation in
place
36
)
Complex scenario with various events:
NFC + delegating the reporting to RSE.
NFC + becomes NFC- and decides to opt out from FC reporting on their behalf in accordance with
Article 9(1 a) but relies on RSE.
NFC – decides to opt-in i.e. to stop delegating to RSE and to start relying on FC in accordance with
Article 9(1a).
The FC uses another TR than RSE.
NFC – is merged into another NFC (noted NFC*) that remains NFC-.
NFC – becomes NFC+.
In this scenario we focus only on the Leg reported on behalf of the NFC.
1. NFC+ delegating the reporting
to an RSE
RSE LEI
NFC LEI
NFC LEI
FC LEI
2. NFC+ becomes NFC- but opts
out from FC reporting on their
behalf under Article 9(1a) and
decides to continue the delegation
to an RSE
NFC notifies FC ahead of the change of status based on the annual
calculation.
NFC notifies FC as well that it decides not to apply the transfer of responsibility
and legal liability in accordance with Article 9(1a). The NFC continues to rely
on its current process and delegates voluntarily to its RSE.
36
In case a delegation to another RSE is made, the logic is the same as when the delegation takes place in case ofan NFC-
opting out from FC reporting in accordance with Article 9(1)(a).

114
Table 2 - Population of the fields pertaining to counterparties, report submitting entity and entity
responsible for reporting
Scenario
Report
submitting
entity (field 1.2)
Entity
responsible for
reporting (field
1.3)
Counterparty
1 (field 1.4)
Counterparty
2 (field 1.9)
RSE LEI
NFC LEI
NFC LEI
FC LEI
3. NFC- opts in for reporting by FC
on their behalf under Article 9(1a)
Prior to the delegation, the NFC notifies the FC that it intends opt-in the regime
foreseen under Article 9(1a) and to transfer the responsibility and legal liability
for reporting to the FC in accordance with Article 9(1a) at least 10 days before
the transfer of responsibility.
The FC and the NFC put in place the arrangements required under Article 9(2)
of the ITS on reporting.
As a pre-condition to the actual transfer of responsibility, NFC initiates and
performs the transfer of data from its RSE’s TR to the TR of the FC in
accordance with the Guidelines on data transfer between TRs and with these
Guidelines.
FC LEI
FC LEI
NFC LEI
FC LEI
4. NFC- is merged into another
NFC- (noted NFC*)
FC or NFC- follow the process described in Article 8 of the ITS on reporting
related to changes of LEI. Once the change is processed by the TR, the new
LEI should be used.
FC LEI
FC LEI
NFC* LEI
FC LEI
5. NFC- becomes NFC+
NFC notifies FC ahead of the change of status based on the annual
calculation.
In accordance with the arrangements put in place between both counterparties
and required under Article 9(2) of the ITS on reporting, the NFC notifies the
FC of the change of status based on the annual calculation.
If required under the arrangements, the FC or the NFC initiates and performs
the transfer of data from its TR to the TR of the NFC in accordance with the
Guidelines on data transfer between TRs and with these Guidelines.
NFC* LEI
NFC* LEI
NFC * LEI
FC LEI
4.4.3 CCP
85. With regards to CCPs, in EMIR CCPs are not considered as Financial
Counterparties under Article 2(8) of EMIR, therefore if an NFC- would enter directly

115
in a derivative contract with a CCP, the CCP would not become responsible and
legally liable for the reporting of the details of the derivative on behalf of the NFC-.
In such cases, the obligation to comply with the reporting obligation remains with
the NFC-.
4.4.4 Funds (UCITS, AIF and IORP that, in accordance with national law, does not
have legal personality)
86. Articles 9(1b), (1c) and (1d) introduce as well the allocation of responsibility for
reporting for funds towards their respective fund manager in certain circumstances.
In these cases, it is considered that the fund managers have all relevant details
available in their respective roles and that the compliance with the provisions on
allocation of responsibility for reporting can be ensured in accordance with the
regulation.
87. As an illustration, please refer to the Table 3 below.
Table 3 – Population of the fields pertaining to counterparties, report submitting entity and entity
responsible for reporting
Scenario
Report
submitting
entity (field
1.2)
Entity
responsible for
reporting (field
1.3)
Counterparty
1(field 1.4)
Counterparty 2
(field 1.9)
Management
company / AIFM
(IFM) reporting
on behalf of the
fund under
Article 9(1c)
Leg
1
LEI IFM
LEI IFM
LEI fund
LEI CPT
Leg
2
LEI CPT
LEI CPT
LEI CPT
LEI fund
Management
Company / AIFM
(IFM) reporting
on behalf of the
fund under
Article 9(1c) and
delegating to the
CPT
Leg
1
LEI CPT
LEI IFM
LEI fund
LEI CPT
Leg
2
LEI CPT
LEI CPT
LEI CPT
LEI fund
Management
Company / AIFM
(IFM) reporting
on behalf of the
fund under
Article 9(1c) and
Leg
1
LEI RSE
LEI IFM
LEI fund
LEI CPT
Leg
2
LEI CPT
LEI CPT
LEI CPT
LEI fund

116
Table 3 – Population of the fields pertaining to counterparties, report submitting entity and entity
responsible for reporting
Scenario
Report
submitting
entity (field
1.2)
Entity
responsible for
reporting (field
1.3)
Counterparty
1(field 1.4)
Counterparty 2
(field 1.9)
delegating to a
RSE
88. In the particular case where a fund that qualifies as an FC enters into an OTC
derivative with an NFC-, the provision on allocation of responsibility for reporting in
the Article 9(1) and the clarifications thereof in the related Guidelines under section
4.4.2 above apply for the OTC derivative from the side of the counterparty.
Therefore, in such a situation:
a. The fund manager is responsible and legally liable to report the OTC derivative
on behalf of the fund;
b. The fund is responsible and legally liable to report the OTC derivative on behalf
of the NFC-.
89. As an illustration, if an AIF (LEI AAAAAAAAAA1111111111) with an AIFM (LEI
AAAAAAAAAA2222222222) enters into an OTC derivative contract with an NFC-
(LEI 123456789ABCDEFGHIJK), the counterparty related fields are to be
populated as follows:
TABLE 4 – EXAMPLE OF FUND RESPONSIBLE TO REPORT THE DERIVATIVE ON BEHALF
OF THE NFC-
Report 1 of the derivative
Report 2 of the derivative
1.3 Entity
Responsible for
Reporting
AIFM LEI:
AAAAAAAAAA2222222222
AIF LEI:
AAAAAAAAAA1111111111
1.4 Counterparty 1
(Reporting
Counterparty)
AIF LEI:
AAAAAAAAAA1111111111
NFC- LEI:
123456789ABCDEFGHIJK
1.9 Counterparty 2
NFC- LEI:
123456789ABCDEFGHIJK
AIF LEI:
AAAAAAAAAA1111111111

117
90. For the avoidance of doubt, ESMA stresses again that all the aforementioned
clarifications apply only to OTC derivatives. Thus, for ETDs, i.e. any derivative
contracts that do not qualify as OTC based on the definition of Article 2(7) of EMIR
as amended by Article 32 of SFTR, the counterparty remains responsible and
legally liable for reporting the details to a TR and the provisions related to the
transfer of responsibility and legal liability do not apply. Counterparties cannot
assume that all options and futures traded on venue are ETDs.
4.5 Delegation of reporting
91. Besides the allocation of responsibility stemming from EMIR Article 9(1a)-(1d) and
covered by section 4.4, EMIR stipulates in Article 9(1f) that the counterparties and
CCPs that are subject to the reporting obligation may delegate that reporting
obligation, this includes any task (individually and separately) related to the
reporting of data. In case of delegation of reporting, the delegating counterparty
should provide the report submitting entity with all the details of the derivative
contracts and it is responsible for ensuring that those details are correct. The
processes and timelines should in case of delegation be the same as in the case
of allocation of responsibility for reporting described in the section 4.4. Although at
the technical level there are many similarities and common processing aspects
between the allocation of responsibility and delegation of reporting, legally they are
different and independent reporting scenarios. It should also be mentioned that EU
counterparties should carefully assess any risks that might be posed to their
compliance with the reporting obligations in case of delegation of reporting to a non-
EU report submitting entity.
92. RTS on reporting provides a specific data element, field 1.2 ‘Report submitting
entity ID’, which should be mandatorily populated and in case where the reporting
counterparty or entity responsible for reporting has not delegated the submission
of the report to a third party or to the other counterparty, the reporting counterparty
or entity responsible for reporting will populate its own LEI. In the case when in the
reporting of a derivative multiple entities are involved, i.e. the reporting is carried
out by a chain of entities, field 1.2 should be populated with the LEI of the entity
ultimately submitting the report to the TR. FR on RTS/ITS (in section 4.1.3) also
clarifies that the RSEs should inform the reporting counterparties and ERRs about
relevant reporting and data quality issues (including data submitted on its behalf,
all the rejections, reconciliation breaks as well as other data quality issues
pertaining to the relevant data) for which the information will not be provided by the
TRs, especially if these reporting counterparties and ERRs are not participants or
users of the TR. ESMA also clarified in the FR on RTS/ITS that responsibilities
regarding the outstanding derivatives should be agreed by the parties and covered
by the delegation agreement. Naturally the delegation agreement needs to cater
for the point in time when it comes into effect and also for the point in time when it
ceases to be effective. Responsibilities of the counterparties and RSEs with regards
to data completeness and accuracy, e.g. update of LEI, and generally the
responsibility for the content of reports remains in case of delegation always with
the entity responsible for reporting. The delegating counterparty (subject to the

118
reporting obligation) should provide the RSE with all the details of the derivative in
a timely manner, and it is responsible for ensuring that those details are correct.
93. Delegation of reporting includes the following scenarios:
a. one counterparty delegates to the other counterparty;
b. one counterparty delegates to a third party;
c. both counterparties delegate to a single third party;
d. both counterparties delegate to two different third parties.
94. In any of the scenarios above the principle of avoiding duplication and ensuring the
continuity of reporting should be followed.
95. ESMA encourages centralised reporting (i.e. by the venue on which a non-OTC
derivative has been concluded or by the CCP in which it is being cleared); however,
this should be always a matter of agreement by the counterparties, based on
delegation agreement. Whenever a third party is performing that function based on
a delegation agreement (on behalf of one or both counterparties), it should ensure
that all relevant data are duly and timely provided by the counterparties to fulfil the
reporting obligation.
96. Further clarifications should be noted with regards to the delegation of tasks in case
a third party is used for reporting and any possible differences in criteria for
delegation depending on the home member state of the delegating entity. Firstly,
the reporting counterparty, ERR or RSE can decide to delegate any task related to
the reporting of data, including the generation of the UTI. Secondly, currently no
specific rules on how the delegation should be performed are determined, however
all EMIR provisions should be respected (timely and accurate reporting, etc.) and
the counterparties should remain liable for the content of the reports and any
misreporting by the third entities they rely upon. Legal documentation covering the
delegation arrangement is recommended (e.g. written agreement between entity
responsible for reporting and the report submitting entity, even if also subject to the
requirement to report, such as the other counterparty or the CCP).
97. For example investment firms that provide only investment services (such as
execution of orders or receipt and transmission of orders) do not have any
obligation to report under EMIR unless they become a counterparty to a derivative
by acting as principal. However, nothing prevents counterparties to a derivative to
use an investment firm (acting as a broker) as a third party for TR reporting.
98. In the case when a portfolio manager is involved, i.e. an entity to which the
execution of (a part of) the investment strategy of a counterparty is delegated, this
portfolio manager should be identified (in the relevant field) only when that entity
performs, de jure or de facto, one of the roles identified in the counterparty data of
a derivative report, e.g. broker. Otherwise that entity should not be identified.

119
4.6 Reporting of lifecycle events
4.6.1 Action types
99. Counterparties should report the conclusion, modification and termination of a
derivative.
100. In case none of the details of the derivative, as expressed in the data fields,
have changed, the counterparties should not report again details of the derivative.
The only exception is the update of the outstanding derivatives in the transition
period as described in the section 4.1.
101. Furthermore, the counterparties that are required to report valuation and
collateral, i.e. FCs, NFC+ and CCPs, should report on a daily basis the details of
valuation and collateral as they stand at the end of the day, for all their outstanding
derivatives.
102. Counterparties should use action type ‘Modify’ to report modifications of the
details of a derivative, ‘Valuation’ to report changes in the value of a derivative and
‘Margin update’ to report modifications of the corresponding collateral.
103. Counterparties should ensure that action types ‘Modify’ and ‘Correct’ are used
correctly. In particular, ‘Modify’ should be used to report modifications to the terms
or details of a previously reported derivative, including when counterparty provides
additional information that previously was not available at the time of reporting.
‘Modify’ should not be used to report corrections of details of derivatives – only
‘Correct’ should be used for that purpose.
104. Similarly, in the case of collateral data, action type ‘Margin update’ should be
used to report the collateral for the first time as well as to report modifications of the
collateral data, but not the corrections of the previously reported collateral details
which should be made with action type ‘Correct’. A change in the collateral portfolio
code should be reported with ‘Modify’ (to update the code for a given derivative in
the portfolio) and ‘Margin update’ (when submitting the details of the collateral at
portfolio level). However, if the change in the portfolio code information is made due
to an initial error in reporting, such change should be reported with action type
‘Correct’.
105. In principle only one report per day, with action type ‘Margin update’ is expected.
However, if a counterparty identifies that it had submitted incorrect collateral data
for a given day, it should submit a collateral report with action type ‘Correct’ for that
day (specifying in the field ‘Event date’ and in the ‘Collateral timestamp’ the day for
which the data are corrected).
106. Collateral at a single derivative level can be reported for the first time either as
part of the derivative report with action type ‘New’ or separately with action type
‘Margin update’. Collateral at portfolio level should be reported for the first time with
action type ‘Margin update’. The new collateral is expected to be reported only
when at least one derivative covered by that collateral was reported and not
errored. Verification that collateral is not reported when no corresponding derivative
was reported should be performed as part of the TRs’ validations. If a counterparty
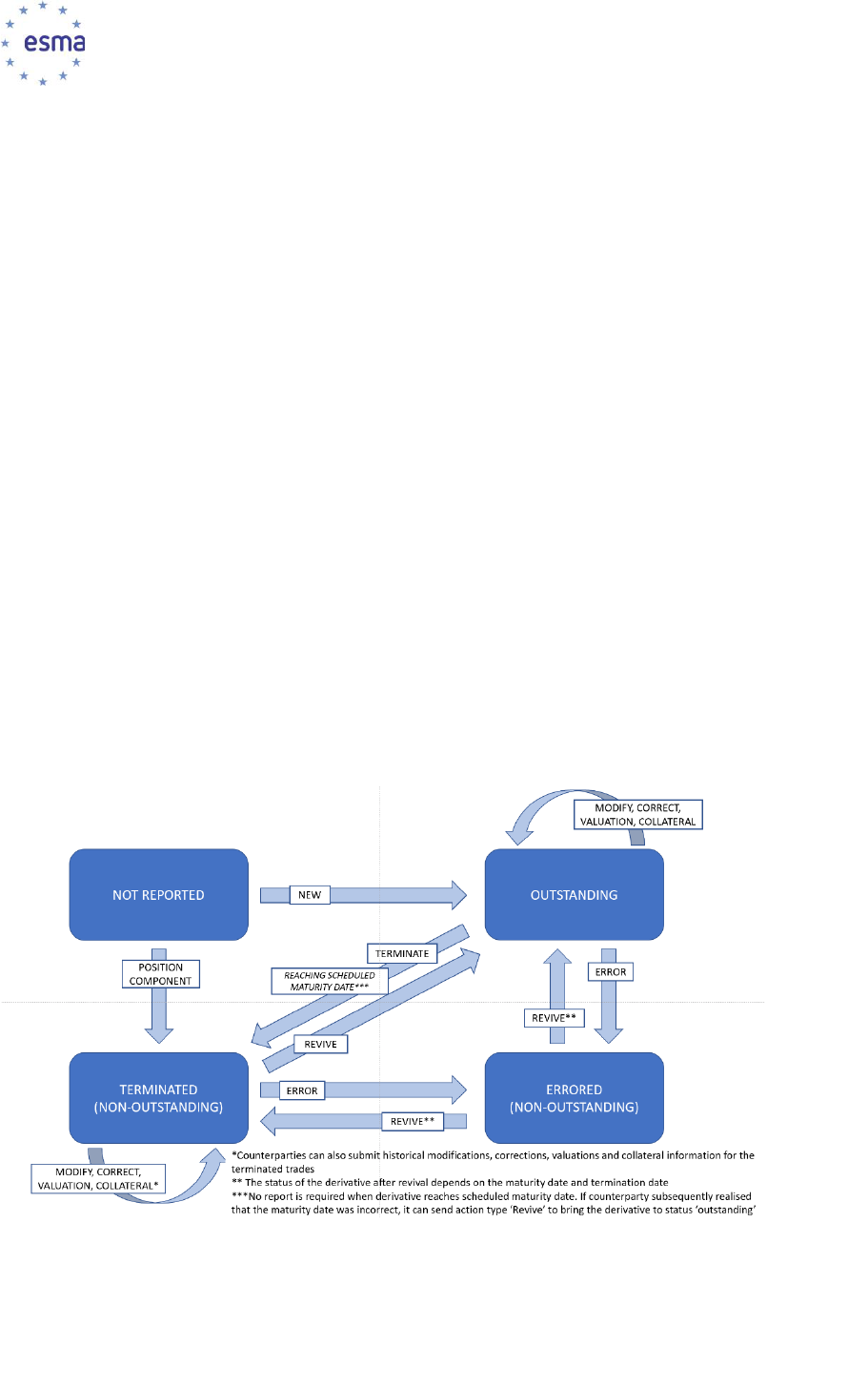
120
submits wrongly both derivatives and corresponding collateral, erroring the
derivatives would result automatically in erroring the collateral as there would no
longer be any corresponding derivatives.
107. In case a margin update report is submitted to a TR by a counterparty without
obligation to report collateral on a daily basis (but the corresponding derivatives are
valid and should not be errored), that counterparty should not submit any further
margin updates.
Sequences of action types
108. In order to ensure logical coherence between different reports pertaining to the
same derivative, TRs’ validation rules cover i.a. the correct sequences of action
types.
FIGURE 6: ALLOWABLE SEQUENCES OF ACTION TYPES
109. The blue boxes in the Figure 6 chart specify the status of a derivative, while the
allowable action types are indicated on the arrows. For example, when a derivative
is reported for a first time with the action type ‘New’, the status changes from ‘Not
reported’ to ‘Outstanding’. If a counterparty reports subsequently ‘Error’ for that
derivative, the status changes from ‘Outstanding’ to ‘Errored (non-outstanding)’.
For a derivative that has such status, the only allowable action type is ‘Revive’ (the

121
only action type on the arrows starting in the blue box with status ‘Errored (non-
outstanding)’. If submitted - it would change the status of the derivative either back
to ‘Outstanding’ or to ‘Terminated (non-outstanding)’, depending on the
maturity/termination date of that derivative. All dependencies between action types
and statuses of derivatives indicated in the chart should be read in this way.
110. All dependencies described in the chart apply to the reports of a given
counterparty. I.e. the reports sent by the other party to the trade do not impact
allowable action types reported by the first counterparty. It applies in particular to
action type ‘Error’, meaning that if one counterparty submitted ‘Error’ for a given
UTI (and has not reported ‘Revive’ afterwards), only that counterparty will not be
able to send further reports (other than ‘Revive’) for this UTI. In this way, if one
counterparty reports ‘Error’ by mistake, it will not prevent the other counterparty
from timely reporting relevant lifecycle events.
111. Action types ‘Modify’, ‘Correct’, ‘Margin update’ and ‘Valuation’ do not impact
the status of the derivative. They are allowed to be reported for terminated trades
only in the case of late reporting but they cannot be used to change the status of
the derivative to outstanding (e.g. by modifying the maturity date). Only the action
type ‘Revive’ can be used to change the status of the derivative to outstanding.
112. Action type 'Revive' can be used to re-open derivatives cancelled (with action
type 'Error'), terminated by mistake (with action type 'Terminate') and to re-open
derivatives that reached (incorrectly reported) maturity date. Furthermore, ‘Revive’
can be used after the action type ‘Position component’, if the latter was reported by
mistake. In such case the revived derivative at the trade level will be perceived as
outstanding, subject to the expiration date. If the counterparty reported new position
or a modification of a position, it would need to be reverted separately (by erroring
or modifying such position, respectively).
113. Counterparties, when reporting ‘Revive’ should provide all applicable details of
the contract as of the time of revival. However, counterparties should also submit
any missing reports that should have been made while the derivative was
temporarily non-outstanding. This includes reports with action type ‘Correct’ to
correct any specific values in the report, except for when the only correction was to
update the derivative to outstanding status (where such status can be inferred from
the ‘Revive’ report itself).
114. Reaching the scheduled maturity date is not an EMIR reportable event by the
counterparties. No action type applies in this case, including but not limited to ‘Error’
and ‘Terminate’. Once a derivative reaches it maturity date, it is considered no
longer outstanding. A derivative that is no longer outstanding and is reported late
with action type ‘New’ after reaching its maturity date, will be considered non-
outstanding.
115. When a derivative is included in the position, the status of that derivative
changes to ‘Terminated (non-outstanding)’. Any subsequent lifecycle events must
be reported at position level with a different UTI (the one of the position), and the
correct sequencing of these reports for that position should also be validated. It is
possible however to send a correction at trade level for a derivative that was

122
reported with action type ‘Position component’, if some details of that derivative
were incorrect.
116. The reports should be sent in a chronological sequence in which the events
occurred, in line with the requirements set out in the ITS on reporting. However, it
is recognised that in the cases where an entity fails to report on time or becomes
aware of the past submission of incorrect information, the entity should send the
reports with past event dates thus breaking the chronological order.
117. If there is an error in a historic valuation submission, only the valuation for that
past date needs to be corrected and there is no need to rereport the correct
valuations submitted after the incorrect valuation message. However, in the case
where multiple ’Valuation’ messages had been incorrectly reported and corrections
were required - the counterparty should submit a correction report for each day
when incorrect valuation was submitted.
118. TRs should validate the correct sequences of action types taking into the
consideration the content of the field ‘Event date’. With regard to how the TRs
should treat the reports with past event dates for the purpose of construction of the
Trade State Report, more details are included in the section 7.1.
4.6.2 Action types and event types combinations
119. Counterparties should report, where applicable, the relevant event type, as
specified in the field 2.152 in the RTS on reporting.
120. The below table specifies the allowable combinations of action types and event
types, as well as sets out whether they apply at trade level, position level or both.
The last column of the table indicates when a given action type can be reported
without an event type.
Table 5 - Allowable action type-event type combinations
Event type
TRADE
STEP-IN
PTRR
EARLY TERMINATION
CLEARING
EXERCISE
ALLOCATION
CREDIT EVENT
INCLUSION IN POSITION
CORPORATE EVENT
UPDATE
No Event Type required
Action type
NEW
T
T,P
T
T
T
T
P
T,P
MODIFY
T,P
T,P
T,P
T,P
T,P
T
T,P
P
T,P
T,P
P
CORRECT
T,P
TERMINATE
T,P
T,P
T,P
T
T,P
T
T,P
T,P
T,P
ERROR
T,P
REVIVE
T,P

123
Table 5 - Allowable action type-event type combinations
Event type
TRADE
STEP-IN
PTRR
EARLY TERMINATION
CLEARING
EXERCISE
ALLOCATION
CREDIT EVENT
INCLUSION IN POSITION
CORPORATE EVENT
UPDATE
No Event Type required
VALUATION
T,P
MARGIN UPDATE
T,P
POSITION
COMPONENT
T
121. Table 6 clarifies the applicability of all allowed action type-event type
combinations as well as provides additional comments on the actual use cases
where such combinations would be reported or, on the contrary, where they should
not be used.
122. The comprehensive mapping between business events and action type-event
type combinations is provided in the section 4.10.
123. It should be noted that no event type is envisaged for porting. ESMA reiterates
that porting should be performed in line with the Guidelines on transfer of data
between TRs
37
. Action types ‘New’ and ‘Terminate’ should not be used for that
purpose.
Table 6 - Applicability of action type – event type combinations
Action type
Event type
Applicability
Comments
New
Trade
When a derivative with a new UTI is
created for the first time through
trade and not because of another
prior event.
Combination ‘New’-‘Clearing’
should be used for the new
derivatives resulting from
clearing, in particular for
derivatives traded on trading
venues and cleared on the same
day by a CCP.
New
Step-in
When a derivative or position with a
new UTI is created for the first time
due to a step-in event.
New
PTRR
When a derivative with a new UTI is
created for the first time due to a
PTRR event.
Combination ‘New’-‘PTRR’ at
position level is not applicable,
as any derivative newly created
due to a PTRR event is expected
37
https://www.esma.europa.eu/sites/default/files/library/esma74-362-2351_final_report_-
_guidelines_on_data_transfer_between_trade_repositories_emir_sftr.pdf

124
Table 6 - Applicability of action type – event type combinations
Action type
Event type
Applicability
Comments
to be reported at trade level
(without prejudice to the
possibility of including such
derivative subsequently in a
position).
Combination ‘New’-‘PTRR’ can
be used in case of rebalancing.
New
Clearing
When a derivative with a new UTI is
created for the first time due to a
clearing event.
This combination includes also a
clearing of OTC derivatives
which were previously bilaterally
agreed among counterparties
and subsequently cleared.
New
Exercise
When a derivative with a new UTI is
created for the first time due to an
exercise event.
This combination should be used
when reporting the underlying
swap following the execution of a
swaption
New
Allocation
When a derivative with a new UTI is
created for the first time due to an
allocation event.
New
Inclusion in
position
When a new position is created by
inclusion of trades in that position for
the first time.
New
Corporate
Event
When a derivative or position with a
new UTI is created for the first time
due to a corporate action on the
underlying equity.
Modify
Trade
When a derivative or position with
an existing UTI is modified due to
renegotiation of the terms of the
trade, because of the changes to the
terms of the trade agreed upfront in
the contract (except for when such
changes are already reported e.g.
notional schedule) or because
previously not available data
elements become available.
Modify
Step-in
When a derivative or position with
an existing UTI is modified due to a
step-in event.
This combination includes also a
transfer of a derivative at trade or
position level from one CCP to
another.
Modify
PTRR
When a derivative or position with
an existing UTI is modified due to a
PTRR event.
Combination ‘Modify’-‘PTRR’ at
position level should only be
used in the case where CCP
positions are subject to PTRR
(rather than bilateral netting and
subsequent reporting at position
level).
Combination ‘Modify’-‘PTRR’
can be used in the case of
compression.

125
Table 6 - Applicability of action type – event type combinations
Action type
Event type
Applicability
Comments
Modify
Early
termination
When a derivative or position with
an existing UTI is modified due to an
early termination agreed in advance
or due to a partial termination.
In the case of an early
termination agreed in advance,
the counterparties should update
the maturity date. In the case of
partial early termination, the
counterparties should update the
notional.
Modify
Exercise
When a derivative or position, is
amended due to the exercise of an
option or swaption.
Modify
Allocation
When a derivative with an existing
UTI is partially allocated. This is
used to report the amended notional
of the existing derivative.
Modify
Credit
event
When a derivative or position with
an existing UTI is modified due to a
Credit event.
Modify
Inclusion in
position
When a position with an existing UTI
is modified because of inclusion of a
new trade.
Modify
Corporate
Event
When a derivative or position with
an existing UTI is modified due to a
corporate action on the underlying
equity.
Modify
Update
When a derivative or position that is
outstanding on the reporting start
date is updated in order to conform
with the amended reporting
requirements.
Modify
No event
type
required
When a position with an existing UTI
is modified due to more than one
type of business events that
occurred intraday.
Intraday reporting is not
mandatory for ETDs,
consequently counterparties are
allowed to report ‘Modify’ at
position level without indicating
the event type, where such
modification is a result of more
than one type of business events
that occurred intraday.
Correct
No event
type
required
When a derivative or position with
an existing UTI or the data related to
the collateral is corrected because
of an earlier submission of incorrect
information.
Terminate
Step-in
When a derivative or position with
an existing UTI is terminated due to
a step-in event. This is used for
terminating the old UTI post step-in.
Terminate
PTRR
When a derivative or position with
an existing UTI is terminated due to
a PTRR event. This is used for
Combination ‘Modify’-‘PTRR’
can be used in the case of
compression.

126
Table 6 - Applicability of action type – event type combinations
Action type
Event type
Applicability
Comments
terminating the old UTI(s) after
PTRR operation.
Terminate
Early
termination
When a derivative or position with
an existing UTI is terminated due to
an early termination (and when no
other cause/event is known as the
reason for that termination).
Terminate
Clearing
When a derivative with an existing
UTI is terminated due to a Clearing
event. This is used for terminating
alpha trades.
In the case of OTC derivatives
concluded bilaterally,
counterparties need to terminate
the previously reported bilateral
trades (with combination
‘Terminate’-‘Clearing’) and report
the new cleared trades (with
combination ‘New’-‘Clearing’).
This also includes a scenario
where existing derivatives
become eligible for clearing at a
later stage.
Terminate
Exercise
When a derivative with an existing
UTI is terminated due to an exercise
event. E.g. this is used for
terminating options/swaptions when
these are being exercised.
‘Terminate’ - ‘Exercise’ should
not be reported when the option
is exercised on the maturity date.
More generally, only
terminations that take place at a
date prior to the maturity date
should be reported.
Terminate
Allocation
When a derivative with an existing
UTI is terminated due to an
allocation event. This is used for
terminating the old UTI post
allocation.
Terminate
Credit
event
When a derivative or position with
an existing UTI is terminated due to
credit event.
This combination should be
reported when a credit event
leads to termination and
settlement of the derivatives, e.g.
single name CDS.
Terminate
Inclusion in
position
When a derivative or position with
an existing UTI is terminated due to
inclusion in a position.
A derivative at trade level that is
immediately included into a
position, should be reported with
action type ‘Position component’.
Only when a derivative is
included in the position after
being reported with action type
‘New’, it should be reported with
action type ‘Terminate’ and event
type ‘Inclusion in position’.
Terminate
Corporate
Event
When a derivative or position with
an existing UTI is terminated due to
a corporate action on the underlying
equity.

127
Table 6 - Applicability of action type – event type combinations
Action type
Event type
Applicability
Comments
Error
No event
type
required
When a derivative or position with
an existing UTI is cancelled due to
an earlier submission of incorrect
information. E.g. this is used to
cancel the UTI of a derivative or
position that should not have been
reported (e.g. it is not a derivative
transaction) or to cancel outstanding
derivatives when the counterparty
starts to benefit from an intragroup
exemption.
Revive
No event
type
required
When a derivatives or position that
has been cancelled is reinstated
due to an earlier submission of
incorrect information. E.g. this is
used to reinstate the UTI of a
derivative or position that has been
erroneously terminated.
This action type should not be
used to reopen a position that
was previously netted and
terminated. ‘Revive’ should only
be used to reopen the trades that
were terminated or cancelled by
mistake or which were cancelled
due to IGT exemption, so that the
counterparties do not need to
regenerate a new UTI. It should
not be used for other reporting
scenarios. In particular in the
case of netted position, the
counterparties need to decide if
they maintain the position open
(and report the valuation
accordingly) or they close the
position. If the counterparties
close the position and then they
enter into another derivative
contract of the same type and
want to report at position level,
they need to report a new
position with a new UTI.
Valuation
No event
type
required
When data related to the valuation
are submitted for a derivative or
position with an existing UTI.
Margin
update
No event
type
required
When data related to the collateral
are submitted for a derivative or
position with an existing UTI.
Position
component
No event
type
required
When a new derivative is concluded
and included in a position on the
same day.
124. Where a counterparty submits by mistake an incorrect event type, there is no
possibility to correct such information, as ‘Event type’ is not applicable for action
type ‘Correct’. The counterparty should ensure to submit an appropriate ‘Event type’
in the subsequent report.

128
4.6.3 Lifecycle events and use of linking IDs (Prior UTI, PTRR ID, Subsequent
position UTI)
125. Counterparties should report, where relevant, linking IDs to allow for
identification of reports pertaining to the same lifecycle events. The linking IDs
envisaged for that purpose are following:
a. ‘Prior UTI’ (field 2.3)
b. ‘Subsequent position UTI’ (field 2.4)
c. ‘PTRR ID’ (field 2.5)
126. Prior UTI should be used in the case of those life cycle events where a single
derivative is terminated and one or more new derivatives are created. In such cases
the prior UTI, i.e. the UTI of the derivative that was terminated, should be populated
in field 2.3 in the reports pertaining to all the derivatives created due to the lifecycle
event. In particular, the prior UTI will be applicable in the following events:
a. Step-in;
b. Clearing (unless the derivative was concluded on a trading venue or a third-
country organised trading platform and cleared by a CCP on the same day);
c. Exercise (in the case of swaptions),
d. Allocation,
e. Corporate event (in the case of a split).
127. Subsequent position UTI should be reported when a derivative is included into
position (and reported either with action type ‘Position component’ or action type
‘Terminate’ and event type ‘Inclusion in position’). It should contain the UTI of the
position in which this derivative is included.
128. PTRR ID should be reported when the event type is ‘PTRR’ and the type of
PTRR technique is either compression with a third-party service provider or
rebalancing. The same PTRR ID, as provided by the PTRR service provider, should
be reported in all reports that are created, modified or terminated due to the same
PTRR event. Each PTRR event should be assigned a different PTRR ID.
129. It is possible to report more than one linking ID for a given derivative (e.g. a
derivative may be reported first with a prior UTI when it is cleared, then it may be
reported with a PTRR ID if it is modified due to a PTRR event and finally it may be
reported with a subsequent position UTI if in the end it is included in a position).
However, only the relevant linking ID should be reported in the report pertaining to
a given lifecycle event (in the above example, the counterparty reporting inclusion
in the position would populate in that report only the field ‘Subsequent position
UTI’).
4.7 Reporting at position level
130. In general terms, ’position’ should be understood as the exposure between a
pair of counterparties, consisting of a set of fungible derivatives (trades) with

129
economic and legal relations among them which allows for a common risk
management that results in a net or reduced volume of the joint exposure. Trade
and transaction are used interchangeably in this section.
131. Following Article 3 of the RTS on reporting, it is possible to report post-trade
events at position level following the initial reporting of the details of a derivative
concluded at transaction level and the termination of that derivative due to its
inclusion in a position, provided that the following conditions are met: the legal
arrangement is such that the risk is at position level, all trade reports made to the
TR relate to products that are fungible with each other and the individual trades
previously reported to the TR have been subsequently replaced by the position
report (e.g. as in the case of trades between a clearing member and a CCP).
132. The categories of derivatives eligible for reporting at position level are: ETDs,
centrally cleared OTC derivatives netted by CCPs and Contracts For Difference
(CFDs). Although in the case of such derivatives the information concerning
positions is most relevant for the assessment of systemic risk, reporting only at
position level is not in line with EMIR requirements under Article 9 of EMIR, which
requires all counterparties to report e.g. conclusion of a derivative at transaction
level.
133. Contracts with no maturity date, such as CFDs, are strongly recommended to
be reported at position level in order to avoid that each individual outstanding
derivative for a financial counterparty needs to receive daily valuation updates until
either 1) the derivative is cancelled or 2) infinity, because these derivatives
generally have no maturity. The valuation can be provided at position level once
the corresponding derivative transactions are included in a position.
134. ESMA acknowledges the potential difficulties in agreeing bilaterally the level of
reporting between counterparties and the impact of such problems on the
reconciliation. Nevertheless, ESMA reiterates that the reporting at position level
should be agreed between the two counterparties as this obligation stems from the
requirement of Article 9(1e) of EMIR to ensure that the details of the derivative
contracts are reported correctly and without duplication. This is also stated in the
Article 3 of the RTS on reporting. The two counterparties to a derivative should
either both include the derivative in a position or both continue to report the relevant
lifecycle events at trade level. Reporting at position level is generally an option,
rather than a requirement and is feasible only when all the relevant conditions are
met, including when the two counterparties agree on reporting at position level. In
the absence of agreement between the counterparties, reporting at trade level is a
default way forward. However, in certain circumstances, the only possible option to
comply with EMIR reporting obligations is reporting at position level (e.g. when the
counterparties are not able to value the individual position components). Even in
these circumstances, agreement between the counterparties involved is a
necessary condition.
135. Intraday reporting at position level is not required for any type of derivatives,
neither for ETD nor for OTC, i.e. there is no need to report lifecycle events (e.g.:
modifications) of a position intraday. But, in order to report correctly a position and
to reflect all the modifications which affect it (also when a trade is included in a

130
position level report on the same day), the updated details and valuation of the
position should be reported by the counterparties at position level at the end of the
day. This is in line with the clarifications developed in the sections 4.6 and 4.9, such
as the one on the possibility of reporting the event type as “blank” when there are
multiple events impacting the same position on a given day in order to simplify the
reporting. At trade level, intraday reporting of lifecycle events for ETD trades is not
mandatory. For OTC trades the reporting of intraday lifecycle events should be as
comprehensive as feasible as of the end of the day.
136. When a position is created, a report with action type ‘New’ and the proper event
type should be reported. Modifications of a position because of inclusion or
termination of trades, etc. should be reported with action type ‘Modify’ and, to the
extent feasible, the adequate event type. A position ends when its maturity date is
reached. If the termination of a position is due to other reasons, an action type
’Terminate’ and the event type which describes the reason for that termination
should be reported by the counterparties. Further details are provided in the section
4.6.
137. Taking into account that it is not allowed to report only positions without
previously reporting the original derivatives at trade level, such derivatives at trade
level should be updated to have an appropriate status so that it is clear that they
are no longer open and to avoid double-counting of the trades that were included
into positions. Consequently, the counterparties should report the terminations of
all the derivatives at trade level that enter into the position. It should be done using
the action type ‘Terminate’ and the event type ’Inclusion in position’ or the action
type ‘Position component’ with no event type required, this latter when reporting a
new trade that is included in the position on the same day. In addition, the field
‘Level’ should be reported as ‘T’ (trade). In this manner, all the trades which have
been included in a position are no longer considered to be outstanding. Then, the
position should be reported using the action type ‘New’ if the position is created for
the first time or action type ‘Modify’ in the case of an update to an existing position.
The field ‘Level’ should be reported as ’P’ (position) for any reporting of the position.
138. When counterparty reports at position level, any subsequent updates,
modifications and life cycle events (including revaluations) should be applied by the
TRs to the report of the derivative position and not to the reports of the original
trades.
139. All the data elements that are required in trade reports are mandatory as well in
position reporting, with the exception of those that are relevant only at trade level.
140. The field ’Notional‘ should be always populated in reports made at position level.
Furthermore, the value of Notional at position level reports should be calculated as
follows:
a. For options: Notional = Total notional quantity x Strike price;
b. For futures: Notional = Total notional quantity x settlement price
38
.
38
Settlement price is not a reportable field

131
141. Reporting of modifications in the field ‘Notional’ at position level should take
place only if an event relevant for the position has taken place (e.g. a new relevant
trade has been included in the position, this new notional value should be taken
into account in the notional of the position). Further details are provided in section
4.17 of these Guidelines.
142. In the case where a position valuation becomes zero, there are only two
possible ways to proceed:
a. Termination of the position and reporting of a new one using a different UTI at
a later stage. No valuations are reported between the termination of the first
position and the creation of the latter.
b. Maintaining the position open and reporting a zero contract value on a daily
basis.
143. The ‘effective date’ is the date as of which the obligations under the derivative
come into effect, as included in the confirmation of the derivative or otherwise
agreed between the counterparties. Where the counterparties did not specify the
effective date as part of the terms of the contract, field ‘Effective date’ should be
populated with the date of execution of the derivative. At position level, the Effective
date should be represented by the effective date of the trade which has the earliest
effective date. If the counterparties did not specify the effective date of the position
as part of the terms of the contract, field ‘Effective date’ at position level should be
populated with the effective date of the derivative trade which has the earliest
effective date or the date part of the execution timestamp (this execution date would
be the earliest execution date of the position) in the case that counterparties did not
specify the effective date of the contract.
144. The ‘expiration date’ is the date as of which obligations under the derivative stop
being effective, as included in the confirmation of the derivative or otherwise agreed
between the counterparties. Early termination does not affect this data element.
Expiration date, at position level, should be the furthest expiration date in the future
among the trades that are included in the position. If there is a subsequent
modification of this expiration date, because this possibility was originally contained
in the contract of this trade, a modification report should be sent, modifying the
‘Expiration date’ field accordingly to reflect the updated expiration date at position
level.
145. The ’early termination date’ is the date on which there is a termination of the
derivative that occurs prior to its maturity due to e.g. a decision of a counterparty or
counterparties. Regarding position level reporting, an action type ‘Terminate’ and
event type ”Early Termination” should be populated when the entire position is
terminated.
146. The ’reporting timestamp’ is the date and time of the submission of a given
derivative report to the trade repository. It applies in the same way to the reports at
position level.
147. The ’execution timestamp’ is the date and time when a derivative (at trade or
position level) was opened for the first time and its UTI was created. In the case of

132
position-level reporting, that field should be populated in a similar manner as the
field ’Effective date’, i.e. with the date of the trade that has the earliest execution
timestamp.
148. The ’event date’ is defined as the date when a given event took place or when
a modification became ’effective‘ (rather than the date of agreement to modify the
derivative). At position level, this field should be populated when relevant events or
modifications relating to the position took place. Further details are provided in the
section 4.9.
149. The ’clearing timestamp’ is the date and time when a trade or position is cleared.
At position level, this field should be reported using the execution timestamp of the
position as the two timestamps are expected to be equal for positions.
150. At position level, the ‘Venue of execution’ field, should be populated with the
MIC code (defined by ISO 10383) of the venue where the highest number of
derivatives that are included in the reported position were executed.
151. A derivative that is a result of PTRR exercise, should be reported at trade level.
152. ESMA reiterates that reporting at position level is a different business case than
reporting of PTRR events, both with different reporting rules. The below table
highlights the key differences between the two instances:
TABLE 7
4.8 Reporting of on-venue derivatives
153. The ETD contracts are derivative contracts that are subject to the rules of a
trading venue (as defined in Article 4(1)(24) of the Directive 2014/65/EU) and are
executed in compliance with those rules. For the purpose of reporting of ‘on-venue
derivatives’, account is also taken of similar trading platforms outside the EU. The
trading venue´s rules provide the execution and processing of the contract on the
trading venue and the subsequent clearing on a central counterparty clearing house
(CCP) within one business day after the execution.

133
154. In order to allow authorities to identify and analyse risk positions, the
counterparties that assume the risk once the contract has been concluded should
be clearly identifiable. Under the principal clearing model, upon clearing, the risk
lies on the clearing member (CM) vis-à-vis the CCP and on the client of the CM vis-
à-vis the CM. For this reason the following parties have EMIR reporting obligations:
a. The CCP clearing the derivative contract.
b. The clearing members of the CCP that are clearing the derivative contract.
c. The MiFID investment firms involved in the trade chain anytime they bear the
risk arising from the derivative by virtue of its contractual relationship with their
counterparties (in particular, with the clearing member).
d. Other parties that do not fall into any of the categories above and that take the
risk arising from the derivative, except when they are exempt because of their
status.
155. If one of these parties assumes more than one role (e.g. an investment firm is
also the clearing member), it should submit one report identifying all the applicable
roles in the relevant fields, it does not have to report separately for each role.
Examples:
Scenario 1: The investment firm bears the risk vis-à-vis the CM and, thus, is itself a
counterparty. In this case the following reports should be submitted:
TABLE 8
Scenario 2: The investment firm does not bear any risk vis-à-vis the clearing member as,
according to the legal arrangements, the client directly bears the risk vis-à-vis the
clearing member, once the latter accepts the contract for clearing.

