
Qlik Enterprise Manager Setup and User Guide
Qlik Enterprise Manager
TM
May 2023
Last updated: September 02, 2024
Copyright © 1993-2024 QlikTech International AB. All rights reserved.
HELP.QLIK.COM
© 2024 QlikTech International AB. All rights reserved. All company and/or product names may be trade names,
trademarks and/or registered trademarks of the respective owners with which they are associated.

Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 3
1 What's new? 9
1.1 Support for Personal Access Tokens as a log in method via the Enterprise Manager API 9
2 Introduction 10
2.1 Example Enterprise Manager environment 11
2.2 Enterprise Manager architecture 12
3 Terminology 13
3.1 Change Data Capture (CDC) 13
3.2 Full load 13
3.3 Apply latency 13
Latency when applying large transactions 13
Latency when no transactions are being applied 13
3.4 Source latency 13
3.5 Target latency 13
3.6 Overall latency 14
3.7 Source endpoint 14
3.8 Target endpoint 14
3.9 Net Changes table 14
4 Installation and setup 15
4.1 Preparing your system for Enterprise Manager 15
Hardware configuration guidelines 15
Sizing guidelines 16
Software requirements 16
Compatibility with Related Qlik Products 17
Replication Management license 17
4.2 Installing Enterprise Manager 18
Installing Qlik Enterprise Manager using the Setup Wizard 19
Upgrading Enterprise Manager 19
Migrating the Enterprise Manager Repository 20
Silently installing Enterprise Manager 21
Silently upgrading Enterprise Manager 22
Silently uninstalling Enterprise Manager 23
4.3 Changing the Enterprise Manager service account 24
4.4 Setting the login authentication method 25
Setting Single Sign-on authentication 25
Setting Single Sign-on authentication with Kerberos 25
Setting form authentication 26
Setting up SAML authentication 27
Setting up Personal Access Token authentication for the API 30
4.5 Starting to work with the Qlik Enterprise Manager Console 33
Registering Licenses 34
5 Security considerations 35
5.1 Setting up HTTPS for the Enterprise Manager console 35
Checking if an SSL Certificate is installed 35
Using the self-signed certificate 35
5.2 Setting up HSTS on Enterprise Manager 38
Enabling HSTS 38
Contents

Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 4
Disabling HSTS 38
5.3 Replacing the self-signed certificate on Windows 39
5.4 Setting the hostname and changing the SSL port 40
5.5 Replacing the Master User Password 41
The Master Key 41
High Availability mode 42
5.6 Encrypting the user permissions file 42
5.7 Controlling execution of user-defined commands 43
Executing operating system commands as a different user 44
6 Managing servers 45
6.1 Server requirements 45
Qlik Replicate Server requirements 45
Qlik Compose Server requirements 46
6.2 Adding Servers 46
6.3 Monitoring servers 48
Customizing server columns 49
Searching for servers 49
6.4 Server settings 50
Global error handling 50
Resource Control 51
File Transfer Service 52
External utilities 54
Logging 54
More options 58
Server management permissions 58
6.5 Additional server management options 60
6.6 Registering a license for a monitored server 62
6.7 Viewing server messages 63
7 Defining and managing tasks 64
7.1 Adding tasks 64
Bidirectional replication 66
7.2 Editing and viewing a task description 69
7.3 Defining and managing endpoints 69
Defining an endpoint 70
Editing endpoint configuration information 70
Viewing endpoint configuration information 71
Testing an endpoint connection 71
Duplicating endpoints 71
Searching for endpoints 71
Deleting endpoints 72
7.4 Adding a source and target endpoint to a task 72
7.5 Selecting tables and/or views for replication 73
Searching for tables/views to use in a replication task 75
Selecting specific tables/views for replication 76
Setting load order 77
Removing specific tables/views from a replication task 77
Contents

Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 5
Creating table/view selection patterns 78
7.6 Editing a replication task 79
7.7 Searching for tasks 80
7.8 Deleting a replication task 80
7.9 Exporting and importing tasks 80
8 Customizing tasks 82
8.1 Table Settings 82
Performing General tasks for a single table/view 83
Defining transformations for a single table/view 84
Using filters 92
Parallel Load 98
Handling LOB columns 103
Message format 106
Full Load 106
8.2 Defining global rules 107
Starting the Global Transformation Rules wizard 107
118
118
Starting the Global Filter Rules wizard 131
Managing global rules 136
8.3 Using the Expression Builder 137
Overview of the Expression Builder 137
Build an expression 139
Parse an expression 140
Test an expression 140
Using elements in the Expression Builder 142
8.4 Task Settings 165
Metadata 166
Bidirectional 170
Full Load 171
Change Processing 174
Error handling 186
Logging 192
Character substitution 194
File uploads 195
Message Format 196
Transformations and Filters 201
More options 202
9 Monitoring and controlling tasks 203
9.1 Monitoring Replicate tasks 203
Task progress summary 203
Viewing specific tasks 207
Monitoring Full Load replication 209
Monitoring Change Processing replication 215
9.2 Monitoring Compose tasks and workflows 222
Task progress summary 222
Monitoring Data Lake tasks 225
Contents

Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 6
Monitoring Data Warehouse tasks 226
Monitoring workflows 227
9.3 Searching for tasks 230
9.4 Customizing task columns 231
9.5 Grouping tasks 232
9.6 Running a task 234
How to run a task 235
Using the Run button options 235
Start Processing 236
Reload target 236
Advanced Run Options 236
Recovering from data folder loss or corruption 241
9.7 Error handling 243
Task error handling 243
Data error handling 243
9.8 Using the monitor tools 244
Logging 244
Downloading a memory report 246
Downloading a diagnostics package 246
9.9 Scheduling jobs 247
10 Messages and notifications 250
10.1 Message Center overview 250
10.2 Customizing the Message Center 252
Searching for messages 253
10.3 Viewing additional information 253
10.4 Notifications 253
Setting a task notification 254
Setting a server notification 261
Managing notifications 264
Required permissions 265
Event IDs in Windows Event Log 265
10.5 Viewing and downloading log files 267
11 Administration 269
11.1 Enterprise Manager settings 269
Enterprise Manager logging settings 269
Message Center purge settings 271
Repository connection settings 272
Qlik Catalog Server connection 273
Analytics - Data collection and purge settings 273
Configuring mail server settings 275
Registering and managing licenses 276
11.2 User permissions 278
Encrypting the User Permissions File 279
Granular access control 279
Roles and permissions 284
Working with local groups 286
Contents

Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 7
Managing user permissions 286
Managing Personal Access Tokens 289
11.3 Creating an audit trail 289
Decoding an encoded stream payload 291
12 Configuring Enterprise Manager using the CLI 293
12.1 Setting the Enterprise Manager host address 293
12.2 Setting the Enterprise Manager HTTP port 293
12.3 Setting the Enterprise Manager HTTPS port 294
12.4 Setting the Enterprise Manager root URL 294
12.5 Showing the Enterprise Manager version 294
12.6 Showing the Enterprise Manager CLI Help 294
12.7 Service Commands 294
12.8 Cleaning the self-signed certificate 295
12.9 Setting the audit trail retention size and age 295
12.10 Master User Password commands 295
Generating a random Master User Password 295
Setting or changing the MUK (Master User Key) 295
Setting or changing the Java MUK (Master User Key) 296
12.11 Showing the connectivity and login settings 297
Connectivity settings 297
SAML settings 297
12.12 Fine tuning performance 297
Turning off the Analytics Server 298
Changing the update intervals 298
13 Cataloging tasks in Qlik Catalog 300
13.1 Terminology 300
13.2 Prerequisites 301
13.3 Setting up connectivity to Qlik Catalog 301
Catalog columns 301
13.4 Limitations and considerations 301
13.5 Catalog operations 302
Cataloging tasks 302
Uncataloging tasks 304
Recataloging tasks 304
14 Analytics 305
14.1 Prerequisites 305
Install PostgreSQL 305
Create a dedicated database and assign the required privileges 306
Configure connectivity to PostgreSQL 306
Set up data collection and purging from PostgreSQL 306
Register a license 306
Obtaining a license 306
Port 307
Hardware 307
14.2 Permissions 307
14.3 Analytics dashboards 307
Contents

Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 8
Trends 308
Trends by server 309
Trends by tasks 310
Top servers 311
Top tasks 312
Capacity planning 313
14.4 Exporting to TSV 315
14.5 Creating filters 315
14.6 Using the Pivot Menu 317
14.7 Analytics repository schema 317
aem_endpoint_type 317
aem_meta_source_database 318
aem_meta_target_database 318
aem_server 318
aem_source_database 318
aem_target_database 319
aem_target_processes 319
aem_task 319
aem_task_name 322
aem_task_previous_metrics 323
aem_task_profile 323
aem_task_state 323
aem_task_stop_reason 323
Sample Queries 323
A Setting up High Availability 327
A.1 Installing Qlik Enterprise Manager in a Windows cluster 327
A.2 Upgrading Qlik Enterprise Manager in a Windows cluster 330
A.3 Uninstalling Qlik Enterprise Manager from a Windows cluster 332
B Impact of DST change on Qlik Replicate 335
Contents

1 What's new?
1 What's new?
This section describes the new and enhanced features in Enterprise Manager May 2023.
In addition to these release notes, customers who are not upgrading from the latest GA version
(Enterprise Manager November 2022 SR1) are advised to review the release notes for all versions
released since their current version.
Customers should also review the Enterprise Manager release notes in ≤ Qlik Community for information
about the following:
l
Migration and upgrade
l
End of life/support features
l
Newly supported versions and third-party software
l
Resolved issues
l
Known issues
1.1 Support for Personal Access Tokens as a log in method
via the Enterprise Manager API
From Enterprise Manager May 2023, customers can use Personal Access Tokens to log in to Enterprise
Manager via the API. Using Personal Access Tokens is the recommended best practice, as it offers significant
security benefits.
The high-level flow involves the following steps:
l
Step 1: In Okta, create an app integration that uses OpenID Connect and assign users to it.
l
Step 2: In Enterprise Manager, enable Enterprise Manager to communicate with Okta (using the CLI)
l
Step 3: In Enterprise Manager, generate a Personal Access Token
l
Step 4: Configure the Enterprise Manager API to log in with a Personal Access Token
Tokens can also be revoked by an Enterprise Manager admin. To facilitate this, a new Personal Access
Tokens tab has been added to the Enterprise Manager settings:
For details, see Setting up Personal Access Token authentication for the API (page 30)
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 9

2 Introduction
2 Introduction
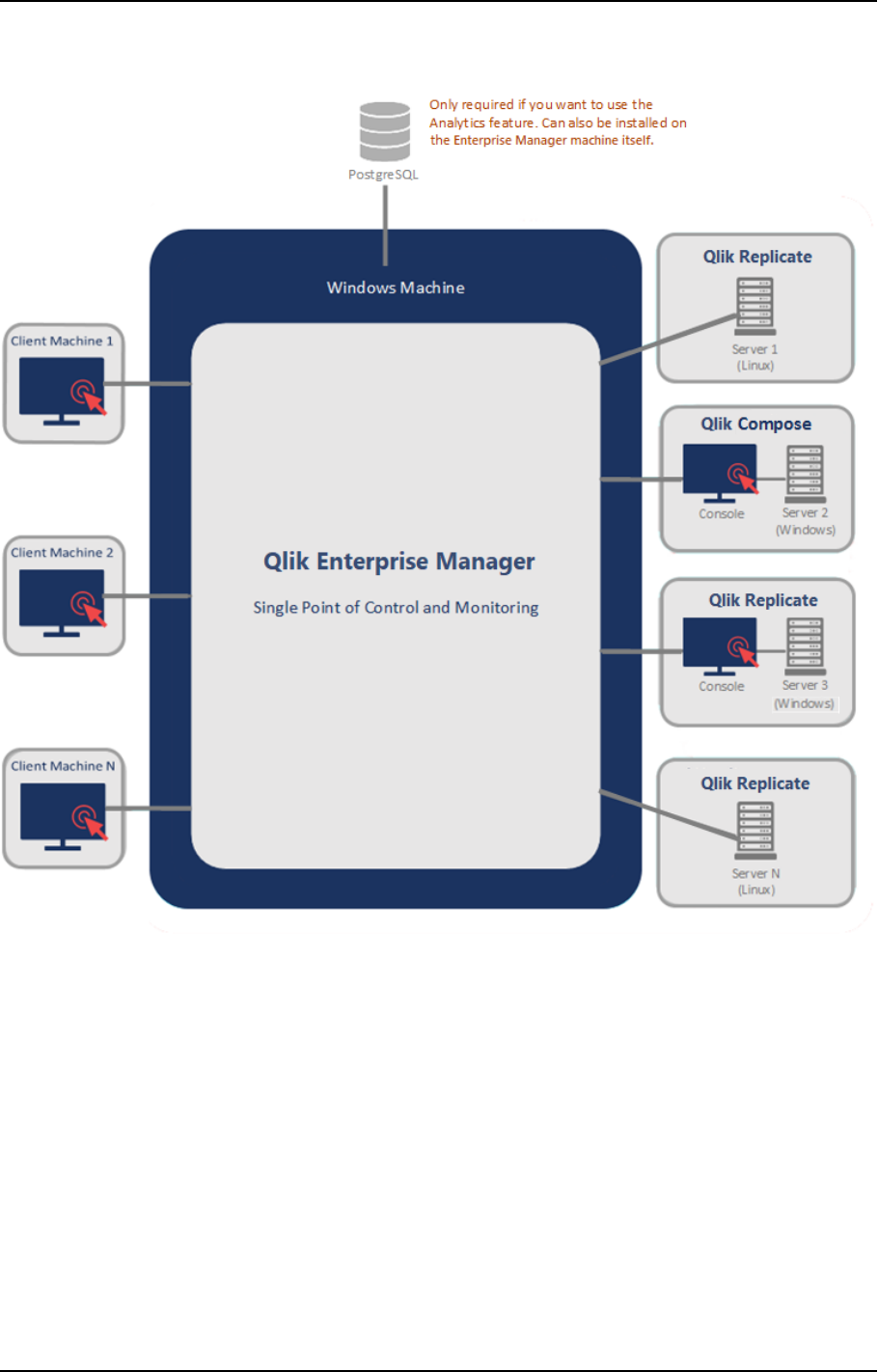
Qlik Enterprise Manager, also referred to as Enterprise Manager, provides a single point of control for
designing, executing, and monitoring Qlik Replicate and Compose tasks throughout your organization. If your
site has multiple Qlik servers with tens, if not hundreds of tasks, Enterprise Manager greatly eases the design,
management, and monitoring of these tasks. Whether your site deploys a single Qlik server or multiple
servers, Enterprise Manager is your single go-to interface to create data endpoints, design tasks, execute
them, and monitor the replication process in near real-time. In addition, Enterprise Manager lets you view all
tasks in a tabular format that offers advanced grouping and filtering capabilities.
The following figures show a high-level view of a possible Enterprise Manager installation environment and a
more detailed architecture diagram.
Note that components labeled as "Qlik Server" can either be Qlik Replicate or Qlik Compose.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 10
2 Introduction
2.1 Example Enterprise Manager environment
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 11