134
TABLE 9
156. Where a give-up occurs from the investment firm to the clearing member within
the T+1 reporting deadline without any change in the economic terms of the original
derivative, the derivative should be reported in its post give-up state. It means that
the investment firm does not bear any risk vis-à-vis the clearing member, thus the
client bears directly the risk vis-à-vis the clearing member with whom it entered into
clearing arrangement. ESMA also reiterates that relevant events impacting
derivatives reported at trade level must be reported accordingly (e.g. allocation of
trades).
157. Partial executions should be reported separately, because parameters and
counterparties will be different.
158. The Report Tracking Number (RTN) is a unique code assigned to the execution
and common for a group of reports related to the same execution. It is a
conditionally mandatory field for action type ‘POSC’ at the trade level (required
when trade is executed on a trading venue). RTN should not be populated at
position level.
159. There is no one-to-one link between the Trading Venue Transaction
Identification Code (TVTIC) required under MiFIR and the Report Tracking number
(RTN). TVTIC is an individual transaction identification code for each transaction
resulting from the full or partial execution of an order disseminated to both the
buying and the selling parties. The RTN is a unique number assigned to the
execution and common among a group of reports related to the same execution, in
order to allow for identification of reports relating to the same execution. Due to the
fact that a systemic internaliser is not considered as a trading venue under the
Directive 2014/65/EU (MIFID II) and a RTN is generated by a trading venue, the
population of the field RTN when trades are concluded on a SI is not required.
160. The investment firms, the clearing members or the CCPs should provide to the
reporting counterparties the respective RTNs. Likewise, the reporting
counterparties should transmit the RTNs to their counterparties to allow them to
fulfil their reporting obligations.
161. The reporting of the RTN for CFD (in case they are executed on a venue and
where a group of CFDs are related to the same execution) follows the same rules
described above.
162. The Unique Trade Identifier (UTI) is a unique code of a derivative between two
counterparties. A pair of counterparties should use a specific UTI for one single
135
derivative, and not reuse that same UTI to report any other derivative under EMIR.
The same principle applies to the UTIs generated for the derivatives reported at
position level. The UTI must be identical in the reports of both counterparties
entering into a derivative. Further details about Unique Trade ID (UTI) are provided
in the section 4.11.
163. The timestamps fields should be populated as follows:
a. The execution timestamp should correspond to the time of execution on the
trading venue.
b. The clearing timestamp should be reported as the time at which the CCP has
legally taken on the clearing of the trade. When clearing takes place using the
open offer model, the clearing timestamp and the execution timestamp used are
expected to be the same. However, if clearing takes place using novation, the
two timestamps may be different.
164. Unless otherwise agreed between the parties, an investment firm is not
expected to submit any report on the value of the collateral as well as any
subsequent modification or termination of the concluded derivative contract when
the process of collateralisation takes place through direct arrangements between
the client (counterparty 1) and the clearing member.
165. At trade level and at position level, for on-venue derivatives trades, intraday
reporting of lifecycle events is not mandatory, it is optional. At trade level and at
position level, for on-venue-derivatives, all lifecycle events can be reported at the
end of the day reflecting the state of the derivative at that point.
166. Example of an on-venue derivative following the RTS on reporting: A
Portuguese credit institution A sends a modification to an on-venue position with a
Spanish investment company counterparty B, due to a corporate event occurring in
the underlying equity. The report pertains to a position of futures traded on trading
venue X on dividends on a share of a Dutch company. The position is collateralised
and settlement will be in cash.
167. Not all the required fields have been included.
TABLE 10 REPORTING OF AN ON-VENUE DERIVATIVE
No
Field
Example
Table 1
1
Reporting timestamp
2021-12-02T09:35:00Z
2
Report submitting entity ID
LEI A
3
Entity responsible for
reporting
LEI A
4
Counterparty 1 (Reporting
counterparty)
LEI A

136
5
Nature of the counterparty 1
F
6
Corporate sector of the
counterparty 1
CDTI
7
Clearing threshold of
counterparty 1
TRUE
8
Counterparty 2 identifier
type
TRUE
9
Counterparty 2
LEI B
11
Nature of the counterparty 2
F
12
Corporate sector of the
counterparty 2
INVF
14
Reporting obligation of the
counterparty 2
FALSE
16
Clearing member
LEI A
17
Direction
BYER
20
Directly linked to
commercial activity or
treasury financing
FALSE
Table 2
1
UTI
ABCDE24680TTTTT22222
7
ISIN
DE000C5XXXXX
9
Product classification
FFVCSX
10
Contract type
FUTR
11
Asset class
EQUI
13
Underlying identification
type
I
14
Underlying identification
NL001154XXXX
19
Settlement currency 1
EUR

137
21
Valuation amount
205.100,00
22
Valuation currency
EUR
23
Valuation timestamp
2021-12-02T00:59:00Z
24
Valuation method
CCPV
26
Collateral portfolio indicator
TRUE
27
Collateral portfolio code
1814145_1145_BSC040XXXX
30
Clearing obligation
UKWN
31
Cleared
Y
32
Clearing timestamp
2021-12-01T00:59:00Z
33
Central counterparty
CCP LEI
37
Intragroup
FALSE
38
PTRR
FALSE
41
Venue of execution
MIC X
42
Execution timestamp
2021-12-01T00:30:00Z
43
Effective date
2021-11-30
44
Expiration date
2021-12-17
47
Delivery type
CASH
48
Price
0,42
49
Price currency
EUR
55
Notional amount of leg 1
1554000
56
Notional currency 1
EUR
60
Total notional quantity of leg
1
3700000
151
Action type
MODI
152
Event type
Corporate Event

138
153
Event date
2021-12-02
154
Level
PSTN
4.9 Timely reporting of conclusion, modification and termination of
a derivative
168. Article 9(1) of EMIR provides that ”Counterparties and CCPs shall ensure that
the details of any derivative contract they have concluded and of any modification
or termination of the contract are reported (…) to a trade repository (…)”.
Furthermore, the relevant details should be reported “no later than the working day
following the conclusion, modification or termination of the contract.
4.9.1 Conclusion of a derivative
169. Each conclusion of a derivative should be reported to a TR. If a derivative that
is concluded is subsequently terminated, then the counterparties or ERR, as
applicable, after reporting it with action type ‘New’ should report it with action type
‘Terminate’.
170. Counterparties should report the conclusion of a derivative even if the
termination of that derivative occurs before the reporting deadline (e.g. for intraday
derivatives). In such case the counterparty should send, within the same reporting
deadline, two reports: one with action type ‘New’ and one with action type
‘Terminate’. If the derivative is terminated on the same day due to inclusion in a
position, the counterparty should send only one report for that derivative, with action
type ‘Position component’.
171. If the original derivative was included in a position and thus reported with the
action type ‘Position Component’, and is subsequently terminated, the
counterparties should not send a report with action type ‘Terminate’ for the original
derivative, however the counterparties should send a report with action type
‘Modification’ for the position in which the original derivative was included in order
to remove this derivative from the position.
172. Action type ‘Error’ should only be used to cancel the derivatives that never came
into existence or that are out of the scope of the reporting obligation under EMIR.
Therefore, in the specific scenario where the counterparties agree to conclude a
derivative which is conditional upon registration with the CCP and the CCP rejects
that derivative, the counterparties should terminate the derivative with action type
’Error‘ because the agreed condition for the contract to take place was not fulfilled,
therefore the derivative never came into existence.

139
4.9.2 Modification or correction of a derivative
173. A modification to a derivative comprises the reporting of the following action
types: ’Modify‘ and ’Correct‘. The timeline for reporting is the same as for the
conclusion of a derivative, meaning that from the point in time when a modification
is effective, it becomes reportable.
174. Counterparties should report only the modifications that have taken place, i.e.
they should not report modifications that were agreed but will become effective in
the future. To give an example, if the counterparties agree to amend the notional
on a future date, this amendment should be reported only once the agreed date
(the effective date of amendment) is reached.
175. With respect to correction, these should be reported as soon as the incorrectly
reported data is identified.
176. It is not necessary to send a correction report if, following a modification of a
derivative, a counterparty has introduced incorrect information only in its own
internal systems but has not reported such incorrect data to the TR. In such cases
that counterparty should only send the modification report containing final, correct
data (i.e. does not have to send modification report with the incorrect data and then
correction).
4.9.3 Reporting of margin and valuation updates
177. In the case of valuation updates, the counterparties should send daily valuations
by the end of the working day following the date of the valuation and populating the
date of valuation date in the field ’Event date‘. It should be equal to the date part of
the field ‘Valuation timestamp’.
178. Margin updates should be sent daily and counterparties should populate the
field ‘Event date’ with the date for which the margin update is reported (i.e. margin
update report should reflect the state of margins at the end of that day). Margin
updates should be reported when they become effective, i.e. on the expected
settlement date, and they should include any margin that is in transit and pending
settlement, without considering temporary settlement failures.
179. In the specific case of margins pre-paid to a CCP in advance of a portfolio of
cleared trades, these should be reported on T+1 of the conclusion of the first
applicable derivative in the related portfolio (linked by a portfolio code), rather than
on the day following the date on which the collateral was lodged.
180. More generally, no margins should be reported if no derivative covered by those
margins was previously reported.
4.9.4 Termination of a derivative
181. Counterparties should not send a report with action type ’Terminate‘, when a
derivative reaches its maturity date and therefore is no longer outstanding. Once

140
the maturity date is reached, the derivative will be automatically treated as non-
outstanding.
182. If the counterparties agree to terminate a derivative prior to the maturity date or
to terminate the open term derivative, they should either:
a. Submit a report with action type ’Terminate‘ where the agreed termination date
is for the same day as the notice of termination, or
b. Submit a report with action type ’Modify‘ where the agreed termination date is
the following day or later. In this case, the counterparties should modify the
maturity date accordingly.
183. The counterparties should not send a report with action type ’Terminate‘ if the
termination date falls on the maturity date. This includes e.g. when a counterparty
exercises an option on the maturity date.
184. In a case of a netted position, counterparties may either decide to keep it open
and report valuation on a daily basis or to terminate such position (and report with
action type ‘New’ and new UTI in case it needs to be reopened). Both counterparties
should report consistently. This aspect is covered in more detail in the section 4.7.
Event date
185. Table 11 specifies what should be reported in the field ’Event date’ for each
action type. The event date, by definition, also indicates what is a trigger for
reporting, e.g. the valuation date in the case of valuation updates. The actual
reports should be submitted by the end of the working day following the event date.
Table 11
Action type
Event date
New
Date of conclusion of the derivative or date
of creation of a position
Modify
Effective date of modification
Correct
Date from which the correction should apply
(typically the date for which previous
incorrect data was reported)
Terminate
Date on which termination becomes
effective
Error
Date of reporting of Error
Revive
Date of reporting of Revive
Valuation
Valuation date

141
Table 11
Action type
Event date
Position
component
Date of conclusion of the derivative and of
its inclusion in the position
Margin update
Expected settlement date of the margin
186. In the case where, future dated early termination is agreed, the modification
should be reported by the end of the working day following the date of the
agreement. Such modification report should contain the agreement date as the
‘Event date’ and the agreed, future date populated in the ‘Expiration date’ field.
187. Event date must be taken into account by the TRs for the purpose of
constructing the Trade State Report of a derivative. More details in this regard are
included in the section 7.1.
4.10 Mapping business events to action types and levels
188. ESMA provides below a mapping between business events and the
corresponding action types and event types the counterparties should use in
connection with the respective events.
189. Table 12 contains a column ‘Reportable?’ which provides clarifications on the
reportability of each event. As a general rule, however, counterparties should report
any new trades that fall under the reporting scope and any modification that affects
the reported details.
190. Some of the business events (e.g. the default of other counterparty) might differ
from a general case presented in the table. Hence, actual sequence of the
reportable events might in some cases differ from the given examples and should
always reflect the real-world events as closely as possible.
191. When reporting early termination events (due to e.g. full termination or early
exercise of the derivative contract), counterparties should choose the reportable
action type based on the effective date of the event. If the agreed termination date
is for the same day as notice of termination, counterparties should use the
‘Terminate’ action type. If the agreed event takes place in the future, counterparties
should use ‘Modify’ action type and update the maturity date to reflect the agreed-
upon termination date.

142
Table 12
Category
Business
Event
Detail
Reporta
ble?
Action type
Event
type
Comment
Amendm
ents and
Cancellati
ons
Amendment
(i.e.
Correction)
Amending details
that were
originally input
incorrectly
Yes, if
affects
reported
details
Correct
Economicall
y Immaterial
Amendment
Yes, if
affects
reported
details
Modify
Trade
Economicall
y Material
Amendment
Yes, if
affects
reported
details
Modify
Trade
Cancellation
Trade booked in
error and
subsequently
cancelled.
Yes
Error
Cancellation
reported by
mistake
Trade has been
cancelled by
mistake and
needs to be
revived
Yes
Revive
Trade
events
New Trade
Yes
New
Trade
Increase
A bilaterally
executed
agreement to
increase the
notional on the
transaction
Yes
Modify
Trade
Full
Termination
Full Unwind
Yes
Terminate/M
odify
Early
terminati
on
Partial
Termination
Partial Unwind
Yes
Modify
Early
terminati
on

143
Table 12
Category
Business
Event
Detail
Reporta
ble?
Action type
Event
type
Comment
Allocation
Original
Unallocated
"Block" Trade
allocated to
principal parties.
Yes
Terminate/M
odify
Allocatio
n
Modify
applicable
for partial
allocations
Subsequent
allocated trades
Yes
New
Allocatio
n
Cleared
Positions/Tr
ades
Original Bilateral
Trade (the "alpha"
trade)
Yes
Terminate
Clearing
Cleared Position
("beta" and
"gamma" trades)
Yes
New
Clearing
Full
Novation
Remaining party
Yes
Terminate+
New
Step-in
Trade with
original
counterparty
is
terminated
Step in
Yes
New
Step-in
Step out
Yes
Terminate
Step-in
Partial
Novation
Remaining party
Yes
Modify+New
Step-in
Step in
Yes
New
Step-in
Step out
Yes
Modify
Step-in
Option
Exercise
Full Exercise
Only if
exercise
takes
place
before
original
expiratio
n
Terminate/M
odify
Exercise
Partial Exercise
Only if
exercise
takes
place
before
Modify
Exercise

144
Table 12
Category
Business
Event
Detail
Reporta
ble?
Action type
Event
type
Comment
original
expiratio
n
Give-
up/Take-up
Remaining party
Only if
the event
takes
place
later than
the
reporting
deadline
(T+1)
Modify
Step-in
Step in
New
Step in
Step out
Terminate
Step in
Position
Transfer
Remaining party
Only if
the event
takes
place
later than
the
reporting
deadline
(T+1)
Modify
Step in
Step in
New
Step in
Step out
Terminate
Step in
Swaption
Exercise
Exercise of a
Swaption
Only if
exercise
takes
place
before
original
expiratio
n
Terminate
Exercise
Resulting Swap
from the exercise
of a Swaption.
Yes
New
Exercise
Compressio
n Event
Original Trade -
Terminated
Yes
Terminate
PTRR
Original Trade -
Amendment
Yes
Modify
PTRR
New resultant
trade
Yes
New
PTRR

145
Table 12
Category
Business
Event
Detail
Reporta
ble?
Action type
Event
type
Comment
Cash
Settlement
The actual cash
settlement of fees,
payments, etc
No
Unwind fees
are reported
in the
termination
message
Maturity of
Contract
Derivative
contract expiring
on the original
maturity date
No
Contract is
automaticall
y updated to
non-
outstanding
state by the
TR
Cascade
Breakdown of a
position into a
more granular
level: the initial
position in, e.g. a
yearly contract
Yes
Terminate
Trade
Resulting
positions in, e.g.
quarterly contracts
Yes
New
Trade
Split
Dividing a trade
and allocating it to
multiple positions
Yes
Terminate
Allocatio
n
Creating/amendin
g the impacted
positions
Yes
New/Modify
Allocatio
n
Intrinsic
changes
Amortizing
Notionals
Changes to the
notional during the
course of a trade.
No (the
amortizin
g
schedule
is already
reported
at the
conclusio
n of the
trade)

146
Table 12
Category
Business
Event
Detail
Reporta
ble?
Action type
Event
type
Comment
Dividend
Resets
No
Equity
Resets
No
Rate Resets
Changes to the
floating rate of a
trade
No
Other
Successor
Events
The other
counterparty is
succeded
LEI
change of
counterp
arty due
to
corporate
events is
covered
in section
4.14
The reference
entity specified in
the transaction is
succeeded by
another entity.
Yes
Modify
Corporat
e Event
Credit
Events
Default on a
transaction e.g.
bankruptcy/restru
cturing/ obligation
default of the other
counterparty.
Yes
Modify/Term
inate
Trade/E
arly
Termina
tion
The exact
sequence of
reportable
events will
depend on
details of
each
bankruptcy
process
Default, e.g.
bankruptcy/restru
cturing/ obligation
default of a
reference entity.
Yes
Modify/Term
inate
Credit
Event
Action type
depends on
the result of
event (trade
is
terminated
or, e.g. index
factor needs
147
Table 12
Category
Business
Event
Detail
Reporta
ble?
Action type
Event
type
Comment
to be
updated)
Corporate
Actions
Bonus
Issue/Capitalisatio
n issue
Yes, if the
reported
underlyin
g
identifier
(e.g. ISIN
or LEI) or
other
trade
terms
change
Modify
Corporat
e Event
Assuming
the
corporate
action takes
place in the
underlying
instrument/i
ssuer
Special Dividend
Modify
Corporat
e Event
Spin-Off
Modify
Corporat
e Event
Stock
Split/Change in
nominal value
Modify
Corporat
e Event
Reverse Stock
split/Change in
nominal value
Modify
Corporat
e Event
Other corporate
actions affecting
reported details
Modify
Corporat
e Event
Conversion
s
Parties mutually
agreeing and
consenting to a
conversion which
results in a
material
amendment.
Example would be
swap on an ADR
that is converted
to swap on the
underlying stock
as agreed by both
parties, or a stock
is dual listed and
is converted from
a GBP line to a HK
line as agreed by
both parties.
Yes
Modify
Trade

148
Table 12
Category
Business
Event
Detail
Reporta
ble?
Action type
Event
type
Comment
Publicly
Traded /
Listed Swap
Index
Swap is
removed/changed
in the index by the
administrator of
the index (i.e. not
at the discretion of
the dealer or
counterparty).
Example would be
quarterly roll for
index CDS. Would
not include
rebalancing of the
index
No, if the
underlyin
g
identifier
or other
trade
terms do
not
change
Triggering
of fallback
rates
Change in floating
rate due to
fallback event
Yes
Modify
Trade
Customized
Basket
Index Swap
Constituents of
the basket are
changed at the
discretion of the
dealer or
counterparty.
Example would be
rebalancing the
basket by closing
a swap on an old
ticker and booking
that swap on a
new ticker.
Yes
Modify
Trade
Only the
financial
instruments
traded on a
trading
venue
Portfolio
Swap
Addition of
Reference
Underlyer to
Long
Portfolio or
Short
Portfolio
Creation of a new
swap contract on
Security XYZ.
Yes
New
Trade
Assuming
the portfolio
components
are reported
as individual
swaps
(potentially

149
Table 12
Category
Business
Event
Detail
Reporta
ble?
Action type
Event
type
Comment
Removal of
Reference
Underlyer
from Long
Portfolio or
Short
Portfolio
Partial or full
termination of
existing swap
contract on
Security XYZ.
Yes
Terminate/M
odify
Early
terminati
on
part of a
complex
trade)
Increase in
Notional
Amount for
Existing
Reference
Underlyer
Increasing long or
short exposure to
Security XYZ.
Yes
Modify
Trade
Decrease in
Notional
Amount for
Existing
Reference
Underlyer
Decreasing long
or short exposure
to Security XYZ in
a portfolio swap
wrapper.
Yes
Modify
Trade
4.11 UTI generation
192. Timely generation and communication of the UTI is crucial to ensure that
counterparties can comply in a timely manner with their reporting obligation. Where
one of the counterparties is responsible for the generation of the UTI, both
counterparties should make the necessary arrangements in order for the generating
counterparty, to timely generate the UTI, use it in its own reporting and
communicate it to the other counterparty, and for the receiving counterparty, to
ingest the UTI and use the same UTI (without alteration or truncation) in its own
reporting. As a best practice, the manual intervention in the process of sharing the
UTI should be avoided and digital means should be favoured.
193. The 10:00 am deadline for UTI generation and communication applies to all
derivatives, including the derivatives reported at position level. In case the
generating party fails to generate or communicate the UTI in due time, which is
10:00 am UTC on T+1, in order to meet the reporting deadline, the receiving party
should contact the generating party and enquire about the process instead of
reporting using an UTI generated on its own.

150
194. The below flowchart illustrates how the counterparties should determine the
entity responsible for the UTI generation in accordance with the Article 7 of the ITS
on reporting.

151
Yes
If the transaction is concluded
between FC and NFC, FC is responsible.
If concluded between NFC+ and NFC-,
NFC+ is responsible (end).
Yes
UTI generation pursuant to the to
rules of the jurisdiction with the
sooner reporting deadline (end).
Agreed entity is responsible (end).
Confirmation platform is responsible (end).
Yes
No

152
195. If the entity responsible for the generation of the UTI (e.g. a third-country venue
or a confirmation platform) is not subject to EMIR and is not able/willing to generate
the UTI, the parties should follow the next step in the UTI-generation waterfall. If
the final step of the waterfall assigns the responsibility to the other counterparty that
is not an EU counterparty and that counterparty does not provide the UTI, the
reporting counterparty should generate an UTI on its own in order to meet the
reporting deadline. However, if the non-EU counterparty provides the UTI late and
the EU counterparty has already reported with its own UTI, the EU counterparty
should Error the reported derivative and rereport with the UTI generated in line with
the ITS on reporting.
196. When the process leads to the ‘counterparty agreement’ step, the
counterparties may decide e.g. that always one of them will be generating the UTI
or may decide to apply other commonly agreed rules, including a tie-breaker logic
of their choice. The chosen logic should be straightforward enough to ensure clear
determination of the counterparty responsible for the UTI generation in all cases.
197. The solution of last resort determines the UTI generating entity by sorting the
LEI identifiers in reversed order. For this purpose, the counterparties should use
the ASCII sorting method, where a digit always precedes a letter:
Table 13
Example 1
Example 2
LEI
CP1:
1111ABCDEABCDEABC123
CP2:
1111AAAAABBBBBCCC23
CP1:
ABCDEABCDEABCDE12345
CP2:
ABCDEABCDEAAAAA12344
LEI in the
reversed order
321CBAEDCBAEDCBA1111
32CCCBBBBBAAAAA1111
54321EDCBAEDCBAEDCBA
44321AAAAAEDCBAEDCBA
Sorted on a
character-by-
character basis, a
digit comes
always before a
letter (ASCII
order)
321CBAEDCBAEDCBA1111
because "1" (digit) comes
before "C" (letter)
44321AAAAAEDCBAEDCBA
because "4" comes before "5"
198. The actual generation of the UTI can be delegated, meaning that any entity
determined as entity responsible for the UTI generation in line with the ITS on
reporting, can delegate the generation of the UTI to a third party. It must ensure

153
however that the third party complies with all the relevant requirements with regards
to the timeliness of the UTI generation, the structure and format of the UTI etc.
4.12 Determining counterparty side
199. Article 4 of the ITS on reporting provides that the counterparty side to the
derivative contract shall be determined at the time of the conclusion of the derivative
on the basis of the type of contract concluded.
200. Based on the above, counterparties should determine the counterparty side at
the time of the conclusion of the derivative and report either Buyer/Seller in field
‘Direction’ or Payer/Receiver in fields ‘Direction of Leg 1’ and ‘Direction of Leg 2’
depending on the type of the derivative concluded, as provided in the table below.
201. Counterparties, once determined the counterparty side, should report the fields
related to ‘Direction’, ‘Direction of Leg 1’ and ‘Direction of Leg 2’ with the opposite
values.
202. This means that in case where the two counterparties concluded a contract
which requires the population of the field ‘Direction’, if the counterparty 1 reports
Buyer in field ‘Direction’, the other counterparty to the contract should report Seller
and vice versa.
203. Similarly, assuming that counterparties should agree on the consistent way of
reporting of the respective legs of the derivative, in case where the two
counterparties concluded a contract which requires the population of the fields
‘Direction of Leg 1’ and ‘Direction of Leg 2’, if the counterparty 1 reports
Payer/Receiver in field ‘Direction of Leg 1’ and Receiver/Payer in field ‘Direction of
Leg 2’, the other counterparty to the contract should report Receiver/Payer in field
‘Direction of Leg 1’ and Payer/Receiver in field ‘Direction of Leg 2’. Please refer to
the section 7.2.4 for more detailed discussion concerning the reporting and
reconciliation of derivatives with two legs.
204. It is also expected that the counterparty which reports Payer in field ‘Direction
of Leg 1’ should report Receiver in field ‘Direction of Leg 2’ and vice versa.
Table 14 Use of Direction fields per product type
Type of contract
Direction
Direction of leg 1
Direction of leg 2
Option
Buyer/Seller
-
-
Swaption
Buyer/Seller
-
-
154
Table 14 Use of Direction fields per product type
Type of contract
Direction
Direction of leg 1
Direction of leg 2
Currency Forward
-
Payer/Receiver
Receiver/Payer
Currency Swap
-
Payer/Receiver
Receiver/Payer
Forward
Buyer/Seller
Non-Deliverable Forward (NDF)
-
Payer/Receiver
Receiver/Payer
Future
Buyer/Seller
CFD
Buyer/Seller
Spreadbet
Buyer/Seller
Dividends Swap
Buyer/Seller
Securities Swap
Payer/Receiver
Receiver/Payer
Interest Rate Swap
Payer/Receiver
Receiver/Payer
Inflation indices Swap
Payer/Receiver
Receiver/Payer
Cross-currency Swap
Payer/Receiver
Receiver/Payer
Instrument for the transfer of
credit risk (except options and
swaptions)
Buyer/Seller
Commodities Swap
Payer/Receiver
Receiver/Payer
Forward Rate Agreement
Payer/Receiver
Receiver/Payer
Derivatives related to variance,
volatility and correlation
Buyer/Seller
205. In relation to the action types ’Valuation’ and ’Margin Update’ the fields
‘Direction’, ‘Direction of Leg 1’ and ‘Direction of Leg 2’ do not have to be reported.
206. When a position is the result of netting of the position to 0, the field ‘Direction’
could be reportable as either Buyer/Seller, Seller/Buyer and the fields ‘Direction of
Leg 1’ and ‘Direction of Leg 2’ could be reportable as either Payer/Receiver,
Receiver/Payer since for the purpose of reconciliation these fields should not be
reconciled in this case. Please refer to the section 7.2.4 for more details concerning
the reporting and reconciliation of fields ‘Direction’, ‘Direction of leg 1’ and ‘Direction
of leg 2’ when positions are netted to zero.

155
4.13 Identification of counterparties
207. Article 3 of the ITS on reporting provides that the counterparty 1 to a derivative
and the entity responsible for reporting shall ensure for the purpose of reporting the
conclusion or modification of a derivative that the reference data related to its ISO
17442 LEI code is renewed in accordance with the terms of any of the accredited
Local Operating Units of the Global LEI System.
208. Furthermore, according to the Article 3 of the ITS on reporting, the ISO 17442
Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) code should be used to identify a broking entity, a CCP,
a clearing member, a counterparty which is a legal entity, a report submitting entity,
an entity responsible for reporting, and a post-trade risk reduction service provider.
209. Article 9(5) of EMIR provides that at least the identities of the parties to the
derivative contracts should be reported. This requirement cannot be waived.
Therefore, a counterparty dealing with counterparties that cannot be identified
because of legal, regulatory or contractual impediments, would not be deemed
compliant with Article 9(5) of EMIR.
210. It should be noted that the counterparties reporting under EMIR should always
identify themselves with the LEI of the headquarters, given that the legal
responsibility for reporting always lies on the legal entity and not on the branch.
211. In order to reduce reporting issues due to lapsed LEI, the LEI code of the
counterparty 1 and the entity responsible for reporting should be, for the purpose
of reporting any new derivative or any modification, duly renewed and maintained
according to the terms of any of the endorsed LOUs (Local Operating Units) of the
Global Legal Entity Identifier System.
212. Entities other than the counterparty 1 and the entity responsible for reporting
could be reported with a lapsed LEI in accordance with the validation rules.
213. When populated, the LEI of counterparty 2, RSE, broking entity, CCP, Clearing
Member and PTRR service provider should be included in the GLEIF database
maintained by the Central Operating Unit, i.e. should be a valid LEI.
214. The point in time relevant for the validation of the LEI status is the date of
reporting, as specified in the validation rules.
215. The field ’Country of the counterparty 2‘ should be populated only when the field
’Counterparty 2 identifier type‘ is ‘False’, i.e. refers to natural persons not acting in
business capacity and should refer to the code of the country of residence of that
person.
216. Fields ‘Corporate sector of the counterparty 1‘ and ’Corporate sector of the
counterparty 2‘ should be populated with the sector of the counterparty itself and
should not refer to the sector of its branch.
217. In case the counterparty 2 to the derivative contract is a natural person not
acting in business capacity, a client code should be used. Client codes should be
reported only when the field ’Counterparty 2 identifier type‘ is populated with ’False’.

156
218. If the counterparty 2 is subject to the reporting obligation under EMIR, the field
’Reporting obligation of the counterparty 2‘ should be populated with ‘True’ since
the indicator of the reporting obligation is independent from the allocation of
responsibility for reporting and from any delegation arrangement.
219. It should be noted that the field ’Reporting obligation of the counterparty 2‘
should be populated with ‘False’ when counterparty 2 to the derivative contract is a
natural person not acting in business capacity, a non-EU counterparty, a non-EU
CCP, an entity referred in Article 1(4) of EMIR (BIS, Central Banks, etc).
Table 15
Counterparty 2
Reporting obligation
of the counterparty 2
EU FC/NFC/CCP
TRUE
NON EU FC/NFC/CCP
FALSE
NATURAL PERSON NOT ACTING IN
BUSINESS CAPACITY
FALSE
ENTITIES IN ART. 1(4) OF EMIR (BIS,
CENTRAL BANKS, etc)
FALSE
ENTITIES IN ART. 1(5) OF EMIR
(MULTILATERAL DEVELOPMENT
BANKS, ESM,ESF, etc)
TRUE
220. Client codes should be reported as ’LEI of Counterparty 1 + Internal Identifier of
Individuals‘, where such internal identifier should be unique at the level of the given
reporting counterparty (counterparty 1), i.e. the client it is not expected to have one
single internal identifier across all entities it trades with. Furthermore, the internal
identifier adopted for the identifications of individuals should not contain information
referred to as personal data (irrespective of its sensitivity).
221. The LEI component of the client code should not be updated when the reporting
counterparty (to which the LEI pertains) undergoes the corporate event.
222. Furthermore, in case of corporate events, where the affected counterparties
have the same individual as a client and the internal identifier associated with that
individual is different between the involved parties, after the merger the reporting
counterparty should identify that individual with one of the previously used internal
identifiers in order to ensure the traceability. In particular for newly concluded
derivatives only one of the client codes should be consistently used, the one starting
with the LEI of the reporting counterparty after the merger. Reportable lifecycle
events for derivatives outstanding at the time of the merger should be reported with
the client codes which were used before the corporate event for those derivatives.
TABLE 16 REPORTING OF CLIENT CODES IN CASE OF A CORPORATE EVENT

157
Before the
merger
Reporting
timestamp
Reporting
Counterparty
Other
Counterparty
Trade ID
Action type
T
LEIAAAA
LEIAAAA123
xyz
Modification
T
LEIBBBB
LEIBBBB456
qwe
Modification
LEIBBBB merges into LEIAAAA at T+1
After the
merger
Reporting
timestamp
Reporting
Counterparty
Other
Counterparty
Trade ID
Action type
T+2
LEIAAAA
LEIAAAA123
xyz
Modification
T+2
LEIAAAA
LEIBBBB456
qwe
Modification
T+2
LEIAAAA
LEIAAAA123
jkl
New
4.14 Procedure when a counterparty undergoes a corporate action
223. Article 8 of the ITS on reporting stipulates that when a counterparty undergoes
a corporate action resulting in the change of its LEI, that counterparty or the ERR
or the entity to which reporting was delegated should notify the relevant TR of the
change and request update of the LEI. Furthermore, Article 2 of the RTS on data
quality provides that the TR to which the request is addressed shall identify the
derivatives outstanding at the time of the corporate restructuring event where the
entity is reported with the old identifier in the field ‘Counterparty 1 (Reporting
counterparty)’ or in the field ‘Counterparty 2’ as informed in the relevant request
and shall replace the old identifier with the new LEI in the reports relating to all
those derivatives pertaining to that counterparty at the time of the corporate event.
224. Article 2 of the RTS on data quality also provides the procedure and the timeline
to be followed by trade repositories in order to properly finalize the update of the
LEIs for all the derivatives pertaining to the counterparty submitting the request
under Article 8 of the ITS on reporting.
225. The LEI update should occur on the date of the corporate restructuring event. If
the request to update the LEI due to a corporate event is received by the TR later
than 30 days prior to the corporate event, the TR should perform the update as
soon as possible and no later than 30 calendar days from receiving the request.
226. To ensure the timely communication between the entity involved in the update
and its TR, the counterparty affected by the change should provide all the
necessary information on the merger to its TR no later than 30 calendar days prior
to the corporate event date.
227. In case the affected counterparty is a third country entity, the EU counterparty
or entity responsible for reporting or the entity to which the EU reporting
counterparty delegated the reporting should be responsible for communicating the
change to the TR.
228. In addition, when a counterparty is not responsible and legally liable for
reporting, the entity responsible for reporting is responsible for communicating the

158
change to the TR. In case of delegation, the responsibility for communicating the
change to the TR should belong to the report submitting entity.
229. It should be noted that where the affected counterparty does not have any
contractual relationship with the TR, it should inform the report submitting entity or
the entity responsible for reporting. Anyway, the responsibility for informing the TR
can be specified by the relevant parties in a delegation act.
230. Furthermore, in order to ensure a proper communication process between TRs,
the TR to which a request for update of a LEI is addressed should inform other TRs
about a new LEI update execution not later than 3 weeks prior to the corporate
event date.
231. To ensure a timely communication process between TRs and their clients, TRs
should inform their clients about a new LEI update execution no later than 2 weeks
prior to the corporate event date.
232. When the TR is broadcasting to its clients information about a corporate event,
a reporting counterparty that has no contractual relationship with the TR should be
informed of such event without undue delay by the entity responsible for reporting
or the report submitting entity, as applicable.
233. Entities involved in the update are expected to provide all the necessary
information to their LOUs in order to ensure a proper and timely update of LEI in
GLEIF database.
234. If the request was received later than thirty calendar days prior to the corporate
event, the TR should update the LEI of all derivatives that were outstanding at the
time the corporate event took place and between the corporate event date and the
date TR performs the update. Therefore, also terminated/expired derivatives
between the two dates should be updated.
235. If the affected entities are reported in fields other than ‘Counterparty 1 (reporting
counterparty’, ’Counterparty 2’ or the ‘Entity responsible for reporting’ of the
derivative (for example the entity affected by the change is the entity reported in
‘Broker ID’ or ‘Clearing member’ fields), these entities should provide to TRs either
the list of UTIs affected by the change or, in case they do not possess this
information, all the necessary details so that TRs are able to identify the impacted

159
derivatives. In this case, the TRs should perform such an update only following a
confirmation of the impacted records by the counterparty 1 or the entity responsible
for reporting, as applicable. Where the counterparty 1 or the entity responsible for
reporting does not reply in due time for the performance of the update, the update
of the relevant details of these derivatives could be performed by submitting the
relevant reports with action type ‘MODI’.
236. In case the corporate event affects only a subset of derivatives (e.g. spin offs),
TRs should put in place common procedures for updating LEI data on those
derivatives contracts that could be affected by partial changes of the LEIs. The
responsibility for indicating which UTIs are affected by the change should remain
with the counterparties or entities responsible for reporting. Both
counterparties/ERRs are expected to communicate the change to their TRs.
237. Trades with the old LEI errored or terminated by mistake that are actually
outstanding at the time of the corporate event should be necessarily “revived”
before (or at the time of) the corporate event. In case the counterparty or the ERR,
as applicable, realizes after the corporate event that a derivative with the old LEI
terminated/errored by mistake has not been revived before (or at the time of) the
corporate event, the counterparty should report that derivative with a new UTI. In
turn the other counterparty should terminate its derivative and re-report it with the
newly generated UTI. This latter scenario should occur only as a last resort option
considering that counterparties affected by a corporate event should carefully
assess the perimeter of outstanding derivatives before the corporate event occurs.
238. TRs should produce any information about the update of the LEI, as specified
in paragraph 3 (b) of Article 2 of RTS on data quality, in machine readable format
in order to favour a timely and automatic process of LEI update by the stakeholders
(TRs, reporting counterparties, report submitting entities, entities responsible for
reporting).
239. The procedure provided in Article 2 of the RTS on data quality and the timelines
provided above should be followed also with reference to the scenario of update
from BIC or other identifiers to LEI.
4.15 Identification and classification of products
General clarifications
240. As specified in the ITS on reporting, the derivatives that are (i) admitted to
trading or traded on a trading venue or (ii) are traded on a systematic internaliser
and their underlying is admitted to trading or traded on a trading venue or is an
index or basket composed of instruments traded on a trading venue; should be
identified in field 2.7 using an ISO 6166 International Securities Identification
Number (ISIN) code. The remaining derivatives should be identified in field 2.8
using an ISO 4914 Unique Product Identifier (UPI) code. In the specific case of
derivatives traded on exchange in a third country, the identification of the product
is not required if both ISIN and UPI are not available. In this way the relevant
derivative products can be uniquely identified, while the counterparties are required

160
to provide only one way of identification for a given product and consistency with
MiFIR reporting requirements is retained.
241. Additionally, the counterparties should classify all derivatives using the ISO
10692 Classification of Financial Instrument (CFI) code (field 2.9). Counterparties
should always use official sources for the CFI. For this purpose, the CFI assigned
by ANNA Derivatives Service Bureau (ANNA DSB) or the relevant National
Numbering Agency (NNA) should be used. Further information can be obtained
from ANNA DSB (https://www.anna-dsb.com/ufaqs/cfi-code/), from ANNA
(http://www.annaweb.org/standards/about-identification-standards/), or from the
relevant NNA of the derivative.
242. Counterparties should report only valid CFIs. In the case of derivatives identified
with a UPI, the CFI is expected to be always available. For the other derivatives, if
the CFI does not exist in the official sources, the counterparties should request it to
the relevant NNA.
Identification of FX swaps
243. If the counterparties enter into an FX swap (regardless of how the product has
been subsequently confirmed or settled), they should report it in a single report and
identify the product with the UPI or ISIN pertaining to that FX swap. It should be
noted that the UPI technical guidance explicitly envisages FX swaps as a separate
product, thus there is no reason why FX swap would need to be decomposed into
FX forwards for the purpose of reporting.
UPI reference data
244. ESMA is of the view that majority or all UPI reference data fields should not be
required to be reported for the products identified with UPI, once the UPI system is
fully in place and both authorities and markets participants gain more experience
with the use of UPI. Additionally, similar consideration applies to the products
identified with ISIN for which reference data are available in the Financial
Instruments Reference Data System (FIRDS). While all reportable data elements
will be required at the beginning of reporting, ESMA is already considering which
data elements could be collected from the UPI reference data library or FIRDS
instead of being reported to the TRs.
245. Once the validation rules are amended at a later stage to make some or all such
fields conditionally mandatory, the counterparties should follow the validation rules
and not report these fields for derivatives identified with a UPI/ISIN.
4.16 Identification of underlying
246. The underlying should be identified by using a unique identification for this
underlying based on its type. Fields 2.13-2.18 describe the underlying, and the field
‘Underlying identification type’ in particular indicates that the underlying is either a
basket, index or asset identified with an ISIN.

161
247. In the case of derivatives on indices, the counterparties should report the ISIN
of the underlying index, if available, rather than the ISIN of the derivative. In
addition, under the RTS on reporting the counterparties should report the
standardised code indicating the index (if available) as well as the name of the index
which should always be populated.
248. In the case of credit derivatives, field ‘Underlying identification’ should be
reported in case of Credit Default Swap (CDS) based on specific reference
obligation. For CDS hedging against the default of an entity, such entity should be
reported in the ‘Reference entity’ field.
4.17 Price, notional and quantity fields
Reporting of the price
249. When reporting derivative contracts, in accordance with Article 6(2) of the RTS
on reporting, counterparties should utilise field 2.48 ‘Price’ only when price
information is not included in another field of the report.
250. According to Article 6(1) of the RTS on reporting, counterparties should
populate field 2.48 when reporting the following derivative types:
a. swaps with periodic payments relating to commodities (fixed price to be
populated in field 2.48);
b. forwards relating to commodities or equities (forward price of the underlying to
be populated in field 2.48);
c. swaps relating to equities, or contracts for difference (initial price of the
underlying to be populated in field 2.48).
251. The list in Article 6(1) of the RTS on reporting is not exhaustive. When there are
derivatives where the price is not specified in another field, ‘Price’ field should be
populated. Examples of such derivatives include futures relating to commodities or
equities, where forward price of the underlying is to be reported in the ‘Price’ field.
252. However, field 2.48 is not applicable and should not be populated when
reporting one of the following derivative types:
a. Interest rate swaps and forward rate agreements, as it is understood that the
information included in fields ‘Fixed rate of leg 1’/’Fixed rate of leg 2’ and
‘Spread of leg 1’/’Spread of leg 2’ should be interpreted as the price of the
derivative.
b. Interest rate options and interest rate swaptions, as it is understood that the
information included in fields ‘Strike price’ and ‘Option premium amount’ should
be interpreted as the price of the derivative.

162
c. Commodity basis swaps, as it is understood that the information included in field
‘Spread of leg 1’/’Spread of leg 2’
39
should be interpreted as the price of the
derivative.
d. Foreign exchange swaps, forwards and options, as it is understood that the
information included in fields ‘Exchange rate 1’, ‘Forward exchange rate’, ‘Strike
price’, and ‘Option premium amount’ should be interpreted as the price of the
derivative.
e. Equity options, as it is understood that the information included in the fields
‘Strike price’ and ‘Option premium amount’ should be interpreted as the price of
the derivative.
f. Credit default swaps and credit total return swaps, as it is understood that the
information included in fields ‘Fixed rate of leg 1’/’Fixed rate of leg 2’, ‘Spread
of leg 1’/’Spread of leg 2’ and ‘Other payment amount’ (when field ‘Other
payment type’ is populated with ‘UFRO’) should be interpreted as the price of
the derivative.
g. Commodity options, as it is understood that the information included in fields
‘Strike price’ and ‘Option premium amount’ should be interpreted as the price of
the derivative.
253. If the derivative contract has price which varies by a schedule throughout the
life of the derivative (and the price information is not reported in another data field),
fields 2.50-2.52 should be populated in order to report the price schedule for the
whole lifecycle.
254. Examples of the reporting of price for different products (either by specifying it
in the dedicated field or through other data fields) can be found in section 6.
Reporting of notional and quantity
255. Notional amount fields (fields 2.55 and 2.64) should be populated in accordance
with Article 5 of the RTS on reporting. Fields 2.57 to 2.59 and 2.66 to 2.68 are
repeatable and should be populated in the case of derivatives involving notional
amount schedules. The notional amount schedule, if applicable, should also be
populated in accordance with Article 5 of the RTS on reporting.
256. When reporting the notional amount schedule, counterparties should indicate:
a. the unadjusted date on which the associated notional amount becomes
effective;
b. the unadjusted end date of the notional amount; and
c. the notional amount which becomes effective on the associated unadjusted
effective date.
39
Even though the Spread fields are in the Interest Rate section of the table of fields, they should be populated when applicable
(according to field descriptions in the RTS). Same approach should be followed when reporting e.g. the spread and fixed rate of
CDS.

163
257. In the case of derivatives involving notional amount schedules, the ‘end-date’ is
not required if the end date is back-to-back with the effective date of the subsequent
period.
258. In the case of derivatives involving notional amount schedules, the notional
amount input in field 2.55 (‘Notional amount of leg 1’), should be input in the notional
amount schedule fields. The same applies for the field ‘notional amount of leg 2’, if
applicable.
259. When reporting a notional amount schedule, the date schedules are to be
reported in chronological order.
260. Any updates to the notional amount that are not linked to an agreed upfront
notional schedule, should be reported as a modification.
261. In the case where a position is netted (the notional becomes zero) there are two
possible ways to proceed:
a. The position can be terminated. If the position is reopened it should be reported
with a new UTI.
b. Counterparties can maintain the open position and report a zero contract value
on a daily basis. If new trades are then incorporated into this position the
notional, and other relevant fields, should be updated accordingly.
262. It has been observed that zero notional is sometimes reported e.g. in the case
of voluntary right issues given to the holder of a CFD or in the case of CFDs
resulting from a corporate action on the underlying (stock split), thus having a
purchase price of zero. This is not considered a correct way of reporting.
263. With regards to the population of Notional at position level please refer to the
clarification provided in the section 4.7.
264. With regards to the notional amount for credit index derivatives following a
change in the index factor due to credit events, the counterparties should - to avoid
double counting of the adjustment - not modify the notional but rather only update
the field 2.147 ‘Index factor’.
265. When reporting non-standard commodity derivatives where the notional is not
known when the contract is executed the following approach should be taken:
report an estimate notional amount, which is periodically reviewed when the
transaction is in delivery. If the notional becomes known during the lifetime of the
derivative contract a modification should be submitted amending the notional
amount.
266. To further elaborate on paragraph above, it is important that the counterparties
to these non-standard commodity derivatives agree on the approach to calculating
the notional in order that the reported notional is consistent. For example, the
notional reported is based on a production forecast. Counterparties also need to
agree when to update the notional to ensure consistency in the updated notional
amounts.
Total notional quantity fields

164
267. Total notional quantity should be understood as the aggregate notional quantity
of the underlying asset for the term of the derivative. Where the total notional
quantity is not known when a new derivative is reported and therefore is reported
with a default value, the total notional quantity should be updated as it becomes
available.
268. Total notional quantity applies to ETDs more generally. This field is relevant for
equities and commodities. If applicable, it should also be populated for the other
asset classes. Fields 2.61 to 2.63 and 2.70 to 2.72 are repeatable and shall be
populated in the case of derivatives involving notional quantity schedules.
269. In the case of derivatives involving notional quantity schedules, the total notional
quantity input in field 2.60 (‘Total notional quantity of leg 1’), will also need to be
input in the notional quantity schedule fields. The same applies for the field ‘Total
notional quantity of leg 2’, if applicable.
270. In the case of derivatives involving notional quantity schedules, the ‘end-date’
is not required if the end date is back-to-back with the effective date of the
subsequent period.
271. When reporting a notional quantity schedule, the date schedules are to be
reported in chronological order.
4.18 Reporting of valuations
272. Please refer to section 7.2.3 for further guidance on the reconciliation of the
valuation data.
Valuation of the contract
273. Article 4 of the RTS on reporting provides that the counterparties should report
valuation as follows:
a. For cleared derivatives - the valuation of the derivative provided by the CCP.
This does not mean that the report should be made by the CCP. The CCP
should make data available to counterparties so that the latter report. The use
of CCP valuation data does not mean duplication of reporting.
b. For uncleared derivatives - the valuation of the derivative performed in
accordance with the methodology defined in International Financial Reporting
Standard 13 Fair Value Measurement as adopted by the Union and referred to
in the Annex to Commission Regulation (EC) No 1126/2008, without applying
any adjustment to the fair value. This means that the counterparties should not
apply for the purpose of reporting under EMIR any valuation adjustments (such
as CVA or DVA), even if such adjustments are applied for the accounting
purposes.
274. When counterparties delegate reporting, including valuations, they retain
responsibility for ensuring that reports submitted on their behalf are accurate. In the
case of allocation of responsibility for reporting under Article 9(1a)-9(1d) of EMIR,

165
the entity responsible for reporting is responsible for the accuracy of the valuation
submitted on behalf of the reporting counterparty.
275. The counterparties should report the actual valuation of the contract (positive or
negative), rather than an absolute value. Typically, the valuation of the contract will
be positive for one counterparty and negative for the other. It should be noted that
under the technical standards valuation will form part of the reconcilable data,
therefore counterparties need to send consistent valuation (i.e. the absolute value
of the valuation should reconcile, while the signs will be opposite).
276. In general, the mark to market value should represent the total value of the
contract, rather than a daily change in the valuation of the contract. However,
where under the Settle-to-Market (STM) model the valuation is reset to zero on a
daily basis and the variation margin is settled, counterparties and CCPs should
report the daily change in the valuation.
277. It should also be noted that it is not permissible to report zero valuation of the
contract exclusively on the grounds that there is no market risk because a variation
margin has been exchanged. Any margin paid or received would be reflected in the
fields 3.12-3.27 and not in the valuation.
278. The valuation requirements apply to CCPs as well as other reporting
counterparties. Pursuant to the Article 4(4) of the draft RTS on reporting, clearing
members are required to follow CCP valuation. This does not imply however that
CCP’s can set deviating standards - CCPs should comply with the requirements
set out in the ITS and RTS on reporting and follow the guidance provided in the
Guidelines or in the Q&As.
279. For some contracts the valuation changes infrequently and may not change
from one day to another. However, data quality would not benefit from making
exceptions and it would be hard to distinguish the cases of stable valuation from
underreporting of the valuations, therefore the counterparties should report
valuations on a daily basis also for these contracts (in line with the Article 2 of the
ITS on reporting). The requirement to report valuation on a daily basis applies also
when the valuation is zero, irrespective of the model used.
280. The first valuation of a given derivative should be reported by the end of the day
following the conclusion of the derivative (reporting deadline), either in the original
report with action type ‘New’ or in a separate report with action type ‘Valuation’.
281. It is not necessary to report valuation on the last day of a derivative. In particular,
it is not necessary to report valuation for intraday derivatives (i.e. derivatives that
are concluded and terminated on the same day).
282. Where counterparties report packages composed of two or more derivatives,
the valuation should be reported on a per derivative basis.
Valuation method
283. The valuation method should be reported in accordance with the applied
method for determination of the valuation. This means that CCP-cleared trades
should have a valuation method indicating that the CCP’s valuation is reported. If

166
at least one valuation input is used that is classified as mark-to-model in the below
table, then the whole valuation should be classified as mark-to-model. If only inputs
are used that are classified as mark-to-market in the table below, then the whole
valuation should be classified as mark-to-market.
Table 17 - Classification of valuation inputs
Bucket
Inputs used
Valuation
method
1
Quoted prices in active markets for
identical assets or liabilities that the entity
can access at the measurement date
[IFRS 13:76]. A quoted market price in an
active market provides the most reliable
evidence of fair value and is used without
adjustment to measure fair value
whenever available, with limited
exceptions. [IFRS 13:77]
An active market is a market in which
transactions for the asset or liability take
place with sufficient frequency and
volume to provide pricing information on
an ongoing basis. [IFRS 13: Appendix A]
Mark-to-market
2
Quoted prices for similar assets or
liabilities in active markets [IFRS 13:81]
(other than quoted market prices included
within bucket 1 that are observable for the
asset or liability, either directly or
indirectly)
Mark-to-market
3
Quoted prices for identical or similar
assets or liabilities in markets that are not
active [IFRS 13:81] (other than quoted
market prices included within bucket 1
that are observable for the asset or
liability, either directly or indirectly).
Mark-to-model – historic
prices from inactive
markets should not be
directly used
4
Inputs other than quoted prices that are
observable for the asset or liability, for
example interest rates and yield curves
observable at commonly quoted intervals,
implied volatilities, credit spreads [IFRS
13:81] (other than quoted market prices
Mark-to-market

167
Table 17 - Classification of valuation inputs
Bucket
Inputs used
Valuation
method
included within bucket 1 that are
observable for the asset or liability, either
directly or indirectly)
5
Inputs that are derived principally from or
corroborated by observable market data
by correlation or other means (“market-
corroborated inputs”) [IFRS 13:81] (other
than quoted market prices included within
bucket 1 that are observable for the asset
or liability, either directly or indirectly)
Mark-to-model – the
inputs can be derived
“principally” from
observable market data,
meaning that
unobservable inputs can
be used
6
Unobservable inputs for the asset or
liability. [IFRS 13:86] Unobservable inputs
are used to measure fair value to the
extent that relevant observable inputs are
not available, thereby allowing for
situations in which there is little, if any,
market activity for the asset or liability at
the measurement date. An entity
develops unobservable inputs using the
best information available in the
circumstances, which might include the
entity’s own data, taking into account all
information about market participant
assumptions that is reasonably available.
[IFRS 13:87-89]
Mark-to-model –
unobservable inputs are
used
Delta
284. Counterparties should report the delta of an option or swaption derivative, at
trade or position level, in field 2.25. The reportable value is the ratio of absolute
change in price (or value) of a derivative to the change in price (or value) of the
underlying. Reported delta should be unadjusted, i.e. the reported value should not
contain adjustments pertaining to e.g. counterparty credit risk.
285. CCPs, financial counterparties and non-financial counterparties referred to in
Article 10 of EMIR should use the ‘Valuation update’ messages to report the delta
value as it stands at the end of each day. In practice this means that only those
counterparties that are required to send valuation updates are required to update
the delta value daily.

168
286. Counterparties other than those referred to in the paragraph above are not
required to report delta.
287. The value of delta may range from -1 to 0 for put options and 0 to 1 for call
options. Reportable delta values are ratios, which means that they don’t have a unit
(e.g. currency). In case an exotic option (such as a binary or knock-in/out option)
has a delta of less than -1 or more than 1, -1 or 1 should be reported, respectively.
288. For the specific case of swaptions, delta should be understood as the ratio
between the change in value of the swaption to the change in value of the
underlying swap.
289. For basket options, delta should not be reported.
4.19 Reporting of margins
290. The collateralisation categories need to be reported in accordance with the
Article 5 of the ITS on reporting.
291. The field ‘Collateralisation’ should be populated based on the agreement and
not on the actual collateral exchanged, i.e. if the agreement considers for a two-
way initial margin and variation margin, the field should be populated with ’FLCL’
even though the current situation might be that no initial margin nor variation margin
is exchanged.
292. The table below shows different scenarios of collateralisation and how they
should be reported using the categories.
TABLE 18 - COLLATERALISATION CATEGORIES
*UNCL – uncollateralised, PRC1 – Partially collateralised: Counterparty 1, PRC2 - Partially collateralised:
Counterparty 2, PRCL - Partially collateralised, OWC1 - One-way collateralised: Counterparty 1 only, OWC2 - One-
way collateralised: Counterparty 2 only, OWP1 – One-way/partially collateralised: Counterparty 1, OWP2 – One-
way/partially collateralised: Counterparty 2, FLCL – Fully collateralised

169
293. As specified in Article 4.2 of the RTS on reporting, collateral can be reported on
a portfolio basis. This means the reporting of each single executed derivative
should not include all the fields related to collateral, to the extent that each single
derivative is assigned to a specific portfolio and the relevant information on the
portfolio is reported on a daily basis (end-of-day).
294. The reporting counterparties, regardless of their need to report collateral, would
need to submit at least one margin report (field 3.28 ‘Action type’ populated with
‘New’), even to advise that the derivative contract is uncollateralised. Should
’UNCL’ be the latest value submitted, no further margin update is expected. For
details regarding the generation of the missing margin information report please
see the section 7.3.2.
295. It is not necessary to report margins on the last day of a derivative. In particular,
it is not necessary to report margins for intraday derivatives (i.e. derivatives that are
concluded and terminated on the same day).
296. When the Settle-to-Market model applies the mark to market exposure is settled
and reset to zero on a daily basis and the variation margin is paid without a
possibility to return. In that case, it is permissible to report zero variation margin.
Post-haircut values of margins depend on associated risk of changes in collateral
value and therefore on the nature of the collateral posted (or collected). In addition,
frequent cash settlement of margin may effectively mitigate this risk completely.
Pre- and post-haircut values need to be reported both. If the risk is mitigated
completely however, the same values are expected for pre- and post-haircut
values.
297. There is only one collateral currency field associated with a collateral type on a
report by a counterparty. Therefore, all collateral for a single portfolio collateral type
should be reported in one single currency value for the corresponding collateral
type. The reporting counterparty should report the currency that has been
contractually agreed between the counterparties. If the currency has not been
contractually agreed, the reporting counterparty is free to decide which currency
should be used as base currency as long as the base currency chosen is one of
the major currencies which represents the greatest weight in the pool and is used
consistently for the purpose of collateral reporting for a given portfolio.
298. Non-cash collateral should be reported as its current cash equivalent as
evaluated at the moment of posting/collecting the collateral.
299. The collateral reported should be just the collateral that covers the exposure
related to the reports made under EMIR. If it is impossible to distinguish within a
pool of collateral the amount which relates to derivatives reportable under EMIR
from the amount which relates to other transactions the collateral reported can be
the actual collateral posted covering a wider set of transactions.
300. The meaning of "it is impossible to distinguish" should be referred to the
framework adopted by the reporting counterparties for the calculation of margins
(and not just to the use of a common margin account). More in particular, NCAs
would expect the following approach:

170
a. if the margin model adopted by the reporting counterparty provides for offsetting
of risks between derivatives reportable under EMIR and transactions that are
not reportable under EMIR, then the reporting of common collateral amount
should be allowed;
b. if margins related to derivatives reportable under EMIR and margins related to
transactions that are not reportable under EMIR are just collected (and held)
together in a common collateral account, but are calculated separately, then
only the collateral amount related to EMIR derivatives should be reported.
301. The collateral should be reported as the total market value that has been posted
or collected by the counterparty responsible for the report. The fact that certain
types of collateral might take a couple of days to reach the other counterparty
should be ignored. Therefore, margin updates should be reported when they
become effective, i.e. on the expected settlement date and they should include any
margin that is in transit and pending settlement, without considering temporary
settlement failures.
302. Although margins data are not reconcilable fields, margins reported by the
counterparties should be consistent.
303. The RTS on reporting specifies that where the collateral related to a contract is
reported on a portfolio basis, the reporting counterparty should report to the trade
repository a code identifying the portfolio related to the reported contract. This field
should only be populated if the field ‘Collateral portfolio indicator’ has the value ‘Y’.
It is up to the reporting counterparty to determine what unique value to populate in
the field ‘Collateral portfolio code’. Therefore, different counterparties to a derivative
contract can use different collateral portfolio codes.
304. The ITS on reporting specifies that the field 3.27 ‘Collateral portfolio code’ can
have up to 52 alphanumerical characters and that special characters are not
allowed. Therefore, a collateral portfolio code that is less than 52 characters in
length is permissible provided that it meets the other criteria laid out here.
305. It is permissible to use a value in this field that is supplied by the CCP, but this
is not required and other values could be used.
306. However, NCAs would expect that portfolios reported by the two counterparties,
irrespective of the codes, cover the same collateral.
307. Excess collateral should capture only additional collateral that is posted or received
separately and independently from the initial and variation margin. If counterparties
decide to post more collateral than required and this additional collateral is not
posted separately and independently of variation margin and initial margin, both
counterparties need to include this in the initial and or variation margin reported.
308. Even though in certain circumstances no collateral is exchanged, for example
because of the existence of an agreed “Minimum Transfer Amount” (MTA), other
collateral transfer agreement or thresholds between the parties, counterparties
should report unchanged margin amount from the previous day. It could occur that
in the first day a derivative is concluded, variation margins may be zero. Therefore,
in this specific case, if the following days an MTA or other thresholds agreed

171
between the parties are not reached, variation margins should be reported as of the
previous day, i.e variation margins fields should be populated with zero.
309. In some circumstances derivatives are exempted from collateral exchange
under EMIR, most notably (1) where an NFC- is counterparty in a derivative, (2)
where a counterparty pair benefits from an intragroup exemption from collateral
exchange or (3) for certain derivatives as per RTS 2016/2251 such as (i) physically
settled foreign exchange forwards and swaps and (ii) single-stock equity options /
index options under transitional provision until 4 January 2024. In these cases,
although counterparties are not required to exchange collateral, the counterparties
are still allowed to have a collateral agreement in place and should report
accordingly to the applicable collateral agreement (i.e. ‘UNCL’ only if no collateral
agreement is in place and no collateral is exchanged).In addition, the counterparties
that are required to report collateral (i.e. CCPs, FCs and NFC+) are expected to
report the actual amount of collateral that is exchanged. Where a counterparty pair
benefits from an intragroup exemption from reporting, the counterparties should
report neither the derivatives nor the collateral.
310. Either variation margin posted or collected should be reported, not both. Please
refer to the example provided in the table and the explaining text below the table.
311. Generally, counterparties and CCPs are required to report the total value of
contract and the margins. Under the STM model, under which the variation margins
are settled on a daily basis, the counterparties and CCPs should report the daily
change in the value of the variation margin.
312. The margin reporting requirements apply to CCP’s as well as other reporting
counterparties. To ensure consistency, clearing members can follow CCP reported
margins.
TABLE 19 REPORTING OF MARGINS
Date
CP
1
CP
2
IM
posted
pre-
haircut
VM
posted
pre-
haircut
IM
posted
post-
haircut
VM
posted
post-
haircut
IM
received
pre-
haircut
VM
received
pre-
haircut
IM
received
post-
haircut
VM
received
post-
haircut
Le-
vel
Day 1
A
B
10.000.000
5.000.000
P
Day 1
B
A
10.000.000
5.000.000
P
Day 2
A
B
10.000.000
5.000.000
P
Day 2
B
A
10.000.000
5.000.000
P
Day 3
A
B
8.000.000
4.000.000
P
Day 3
B
A
8.000.000
4.000.000
P

172
Day 4
A
B
13.000.000
6.500.000
P
Day 4
B
A
13.000.000
6.500.000
P
Day 5
A
B
7.000.000
3.500.000
P
Day 5
B
A
7.000.000
3.500.000
P
Day 6
A
B
2.000.000
1.000.000
P
Day 6
B
A
2.000.000
1.000.000
P
Day 7
A
B
0
0
P
Day 7
B
A
0
0
P
313. A “VM requirement” is determined as the amount of margins owed by the
counterparty “in debt” in order to cover its exposure against the counterparty “in
credit” at the time of the valuation of the contract.
314. Moreover, it is assumed that:
a. A 50% haircut is applied to the collateral exchanged between the
counterparties.
b. The counterparty “in debt” must post to the counterparty “in credit” an amount
of collateral whose post-haircut value is equal to the “VM requirement”.
c. A Minimum Transfer Amount (MTA) of 500,000 is assumed to be in place as
threshold for collateral transfer.
d. If the difference between the “VM requirement” and the collateral posted (VM
post-haircut) is below the MTA, no collateral is exchanged between the
counterparties.
e. If the difference between the “VM requirement” and the collateral posted (VM
post-haircut) exceeds the MTA, an exchange of collateral occurs between the
counterparties.
Day 1: Due to valuation of the contract, a VM requirement of 5 million must be
posted from B to A.
B posts an amount of collateral whose post-haircut value is equal to 5 million (VM
posted/received post haircut = 5 million; VM received/posted pre-haircut = 10
million).
Day 2: The valuation of the contract results in a reduction of the VM requirement
owed by B from 5 million to 4.9 million.

173
Given that the amount A would have to return to B (to align the collateral posted
by B with the VM request) is below the MTA (5 million – 4.9 million = 100.000 <
MTA = 500.000), no exchange of margins occurs.
The Variation Margins reported are the same as of Day 1
Day 3: The valuation of the contract results in a further reduction of the VM
requirement owed by B from 4.9 million to 4 million.
The difference between the updated value of the “VM requirement” and the
collateral posted is equal to 1 million (900.000 from day 3 + 100.000 from day 2).
Given that such difference exceeds the MTA, the transfer of collateral takes place:
A returns to B a quantity of collateral whose post-haircut value is 1 million.
The updated values of VMs are reported accordingly (VM received/posted post-
haircut = 4 million; VM posted/received pre-haircut = 8 million).
Day 4: The valuation of the contract results in an increase of the VM requirement
owed by B from 4 million to 6.5 million.
Given that such a difference exceeds the MTA, the transfer of collateral takes
place: B posts additional collateral to A in order to match the new VM requirement.
The updated values of VMs posted/received are reported accordingly (VM
received/posted post-haircut value = 6.5 million; VM posted/received pre-haircut
value = 13 million)
Day 5: The valuation of the contract results in a change of the direction of the
exposure: the contract turns negative for A, which must cover a VM requirement
equal to 3.5 million.
Therefore, A returns to B the full amount of collateral previously posted by B. In
turn A posts to B additional collateral whose post-haircut value is 3.5 million. Given
that such difference exceeds the MTA, the transfer of collateral takes place.
The updated values of VMs are reported accordingly: A becomes the counterparty
posting collateral (VM posted post-haircut = 3.5 million; VM posted pre-haircut
value = 7 million) and B becomes the counterparty receiving the collateral (VM
received post-haircut = 3.5 million; VM received pre-haircut = 7 million)
Day 6: A reduces its exposure to B by partially selling the contract. Consequently,
the valuation of the contract results in a reduction of the VM requirement owed by
A from 3.5 million to 1 million.
The updated values of VMs are reported accordingly (VM posted/received post-
haircut = 1 million; VM received/posted pre-haircut = 2 million)

174
Day 7: A and B netted the position to zero and therefore exchange all outstanding
margins, reporting zero in the VM fields. If the counterparties closed the position,
they would not need to report margins on the last day of the derivative.
315. Regarding the reporting of value of the collateral for ETDs, in the particular case
when the investment firm is not involved in the process of collecting and/or posting
any collateral for the client because of the direct arrangements between the client
and the clearing member, the investment firm is not expected to submit any report
on the value of the collateral, or on any subsequent modification as well as
termination of the concluded derivative contract.
4.20 Identification of the trading venue
316. Field 2.41 ‘Venue of execution’ should be used to report the venue where the
derivative was executed, notwithstanding the qualification of the transaction as ETD
or OTC.
317. Where a derivative was concluded OTC and the respective instrument is not
admitted to trading or traded on a trading venue and no request for admission has
been made, MIC code ‘XXXX’ should be used.
318. Where a derivative was concluded OTC and the respective instrument is
admitted to trading or traded on a trading venue or a request for admission was
made, MIC code ‘XOFF’ should be used.
319. The ‘BILT’ value proposed in the CDE guidance should be used when the
reporting counterparty cannot determine whether the instrument is listed or not, as
per jurisdictional requirements. Nevertheless, this situation should not arise in the
EU since all instruments admitted to trading or traded on a trading venue are made
publicly available in the Financial Instruments Reference Data System (FIRDS) on
ESMA’s website
40
, therefore the counterparties are expected to be able to
determine whether they should report ‘XOFF’ or ‘XXXX’ and the value ‘BILT’ is not
allowed in the reporting under EMIR.
320. For derivatives contracts traded on regulated markets or third country trading
venues considered as equivalent to a regulated market, the segment MIC Code will
be required (or alternatively the operating MIC in case the segment MIC code does
not exist).
321. For derivatives contracts traded on MTFs, OTFs, SIs and organized trading
platforms outside of the Union, the segment MIC code will be required (or
alternatively the operating MIC in case the segment MIC code does not exist), even
if the derivatives concluded on these venues are OTC derivatives under the
definition set out in EMIR.
322. Transactions executed on or pursuant to the rules of venues should be
considered as on venue trading for RMs or third country venues considered as
equivalent, MTFs, OTFs, SIs and organized trading platforms outside of the Union.
40
https://registers.esma.europa.eu/publication/searchRegister?core=esma_registers_firds

175
For example, transactions such as bilaterally negotiated or pre-arranged
transactions formalised pursuant to the rules of a venue, should be reported with
the relevant platform identifier.
323. MIC codes are defined by ISO 10383. This standard identifies two sorts of MIC
code: ‘MIC’ and ‘operating MIC’, also known as ‘segment MIC’ and ‘organisation
MIC’ respectively. For EMIR reports, RMs, MTFs, OTFs and SIs should be
identified by the relevant MIC code as defined in the ESMA Register at
http://registers.esma.europa.eu/publication (segment MIC code). The other venues
should be identified using the segment MICs (or alternatively the operating MIC in
case the segment MIC code does not exist).
324. In the case where two SIs face each other, those two counterparties should
determine which of them is acting in the SI capacity for the given transaction and
report the MIC code of that counterparty as the identifier of the venue.
325. ESMA recalls that derivatives executed on UK regulated markets before Brexit
would be considered ETD. However, derivatives executed on UK regulated markets
after Brexit would be considered OTC. The field ’Venue of execution’ would still be
identified with the corresponding MIC code. However, such transactions are to be
declared as OTC and other fields like the field ’Intragroup‘ and field ’Clearing
obligation‘ are required.
4.21 Fields related to clearing
326. With respect to the field ‘Cleared’, under the ITS on reporting only two statuses
are allowed, namely cleared (‘Y) and non-cleared (‘N’).
327. In some markets a CCP extends an “open offer” to act as counterparty to market
participants and is interposed between participants at the time trades are executed
(open offer model). In other markets, the participants themselves initially are the
counterparties. Subsequently the trades may be submitted to a CCP, which is
substituted as the seller to the buyer and the buyer to the seller (novation clearing
model).
328. Article 2 of the RTS on reporting prescribes that where a derivative contract
whose details have already been reported pursuant to Article 9 EMIR is
subsequently cleared by a CCP, that contract should be reported as terminated
using the action type ’Terminate‘. The new contracts resulting from clearing should
be reported with action type ’New’.
329. The same Article also provides that where a contract is both concluded on a
trading venue and cleared on the same day by a CCP, only the contracts resulting
from clearing should be reported (novation clearing model). If the clearing does not
occur on same day, the reporting process set in previous paragraph should be
applied.
330. With regard to derivatives executed on third country venues and cleared by a
CCP on the same day, Article 2(2) from the RTS on reporting specifies that where
a derivative is both concluded on a trading venue or on an organised trading
platform located outside of the Union and cleared by a CCP on the same day, only

176
the derivatives resulting from clearing should be reported. These derivatives should
be reported by specifying in fields ‘Action type’ and ‘Event type’ either the action
type ‘New’ and event type ‘Clearing’, or the action type ‘Position component’ , in
accordance with Article 3(2).
331. Execution timestamp for cleared trades should correspond to the time of
execution on the venue of execution. The clearing timestamp should be reported
as the time at which the CCP has legally taken on the clearing of the trade. For
markets where clearing takes place using the open offer model, execution
timestamp and clearing timestamp are expected to be the same. For markets where
clearing takes place using novation, these two timestamps may be different.
332. The field ‘Clearing obligation’ is not applicable to the derivatives executed on a
regulated market or a third-country equivalent market and it should be left blank. In
the case of cleared trades, this field should be populated with ‘UKWN’ and the field
‘Cleared’ with ‘Y’.
333. The field ‘Central counterparty’ should only be populated with the identifier of a
CCP, i.e. a central counterparty which meets the definition of Article 2(1) of EMIR.
Therefore, when a derivative contract is cleared by an entity which is not a CCP
within the meaning of EMIR, the clearing house should not be identified in the field
‘Central counterparty’.
334. When a derivative is executed in an anonymised market and cleared by a
clearing house, the counterparty executing the derivative should request the trading
venue or the clearing house that matches the counterparties to disclose the identity
of the other counterparty before the reporting deadline.
4.22 Fields related to confirmation
335. Date and time of confirmation, as determined pursuant to Article 12 of the RTS
on clearing arrangements constitute the ‘Confirmation timestamp‘ that should be
reported in the field 2.28, confirmation means should be reported in the field 2.29
’Confirmed’.
336. The timely confirmation requirement applies only to non-cleared OTC contracts
(confirmation timestamp and confirmation means should not be reported for ETDs
nor for cleared OTC derivatives). It applies wherever a new derivative contract is
concluded, including as a result of novation and portfolio compression of previously
concluded contracts. The requirement does not apply to terminations provided that
the termination removes all residual obligations in respect of that derivative. The
fields ’Confirmed’ and ’Confirmation timestamp’ should be updated and reported
accordingly to the extent that they are required for a given trade.
337. For the field ’Confirmed’, the value ‘NCNF’ (unconfirmed) should be used when
the derivative has to be confirmed by the counterparties but has not been confirmed
yet.
338. In other cases, the counterparties should report the ‘ECNF’ or ‘YCNF’ value for
this field depending on the confirmation means used (electronic or non-electronic)

177
and the field ’Confirmation timestamp‘ should be populated. If the value ‘NCNF’ is
used, the field ’Confirmation timestamp‘ should be left blank.
339. In the case of trades executed on third-country venues that are not equivalent
to regulated market, those trades are considered OTC under certain provisions of
EMIR. This means that fields ’Confirmation timestamp’ and ’Confirmed’ have to be
reported to the extent that these trades are not cleared. In the case of derivatives
concluded on venue (not cleared) for which the trading supposes the acceptance
of transaction terms between parties, if the OTC derivative is automatically
documented and agreed upon, it should be regarded as electronically confirmed
(field ’Confirmed’ populated with ’ECNF’). On the contrary, if the OTC derivative
needs further documentation to be agreed upon, it should be regarded as non-
confirmed (field ’Confirmed’ populated with ‘NCNF‘).
4.23 Fields related to settlement
340. The ‘Settlement currency‘ field should be populated for all single currency cash-
settled derivatives, as well as those with a specific FX component. The field should
not be populated in the case of a physically settled derivative. The ’Settlement
currency‘ field should be specified for each leg of the multicurrency products.
341. An example on the way to report the settlement currency for the two legs of an
FX swap has been included in the section 5.4.
342. Counterparties should report the valid currencies as per ISO 4217 standard.
Currencies which are not covered by ISO standard won't be accepted, therefore
the counterparties should report the relevant values in the respective onshore
currencies recognized in the ISO standard.
4.24 Reporting of regular payments
343. Counterparties should report only those fields related to data elements of
regular payments that are applicable to a given derivative. Therefore, taking into
consideration the contract type, the report will contain information on dedicated
fields specific for each fixed or floating leg of a derivative. The same rule applies to
the data elements describing the reset frequency and reference period of the
floating rates.
344. For each leg of a derivative with periodic payments, the fixed rate has to be
reported, where applicable, by specifying positive or negative values expressed as
percentages (e.g. 2.57 instead of 2.57%).
345. In the case of floating legs, the periodic payments are calculated based on an
underlying reference rate on predefined dates. Floating rates should be identified,
where available, with an ISIN and/or with a 4-letter standardized code, explicitly
included in the ITS on reporting.
346. Furthermore, the floating rates should be always identified by using the official
name of the rate as assigned by the index provider.

178
347. There are no expectations to transform the value of the payment frequency
period into another payment frequency period. For example, in the case of yearly
payments, counterparties should report a payment frequency of 1 year, rather than
12 months or 365 days.
4.25 Reporting of other payments
348. The option premium payment is not included as another payment type, as
premiums for option are reported using the option premium dedicated data element.
349. Novation fees are not included in the RTS on reporting as derivatives-related
cash flows between entities that are not regularly scheduled. Therefore, novation
fees are also not reportable as other payments.
350. The allowable values for other payment types are:
a. UFRO = Upfront payment, i.e. the initial payment made by one of the
counterparties either to bring a transaction to fair value or for any other reason
that may be the cause of an off-market transaction;
b. UWIN = Unwind or Full termination, i.e the final settlement payment made when
a transaction is unwound prior to its end date; payments that may result due to
full termination of derivative transaction(s);
c. PEXH = Principal exchange, i.e. exchange of notional values for cross-currency
swaps.
351. The information provided in other payment fields is only to be reported for the
reportable event to which the payment relates and once the payment details have
been reported, the values should not persist in the reports of all subsequent events
reported by the counterparty for that trade.
352. Therefore, if a derivative involves both upfront and unwind payment, the
counterparty should report the sequence of payments in subsequent reports, as
follows:
Table 20
Action type
Event type
Other payment type
New
Trade
UFRO
Terminate
Early termination
UWIN
353. Data elements pertaining to the ’other payments‘ can be reported multiple times,
for multiple payments.
354. In the case of the exchange of notional values for cross-currency swaps, the
information related to the payments should be reported at the same time as the
derivative contract is reported for the first time, through the ‘NEWT’ report.

179
4.26 Dates and timestamps fields
Effective date
355. Effective date is the date at which obligations under the derivative come into
effect, as included in the confirmation. If the counterparties did not specify the
effective date as part of the terms of the contract, field ‘Effective date’ should be
populated with the date of execution of the derivative.
356. This also applies to cash-settled commodity derivatives as well as in the case
of novations.
357. Execution timestamp should reflect the date and time when the derivative was
originally executed. It should therefore not be changed when counterparties report
lifecycle events (e.g. partial termination) for a given derivative.
Expiration date / early termination date
358. The expiration date is the unadjusted date at which obligations under the
derivative stop being effective, as included in the confirmation. Early termination
does not affect this data element. The expiration date can be used to determine
whether the trade is outstanding or not. The content of this field in case of non-
confirmed trades should be as specified in the contract between the counterparties.
359. This applies to both OTC and ETD derivatives.
360. Under Article 9 of EMIR there is a duty to report the termination. However, where
termination takes place in accordance with the original terms of the contract, it can
be assumed that such a termination was originally reported, provided that the
expiration date has been duly reported. Therefore, only terminations that take place
at a different date should be reported.
361. The definition of field 2.44 ‘Expiration date’ in the RTS on reporting specifies
that early terminations of a derivative are not reflected in this field. Accordingly,
when an opening of a new contract occurs, the ‘Expiration date’ field represents the
original date of expiry of the reported contract. However, when the maturity date of
an existing contract is subject to changes which are already foreseen in the original
contract specifications, counterparties send a modification report to the initial entry,
modifying the ‘Expiration date’ field accordingly to reflect the updated expiration
date.
362. The counterparties should report the unadjusted expiration date, as agreed in
the contract, even if it falls on a weekend or a bank holiday.
363. The below example clarifies how to populate field ‘Expiration date’ for an OTC
Fixed for Floating derivative on natural gas with following characteristics:
a. Trade date: 25-Aug-2017Commodity: Natural Gas
b. Effective date: 01-Nov-2017
c. Termination date: 31-Mar-2018

180
d. Payment dates: Ten business days after the end of each calculation period
subject to
e. adjustment in accordance with the Modified Following Business Day
Convention.
The correct expiration date would be 31/03/2018 as this is the agreed termination date.
364. The following paragraphs clarify how a ’working day‘ should be understood for
the purpose of determining the deadline for reporting.
365. Counterparties should follow their local time to determine the day on which the
derivative was concluded, modified or terminated. The deadline for reporting is the
end of the working day following that day. The determination of the deadline for
reporting in the local time does not affect the way in which the relevant dates and
times (such as execution timestamp) are reported to the TRs. The time convention
for reporting is defined in the ITS on reporting.
366. The counterparties should follow the relevant calendar of their Member State to
determine whether a given day is a working day or holiday.
367. This guidance applies also when the two counterparties to the same derivative
follow different calendars and/or are located in different timezones, meaning that
each counterparty should follow its own local calendar and use the local time to
determine the deadline for reporting.
4.27 Reporting of derivatives on crypto-assets
368. Having taken into consideration the ongoing developments in regulation that are
currently being discussed about the crypto-assets, the RTS on reporting do not
stipulate any detailed requirements with regard to the reporting of derivatives based
on them. Notwithstanding, ESMA has decided to include in the RTS on reporting
an additional field named ’Derivative based on crypto-assets‘ in which
counterparties would be expected to indicate whether a given derivative is based
on a crypto-asset or not. The field is a simple indicator populated with a boolean
value. This will allow to assess the trading volumes and outstanding risk in this type
of instruments as well as to analyse how these instruments are currently reported.
369. Only derivatives on crypto-assets that fulfil the definition of derivatives under
MiFID are expected to be reported (in line with the general scope of reporting under
EMIR).
370. The currency fields in EMIR reporting only allow to be populated with currencies
listed on ISO 4217 Currency Codes. Therefore these fields currently should not be
populated with codes relating to crypto-assets that are commonly denominated
“crypto-currencies”.
371. ESMA may develop further guidance on such derivatives based on crypto-
assets once the relevant regulations have been approved.

181
4.28 Reporting of complex products
372. In accordance with the CPMI-IOSCO CDE Guidance the RTS on reporting
introduced new package-related fields. This includes field 2.6 ’Package identifier’,
which should, on the one hand, be used by reporting counterparties or entities
responsible for reporting as a unique link between reports belonging to the same
derivative contract, where the table of fields does not allow to submit the details in
only one report and, on the other hand, where the package transaction is composed
of a combination of derivative contracts that are negotiated together as the product
of a single economic agreement (see also recital 3 and 4 of the RTS on reporting).
373. While there is a requirement for both counterparties to agree on the number of
reports to be submitted for a given contract or package transaction and on the UTI’s
assigned to those reports, there is no need to agree on the identifier between the
two counterparties. The ’Package identifier‘ will be unique for a set of reports
belonging together and assigned by each reporting counterparty or entity
responsible for reporting on their own. For this reason there is no need to consume
a package identifier from trading venues or the other counterparty.
374. Table 21 illustrates the reporting of UTIs and package identifiers in the case of
package transactions:
Table 21
Report #1
CP 1
Report #2 CP 1
Report #1 CP
2
Report #2 CP
2
Counterparty 1
LEI of CP 1
LEI of CP 1
LEI of CP 2
LEI of CP 2
Counterparty 2
LEI of CP 2
LEI of CP 2
LEI of CP 1
LEI of CP 1
UTI
1234
ABCD
1234
ABCD
Package ID
PCK1
PCK1
Package987
Package987
375. In the case a package transaction includes reportable and non-reportable
contracts, only the contracts that are in scope of Article 9 of EMIR need to be
reported. For example a combination of an FX Spot contract and FX Forward (which
is not executed as an FX swap), only the FX Forward would be in scope of Article
9 of EMIR and therefore reportable. Nevertheless the fields related to the entire
package (e.g. ’Package transaction price’) need to be populated to provide
regulators a holistic view on the package transaction executed.
376. If a derivative contract ceases to exist, but gives birth to another derivative
contract, which is materially different (e.g. an option on a future), those two
contracts should be considered individually and not be reported as a package
transaction, thus no package identifier should be used to link those reports in such

182
circumstance, while at the same time the field ’Prior UTI‘ would be relevant and
would need to be reported.
377. The reporting field 2.53 ’Package transaction price‘ and field 2.54 ’Package
transaction price currency‘ should be populated with the relevant price and currency
for the entire package transaction rather than the price and currency of the
individual components. If the individual components have individual prices and
currencies those should be populated in the relevant report in field 2.28 ’Price‘ and
field 2.29 ’Price currency‘ in addition to the population of the field ‘Package
transaction price’.
Table 22
Report #1
CP 1
Report #2 CP 1
Report #1 CP
2
Report #2 CP
2
Counterparty 1
LEI of CP 1
LEI of CP 1
LEI of CP 2
LEI of CP 2
Counterparty 2
LEI of CP 2
LEI of CP 2
LEI of CP 1
LEI of CP 1
UTI
1234
ABCD
1234
ABCD
Package ID
PCK1
PCK1
Package987
Package987
Price
10.23
210.75
10.23
210.75
Price currency
EUR
EUR
EUR
EUR
Package
transaction
price
220.98
220.98
220.98
220.98
Package
transaction
price currency
EUR
EUR
EUR
EUR
378. There can be instances where a price for the package transaction becomes
available only after the reporting deadline (T+1). If such instance occurs the
package transaction price should be reported with the defined default value, as
specified in the validation rules, and should be updated accordingly once it
becomes available by using ‘MODI’ in field 2.151 ‘Action type’. Until
379. In the case that the price for an entire package transaction is expressed as a
spread, i.e. the difference between two reference prices, such spread should be
populated in field 2.112 ‘Package transaction spread’ together with field 2.113
‘Package transaction spread currency’. If such spread is not known at the point in

183
time of conclusion of the package transaction it should be reported with the default
specified in the validation rules and be updated later when it becomes known. Again
this update should be sent by using ‘MODI in field 2.151 ‘Action type’.
4.29 Ensuring data quality by counterparties
380. According to the Article 9(1e) of EMIR, counterparties and CCPs should report
correctly and without duplication. Quality of data reported by counterparties is a key
aspect to ensure wide usability and quality of data analytical results. Further
requirements for ensuring the data quality on the counterparty side are set out in
Article 9 of the ITS on reporting and Article 1 and 3 of the RTS on data quality.
381. To ensure compliance with the requirement to report correctly, to ensure the
consistency of data, as well as to achieve the reduction of reporting burden and
alignment of incentives with the entity’s own priorities, counterparties should use
the regulatory data for their own internal risk and compliance management
processes.
382. Apart from implementing a common set of validation rules providing an
immediate response on the quality of data at the point of data submission, TRs
should implement a reconciliation process consisting in paring and matching of the
reports pertaining to both sides of the derivative to compare the content of the
reports and flag the inconsistencies indicating misreporting by at least one of the
counterparties. TRs should provide detailed information on rejections and
reconciliation to the relevant participants and users of the TR and also to NCAs.
Reporting counterparties, report submitting entities and entities responsible for
reporting, as applicable, should investigate the data quality issues flagged by
reports’ rejections and unsuccessful reconciliation, and ensure data correction. The
ITS on reporting also specifically requires the entities responsible for reporting and
the report submitting entities, as applicable, to have in place arrangements which
ensure that the feedback on the reconciliation failures provided by the TRs is taken
into account.
383. With regards to historical records the counterparties and ERRs are expected to
back report all identified omitted data and correct all data misreported to the TRs.
384. To complement the rejection and reconciliation statistics provided by the TRs to
NCAs, the entity responsible for reporting should promptly (as soon as it becomes
aware of them) notify its competent authority and, if different, also the competent
authority of the reporting counterparty of any of the following instances:
a. any misreporting caused by flaws in the reporting systems that would affect a
significant number of reports,
b. any reporting obstacle preventing the report submitting entity from sending
reports to a Trade Repository within the deadline set out in the Article 9 of EMIR,
c. any significant issue resulting in reporting errors that would not cause rejection
by a trade repository in accordance with the RTS on data quality.

184
385. The notification should indicate at least the basic information on and
identification of the notification, ERR and RSE(s), the scope of the affected reports,
the type of the errors or omissions, the reasons for the errors or omissions, steps
taken or planned to resolve the issue, the date of the occurrence, and the timeline
for resolution of the issue and data submission or correction. The entity responsible
for reporting should provide the notification in a common template published on
ESMA website.
386. Each identified data quality issue should be provided within a separate
notification, unless several data quality issues are identified where these issues are
closely related, e.g. induced by a common cause, with coinciding resolution
timelines or common bug-fixes, or otherwise interlinked and impossible to separate
into individual notifications. In such case it is possible to provide single notification
for all these related data quality issues.
387. The assessment of significance should be performed as soon as the scope of
the misreporting is identified and the number of records affected by the reporting
issue is determined. The notification to NCAs should be sent without undue delay
after the assessment is concluded and all the relevant information is gathered. If
after the first assessment more affected records are identified, another assessment
should be performed and the NCAs should be notified with an update. Since the
assessment will be mostly executed on an ad-hoc basis, ESMA does not expect
the ERRs to provide the notifications to competent authorities on regular basis.
388. ESMA is aware of the need to specify in more detail the key metrics and
thresholds to assess the scope of notifications, as well as the need to carefully
calibrate the proposal. The need for clarification pertains particularly to the
“significant number of reports” under point a. and “significant issue” under point c.
above. ESMA provides below examples of relevant scenarios and clarifies the
metrics for assessing the scope of notifications.
389. Under Article 9(1)(a) of the ITS on reporting any misreporting caused by flaws
in the reporting systems that would affect a significant number of reports should be
notified. The requirement pertains to any flaw in the reporting systems on either
ERR or RSE side, or at any other third-party reporting system if outsourcing is
utilized. This scenario includes for example cases of technical problems excluding
a large percentage of records from submission, systematic omission of certain
fields in the reports, systematic reporting of incorrect or abnormal values in the
reports (e.g. system errors in orders of numerical fields). Since the requirement to
notify the authorities pertains to the ERR, RSE or any other third party involved in
reporting should inform all the relevant ERRs if they experience system failures or
identify any other flaw in their reporting systems. The RSE should send the
notification to NCAs only if it is ERR for some or all of the counterparties on whose
behalf it reports. Otherwise, if the RSE or any other third party involved in reporting
is experiencing data quality issues, it should only inform the relevant ERRs about
the details of the issue so that the ERRs are able to perform the assessment of
significance of the issue. ERRs and RSEs are expected to have in place sufficient
controls at the level of data reporting processes such that any of the above-

185
mentioned issues are timely identified, reported to authorities and permanently
remedied.
390. Significant number of reports should be assessed separately for each of the
following categories:
d. Category 1 – reports with action types ‘New’, ‘Modify’, ‘Correct’, ‘Terminate’,
‘Error’, ‘Revive’, ‘Position component’,
e. Category 2 – reports with action type ‘Valuation’,
f. Category 3 – reports with action type ‘Margin update’.
391. If the number of reports affected by the reporting issue is significant in at least
one of the categories, the competent authorities should be notified of the reporting
issue.
392. Number of reports affected by misreporting is significant if it exceeds the
following threshold:
NumOfAffReports / AverageMonthNum > Y% and NumOfAffReports > X
i.e. NumOfAffReports >= Threshold = max {X; Y% of AverageMonthNum},
where X and Y are calibration constants, and AverageMonthNum is the average
monthly number of submissions calculated on the day of assessment as
(NumOfReportsMonth
-12
+ NumOfReportsMonth
-11
+ … + NumOfReportsMonth
-2
+
NumOfReportsMonth
-1
) / 12 = NumOfReportsLast12Months / 12
using the actual numbers of reports submitted during the last 12 months.
393. To take into account how significant the ERR or RSE is, ESMA intends to
specify the buckets and corresponding calibration constants on the basis of
average number of submitted reports as shown in the example in the Table 23 .
394. The assessment of significance should be performed at ERR level or at RSE
level if applicable. The RSE should perform the assessment only if it is ERR for
some or all of the counterparties on whose behalf it reports. It is not deemed
necessary to calculate the average number of submissions separately for each
counterparty, if the ERR or RSE report on behalf of multiple counterparties. As
ESMA’s intention is that systematic issues are captured, even if for a single
counterparty a threshold is exceeded, the overall picture at the RSE should be
considered. Following scenarios aim at facilitating the understanding.
395. Let’s consider the following buckets and thresholds:
TABLE 23
Average monthly number of submissions (AverageMonthNum)
0<=A<100 000
100 000<=A<1 000 000
1 000 000<=A
X
100
20000
150000
Y %
20%
15%
10%

186
Scenario A: Three counterparties rely on the same Report Submitting Entity to submit the
reports. RSE is below the thresholds, one counterparty is exceeding the threshold.
TABLE 24
Monthly average
Affected
reports
X
Y
Thresholds
exceeded
Cpt 1
1000
10
10 < 100
1% < 20%
No
Cpt 2
1000
250
250 > 100
25% > 20%
Yes
Cpt 3
500
10
10 < 100
2% < 20%
No
Total RSE
2 500
270
270 > 100
11% < 20%
No
Even though for counterparty 2, the thresholds are exceeded, the calculation at the level
of the RSE is below the thresholds and therefore there is no need for the RSE to notify the
relevant NCAs. However, if the RSE is not ERR for all the affected counterparties, it should
duly inform all the ERRs of those counterparties about the reporting issue, so that they can
assess their overall situation and notify their NCAs if crossing the thresholds.
Scenario B: Three counterparties rely on the same Report Submitting Entity to submit the
reports. RSE is above the threshold, two counterparties are below the threshold. RSE is
ERR only for Cpt 2.
TABLE 25
Monthly average
Affected
reports
X
Y
Threshold
exceeded
Cpt 1
1000
180
180 > 100
18% < 20%
No
Cpt 2
1000
800
800 > 100
80% > 20%
Yes
Cpt 3
500
10
10 < 100
2% < 20%
No
Total RSE
2 500
990
990 > 100
40% > 20%
Yes
RSE has a significant issue, but Cpt 1 and Cpt 3 are only slightly affected. In this case the
notification to NCAs should include details, such as number of affected reports, which only
relate to Cpt 2.