2 Introduction
2.2 Enterprise Manager architecture
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 12

3 Terminology
3 Terminology
The following section describes some key terms used throughout this Help.
3.1 Change Data Capture (CDC)
Captures changes in the source data or metadata as they occur and applies them to the target endpoint as
soon as possible, in near-real-time. The changes are captured and applied as units of single committed
transactions and several different target tables may be updated as the result of a single source commit. This
guarantees transactional integrity in the target endpoint. The CDC process for any file or table starts as soon
as the data loading operation for the file or table begins.
3.2 Full load
Creates all defined files or tables on the target endpoint, automatically defines the metadata that is required
at the target, and populates the tables with data from the source.
3.3 Apply latency
The gap in seconds between capturing a change in one of the source tables and applying that change to the
target endpoint.
Latency when applying large transactions
This is best explained by way of example. When the most recent Apply Latency value was 10 seconds and now
a transaction of one million rows gets committed at the source endpoint, Replicate starts to apply that
transaction to the selected target and it will take some time to write all the changes to the target (for example
60 seconds). During the next 60 seconds, the latency value gradually grows to 70 seconds for the last change
in the transaction. Once the transaction is committed, the latency drops back to the 'regular' latency (10
seconds in this case).
Latency when no transactions are being applied
When a time period passes with no changes applied to the target, the latency calculation is based on the time
difference between the current time and the timestamp of the last change event read from the transaction
log. This could happen, for example, if there is a high volume of activity on tables that were not selected for
replication in the current task.
3.4 Source latency
The gap in seconds between when the source database wrote an event to its transaction log and when
Replicate captured that change.
3.5 Target latency
The gap between when a commit is seen by Replicate (reading the source transaction log) and when the
changes of that commit are seen in the target.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 13

3 Terminology
3.6 Overall latency
The overall latency is defined as the time gap between when a change is committed in the source database
and when it is visible in the target database.
3.7 Source endpoint
A collection of files or tables managed by an endpoint management system (such as, Oracle, SQL Server) that
is part of the main computing service of the IT organization of an enterprise. This source continuously
updated, may need to provide a high throughput rate, may have strict 24/7 up-time requirements, and may
reference or update a number of tables in the course of a single logical transaction while providing
transactional consistency and integrity for the data.
3.8 Target endpoint
A collection of files or tables managed by an Endpoint Management System (DBMS), which may be different
from the DBMS managing the source endpoint. It contains data that is derived from the source. It may contain
only a subset of the tables, columns, or rows that appear in the source. Its tables may contain columns that
do not appear in the source but are transformations or computations based on the source data.
3.9 Net Changes table
Replicate performs data replication based on changes that appear in the source database's transaction log. A
single update operation on the source, such as "UPDATE MyTable SET f1=..., f2=..." could
potentially update many rows in the source database and create a large number of change records that
Replicate will need to apply to the target. Replicate offers two Change Processing modes:Transactional
apply and Batch optimized apply. In Transactional apply Change Processing mode, Replicate essentially
applies each change to the target, which may take much longer than the original UPDATE took on the source.
Batch optimized apply mode, on the other hand, is designed to handle efficient replication of a large number
of changes. In this mode, Replicate accumulates changes for multiple tables in a memory cache. Repeated
changes to the same row are updated in the memory cache. When the maximum memory cache size defined
for the task is reached (or when the configured time has elapsed), Replicate does the following:
a. Writes the cached (net) changes to a special table on the target (the Net Changes table),
b. Bulk uploads the changes to the target table
c. Uses SQL statements to update the target tables based on the data in the Net Changes table.
Note that for Oracle, Replicate uses a Net Changes table per each source table with changes, while
for other source endpoints a single Net Changes table is used.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 14

4 Installation and setup
4 Installation and setup
This section describes how to install and set up Qlik Enterprise Manager (Enterprise Manager).
For instruction on installing Enterprise Manager in a Windows Cluster, see Installing Qlik Enterprise
Manager in a Windows cluster (page 327).
Enterprise Manager collects information from Qlik Replicate and/or Qlik Compose Servers to allow a central
point of monitoring for all Replicate and/or Compose Servers in your organization. Therefore, you also need to
install Qlik Replicate and/or Qlik Compose in your organization. For a description of the respective installation
procedures, refer to the Qlik Replicate and/or Qlik Compose product Help.
In this section:
l
Preparing your system for Enterprise Manager (page 15)
l
Installing Enterprise Manager (page 18)
l
Changing the Enterprise Manager service account (page 24)
l
Setting the login authentication method (page 25)
l
Starting to work with the Qlik Enterprise Manager Console (page 33)
4.1 Preparing your system for Enterprise Manager
This section describes the hardware and software requirements for Qlik Enterprise Manager and the
monitored Replicate Servers.
In this section:
l
Hardware configuration guidelines (page 15)
l
Software requirements (page 16)
l
Sizing guidelines (page 16)
l
Compatibility with Related Qlik Products (page 17)
l
Replication Management license (page 17)
Hardware configuration guidelines
It is recommended that the machine hosting Qlik Enterprise Manager meets or exceeds the hardware
configuration shown in the following table:
Medium System Large System
Processor 4-core base 16-core base
Memory 8 GB 32 GB
Disk requirements 128 GB 256 GB
Network 1 Gbps 1 Gbps
Hardware requirements
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 15