187
Similarly to the previous scenario, if the RSE is not ERR for all the affected counterparties,
it should duly inform all the ERRs of those counterparties (in this scenario Cpt 1 and Cpt
3) about the reporting issue, so that they can assess their overall situation and notify their
NCAs if crossing the thresholds.
Scenario C: A counterparty (ERR) is delegating reporting to 2 RSEs and partially reports
by itself. At counterparty level, only a subset of reports is affected by the reporting issue at
an RSE.
TABLE 26
Monthly
average
Affected
reports
affected by an
issue
X
Y
Threshold
s
exceeded
Cpt
1000
0
0 < 100
0% < 20%
No
RSE 1
1000
250
250 > 100
25% > 20%
Yes
RSE 2
500
0
0 < 100
0% < 20%
No
Total ERR
2500
250
250 > 100
10% < 20%
No
RSE1 has potentially a significant issue but on the overall level of the counterparty the
issue is not significant. In this case the counterparty is not expected to notify its NCA.
Nevertheless, it is not prohibited for RSE 1 to notify the counterparty’s NCA if the issue is
significant at the level of the RSE 1 and the counterparty relies on the RSE 1 to notify the
NCAs.
396. Under Article 9(1)(b) of the ITS on reporting any reporting obstacle preventing
the report submitting entity from submitting reports within the reporting deadline
should be notified. These cases include primarily system failures but should not be
understood as limited only to technical problems, e.g. operational issues (COVID-
19), lack of LEI update, impossibility to generate the UTI. To further differentiate
from the cases of misreporting and record omission of Article 9(1)(a), ESMA
emphasizes that cases under Article 9(1)(b) pertain to complete inability to send
any records to the TRs, while data quality issues under Article 9(1)(a) affect only
subset of reported records.
397. Under Article 9(1)(c) of the ITS on reporting any significant issue resulting in
reporting errors that would not cause rejection by a trade repository should be
notified.
398. Significant issue under Article 9(1)(c) of the ITS on reporting should be
assessed according to the following non exhaustive list of qualitative criteria:
a. Non-reporting or over-reporting of a derivative due to erroneous assessment of
its reportability;

188
b. Incorrect or inconsistent interpretation of the number of reports to be reported
for a specific derivative (e.g. in dispute with the other counterparty);
c. Incorrect or inconsistent interpretation of the content of the fields (e.g. in dispute
with the other counterparty);
d. Reporting of non-standard derivatives for which the fields are not fully suited;
e. Errors and omissions that pertain to
i. Incorrect data in the parties identification: fields 1.2 to 1.16, 1.20, 2.33, 2.37;
ii. Incorrect trade details: fields 1.17 to 1.19, 2.1 to 2.12, 2.38 to 2.41;
iii. Incorrect details on underlying: fields 2.13 to 2.18 – in particular when the basket
is not complete;
iv. Amounts and currencies in all related fields (notional, valuation, collateral, price,
strike …);
v. Dates / timestamps: execution, event confirmation, expiration;
vi. Clearing fields 2.30 to 2.32;
vii. Incorrect report details: fields 2.151, 2.152 and 2.154;
viii. Collateral portfolio code: field 3.9;
ix. Errors in valuation methods resulting in incorrect reporting of valuation.
399. Significant issue under Article 9(1)(c) of the ITS on reporting should be further
(accumulatively) assessed according to the quantitative criteria specifying
significant number of records affected by the qualitatively significant data quality
issue. Scenarios of example above apply analogously for significant issues under
Article 9(1)(c) of the ITS on reporting.
400. The entity responsible for reporting should have processes in place to be able
at any time to assess the significance of identified cases of misreporting as outlined
above and to promptly notify them to the relevant NCAs. Specifically, this includes
swift identification of impacted records and their numbers and the computation of
relevant metrics to assess whether thresholds have been exceeded or not.
401. Counterparties, ERRs or RSEs will need to submit their notifications to the
NCAs in accordance with the procedures adopted by those NCAs in each Member
State.
402. Many data quality issues are related to inconsistent interpretation of the rules
for reporting of the derivatives. The aim of these Guidelines is to provide in the
relevant sections the necessary guidance for the various reporting scenarios and
derivative contracts, including detailed illustrative examples.
403. The population of fields that are specified as optional in the validation rules is
not left at the discretion of the reporting counterparties. Optional fields should be
always populated in all cases where the field is relevant in the given scenario or for
the given derivative.

189
5 Reporting per product type
404. This section includes clarifications and examples illustrating reporting of certain
derivative products.
405. The examples are provided in form of tables, where each table shows the
reporting fields under the ITS on reporting. The column ‘Field’ shows each field
name, and the column ‘Example’ provides an example of what would be included
in that field. The final column entitled ‘XML Message’ shows the format of the XML
message which should be submitted in the report.
406. Unless otherwise stated in the specific scenario, the following background
information applies to all scenarios set out in this section:
Counterparty A is a German financial counterparty identified with LEI 12345678901234500000
Counterparty B is an Italian financial counterparty identified with LEI ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
Counterparty C is a Spanish NFC- identified with LEI 123456789ABCDEFGHIJK
Counterparty D is a French NFC+ identified with LEI 11223344556677889900
Counterparty J acts also as a clearing member and is identified with LEI
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
CCP O is identified with LEI BBBBBBBBBB1111111111
5.1 Reporting of IRS
407. When reporting IRS, the counterparties should describe the underlying fixed or
floating rates in the dedicated rate fields for leg 1 and leg 2 (fields 2.79-2.110),
rather than e.g. providing the floating rate in the underlying index field.
408. There are three distinct fields to describe a floating rate:
a. Identifier (fields 2.83 and 2.99), which should be populated with ISIN,
b. Indicator (fields 2.84 and 2.100) which should be populated with a standardised
4-letter code, and
c. Name (fields 2.85 and 2.101), which should be populated with the full name of
the rate.
409. Counterparties should always report ISIN and 4-letter code, to the extent that
they are available for a given rate. The name of the rate should be reported in all
cases.
Fixed-to-floating IRS

190
410. A single currency fixed-to-floating 5-year IRS on 3M EURIBOR vs 0.5% (with
no additional spread). Counterparties exchange payments each six months and
reset frequency is set to annual. The day count convention is Actual/360.
Table 27 – Reporting of a fixed-to-floating IRS
No
Field
Example
XML message
79
Fixed rate of leg
1 or coupon
0.5
<IntrstRate>
<FrstLeg>
<Fxd>
<Rate>
<Rate>0.5</Rate>
</Rate>
<DayCnt>
<Cd>A004</Cd>
</DayCnt>
<PmtFrqcy>
<Term>
<Unit>MNTH</Unit>
<Val>6</Val>
</Term>
</PmtFrqcy>
</Fxd>
</FrstLeg>
<ScndLeg>
<Fltg>
<Id>EU0009652783</Id>
<Nm>Euro Interbank Offered
Rate</Nm>
<Rate>
<Cd>EURI</Cd>
</Rate>
<RefPrd>
<Unit>MTH</Unit>
<Val>3</Val>
</RefPrd>
<Sprd>
<Pctg>0</Pctg>
</Sprd>
<DayCnt>
<Cd>A004</Cd>
</DayCnt>
<PmtFrqcy>
<Term>
<Unit>MNTH</Unit>
<Val>6</Val>
</Term>
</PmtFrqcy>
<RstFrqcy>
<Term>
<Unit>YEAR</Unit>
<Val>1</Val>
</Term>
</RstFrqcy>
</Fltg>
80
Fixed rate or
coupon day
count
convention leg 1
A004
81
Fixed rate or
coupon payment
frequency period
leg 1
MNTH
82
Fixed rate or
coupon payment
frequency period
multiplier leg 1
6
99
Identifier of the
floating rate of
leg 2
EU0009652783
100
Indicator of the
floating rate of
leg 2
EURI
101
Name of the
floating rate of
leg 2
Euro Interbank
Offered Rate
102
Floating rate day
count
convention of leg
2
A004
103
Floating rate
payment
frequency period
of leg 2
MNTH
104
Floating rate
payment
frequency period
multiplier of leg 2
6
105
Floating rate
reference period
of leg 2 – time
period
MNTH
106
Floating rate
reference period
3

191
Table 27 – Reporting of a fixed-to-floating IRS
No
Field
Example
XML message
of leg 2 –
multiplier
</ScndLeg>
</IntrstRate>
107
Floating rate
reset frequency
period of leg 2
YEAR
108
Floating rate
reset frequency
multiplier of leg 2
1
109
Spread of leg 2
0
110
Spread currency
of leg 2
5.2 Reporting of swaptions
411. When reporting swaptions, the counterparties should provide both the fields
related to options (fields 2.132-2.142) as well as the fields characterising the
underlying swap (fields 2.79-2.110).
412. Exercise of the swaption should be reported with action type ‘Terminate’ and
event type ‘Exercise’. The resulting swap should be reported with action type ‘New’
and event type ‘Exercise’ as well as with the field 2.3 ‘Prior UTI’ populated.
413. The tables below illustrate how to report an original swaption, exercise of that
swaption and the resulting swap.
5.2.1 Swaption on a fixed-to-floating IRS
414. Counterparty enters into an American put option on a fixed-to-floating IRS
based on 1D SONIA vs 0.75% (with no additional spread). The premium is 200,000
GBP. If exercised, the reporting counterparty will pay fixed rate and the
counterparties will exchange payments each 3 months and reset frequency is set
to annual. The day count convention is Actual/Actual ISDA.
Table 28 – Reporting of a swaption on a fixed-to-floating IRS
No
Field
Example
XML message
1
UTI
AAAAABBBBBCCCCCD
DDDD12345
<Rpt><New><CmonTradData>
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
AAAAABBBBBCCCCCDDDDD12345
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
79
Fixed rate of leg 1
or coupon
0.75

192
Table 28 – Reporting of a swaption on a fixed-to-floating IRS
No
Field
Example
XML message
80
Fixed rate or
coupon day count
convention leg 1
A008
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>TRAD</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
…
<IntrstRate>
<FrstLeg>
<Fxd>
<Rate>
<Rate>0.75</Rate>
</Rate>
<DayCnt>
<Cd>A008</Cd>
</DayCnt>
<PmtFrqcy>
<Term>
<Unit>MNTH</Unit>
<Val>3</Val>
</Term>
</PmtFrqcy>
</Fxd>
</FrstLeg>
<ScndLeg>
<Fltg>
<Id>GB00B56Z6W79</Id>
<Nm>Sterling Overnight
Index Average</Nm>
<Rate>
<Cd>SONA</Cd>
</Rate>
<RefPrd>
<Unit>DAIL</Unit>
<Val>1</Val>
</RefPrd>
<Sprd>
<Pctg>0</Pctg>
</Sprd>
<DayCnt>
<Cd>A008</Cd>
</DayCnt>
<PmtFrqcy>
<Term>
<Unit>MNTH</Unit>
<Val>3</Val>
</Term>
</PmtFrqcy>
<RstFrqcy>
<Term>
<Unit>YEAR</Unit>
<Val>1</Val>
</Term>
</RstFrqcy>
</Fltg>
</ScndLeg>
</IntrstRate>
81
Fixed rate or
coupon payment
frequency period
leg 1
MNTH
82
Fixed rate or
coupon payment
frequency period
multiplier leg 1
3
99
Identifier of the
floating rate of leg
2
GB00B56Z6W79
100
Indicator of the
floating rate of leg
2
SONA
101
Name of the
floating rate of leg
2
Sterling Overnight Index
Average
102
Floating rate day
count convention
of leg 2
A008
103
Floating rate
payment
frequency period
of leg 2
MNTH
104
Floating rate
payment
frequency period
multiplier of leg 2
3
105
Floating rate
reference period
of leg 2 – time
period
DAIL
106
Floating rate
reference period
of leg 2 –
multiplier
1
107
Floating rate reset
frequency period
of leg 2
YEAR
108
Floating rate reset
frequency
multiplier of leg 2
1
109
Spread of leg 2
0

193
Table 28 – Reporting of a swaption on a fixed-to-floating IRS
No
Field
Example
XML message
110
Spread currency
of leg 2
<Optn>
<Tp>PUTO</Tp>
<ExrcStyle>AMER</ExrcStyle>
<StrkPric>
<Pctg>0.75</Pctg>
</StrkPric>
<PrmAmt Ccy="GBP">200000.00
< </PrmAmt>
<PrmPmtDt>2022-07-01
< </PrmPmtDt>
<MtrtyDtOfUndrlyg>2025-12-01
< </MtrtyDtOfUndrlyg>
</Optn>
</TxData>
</CmonTradData></New></Rpt>
132
Option type
PUTO
133
Option style
AMER
134
Strike price
0.75
138
Strike price
currency/currency
pair
139
Option premium
amount
200000
140
Option premium
currency
GBP
141
Option premium
payment date
2022-07-01
142
Maturity date of
the underlying
2025-12-01
151
Action type
NEWT
152
Event type
TRAD
Table 29 - Reporting of an exercise of a swaption
No
Field
Example
XML message
1
UTI
AAAAABBBBBCCCCCDDD
DD12345
<Rpt><Termntn><CmonTradData>
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
3
Prior
UTI

194
Table 29 - Reporting of an exercise of a swaption
No
Field
Example
XML message
45
Early
termina
tion
date
2022-11-01
AAAAABBBBBCCCCCDDDDD12345
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
<EarlyTermntnDt>2022-11-01
< </EarlyTermntnDt>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>EXER</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
</TxData>
</CmonTradData></Termntn></Rpt>
15
1
Action
type
TERM
15
2
Event
type
EXER
Table 30 - Reporting of a swap after exercise of the swaption
No
Field
Example
XML message
1
UTI
AAAAABBBBBCCCCCDD
DDD67890
<Rpt><New><CmonTradData>
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
AAAAABBBBBCCCCCDDDDD67890
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
<PrrTxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
AAAAABBBBBCCCCCDDDDD12345
</UnqTxIdr>
</PrrTxId>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>EXER</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
…
<IntrstRate>
<FrstLeg>
<Fxd>
<Rate>
<Rate>0.75</Rate>
</Rate>
<DayCnt>
<Cd>A008</Cd>
</DayCnt>
<PmtFrqcy>
<Term>
<Unit>MNTH</Unit>
<Val>3</Val>
3
Prior UTI
AAAAABBBBBCCCCCDD
DDD12345
79
Fixed rate
of leg 1 or
coupon
0.75
80
Fixed rate
or coupon
day count
convention
leg 1
A008
81
Fixed rate
or coupon
payment
frequency
period leg
1
MNTH
82
Fixed rate
or coupon
payment
frequency
period
multiplier
leg 1
3
99
Identifier
of the
floating
GB00B56Z6W79
195
Table 30 - Reporting of a swap after exercise of the swaption
No
Field
Example
XML message
rate of leg
2
</Term>
</PmtFrqcy>
</Fxd>
</FrstLeg>
<ScndLeg>
<Fltg>
<Id>GB00B56Z6W79</Id>
<Nm>Sterling Overnight
Index Average</Nm>
<Rate>
<Cd>SONA</Cd>
</Rate>
<RefPrd>
<Unit>DAIL</Unit>
<Val>1</Val>
</RefPrd>
<Sprd>
<Pctg>0</Pctg>
</Sprd>
<DayCnt>
<Cd>A008</Cd>
</DayCnt>
<PmtFrqcy>
<Term>
<Unit>MNTH</Unit>
<Val>3</Val>
</Term>
</PmtFrqcy>
<RstFrqcy>
<Term>
<Unit>YEAR</Unit>
<Val>1</Val>
</Term>
</RstFrqcy>
</Fltg>
</ScndLeg>
</IntrstRate>
</TxData>
</CmonTradData></New></Rpt>
100
Indicator
of the
floating
rate of leg
2
SONA
101
Name of
the floating
rate of leg
2
Sterling Overnight Index
Average
102
Floating
rate day
count
convention
of leg 2
A008
103
Floating
rate
payment
frequency
period of
leg 2
MNTH
104
Floating
rate
payment
frequency
period
multiplier
of leg 2
3
105
Floating
rate
reference
period of
leg 2 –
time
period
DAIL
106
Floating
rate
reference
period of
leg 2 –
multiplier
1
107
Floating
rate reset
frequency
period of
leg 2
YEAR
108
Floating
rate reset
frequency
1

196
Table 30 - Reporting of a swap after exercise of the swaption
No
Field
Example
XML message
multiplier
of leg 2
109
Spread of
leg 2
0
110
Spread
currency
of leg 2
151
Action
type
NEWT
152
Event type
EXER
5.3 Reporting of other IR products
415. Forward Rate Agreements (FRAs), cross-currency swaps, caps and floors
should be classified as interest derivatives.
416. When reporting FRAs the counterparties should pay attention to the following:
a. The underlying rate should be reported in the fields pertaining to the underlying
section (fields 2.13-2.16).
b. Execution timestamp should be populated with the relevant date and time when
the derivative was concluded by the counterparties and following the
specifications in the validation rules.
c. Effective date is the date when obligations under the contract come into effect.
Unless the obligations between the counterparties are postponed to a future
date, this is the same as the date part of the execution timestamp. Effective date
is not the settlement date referred to in the FRA documentation.
d. Maturity date is the date agreed by the counterparties when the obligations
under the derivative expire. In the case of FRAs, this is the date on which the
exposures between the counterparties are extinguished by the determination of
the payment covering the difference between the agreed rate and the prevailing
market rate. This is not the final date of the underlying rate.
e. Settlement date is the date on which the counterparties settle the underlying.
The underlying of a FRA is a forward interest rate and the settlement of the
difference between the agreed rate and the prevailing market rate either
coincides with the maturity date or it takes place on a later date.
417. Example of a FRA (represented using industry terminology):
• Executed on 22 February
• Fixing Date (2 day fixing) 20 May
• Effective Date (3M) 22 May

197
• Maturity Date (6M) 22 August
• Settlement Date 22 May
418. In the above example, for the purpose of reporting the effective date is 22
February - unless the counterparties agree to postpone the date on which the
obligations come into effect - and the maturity date is 20 May.
419. In the case of caps and floors, the counterparties should populate both the fields
relevant for options and fields relevant for interest rate derivatives (similarly to the
example of swaption illustrated in the section 5.2).
420. In the case of cross-currency swaps, the counterparties should populate both
the fields relevant for foreign exchange derivatives and fields relevant for interest
rate derivatives.
5.4 Reporting of FX swaps and forwards
421. The Final contractual settlement date as specified in the RTS on reporting is not
a repeatable field, therefore it is not possible to report both settlement dates – of
the near and far leg – in this field.
422. FX swap is reported in a single report; therefore the Package identifier should
not be populated.
423. The below examples illustrate how an FX swap and a lifecycle event affecting a
single leg of a swap should be reported under Article 9 of EMIR.
5.4.1 FX swaps (spot-forward and forward-forward)
424. Following scenarios are considered:
f. -Scenario A: Reporting of an FX swap composed of a spot and forward leg.
g. Scenario B: Reporting of an FX swap composed of two forward legs.
425. In both scenarios the derivatives have the following characteristics:
- Banks A and B enter in a EUR/GBP swap instrument on 1 June 2018 (regardless of
how the instrument has been subsequently confirmed or settled);
- notional of the contract: 1,000,000 EUR;
- maturity date of the contract: 31 December 2018;
- the swap is physically settled;
- Bank A delivers GBP and receives EUR for the far leg; thus it is identified as the
receiver of leg 1 ( i.e. it receives the currency reported in the field ‘Notional currency 1’,
EUR);
- the exchange rate of the near leg is 0.88 EUR/GBP, while the exchange rate of the
far leg is 0.865 EUR/GBP.

198
Table 31 - Reporting of an FX swap composed of a spot and forward leg
Item
Field
Example
XML message
1
Reporting
timestamp
2018-06-01T12:00:00Z
<New>
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl>
<LEI>12345678901234500000
> </LEI>
</Lgl>
</Id>
…
<DrctnOrSd><Drctn>
<DrctnOfTheFrstLeg>TAKE
> </DrctnOfTheFrstLeg>
<DrctnOfTheScndLeg>MAKE
> </DrctnOfTheScndLeg>
</Drctn></DrctnOrSd>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl>
<LEI>ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
> </LEI>
</Lgl>
</IdTp>
…
</OthrCtrPty>
</CtrPty>
<RptgTmStmp>2018-06-01T12:00:00Z
> </RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CmonTradData>
<CtrctData>
<CtrctTp>SWAP</CtrctTp>
<AsstClss>CURR</AsstClss>
<PdctClssfctn>SFAXXP
> </PdctClssfctn>
</CtrctData>
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>123456
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
<NtnlAmt>
<FrstLeg>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">1000000</Amt>
</FrstLeg>
<ScndLeg>
<Amt Ccy="GBP">865000</Amt>
</ScndLeg>
</NtnlAmt>
…
<DlvryTp>PHYS</DlvryTp>
<ExctnTmStmp>2018-06-01T12:00:
4
Counterparty
1
(Reporting
counterparty)
12345678901234500000
9
Counterparty
2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRS
T
18
Direction of
leg 1
TAKE
19
Direction of
leg 2
MAKE
1
UTI
123456
199
Table 31 - Reporting of an FX swap composed of a spot and forward leg
Item
Field
Example
XML message
> 00Z</ExctnTmStmp>
<FctvDy>2018-06-01</FctvDy>
<XprtnDt>2018-12-31</XprtnDt>
<SttlmDt>2018-12-31</SttlmDt>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>TRAD</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
…
<Ccy>
<XchgRate>0.88</XchgRate>
<FwdXchgRate>0.865
> </FwdXchgRate>
<XchgRateBsis>
<CcyPair>
<BaseCcy>EUR</BaseCcy>
<QtdCcy>GBP</QtdCcy>
</CcyPair>
</XchgRateBsis>
</Ccy>
</TxData>
</CmonTradData>
</New>
6
Package
identifier
9
Product
classification
SFAXXP
10
Contract type
SWAP
11
Asset class
CURR
19
Settlement
currency 1
20
Settlement
currency 2
42
Execution
timestamp
2018-06-
01T12:00:00Z

200
Table 31 - Reporting of an FX swap composed of a spot and forward leg
Item
Field
Example
XML message
43
Effective
date
2018-06-01
44
Expiration
date
2018-12-31
46
Final
contractual
settlement
date
2018-12-31
47
Delivery type
PHYS
48
Price
49
Price
currency
55
Notional
amount of
leg 1
1000000
64
Notional
amount of
leg 2
865000
56
Notional
currency 1
EUR
65
Notional
currency 2
GBP
113
Exchange
rate 1
0.88
114
Forward
exchange
rate
0.865

201
Table 31 - Reporting of an FX swap composed of a spot and forward leg
Item
Field
Example
XML message
115
Exchange
rate basis
EUR/GBP
151
Action type
NEWT
152
Event type
TRAD
Table 32 - Reporting of an FX swap composed of two forward legs
Item
Field
Example
XML message
1
Reporting
timestamp
2018-06-01T12:00:00Z
<New>
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl>
<LEI>12345678901234500000
> </LEI>
</Lgl>
</Id>
…
<DrctnOrSd><Drctn>
<DrctnOfTheFrstLeg>TAKE
> </DrctnOfTheFrstLeg>
<DrctnOfTheScndLeg>MAKE
> </DrctnOfTheScndLeg>
</Drctn></DrctnOrSd>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl>
<LEI>ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
> </LEI>
</Lgl>
</IdTp>
…
</OthrCtrPty>
</CtrPty>
<RptgTmStmp>2018-06-01T12:00:00Z
> </RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CmonTradData>
<CtrctData>
<CtrctTp>SWAP</CtrctTp>
<AsstClss>CURR</AsstClss>
<PdctClssfctn>SFCXXP
> </PdctClssfctn>
</CtrctData>

202
Table 32 - Reporting of an FX swap composed of two forward legs
Item
Field
Example
XML message
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
123457
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
<NtnlAmt>
<FrstLeg>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">
> 1000000</Amt>
</FrstLeg>
<ScndLeg>
<Amt Ccy="GBP">
> 865000</Amt>
</ScndLeg>
</NtnlAmt>
…
<DlvryTp>PHYS</DlvryTp>
<ExctnTmStmp>2018-06-01T
12:00:00Z</ExctnTmStmp>
<FctvDy>2018-06-01</FctvDy>
<XprtnDt>2018-12-31</XprtnDt>
<SttlmDt>2018-12-31</SttlmDt>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>TRAD</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
…
<Ccy>
<XchgRate>0.88</XchgRate>
<FwdXchgRate>0.865
> </FwdXchgRate>
<XchgRateBsis>
<CcyPair>
<BaseCcy>EUR</BaseCcy>
<QtdCcy>GBP</QtdCcy>
</CcyPair>
</XchgRateBsis>
</Ccy>
</TxData>
</CmonTradData>
</New>
4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
12345678901234500000
9
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQ
RST
18
Direction of leg
1
TAKE

203
Table 32 - Reporting of an FX swap composed of two forward legs
Item
Field
Example
XML message
19
Direction of leg
2
MAKE
1
UTI
123457
6
Package
identifier
9
Product
classification
SFCXXP
10
Contract type
SWAP
11
Asset class
CURR
19
Settlement
currency 1
20
Settlement
currency 2
42
Execution
timestamp
2018-06-
01T12:00:00Z
43
Effective date
2018-06-01
44
Expiration date
2018-12-31
46
Final
contractual
settlement
date
2018-12-31
47
Delivery type
PHYS
48
Price

204
Table 32 - Reporting of an FX swap composed of two forward legs
Item
Field
Example
XML message
49
Price currency
55
Notional
amount of leg 1
1000000
64
Notional
amount of leg 2
865000
56
Notional
currency 1
EUR
65
Notional
currency 2
GBP
113
Exchange rate 1
0.88
114
Forward
exchange rate
0.865
115
Exchange rate
basis
EUR/GBP
151
Action type
NEWT
152
Event type
TRAD
5.4.2 Compression of the near leg of the FX swap
426. The following scenario is considered:
- The derivative is concluded on 1 June 2018;
- notional of the contract: 1,000,000 EUR;
- maturity date of the contract: 31 December 2018;
- the swap is physically settled;
- Bank A sells EUR and gets GBP for the near leg (and delivers GBP and receives EUR
for the far leg);
- the exchange rate of the near leg is 0.88 EUR/GBP, while the exchange rate of the
far leg is 0.865 EUR/GBP;

205
- the two settlement dates are 01/08/2018 and 31/12/2018.
427. On 17 July there is a compression of the near leg, while the far leg continues.
Therefore, the FX swap needs to be terminated with action type ‘TERM’ and event
type ’COMP’ and the FX forward contract arising from this compression has to be
reported with a new UTI and flagging the ‘PTRR’ field as true. ‘PTRR ID’ is provided
by the PTRR service provider WWWWWXXXXXYYYYYZZZZZ and populated both
for the FX forward and the termination report of the FX swap.
428. This way of reporting is envisaged only in the cases where lifecycle events
impact a single leg of an FX swap. It should not be followed in case of a normal
settlement of a near leg, as envisaged in the original contract.
429. In line with the validation rules, only a limited subset of fields is required for
action type ’TERM’.
Table 33 - New Report (for a swap)
No
Field
Example
XML message
1
Reporting
timestamp
2018-06-
01T12:00:00Z
<New>
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl>
<LEI>12345678901234500000 >
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</Id>
…
<DrctnOrSd><Drctn>
<DrctnOfTheFrstLeg>TAKE
> </DrctnOfTheFrstLeg>
<DrctnOfTheScndLeg>MAKE
> </DrctnOfTheScndLeg>
</Drctn></DrctnOrSd>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl>
<LEI>ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST >
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</IdTp>
…
</OthrCtrPty>
</CtrPty>
<RptgTmStmp>2018-06-01T
12:00:00Z</RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CmonTradData>
<CtrctData>

206
Table 33 - New Report (for a swap)
No
Field
Example
XML message
<CtrctTp>SWAP</CtrctTp>
<AsstClss>CURR</AsstClss>
<PdctClssfctn>SFCXXP
> </PdctClssfctn>
</CtrctData>
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
123456
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
<NtnlAmt>
<FrstLeg>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">
> 1000000</Amt>
</FrstLeg>
<ScndLeg>
<Amt Ccy="GBP">
> 865000</Amt>
</ScndLeg>
</NtnlAmt>
…
<DlvryTp>PHYS</DlvryTp>
<ExctnTmStmp>2018-06-01T
12:00:00Z</ExctnTmStmp>
<FctvDy>2018-06-01</FctvDy>
<XprtnDt>2018-12-31
</XprtnDt>
<SttlmDt>2018-12-31
</SttlmDt>
…
<PstTradRskRdctnFlg>FALSE
> </PstTradRskRdctnFlg>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>TRAD</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
…
<Ccy>
<XchgRate>0.88</XchgRate>
<FwdXchgRate>0.865
> </FwdXchgRate>
<XchgRateBsis>
<CcyPair>
<BaseCcy>EUR</BaseCcy>
<QtdCcy>GBP</QtdCcy>
</CcyPair>
</XchgRateBsis>
</Ccy>
</TxData>
</CmonTradData>
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</New>

207
Table 33 - New Report (for a swap)
No
Field
Example
XML message
4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
12345678901234500000
9
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRS
T
18
Direction of leg 1
TAKE-
19
Direction of leg 2
MAKE
1
UTI
123456
5
PTRR ID
9
Product
classification
SFCXXP
10
Contract type
SWAP
11
Asset class
CURR
19
Settlement
currency 1
20
Settlement
currency 2
38
PTRR
FALSE
42
Execution
timestamp
2018-06-
01T12:00:00Z
43
Effective date
2018-06-01

208
Table 33 - New Report (for a swap)
No
Field
Example
XML message
44
Expiration date
2018-12-31
45
Early termination
date
46
Final contractual
settlement
date
2018-12-31
47
Delivery type
PHYS
48
Price
49
Price currency
55
Notional amount
of leg 1
1000000
64
Notional amount
of leg 2
865000
56
Notional currency
1
EUR
65
Notional currency
2
GBP
113
Exchange rate 1
0.88
114
Forward
exchange rate
0.865
115
Exchange rate
basis
EUR/GBP
151
Action type
NEWT
152
Event type
TRAD
154
Level
TCTN

209
Table 34 – Termination (due to compression) of leg 1
No
Field
Example
XML example
1
Reporting
timestamp
2018-07-
17T12:00:00Z
<Termntn>
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl>
<LEI>12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</Id>
…
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl>
<LEI>ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</IdTp>
…
</OthrCtrPty>
</CtrPty>
<RptgTmStmp>2018-07-
17T12:00:00Z
</RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CmonTradData>
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
123456
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
<EarlyTermntnDt>2018-07-17
</EarlyTermntnDt>
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>COMP</Tp>
<Id>
<PstTradRskRdctnIdr>
<Strr>WWWWWXXXXX
YYYYYZZZZZ</Strr>
<Id>1234567</Id>
4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
12345678901234500000
9
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMN OPQRST
18
Direction of leg 1
-
19
Direction of leg 2
-
1
UTI
123456
5
PTRR ID
WWWWWXXXXXYYYYYZZZZZ1234567
9
Product
classification
-
10
Contract type
-
11
Asset class
-
19
Settlement
currency 1
20
Settlement
currency 2
38
PTRR
42
Execution
timestamp
-
43
Effective date
-
44
Expiration date
-

210
Table 34 – Termination (due to compression) of leg 1
No
Field
Example
XML example
45
Early termination
date
2018-07-17
</PstTradRskRdctnIdr>
</Id>
</DerivEvt>
…
</TxData>
</CmonTradData>
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</Termntn>
46
Final contractual
settlement
date
47
Delivery type
48
Price
49
Price currency
55
Notional amount
of leg 1
64
Notional amount
of leg 2
-
56
Notional currency
1
65
Notional currency
2
113
Exchange rate 1
114
Forward
exchange rate
115
Exchange rate
basis
151
Action type
TERM
152
Event type
COMP
154
Level
TCTN

211
Table 35 – New report of FX forward (for the far leg of the previous swap)
No
Field
Example
XML schema
1
Reporting
timestamp
2018-07-
17T12:00:00Z
<New>
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPrty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</Id>
<DrctnOrSd><Drctn>
<DrctnOfTheFrstLeg>
TAKE
</DrctnOfTheFrstLeg>
<DrctnOfTheScndLeg>
MAKE
<DrctnOfTheScndLeg>
</Drctn></DrctnOrSd>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl>
<LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</Id>
</OthrCtrPty>
</CtrPty>
<RptgTmStmp>2018-07-17T
12:00:00Z</RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CmonTradData>
<CtrctData>
<CtrctTp>FORW</CtrctTp>
<AsstClss>CURR</AsstClss>
<PdctClssfctn>
a JFTXFP
</PdctClssfctn>
</CtrctData>
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>789ABC
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
<NtnlAmt>
<FrstLeg>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">
> 1000000</Amt>
</FrstLeg>
4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
12345678901234500000
9
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
18
Direction of leg 1
TAKE
19
Direction of leg 2
MAKE
1
UTI
789ABC
5
PTRR ID
WWWWWXXXXXYYYYYZZZZZ1
234567
9
Product
classification
JFTXFP
10
Contract type
FORW
11
Asset class
CURR
19
Settlement
currency 1
20
Settlement
currency 2

212
Table 35 – New report of FX forward (for the far leg of the previous swap)
No
Field
Example
XML schema
38
PTRR
TRUE
<ScndLeg>
<Amt Ccy="GBP">
> 865000</Amt>
</ScndLeg>
</NtnlAmt>
…
<DlvryTp>PHYS</DlvryTp>
<ExctnTmStmp>2018-06-01
T12:00:00Z</ExctnTmStmp>
<FctvDy>2018-07-17
</FctvDy>
<XprtnDt>2018-12-31
</XprtnDt>
<SttlmDt>2018-12-31
</SttlmDt>
…
<PstTradRskRdctnFlg>
true
</PstTradRskRdctnFlg>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>COMP</Tp>
<Id>
<PstTradRskRdctnIdr>
<Strr>WWWWWXXXXX
YYYYYZZZZZ</Strr>
<Id>1234567</Id>
</PstTradRskRdctnIdr>
</Id>
</DerivEvt>
…
<Ccy>
<FwdXchgRate>0.865
> </FwdXchgRate>
<XchgRateBsis>
<CcyPair>
<BaseCcy>EUR
</BaseCcy>
<QtdCcy>GBP
</QtdCcy>
</CcyPair>
</XchgRateBsis>
</Ccy>
</TxData>
</CmonTradData>
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</New>
42
Execution
timestamp
2018-06-
01T12:00:00Z
43
Effective date
2018-07-17
44
Expiration date
2018-12-31
45
Early termination
date
46
Final contractual
settlement
date
2018-12-31
47
Delivery type
PHYS
48
Price
49
Price currency
55
Notional amount
of leg 1
1000000

213
Table 35 – New report of FX forward (for the far leg of the previous swap)
No
Field
Example
XML schema
64
Notional amount
of leg 2
865000
56
Notional currency
1
EUR
65
Notional currency
2
GBP
113
Exchange rate 1
114
Forward
exchange rate
0.865
115
Exchange rate
basis
EUR/GBP
151
Action type
NEWT
152
Event type
COMP
154
Level
TCTN
5.4.3 FX option
430. Considering a currency option with the following setup:
- Banks A and B enter in a EUR/GBP European call option instrument on 1 June 2018
- notional of the contract: 1,000,000 EUR;
- maturity date of the contract: 31 December 2018;

214
- the option is physically settled;
- Bank A is the buyer of the option;
- the strike of the option is 0.87;
- option premium is 200,000 EUR and is paid on 5 June 2018.
431. The option has only one leg and the direction should be defined in accordance
with the buyer/seller model. It should be determined by which counterparty buys or
sells the option.
Table 36 – Reporting of a new FX option
Ite
m
Field
Example
XML example
1
Reporting
timestamp
2018-06-
01T12:00:00Z
<New>
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl>
<LEI>12345678901234500000
> </LEI>
</Lgl>
</Id>
…
<DrctnOrSd>
<CtrPtySd>BYER</DrctnOrSd>
</DrctnOrSd>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl>
<LEI>ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
> </LEI>
</Lgl>
</IdTp>
…
</OthrCtrPty>
</CtrPty>
<RptgTmStmp>2018-06-01T12:00:00Z
> </RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CmonTradData>
<CtrctData>
<CtrctTp>OPTN</CtrctTp>
<AsstClss>CURR</AsstClss>
<PdctClssfctn>HFTAVP
> </PdctClssfctn>
</CtrctData>
<TxData>
<TxId>
4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
1234567890123450000
0
9
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOP
QRST
17
Direction
BYER
1
UTI
123OPT
9
Product
classification
HFTAVP
10
Contract type
OPTN
11
Asset class
CURR
19
Settlement currency
1
20
Settlement currency
2
42
Execution
timestamp
2018-06-
01T12:00:00Z

215
Table 36 – Reporting of a new FX option
Ite
m
Field
Example
XML example
43
Effective date
2018-06-01
<UnqTxIdr>123OPT</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
<NtnlAmt>
<FrstLeg>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">
> 1000000</Amt>
</FrstLeg>
<ScndLeg>
<Amt Ccy="GBP">
> 870000</Amt>
</ScndLeg>
</NtnlAmt>
…
<DlvryTp>PHYS</DlvryTp>
<ExctnTmStmp>2018-06-1T12:00:
> 00Z</ExctnTmStmp>
<FctvDy>2018-06-01</FctvDy>
<XprtnDt>2018-12-31</XprtnDt>
<SttlmDt>2019-01-02</SttlmDt>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>TRAD</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
…
<Ccy>
<XchgRateBsis>
<CcyPair>
<BaseCcy>EUR</BaseCcy>
<QtdCcy>GBP</QtdCcy>
</CcyPair>
</XchgRateBsis>
</Ccy>
<Optn>
<Tp>CALL</Tp>
<ExrcStyle>EURO</ExrcStyle>
<StrkPric>
<Pctg>0.87</Pctg>
</StrkPric>
<PrmAmt>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">200000</Amt>
</PrmAmt>
<PrmPmtDt>2018-06-05
x </PrmPmtDt>
</Optn>
</TxData>
</CmonTradData>
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</New>
44
Expiration date
2018-12-31
46
Final contractual
settlement
date
2019-01-02
47
Delivery type
PHYS
48
Price
49
Price currency
55
Notional amount of
leg 1
1000000
56
Notional currency 1
EUR
64
Notional amount of
leg 2
870000
65
Notional currency 2
GBP
132
Option type
CALL
133
Option style
EURO
134
Strike price
0.87
138
Strike price
currency/currency
pair
EUR/GBP
139
Option premium
amount
200000

216
Table 36 – Reporting of a new FX option
Ite
m
Field
Example
XML example
140
Option premium
currency
EUR
141
Option premium
payment date
2018-06-
05
151
Action type
NEWT
152
Event type
TRAD
154
Level
TCTN
5.4.4 Additional considerations on the reporting of currencies
432. The reporting of the direction of the derivative and of the currencies involved
should be done by parties taking into account their own booking irrespective of the
other party booking. Consequently the direction and the order of currencies may
vary in the reporting. Such difference should be managed by TRs in their
reconciliation process so that direction of the derivative is considered based on the
currencies provided in the reporting.
5.5 Reporting of NDFs
433. Non-deliverable forwards (NDFs) are cash-settled foreign exchange forward
contracts. Such a cash-settled forward contract specifies an exchange rate against
the currency of delivery (the convertible currency), typically the US dollar, a notional
amount of the non-convertible currency and a settlement date. A cash-settled FX
forward contract is akin to a classical physically-settled FX forward contract, but
contrary to the former there is no physical delivery of the designated currencies at
maturity. On the maturity date, the spot market exchange rate is instead compared
to the forward rate in order to value the NDF. The cash-settled contract is settled
on a net basis, in the convertible currency based on the notional amount.
5.5.1 NDF
434. Considering a currency non-deliverable forward (NDF) with the following setup:
- Banks A and B enter in a BRL/USD NDF instrument on 1 June 2018
- notional of the contract: 1,000,000 BRL;
- maturity date of the contract: 31 December 2018;
-settlement date of the contract: 2 January 2019;
- the forward is cash-settled because of its non-deliverable nature;

217
- Bank A delivers or receives the difference (according to its sign) in USD between the
spot and the forward at the settlement date;
- USD is populated in Settlement Currency 1;
- the forward exchange rate is 0.29 BRL/USD.
435. In the case of forwards related to currencies, the counterparty 1 should identify
itself as either the payer or the receiver for leg 1 (BRL in this example). Given that
in this example the reporting counterparty would receive the difference in case of
increase in the BRL value (decrease in the exchange rate), it is identified as the
receiver of leg 1.
436. Price is not populated as the price information is considered to be included in
the forward exchange rate field.
437. Given that there is just one settlement currency, it should be always populated
as settlement currency 1.
Table 37 – Reporting of an NDF
No
Field
Example
XML schema
1
Reporting
timestamp
2018-06-
01T12:00:00Z
<New>
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl>
<LEI>12345678901234500000
> </LEI>
</Lgl>
</Id>
…
<DrctnOrSd><Drctn>
<DrctnOfTheFrstLeg>TAKE
> </DrctnOfTheFrstLeg>
<DrctnOfTheScndLeg>MAKE
> </DrctnOfTheScndLeg>
</Drctn></DrctnOrSd>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl>
<LEI>ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
> </LEI>
</Lgl>
</IdTp>
…
</OthrCtrPty>
</CtrPty>
<RptgTmStmp>2018-06-01T12:00:00Z
> </RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CmonTradData>
<CtrctData>
4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
1234567890123450000
0
9
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQR
ST
18
Direction of leg
1
TAKE
19
Direction of leg
2
MAKE
1
UTI
123NDF
9
Product
classification
JFTXFC
10
Contract type
FORW
11
Asset class
CURR
19
Settlement
currency 1
USD
20
Settlement
currency 2
-
42
Execution
timestamp
2018-06-
01T12:00:00Z
218
Table 37 – Reporting of an NDF
No
Field
Example
XML schema
43
Effective date
2018-06-01
<CtrctTp>FORW</CtrctTp>
<AsstClss>CURR</AsstClss>
<PdctClssfctn>JFTXFC
> </PdctClssfctn>
<SttlmCcy><Ccy>USD</Ccy>
</SttlmCcy>
</CtrctData>
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>123NDF</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
<NtnlAmt>
<FrstLeg>
<Amt Ccy="BRL">1000000</Amt>
</FrstLeg>
<ScndLeg>
<Amt Ccy="USD">290000</Amt>
</ScndLeg>
</NtnlAmt>
…
<DlvryTp>CASH</DlvryTp>
<ExctnTmStmp>2018-06-01T12:00:
> 00Z</ExctnTmStmp>
<FctvDy>2018-06-01</FctvDy>
<XprtnDt>2018-12-31</XprtnDt>
<SttlmDt>2019-01-02</SttlmDt>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>TRAD</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
…
<Ccy>
<FwdXchgRate>0.29
> </FwdXchgRate>
<XchgRateBsis>
<CcyPair>
<BaseCcy>BRL</BaseCcy>
<QtdCcy>USD</QtdCcy>
</CcyPair>
</XchgRateBsis>
</Ccy>
</TxData>
</CmonTradData>
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</New>
44
Expiration date
2018-12-31
46
Final
contractual
settlement
date
2019-01-02
47
Delivery type
CASH
48
Price
49
Price currency
55
Notional
amount of leg 1
1000000
56
Notional
currency 1
BRL
64
Notional
amount of leg 2
290000
65
Notional
currency 2
USD
114
Forward
exchange rate
0.29
115
Exchange rate
basis
BRL/USD
151
Action type
NEWT
152
Event type
TRAD
154
Level
TCTN
5.6 Reporting of CFDs
438. Contracts for Difference (CFDs) generally do not have any specified maturity
date and at the moment of their conclusion the termination date is also not specified.
Counterparties may at any moment decide to close the contract, with immediate

219
effect. They can also close it partially as counterparties may terminate only a part
of the volume on one day and the other part or parts of the contract on any other
day.
439. Each opening of a new contract should be reported by the counterparties to the
TR as a new entry. This means that each CFD be reported with its distinct Unique
Trade Identifier and action type ‘New’ or if the trade is included in a position on the
same day it can be reported with action type ‘Position Component’, even if they are
executed and then netted or terminated for other reasons during the same day.
440. Furthermore, the CFDs have to be reported even if they are concluded with a
counterparty that is not subject to the reporting obligation, such as an individual not
carrying out an economic activity and who is consequently not considered as an
undertaking.
441. Subsequent CFDs do not have to be included in a position, however, it is
strongly recommended to do so. As these derivatives have no maturity, it would
imply that without including in a position each individual CFD by a financial
counterparty would need to receive daily valuation updates until either 1) the CFD
is terminated or 2) infinity. Outstanding CFDs need valuation updates, but when
included in a position, the valuation can be provided at position level in accordance
with the section 4.7.
442. Similarly to any other contract, the reported valuation of a CFD should represent
the total value of the contract, rather than a daily change in its valuation.
443. ESMA considers offsetting CFDs to be reportable derivatives requiring a Unique
Trade Identifier for each derivative. In case CFDs are not netted into a position,
offsetting CFDs need to be terminated.
444. Once the CFD is closed, the counterparty should send a termination report to
the initial entry, completing the field ’Early termination date‘. If the CFD is closed
partially, counterparties send a report with action type ‘Modify’ and event type ‘Early
termination’ to the initial entry, reducing only its notional amount (remaining volume
is equal to the not yet terminated volume). If there is another partial close, yet
another modification report is sent – until the contract is finally closed in whole.
Then, the counterparties send a termination report with action type ‘Terminate’ and
event type ‘Early termination’, completing the field “Early termination date”. In these
cases, the opening price of the contract is reported only in the first report (with
action type ‘New’) and it is not updated in the following modification reports. Please
note that the possibility to modify the notional of a given trade, as just described,
should only be used in the event that both parties in fact agree to partially terminate
that trade. If however they agree to conclude an offsetting trade with a smaller
notional, then a report with action type ‘New’ is required.
5.6.1 CFD
445. The below table illustrates population of fields for a new CFD (that is not
included in a position) on a share XS1234567890. The UPI assigned to that CFD

220
product is AAA111222333. The initial price of the share is 30 EUR and the reporting
counterparty A buys a CFD on 1,000 shares.
Table 38 - Reporting of a new CFD
No
Field
Example
XML message
1
Reporting
timestamp
2023-06-
06T12:00:00Z
<New>
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl>
<LEI>12345678901234500000
> </LEI>
</Lgl>
</Id>
…
<DrctnOrSd>
<CtrPtySd>BYER</CtrPtySd>
</DrctnOrSd>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl>
<LEI>ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
> </LEI>
</Lgl>
</IdTp>
…
</OthrCtrPty>
</CtrPty>
<RptgTmStmp>2023-06-06T12:00:
x 00Z</RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CmonTradData>
<CtrctData>
<CtrctTp>CFDS</CtrctTp>
<AsstClss>EQUI</AsstClss>
<PdctClssfctn>JESXCC
> </PdctClssfctn>
<PdctId><UnqPdctIdr><Id>
AAA111222333
</Id></UnqPdctIdr></PdctId>
<UndrlygInstrm><ISIN>
XS1234567890
</ISIN></UndrlygInstrm>
<SttlmCcy><Ccy>EUR</Ccy>
</CtrctData>
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>123CFD</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
<TxPric>
<Pric>
<MntryVal>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">30</Amt>
4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
12345678901234500000
9
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQR
ST
17
Direction
BYER
1
UTI
123CFD
8
UPI
AAA111222333
9
Product
classification
JESXCC
10
Contract type
CFDS
11
Asset class
EQUI
13
Underlying
identification
type
I
14
Underlying
identification
XS1234567890
19
Settlement
currency 1
EUR
20
Settlement
currency 2
-
42
Execution
timestamp
2023-06-
05T11:43:00Z
43
Effective date
2023-06-05
44
Expiration date
-
46
Final
contractual
settlement
date
-
47
Delivery type
CASH

221
Table 38 - Reporting of a new CFD
No
Field
Example
XML message
48
Price
30
</MntryVal>
</Pric>
</TxPric>
…
<NtnlAmt>
<FrstLeg>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">
> 30000</Amt>
</FrstLeg>
</NtnlAmt>
<NtnlQty>
<FrstLeg>
<TtlQty>1000</TtlQty>
</FrstLeg>
</NtnlQty>
…
<DlvryTp>CASH</DlvryTp>
<ExctnTmStmp>2023-06-05
x T11:43:00Z</ExctnTmStmp>
<FctvDy>2023-06-05</FctvDy>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>TRAD</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
…
</TxData>
</CmonTradData>
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</New>
49
Price currency
EUR
55
Notional
amount of leg
1
30000
56
Notional
currency 1
EUR
60
Total notional
quantity of leg
1
1000
15
1
Action type
NEWT
15
2
Event type
TRAD
15
4
Level
TCTN
5.7 Reporting of equity derivatives
446. Equity derivatives are a type of derivatives whose value is derived, at least
partly, from one or more underlying equity securities. Options and futures are the
most common equity derivatives. The type of contract should be specified in field
2.10 and the asset class (EQUI) should be specified in field 2.11 as indicated in the
RTS and the ITS on reporting.
447. A Total Return Swap is a contract between two parties who exchange returns
from a financial asset (underlying) between them. In this kind of derivatives, one
party makes payments based on a set rate while the other party makes payments
based on the total return of the underlying asset. The underlying assets are usually
a bond, equity, equity index, interest, or loan.
448. For example, a Total Return Swap on an equity index should be reported with
the value ’EQUI’ in field 2.11 ‘Asset Class’, whereas a Total Return Swap on a bond
or loan should be reported with the value ’CRDT’ in field 2.11 ‘Asset Class’.