4 Installation and setup
Sizing guidelines
Depending on the number of Replicate tasks and concurrent users, you might need to balance the system
load between multiple Enterprise Manager machines. For example, if your hardware configuration is set up for
a large system (40 Replicate servers), it is recommended to monitor no more than 4000 Replicate tasks on a
single Enterprise Manager machine. When you near this threshold, then the recommendation is to split the
tasks between at least two Enterprise Manager machines by dividing the number of monitored Replicate
servers between the Enterprise Manager machines. Similarly, if your hardware configuration is set up for a
medium system and the number of Replicate tasks and users concurrently accessing the system is
approaching the maximum threshold (see table below), then best practice is to split the monitored Replicate
servers between at least two Enterprise Manager machines.
For information on hardware configuration guidelines, see Hardware configuration guidelines (page 15).
Medium
System
Large
System
Replicate servers 8 40
Tasks 800 4000
Concurrent users(Rate of public API calls may affect these numbers) 10 80
Sizing guidelines
To some extent, how you set up granular access control might also impact performance. This is
usually only a factor when many users are assigned different roles and permissions.
Software requirements
Parts of the software use Java components utilizing OpenJDK JRE, which is included in the
Enterprise Manager installation.
Supported Windows platforms
It is strongly recommended to install Qlik Enterprise Manager on a dedicated Windows server, separate from
the Replicate and/or Compose Servers that it manages.
Enterprise Manager can be installed on any of the following Windows platforms:
l
Windows Server 2012 R2 (64-bit)
l
Windows Server 2016 (64-bit)
l
Windows Server 2019 (64-bit)
l
Windows Server 2022 (64-bit)
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 16

4 Installation and setup
Windows Server 2022 is supported from Qlik Enterprise Manager May 2022 Service Release 02
only.
Supported browsers
The following browsers can be used to access the Enterprise Manager Console:
l
Microsoft Edge (with automatic updates turned on)
l
Mozilla Firefox (with automatic updates turned on)
l
Google Chrome (with automatic updates turned on)
Port
Port 443 must be opened for inbound connections on the Enterprise Manager machine.
Additional software requirements
Qlik Enterprise Manager requires the following software:
l
Microsoft Visual Studio C++ 2010 X64 Redistributable and 2015 X64 Redistributable
l
.NET Framework 4.8 or later
l
To use the Analytics feature, PostgreSQL 12.16 or later should be installed either on the Enterprise
Manager machine or on a machine that is accessible from Enterprise Manager.
l
TLS 1.2 or later must be supported in the underlying OS.
On Windows Server 2012 R2, TLS 1.2 should be turned on by default. If it is not, refer to the
Microsoft online help for instructions on how to turn it on.
See also: Compatibility with Related Qlik Products (page 17).
Compatibility with Related Qlik Products
Enterprise Manager May 2023 Initial Release
l
Qlik Replicate - Enterprise Manager May 2023 is compatible with Replicate May 2023, Replicate
November 2022, Replicate May 2022, and Replicate November 2021.
l
Qlik Compose - Enterprise Manager May 2023 is compatible with Qlik Compose May 2022 (and its
Service Releases) only.
l
Qlik Catalog - Enterprise Manager May 2023 is compatible with Qlik Catalog November 2022 only.
Replication Management license
This section explains how to obtain a Replication Management license and lists the processes that continue
even when the license expires or is invalid.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 17

4 Installation and setup
Obtaining a Replication Management license
A Replication Management license is required in order to use Qlik Enterprise Manager. If no license is detected,
a Register License message will be displayed when you open the Qlik Enterprise Manager Console.
The procedure below does not apply when installing Enterprise Manager in a High Availability
Cluster. To obtain a Replication Management license for Enterprise Manager in a High Availability
Cluster, you must provide your Qlik Sales Representative with the following information, depending
on which Windows version the cluster is running:
l
Windows Server 2016: The official cluster FQDN.
l
Windows Server 2012 R2: The FQDN of each of the cluster nodes and the official cluster
FQDN.
To obtain a license
1. Open the Qlik Enterprise Manager Console and copy the Enterprise Manager machine name from either
of the following locations:
l
The Register License message that is displayed when you open the Qlik Enterprise Manager
Console.
l
The bottom of the Licenses tab in the Settings window.
2. Request a license from your Qlik Sales Representative, making sure to include the Enterprise Manager
machine name in your request.
Process that continue if the license expires or is invalid
The following processes will continue, even if the Replication Management license expires or is invalid:
l
Notifications will continue to be sent.
l
Tasks monitoring information and messages will continue to be collected from Replicate. However,
they will not be visible until a valid Replication Management license is installed.
In such a situation, do one of the following:
l
Register a valid Replication Management license.
l
Stop the Enterprise Manager service or uninstall the product if you do not intend to use it anymore.
4.2 Installing Enterprise Manager
Enterprise Manager must be installed under an Administrator account.
In this section:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 18

4 Installation and setup
l
Installing Qlik Enterprise Manager using the Setup Wizard (page 19)
l
Silently installing Enterprise Manager (page 21)
l
Silently upgrading Enterprise Manager (page 22)
l
Silently uninstalling Enterprise Manager (page 23)
Installing Qlik Enterprise Manager using the Setup Wizard
The following section describes how to install Enterprise Manager.
To install Enterprise Manager:
1. Run the Enterprise Manager setup file (QlikEnterpriseManager_<version.build>_<systemtype>.exe, such
as QlikEnterpriseManager_7.0.0.105_X64.exe).
The Enterprise Manager setup wizard opens.
2. Optionally, change the installation directory; then click Next.
3. Optionally, change the data directory; then click Next.
All of the data that is created when you use Enterprise Manager is stored in a directory called data. By
default, this directory is located in the installation directory where you install Enterprise Manager.
If you change the data directory location, you must prefix all command line actions with:
-d path_to_the_data_directory
Example:
<product_dir>\bin\AemCtl.exe -d F:\data configuration set -a 123.123.12.1
4. Click Next again to start the installation.
5. When the installation completes, click Finish.
As part of the installation, a new Windows Service called Enterprise Manager is created.
The Enterprise Manager analytics module require a PostgreSQL database. If you plan on using this
module, you will need to install PostgreSQL on either the Enterprise Manager machine or on a machine
that is accessible from Enterprise Manager.
For your convenience, PostgreSQL is included with Enterprise Manager and you will be prompted to
install it after clicking Finish.
6. Click Yes to install PostgreSQL on the Enterprise Manager server or No to exit without installing
PostgreSQL. You can always install PostgreSQL at a later time by running the PostgreSQL installer from
the following location:
<Enterprise_Manager_INSTALLATION_FOLDER>\postgresqlkit
For instructions on installing and maintaining PostgreSQL, refer to the PostgreSQL Help.
7. Open the Enterprise Manager console as described in Starting to work with the Qlik Enterprise Manager
Console (page 33).
Upgrading Enterprise Manager
The upgrade process also describes how to back up the Enterprise Manager "data" folder, which will allow you
to restore your settings if you encounter any issues with the upgrade.
To upgrade Enterprise Manager:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 19

4 Installation and setup
1. Back up your currently installed version, by copying the Enterprise Manager data folder to a location
outside the product folder. The default data folder location is C:\Program Files\Attunity\Enterprise
Manager\data.
2. Run the Enterprise Manager setup wizard to install the new version.
3. If you notice an issue with the upgrade, you can revert to the previous version as described below or
do the following:
a. Stop all the Enterprise Manager services.
b. Overwrite the data folder with the data folder that you backed up earlier.
c. Start all the Enterprise Manager services.
Reverting to a Previous Version
To revert to a previous version:
1. Back up the Enterprise Manager data directory to a location outside the product folder.
2. Uninstall the product and then reinstall to the same directory.
3. Once the installation is complete, stop all Enterprise Manager services.
4. Overwrite the data directory with the data directory that you backed up earlier.
5. Start all Enterprise Manager services.
Migrating the Enterprise Manager Repository
In certain situations, you may need to migrate Replicate or Compose Servers and settings from one Enterprise
Manager Server to another. This may be required, for example, if you need to move from a test environment
to a production environment or if you need to decommission the Enterprise Manager Server machine. In the
migration procedure, which is described below, Server A is the Enterprise Manager Server configured with
Replicate or Compose Servers, while Server B is a clean installation of Enterprise Manager Server.
All commands should be run as administrator.
1. On Server A:
a. Run the following commands:
Command 1 - Sets the Master User Key:
<INSTALL_DIR>\bin\aemctl.exe [-d data_folder_path] masterukey set -
p password
where -d data_folder_path is only required if the <INSTALL_DIR>\data folder is in a non-
default location.
Command 2 - Sets the Java Master User Key:
<INSTALL_DIR>\java\bin\atajs.bat [-d java_data_folder_path]
masterukey set password
where -d java_data_folder_path is only required if the <INSTALL_DIR>\data\java
folder is in a non-default location.
b. Restart the QlikEnterprise Manager service.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 20

4 Installation and setup
2. On Server B:
a. Stop the Qlik Enterprise Manager service.
b. Delete the <INSTALL_DIR>\data folder.
c. Copy the data folder from Server A to Server B.
d. Run the following commands:
Command 1:
<INSTALL_DIR>\bin\aemctl.exe [-d data_folder_path] masterukey set -
p password
where -d data_folder_path is only required if the <INSTALL_DIR>\data folder is in a non-
default location.
Command 2:
<INSTALL_DIR>\java\bin\atajs.bat [-d java_data_folder_path]
masterukey set password
e. Start the QlikEnterprise Manager service.
f. Log in to Enterprise Manager and verify that the Replicate and Compose Servers have been
migrated from Server A to Server B, and that all of Server A's configuration settings have been
migrated as well.
Silently installing Enterprise Manager
Enterprise Manager can be installed silently (i.e. without requiring user interaction). This option is useful, for
example, if you need to install Enterprise Manager on several machines throughout your organization.
Before commencing the installation, make sure that the prerequisites have been met.
The installation process consists of two stages:
1. Creating a response file (page 21)
2. Running the silent install (page 22)
Creating a response file
Before starting the installation, you need to create a response file.
To create the response file:
1. From the directory containing the Qlik Enterprise Manager setup file, run the following command(note
that this will also install Enterprise Manager):
QlikEnterpriseManager_version_X64.exe /r /f1my_response_file
where:
my_response_file is the full path to the response file that will be generated.
Example:
QlikEnterpriseManager_6.1.0.536_X64.exe /r /f1C:\Enterprise Manager_install.iss
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 21

4 Installation and setup
At the end of the Enterprise Manager installation, when you are prompted to run the
PostgreSQL installer, click No.
2. To change the default installation directory, open the response file in a text editor and edit the first
szDir value as necessary.
3. To change the default data directory, edit the third szDir value as necessary.
4. Save the file as <name>.iss, e.g. silent_inst_64.iss.
Running the silent install
To silently install Qlik Enterprise Manager, open a command prompt and change the working directory to the
directory containing the Enterprise Manager setup file. Then issue the following command:
Syntax:
QlikEnterpriseManager_version_X64.exe /s /f1my_response_file [/f2log_file]
where:
my_response_file is the full path to the response file you created earlier and log_file is the path to the
optional log file.
Example:
C:\>QlikEnterpriseManager_6.1.0.536_X64.exe /s /f1C:\temp\1\Enterprise Manager_install.iss
/f2C:\temp\1\silent_x64_install.log
If the installation was successful, the log file should contain the following rows:
[ResponseResult]
ResultCode=0
Silently upgrading Enterprise Manager
Silently upgrading Enterprise Manager consists of two stages:
1. Creating a response file (page 22)
2. Running a silent upgrade (page 22)
Creating a response file
Before starting the upgrade, you need to create a response file. You may also want to back up your current
installation as described in Upgrading Enterprise Manager (page 19).
For an explanation of how to create a response file, see Step 1 of Creating a response file (page 21).
Running a silent upgrade
To silently upgrade Enterprise Manager, open a command prompt and change the working directory to the
directory containing the Enterprise Manager setup file.
Then issue the following command:
Syntax:
QlikEnterpriseManager_version_X64.exe /s /f1my_response_file [/f2log_file]
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 22

4 Installation and setup
where:
my_response_file is the full path to the response file you created earlier and log_file is the path to the
optional log file.
Example:
C:\>QlikEnterpriseManager_6.1.0.536_X64.exe /s /f1C:\temp\1\Enterprise Manager_upgrade.iss
/f2C:\temp\1\silent_x64_up.log
If the upgrade was successful, the log file should contain the following rows:
[ResponseResult]
ResultCode=0
Silently uninstalling Enterprise Manager
Silently uninstalling Enterprise Manager consists of two stages:
1. Creating a response file (page 23)
2. Running a silent uninstall (page 23)
Creating a response file
Before starting the uninstall, you need to create a response file.
To create the response file:
1. Copy the following (response file) text into a text editor:
[{999A7077-16C9-4B3B-AFD2-CBBA9FA72C15}-DlgOrder]
Dlg0={999A7077-16C9-4B3B-AFD2-CBBA9FA72C15}-SdWelcomeMaint-0
Count=3
Dlg1={999A7077-16C9-4B3B-AFD2-CBBA9FA72C15}-MessageBox-0
Dlg2={999A7077-16C9-4B3B-AFD2-CBBA9FA72C15}-SdFinish-0
[{999A7077-16C9-4B3B-AFD2-CBBA9FA72C15}-SdWelcomeMaint-0]
Result=303
[{999A7077-16C9-4B3B-AFD2-CBBA9FA72C15}-MessageBox-0]
Result=6
[{999A7077-16C9-4B3B-AFD2-CBBA9FA72C15}-SdFinish-0]
Result=1
bOpt1=0
bOpt2=0
2. Save the file as <name>.iss, e.g. silent_uninst_64.iss.
Running a silent uninstall
To silently uninstall Enterprise Manager, open a command prompt and issue the following command:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 23

4 Installation and setup
Syntax:
"C:\Program Files (x86)\InstallShield Installation Information\<directory_containing_setup_
file>\setup.exe" /s /f1my_response_file /f2log_file
where:
my_response_file is the full path to the response file you created earlier and log_file is the path to the
optional log file.
The directory containing the Enterprise Manager setup file always ends with the following string:
CBBA9FA72C15
Example:
C:\>"C:\Program Files (x86)\InstallShield Installation Information\{999A7077-16C9-4B3B-AFD2-
CBBA9FA72C15}\setup.exe" /s /f1C:\temp\response.iss /f2C:\temp\1\silent_uninstall.log
If the uninstall was successful, the log file should contain the following rows:
[ResponseResult]
ResultCode=0
4.3 Changing the Enterprise Manager service account
By default, Enterprise Manager is installed with Administrator privileges. For secuirty reasons, you may want
Enterprise Manager to run under a user account that does not have Administrator privileges.
To do this:
1. Install Enterprise Manager.
2. Create a local user without administrative privileges.
3. Reserve the URL for the user you just created by running the following commands:
netsh http add urlacl url=https://+:443/AttunityEnterpriseManager
user=DOMAIN\youruser
netsh http add urlacl url=http://+:80/AttunityEnterpriseManager
user=DOMAIN\youruser
4. Grant the new user the Full control permission for the Enterprise Manager data folder (<EM_INSTALL_
DIR>\data).
5. Open the Local Security Policy window and select Local Policies>User Rights Assignment. Then
grant the Log on as a service policy to the new user.
6. Stop the Enterprise Manager service.
7. In the Log On tab of the Enterprise Manager service properties, select This account and specify the
new user name in the following format:
.\NewUser
8. Save your changes.
9. Start the Enterprise Manager service.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 24