222
449. The event type ‘Corporate Event’ should be used in the case of lifecycle events
triggered by corporate actions on the underlying equities. See section 4.6 for more
details.
450. The direction of the trade of most equity swaps should be reported following the
approach in which the counterparties would indicate whether the reporting
counterparty is payer/receiver for a given leg at the time of the derivative, using an
indicator in the dedicated fields ( ’Direction of leg 1’ or ’Direction of leg 2‘). See the
section 4.12 of these Guidelines for further details.
451. In addition, as stated in the Article 4 of the ITS on reporting, in the swaps related
to dividends, the counterparty receiving the equivalent dividend amount payments
should be identified as the buyer and the counterparty paying that equivalent
dividend amount payments should be identified as the seller. Furthermore, for
swaps related to securities other than dividend swaps, the counterparty 1 should
identify itself as either the payer or the receiver for leg 1, and the opposite for leg
2. The counterparty 2 should populate these two fields with the opposite values
related to the counterparty 1.
452. More details on the reporting of notional and prices are provided in the section
4.17 of these Guidelines.
453. The strike price of equity options, when this strike price is expressed as
monetary amount, should be reported with any value up to 18 numeric characters
including up to 13 decimal places; e.g.: USD 6.39 expressed as 6.39. If the value
has more than 13 digits after the decimal, reporting counterparties should round
half-up (field 2.134 in the RTS/ITS on reporting).
454. The strike price of equity options should be reported in the currency in which
the strike price is denominated (fields 2.137 and 2.138 in the RTS/ITS on reporting).
5.7.1 Dividend swap
455. A credit institution concludes and reports an equity swap derivative on a single
stock where the return or payout trigger is the dividend. The entity reports also a
collateral and valuation update, according to its internal model. The other
counterparty is an investment firm of its group. The notional amount is EUR 1
million, the transaction is fully collateralised.
Table 39 – Reporting of an equity derivative
No
Field
Example
XML schema
Table 1
<ValtnUpd>
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id><Lgl><LEI>
12345678901234500000
1
Reporting
timestamp
2021-02-24T17:00:00Z
2
Report
submitting
entity ID
12345678901234500000

223
Table 39 – Reporting of an equity derivative
No
Field
Example
XML schema
3
Entity
responsible for
reporting
12345678901234500000
</LEI></Lgl></Id>
<Ntr>
<FI>
<Sctr>
<Cd>CDTI</Cd>
</Sctr>
<ClrThrshld>true
</ClrThrshld>
</FI>
</Ntr>
<DrctnOrSd><Drctn>
<CtrPtySd>SLLR</CtrPtySd>
</Drctn></DrctnOrSd>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl>
<LEI>ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</IdTp>
<Ntr>
<FI>
<Sctr>
<Cd>INVF</Cd>
</Sctr>
<ClrThrshld>true
</ClrThrshld>
</FI>
</Ntr>
</OthrCtrPty>
<SubmitgAgt>
<LEI>12345678901234500000</LEI>
</SubmitgAgt>
<NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<LEI>12345678901234500000</LEI>
</NttyRspnsblForRpt>
</CtrPty>
<Valtn>
<CtrctVal>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">6827412379
</Amt>
</CtrctVal>
<TmStmp>2021-03-02T17:00:00Z
</TmStmp>
<Tp>MTMO</Tp>
</Valtn>
<RptgTmStmp>2021-02-24T17:00:00Z
</RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CmonTradData>
<CtrctData>
<CtrctTp>SWAP</CtrctTp>
4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
12345678901234500000
5
Nature of the
counterparty 1
F
6
Corporate
sector of the
counterparty 1
CDTI
7
Clearing
threshold of
counterparty 1
TRUE
8
Counterparty 2
identifier type
TRUE
9
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
11
Nature of the
counterparty 2
F
12
Corporate
sector of the
counterparty 2
INVF
17
Direction
SLLR
Table 2
1
UTI
AAAAABBBBBCCCCCDDDDD
5
PTRR ID
9
Product
classification
SESDXC
10
Contract type
SWAP
11
Asset class
EQUI
13
Underlying
identification
type
I
14
Underlying
identification
ES1234567890
21
Valuation
amount
6827412379
22
Valuation
currency
EUR
23
Valuation
timestamp
2021-03-02T17:00:00Z
24
Valuation
method
MTMO

224
Table 39 – Reporting of an equity derivative
No
Field
Example
XML schema
26
Collateral
portfolio
indicator
FALSE
<AsstClss>EQUI</AsstClss>
<PdctClssfctn>SESDXC
</PdctClssfctn>
<UndrlygInstrm><ISIN>
ES1234567890
</ISIN></UndrlygInstrm>
<SttlmCcy><Ccy>EUR</Ccy>
</SttlmCcy>
</CtrctData>
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
AAAAABBBBBCCCCCDDDDD
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
<CollPrtflCd>
<Prtfl><NoPrtfl>NOAP
</NoPrtfl></Prtfl>
</CollPrtflCd>
<PltfmIdr>XXXX</PltfmIdr>
<NtnlAmt>
<FrstLeg>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">
1000000</Amt>
</FrstLeg>
</NtnlAmt>
…
<DlvryTp>CASH</DlvryTp>
<ExctnTmStmp>2021-02-23T17:00
:00Z</ExctnTmStmp>
<FctvDy>2021-02-24</FctvDy>
<XprtnDt>2024-06-15</XprtnDt>
<PstTradRskRdctnFlg>
false
</PstTradRskRdctnFlg>
<TradClr>
<ClrOblgtn>FLSE</ClrOblgtn>
<ClrSts><NonClrd><Rsn>
NORE
</Rsn></NonClrd></ClrSts>
<IntraGrp>true</IntraGrp>
</TradClr>
…
</TxData>
</CmonTradData>
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</ValtnUpd>
30
Clearing
obligation
FALSE
31
Cleared
N
37
Intragroup
TRUE
38
PTRR
FALSE
41
Venue of
execution
XXXX
42
Execution
timestamp
2021-02-23T17:00:00Z
43
Effective date
2021-02-24
44
Expiration date
2024-06-15
47
Delivery type
CASH
55
Notional
amount of leg 1
1000000
56
Notional
currency 1
EUR
151
Action type
VALU
152
Event type
154
Level
TCTN
Table 3
7
Collateral
timestamp
2021-03-24T17:00:00Z
<MrgnUpd>
<EvtDt>2021-03-24</EvtDt>

225
Table 39 – Reporting of an equity derivative
No
Field
Example
XML schema
8
Collateral
portfolio
indicator
FALSE
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
AAAAABBBBBCCCCCDDDDD
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
<Coll>
<CollPrtflCd>
<Prtfl>
<NoPrtfl>NOAP<NoPrtfl>
<Prtfl>
</CollPrtflCd>
<CollstnCtgy>FLCL</CollstnCtgy>
<TmStmp>2021-03-24T17:00:00Z
</TmStmp>
</Coll>
<PstdMrgnOrColl>
<InitlMrgnPstdPreHrcut>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">5000000</Amt>
</InitlMrgnPstdPreHrcut>
<InitlMrgnPstdPstHrcut>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">4500000</Amt>
</InitlMrgnPstdPstHrcut>
<VartnMrgnPstdPreHrcut>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">1000000</Amt>
</VartnMrgnPstdPreHrcut>
<VartnMrgnPstdPstHrcut>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">800000</Amt>
</VartnMrgnPstdPstHrcut>
</PstdMrgnOrColl>
<RcvdMrgnOrColl>
<InitlMrgnRcvdPreHrcut>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">5000000</Amt>
</InitlMrgnRcvdPreHrcut>
<InitlMrgnRcvdPstHrcut>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">4300000</Amt>
</InitlMrgnRcvdPstHrcut>
</RcvdMrgnOrColl>
</MrgnUpd>
9
Collateral
portfolio code
10
UTI
AAAAABBBBBCCCCCDDDDD
11
Collateralisation
category
FLCL
12
Initial margin
posted by
counterparty 1
(pre haircut)
5000000
13
Initial margin
posted by the
counterparty 1
(post haircut)
4500000
14
Currency of the
initial margin
posted
EUR
15
Variation
margin posted
by the
counterparty 1
(pre-haircut)
1000000
16
Variation
margin posted
by the
counterparty 1
(post-haircut)
800000
17
Currency of the
variation
margins posted
EUR
20
Initial margin
collected by the
counterparty 1
(pre-haircut)
5000000
21
Initial margin
collected by the
counterparty 1
(post-haircut)
4300000
22
Currency of
initial margin
collected
EUR
23
Variation
margin
collected by the
counterparty 1
(pre-haircut)

226
Table 39 – Reporting of an equity derivative
No
Field
Example
XML schema
24
Variation
margin
collected by the
counterparty 1
(post-haircut)
25
Currency of
variation margin
collected
28
Action type
MARU
29
Event date
2021-03-24
456. Another example on ETDs future on equities can be found in the section 4.8.
5.8 Reporting of credit derivatives
457. A credit derivative is a financial contract in which the underlying is a credit asset
(debt or fixed-income instrument). The purpose of a credit derivative is to transfer
credit risk without transferring the asset itself. The type of contract should be
specified in field 2.10 and the asset class (’CRDT’) should be specified in the field
2.11.
458. Total Return Swaps (defined above in the section Reporting of equity
derivatives of these Guidelines) should be classified based on the underlying. For
example, a Total Return Swap on an equity index should be reported with the value
’EQUI’ in the field 2.11 whereas a Total Return Swap on a bond or loan should be
reported with the value ‘CRDT’.
459. In the case of credit derivatives following a change in the index factor (field 2.147
in the RTS on reporting) due to credit events, the counterparties should not modify
the notional, but rather they should only update the index factor.
460. With regard to the reporting of reference entity (field 2.144) for credit derivatives,
ISO 3166 and ISO 3166-2 codes should only be used in the case of credit
derivatives where the reference entity is a supranational, a sovereign or a
municipality, respectively. In all other cases the reference entity should be identified
with a LEI.
461. In the case of the reporting of a CDS with a coupon payment realised in a single
payment on the maturity date rather than with a monthly, quarterly, semi-annual or
annual frequency, counterparties should populate the field 2.81 ’Fixed rate or
coupon payment frequency period leg 1‘ of the ITS on reporting using the code
‘EXPI’ = payment at term.
462. CDS index tranches are standardised synthetic collateralised debt obligations
(CDOs) based on a CDS index, where each tranche references a different segment

227
of the loss distribution of the underlying CDS index. The riskiness of a tranche
decreases with the tranche’s seniority in the securitisation’s capital structure. This
enables investors to take on exposures to specific segments of the CDS index
default loss distribution where each tranche has a different sensitivity to credit risk
correlations among entities in the index.
463. Tranches of a CDS index that absorb losses sequentially are defined by an
attachment and a detachment point. They are defined in the fields 2.149 and 2.150
of the RTS on reporting.
464. Both data elements, attachment and detachment points, are not applicable if
the derivative is not a CDS tranche derivative (index or custom basket).
465. For example, the notional in a tranche with an attachment point of 3% and a
detachment point of 6% will be reduced after there have been 3% of losses in the
portfolio. 6% losses in the portfolio deplete the notional of the tranche.
466. ’Credit event’ event type applies only to credit derivatives. It is defined as a credit
event that results in a modification of a credit derivative, at a trade or position level.
For further details see section 4.6 in these Guidelines.
467. In accordance with the Article 4 of ITS on reporting, in the case of derivative
instruments for the transfer of credit risk as the credit derivatives (mainly CDSs),
the counterparty buying the protection should be identified as the buyer and the
counterparty selling the protection should be identified as the seller. In the case of
options and swaptions the rule under Article 4(2) of the ITS on reporting applies,
i.e. the buyer of the option/swaption should be identified as the buyer.
468. The price of credit default swaps and credit total return swaps should be
reported in the fields ‘Fixed rate’, ‘Spread’ and ‘Other payment amount’ (with field
‘Other payment type’ =’UFRO’). More details are provided in the section 4.174.17
of this guideline.
469. For Credit Default Swaps (CDS), when an underlying is reported, the ISIN of
the reference obligation should be provided (field 2.14).
470. The strike price of credit swaptions quoted in spread, when this strike price is
expressed as percentage, should be reported with value up to 11 numeric
characters including up to 10 decimal places; e.g.: 2.1 instead of 2.1% (fields 2.134
and 2.137).
471. The seniority of the debt security, or debt basket or index underlying a derivative
should be reported in ‘Seniority’ field for credit derivatives (field 2.143).
472. If it is applicable, the series number of the composition of the index used should
be reported for credit derivatives as well as a new version of a series is issued if
one of the constituents defaults and the index has to be re-weighted to account for
the new number of total constituents within the index (fields 2.145 and 2.146).
473. If a credit derivative contract is tranched, field 2.148 ‘Tranche’ should be
reported as ‘True’.
474. The field 2.47 ‘Delivery type’ for credit derivatives in the case of credit event
auction should be reported as ‘CASH‘ (Cash) for credit derivatives that are cash-

228
settled. However, the counterparties should report ‘PHYS’ (Physical) in the case of
physical delivery of the underlying of the credit derivative from the counterparty that
is protection buyer to the other counterparty.
5.8.1 CDS
475. A French investment firm reports the recent purchase, priced with an internal
model, of a default protection. This protection is based on a bilateral derivative
entered into with an Irish investment entity. The notional of the derivative is
520.000.000 EUR. The derivative falls into the category of CDS tranche derivative
with an attachment point of 10% and detachment point of 20%. The underlying of
the derivative corresponds to a certain series of the Itraxx Europe index. A fixed
monthly coupon of 1% is paid. The derivative is partially collateralised by the
purchaser.
Table 40 - Reporting of a CDS
No
Field
Example
XML schema
Table 1
<New>
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPrty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl>
<LEI>12345678901234500000</LEI>
</Lgl>
</Id>
<Ntr>
<FI>
<Sctr>
<Cd>INVF</Cd>
</Sctr>
<ClrThrshld>true
</ClrThrshld>
</FI>
</Ntr>
<DrctnOrSd>
<Drctn>
<CtrPtySd>BYER
</CtrPtySd
</Drctn>
</DrctnOrSd>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl>
<LEI>ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI>
</Lgl>
1
Reporting
timestamp
2020-05-19T14:23:26Z
2
Report
submitting
entity ID
12345678901234500000
3
Entity
responsible for
reporting
12345678901234500000
4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
12345678901234500000
5
Nature of the
counterparty 1
F
6
Corporate
sector of the
counterparty 1
INVF
7
Clearing
threshold of
counterparty 1
TRUE
8
Counterparty 2
identifier type
TRUE
9
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRS
T
11
Nature of the
counterparty 2
F
12
Corporate
sector of the
counterparty 2
INVF

229
Table 40 - Reporting of a CDS
No
Field
Example
XML schema
17
Direction
BYER
</Id>
<Ntr>
<FI>
<Sctr>
<Cd>INVF</Cd>
</Sctr>
</FI>
</Ntr>
</OthrCtrPty>
<SubmitgAgt>
<LEI>1234567890
1234500000</LEI>
</SubmitgAgt>
<NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000</LEI>
</NttyRspnsblForRpt>
</CtrPrty>
<Valtn>
<CtrctVal>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">
8954030.09</Amt>
</CtrctVal>
<TmStmp>
2020-05-19T14:23:26Z
</TmStmp>
<Tp>MTMO</Tp>
</Valtn>
<RptgTmStmp>2020-05-19T
14:23:26Z</RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CmonTradData>
<CtrctData>
<CtrctTp>SWAP</CtrctTp>
<AsstClss>CRDT</AsstClss>
<PdctClssfctn>SCVCCA
</PdctClssfctn>
<UndrlygInstrm>
<Indx>
<Nm>ITRAXX EUROPE SERIES
28 V</Nm>
</Indx>
</UndrlygInstrm>
</CtrctData>
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
AABBCCDDEEFF
GGHHIIPP
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
<CollPrtflCd>
<Prtfl>
<NoPrtfl>NOAP</NoPrtfl>
Table 2
1
UTI
AABBCCDDEEFFGGHHIIPP
5
PTRR ID
9
Product
classification
SCVCCA
10
Contract type
SWAP
11
Asset class
CRDT
13
Underlying
identification
type
X
14
Underlying
identification
15
Indicator of the
underlying
index
16
Name of the
underlying
index
ITRAXX EUROPE SERIES
28 V
21
Valuation
amount
8954030.09
22
Valuation
currency
EUR
23
Valuation
timestamp
2020-05-19T14:23:26Z
24
Valuation
method
MTMO
26
Collateral
portfolio
indicator
FALSE
28
Confimation
timestamp
2020-05-18T14:39:32Z
29
Confirmed
ECNF
30
Clearing
obligation
UKWN
31
Cleared
N
37
Intragroup
FALSE
38
PTRR
FALSE
41
Venue of
execution
XXXX
42
Execution
timestamp
2020-05-18T14:39:32Z
43
Effective date
2020-05-19
44
Expiration date
2022-12-20
47
Delivery type
PHYS

230
Table 40 - Reporting of a CDS
No
Field
Example
XML schema
55
Notional
amount of leg 1
520000000
</Prtfl>
</CollPrtflCd>
<PltfmIdr>XXXX</PltfmIdr>
<NtnlAmt>
<FrstLeg>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">
520000000</Amt>
</FrstLeg>
</NtnlAmt>
<DlvryTp>PHYS</DlvryTp>
<ExctnTmStmp>2020-05-18
T14:39:32Z</ExctnTmStmp>
<FctvDt>2020-05-19</FctvDt>
<XprtnDt>2022-12-20</XprtnDt>
<PstTradRskRdctnEvt>
false</PstTradRskRdctnEvt>
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>TRAD</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
<TradConf>
<Confd>
<Tp>ECNF</Tp>
<TmStmp>
2020-05-18T14:39:32Z
</TmStmp>
</Confd>
</TradConf>
<TradClr>
<ClrOblgtn>UKWN</ClrOblgtn>
<ClrSts>
<NonClrd><Rsn>NORE</Rsn>
</NonClrd>
</ClrSts>
<IntraGrp>false</IntraGrp>
</TradClr>
<IntrstRate>
<FrstLeg>
<Fxd>
<Rate>
<Rate>0.01</Rate>
</Rate>
<DayCnt><Cd>A004
</Cd></DayCnt>
<PmtFrqcy>
<Term>
<Unit>MNTH</Unit>
<Val>1</Val>
</Term>
</PmtFrqcy>
</Fxd>
</FrstLeg>
</IntrstRate>
<Cdt>
<Snrty>SNDB</Snrty>
<Srs>28</Srs>
56
Notional
currency 1
EUR
79
Fixed rate of
leg 1 or coupon
0.01
80
Fixed rate or
coupon day
count
convention leg
1
A004
81
Fixed rate or
coupon
payment
frequency
period leg 1
MNTH
82
Fixed rate or
coupon
payment
frequency
period multiplier
leg 1
1
143
Seniority
SNDB
144
Reference
entity
145
Series
28
146
Version
2
147
Index factor
1
148
Tranche
TRUE
149
CDS index
attachment
point
0.10
150
CDS index
detachment
point
0.20
151
Action type
NEWT
152
Event type
TRAD
154
Level
TCTN

231
Table 40 - Reporting of a CDS
No
Field
Example
XML schema
<Vrsn>2</Vrsn>
<IndxFctr>1</IndxFctr>
<Trch>
<Trnchd>
<AttchmntPt>0.10
</AttchmntPt>
<DtchmntPt>0.20
</DtchmntPt>
</Trnchd>
</Trch>
</Cdt>
</TxData>
</CmonTradData>
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</New>
Table 3
7
Collateral
timestamp
2020-05-18T14:39:32Z
<MrgnUpd>
<EvtDt>2020-05-18</EvtDt>
<Coll>
<CollPrtflCd>
<Prtfl>
<NoPrtfl>NOAP</NoPrtfl>
</Prtfl>
</CollPrtflCd>
<CollstnCtgy>PRC1</CollstnCtgy>
<TmStmp>2020-05-
18T14:39:32Z</TmStmp>
</Coll>
<PstdMrgnOrColl>
<VartnMrgnPstdPreHrcut>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">1000000</Amt>
</VartnMrgnPstdPreHrcut>
<VartnMrgnPstdPstHrcut>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">745000</Amt>
</VartnMrgnPstdPstHrcut>
</PstdMrgnOrColl>
</MrgnUpd>
8
Collateral
portfolio
indicator
FALSE
9
Collateral
portfolio code
11
Collateralisatio
n category
PRC1
12
Initial margin
posted by the
counterparty 1
(pre-haircut)
13
Initial margin
posted by the
counterparty 1
(post-haircut)
14
Currency of the
initial margin
posted
15
Variation
margin posted
by the
counterparty 1
(pre-haircut)
1000000
16
Variation
margin posted
by the
counterparty 1
(post-haircut)
745000

232
Table 40 - Reporting of a CDS
No
Field
Example
XML schema
17
Currency of the
variation
margins posted
EUR
20
Initial margin
collected by the
counterparty 1
(pre-haircut)
21
Initial margin
collected by the
counterparty 1
(post-haircut)
22
Currency of
initial margin
collected
23
Variation
margin
collected by the
counterparty 1
(pre-haircut)
24
Variation
margin
collected by the
counterparty 1
(post-haircut)
25
Currency of
variation
margin
collected
28
Action type
MARU
29
Event date
2020-05-18
5.9 Reporting of commodity derivatives
476. Table 2 of the RTS on reporting contains dedicated fields for reporting of
commodity derivatives: fields 2.116-2.118 for all commodity deriatives and
additional fields 2.119-2.131 for energy derivatives.
477. In particular, the classification of commodities should be reported in the fields
2.116-2.118 in line with the categories specified in the Table 4 of the ITS on
reporting. The reported classification of the underlying commodity should be as
granular as possible. For example, in the case of derivatives on gold, the
counterparty should specify ‘Metals’, ‘Precious’ and ‘Gold’ in the fields 2.116, 2.117
and 2.118, respectively. Only if the underlying commodity does not correspond to
any of the specific categories included in the ITS on reporting, it should be reported
as ‘Other’. In case no specific values are set out in the ITS on reporting for a given
product for fields 2.117 and 2.118 (e.g. for the category ‘Multi Commodity Exotic’),

233
the counterparty should not report any values for these fields, in line with the XML
schema.
478. The counterparties should not identify commodities in the currency fields, even
if a dedicated code has been designated to such commodity in the ISO 4217
standard (e.g.XAU for gold or XBA for silver). The commodities should only be
identified via commodity classification fields.
479. The commodity classification fields (2.116-2.118) are not repeatable. Therefore,
in the case of commodity swaps including two commodity underlyings, the
counterparty should report such swap as a complex trade composed of two
commodity forwards and populate the Package ID in both reports (see section
4.28).
480. In the case of derivatives based on electricity or natural gas, the counterparties
should report fields 2.119-2.131 (in addition to other relevant reportable details
concerning the derivative and the counterparties, as illustrated in other sections).
481. The fields 2.122-2.131 for energy derivatives are repeatable. Additionally, for
the field 2.127 ‘Days of the week’ it is possible to report multiple values, e.g. MOND,
TUED (Mo-Tu) or WDAY, XBHL (weekdays excluding bank holidays) or other
combinations.
5.9.1 Electricity future
482. Table 41 shows an example of a peak load future on the price of electricity in
the Spanish wholesale market. The contract is negotiated in MWh/h and the
delivery should take place in Q2 2022 for a 100 MWh at 58 euros.
Table 41- Reporting of a peak-load electricity future
No
Field
Example
XML message
116
Base product
NRGY
<Cmmdty>
<Ngry>
<Elctrcty>
<BasePdct>NRGY</BasePdct>
<SubPdct>ELEC</SubPdct>
<AddtlSubPdct>PKLD
</AddtlSubPdct>
</Elctrcty>
</Ngry>
</Cmmdty>
<NrgySpcfcAttrbts>
<DlvryPtOrZone>
<Cd>10YES-REE------0</Cd>
</DlvryPtOrZone>
<IntrCnnctnPt>
<Cd>XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX</Cd>
</IntrCnnctnPt>
<LdTp>PKLD</LdTp>
<DlvryAttr>

234
Table 41- Reporting of a peak-load electricity future
No
Field
Example
XML message
<DlvryIntrvl>
<FrTm>08:00:00Z</FrTm>
<ToTm>19:59:59Z</ToTm>
</DlvryIntrvl>
<DlvryDt>
<FrDt>2022-04-01</FrDt>
<ToDt>2022-06-30</ToDt>
</DlvryDt>
<Drtn>QURT</Drtn>
<WkDay>WDAY</WkDay>
<DlvryCpcty>
<Qty>100</Qty>
</DlvryCpcty>
<QtyUnit>
<Cd>MWHH</Cd>
</QtyUnit>
<PricTmIntrvlQty>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">58</Amt>
</PricTmIntrvlQty>
</DlvryAttr>
</NrgySpcfcAttrbts>
117
Sub-product
ELEC
118
Further sub-
product
PKLD
119
Delivery point or
zone
10YES-REE------0
120
Interconnection
point
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
121
Load type
PKLD
122
Delivery interval
start time
08:00:00Z
123
Delivery interval
end time
19:59:59Z
124
Delivery start
date
2022-04-01
125
Delivery end
date
2022-06-30

235
Table 41- Reporting of a peak-load electricity future
No
Field
Example
XML message
126
Duration
QURT
127
Days of the
week
WDAY
128
Delivery
capacity
100
129
Quantity unit
MWHH
130
Price/time
interval quantity
58
131
Currency of the
price/time
interval quantity
EUR
6 EMIR Tables of fields
483. Article 1(1) of the RTS on reporting provides that “Reports to trade repositories
made pursuant to Article 9 of Regulation (EU) No 648/2012 shall include the
complete and accurate details set out in Tables 1, 2 and 3 of the Annex that pertain
to the derivative concerned.” The use cases included in sections 6.1, 6.2, and 6.3
do not necessarily include all the fields that pertain to the derivative concerned, but
they focus on specific sections of data fields in order to provide more granular and
detailed guidance on the reporting without any unnecessary repetition or inclusion
of other data elements.
484. The validation rules contain the complete guidance on applicable fields per
action type and level, as well as the relevant dependencies.
485. The following sections include various scenarios and corresponding tables
clarifying how these scenarios should be reported. Each table shows the reporting
fields under the ITS on reporting. The column ‘Field’ shows each field name, and
the column ‘Example’ provides an example of what would be included in that field.
The final column entitled ‘XML Message’ shows the format of the XML message
which should be submitted in the report.
486. Unless otherwise stated in the specific scenario, the following background
information applies to all scenarios set out in section 6:
Counterparty A is a German financial counterparty identified with LEI 12345678901234500000

236
Counterparty B is an Italian financial counterparty identified with LEI ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
Counterparty C is a Spanish NFC- identified with LEI 123456789ABCDEFGHIJK
Counterparty D is a French NFC+ identified with LEI 11223344556677889900
Counterparty J acts also as a clearing member and is identified with LEI
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
CCP O is identified with LEI BBBBBBBBBB1111111111
6.1 Table 1 Counterparty data
487. This section of the Guidelines details the population of the counterparty data
section for several different use cases. The actual reporting in accordance with the
ISO 20022 XML schemas is provided too.
488. When a derivative is cleared, each counterparty should report in the ‘Clearing
member’ field its clearing member.
489. When a voluntary delegation of reporting or allocation of responsibility exists,
the report submitting entity or entity responsible for reporting should submit
separately the counterparty data, the contract data and collateral data for each of
the two sides reported.
490. When there are use cases that cover two or more of the use cases included
below, the reporting counterparties, the entities responsible for reporting or the
report submitting entities should include all the relevant details based on the below
guidance.
Table 42
Use Cases
Cleared Option between FCs (ETD)
Cleared Option between FCs with voluntary delegation agreement (ETD)
Non-Cleared Option between FCs
OTC Option between NFC - and FC
OTC Option between NFC - and NFC +
OTC Contract type between FCs which requires the population of fields
‘Direction of Leg 1’ and ‘Direction of Leg 2’
6.1.1 Cleared Option between FCs (ETD)
491. Table 43 illustrates reporting of an ETD cleared option where the counterparty
1 (counterparty A with LEI 12345678901234500000) is a German Financial
Counterparty above the clearing thresholds, submit its own report (i.e. there is no
separate report submitting entity) and is the entity responsible for reporting. The

237
option is concluded with the counterparty 2 (counterparty B with LEI
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST) which is an Italian Financial Counterparty above the
clearing threshold. Counterparty A accesses the CCP via clearing member J
(counterparty J with LEI CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC).
492. It should be noted that ‘Central counterparty’ field pertains to Table 2, and hence
its population is covered in section 6.2.
Table 43 - Cleared Option between FCs (ETD)
No
Field
Example
Xml message
1
Reporting
timestamp
2021-03-
17T15:17:00Z
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPrty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl><LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI></Lgl>
</Id>
<Ntr>
<FI>
<Sctr>
<Cd>CDTI</Cd>
</Sctr>
<ClrThrshld>true
</ClrThrshld>
</FI>
</Ntr>
<DrctnOrSd>
<Drctn>
<CtrPtySd>BYER
</CtrPtySd
</Drctn>
</DrctnOrSd>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl><LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI></Lgl>
</Id>
<Ntr>
<FI>
<Sctr>
<Cd>CDTI</Cd>
</Sctr>
<ClrThrshld>true
</ClrThrshld>
</FI>
</Ntr>
<RptgOblgtn>true
</RptgOblgtn>
</OthrCtrPty>
2
Report submitting
entity ID
12345678901234500000
3
Entity responsible
for reporting
12345678901234500000
4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
12345678901234500000
5
Nature of the
counterparty 1
F
6
Corporate sector of
the counterparty 1
CDTI
7
Clearing threshold
of counterparty 1
TRUE
8
Counterparty 2
identifier type
TRUE
9
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
10
Country of the
counterparty 2
11
Nature of the
counterparty 2
F
12
Corporate sector of
the counterparty 2
CDTI
13
Clearing threshold
of counterparty 2
TRUE

238
Table 43 - Cleared Option between FCs (ETD)
No
Field
Example
Xml message
14
Reporting
obligation of the
counterparty 2
TRUE
<SubmitgAgt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</SubmitgAgt>
<NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<ClrMmb>
<Lgl><LEI>
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
</LEI></Lgl>
</ClrMmb>
</CtrPrty>
<RptgTmStmp>2020-05-19T
14:23:26Z</RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
15
Broker ID
16
Clearing member
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
C
17
Direction
BYER
18
Direction of leg 1
19
Direction of leg 2
20
Directly linked to
commercial activity
or treasury
financing
6.1.2 Cleared Option between FCs with voluntary delegation agreement (ETD)
493. Table 44 illustrates reporting of an ETD cleared option where the counterparty
1 (counterparty A with LEI 12345678901234500000) is a German Financial
Counterparty above the clearing thresholds, is the entity responsible for reporting
but delegates its reporting to the other counterparty (counterparty B with LEI
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST). The option is concluded with the counterparty 2
(counterparty B) which is an Italian Financial Counterparty above the clearing
threshold.
494. Counterparty A accesses the CCP via clearing member J (counterparty J with
LEI CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC).
495. It should be noted that ‘Central counterparty’ field pertains to Table 2, and hence
its population is covered in section 6.2.
Table 44 - Cleared Option between FCs with voluntary delegation agreement (ETD)
No
Field
Example
Xml message
1
Reporting
timestamp
2021-03-
17T15:17:00Z
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl><LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI></Lgl>
2
Report
submitting
entity ID
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
3
Entity
responsible for
reporting
12345678901234500000

239
Table 44 - Cleared Option between FCs with voluntary delegation agreement (ETD)
No
Field
Example
Xml message
4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
12345678901234500000
</Id>
<Ntr>
<FI>
<Sctr>
<Cd>CDTI</Cd>
</Sctr>
<ClrThrshld>true
</ClrThrshld>
</FI>
</Ntr>
<DrctnOrSd>
<Drctn>
<CtrPtySd>BYER
</CtrPtySd
</Drctn>
</DrctnOrSd>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl>
<LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</IdTp>
<Ntr>
<FI>
<Sctr>
<Cd>CDTI</Cd>
</Sctr>
<ClrThrshld>true
</ClrThrshld>
</FI>
</Ntr>
<RptOblgtn>true
</RptOblgtn>
</OthrCtrPty>
<SubmitgAgt>
<LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI>
</SubmitgAgt>
<NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<ClrMmb>
<LEI>
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
</LEI>
</ClrMmb>
</CtrPty>
<RptgTmStmp>
5
Nature of the
counterparty 1
F
6
Corporate
sector of the
counterparty 1
CDTI
7
Clearing
threshold of
counterparty 1
TRUE
8
Counterparty 2
identifier type
TRUE
9
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
10
Country of the
counterparty 2
11
Nature of the
counterparty 2
F
12
Corporate
sector of the
counterparty 2
CDTI
13
Clearing
threshold of
counterparty 2
TRUE
14
Reporting
obligation of
the
counterparty 2
TRUE
15
Broker ID
16
Clearing
member
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
17
Direction
BYER
18
Direction of leg
1
19
Direction of leg
2
20
Directly linked
to commercial
activity or
treasury
financing
240
Table 44 - Cleared Option between FCs with voluntary delegation agreement (ETD)
No
Field
Example
Xml message
2021-03-17T15:17:00Z
</RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
6.1.3 Non-Cleared Option between FCs
496. Table 45 illustrates reporting of a non cleared option where the counterparty 1
(counterparty A with LEI 12345678901234500000) is a German Financial
Counterparty above the clearing thresholds, is the entity responsible for reporting
and report its own report. The option is concluded with the counterparty 2
(counterparty B with LEI ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST) which is an Italian
Financial Counterparty above the clearing threshold.
Table 45 – Non cleared option between FCs
No
Field
Example
Xml message
1
Reporting timestamp
2021-03-
17T15:17:00Z
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl><LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI></Lgl>
</Id>
<Ntr>
<FI><Sctr>
<Cd>CDTI</Cd>
</Sctr>
<ClrThrshld>true
</ClrThrshld></FI>
</Ntr>
<DrctnOrSd>
<Drctn>
<CtrPtySd>BYER
</CtrPtySd
</Drctn>
</DrctnOrSd>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl>
<LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
2
Report submitting
entity ID
12345678901234500000
3
Entity responsible for
reporting
12345678901234500000
4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
12345678901234500000
5
Nature of the
counterparty 1
F

241
Table 45 – Non cleared option between FCs
No
Field
Example
Xml message
6
Corporate sector of
the counterparty 1
CDTI
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</IdTp>
<Ntr>
<FI><Sctr>
<Cd>CDTI</Cd>
</Sctr>
<ClrThrshld>true
</ClrThrshld></FI>
</Ntr>
<RptOblgtn>true
</RptOblgtn>
</OthrCtrPty>
<SubmitgAgt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</SubmitgAgt>
<NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</NttyRspnsblForRpt>
</CtrPty>
<RptgTmStmp>
2021-03-17T15:17:00Z
</RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
7
Clearing threshold of
counterparty 1
TRUE
8
Counterparty 2
identifier type
TRUE
9
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQ
RST
10
Country of the
counterparty 2
11
Nature of the
counterparty 2
F
12
Corporate sector of
the counterparty 2
CDTI
13
Clearing threshold of
counterparty 2
TRUE
14
Reporting obligation
of the counterparty 2
TRUE
15
Broker ID
16
Clearing member

242
Table 45 – Non cleared option between FCs
No
Field
Example
Xml message
17
Direction
BYER
18
Direction of leg 1
19
Direction of leg 2
20
Directly linked to
commercial activity
or treasury financing
6.1.4 OTC Option between NFC - and FC
497. Table 46 illustrates reporting of OTC option where the counterparty 1
(counterparty C with LEI 123456789ABCDEFGHIJK) is a Spanish Non-Financial
Counterparty below the clearing thresholds. The option is concluded with the
counterparty 2 (counterparty A with LEI 12345678901234500000) which is a
German Financial Counterparty above the clearing threshold. In this case the
counterparty A is entity responsible for reporting and the report submitting entity in
accordance with the provisions on allocation of responsibility for reporting.
Table 46 – OTC between NFC- and FC
No
Field
Example
Xml message
1
Reporting timestamp
2021-03-
17T15:17:00Z
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl><LEI>
123456789ABCDEFGHIJK
</LEI></Lgl>
</Id>
<Ntr>
<NFI><Sctr><Id>K
</Id></Sctr>
<ClrThrshld>false
</ClrThrshld>
<DrctlyLkdActvty>
false
</DrctlyLkdActvty>
</NFI>
2
Report submitting entity
ID
123456789012345000
00
3
Entity responsible for
reporting
123456789012345000
00
4
Counterparty 1 (Reporting
counterparty)
123456789ABCDEFG
HIJK
5
Nature of the counterparty
1
N

243
Table 46 – OTC between NFC- and FC
No
Field
Example
Xml message
6
Corporate sector of the
counterparty 1
K
</Ntr>
<DrctnOrSd>
<Drctn>
<CtrPtySd>BYER
</CtrPtySd
</Drctn>
</DrctnOrSd>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</IdTp>
<Ntr>
<FI><Sctr><Cd>CDTI
</Cd></Sctr>
<ClrThrshld>true
</ClrThrshld></FI>
</Ntr>
<RptOblgtn>true
</RptOblgtn>
</OthrCtrPty>
<SubmitgAgt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</SubmitgAgt>
<NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</NttyRspnsblForRpt>
</CtrPty>
<RptgTmStmp>
2021-03-17T15:17:00Z
</RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
…
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
7
Clearing threshold of
counterparty 1
FALSE
8
Counterparty 2 identifier
type
TRUE
9
Counterparty 2
123456789012345000
00
10
Country of the
counterparty 2
11
Nature of the counterparty
2
F
12
Corporate sector of the
counterparty 2
CDTI
13
Clearing threshold of
counterparty 2
TRUE
14
Reporting obligation of the
counterparty 2
TRUE
15
Broker ID
16
Clearing member
-
17
Direction
BYER
18
Direction of leg 1
19
Direction of leg 2
20
Directly linked to
commercial activity or
treasury financing
FALSE
15
4
Level
TCTN
6.1.5 OTC Option between NFC - and NFC +
498. Table 47 illustrates reporting of OTC option where the counterparty 1
(counterparty C with LEI 123456789ABCDEFGHIJK) is a Spanish Non-Financial
Counterparty below the clearing thresholds. The option is concluded with the
counterparty 2 (counterparty D with LEI 11223344556677889900) which is a