4 Installation and setup
4.4 Setting the login authentication method
By default, Enterprise Manager uses Single Sign-on through Windows Authentication to authenticate users.
This allows users to open the Enterprise Manager Console without providing additional authentication. To
require users to authenticate themselves at login, you can change the authentication method to Form or
SAML. Setting the authentication method is done using the Enterprise Manager CLI, as described below.
To see the current authentication settings, run the command described in Showing the connectivity and login
settings (page 297).
l
All commands in this section should be "Run as administrator" from the Enterprise Manager
bin directory. The default location is C:\Program Files\Attunity\Enterprise Manager\bin.
l
When the Enterprise Manager data folder is in a non-default location (such as in a cluster
installation), make sure to include the --d data_folder parameter in all commands,
where data_folder is the location of the data folder. The parameter should immediately
follow the name of the Enterprise Manager executable file (e.g. aemctl --d
f:\mydatafolder {command} {parameters})
l
Changes to the authentication method will take affect only after you restart the Enterprise
Manager service.
l
If Form authentication is used, all Login/Logout operations are reported to the Audit Trail.
Setting Single Sign-on authentication
This is the default authentication method, which uses Windows authentication.
To set the authentication method to single sign-on, run:
aemctl.exe configuration set --authentication_method sso
Abbreviated form of --sso: -w
Setting Single Sign-on authentication with Kerberos
Kerberos is an enterprise authentication protocol that uses the concept of tickets and three-way
authentication to enable users and computers to identify themselves and secure access to resources.
Using Kerberos SSO, users can seamlessly log into Enterprise Manager and administrators can completely
externalize and centrally manage users or group memberships using their existing Kerberos infrastructure.
To set the authentication method to single sign-on with Kerberos, run:
aemctl.exe configuration set --authentication_method sso-kerberos
If the Kerberos protocol fails, Enterprise Manager will try to log in using NTLM authentication. If
NTLM authentication is not enabled in the system, an error will be returned.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 25

4 Installation and setup
Setting form authentication
As opposed to Single Sign-on through Windows Authentication, this method requires users to provide a user
name and password at login.
To set the authentication method to Form, run:
aemctl.exe configuration set --authentication_method form
Abbreviated parameter: -f
Setting a user timeout
Parameter: --user_timeout
Abbreviated form: -u
When setting --form authentication, you can use this parameter to override the default user idle timeout
period (5 minutes) or to disable user idle timeout entirely.
When a user idle timeout value is specified, Enterprise Manager will automatically log out users that have
been inactive for the specified time period (or longer).
To set a user timeout when using Form authentication, run:
aemctl.exe configuration set --authentication_method form --user_timeout
timeout
Where timeout is the length of time in minutes after which users will be logged out. The minimum permitted
value is 1 minute.
For example, to set a user-idle timeout period of two minutes, run:
aemctl.exe configuration set --authentication_method form --user_timeout 2
To disable the user-idle timeout entirely, run:
aemctl.exe configuration set --authentication_method form --user_timeout -1
Specifying an Active Directory domain
Parameter: --domain
Abbreviated form: -m
When setting --form authentication, you can use this parameter to specify an Active Directory domain name
that will be used when a user logs in with a user name only (i.e. without a domain name).
To set a user timeout when using Form authentication, run:
aemctl.exe configuration set --authentication_method form --domain
DomainName
Where DomainName is the name of the domain.
For example, to set the domain to ad2_acme, run:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 26

4 Installation and setup
aemctl.exe configuration set --authentication_method form --domain ad2_acme
By default, when only a user name is provided in the login form, the domain of the server is used. If the server
does not belong to any domain the server machine name will be used instead.
A user who logs in as "doe" will be assumed to identify as "ad2_acme\doe". If a user specifies a fully qualified
domain name when logging in, this parameter is ignored.
Setting up SAML authentication
This method requires you to log in via your organization's SAML Identity Provider. The command parameters
for setting SAML authentication are the same regardless of your SAML provider, although the parameter values
are slightly different.
The setup procedure consists of the following steps:
l
Step 1: Set up SAML on Enterprise Manager (page 28)
l
Step 2: Set Up an Enterprise Manager Superuser (page 29)
l
Step 3: Log in to Enterprise Manager and create SAML users (page 29)
Before running the commands, you must have already configured Enterprise Manager as an
application in your SAML Identity Provider.
When Enterprise Manager is not installed in a Cluster, the Enterprise Manager Assertion
Consumer Service (ACS) URL is:
https://{host_name}/attunityenterprisemanager/rest/?action=login_saml
When Enterprise Manager is installed in a Cluster, make sure to fulfill the following
prerequisites:
l
Finish the cluster install on all nodes before configuring SAML.
l
In order to propagate the configuration changes, make sure to include the -d data_
folder parameter in the SAML configuration commands described below, where data_
folder is the location of the cluster's shared data folder.
l
The Assertion Consumer Service (ACS) URL which the IDP should call when redirecting SAML
calls should be the cluster wide DNS name (as opposed to a specific machine name).
This is how it should look:
https://{em-cluster-fqdn}/attunityenterprisemanager/?action=login_saml
For more information about setting up Enterprise Manager in a cluster, see Installing Qlik Enterprise
Manager in a Windows cluster (page 327).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 27

4 Installation and setup
Step 1: Set up SAML on Enterprise Manager
To set the Enterprise Manager authentication method to SAML, run:
Syntax:
aemctl [--d data_folder] configuration set --authentication_method SAML --idp_url
SsoUrl
--
idp_issuer
issuer_name
--idp_certificate_file
CertificateFile
[--idp_user_displayname_
attribute
displayname
] [--idp_username_attribute
username
] [--idp_user_groups_attribute
groups
]
Example: Using Microsoft Azure as the SAML IdP
aemctl configuration set --authentication_method SAML --idp_url
https://login.microsoftonline.com/12854727-3c42-4866-ab29-0c418b8310a1/saml2 --idp_issuer
aemdevtest --idp_certificate_file AEMDevTest.pem
Where:
l
SsoUrl is the URL of the SAML IdP (Identity Provider) that handles sign-in requests.
When using Okta, this is the Okta Single Sign-On URL.
When using Microsoft Azure, this is the AzureAD SAML single sign-on URL.
Enterprise Manager will direct users to this URL to complete the SAML login operation.
l
issuer_name is a unique name that the identity provider uses for SAML 2.0.
When using Okta, this should be a URL.
When using Azure, this should be a string.
l
CertificateFile - The certificate is used by the IdP to sign the SAML assertions sent to Enterprise
Manager. The certificate file can be anywhere on the Enterprise Manager machine, but only needs to be
specified with a path when it does not reside in the Enterprise Manager bin directory.
When using Okta, the certificate must be in .cert format.
When using Microsoft Azure, the certificate must be in .pem format.
l
data_folder - The location of the data folder when it is not the default location such as when
Enterprise Manager is installed in a Windows cluster.
Optional Parameters:
The following parameters are optional and should only be used if required by your SAML IdP:
l
--idp_user_displayname_attribute - The user display name attribute.
l
--idp_username_attribute - By default, with SSO, the SAML Assertion’s “Subject” attribute is used to
define the username. Using the subject is the right solution in most situations, but in extreme cases
(such as the subject being a transient ID) it may be necessary to provide the username in some other
form.
l
--idp_user_groups_attribute - The user group attribute.
Once you have set up SAML, you need to restart the Qlik Enterprise Manager service for the settings
to take effect.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 28

4 Installation and setup
Step 2: Set Up an Enterprise Manager Superuser
The first time you log in to Enterprise Manager using SAML, you must log in as an Enterprise Manager
superuser. This is because none of the existing (or default) Enterprise Manager users are authorized SAML
users.
The instructions below assume that you have already changed the default Master User key. For
instruction on how to do this, see Configuring Enterprise Manager using the CLI (page 293) and
Configuring Enterprise Manager using the CLI (page 293) respectively.
To set up a superuser, run the following command:
aemctl authorization setsuperuser -s username -e ExpirationTimeoutInMinutes -
m MasterUserKey
Where:
l
username is the superuser user name. The user must be an existing SAML user and can contain any
Unicode character up to 255 characters.
l
ExpirationTimeInMinutes is the expiration time for the specified user. The maximum is 60
minutes.
l
MasterUserKey is your Master User Key.
Step 3: Log in to Enterprise Manager and create SAML users
After setting up SAML authentication, you will be presented with the following page when you try to open the
Qlik Enterprise Manager console:
1. Click Log In with SAML.
You will be redirected to Okta or Microsoft Azure to provide your SAML login credentials.
2. Authenticate yourself with SAML.
After successful authentication, you will be redirected back to the Enterprise Manager Console.
3. Add authorized SAML users and groups, as described in Managing user permissions (page 286).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 29

4 Installation and setup
For information about other CLI options, see Configuring Enterprise Manager using the CLI (page 293).
Switching between SAML and SSO/Form authentication
If you wish to switch from SAML to SSO/Form authentication (or vice versa), you may need to clear the existing
users from Enterprise Manager. When switching from SAML to SSO/Form authentication, you will not be able
to change user permissions or add users unless you clear the existing SAML users. However, when switching
from SSO/Form authentication to SAML, you do not need to clear the existing users in order to add/delete
users or edit user permissions. You may still want to do this however if you find the presence of non-SAML
users distracts you from managing the SAML users.
Before clearing the users, it is strongly recommended to export them as this will save time (by
importing them) should you later need to revert the authentication type.
To export all users to a JSON file, run the following command:
aemctl repository export_acl -f [fullpath\]filename
where filename is the name of the file to which the users will be exported. By default, the file will be exported
to the Enterprise Manager bin directory. If you wish the file to be exported to a custom path, include
[fullpath\] in the command.
Example:
aemctl repository import_acl -f C:\temp\Enterprise ManagerUsers
To clear all users, run the following command:
aemctl repository clear_acl
To import users from the exported JSON file, run the following command:
aemctl repository import_acl -f [fullpath\]filename
where filename is the name of the file to import. Unless you specified a custom export path, the file will be
located in the Enterprise Manager bin directory. If you wish the file to be imported from a custom path,
include [fullpath\] in the command.
Example:
aemctl repository import_acl -f C:\temp\Enterprise ManagerUsers
Setting up Personal Access Token authentication for the API
Personal Access Token authentication is only supported with the Enterprise Manager API.
Azure Active Domain is not supported.
The high-level flow consists of the following steps:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 30

4 Installation and setup
l
Step 1: In Okta, create an app integration that uses OpenID Connect
l
Step 2: In Enterprise Manager, enable Enterprise Manager to communicate with Okta
l
Step 3: In Enterprise Manager, generate a Personal Access Token
l
Step 4: Configure the Enterprise Manager API to log in using the Personal Access Token
Step 1: In Okta, create an app integration that uses OpenID Connect
Enterprise Manager uses OpenID Connect to log in with the API. Therefore, before you can use OpenID
Connect with Enterprise Manager, you must create a web integration in Okta.
To create a web integration in Okta for use with Enterprise Manager:
1. Log in to your Okta account.
2. Navigate to Applications>Applications and click Create App Integration.
3. In the Create a new app integration dialog, select OIDC - Open IDConnect.
4. Select Web Application as the Application type and click Next.
5. In the New Web Integration page, configure the following fields:
l
App Integration Name:The name of your App integration. For example,QEM OpenID
Connect.
l
Select Refresh Token.
l
In the Sign-in redirect URIs field, enter the following:
https://
EnterpriseManagerMachine/attunityenterprisemanager/rest/login_
openid
Where EnterpriseManagerMachine is the host name or IP address of your Enterprise
Manager machine.
6. Clear the Enable immediate access with Federation Broker Mode option, and then click Save.
7. Copy your Client ID and Client secret. You will need to provide these parameters in the next stage.
8. Assign the app integration to the users or groups that you want to allow to use the Personal Access
Token.
For details, see ≤ Assign app integrations.
Step 2: In Enterprise Manager, enable Enterprise Manager to communicate with Okta
To enable Enterprise Manager to communicate with Okta, open a CMDprompt as admin and change the
working directory to <Enterprise Manager-INSTALL-DIR>\bin.
Then run the following command:
Syntax
aemctl.exe configuration set --open_id_authority
your-openid-connect-authority
--open_id_
client_id
your-client-id
--open_id_client_secret
your-secret
Example using Okta
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 31