244
French Non-Financial Counterparty above the clearing threshold. Counterparty C
is the entity responsible for reporting and the report submitting entity.
Table 47 – OTC between NFC- and NFC+
No
Field
Example
Xml message
1
Reporting
timestamp
2021-03-
17T15:17:00Z
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl><LEI>
123456789ABCDEFGHIJK
</LEI></Lgl>
</Id>
<Ntr>
<NFI><Sctr><Id>K
</Id></Sctr>
<ClrThrshld>false
</ClrThrshld>
<DrctlyLkdActvty>
false
</DrctlyLkdActvty>
</NFI>
</Ntr>
<DrctnOrSd>
<Drctn>
<CtrPtySd>BYER
</CtrPtySd
</Drctn>
</DrctnOrSd>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl>
<LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</IdTp>
<Ntr>
<NFI><Sctr><Id>L
</Id></Sctr>
<ClrThrshld>true
</ClrThrshld>
</NFI>
</Ntr>
<RptOblgtn>true
</RptOblgtn>
</OthrCtrPty>
<SubmitgAgt>
<LEI>
123456789ABCDEFGHIJK
</LEI>
</SubmitgAgt>
<NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<LEI>
123456789ABCDEFGHIJK
2
Report
submitting
entity ID
123456789ABCDEFGHIJK
3
Entity
responsible for
reporting
123456789ABCDEFGHIJK
4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
123456789ABCDEFGHIJK
5
Nature of the
counterparty 1
N
6
Corporate
sector of the
counterparty 1
K
7
Clearing
threshold of
counterparty 1
FALSE
8
Counterparty 2
identifier type
TRUE
9
Counterparty 2
11223344556677889900
10
Country of the
counterparty 2
11
Nature of the
counterparty 2
N
12
Corporate
sector of the
counterparty 2
L
13
Clearing
threshold of
counterparty 2
TRUE
14
Reporting
obligation of
the
counterparty 2
TRUE
15
Broker ID
16
Clearing
member
17
Direction
BYER
18
Direction of leg
1

245
Table 47 – OTC between NFC- and NFC+
No
Field
Example
Xml message
19
Direction of leg
2
</LEI>
</NttyRspnsblForRpt>
</CtrPty>
<RptgTmStmp>
2021-03-17T15:17:00Z
</RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
…
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
20
Directly linked
to commercial
activity or
treasury
financing
FALSE
154
Level
TCTN
6.1.6 OTC Contract type which requires the population of fields ‘Direction of Leg 1’
and ‘Direction of Leg 2’ between FCs
499. Table 48 illustrates reporting of an OTC Contract type which requires the
population of fields ‘Direction of Leg 1’ and ‘Direction of Leg 2’ where the
counterparty 1 (counterparty A with LEI 12345678901234500000) is a German
Financial Counterparty above the clearing thresholds. The contract is concluded
with the counterparty 2 (counterparty B with LEI ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST)
which is an Italian Financial Counterparty above the clearing threshold.
Table 48 - OTC Contract type which requires the population of fields Direction of Leg
1 and Direction of Leg 2 between FCs
No
Field
Example
Xml message
1
Reporting
timestamp
2021-03-
17T15:17:00Z
<<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl><LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI></Lgl>
</Id>
<Ntr>
<FI><Sctr><Cd>CDTI</Cd>
</Sctr><ClrThrshld>true
</ClrThrshld></FI>
</Ntr>
<DrctnOrSd><Drctn>
<DrctnOfTheFrstLeg>MAKE
> </DrctnOfTheFrstLeg>
<DrctnOfTheScndLeg>TAKE
</DrctnOfTheScndLeg>
</Drctn></DrctnOrSd>
2
Report
submitting
entity ID
12345678901234500000
3
Entity
responsible for
reporting
12345678901234500000
4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
12345678901234500000
5
Nature of the
counterparty 1
F
246
Table 48 - OTC Contract type which requires the population of fields Direction of Leg
1 and Direction of Leg 2 between FCs
No
Field
Example
Xml message
6
Corporate
sector of the
counterparty 1
CDTI
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl>
<LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</IdTp>
<Ntr>
<FI><Sctr><Cd>CDTI</Cd>
</Sctr><ClrThrshld>true
</ClrThrshld></FI>
</Ntr>
<RptOblgtn>true
</RptOblgtn>
</OthrCtrPty>
<SubmitgAgt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</SubmitgAgt>
<NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</NttyRspnsblForRpt>
</CtrPty>
<RptgTmStmp>
2021-03-17T15:17:00Z
</RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
7
Clearing
threshold of
counterparty 1
TRUE
8
Counterparty 2
identifier type
TRUE
9
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
10
Country of the
counterparty 2
11
Nature of the
counterparty 2
F
12
Corporate
sector of the
counterparty 2
CDTI
13
Clearing
threshold of
counterparty 2
TRUE
14
Reporting
obligation of
the
counterparty 2
TRUE
15
Broker ID
16
Clearing
member
17
Direction
-
18
Direction of leg
1
MAKE
19
Direction of leg
2
TAKE
20
Directly linked
to commercial
activity or
treasury
financing

247
6.2 Table 2 Common data
500. Following the population of the counterparty data fields, the population of the
common data fields for different use cases is included. The reporting in accordance
with the ISO 20022 XML schemas is provided too.
501. Each of the subsections includes a short description of the reporting logic for
the relevant fields.
6.2.1 Reporting of action types at trade and position level
502. This subsection illustrates population of relevant fields to report lifecycle events.
6.2.1.1 New bilateral derivative at trade level that is not cleared
503. Table 49 illustrates the population of the reporting fields in case of a new
derivative, which is not cleared. This is how the derivatives that are bilateral should
be reported, at trade level.
Table 49 - New derivative at trade level that is not cleared
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
UTI1
<New>
…
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>TRAD</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
…
<TradClr>
<ClrSts>
<NonClrd>
<Rsn>NORE</Rsn>
</NonClrd>
</ClrSts>
</TradClr>
</TxData>
…
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</New>
2.31
Cleared
N
2.151
Action type
NEWT
2.152
Event type
TRAD
2.154
Level
TCTN

248
6.2.1.2 New bilateral derivative at trade level that is cleared on the same day or after
504. Table 50, Table 51 and Table 52 illustrate the population of the reporting fields
by a counterparty in case a new derivative is concluded bilaterally and cleared
afterwards on the same day or after. Counterparties should submit a derivative
report with action type ‘Terminate’ and event type ‘Clearing’ to indicate the
termination of the trade reported as uncleared. Afterwards the counterparty should
submit a derivative report with action type ‘New’ and event type ‘Clearing’ to
indicate that the derivative has been cleared. The counterparty should provide ‘Prior
UTI’ in this last report. The sequence of the submissions is illustrated in the below
tables.
Table 50 - New bilateral derivative at trade level that is cleared on the same
day or after
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
UTI1
<New>
…
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>TRAD</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
…
<TradClr>
<ClrSts>
<NonClrd>
<Rsn>NORE</Rsn>
</NonClrd>
</ClrSts>
</TradClr>
</TxData>
…
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</New>
2.31
Cleared
N
2.151
Action type
NEWT
2.152
Event type
TRAD
2.154
Level
TCTN
Table 51 - Termination of the bilateral derivative at trade level due to clearing
on the same day or after
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
UTI1
<Termntn>
…

249
Table 51 - Termination of the bilateral derivative at trade level due to clearing
on the same day or after
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.151
Action type
TERM
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>CLRG</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
…
</TxData>
…
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</Termntn>
2.152
Event type
CLRG
2.154
Level
TCTN
Table 52 - New cleared derivative at trade level resulting from clearing of a
bilateral derivative on the same day or after
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
UTI2
<New>
…
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI2
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
<PrrTxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</PrrTxId>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>CLRG</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
…
<TradClr>
<ClrSts>
<Clrd>
…
</Clrd>
</ClrSts>
</TradClr>
2.3
Prior UTI
UTI1
2.31
Cleared
Y
2.151
Action type
NEWT
2.152
Event type
CLRG
2.154
Level
TCTN

250
Table 52 - New cleared derivative at trade level resulting from clearing of a
bilateral derivative on the same day or after
No
Field
Example
XML Message
</TxData>
…
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</New>
505. Note that Table 50 and Table 51 report is not expected if the trade is concluded
on a trading venue and cleared by a CCP on the same day, only Table 52 report is
expected in such case (without ‘Prior UTI’ field). Furthermore, Table 52 illustrates
the reporting in the case where a cleared derivative is not included immediately in
a position (in which case it would be reported with action type POSC as clarified in
the subsequent examples).
6.2.1.3 New bilateral derivative at trade level that is cleared on the same day or after and
immediately included in the position
506. Table 53, 54, 55 and 56 illustrate the population of the reporting fields by a
counterparty in case of a new derivative is concluded bilaterally, cleared afterwards
on the same day or after and immediately included into a position. Counterparties
should submit a derivative report with action type ‘Terminate’ and event type
‘Clearing to indicate the termination of the trade which is cleared. Subsequently,
they should report that cleared derivative, which is immediately included into a
position, with action type ‘Position component’. In the context of the examples for
derivatives at position level, these are identified with Unique Trade Identifier (UTI)
of the position, ‘PUTI1’. Position UTI should also be reported in the field
‘Subsequent position UTI’ in the derivative at trade level that is included in the
position so that the reports can be linked. Afterwards the counterparty should
submit a derivative report with action type ‘Modify’ to indicate that the respective
derivative at position level has been updated due to an inclusion of a trade. The
sequence of the submissions is illustrated in the below tables.
Table 53 - New bilateral derivative at trade level that is cleared on the same
day or after
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
UTI1
<New>
…
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
2.31
Cleared
N
2.151
Action type
NEWT

251
Table 53 - New bilateral derivative at trade level that is cleared on the same
day or after
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.152
Event type
TRAD
</TxId>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>TRAD</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
…
<TradClr>
<ClrSts>
<NonClrd>
<Rsn>NORE</Rsn>
</NonClrd>
</ClrSts>
</TradClr>
</TxData>
…
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</New>
2.154
Level
TCTN
Table 54 - Termination of the bilateral derivative at trade level due to clearing
on the same day or after
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
UTI1
<Termntn>
…
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>CLRG</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
…
</TxData>
…
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</Termntn>
2.151
Action type
TERM
2.152
Event type
CLRG
2.154
Level
TCTN

252
TABLE 55- NEW CLEARED DERIVATIVE WHICH IS INCLUDED IMMEDIATELY INTO A
POSITION
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
UTI2
<PosCmpnt>
…
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI2
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
<PrrTxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</PrrTxId>
<SbsqntTxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
PUTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</SbsqntTxId>
…
<TradClr>
<ClrSts>
<Clrd>
…
</Clrd>
</ClrSts>
</TradClr>
</TxData>
…
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</PosCmpnt>
2.3
Prior UTI
UTI 1
2.4
Subsequent
position UTI
PUTI1
2.31
Cleared
Y
2.151
Action type
POSC
2.152
Event type
2.154
Level
TCTN
Table 56 – Modification of a derivative at position level resulting from the
inclusion of a trade
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
PUTI1
<Mod>
…
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
PUTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
2.31
Cleared
Y
2.151
Action type
MODI

253
Table 56 – Modification of a derivative at position level resulting from the
inclusion of a trade
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.152
Event type
INCP
</TxId>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>INCP</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
…
<TradClr>
<ClrSts>
<Clrd>
…
</Clrd>
</ClrSts>
</TradClr>
</TxData>
…
<Lvl>PSTN</Lvl>
</Mod>
2.154
Level
PSTN
6.2.1.4 New derivative concluded on a trading venue and cleared on the same day,
reported as position component
507. Table 57 and Table 58 illustrate the population of the reporting fields in case of
a new derivative that is concluded on a trading venue or an organized trading
platform and cleared by a central counterparty on the same day as well as included
in a position on that same day. In particular, only the derivative in its cleared form
should be reported. In the context of the examples for derivatives at position level,
these are identified with Unique Trade Identifier (UTI) of the position, ‘PUTI1’.
Position UTI should also be reported in the field ‘Subsequent position UTI’ in the
derivative at trade level that is included in the position so that the reports can be
linked.
Table 57 - New derivative concluded on a trading venue and cleared by a CCP
on the same day and reported with position component at trade level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
UTI1
<PosCmpnt>
…
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
2.4
Subsequent
position UTI
PUTI2

254
Table 57 - New derivative concluded on a trading venue and cleared by a CCP
on the same day and reported with position component at trade level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.31
Cleared
Y
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
<SbsqntTxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
PUTI2
</UnqTxIdr>
</SbsqntTxId>
…
<TradClr>
<ClrSts>
<Clrd>
…
</Clrd>
</ClrSts>
</TradClr>
</TxData>
…
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</PosCmpnt>
2.151
Action type
POSC
2.152
Event type
2.154
Level
TCTN
Table 58 - New derivative reported at position level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
PUTI2
<New>
…
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
PUTI2
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>INCP</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
…
<TradClr>
<ClrSts>
<Clrd>
…
2.31
Cleared
Y
2.151
Action type
NEWT
41
2.152
Event type
INCP
2.154
Level
PSTN
41
In this example a new position is created. In the case where a cleared transaction is included in an existing position, it would be
reported as modification of that position (with action type MODI) as in the example…

255
Table 58 - New derivative reported at position level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
</Clrd>
</ClrSts>
</TradClr>
</TxData>
…
<Lvl>PSTN</Lvl>
</New>
6.2.1.5 Modification of a derivative at position level due to inclusion of a new derivative
into the position
508. This example illustrates how to report modification of a position when a new
derivative at trade level is included in that position.
Table 59 - Modification of a derivative at position level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
PUTI1
<Mod>
…
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
PUTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>INCP</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
…
</TxData>
…
<Lvl>PSTN</Lvl>
</Mod>
2.151
Action type
MODI
2.152
Event type
INCP
2.154
Level
PSTN
6.2.1.6 Modification of a derivative at position level due to multiple lifecycle events
509. This example illustrates how to report modification of a derivative at position
level, when the position is impacted by several events during the day and it is not
possible to specify the event type due to which the modification occured.

256
Table 60 - Modification of a derivative at position level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
PUTI1
<Mod>
…
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
PUTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
</TxData>
…
<Lvl>PSTN</Lvl>
</Mod>
2.151
Action type
MODI
2.152
Event type
2.154
Level
PSTN
6.2.1.7 Modification of a derivative at trade level
510. Table 61 illustrates the population of the reporting fields in case a previously
reported derivative at trade level is modified following to the counterparties’
agreement to amend certain terms of the derivative.
Table 61 - Modification of a derivative at trade level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
UTI1
<Mod>
…
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>TRAD</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
…
</TxData>
…
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</Mod>
2.151
Action type
MODI
2.152
Event type
TRAD
2.154
Level
TCTN

257
6.2.1.8 Correction of a derivative at trade level
511. Table 62 illustrates the population of the reporting fields when there is a
correction of data fields that were submitted wrongly in a previous report of a
derivative at trade level.
Table 62 - Correction of a derivative at trade level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
UTI1
<Crrctn>
…
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
</TxData>
…
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</Crrctn>
2.151
Action type
CORR
2.152
Event type
2.154
Level
TCTN
6.2.1.9 Correction of the valuation of a derivative at trade level
512. Table 63 illustrates the population of the reporting fields when there is a
correction of data fields pertaining to the valuation that were submitted wrongly in
a previous report of a derivative at trade level. Please note that the population of
the valuation fields is shown in a separate example in section 6.2.2.3.
Table 63 - Correction of a derivative at trade level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
UTI1
<Crrctn>
…
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
</TxData>
…
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</Crrctn>
2.151
Action type
CORR
2.152
Event type
2.154
Level
TCTN

258
6.2.1.10 Valuation of a derivative at trade level
513. Table 64 illustrates the population of the reporting fields when the counterparty
submits a daily valuation update for a previously reported derivative at trade level.
Please note that the population of the valuation fields is shown in a separate
example in section 6.2.2.3.
Table 64 - Valuation of a derivative at trade level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
UTI1
<ValtnUpd>
…
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
</TxData>
…
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</ValtnUpd>
2.151
Action type
VALU
2.152
Event type
2.154
Level
TCTN
6.2.1.11 Reporting of margin update for a derivative collateralized at trade level
514. Table 65 illustrates the population of the reporting fields when the counterparty
submits a daily margin update for a previously reported derivative at trade level and
that derivative is individually collateralized. Please note that the population of the
margin fields is shown in separate examples in section 6.3.
Table 65 - Margin update for a trade-level derivative collateralized at trade level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
3.8
Collateral
portfolio
indicator
FALSE
<MrgnUpd>
…
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
<Coll>
<CollPrtflCd>
<Prtfl>
<NoPrtfl>
NOAP
</NoPrtfl>
3.9
Collateral
portfolio code
3.10
UTI
UTI1
3.28
Action type
MARU

259
Table 65 - Margin update for a trade-level derivative collateralized at trade level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
</Prtfl>
</CollPrtflCd>
…
<MrgnUpd>
6.2.1.12 Reporting of margin update for a derivative collateralized at portfolio level
515. Table 66 illustrates the population of the reporting fields when the counterparty
submits a daily margin update in case of a collateralisation at portfolio level. Please
note that the population of the margin fields is shown in separate examples in
section 6.3.
Table 66 - Margin update for a trade-level derivative collateralized at portfolio
level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
3.8
Collateral
portfolio
indicator
TRUE
<MrgnUpd>
…
<Coll>
<CollPrtflCd>
<Prtfl>
<Cd>
COLLPCODE1
</Cd>
</Prtfl>
</CollPrtflCd>
…
</MrgnUpd>
3.9
Collateral
portfolio code
COLLPCODE1
3.10
UTI
3.28
Action type
MARU
6.2.1.13 Correction of margin data at portfolio level
516. Table 67 illustrates the population of the reporting fields when there is a
correction of margin data fields that were submitted wrongly in a previous report of
collateral at portfolio level.
Table 67 - Correction of margin data at portfolio level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
3.8
Collateral
portfolio
indicator
TRUE
<Crrctn>
…
<Coll>
<CollPrtflCd>

260
Table 67 - Correction of margin data at portfolio level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
3.9
Collateral
portfolio code
COLLPCODE1
<Prtfl>
<Cd>
COLLPCODE1
</Cd>
</Prtfl>
</CollPrtflCd>
…
</Crrctn>
3.10
UTI
3.28
Action type
CORR
6.2.1.14 Early termination of a derivative at trade level
517. Table 68 illustrates the population of reporting fields when a derivative at trade
level is terminated prior to its maturity date following the counterparties’ agreement
to early terminate (rather than due to a specific event resulting in a termination of a
derivative).
Table 68 - Early termination of a derivative at trade level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
UTI1
<Termntn>
…
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>ETRM</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
…
</TxData>
…
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</Termntn>
2.151
Action type
TERM
2.152
Event type
ETRM
2.154
Level
TCTN
6.2.1.15 Early termination of a derivative at position level
518. Table 69 illustrates the population of reporting fields when a derivative at
position level is terminated prior to its maturity date following the counterparties’
agreement to early terminate (rather than due to a specific event resulting in a
termination of a derivative). This can occur for example when the position is netted

261
to zero and the counterparties prefer to close the position rather than to continue to
report valuation on a daily basis.
Table 69 - Early termination of a derivative at position level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
PUTI1
<Termntn>
…
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
PUTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>ETRM</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
…
</TxData>
…
<Lvl>PSTN</Lvl>
</Termntn>
2.151
Action type
TERM
2.152
Event type
ETRM
2.154
Level
PSTN
6.2.1.16 Erroring a derivative at trade level
519. Table 70 illustrates the population of reporting fields in case of a cancellation of
a wrongly submitted entire report where the derivative never came into existence
or was not subject to EMIR reporting requirements, but which was reported to a TR
by mistake.
Table 70 - Erroring a derivative at trade level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
UTI1
<Err>
…
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
</TxData>
…
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</Err>
2.151
Action type
EROR
2.152
Event type
2.154
Level
TCTN

262
6.2.1.17 Reviving a derivative at trade level
520. Table 71 illustrates the population of reporting fields in case where a derivative
that was terminated or errored by mistake is revived.
Table 71 - Reviving a derivative at trade level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
UTI1
<Revi>
…
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
…
</TxData>
…
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</Revi>
2.151
Action type
REVI
2.152
Event type
2.154
Level
TCTN
6.2.2 Other reportable details
6.2.2.1 Reporting of cleared / non-cleared trade
6.2.2.1.1 Cleared trade in an open offer model
521. When a trade is cleared in an open offer model, the clearing takes place at same
time as the conclusion of the trade. Hence, execution timestamp and clearing
timestamp are expected to be the same.
522. Table below illustrates the population of the Table 2 fields of the above-
mentioned situation from the CCP (with LEI BBBBBBBBBB1111111111) and
Counterparty 1 perspective, as in this case, it is identical.
523. The following group of reporting fields should be reported:
’Cleared‘ (field 2.31) is populated with 'Y';
’Clearing timestamp‘ (field 2.32) is equal to field ’Execution timestamp’ (field 2.42);
’Central counterparty‘ (field 2.33) is populated with the LEI of the CCP.

263
Table 72 - Cleared trade in an open offer model
Item
Field
Example
XML Message
31
Cleared
Y
<CmonTradData>
<TxData>
<ExctnTmStmp>
2021-03-17T15:17:00Z
</ExctnTmStmp>
<MstrAgrmt>
<Tp>
<Tp>OTHR</Tp>
</Tp>
<OthrMstrAgrmtDtls>
CCP Clearing Conditions
</OthrMstrAgrmtDtls>
</MstrAgrmt>
<TradClr>
<ClrSts><Clrd>
<Dtls>
<CCP>
<LEI>BBBBBBBBBB
1111111111
</LEI>
</CCP>
<ClrDtTm>2021-03-
17T15:17:00Z
</ClrDtTm>
</Dtls></Clrd>
</ClrSts>
</TradClr>
</TxDate>
</CmonTradData>
32
Clearing
timestamp
2021-03-
17T15:17:00Z
33
Central
counterparty
BBBBBBBBBB1111111111
34
Master
Agreement type
OTHR
35
Other master
agreement type
CCP Clearing
Conditions
43
Execution
timestamp
2021-03-
17T15:17:00Z
6.2.2.1.2 Cleared trade in a novation model.
524. When a derivative is cleared in a novation model, the clearing takes place after
the time of conclusion of the trade.

264
525. The table below illustrates the population of fields, from the CCP and the CP1
perspective, when a derivative is cleared by the CCP in a novation model.
526. In this respect, the following group of reporting fields should be reported:
’Prior UTI‘ (field 2.3) should be reported with the prior UTI (that of the original bilateral derivative
in the case of CCP-cleared derivatives);
’Cleared‘ (field 2.31) is populated with 'Y';
’Clearing timestamp‘ (field 2.32) time is after the time provided in field ’Execution timestamp’
(field 2.42);
’Central counterparty‘ (field 2.33) is populated with the LEI of the CCP.
Table 73 - Cleared derivative in a novation model
Item
Field
Example
XML Message
1
UTI
UTI2
<New>
...
<CmonTradData>
<TxDate>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>UTI2</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
<PrrTxId>
<UnqTxIdr>UTI1</UnqTxIdr>
</PrrTxId>
<ExctnTmStmp>
2021-03-17T15:17:00Z
</ExctnTmStmp>
<MstrAgrmt>
<Tp>
<Tp>OTHR</Tp>
</Tp>
<OthrMstrAgrmtDtls>
CCP Clearing Conditions
</OthrMstrAgrmtDtls>
</MstrAgrmt>
...
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>CLRG</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
<TradClr>
<ClrSts><Clrd>
<Dtls>
<CCP>
<LEI
BBBBBBBBBB1111111111
</LEI>
3
Prior UTI
UTI1
31
Cleared
Y
32
Clearing
timestamp
2021-03-
18T18:00:00Z
33
Central
counterparty
BBBBBBBBBB1111111111
34
Master
Agreement type
OTHR
35
Other master
agreement type
CCPClearing
Conditions
43
Execution
timestamp
2021-03-

265
Table 73 - Cleared derivative in a novation model
Item
Field
Example
XML Message
17T15:17:00Z
</CCP>
<ClrDtTm>
2021-03-18T18:00:00Z
</ClrDtTm>
</Dtls></Clrd>
</ClrSts>
</TradClr>
...
</TxDate>
</CmonTradData>
</New>
151
Action type
NEWT
152
Event type
CLRG
Table 74 - Termination of a previous derivative (alpha trade) in a novation model
Item
Field
Example
XML Message
1
UTI
UTI1
<Termntn>
...
<CmonTradData>
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
<EarlyTermntnDt>
2021-03-18
</EarlyTermntnDt>
...
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>CLRG</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
...
</TxData>
</CmonTradData>
</Termntn>
45
Early termination
date
2021-03-18
151
Action type
TERM
152
Event type
CLRG

266
6.2.2.1.3 Non-cleared trade
527. The field ’Cleared‘ (field 2.31) is populated with 'N'. The rest of the fields related
to clearing are not populated.
Table 75 - Non cleared trade
No
Field
Example
XML Message
1
UTI
UTI1
<CmonTradData>
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
<ExctnTmStmp>
2021-03-17T15:17:00Z
</ExctnTmStmp>
<TradClr>
<ClrSts>
<NonClrd>
<Rsn>NORE</Rsn>
</NonClrd>
</ClrSts>
</TradClr>
</TxData>
</CmonTradData>
2
Report tracking
number
31
Cleared
N
32
Clearing
timestamp
33
Central
counterparty
43
Execution
timestamp
2021-03-
17T15:17:00Z
6.2.2.2 Trading venue
528. The field ’Venue of execution‘ (field 2.41) should be populated in accordance
with the type of conclusion of the derivative.
529. The counterparties should use the ISO 10383 segment MIC for derivatives
executed on a trading venue, Systematic Internaliser (SI) or organised trading
platform outside of the Union. Where the segment MIC does not exist, they should
use the operating MIC.
530. The counterparties should use the MIC code 'XOFF' for financial instruments
admitted to trading or traded on a trading venue or for which a request for admission
was made, where the derivative on that financial instrument is not executed on a
trading venue, SI or organised trading platform outside of the Union, or where a
counterparty does not know it is trading with a counterparty 2 acting as an SI.

267
531. The counterparties should use the MIC code 'XXXX' for financial instruments
that are not admitted to trading or traded on a trading venue or for which no request
for admission has been made and that are not traded on an organised trading
platform outside of the Union.
6.2.2.2.1 Example of two SIs facing each other
532. Two counterparties, A and B, that are both SIs, trade with each other. For this
derivative, counterparty A acts in the SI capacity, thus both entities should report
MIC of that counterparty in the venue field.
533. Counterparty A is identified with LEI 12345678901234500000 and MIC 1234.
534. Counterparty B is identified with LEI ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST and MIC
ABCD.
Table 76 - Reporting of the trading venue from the counterparty A perspective
Item
Field
Example
XML Message
4
Counterparty 1
12345678901234500000
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl>
<Id>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</Id>
</Lgl>
</Id>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl>
<Id>
<LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI>
</Id>
</Lgl>
</IdTp>
</OthrCtrPty>
...
</CtrPty>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CmonTradData>
<TxData>
...
<PltfmId>1234</PltfmId>
</TxData>
</CmonTradData>
9
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
41
Venue of
execution
1234

268
Table 76 - Reporting of the trading venue from the counterparty A perspective
Item
Field
Example
XML Message
Table 77 - Reporting of the trading venue from the counterparty B perspective
Item
Field
Example
XML Message
4
Counterparty 1
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl>
<Id>
<LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI>
</Id>
</Lgl>
</Id>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl>
<Id>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</Id>
</Lgl>
</IdTp>
</OthrCtrPty>
...
</CtrPty>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CmonTradData>
<TxData>
...
<PltfmId>1234</PltfmId>
</TxData>
</CmonTradData>
9
Counterparty 2
12345678901234500000
41
Venue of
execution
1234

269
Table 77 - Reporting of the trading venue from the counterparty B perspective
Item
Field
Example
XML Message
6.2.2.2.2 Example of post Brexit derivative executed on a UK regulated market
535. Derivatives executed on UK regulated markets before Brexit would be
considered ETD.
536. On the other hand, derivatives executed on UK regulated markets after Brexit
would be considered OTC. The field ‘Venue of execution’ should still be populated
with the corresponding MIC code. However, it would have impact on other fields
such as the field ’Intragroup‘ and ’Clearing obligation‘ which are required for OTC
derivatives.
Table 78 - Derivative executed before Brexit
Item
Field
Example
XML Message
41
Venue of
execution
XLON
<CmonTradData>
<TxData>
…
<PltfmId>XLON</PltfmId>
<ExctnTmStmp>
2020-12-31T17:00:00Z
</ExctnTmStmp>
…
</TxData>
</CmonTradData>
43
Execution
timestamp
2020-12-
31T17:00:00Z
30
Clearing
obligation
37
Intragroup

270
Table 79 - Derivative executed after Brexit
Item
Field
Example
XML Message
41
Venue of
execution
XLON
<CmonTradData>
<TxData>
…
<PltfmId>XLON</PltfmId>
<ExctnTmStmp>
2021-01-04T15:00:00Z
</ExctnTmStmp>
…
<TradClr>
<ClrOblgtn>false
</ClrOblgtn>
<IntraGrp>false</IntraGrp>
</TradClr>
…
</TxData>
</CmonTradData>
43
Execution
timestamp
2021-01-
04T15:00:00Z
30
Clearing
obligation
FALSE
37
Intragroup
FALSE
6.2.2.3 Reporting of valuations
537. Table 80 illustrates the population of the valuation data when the counterparty
submits a daily valuation update for a previously reported derivative at trade level.
6.2.2.3.1 Valuation of a derivative at trade level
538. In this example, the counterparty A (with LEI 12345678901234500000) is buyer
of a call option that is in-the-money and which has been valued on the preceding
day at 221,100 EUR. Given that the derivative concerned is an option, the delta is
computed and populated (0.6). Counterparty B (with LEI
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST) is the seller.
Table 80 - Valuation of a derivative at trade level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
1.1
Reporting
timestamp
2023-05-16T19:15:05Z
<ValtnUpd>
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl>
<Lgl><Id><LEI>
12345678901234500000
1.2
Report
submitting entity
ID
12345678901234500000

271
Table 80 - Valuation of a derivative at trade level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
1.3
Entity
responsible for
reporting
12345678901234500000
</LEI></Id></Lgl>
</Id>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl><Id><LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI></Id></Lgl>
</IdTp>
</OthrCtrPty>
<SubmitgAgt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</SubmitgAgt>
<NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</NttyRspnsblForRpt>
</CtrPty>
<Valtn>
<CtrctVal>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">
221100</Amt>
</CtrctVal>
<TmStmp>
2023-05-15T18:00:00Z
</TmStmp>
<Tp>MTMA</Tp>
<Dlta>0.6</Dlta>
</Valtn>
<RptgTmStmp>
2023-05-16T19:15:05Z
</RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CmonTradData>
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTradIdr>
UTI1</UnqTradIdr>
</TxId>
<DerivEvt>
<TmStmp>
2023-05-15
</TmStmp>
</DerivEvt>
</TxData>
</CmonTradData>
<Lvl><TCTN</Lvl>
</ValtnUpd>
1.4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
12345678901234500000
2.8
Counterparty 2
identifier type
TRUE
2.9
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
2.1
UTI
UTI1
2.21
Valuation
amount
221100
2.22
Valuation
currency
EUR
2.23
Valuation
timestamp
2023-05-15T18:00:00Z
2.24
Valuation
method
MTMA
2.25
Delta
0.6
2.151
Action type
VALU
2.153
Event date
2023-05-15
2.154
Level
TCTN

272
6.2.2.3.2 Valuation of a derivative at position level
539. Table 81 illustrates the population of the valuation data for an IRS position when
the position is netted to zero and the counterparties decide to maintain the position
open (and thus submit the valuation daily).
Table 81 - Valuation of a derivative at position level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
1.1
Reporting
timestamp
2023-06-06T20:00:00Z
<ValtnUpd>
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl>
<Lgl><Id><LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI></Id></Lgl>
</Id>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl><Id><LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI></Id></Lgl>
</IdTp>
</OthrCtrPty>
<SubmitgAgt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</SubmitgAgt>
<NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</NttyRspnsblForRpt>
</CtrPty>
<Valtn>
<CtrctVal>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">
0</Amt>
</CtrctVal>
<TmStmp>
2023-06-06T20:00:00Z
</TmStmp>
<Tp>MTMA</Tp>
</Valtn>
<RptgTmStmp>
2023-05-16T19:15:05Z
</RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CmonTradData>
<TxData>
1.2
Report
submitting
entity ID
12345678901234500000
1.3
Entity
responsible for
reporting
12345678901234500000
1.4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
12345678901234500000
2.8
Counterparty 2
identifier type
TRUE
2.9
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
2.1
UTI
PUTI1
2.21
Valuation
amount
0
2.22
Valuation
currency
EUR
2.23
Valuation
timestamp
2023-06-05T19:00:00Z
2.24
Valuation
method
MTMA
2.151
Action type
VALU
2.153
Event date
2023-06-05

273
Table 81 - Valuation of a derivative at position level
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.154
Level
PSTN
<TxId>
<UnqTradIdr>
PUTI1</UnqTradIdr>
</TxId>
<DerivEvt>
<TmStmp>
2023-06-05
</TmStmp>
</DerivEvt>
</TxData>
</CmonTradData>
<Lvl>PSTN</Lvl>
</ValtnUpd>
6.2.2.4 Reporting of other payments
6.2.2.4.1 Reporting of upfront payment
540. Table 82 illustrates the population of the reporting fields when the counterparty
A (with LEI12345678901234500000) which takes responsibility for the risk makes
an initial payment to the counterparty B (with LEI ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST) to
cover any future defaults and submits a report at the trade level.
Table 82 - Reporting of upfront payment
No
Field
Example
XML Message
1.1
Reporting
timestamp
2021-03-06T18:20:05Z
<New>
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl>
<Lgl><Id><LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI></Id></Lgl>
</Id>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl><Id><LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI></Id></Lgl>
</IdTp>
1.2
Report
submitting
entity ID
12345678901234500000
1.3
Entity
responsible for
reporting
12345678901234500000
1.4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
12345678901234500000
1.9
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST

274
Table 82 - Reporting of upfront payment
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.1
UTI
123456
</OthrCtrPty>
<SubmitgAgt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</SubmitgAgt>
<NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</NttyRspnsblForRpt>
</CtrPty>
<RptgTmStmp>
2023-03-06T18:20:05Z
</RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CmonTradData>
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTradIdr>
123456</UnqTradIdr>
</TxId>
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>TRAD</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
<OthrPmt>
<PmtAmt>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">
100000
</Amt>
</PmtAmt>
<PmtTp>
<Tp>UFRO</Tp>
</PmtTp>
<PmtDt>
2021-03-05
</PmtDt>
<PmtPyer>
<Lgl><LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI></Lgl>
</PmtPyer>
<PmtRcvr>
<Lgl>
<Lgl><LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
2.73
Other payment
type
UFRO
2.74
Other payment
amount
100000
2.75
Other payment
currency
EUR
2.76
Other payment
date
2021-03-05
2.77
Other payment
payer
12345678901234500000
2.78
Other payment
receiver
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
2.151
Action type
NEWT
2.152
Event type
TRAD
2.154
Level
TCTN

275
Table 82 - Reporting of upfront payment
No
Field
Example
XML Message
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</PmtRcvr>
</OthrPmt>
…
</TxData>
</CmonTradData>
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</New>
6.2.2.4.2 Reporting of unwind payment
541. Table 83 illustrates the population of the reporting fields when the same
counterparty A unwinds the full termination payment and submits a report at the
trade level.
Table 83 - Reporting of unwind payment
No
Field
Example
XML Message
1.1
Reporting
timestamp
2021-03-06T18:20:05Z
<Termntn>
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl><Id><LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI></Id></Lgl>
</Id>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl><Id><LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI></Id></Lgl>
</IdTp>
</OthrCtrPty>
<SubmitgAgt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</SubmitgAgt>
1.2
Report
submitting
entity ID
12345678901234500000
1.3
Entity
responsible for
reporting
12345678901234500000
1.4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
12345678901234500000
1.9
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
2.1
UTI
456789
2.45
Early
termination
date
2021-03-05

276
Table 83 - Reporting of unwind payment
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.73
Other payment
type
UWIN
<NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</NttyRspnsblForRpt>
</CtrPty>
<RptgTmStmp>
2023-03-06T18:20:05Z
</RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CmonTradData>
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTradIdr>
456789</UnqTradIdr>
</TxId>
<EarlyTermntnDt>
2021-03-05
</EarlyTermntnDt>
<DerivEvt>
<Tp>ETRM</Tp>
</DerivEvt>
<OthrPmt>
<PmtAmt>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">
70000
</Amt>
</PmtAmt>
<PmtTp>
<Tp>UWIN</Tp>
</PmtTp>
<PmtDt>
2021-03-05
</PmtDt>
<PmtPyer>
<Lgl><LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI></Lgl>
</PmtPyer>
<PmtRcvr>
<Lgl>
<Lgl><LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI></Lgl>
</Lgl>
</PmtRcvr>
</OthrPmt>
…
2.74
Other payment
amount
70000
2.75
Other payment
currency
EUR
2.76
Other payment
date
2021-03-05
2.77
Other payment
payer
12345678901234500000
2.78
Other payment
receiver
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
2.151
Action type
TERM
2.152
Event type
ETRM
2.154
Level
TCTN
277
Table 83 - Reporting of unwind payment
No
Field
Example
XML Message
</TxData>
</CmonTradData>
<Lvl>TCTN</Lvl>
</Termntn>
6.2.2.4.3 Reporting of principal exchange
542. Table 84 illustrates the population of the reporting fields when a principal
exchange takes place, related to a cross-currency swap.
543. In this example, counterparties A and B agreed an OTC derivative contract,
which specifies:
- an initial exchange of notional currency in each different currency and the terms
of that repayment of notional currency over the life of the swap;
- an exchange of regular payments benchmarked against two interest rates,
denominated in two different currencies.
544. The counterparty A will pay 5M EUR and counterparty B will pay 4.3M GBP, as
initial principal exchange for each of them. Counterparties will exchange payments
each 6 months for agreed float-to-float 3-year IRS
545. The re-exchange of the same notional of currencies will take place at the
maturity date.
546. The below table illustrates the reporting of principal exchange payments from
the perspective of the counterparty A. The counterparty reports both the payments
made and received, on the initial and final exchange date – given that all these
payments are known at the time of reporting.
Table 84 - Reporting of notional exchanges from Counterparty A perspective
No
Field
Example
XML Message
1.1
Reporting
timestamp
2021-05-20T18:00:15Z
<CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CtrPty>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl>
<Id>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</Id>
</Lgl>
</Id>
<DrctnOrSd><Drctn>
1.2
Report
submitting
entity ID
12345678901234500000
1.3
Entity
responsible
for reporting
12345678901234500000

278
Table 84 - Reporting of notional exchanges from Counterparty A perspective
No
Field
Example
XML Message
1.4
Counterparty
1 (Reporting
counterparty)
12345678901234500000
<DrctnOfTheFrstLeg>
TAKE
</DrctnOfTheFrstLeg>
<DrctnOfTheScndLeg>
MAKE
</DrctnOfTheScndLeg>
</Drctn></DrctnOrSd>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl>
<Id>
<LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI>
</Id>
</Lgl>
</IdTp>
</OthrCtrPty>
<SubmitgAgt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</SubmitgAgt>
<NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</NttyRspnsblForRpt>
</CtrPty>
<RptgTmStmp>
2021-05-20T18:00:15Z
</RptgTmStmp>
</CtrPtySpcfcData>
<CmonTradData>
<CtrctData>
<CtrctTp>SWAP</CtrctTp>
</CtrctData>
<TxData>
<TxId>
<UnqTradIdr>
AABB123456
</UnqTradIdr>
</TxId>
…
<NtnlAmt>
<FrstLeg><Amt>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">5000000
</Amt></Amt></FrstLeg>
1.9
Counterparty
2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
1.18
Direction of
leg 1
TAKE
1.19
Direction of
leg 2
MAKE
2.1
UTI
AABB123456
2.10
Contract type
SWAP
2.42
Execution
timestamp
2021-05-19T13:10:25Z
2.
44
Expiration
date
2024-05-18
2.55
Notional
amount of
leg 1
5000000
2.56
Notional
currency 1
EUR
2.64
Notional
amount of
leg 2
4300000
2.65
Notional
currency of
leg 2
GBP
2.73
Other
payment
type
PEXH

279
Table 84 - Reporting of notional exchanges from Counterparty A perspective
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.74
Other
payment
amount
5000000
<ScndLeg><Amt>
<Amt Ccy="GBP">4300000
</Amt></Amt></ScndLeg>
</NtnlAmt>
<ExctnTmStmp>
2021-05-19T13:10:25Z
</ExctnTmStmp>
<XprtnDt>
2024-05-18
</XprtnDt>
<OthrPmt>
<PmtAmt>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">
5000000</Amt>
</PmtAmt>
<PmtTp>
<Tp>PEXH</Tp>
</PmtTp>
<PmtDt>
2021-05-20
</PmtDt>
<PmtPyer>
<Lgl>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</PmtPyer>
<PmtRcvr>
<Lgl>
<LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</PmtRcvr>
</OthrPmt>
<OthrPmt>
<PmtAmt>
<Amt Ccy="GBP">
4300000</Amt>
</PmtAmt>
<PmtTp>
<Tp>PEXH</Tp>
</PmtTp>
<PmtDt>
2021-05-20
</PmtDt>
<PmtPyer>
<Lgl>
<LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
2.75
Other
payment
currency
EUR
2.76
Other
payment
date
2021-05-20
2.77
Other
payment
payer
12345678901234500000
2.78
Other
payment
receiver
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
2.73
Other
payment
type
PEXH
2.74
Other
payment
amount
4300000
2.75
Other
payment
currency
GBP
2.76
Other
payment
date
2021-05-20
2.77
Other
payment
payer
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
2.78
Other
payment
receiver
12345678901234500000
280
Table 84 - Reporting of notional exchanges from Counterparty A perspective
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.73
Other
payment
type
PEXH
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</PmtPyer>
<PmtRcvr>
<Lgl>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</PmtRcvr>
</OthrPmt>
<OthrPmt>
<PmtAmt>
<Amt Ccy="GBP">
4300000</Amt>
</PmtAmt>
<PmtTp>
<Tp>PEXH</Tp>
</PmtTp>
<PmtDt>
2021-05-18
</PmtDt>
<PmtPyer>
<Lgl>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</PmtPyer>
<PmtRcvr>
<Lgl>
<LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</PmtRcvr>
</OthrPmt>
<OthrPmt>
<PmtAmt>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">
5000000</Amt>
</PmtAmt>
<PmtTp>
<Tp>PEXH</Tp>
</PmtTp>
<PmtDt>
2021-05-18
</PmtDt>
<PmtPyer>
<Lgl>
<LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
2.74
Other
payment
amount
4300000
2.75
Other
payment
currency
GBP
2.76
Other
payment
date
2024-05-18
2.77
Other
payment
payer
12345678901234500000
2.78
Other
payment
receiver
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
2.73
Other
payment
type
PEXH
2.74
Other
payment
amount
5000000
2.75
Other
payment
currency
EUR
2.76
Other
payment
date
2024-05-18
2.77
Other
payment
payer
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST

281
Table 84 - Reporting of notional exchanges from Counterparty A perspective
No
Field
Example
XML Message
2.78
Other
payment
receiver
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</PmtPyer>
<PmtRcvr>
<Lgl>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</Lgl>
</PmtRcvr>
</OthrPmt>
6.3 Table 3 Margin data
547. Counterparties should report all relevant types of collateral (initial margin,
variation margin and excess collateral), providing both pre- and post-haircut values.
Each type of collateral should be reported as a single figure, being the sum of the
values of all assets posted/received expressed in a single currency.
548. Collateral can be reported on a portfolio basis. It is up to the reporting
counterparty to determine what unique value to put in the field ‘Collateral Portfolio
Code’, but this value should be consistent over the lifetime of the portfolio and not
be re-assigned every day for the same portfolio. At the same time, different
counterparties can use different collateral portfolio codes for the same set of
derivatives.
6.3.1 Reporting of margin update for a new uncollateralised derivative
549. Table 85 illustrates the population of the reporting fields when the counterparty
submits the margin report for an uncollateralised derivative . There is no need to
send any further margin updates, unless the collateralisation category changes.
Table 85 – Report of margin update for an uncollateralized derivative
No
Field
Example
XML Message
3.8
Collateral portfolio
indicator
FALSE
<Rpt>
<MrgnUpd>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI3
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
<Coll>
<CollPrtflCd>
3.9
Collateral portfolio
code
3.10
UTI
UTI3

282
Table 85 – Report of margin update for an uncollateralized derivative
No
Field
Example
XML Message
3.11
Collateralisation
category
UNCL
<Prtfl>
<NoPrtfl>
<Rsn>NOAP</Rsn>
</NoPrtfl>
</Prtfl>
</CollPrtflCd>
<CollstnCtgy>
UNCL
</CollstnCtgy>
</MrgnUpd>
</Rpt>
3.28
Action type
MARU
6.3.2 Reporting of margin for a new derivative collateralized at portfolio level
550. In the scenario below, the reporting counterparty, Counterparty J (with LEI
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC) is also a clearing member. It reports the amount
of 1,000,000 EUR posted as initial margin and the amount of 300,000 EUR as
variation margin posted to CCP O (with LEI BBBBBBBBBB1111111111). The
counterparty also reports excess collateral of 100,000 EUR.
Table 86 - Margin update at portfolio level for a cleared derivative
No
Field
Example
XML Message
3.1
Reporting
timestamp
2023-07-19T18:05:45Z
<MrgnUpd>
<RptgTmStmp>
2023-07-19T18:05:45Z
</RptgTmStmp>
<CtrPtyId>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl>
<Id>
<LEI>
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
</LEI>
</Id>
</Lgl>
</Id>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl>
<Id>
<LEI>
BBBBBBBBBB1111111111
</LEI>
</Id>
</Lgl>
3.2
Report
submitting
entity ID
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
CCCCC
3.3
Entity
responsible for
reporting
CCCCCCCCCCCCCC
CCCCCC
3.4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
CCCCCCCCCCCCCC
CCCCCC
3.5
Counterparty 2
identifier type
TRUE
3.6
Counterparty 2
BBBBBBBBBB111111
1111

283
Table 86 - Margin update at portfolio level for a cleared derivative
No
Field
Example
XML Message
3.7
Collateral
timestamp
2023-07-18T18:00:00Z
</IdTp>
</OthrCtrPty>
<SubmitgAgt>
<LEI>
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
</LEI>
</SubmitgAgt>
<NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<LEI>
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
</LEI>
</NttyRspnsblForRpt>
</CtrPtyId>
<EvtDt>
2023-07-18
</EvtDt>
<Coll>
<CollPrtflCd>
<Prtfl>
<Cd>
CODEPORTFOLIO123
</Cd>
</Prtfl>
</CollPrtflCd>
<CollstnCtgy>
OWC1
</CollstnCtgy>
<TmStmp>
2023-07-18T18:00:00Z
</TmStmp>
<PstdMrgnOrColl>
<InitlMrgnPstdPreHrcut
Ccy="EUR">1000000
</InitlMrgnPstdPreHrcut>
<InitlMrgnPstdPstHrcut
Ccy="EUR">1000000
</InitlMrgnPstdPstHrcut>
<VartnMrgnPstdPreHrcut
Ccy="EUR">300000
</VartnMrgnPstdPreHrcut>
<VartnMrgnPstdPstHrcut
Ccy="EUR">300000
</VartnMrgnPstdPstHrcut>
<XcssCollPstd
Ccy="EUR">100000
</XcssCollPstd>
</PstdMrgnOrColl>
</MrgnUpd>
3.8
Collateral
portfolio
indicator
TRUE
3.9
Collateral
portfolio code
CODEPORTFOLIO123
3.10
UTI
3.11
Collateralisation
category
OWC1
3.12
Initial margin
posted by the
counterparty 1
(pre-haircut)
1000000
3.13
Initial margin
posted by the
counterparty 1
(post-haircut)
1000000
3.14
Currency of the
initial margin
posted
EUR
3.15
Variation
margin posted
by the
counterparty 1
(pre-haircut)
300000
3.16
Variation
margin posted
by the
counterparty 1
(post-haircut)
300000

284
Table 86 - Margin update at portfolio level for a cleared derivative
No
Field
Example
XML Message
3.17
Currency of the
variation
margins posted
EUR
3.18
Excess
collateral
posted by the
counterparty 1
100000
3.19
Currency of the
excess
collateral
posted
EUR
3.20
Initial margin
collected by the
counterparty 1
(pre-haircut)
3.21
Initial margin
collected by the
counterparty 1
(post-haircut)
3.22
Currency of
initial margin
collected
3.23
Variation
margin
collected by the
counterparty 1
(pre-haircut)
3.24
Variation
margin
collected by the
counterparty 1
(post-haircut)
3.25
Currency of
variation margin
collected
285
Table 86 - Margin update at portfolio level for a cleared derivative
No
Field
Example
XML Message
3.26
Excess
collateral
collected by the
counterparty 1
3.27
Currency of
excess
collateral
collected
3.28
Action type
MARU
3.29
Event date
2023-07-18
6.3.3 Reporting of margin update at an individual transaction level for an uncleared
derivative
551. In the next scenario, two counterparties exchange collateral for an uncleared
derivative. Both counterparties post IM and VM according to the collateral
agreement. Counterparty A (with LEI 12345678901234500000) posted 800,000
EUR of IM in cash and 220,000 EUR of IM in securities subject to 10% haircut.
Counterparty B (with LEI ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST ) posted 1,000,000 EUR of
IM in cash. Counterparty B would also be expected to post 100,000 EUR of VM
based on the most recent valuation of the contract, however this amount is below
the minimum transfer amount (MTA) agreed between the counterparties.
Table 87- Margin update at an individual transaction level for an uncleared
derivative
No
Field
Example
XML Message
3.1
Reporting
timestamp
2023-04-07T10:00:00Z
<MrgnUpd>
<RptgTmStmp>
2023-04-07T10:00:00Z
</RptgTmStmp>
<CtrPtyId>
<RptgCtrPty>
<Id>
<Lgl>
3.2
Report
submitting
entity ID
1234567890123450
0000

286
Table 87- Margin update at an individual transaction level for an uncleared
derivative
No
Field
Example
XML Message
3.3
Entity
responsible for
reporting
1234567890123450
0000
<Id>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</Id>
</Lgl>
</Id>
</RptgCtrPty>
<OthrCtrPty>
<IdTp>
<Lgl>
<Id>
<LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI>
</Id>
</Lgl>
</IdTp>
</OthrCtrPty>
<SubmitgAgt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</SubmitgAgt>
<NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</NttyRspnsblForRpt>
</CtrPtyId>
<EvtDt>
2023-04-06
</EvtDt>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>UTI1</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
<Coll>
<CollPrtflCd>
<Prtfl>
<NoPrtfl>
NOAP
</NoPrtfl>
</Prtfl>
</CollPrtflCd>
<CollstnCtgy>
FLCL
</CollstnCtgy>
<TmStmp>
2023-04-06T20:30:00Z
3.4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
1234567890123450
0000
3.5
Counterparty 2
identifier type
TRUE
3.6
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLMN
OPQRST
3.7
Collateral
timestamp
2023-04-06T20:30:00Z
3.8
Collateral
portfolio
indicator
FALSE
3.9
Collateral
portfolio code
3.10
UTI
UTI1
3.11
Collateralisation
category
FLCL
3.12
Initial margin
posted by the
counterparty 1
(pre-haircut)
1020000
3.13
Initial margin
posted by the
counterparty 1
(post-haircut)
998000
3.14
Currency of the
initial margin
posted
EUR

287
Table 87- Margin update at an individual transaction level for an uncleared
derivative
No
Field
Example
XML Message
3.15
Variation
margin posted
by the
counterparty 1
(pre-haircut)
</TmStmp>
<PstdMrgnOrColl>
<InitlMrgnPstdPreHrcut
Ccy="EUR">1020000
</InitlMrgnPstdPreHrcut>
<InitlMrgnPstdPstHrcut
Ccy="EUR">998000
</InitlMrgnPstdPstHrcut>
</PstdMrgnOrColl>
<RcvdMrgnOrColl>
<InitlMrgnRcvdPreHrcut
Ccy="EUR">
1000000
</InitlMrgnRcvdPreHrcut>
<InitlMrgnRcvdPstHrcut
Ccy="EUR">
1000000
</InitlMrgnRcvdPstHrcut>
<VartnMrgnRcvdPreHrcut
Ccy="EUR">
0
</VartnMrgnRcvdPreHrcut>
<VartnMrgnRcvdPstHrcut
Ccy="EUR">
0
</VartnMrgnRcvdPstHrcut>
</RcvdMrgnOrColl>
</MrgnUpd>
3.16
Variation
margin posted
by the
counterparty 1
(post-haircut)
3.17
Currency of the
variation
margins posted
3.18
Excess
collateral
posted by the
counterparty 1
3.19
Currency of the
excess
collateral
posted
3.20
Initial margin
collected by the
counterparty 1
(pre-haircut)
1000000
3.21
Initial margin
collected by the
counterparty 1
(post-haircut)
1000000
3.22
Currency of
initial margin
collected
EUR
3.23
Variation
margin
collected by the
0

288
Table 87- Margin update at an individual transaction level for an uncleared
derivative
No
Field
Example
XML Message
counterparty 1
(pre-haircut)
3.24
Variation
margin
collected by the
counterparty 1
(post-haircut)
0
3.25
Currency of
variation margin
collected
EUR
3.26
Excess
collateral
collected by the
counterparty 1
3.27
Currency of
excess
collateral
collected
3.28
Action type
MARU
3.29
Event date
2023-04-06
7 Guidelines on derivatives data management
7.1 Trade State Report
7.1.1 Introduction
552. The correct preparation of the Trade State Report (TSR) by TRs is essential to
ensure the achievement of one of the main objectives of EMIR – the monitoring of
systemic risks to financial stability.

289
553. TRs should include the most up-to-date information relating to outstanding
derivatives in the TSR in order to allow the authorities to have a direct and
immediate access to the most granular information on existing risk exposures
between counterparties. TRs should also allow each individual counterparty to have
a clear understanding of its own exposures vis-à-vis each market participant with
which it has an open derivative.
554. The requirements for TRs to produce TSR are included in Article 2 and 5 of the
RTS on data access and Article 4 of the RTS on data quality.
555. In sections 0 and 4.6.2, ESMA provides clarifications on the allowable
sequences of action types and on the allowable combinations between action types
and event types. Furthermore, in section 4.9 ESMA includes guidance with regards
to the timeliness of reporting of the conclusion, modification and termination of a
derivative.
556. TRs should use the information reported by counterparties, ERRs and RSEs to
prepare the TSR. The only instance where the TRs are allowed to update the most
current TSR without an action by the aforementioned entities is detailed in section
7.1.7.
557. If a counterparty uses a third party to report their transactions, but the
counterparty submits its valuation reporting itself, it should be possible for all the
reporting information to be amalgamated in the TSR so that all the parties have all
the relevant information available. In particular, the TSR provided to the authorities
should contain all the information, including trade, valuation and margin data.
7.1.2 Treatment of event date
558. When constructing the TSR, TRs should take into account the lifecycle events
based on the logical order derived from the fields ‘Event date’, ’Action type‘ and
’Event type‘. TRs should update the TSR based on the latest information for a given
derivative as derived from the field ’Event date‘. In the case of valuation and
margins reports with the same event date, the TRs should also consider the fields
‘Valuation timestamp’ and ‘Collateral timestamp’, respectively.
559. Where for a given event date there are several lifecycle events that affect the
data reported for a given derivative, they should all be included in the latest report
for that event date and the given action type. TRs should therefore consider the
field ’Reporting timestamp‘ only with regards to the given event date.
560. TRs should ensure that derivative contracts that mature on a given day should
still be included in the TSR for that day.
561. The information from previously submitted lifecycle events should in general
persist in the TSR when counterparties report subsequent lifecycle events for which
certain fields are not requested to be populated (i.e. not applicable). On the
contrary, TRs should not preserve the previous information in the updated TSR
when subsequent lifecycle events submitted by counterparties leave certain
optional fields blank. Counterparties should consistently report optional information

290
in order to avoid the deletion of available information, which otherwise could lead
to reconciliation breaks and missing information in the latest trade state.
562. TRs should update the state in the past for all outstanding derivatives, whereas
for non-outstanding derivatives TRs should be in a position to update their state for
up to ten years following their maturity or termination. This limit is related to the
requirement under Article 80(3) of EMIR for TRs to keep records of derivatives for
at least ten years following their maturity or termination.
563. Updating the state in the past does not imply that TRs should reproduce and
dispatch corrected historical TSRs on a recurrent basis and in an automated
manner every time late reports or lifecycle events referring to event dates in the
past are received. The TSR produced for a specific date should be considered as
a snapshot of all available information at a certain point in time. However, it is
essential that TRs’ internal databases should always be updated accordingly when
such reports are received.
564. TRs should have in place a process for reproducing and dispatching corrected
historical TSRs based on ad-hoc requests made by authorities or counterparties,
RSEs and ERRs. Such TSRs, when reproduced, should include missing
information from late submitted reports and lifecycle events referring to event dates
in the past which were not included in the original TSR produced at a specific point
in time in the past. TRs should make use of the versioning prefix part of the TRACE
file name convention to distinguish old versions from more recent versions.
565. Below tables illustrate the logic for different use cases:
Use case 1: Lifecycle event ‘NEWT’ for a previous event date
Lifecycle
event
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
NEWT
T
T-3
100
-
-
TR’s
database
before
update
TSR Date
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
T-4
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-3
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-2
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-1
-
-
-
-
-
-
T
-
-
-
-
-
-
TR’s
database
after
update
TSR Date
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
T-4
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-3
NEWT
T
T-3
100
-
-
T-2
NEWT
T
T-3
100
-
-
T-1
NEWT
T
T-3
100
-
-
T
NEWT
T
T-3
100
-
-
The TR should populate its database with the history from T-3 to T.
Use case 2: Lifecycle event ‘MODI’ for a previous event date

291
Lifecycle
event
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
MODI
T
T-2
120
-
-
TR’s
database
before
update
TSR Date
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
T-4
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-3
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
-
T-2
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
-
T-1
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
-
T
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
TR’s
database
after
update
TSR Date
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
T-4
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-3
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
-
T-2
MODI
T
T-2
120
-
-
T-1
MODI
T
T-2
120
-
-
T
MODI
T
T-2
120
-
-
The TR should modify the information stored in its database from T-2 to T.
Use case 3: Lifecycle event ‘CORR’ including both trade and valuation details for a previous
event date
Lifecycle
event
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
CORR
T
T-2
140
110
T-2
TR’s
database
before
update
TSR Date
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
T-4
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-3
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
T-3
T-2
VALU
T-2
T-2
100
95
T-2
T-1
VALU
T-1
T-1
100
94
T-1
T
VALU
T
T
100
93
T
TR’s
database
after
update
TSR Date
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
T-4
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-3
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
T-3
T-2
CORR
T
T-2
140
110
T-2
T-1
CORR
T
T-2
140
94
T-1
T
CORR
T
T-2
140
93
T
The TR should correct the trade details from T-2 to T and the valuation details should only be
corrected from T-2 to T-2 in order to preserve the more recent valuation updates.
Use case 4: Lifecycle event ‘CORR’ including both trade and valuation details for a previous
event date which falls in between ‘NEWT’ and another lifecycle event (e.g. ‘MODI’)
Lifecycle
event
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp

292
CORR
T
T-2
140
110
T-2
TR’s
database
before
update
TSR Date
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
T-4
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-3
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
T-3
T-2
VALU
T-2
T-2
100
95
T-2
T-1
VALU
T-1
T-1
100
94
T-1
T
MODI
T
T
120
94
T-1
TR’s
database
after
update
TSR Date
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
T-4
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-3
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
T-3
T-2
CORR
T
T-2
140
110
T-2
T-1
CORR
T
T-2
140
94
T-1
T
MODI
T
T
120
94
T-1
The TR should correct the trade details from T-2 to T-1 in order to avoid overwriting the
information from the more recent ‘MODI’ lifecycle event, and the valuation details should only
be corrected from T-2 to T-2 in order to preserve the more recent valuation updates.
Use case 5: Lifecycle event ‘TERM’ for a previous event date
Lifecycle
event
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event date
Notional
Val.amount
Early
term.date
TERM
T
T-2
-
-
T-2
TR’s
database
before
update
TSR Date
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Early
term.date
T-4
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-3
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
T-3
T-2
VALU
T-2
T-2
100
95
T-2
T-1
VALU
T-1
T-1
100
94
T-1
T
VALU
T
T
100
93
T
TR’s
database
after
update
TSR Date
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Early
term.date
T-4
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-3
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
T-3
T-2
TERM
-
-
-
-
-
T-1
-
-
-
-
-
-
T
-
-
-
-
-
-
The TR should log the termination of the outstanding derivative on T-2 and should remove
the history from that date onwards.
Use case 6: Lifecycle event ‘VALU’ for a previous event date
Lifecycle
event
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
VALU
T
T-2
-
100
T-2

293
TR’s
database
before
update
TSR Date
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
T-4
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-3
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
-
T-2
MODI
T-2
T-2
120
-
-
T-1
MODI
T-2
T-2
120
-
-
T
MODI
T-2
T-2
120
-
-
TR’s
database
after
update
TSR Date
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
T-4
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-3
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
-
T-2
VALU
T
T-2
120
100
T-2
T-1
VALU
T
T-2
120
100
T-2
T
VALU
T
T-2
120
100
T-2
Since there is not any more recent valuation information, the TR should update the relevant
valuation information from T-2 to T,and not only for T-2, trade detail information remains
unchanged.
Use case 7: Lifecycle event ‘VALU’ for a previous event date which falls in between ‘NEWT’
and another ‘VALU’ lifecycle event
Lifecycle
event
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
VALU
T
T-2
-
90
T-2
TR’s
database
before
update
TSR Date
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
T-4
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-3
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
-
T-2
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
-
T-1
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
-
T
VALU
T
T
100
95
T
TR’s
database
after
update
TSR Date
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
T-4
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-3
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
-
T-2
VALU
T
T-2
100
90
T-2
T-1
VALU
T
T-2
100
90
T-2
T
VALU
T
T
100
95
T
The TR should update the relevant valuation information from T-2 to T-1 and preserve the
valuation information from the more recent ‘VALU’ lifecycle event.
Use case 8: Lifecycle event ‘EROR’
Lifecycle
event
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
EROR
T
T
-
-
-

294
TR’s
database
before
update
TSR Date
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
T-4
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-3
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
-
T-2
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
-
T-1
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
-
T
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
-
TR’s
database
after
update
TSR Date
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
T-4
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-3
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-2
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-1
-
-
-
-
-
-
T
-
-
-
-
-
-
The event date of an ‘EROR’ lifecycle event should always be equal to the reporting date.
The TR should nevertheless remove the information from the inception date, i.e. the event
date of ‘NEWT’.
Use case 9: Lifecycle event ‘REVI’
Lifecycle
event
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Expiration.date
REVI
T
T
100
94
T+20
TR’s
database
before
update
TSR
Date
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Expiration.date
T-4
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-3
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
T+20
T-2
VALU
T-2
T-2
100
94
T+20
T-1
TERM
T-1
T-1
T
-
-
-
-
-
-
TR’s
database
after
update
TSR
Date
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Expiration.date
T-4
-
-
-
-
-
-
T-3
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
-
T-2
VALU
T-2
T-2
100
94
-
T-1
REVI
T
T
100
94
T+20
T
REVI
T
T
100
94
T+20
The event date of a ‘REVI’ lifecycle event should always be equal to the reporting date. The
TR should nevertheless revive the derivative contract starting from the date of termination,
i.e. T-1 in this case.
Use case 10: Reporting of multiple valuations for the same event date
Lifecycle
event
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
VALU
T
T-1
95
T 18:00:00

295
TR’s
database
before
update
TSR Date
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
T-4
T-3
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
T-3 18:00:00
T-2
VALU
T-2
T-2
100
95
T-2 18:00:00
T-1
VALU
T-1
T-1
100
94
T-1 16:00:00
T
VALU
T
T
100
93
T 18:00:00
TR’s
database
after
update
TSR Date
Action
type
Reporting
timestamp
Event
date
Notional
Val.amount
Val.timestamp
T-4
T-3
NEWT
T-3
T-3
100
-
T-3 18:00:00
T-2
VALU
T-2
T-2
100
95
T-2 18:00:00
T-1
VALU
T-1
T-1
100
95
T-1 18:00:00
T
VALU
T
T
100
93
T 18:00:00
The entity has sent more than one valuation report for the same event date. In this case the
TR should update the TSR for date T-1, because the valuation timestamp submitted in the
second report is later than the valuation timestamp submitted in the first report.
The same logic should apply in the case of multiple margins reports for the same event date –
in this case he TRs should consider the collateral timestamp.
7.1.3 Uniqueness of derivatives and special fields
566. The uniqueness of a derivative until the application of the revised RTS on
reporting was ensured at the level of the combination of LEI1-LEI2-UTI. It should
be noted that TRs used this unique combination to incorporate any modification or
the termination to the derivative.
567. From the date of application of the revised technical standards on reporting
under EMIR the uniqueness of derivatives concluded after that date should be
ensured at the level of the UTI, i.e. for the derivatives concluded after that date
there should not be two same UTIs, no matter the combination of counterparties.
This is of course notwithstanding that for double-sided reports (i.e. where both sides
report under EMIR), the same UTI would appear twice, reported by either of the
counterparties.
568. From that date onwards, TRs should therefore use the full triplet (LEI1-LEI2-
UTI) only to update the state of the derivatives concluded prior to the application
date of the RTS on reporting. To update the state of derivatives concluded after the
application date of the RTS on reporting, the TRs can use the combination LEI1-
UTI. For simplicity, the TRs can use full triplet in all cases to update the state of the
derivative (incl. derivatives concluded after the application date of the RTS on
reporting). The uniqueness of the newly reported UTIs should be ensured by the
counterparties and ERRs when reporting and by the TRs when verifying the reports
in accordance with the validation rules.

296
569. Counterparties and TRs should be reminded that the requirement included in
Article 8 of the ITS on reporting is the only way for reporting counterparties and
ERRs to update the two LEIs.
570. Counterparties should not amend fields 1.4 ’Counterparty 1’, 1.9 ’Counterparty
2’ and 2.1 ‘UTI’ of previous submissions by submitting a report with action type
’CORR’ and TRs should not accept any such submissions. Furthermore, it is not
possible to correct information reported in the fields ‘Event date’, ‘Event type’,
‘Reporting timestamp’ and ‘Action type’, as the information included in these fields
in the report with action type ‘CORR’ will refer to the correction, rather than to the
previous submissions.
7.1.4 Treatment of action type ‘Revive’.
571. When the counterparty or the ERR submits a report with action type ’Revive‘,
the TR should process the report and based on the information included in the fields
’Expiration date‘ or ’Early termination date‘, assess whether to reinclude it in the
TSR or simply update its internal database relating to that derivative (see also an
example on update of TSR after a report with action type ‘Revive’ in section 7.1.2).
572. The reporting counterparty or the ERR should provide complete information
regarding the expiration date and the early termination date of a derivative. The
provided information should follow the logical timeline sequence included in the
validation rules. In particular, early termination date should not be in the future.
573. The field ‘Event date’ and the date part of the field ‘Reporting timestamp’ for
reports with action type ‘Revive’ should be the same.
574. Where the expiration date in the derivative report is in the future or it is not
populated, and the early termination date is not populated, the TR should include
the derivative in the TSR with all the values that have been included in the
submission with action type ’Revive‘.
575. Where the expiration date or the early termination date are both in the past, the
TR should update its own records, but not the TSR.
576. Where the expiration date is in the future, but the early termination date is in the
past, the TR should update its own records, but not the TSR.
577. Where the early termination date is populated with a date later than the event
date or when it is populated with a date equal to or later than the expiration date,
such report would not impact the TSR as it would be rejected due to its non-
compliance with the validation rules. The below table summarises the relevant
instances.

297
Table 88 - Interaction between TSR and reports with action type ’Revive’
Expiration date
Early termination date
Impact to the TSR
Earlier than event date
Earlier than event date
No impact to the TSR, only
internal database should be
updated
Equal to event date
Empty
Update TSR and internal
database
Equal to event date
Earlier than event date
No impact to the TSR, only
internal database should be
updated
Later than event date or
empty
Empty
Update TSR and internal
database
Later than event date or
empty
Equal to or earlier than
event date
No impact to the TSR, only
internal database should be
updated
Later than event date or
empty
Earlier than expiration
date, but later than event
date
No impact to the TSR (rejected)
Earlier, equal to or later
than event date
Equal to or later than
expiration date
No impact to the TSR (rejected)
7.1.5 Reporting with action type ‘EROR‘ and ‘REVI’
578. Where a counterparty sends an ‘EROR‘ report for its side of the derivative, the
TR that has received such report should remove the derivative reported by that
counterparty from the TSR. The TR should do so even when the other counterparty
reports to the same TR and has not made the same report. Counterparties should
be responsible for resolving any type of mismatch caused by the usage of ‘EROR’
reports.
579. The TR should restore the derivative to the TSR when a report with action type
‘Revive‘ has been received and it is compliant with the validation rules and the
logical rules included in table under paragraph 576. The TR should do so even
when the other counterparty reports to the same TR and has not made the same
report. Counterparties should be responsible for resolving any type of mismatch
caused by the usage of ‘REVI’ reports.

298
7.1.6 Inclusion in the TSR of schedule information
580. The RTS and the ITS on reporting detail the requirements for reporting of
notional schedules and other payments.
581. TRs should include in the TSR only the current value from the schedules
reported, as opposed to including all the values from the schedules. This should be
applied for the following schedule fields: 2.50-2.52 (‘Price’), 2.57-2.59 (‘Notional
amount of leg 1’), 2.61-2.63 (‘Notional quantity of leg 1’), 2.66-2.68 (‘Notional
amount of leg 2’), 2.70-2.72 (‘Notional quantity of leg 2’), and 2.135-2.137 (‘Strike
price’). This will reduce the amount of data provided to authorities and would
facilitate the immediate assessment of exposures.
582. TRs should use the date fields referring to the effective date and end date of the
information contained in the schedule to determine which data point to include in
the TSR. For example, a schedule with the following characteristics is reported:
‘value’ {100, 150, 200}, ‘effective date’ {T, T+10, T+20}, ‘end date’ {T+9, T+19,
T+29}. The TSRs generated for reporting dates T to T+9 should display the value
100, the TSRs generated for reporting dates T+10 to T+19 should display the value
150, and finally, the TSRs generated for reporting dates T+20 to T+29 should
display the value 200.
583. For fields 2.73-2.78, referring to other payments, TRs should include in the TSR
all relevant payments. Payments of different types should not be overwritten. This
means that if a counterparty reports the same payment type more than one time (in
different reports), the TSR should update such value. Below example illustrates the
logic:
Event date
CP reports
TSR for that day
T
UFRO, 100
UFRO, 100
T+1
PEXH, 150; PEXH,
200
UFRO, 100; PEXH, 150; PEXH, 200
T+2
PEXH, 250; PEXH,
300
UFRO, 100; PEXH, 250; PEXH, 300
T+3
UWIN, 50
UFRO, 100; PEXH, 250; PEXH, 300; UWIN, 50
584. For fields 2.122-2.131, referring to commodities, TRs should include all the
information as it is reported by counterparties.
585. The most up-to-date linking IDs should persist in the TSR when a counterparty
reports a lifecycle event where these fields are not applicable. On the contrary, the
linking IDs should not persist in the TSR when a counterparty reports a lifecycle
event where these fields are optional and reported as blank. The same approach
should apply also to fields like ‘Event type’.

299
7.1.7 Dead derivatives
586. Where a counterparty ceases to exist, without being acquired or merged, no
derivatives should remain outstanding at the trade repository.
587. If the reporting counterparty reports directly to the TR and notifies the TR in
order to cancel its membership, the TR should liaise with the reporting counterparty
to terminate the relevant derivatives, while it is still active, by submitting reports with
action types ‘TERM‘ where the termination date is at the latest the date of the
dissolution of the reporting counterparty.
588. If the reporting counterparty does not report directly to the TR, and the ERR or
RSE notifies the TR, the TR should liaise with that entity so that the ERR or RSE
terminates the relevant derivatives, while the reporting counterparty is still active,
by submitting reports with action types ‘TERM’ where the termination date is at the
latest the date of the dissolution of the reporting counterparty.
589. Where the reporting counterparty has ceased to exist and has not terminated
the outstanding derivatives and the TR becomes aware of this situation, the
following waterfall should be followed:
a. If the ERR is different from the reporting counterparty and that ERR has not
used RSE, the TR should contact the ERR, should request the submission of
reports with action types ‘TERM where the termination date is at the latest the
date of the dissolution of the reporting counterparty and, simultaneously, should
raise the issue to the NCA of the reporting counterparty. If the reporting
counterparty or the ERR has used a RSE and that entity is still an active RSE
at the TR, the TR should contact the RSE, should request the submission of
reports with action types ‘TERM’ where the termination date is at the latest the
date of the dissolution of the reporting counterparty and, simultaneously, should
raise the issue to the NCA of the reporting counterparty.
b. If the previous step in point a is not applicable, the TR should assess the
maturity date of the outstanding derivatives that should be terminated to assess
whether they would naturally expire in the following twelve months. If that is the
case, no further action should be undertaken by the TR. This is to alleviate the
work of TRs and minimise the risks associated with the process of excluding
dead derivatives.
c. If the previous step in point b is not applicable, the TR should contact the other
counterparty/ies to the outstanding derivatives, where those entities report
directly to the TR, and request them to terminate the outstanding derivatives on
behalf of the reporting counterparty while, if possible, raise the issue to the
NCA(s) to follow-up with the other counterparty/ies.
d. Finally, in case none of the above is applicable, the TR, upon confirming with
the NCA and notifying ESMA, should flag the relevant derivatives accordingly
and not take them into consideration for the purposes of TSR, reconciliation
process or any subsequent aggregations such as position reports.

300
590. In the case of derivatives that have remained outstanding at the date of
application of the new reporting requirements, the process referred to in paragraph
589, should be performed by the TRs at the earliest opportunity and no later than
by the end of the transition period.
7.2 Reconciliation
7.2.1 Scope of data subject to reconciliation
591. TRs should ensure consistent determination of the scope of data subject to
reconciliation. TRs therefore should only include in the reconciliation process
derivatives, both at trade and at position level, where all the below conditions are
fulfilled:
a. Counterparty 1 has reporting obligation, i.e. it is a counterparty established in
the EU or an AIF, whose AIFM is established in the EU, based on the GLEIF.
b. Counterparty 2 has reporting obligation as indicated if established in the EU or
an AIF, whose AIFM is established in the EU, based on the GLEIF or the field
1.14 ‘Reporting obligation of the counterparty 2’ is populated with ‘True’.
c. The derivative has not been subject to a report with action type ‘EROR’, unless
it has been followed by a report with action type ‘REVI’.
d. The derivative is outstanding, as referred to in Article 2(2)(a) and 2(2)(b) of the
ITS on reporting, or it has been outstanding in the last thirty calendar days.
592. TRs should include late reported derivatives in the reconciliation process if the
late report refers to an outstanding derivative subject to reconciliation.
593. TRs should remove derivatives from the reconciliation process that have been
non-outstanding for thirty-one calendar days or more, and this should be
determined based on the earliest date reported in either field ’Expiration date’ or
field ‘Early termination date’. Moreover, derivatives that have received a report with
action type ’EROR’ should also be removed.
594. It is worth recalling that TRs should reconcile the data in line with the relevant
reconciliation tolerance, as well as the relevant start date as included in Table 2 of
the Annex to the RTS on data quality.
7.2.2 Position-level vs trade-level reconciliation
595. TRs should therefore reconcile, both position-level and trade-level reports, as
determined by the latest applicable event date, which should be two working days
before the date on which the reconciliation takes place. For instance, in case the
reconciliation takes place on Wednesdays, TRs should include the derivatives
reported whose event date is Monday or earlier. In case the reconciliation takes
place on Monday, the TRs should include the derivatives whose event date is
Thursday or earlier. TARGET 2 calendar should be used to determine working
days.

301
Table 89– Information flow asymmetries between the reconciliation process performed
with a 2-day lag and the TSR
Business
day
Event
date
Events
T
T
• Counterparties 1 and 2 execute a new derivative contract on
event date T
• Counterparty 1 sends the report to the TR on business day T
T+1
T+1
• Counterparty 2 sends the report to the TR on business day
T+1
• TSR delivered on business day T+1 by 06.00 UTC to entities
/ 12.00 UTC to authorities include the latest state of reported
derivatives on business day T with event date T-1 or earlier,
i.e. above derivative is not included.
• Reconciliation report delivered on business day T+1 by 06.00
UTC to entities / 12.00 UTC to authorities for event date T-2
or earlier does not include the above derivative
• Reconciliation process runs until midnight UTC for reported
derivatives during business day T or earlier with event date
T-1 or earlier.
T+2
T+2
596. TSR delivered on business day T+2 by 06.00 UTC to
entities / 12.00 UTC to authorities include the latest state
of reported derivatives on business day T+1 with event
date T or earlier, i.e. above derivative is included but has
not yet been subject to reconciliation (reconciliation flag =
“NA”).
• Reconciliation report delivered on business day T+2 by 06.00
UTC to entities / 12.00 UTC to authorities for event date T-1
or earlier does not include the above derivative
• Reconciliation process runs until midnight UTC for reported
derivatives during business day T+1 or earlier with event date
T or earlier.
T+3
T+3
597. TSR delivered on business day T+3 by 06.00 UTC to
entities / 12.00 UTC to authorities include the latest state
of reported derivatives on business day T+2 with event
date T+1 or earlier, i.e. above derivative is included and has

302
been subject to reconciliation (reconciliation flag is updated
accordingly)
• Reconciliation report delivered on business day T+3 by 06.00
UTC to entities / 12.00 UTC to authorities for event date T
or earlier include above derivative.
7.2.3 Reconciliation of valuation
598. The reconciliation of valuation from trade-level or position-level perspective
should follow the guidance provided in section 7.2.2.
599. When one of the counterparties to the derivative is an NFC-, that entity is not
required to report valuation data. Even if an entity not obliged to report valuation
information does so, TRs should omit such information from the reconciliation
process.
600. When both counterparties have an obligation to report valuations, TRs should
include all the relevant valuation data in the reconciliation process and flag the
derivatives where one of the counterparties have not reported valuation or where
there are reconciliation breaks between the information as not reconciled.
601. Please refer to section 7.3.3 on the interplay of the reconciliation of valuation
status with the reconciliation status of the derivative.
7.2.4 Derivatives with two legs
2. TRs should reconcile derivatives with two legs by reconciling each of the
legs as reported by the counterparties.
602. It is worth noting that in the case of most types of derivatives with two legs such
as interest-rate swaps, cross-currency swaps and FX swaps, the order of the legs
cannot be unequivocally defined, as there is no specific prevalence of one leg over
the other. Therefore, when counterparties report inconsistently the two legs of the
derivative, the TR should intend matching the two legs irrespective of the sequence,
taking into account the values reported by the two counterparties under field
‘Direction of leg 1’ by matching the legs with opposite values. In case counterparty
1 has reported it with ‘payer’ the TR should reconcile it with the leg that is identified
as ‘receiver’ or with the leg that is not identified, when leg 1 is identified with ‘payer’.
603. When an outstanding position is the result of netting of a position to zero (Level
= P and Quantity=0), TR should exclude from the reconciliation the fields ‘Direction’,
‘Direction of leg 1’ and ‘Direction of leg 2’.
7.2.5 Reconciliation of schedule information
604. TRs should only reconcile the data on schedule fields that are included in the
TSR. This approach is aligned with the one described in section 7.1.6 Inclusion in
the TSR of schedule information.

303
7.3 Data Quality feedback
7.3.1 Rejection feedback
605. Article 1(1) of the RTS on data quality requires the TRs to verify the data they
receive from the report submitting entities upon their reception. In accordance with
Article 1(3) of the RTS on data quality TRs shall provide the RSEs with detailed
information on the results of the data verification. This immediate rejection feedback
shall be provided to the relevant RSE within 60 minutes from the reception of the
data, i.e. from the moment the submitted file enters the system of the TR.
606. Apart from the provision of immediate rejection response to the RSE, the TR
can provide this feedback also to the reporting counterparties and entities
responsible for reporting if those have access to the TR and they express interest
to receive the immediate rejection response.
607. Article 1(1) of the RTS on data quality provides a list of specific verification
checks which should be executed by the TRs. Authentication according to Article
1(1)(a) should be performed upfront, therefore no specific rejection feedback should
be provided with respect to this first verification step. The remaining verification
checks should be performed at the point of submission and result in rejection
feedback in accordance with the following rejection categories:
a. Schema validation of a submission as per Article 1(1)(b);
b. Authorization / permission of a report submitting entity as per Article 1(1)(c);
c. Logical validation of a submission as per Articles 1(1)(d) to 1(1)(k);
d. Business rules or content validation of a submission as per Article 1(1)(l), as
clarified by these Guidelines.
608. Under Article 1(2) of the RTS on data quality a TR shall “reject a derivative report
that does not comply with one of the requirements set out in paragraph 1 and assign
to it one of the rejection categories” mentioned above.
609. To implement these verification checks TRs should apply validation rules to
ensure that reporting is performed according to the EMIR regime, including the
specifications of the technical standards, as clarified by these Guidelines.
Accordingly, reporting counterparties or submitting entities should comply with the
reporting requirements specified by the validation rules which are published
together with these Guidelines on ESMA’s website.
610. To keep the technical aspects of the data quality requirements relevant and
correctly applied, ESMA updates the validation rules when necessary or
appropriate. When the validation rules are updated, ESMA specifies the effective
day of application of the updated validation rules and the TRs should ensure that
they implement the changes in the specified timeframe and start performing the
verification checks with the updated validation rules on the designated date of
application.

304
611. Similarly the reporting counterparties, ERRs or RSEs as applicable should
update their reporting systems so that the submitted reports are compliant with the
new validation rules on the designated date of application.
612. The validation rules contain a specific error code and error message containing
an xml path for each of the validation rules and the TRs should use these error
codes and messages to specify the rejection reason when communicating
rejections to the relevant parties. When a derivative report is rejected, the rejection
response should contain all the error codes of the validation rules that the submitted
derivative report failed. Therefore, the information on the error codes should be
provided at report level.
613. If the submitted report is correct and compliant with all the reporting
requirements, and with the technical specifications in the validation rules, the
feedback should indicate that the derivative report was accepted.
614. The TR should verify compliance of the file with the XML schema (syntax of the
whole file and specific derivative reports). If the file is not compliant, the whole file
(all derivatives included in the file) is rejected, and the reason will be that the file is
‘corrupted’. In the statistics this should be reported as 1 file rejection even if the file
contradicts the XML schema in multiple instances.
615. If, however, the file is compliant with the XML schema and contains e.g. 3
derivatives, but all the derivatives fail validations, the statistics should show the file
as accepted with 3 rejected and 0 accepted derivatives.
616. Following the receipt of an immediate rejection response, to ensure their
compliance with the reporting obligation under Article 9 of EMIR, the reporting
counterparties or ERR should, either directly or through a RSE, submit correct and
complete reports by the reporting timeline.
617. Further to the immediate rejection feedback, Article 4(1)(c) of the RTS on data
quality requires the TRs to make available to the reporting counterparties, RSEs,
ERRs and third parties which have been granted an access to EMIR data under
Article 78(7) of EMIR end-of-day reports of derivatives that have been rejected
during that day. As specified in the RTS on data quality, this report shall be made
accessible by 6:00 UTC to entities and 12.00 UTC to authorities on the following
working day. For the determination of working days TARGET 2 calendar should be
used.
618. The TRs should use all the data they have collected to determine what
information they should provide and to which RSEs, ERRs and counterparties.
Information on errors pertaining to the whole file should be made available to the
RSE of the file and to all ERRs and counterparties populated in fields 1.3 and 1.4
in that rejected file as applicable, assuming it is possible to read the information
from the rejected file. Information on errors pertaining to a specific record should
be made available to the RSE, ERR and counterparty 1 populated in this record to
the extent the entities are on-boarded.
619. Regarding the deadlines for provision of (immediate and end-of-day) rejection
response under special circumstances, such as scheduled or non-scheduled

305
maintenance, the TRs should proceed analogously to the existing guidance on
operational aspects on data access, as detailed in section 7.4.1.
7.3.1.1 Immediate rejection feedback
620. Immediate rejection response shall according to Article 1(3) of the RTS on data
quality be provided by the TRs in the standardized response messages compliant
with ISO 20022 format, specifically the XSD schema. It should contain the following
information:
Table 90 - Immediate rejection feedback
No.
Field
Details to be reported
XML Message
1
File identification
Textual value
…
<RjctnSttstcs>
<CtrPtyId>
<RptgCtrPrty>
<LEI>12345678901234500000</LEI>
</RptgCtrPrty>
<RptSubmitgNtty>
<LEI>12345678901234500000</LEI>
</RptSubmitgNtty>
<NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<LEI>12345678901234500000</LEI>
</NttyRspnsblForRpt>
</CtrPtyId>
<RptSttstcs>
<TtlNbOfRpts>1</TtlNbOfRpts>
<TtlNbOfRptsAccptd>1
</TtlNbOfRptsAccptd>
<TtlNbOfRptsRjctd>0
</TtlNbOfRptsRjctd>
</RptSttstcs>
<DerivSttstcs>
<DtldSttstcs>
<TtlNbOfTxs>10
</TtlNbOfTxs>
<TtlNbOfTxsAccptd>9
</TtlNbOfTxsAccptd>
<TtlNbOfTxsRjctd>1
</TtlNbOfTxsRjctd>
<TxsRjctnsRsn>
<TxId>
<ActnTp>NEWT</ActnTp>
<RptgTmStmp>
2025-0407T10:00:00Z
</RptgTmStmp>
<DerivEvtTp>TRAD
</DerivEvtTp>
<EvtTmStmp><Dt>
2025-04-07
</Dt></EvtTmStmp>
<OthrCtrPty>
<Lgl><LEI>
2
Rejection reason
Error code
3
Rejection description
Error description
4
Number of derivatives
received
10
5
Number of derivatives
accepted
9
6
Number of derivatives
rejected
1
7
Identification of the
derivatives
8
Counterparty 1 (Reporting
counterparty)
123456789012345
00000
9
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLM
NOPQRST
10
UTI
UTI1
11
Reporting timestamp
2025-04-07T10:00:00Z
12
Event date
2025-04-07
13
Event type
TRAD
14
Action type
NEWT
15
Status Accepted
ACPT
16
Status Rejected
RJCT
17
Rejection reason
EMIR-VR-1001-6

306
621. Where the rejection pertains to field 1.4 ‘Counterparty 1 (Reporting
counterparty)’ or field ‘1.9 Counterparty 2’, these fields might not be populated in
the rejection report.
7.3.1.2 End-of-day rejection report
622. End-of-day rejection report shall be provided by the TRs in the standardized
response messages compliant with ISO 20022 format in accordance with Article
4(1)(c) of the RTS on data quality, specifically the XSD schema. It should contain
the following information:
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI></Lgl>
</OthrCtrPty>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
<Sts>RJCT</Sts>
<DtldVldtnRule>
<Id>EMIR-VR-1001-6</Id>
<Desc>Xpath of the
Erroneous field</Desc>
</DtldVldtnRule>
</TxsRjctnsRsn>
</DtldSttstcs>
…
18
Rejection description
Xpath of the erroneous
field
Table 91 - End-of-day rejection report
No.
Field
Details to be
reported
XML Message
1
Number of files received
3
…
<RjctnSttstcs>
<CtrPtyId>
<RptgCtrPrty>
<LEI>12345678901234500000</LEI>
</RptgCtrPrty>
<RptSubmitgNtty>
<LEI>12345678901234500000</LEI>
</RptSubmitgNtty>
<NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<LEI>12345678901234500000</LEI>
</NttyRspnsblForRpt>
</CtrPtyId>
<RptSttstcs>
<TtlNbOfRpts>3</TtlNbOfRpts>
<TtlNbOfRptsAccptd>2
2
No. of files accepted
2
3
No. of files rejected
1
4
File identification
REPORT1
5
Rejection reason
CRPT
6
Rejection description
File is corrupted
7
Number of derivatives
received
10
8
Number of derivatives
accepted
9
9
Number of derivatives s
rejected
1
10
Identification of the
derivatives

307
11
Counterparty 1 (Reporting
counterparty)
123456789012345
00000
</TtlNbOfRptsAccptd>
<TtlNbOfRptsRjctd>1
</TtlNbOfRptsRjctd>
<NbOfRptsRjctdPerErr>
<DtldNb>1</DtldNb>
<RptSts>
<MsgRpId>REPORT1</MsgRpId>
<Sts>CRPT</Sts>
</RptSts>
</NbOfRptsRjctdPerErr>
</RptSttstcs>
<DerivSttstcs>
<DtldSttstcs>
<TtlNbOfTxs>10
</TtlNbOfTxs>
<TtlNbOfTxsAccptd>9
</TtlNbOfTxsAccptd>
<TtlNbOfTxsRjctd>1
</TtlNbOfTxsRjctd>
<TxsRjctnsRsn>
<TxId>
<ActnTp>NEWT</ActnTp>
<RptgTmStmp>
2025-0407T10:00:00Z
</RptgTmStmp>
<DerivEvtTp>TRAD
</DerivEvtTp>
<EvtTmStmp><Dt>
2025-04-07
</Dt></EvtTmStmp>
<OthrCtrPty>
<Lgl><LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI></Lgl>
</OthrCtrPty>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
<Sts>RJCT</Sts>
<DtldVldtnRule>
<Id>EMIR-VR-1001-6</Id>
<Desc>Xpath of the
erroneous field</Desc>
</DtldVldtnRule>
</TxsRjctnsRsn>
</DtldSttstcs>
…
12
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLM
NOPQRST
13
UTI
UTI1
14
Reporting timestamp
2025-04-
07T10:00:00Z
15
Event date
2025-04-07
16
Event type
TRAD
17
Action type
NEWT
18
Status Accepted
ACPT
19
Status Rejected
RJCT

308
623. Where the rejection pertains to field 1.4 ‘Counterparty 1 (Reporting
counterparty)’ or field 1.9 ‘Counterparty 2’, these fields might not be populated in
the rejection report.
624. End-of-day rejection report should be provided electronically in ISO 20022 XML
message. TRs could, in addition, use another interface so that e.g. in case the
reporting counterparty or the entity responsible for reporting are not reporting
directly to the TR, but have a view only account, will be able to have detailed
understanding on their compliance with the reporting obligation under EMIR.
7.3.2 Warnings feedback
625. Article 4(1)(e) to 4(1)(g) of the RTS on data quality requires the TRs to make
available to the reporting counterparties, RSEs, ERRs and third parties which have
been granted an access to EMIR data under Article 78(7) of EMIR end-of-day
reports on missing valuations of outstanding derivatives, missing margin
information of outstanding derivatives, as well as on abnormal values reported in
the fields.
626. These end-of-day reports shall be made accessible to entities by 6:00 UTC and
to authorities by 12.00 UTC on the following working day. For the determination of
working days TARGET 2 calendar should be used.
627. The TRs should use all the data they have collected to determine what
information they should provide and to which RSEs, ERRs and counterparties.
628. The inclusion of derivatives into the end-of-day warnings feedback reports for
missing valuations and margin information should follow the same rules as the
inclusion of derivatives into the Trade State Report as described in detail in section
7.1. Therefore, the warnings should be provided on the basis of TSR and for
example dead derivatives should be excluded (as explained in section 7.1.7).
629. The inclusion of derivatives into the end-of-day warnings feedback report for
abnormal values should instead be based on the TAR, where reports received with
action type ‘New’, ‘Position component’, ‘Modify’ or ‘Correct’ should be used for this
purpose.
630. The number of derivatives included in the warnings feedback reports should be
assessed from the viewpoint of counterparty 1.
631. End-of-day warnings feedback reports on missing valuations and margin
information should exclude records pertaining to counterparties who are not obliged
to submit daily valuations and margin information on outstanding derivatives. The
identification of these out-of-scope records should be achieved by filtering field 1.5
‘Nature of counterparty 1’ = ‘N’ and field 1.7 ‘Clearing threshold of counterparty 1’
= ‘False’. Moreover, the warnings feedback report on missing margin information
20
Rejection reason
EMIR-VR-1001-6
21
Rejection description
Xpath of the
erroneous field

309
should exclude uncollateralized trades. The identification of the out-of-scope
uncollateralized records should be achieved by filtering field 3.11 ‘Collateralisation
category’ = ‘UNCL’.
632. The TRs should provide the relevant data in scope for the warnings feedback
reports to the relevant RSEs, and to all ERRs and counterparties as applicable.
633. End-of-day reports providing information on missing or abnormal data do not
entail rejection of derivative reports, they are of informative nature and should
provide warnings on possible faults in reporting to the relevant parties.
Nevertheless, despite the informative nature, the reporting counterparties, ERRs
and RSEs as applicable should always investigate the identified issues and if
misreporting is confirmed the data should be corrected or missing data reported
without undue delay.
634. Regarding the deadlines for provision of end-of-day warnings feedback reports
under special circumstances, such as scheduled or non-scheduled maintenance,
the TRs should proceed analogously to the existing guidance on operational
aspects on data access included under section 7.4.1.
635. End-of-day warnings feedback reports should be provided electronically in the
standardized response messages compliant with ISO 20022 format. TRs could, in
addition, use another interface so that e.g. in case the reporting counterparty or the
entity responsible for reporting are not reporting directly to the TR, but have a view
only account, will be able to have detailed understanding on their compliance with
the reporting obligation under EMIR Refit.
7.3.2.1 Missing valuations report
636. According to Article 4(1)(e) of the RTS on data quality the outstanding
derivatives for which no valuation has been reported, or the valuation that was
reported is dated more than fourteen calendar days earlier than the day for which
the report is generated shall be included in the end-of-day missing valuations
report. To provide the missing valuations feedback the TRs should use as reference
the TSR generated in accordance with section 7.1.
637. Therefore, this report should include:
a) any outstanding derivative in scope of valuation reporting requirements for which field
2.21 ‘Valuation amount’ was never reported as well as
b) any outstanding derivative in scope of valuation reporting requirements for which field
2.21 ‘Valuation amount’ was reported at least once, but the most recent value of this
field, i.e. with most recent field 2.23 ‘Valuation timestamp’, has the value of this
timestamp more than fourteen calendar days earlier than the day for which the report
is generated.
638. End-of-day missing valuations report provided by the TRs in the standardized
response messages compliant with ISO 20022 format, specifically the XSD
schema, should contain the information specified in the Table 92.

310
Table 92 - End-of-day missing valuations report
No.
Field
Details to be
reported
XML Message
1
Number of outstanding
derivatives
10
<MssngValtn>
<Rpt>
<NbOfOutsdngDerivs>10
</NbOfOutsdngDerivs>
<NbOfOutsdngDerivsWithNoValtn>1
</NbOfOutsdngDerivsWithNoValtn>
<NbOfOutsdngDerivsWithOutdtValtn>0
</NbOfOutsdngDerivsWithOutdtValtn>
<Wrnngs>
<CtrPtyId>
<RptgCtrPrty>
<LEI>12345678901234500000</LEI>
</RptgCtrPrty>
<RptSubmitgNtty>
<LEI>12345678901234500000</LEI>
</RptSubmitgNtty>
<NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<LEI>12345678901234500000</LEI>
</NttyRspnsblForRpt>
</CtrPtyId> <NbOfOutsdngDerivs>10
</NbOfOutsdngDerivs>
<NbOfOutsdngDerivsWithNoValtn>1
</NbOfOutsdngDerivsWithNoValtn>
<NbOfOutsdngDerivsWithOutdtValtn>0
</NbOfOutsdngDerivsWithOutdtValtn>
<TxDtls>
<TxId>
<OthrCtrPty>
<Lgl><LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI></Lgl>
</OthrCtrPty>
<UnqIdr>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</UnqIdr>
</TxId>
<ValtnAmt><Amt Ccy="EUR">5000000
</Amt></ValtnAmt>
<ValtnTmStmp>
2023-04-07T10:00:00Z
</ValtnTmStmp>
</TxDtls>
</Wrnngs>
</MssngValtn>
2
Number of outstanding
derivatives with no valuation
1
3
Number of outstanding
derivatives with outdated
valuation
0
4
Identification of the
derivatives
5
Counterparty 1
(Reporting counterparty)
123456789012345
00000
6
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLM
NOPQRST
7
UTI
UTI1
8
Valuation amount
5000000 EUR
9
Valuation timestamp
2023-04-
07T10:00:00Z
311
7.3.2.2 Missing margin information report
639. According to Article 4(1)(f) of the RTS on data quality the outstanding derivatives
for which no margin information has been reported, or the margin information that
was reported is dated more than fourteen calendar days earlier than the day for
which the report is generated shall be included in the end-of-day missing margin
information report. To provide the missing margin information feedback the TRs
should use as reference the TSR generated in accordance with section 7.1.
640. Therefore, this report should include:
a. any outstanding derivative in scope of margin reporting requirements for which
margin report was never reported with action type ‘MARU’ for the given UTI (or
it was reported but then the UTI with corresponding margin was errored and no
margin information was reported after reviving the derivative) and
b. any outstanding derivative in scope of margin reporting requirements for which
margin report was reported at least once, but the most recent report, i.e. with
most recent field 3.7 ‘Collateral timestamp’, has the date value of this timestamp
more than fourteen calendar days earlier than the day for which the report is
generated.
641. End-of-day missing margin information report provided by the TRs in the
standardized response messages compliant with ISO 20022 format, specifically the
XSD schema, should contain the information included in the below table.
Table 93 - End-of-day missing margin information report
No.
Field
Details to be
reported
XML Message
1
Number of outstanding
derivatives
10
<MssngMrgnInf>
<Rpt>
<NbOfOutsdngDerivs>10
</NbOfOutsdngDerivs>
<NbOfOutsdngDerivsWithNoMrgnInf>1
</NbOfOutsdngDerivsWithNoMrgnInf>
<NbOfOutsdngDerivsWithOutdtMrgnInf>0
</NbOfOutsdngDerivsWithOutdtMrgnInf>
<Wrnngs>
<CtrPtyId>
<RptgCtrPrty>
<LEI>12345678901234500000</LEI>
</RptgCtrPrty>
<RptSubmitgNtty>
<LEI>12345678901234500000</LEI>
</RptSubmitgNtty>
<NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<LEI>12345678901234500000</LEI>
</NttyRspnsblForRpt>
</CtrPtyId>
<NbOfOutsdngDerivs>10
2
Number of outstanding
derivatives with no margin
information
1
3
Number of outstanding
derivatives with outdated
margin information
0
4
Identification of the
derivatives
5
Counterparty 1 (Reporting
counterparty)
123456789012345
00000
6
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLM
NOPQRST
7
UTI
UTI1
8
Collateral timestamp
2023-04-
07T10:00:00Z

312
7.3.2.3 Abnormal values report
642. According to Article 4(1)(g) of the RTS on data quality the derivatives that were
received with action type ‘New’, ‘Position component’, ‘Modify’ or ‘Correct’ whose
notional amount is greater than a threshold for that class of derivatives shall be
included in the end-of-day abnormal values report.
643. Derivative reports received on the working day prior to the working day when
the feedback is generated by 6 a.m. UTC should be included in the warnings
feedback report for the given day. If the TR accepts also submissions on non-
working days, the warnings feedback report should include also submitted reports
received on non-working days preceding the working day when the feedback is
generated (e.g. for Monday warnings feedback report submissions received on
Friday, Saturday and Sunday).
644. Abnormal values (outliers) should be identified for the following fields:
c. 2.55 ‘Notional amount of leg 1’,
d. 2.59 ‘Notional amount in effect on associated effective date of leg 1’,
e. 2.60 ‘Total notional quantity of leg 1’,
f. 2.63 ‘Notional quantity in effect on associated effective date of leg 1’,
g. 2.64 ‘Notional amount of leg 2’,
h. 2.68 ‘Notional amount in effect on associated effective date of leg 2’,
</NbOfOutsdngDerivs>
<NbOfOutsdngDerivsWithNoMrgnInf>1
</NbOfOutsdngDerivsWithNoMrgnInf>
<NbOfOutsdngDerivsWithOutdtMrgnInf>0
</NbOfOutsdngDerivsWithOutdtMrgnInf>
<TxDtls>
<TxId>
<OthrCtrPty>
<Lgl><LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI></Lgl>
</OthrCtrPty>
<UnqIdr>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</UnqIdr>
</TxId>
<CollTmStmp>
2023-04-07T10:00:00Z
</CollTmStmp>
</TxDtls>
</Wrnngs>
</MssngMrgnInf>

313
i. 2.69 ‘Total notional quantity of leg 2’,
j. 2.72 ‘Notional quantity in effect on associated effective date of leg 2’.
645. A derivative report should be included into the warnings feedback report when
at least one of the listed fields was populated with an abnormal value. If the
derivative report contains abnormal values for more than one field, all of these
abnormal values should be indicated in the feedback.
646. The values of these fields should be converted into the EUR equivalent amounts
for the purpose of abnormal values detection.
647. Abnormal values should be identified for each class and level of derivatives
(credit, commodity, currency, equity, interest rates), as categorized by field 2.11
‘Asset class’, and field 2.154 ‘Level’ separately.
648. To ensure compliance with Article 4(1)(g) of the RTS on data quality, the TR
should inform ESMA on the outlier detection method chosen and the thresholds
applied for that particular method.
649. The TR should also make the information on outlier detection method and
thresholds available to the relevant entities receiving end-of-day abnormal values
reports, so that they are fully informed about the content of these reports.
650. End-of-day abnormal values report provided by the TRs in the standardized
response messages compliant with ISO 20022 format, specifically the XSD
schema, should contain the information included in the below table.
Table 94 - End-of-day abnormal values report
No.
Field
Details to be
reported
XML Message
1
Number of derivatives
reported with NEWT,
POSC, MODI, CORR
10
<AbnrmlVals>
<Rpt>
<NbOfDerivsRptd>10
</NbOfDerivsRptd>
<NbOfDerivsRptdWthOtlrs>1
</NbOfDerivsRptdWthOtlrs>
<Wrnngs>
<CtrPtyId>
<RptgCtrPrty>
<LEI>12345678901234500000</LEI>
</RptgCtrPrty>
<RptSubmitgNtty>
<LEI>12345678901234500000</LEI>
</RptSubmitgNtty>
<NttyRspnsblForRpt>
<LEI>12345678901234500000</LEI>
</NttyRspnsblForRpt>
</CtrPtyId>
<NbOfDerivsRptd>10
</NbOfDerivsRptd>
<NbOfDerivsRptdWthOtlrs>1
</NbOfDerivsRptdWthOtlrs>
2
Number of derivatives
reported with outliers
1
3
Identification of the
derivatives
4
Counterparty 1
(Reporting
counterparty)
123456789012345
00000
5
Counterparty 2
ABCDEFGHIJKLM
NOPQRST
6
UTI
UTI1

314
<TxDtls>
<TxId>
<ActnTp>NEWT</ActnTp>
<RptgTmStmp>
2025-0407T10:00:00Z
</RptgTmStmp>
<DerivEvtTp>TRAD
</DerivEvtTp>
<DerivEvtTmStmp><Dt>
2025-04-07
</Dt></DerivEvtTmStmp>
<OthrCtrPty>
<Lgl><LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI></Lgl>
</OthrCtrPty>
<TxId>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</TxId>
<NtnlAmt>
<FrstLeg>
<Amt>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">10000</Amt>
</Amt>
<SchdlPrd>
<Amt>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">10000</Amt>
</Amt>
</SchdlPrd>
</FrstLeg>
<ScndLeg>
<Amt>
<Amt Ccy="GBP">3000</Amt>
</Amt>
<SchdlPrd>
<Amt>
<Amt Ccy="EUR">3000</Amt>
</Amt>
</SchdlPrd>
</ScndLeg>
</NtnlAmt>
</TxDtls>
</Wrnngs>
</AbnrmlVals>
7
Reporting timestamp
2025-04-
07T10:00:00Z
8
Event date
2025-04-07
9
Event type
TRAD
10
Action type
NEWT
11
Notional amount of leg
1
Field 2.55 or blank
if no outlier
detected

315
7.3.3 Reconciliation feedback
651. In Table 3 to the Annex of the RTS on data quality, ESMA has included different
categories of statuses for a derivative, as follows:
Table 95
Reconciliation categories
Allowable values
Reporting requirement for both counterparties
Yes/No
Reporting type
Single-sided/dual-sided
Pairing
Paired/unpaired
Reconciliation
Reconciled/not reconciled
Valuation reconciliation
Reconciled/not reconciled
Revived
Yes/No
Further modifications:
Yes/No
652. The category ‘Reporting requirement for both counterparties’ should be filled by
the TR based on the information in field 1.14. Where the field is populated ‘True’,
then the status of the reconciliation category should be ‘Yes’, otherwise it should
be ‘No’.
653. The category ‘Reporting type’ should be populated with ‘Single-sided’ when the
TR has received only one side of the derivatives, and ‘Dual-sided’ when both
counterparties have reported to the same TR.
12
Notional amount in
effect on associated
effective date of leg 1
Field 2.59 or blank
if no outlier
detected
13
Total notional quantity
of leg 1
Field 2.60 or blank
if no outlier
detected
14
Notional quantity in
effect on associated
effective date of leg 1
Field 2.63 or blank
if no outlier
detected
15
Notional amount of leg
2
Field 2.64 or blank
if no outlier
detected
16
Notional amount in
effect on associated
effective date of leg 2
Field 2.68 or blank
if no outlier
detected
17
Total notional quantity
of leg 2
Field 2.69 or blank
if no outlier
detected
18
Notional quantity in
effect on associated
effective date of leg 2
Field 2.72 or blank
if no outlier
detected
316
654. The category ‘Pairing’ should be populated with ‘Paired’ when the TR has been
able to identify the two sides of the same derivative or ‘Unpaired’ when it has not
yet been able to do so. When a TR identifies a derivative as ‘Dual-sided’ in the
category ‘Reporting type’, it should only identify it as ‘Paired’ in the category
‘Pairing’.
655. Only derivatives that have been paired can be reconciled. Therefore status of
‘Reconciled’ for either the category ’Reconciliation‘ or the category ‘Valuation
reconciliation’ should only be assigned by the TR for derivatives that are ‘Paired’.
656. The TRs should take into account that valuation updates for ETD trades are
reported at position level and that NFC- are not obliged to submit valuation updates
for their derivatives. These cases should be flagged in the schema as ‘Not
applicable’ as opposed to categorising them as ‘Not reconciled’.
657. The TRs should identify as ‘Reconciled’ only those derivatives for which all the
reconcilable fields are within the allowed tolerances of reconciliation.
658. Finally, the population of the categories ‘Revived’ and ‘Further modifications’ is
independent from the rest of reconciliation categories. Category ‘Further
modifications’ should be set to ‘Yes’ when a lifecycle event other than ‘NEWT’ is
received, and this value should be kept until the updated derivative contract is
reconciled. Category ‘Revive’ should be set to ‘Yes’ when a lifecycle event ‘REVI’
is received, and this value should be kept until the derivative contract is no longer
outstanding.
659. In the table included below all the allowable combinations are included. TRs
should only use the below combinations when providing reconciliation feedback.
Table 96
Reporting
requirement
for both
counterparties
Reporting
type
Pairing
Reconciliation
Valuation
reconciliation
*
Revived
Further
modifications
No
Single-sided
Unpaired
Not reconciled
Not reconciled
No
No
No
Single-sided
Unpaired
Not reconciled
Not reconciled
Yes
No
No
Single-sided
Unpaired
Not reconciled
Not reconciled
No
Yes
No
Single-sided
Unpaired
Not reconciled
Not reconciled
Yes
Yes
Yes
Single-sided
Unpaired
Not reconciled
Not reconciled
No
No
Yes
Single-sided
Unpaired
Not reconciled
Not reconciled
Yes
No
Yes
Single-sided
Unpaired
Not reconciled
Not reconciled
No
Yes
Yes
Single-sided
Unpaired
Not reconciled
Not reconciled
Yes
Yes
Yes
Single-sided
Paired
Not reconciled
Not reconciled
No
No
Yes
Single-sided
Paired
Not reconciled
Not reconciled
Yes
No
Yes
Single-sided
Paired
Not reconciled
Not reconciled
No
Yes

317
7.3.3.1 Immediate feedback
660. When providing the immediate reconciliation feedback in accordance with
Article 3(5) of the RTS on data quality, the TRs shall provide information only about
those derivatives that have been subject to reconciliation in the relevant
reconciliation cycle.
661. The following information should be included in the reconciliation feedback:
Yes
Single-sided
Paired
Not reconciled
Not reconciled
Yes
Yes
Yes
Single-sided
Paired
Reconciled
Not reconciled
No
No
Yes
Single-sided
Paired
Reconciled
Not reconciled
Yes
No
Yes
Single-sided
Paired
Reconciled
Not reconciled
No
Yes
Yes
Single-sided
Paired
Reconciled
Not reconciled
Yes
Yes
Yes
Single-sided
Paired
Reconciled
Reconciled
No
No
Yes
Single-sided
Paired
Reconciled
Reconciled
Yes
No
Yes
Single-sided
Paired
Reconciled
Reconciled
No
Yes
Yes
Single-sided
Paired
Reconciled
Reconciled
Yes
Yes
Yes
Single-sided
Paired
Not reconciled
Reconciled
No
No
Yes
Single-sided
Paired
Not reconciled
Reconciled
Yes
No
Yes
Single-sided
Paired
Not reconciled
Reconciled
No
Yes
Yes
Single-sided
Paired
Not reconciled
Reconciled
Yes
Yes
Yes
Dual-sided
Paired
Not reconciled
Not reconciled
No
No
Yes
Dual-sided
Paired
Not reconciled
Not reconciled
Yes
No
Yes
Dual-sided
Paired
Not reconciled
Not reconciled
No
Yes
Yes
Dual-sided
Paired
Not reconciled
Not reconciled
Yes
Yes
Yes
Dual-sided
Paired
Reconciled
Not reconciled
No
No
Yes
Dual-sided
Paired
Reconciled
Not reconciled
Yes
No
Yes
Dual-sided
Paired
Reconciled
Not reconciled
No
Yes
Yes
Dual-sided
Paired
Reconciled
Not reconciled
Yes
Yes
Yes
Dual-sided
Paired
Reconciled
Reconciled
No
No
Yes
Dual-sided
Paired
Reconciled
Reconciled
Yes
No
Yes
Dual-sided
Paired
Reconciled
Reconciled
No
Yes
Yes
Dual-sided
Paired
Reconciled
Reconciled
Yes
Yes
Yes
Dual-sided
Paired
Not reconciled
Reconciled
No
No
Yes
Dual-sided
Paired
Not reconciled
Reconciled
Yes
No
Yes
Dual-sided
Paired
Not reconciled
Reconciled
No
Yes
Yes
Dual-sided
Paired
Not reconciled
Reconciled
Yes
Yes
*Should be populated in certain cases with “Not applicable” as per paragraph 656

318
Table 97 - Reconciliation Feedback
No.
Field
Details to be
reported
XML Message
1
Reporting
counterparty
123456789012345
00000
<Rpt>
…
<RcncltnCtgrs>
<RptgRqrmnt>
<RptgTp>TWOS</RptgTp>
<Pairg>PARD</Pairg>
<Rcncltn>RECO</Rcncltn>
<ValtnRcncltn>RECO
</ValtnRcncltn>
<Rvvd>true</Rvvd>
<FrthrMod>true</FrthrMod>
</RptgRqrmnt>
</RcncltnCtgrs>
<TtlNbOfTxs>10</TtlNbOfTxs>
<TxDtls>
<CtrPtyId>
<RptgCtrPrty>
<LEI>
12345678901234500000
</LEI>
</RptgCtrPrty>
…
</CtrPtyId>
<TtlNbOfTxs>10</TtlNbOfTxs>
<RcncltnRpt>
<TxId>
<OthrCtrPty>
<Lgl><LEI>
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
</LEI></Lgl>
</OthrCtrPty>
<UnqIdr>
<UnqTxIdr>
UTI1
</UnqTxIdr>
</UnqIdr>
</TxId>
<MtchgCrit>
…
</MtchgCrit>
</RcncltnRpt>
</TxDtls>
</Rpt>
2
UTI
Field 2.1
3
Other
counterparty
Field 1.11
4
Reporting
requirement
for both
counterparties
True
5
Reporting
type
Dual-sided
6
Pairing
Paired
7
Reconciliation
Reconciled
8
Valuation
reconciliation
Reconciled
9
Revived
True
10
Further
modifications
True

319
7.3.3.2 End-of-day reconciliation information
662. When providing end-of-day reconciliation information included in Article 4(1)(d)
of the RTS on data quality, the TR should provide information about all derivatives
that are in the scope of the reconciliation process.
7.4 Data access
7.4.1 Operational aspects
663. When providing access to transaction data in accordance with Article 2 of the
RTS on data access, TRs should include all details of derivatives, irrespective of
whether the report for a derivative has been accepted or rejected by the TR. Further
clarifications to the requirement in the RTS on data access are provided in the
below paragraphs.
664. A Union competent authority (including the competent authorities of the EU
Member States) has access to all transaction data on all derivatives concluded by
a counterparty that fall within the scope of that authority, where such counterparty
is reported under field 1.4 ‘Counterparty 1 (reporting counterparty )’ or field 1.9
‘Counterparty 2’).
665. A competent authority from a Member State has access to all transaction data
on all derivatives concluded by a counterparty that is from the same Member State,
where these competent authorities should be provided with access to data in
accordance with Article 81(3) of EMIR.
666. Union securities and market authorities, as referred to in Article 81(3)(j) of EMIR,
should be given access to all transaction data on derivatives when it is the Relevant
Competent Authority (RCA) according to FIRDS either in relation to the derivative
itself (field 2.7) or the underlying (field 2.14). Considering that the RCA may change
over time, trade repositories are expected to provide access to the authority
designated as RCA at the time the report is generated.
667. Union securities and market authorities, as referred to in Article 81(3)(j) of EMIR,
should be given access to all transaction data on derivatives where the field
‘Underlying identification type’ (field 2.13) is reported with an ‘X’ or a ‘B’ and the
field ‘Underlying identification’ (field 2.14) is populated with either:
a. ISIN of the underlying index or an ISIN belonging to any of the individual
components of the underlying basket, whose first two letters represent the
country code of that competent authority, or an ISIN belonging to any of the
individual components of the underlying basket, where the Relevant Competent
Authority (RCA) as determined in the FIRDS database is that competent
authority, or
b. ISIN of the underlying index or an ISIN belonging to any of the individual
components of the underlying basket of indices, whose first two letters do not
represent the country code of that competent authority, however is needed for
that authority in order to perform its responsibilities and mandates, or

320
c. full names (assigned by index providers) or standardised 4-letter codes of
additional indices that, though not identified by ISIN, are needed for that
authority in order to perform its responsibilities and mandates.
668. In that regard, each competent authority can provide ESMA with an up to date
list of the ISINs and/or full names (assigned by index providers) of additional indices
and/or indicators of the underlying index for which that authority also requires
access to transaction data if a given index is identified in the report as the underlying
index or a component of the underlying basket or a list with principles, e.g.
derivatives referring to stock issued in a member state if a detailed list of derivative
types or underlyings is not feasible and might result in an undue restriction of data
access. That list should be maintained by ESMA, based on the information provided
by the authorities, and made available to Trade Repositories. The TRs should filter
the list of indices without taking into account case-sensitiveness of the reported
characters.
669. From the perspective of providing access based on the UPI, the TRs should
make use of the available information published by ANNA-DSB.
670. The TRs should establish the data access of the third country authorities in
accordance with Article 3 of the RTS on data access.
671. Articles 5(7) and 5(8) of the RTS on data access, do not refer to the timelines
that trade repositories should follow in the event of carrying out scheduled
maintenance that impacts TR services related to authorities’ access to data,
irrespective of the channel or format used.
672. Trade repositories should plan carefully the scheduled maintenance that
impacts TR services related to authorities’ access to data so that it does not
coincide with working days determined in accordance with a calendar consistently
agreed in the Union such as the TARGET 2 calendar. Where under exceptional
circumstances it coincides with such a working day, the scheduled maintenance
should be carried out outside normal working hours, i.e. very early in the morning
or very late at night. The trade repositories should make sure that the
aforementioned scheduled maintenance is not performed in a way that circumvents
the timely availability of derivatives information to authorities.
673. Trade repositories should use electronic means to notify all authorities of the
start and end dates and times of their scheduled maintenance as fast as technically
possible.
674. Where an annual planning of scheduled maintenance windows that impact TR
services related to authorities’ access to data exists at the TR, the TR should notify
all authorities of that planning on an annual basis and with at least three working
days’ notice. Furthermore, any additional specific notifications on scheduled
maintenance that impact TR services related to authorities’ access to data, that are
not notified on an annual basis, should be made at the earliest opportunity and at
least three working days before the starting date of the scheduled maintenance that
impacts TR services related to authorities’ access to data.

321
675. Trade repositories should keep a record of the relevant notifications that can be
made available to ESMA upon request. The records related to scheduled
maintenance notifications should contain, at least, the following information: the
timestamp of the notification, the start and the end of the scheduled maintenance
that impacts TR services related to authorities’ access to data and the relevant list
of users notified.
676. In the case of verification of requests under Article 5(8) of the RTS on data
access, trade repositories should confirm receipt and verify the correctness and
completeness of any request to access data, at the earliest opportunity and no later
than sixty minutes after the finalisation of the relevant scheduled maintenance that
impacts TR services related to authorities’ access to data.
677. In the case of non-scheduled maintenance, the trade repositories should meet
the timelines included in Articles 5(7) and 5(8) of the RTS on data access and these
timelines will be taken as reference when assessing the compliance of the trade
repository.
678. Trade repositories should notify ESMA and the entities listed in Article 81(3) of
EMIR that have access to data at that TR of the non-scheduled maintenance in
accordance with their procedures.
7.4.2 Template form for data access
679. TRs should use the following template, presented across the below subsections
to set up the access to derivatives data pursuant to Article 4 of the RTS on data
access.
680. As positions and tasks may change, an entity listed in Article 81(3) of EMIR
should only lay down its mandate, but not any information regarding their internal
organisation.
681. TRs should ensure regular review of data access for authorities, on an ongoing
basis as soon as they become aware of a change and at least once per year and
should update the data access in accordance with the same timeline for the initial
set up of access as per Article 4(1) of the RTS on data access.
682. As per Article 4 (1) (d) of the RTS on data access, TRs should set up access to
details of transaction data on derivatives for the entities listed in Article 81(3) of
EMIR based on the information provided in the form referred to in the Article 4(2)
of the RTS on data access. It is therefore important that the information provided in
the form is as accurate and complete as possible and to this end TRs are expected
to proactively engage with the authorities. In particular, if a TR, based on the
information it has collected and analyzed, believes that there are errors or
omissions in the form (for instance, a specific mandate has not been ticked by an
authority), the TR should contact the authority and confirm the scope of its mandate,
as soon as feasible and with a view to ensure the provision of access as per the
timeline set out in Article 4(1) (f) of the RTS on data access. TRs should make use
of publicly available data, for instance ESMA registers for CCP and trading venues,

322
to confirm the information included by Authorities in the data access form as well
as to monitor any potential updates to their mandates.
683. For the provision of access to authorities under Article 81(3) (f) of EMIR TRs
should be provided by each authority with the list of MIC codes under its supervision
in the access form.
684. The list of EMIR fields to be used by TRs for filtering data for each of the
mandates listed in Article 81(3) of EMIR can be found in Table 96 below. If at least
one field contains information based on which it can be determined that the
authority is entitled to receive the data, then this data should be made available to
this authority.
685. With regard to calculated position data access, each specific regulatory field
should be used by TRs to determine which position data should be made available
to authorities, e.g. by currency. To establish the access to derivatives reported at
position level, TRs should follow the same rules as for derivatives reported at
transaction level.
686. With regard to takeover bids, TRs should retrieve data related to all the involved
parties as e.g. in takeover bids / offers / securities as defined in Article 2 of Directive
2004/25/EC.
7.4.2.1 Contact information
TABLE 98
Regulator Information and Authorised signatory
Full name of the entity (with English translation
where appropriate)
Click or tap here to enter text.
Website of the entity listed in Article 81(3) EMIR
Click or tap here to enter text.
Authorised signatory contact name
Click or tap here to enter text.
Authorised signatory mailing address
Click or tap here to enter text.
Authorised signatory email address
Click or tap here to enter text.
7.4.2.2 Contact details for TR data user (or team) at the entity listed under Article 81(3)
EMIR to receive important notifications

323
TABLE 99
Contact name
Click or tap here to enter text.
Email address
Click or tap here to enter text.
Phone number
Click or tap here to enter text.
Credentials for a secure SSH FTP connection
Click or tap here to enter text.
TRACE code of the authority
Click or tap here to enter text.
Key of the authority
Click or tap here to enter text.
Any other technical information relevant to the
entity's access to details of derivatives.
Click or tap here to enter text.
7.4.2.3 EMIR Mandates applicable to a given entity listed in Article 81(3) EMIR
TABLE 100
(EU) 648/2012, Article 81(3)
Comments (Please indicate each of the mandates that in
your view allow you access to data and the relation
between such mandate and the data requested. In the
comments section please identify the legal instrument or
enabling legislation in your jurisdiction that sets out the
relevant mandate).
Entity listed in Article 81(3) EMIR
Comments
Please
Tick
(A) ESMA
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
(B) EBA
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
(C) EIOPA
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
(D) The ESRB
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
(E)The competent authority supervising
CCPs accessing the trade repositories
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
(F) The competent authority supervising
the trading venues where the reported
derivatives were concluded
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐

324
Entity listed in Article 81(3) EMIR
Comments
Please
Tick
(G1) A member of the ESCB, whose
currency is the euro
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
(G2) A member of the ESCB, whose
currency is not the euro
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
(G3) The ECB
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
(H) The relevant authorities of a third
country that has entered into an
international agreement with the Union
as referred to in Article 75.
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
(I) Supervisory authorities designated
under Article 4 of Directive 2004/25/EC
of the European Parliament and of the
Council.
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
(J) The relevant European Union
securities and market authorities whose
respective supervisory responsibilities
and mandate cover contracts, markets,
benchmarks, participants and
underlying which fall within the scope of
EMIR
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
(K) The relevant authorities of a third
country that has entered into a
cooperation arrangement with ESMA,
as referred to in Article 76
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
(L) The Authority for the Cooperation of
Energy Regulators established by
Regulations (EC) No 713/2009 of the
European Parliament and of the Council
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
(M) The resolution authorities
designated under Article 3 of Directive
2014/59/EU of the European
Parliament and the Council
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
(N) The Single Resolution Board
established by Regulation (EU) No
806/2014
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
(O) Competent authorities or national
competent authorities within the
meaning of Regulations (EU) No
1024/2013 and (EU) No 909/2014 and
of Directives 2003/41/EC, 2001/61/EU,
2013/36/EU and, 2014/65/EU and
supervisory authorities within the
meaning of Directive 2009/138/EC
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
(P) The competent authorities
designated in accordance with Article
10(5) of this regulation.
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐

325
(Q) The relevant authorities of a third
country in respect of which an
implementing act pursuant to Article
76a has been adopted.
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
(R) the resolution authorities
designated under Article 3 of
Regulation (EU) 2021/23
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
7.4.2.4 Relevant data fields for filtering
TABLE 101
The applicant is competent for
counterparties in its Member State, the
euro area or the Union
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
The types of counterparties for which
the entity is competent as per the
classification in Table 1 of Annex I to the
RTS on reporting
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
Types of underlyings to derivatives for
which the authority is competent
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
Trading venues that are supervised by
the entity, if any
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
CCPs that are supervised or overseen
by the entity, if any
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
Currency that is issued by the entity, if
any
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
Delivery and interconnection points;
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
Benchmarks used in the Union, for
whose administrator the entity is
competent
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
Characteristics of underlyings that are
supervised by that entity
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐
Relevant clearing members, brokers
and reference entity
Click or tap here to enter text.
☐

326
Authorised Signatory:
Name:
Click or tap here to enter text.
Title:
Click or tap here to enter text.
Signature:
Date (dd/mmm/yyyy):
Click or tap here to enter text.
7.4.3 EMIR fields for data filtering
687. According to Article 81(3) of EMIR a trade repository shall make the necessary
information available to the following entities to enable them to fulfil their respective
responsibilities and mandates. In this regard the TRs should use the clarifications
in the following table. The indicated fields are based on the existing empowerments
and mandates at the time of the drafting of these Guidelines, hence TRs should not
be bound by the clarifications included in these Guidelines, but proactively monitor
the evolutions of the relevant responsibilities and mandates and adjust the access
to authorities accordingly. Prior to implementing an adjustment, TRs should confirm
it with ESMA and the relevant authority.
TABLE 102
List of entities in
Article 81 (3) EMIR
Fields for filtering
Values for filtering
a) ESMA
N/A
N/A
b) EBA
N/A
N/A
c) EIOPA
N/A
N/A
d) The ESRB
N/A
N/A
e) The competent
authority supervising
CCPs accessing the
trade repositories
Field 2.33 ‘Central counterparty’
List of LEIs provided by the Authority
Field 1.4 ‘Counterparty 1
(Reporting counterparty)’
List of LEIs provided by the Authority
Field 1.9 ‘Counterparty 2’
List of LEIs provided by the Authority
f) The competent
authority supervising
the trading venues of
the reported contracts
Field 2.41 ‘Venue of execution’
ISO list for MIC codes, country code provided by the
Authority

327
g) The relevant
members of the ESCB,
including the ECB in
carrying out its tasks
within a single
supervisory
mechanism under
Council Regulation
(EU) No 1024/2013
Field 2.144 ‘Reference entity’
GLEIF database filtered by euro area and a list of
entities in non-euro area Member state subject to
ECB SSM, as applicable
Field 2.14 ‘Underlying
identification’
Prefix for the Member State, EU, EZ, XS, XA, XB,
XC, XD
Field 1.4 ‘Counterparty 1
(Reporting counterparty)’
GLEIF database filtered by euro area and a list of
entities in non-euro area Member state subject to
ECB SSM, as applicable
Field 1.9 ‘Counterparty 2’
GLEIF database filtered by euro area and a list of
entities in non-euro area Member state subject to
ECB SSM, as applicable
Field 1.15 ‘Broker ID’
GLEIF database filtered by euro area and a list of
entities in non-euro area Member state subject to
ECB SSM, as applicable
Field 1.16 ‘Clearing member’
GLEIF database filtered by euro area and a list of
entities in non-euro area Member state subject to
ECB SSM, as applicable
h) The relevant
authorities of a third
country that has
entered into an
international
agreement with the
Union as referred to in
Article 75
N/A
N/A
i) Supervisory
authorities designated
under Article 4 of
Directive 2004/25/EC
of the European
Parliament and of the
Council
Field 2.14 ‘Underlying
identification’
Prefix for the Member State, EU, EZ, XS, XA, XB,
XC, XD, and
List of ISIN(s) provided by the Authority
j) The relevant
Union securities and
market authorities
whose respective
supervisory
responsibilities and
mandate cover
contracts, markets,
benchmarks,
participants and
underlying which fall
within the scope of
EMIR
Field 1.4 ‘Counterparty 1
(Reporting counterparty)’
GLEIF database filtered by euro area or non-euro
area Member state, as applicable
Field 1.9 ‘Counterparty 2’
GLEIF database filtered by euro area or non-euro
area Member state, as applicable
Field 1.15 ‘Broker ID’
GLEIF database filtered by euro area or non-euro
area Member state, as applicable
Field 1.16 ‘Clearing member’
GLEIF database filtered by euro area or non-euro
area Member state, as applicable
Field 2.14 ‘Underlying
identification’
Relevant competent authority (RCA) from FIRDS
database, prefix for the Member State, EU, EZ, XS,
XA, XB, XC, XD
Field 2.7 ‘ISIN’
Relevant competent authority (RCA) from FIRDS
database, prefix for the Member State, EU, EZ, XS,
XA, XB, XC, XD
Field 2.41 ‘Venue of execution’
ISO list for MIC codes, country code to be provided
by the Authority
Field 2.8 ‘UPI’
List of UPI(s) provided by the Authority
42
Field 2.15 ‘Indicator of the
underlying index’
List of benchmark(s) provided by the Authority
Field 2.16 ‘Name of the
underlying index’
List of benchmark(s) provided by the Authority
42
Access to data based on the UPI comes in addition to any other mandates

328
Field 2.83 ‘Identifier of the floating
rate of leg 1’
List of benchmark(s) provided by the Authority
Field 2.84 ‘Indicator of the floating
rate of leg 1’
List of benchmark(s) provided by the Authority
Field 2.85 ‘Name of the floating
rate of leg 1’
List of benchmark(s) provided by the Authority
Field 2.99 ‘Identifier of the floating
rate of leg 2’
List of benchmark(s) provided by the Authority
Field 2.100 ‘Indicator of the
floating rate of leg 2’
List of benchmark(s) provided by the Authority
Field 2.101 ‘Name of the floating
rate of leg 2’
List of benchmark(s) provided by the Authority
k) the relevant
authorities of a third
country that have
entered into a
cooperation
arrangement with
ESMA, as referred to in
Article 76;
N/A
N/A
l) the Agency for the
Cooperation of Energy
Regulators established
by Regulation (EC) No
713/2009 of the
European Parliament
and of the Council;
Field 2.116 ‘Base product’
Field 2.117 ‘Sub-product’
[(field 2.16 ‘Base product’ = 'NRGY') and (field 2.17
‘Sub-product’ = ‘ELEC’ or field 2.17 ‘Sub-product’ =
‘NGAS’)] or [(field 2.16 ‘Base product’ = ‘ENVR' and
field 2.17 ‘Subproduct’ = ‘EMIS’]
m) the resolution
authorities designated
under Article 3 of
Directive 2014/59/EU
of the European
Parliament and the
Council;
Field 1.4 ‘Counterparty 1
(Reporting counterparty)’
Field 1.6 ‘Corporate sector of the
counterparty 1’
GLEIF database filtered by the Member State,
where field 1.6 ‘Corporate sector of the counterparty
1’ equals ‘INVF' Investment firm authorized in
accordance with Directive 2014/65/EU or 'CDTI'
credit institution authorised in accordance with
Directive (EU) 2013/36/EU
Field 1.9 ‘Counterparty 2’
Field 1.12 ‘Corporate sector of the
counterparty 2’
GLEIF database filtered by the Member State,
where field 1.12 ‘Corporate sector of the
counterparty 2’ are equal to ‘INVF' Investment firm
authorized in accordance with Directive 2014/65/EU
or 'CDTI' credit institution authorised in accordance
with Directive (EU) 2013/36/EU
Field 1.15 ‘Broker ID’
List of LEIs provided by the Authority
Field 1.16 ‘Clearing member’
List of LEIs provided by the Authority
n) the Single
Resolution Board
established by
Regulation (EU) No
806/2014;
Field 1.4 ‘Counterparty 1
(Reporting counterparty)’
List of LEIs subject to the SRB, provided by SRB
Field 1.9 ‘Counterparty 2’
List of LEIs subject to the SRB, provided by SRB
Field 1.15 ‘Broker ID’
List of LEIs subject to the SRB, provided by SRB
Field 1.16 ‘Clearing member’
List of LEIs subject to the SRB, provided by SRB
o) competent
authorities or national
competent authorities
within the meaning of
Field 1.4 ‘Counterparty 1
(Reporting counterparty)’
Field 1.6 ‘Corporate sector of the
counterparty 1’
GLEIF database filtered by the Member State where
field 1.6 ‘Corporate sector of the counterparty 1’
equals:

329
Regulations (EU) No
1024/2013 and (EU)
No 909/2014 and of
Directives 2003/41/EC,
2009/65/EC,
2011/61/EU,
2013/36/EU and
2014/65/EU, and
supervisory authorities
within the meaning of
Directive 2009/138/EC;
'CDTI' credit institution authorised in accordance
with Directive (EU) 2013/36/EU; or
'CSDS' central securities depository authorised in
accordance with Regulation (EU) No 909/2014; or
'INVF' Investment firm authorized in accordance
with Directive 2014/65/EU; or
'INUN' insurance undertaking or reinsurance
undertaking authorised in accordance with Directive
2009/138/EC; or
'AIFD' an alternative investment fund as defined in
Directive 2011/61/EU; or
'UCIT' a UCITS and, where relevant, its
management company authorised in accordance
with Directive 2009/65/EC; or
'ORPI' an institution for occupational retirement
provision (IORP) as defined under Directive
2016/2341
Field 1.9 ‘Counterparty 2’
Field 1.12 ‘Corporate sector of the
counterparty 2’
GLEIF database filtered by the Member State where
field 1.12 ‘Corporate sector of the counterparty 2’
equals:
'CDTI' credit institution authorised in accordance
with Directive (EU) 2013/36/EU; or
'CSDS' central securities depository authorised in
accordance with Regulation (EU) No 909/2014; or
'INVF' Investment firm authorized in accordance
with Directive 2014/65/EU; or
'INUN' insurance undertaking or reinsurance
undertaking authorised in accordance with Directive
2009/138/EC; or
'AIFD' an alternative investment fund as defined in
Directive 2011/61/EU; or
'UCIT' a UCITS and, where relevant, its
management company authorised in accordance
with Directive 2009/65/EC; or
'ORPI' an institution for occupational retirement
provision (IORP) as defined under Directive
2016/2341
Field 2.10 ‘Country of the
counterparty 2’
Filtered by the Member State
p) the competent
authorities designated
in accordance with
Article 10(5) of EMIR
Field 1.4 ‘Counterparty 1
(Reporting counterparty)’
Field 1.5 ‘Nature of the
counterparty 1’
GLEIF database filtered by the Member State and
‘Nature of the counterparty 1’=’N
where ‘N’ stands for non-financial counterparty
Field 1.9 ‘Counterparty 2’
Field 1.11 ‘Nature of the
counterparty 2’
GLEIF database filtered by the Member State and
‘Nature of the counterparty 2’=’N
where ‘N’ stands for non-financial counterparty
q) the relevant
authorities of a third
country in respect of
which an implementing
act pursuant to Article
76a has been adopted
N/A
N/A