4 Installation and setup
aemctl.exe configuration set --open_id_authority "https://dev-13465054.okta.com" --open_id_
client_id "0oa8ohkl5ftweZNWTT5d7" --open_id_client_secret "FJxXqWOpJsROGrthsaVzfUIcNthG6JLA1-
nAJH0"
Where:
l
--open_id_authority is your Okta URL. For example, https://dev-13465054.okta.com
l
--open_id_client_id is the client ID generated in Step 1: Create an app integration that uses
OpenID Connect above.
l
--open_id_id_client_secret is the client secret generated in Step 1: Create an app
integration that uses OpenID Connect above.
Optional Parameters:
The following parameters are optional and should only be used if required by Okta:
l
--open_id_additional_scopes - Additional scopes that are added to the scope list when an
OpenId Connect login occurs. The default is "groups"
l
--api_token_daily_maintenance_time - Determines when the API token maintenance
background process runs each day. This should be formatted as HH:mm. The default is "00:30"
l
--api_token_lifetime - The number of days a Personal Access Token is valid. The default is
"180"
l
--open_id_refresh_token_lifetime - The number of days a refresh token is valid. The default
is "0" meaning it is valid forever.
l
--open_id_user_name_field - The field name for the OpenID Connect user name. The default is
"preferred_username".
l
--open_id_display_name_field - The field name for the OpenID Connect user display name.
The default is "name".
l
--open_id_group_field - The field name for an OpenID Connect group. The default is "groups".
After you have run the OpenID Connect command, you need to restart the Qlik Enterprise Manager
service for the settings to take effect.
Step 3: In Enterprise Manager, generate a Personal Access Token
1. Log in to Enterprise Manager as a SAML user. This must be one of the users/groups that was assigned
to the app integration in Step 1: In Okta, create an app integration that uses OpenID Connect
above.
For information on setting up SAML, see Setting up SAML authentication above.
2. In the top right of Enterprise Manager, click the inverted triangle to the right of the user name and
select Generate Personal Access Token.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 32
4 Installation and setup
The Generate Personal Access Token dialog opens.
In the Generate Personal Access Token dialog, you will see one of the following:
l
You do not have a Personal Access Token. This is shown if you have not previously generated
a Personal Access Token:
l
Your Personal Access Token expired on <Date>. This is shown if your Personal Access Token
has expired.
l
Your Personal Access Token expires on <Date>. This is shown if you already have a Personal
Access Token.
When regenerating a token, you will need to confirm that you want to regenerate the
token. This is because API login with the original token will stop working as soon as
you generate a new token.
3. Click Generate token.
The Copy Personal Access Token dialog is displayed.
4. Copy your personal access token. You will need this to log in with the Enterprise Manager API.
See also: Managing Personal Access Tokens (page 289)
Step 4: Configure the Enterprise Manager API to log in using the Personal Access
Token
For instructions, see:
l
REST API: Login
l
.NET API: Getting started - Login
l
Python API: Getting started - Login
4.5 Starting to work with the Qlik Enterprise Manager
Console
To start working with Enterprise Manager, you need to open the Qlik Enterprise Manager Console and register
a Replication Management license.
You can use a Web browser to access the Console from any computer in your network. For information on
supported browsers, see Preparing your system for Enterprise Manager (page 15).
The user logged into Enterprise Manager must be an authorized Qlik Enterprise Manager user.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 33

4 Installation and setup
To access the Qlik Enterprise Manager Console:
l
From the machine on which it is installed, select All Programs > Qlik Enterprise Manager > Qlik
Enterprise Manager Console from the Windows Start menu.
OR
Type the following address in the address bar of your Web browser:
https://<computer name>/attunityenterprisemanager
On a machine running Microsoft Windows 10 or Windows Server 2012, you need to run the Console as
Administrator.
l
From a remote browser, type the following address in the address bar of your Web browser:
https://<computer name>/attunityenterprisemanager
where <computer name> is the name or IP address of the computer where Qlik Enterprise Manager is
installed.
If no server certificate is installed on the Enterprise Manager machine, a page stating that the connection is
untrusted opens. This is because when Enterprise Manager detects that no server certificate is installed, it
installs a self-signed certificate. Because the browser has no way of knowing whether the certificate is safe, it
displays this page.
For more information, see Setting up HTTPS for the Enterprise Manager console (page 35).
If prompted, enter your user name and password.
The user name may need to include domain information in the following format:
<domain name>@<user name>
For more information, see Setting the login authentication method (page 25).
Registering Licenses
If this is the first time you are using Enterprise Manager, you will be prompted to register a Replication
Management license when the console opens. You may also need to register a Replication Analytics license
(required for the Analytics (page 305) module), depending on whether you have obtained such a license from
your Qlik Sales Representative.
For information on registering licenses, see Registering and managing licenses (page 276).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 34

5 Security considerations
5 Security considerations
This section provides a detailed rundown of the various security-related procedures that need to be
performed to ensure that your data is secure.
In this section:
l
Setting up HTTPS for the Enterprise Manager console (page 35)
l
Setting up HSTS on Enterprise Manager (page 38)
l
Replacing the self-signed certificate on Windows (page 39)
l
Setting the hostname and changing the SSL port (page 40)
l
Replacing the Master User Password (page 41)
l
Encrypting the user permissions file (page 42)
l
Controlling execution of user-defined commands (page 43)
5.1 Setting up HTTPS for the Enterprise Manager console
Industry-standard security practices dictate that web user interface for enterprise products must use secure
HTTP (HTTPS). Qlik Enterprise Manager enforces the use of HTTPS and will not work if HTTPS is configured
incorrectly.
As Enterprise Manager uses the built-in HTTPS support in Windows, it relies on the proper setup of the
Windows machine it runs on to offer HTTPS access. In most organizations, the IT security group is responsible
for generating and installing the SSL server certificates required to offer HTTPS. It is strongly recommended
that the machine on which Enterprise Manager is installed already has a valid SSL server certificate installed
and bound to the default HTTPS port (443).
Checking if an SSL Certificate is installed
To check whether an SSL certificate is installed, you can use the following command:
netsh http show sslcert | findstr /c:":443"
If an SSL certificate is installed, the output should look like this:
netsh http show sslcert | findstr /c:":443 "
IP:port : 192.168.1.13:443
IP:port : 192.168.1.11:443
IP:port : [fe80::285d:599c:4a55:1092%11]:443
IP:port : [fe80::3d0e:fb1c:f6c3:bc52%23]:443
With a valid SSL certificate installed, the Enterprise Manager web user interface will automatically be available
for secure access from a web browser using the following URL:
https://<machine-name>/attunityenterprisemanager
Using the self-signed certificate
Due to the way the HTTPS protocol works, there is no way for Enterprise Manager to automatically provide
and install a valid SSL server certificate. Still, in the event that no SSL server certificate is installed, Enterprise
Manager automatically generates and installs a self-signed SSL server certificate (as a temporary measure).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 35

5 Security considerations
This certificate is generated on the Enterprise Manager machine and cannot be exported or used elsewhere.
It should be noted that browsers do not consider the certificate to be valid because it was not signed by a
trusted certificate authority (CA). When connecting with a browser to a server that uses a self-signed
certificate, a warning page is shown such as this one in Chrome:
Or this one in Firefox:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 36

5 Security considerations
The warning page informs you that the certificate was signed by an unknown certificate authority. All
browsers display a similar page when presented with a self-signed certificate. If you know that the self-signed
certificate is from a trusted organization, then you can instruct the browser to trust the certificate and allow
the connection. Instructions on how to trust the certificate vary between browsers and even between different
versions of the same browser. If necessary, refer to the help for your specific browser.
Some corporate security policies prohibit the use of self-signed certificates. In such cases, it is
incumbent upon the IT Security department to provide and install the appropriate SSL server
certificate (as is the practice with other Windows products such as IIS and SharePoint). If a self-
signed certificate was installed and needs to be removed, then the following command can be used:
<product_dir>\bin\AemCtl.exe certificate clean
Note that after the self-signed certificate is deleted, connections to the Enterprise Manager machine
will not be possible until a valid server certificate is installed. Should you want to generate a new
self-signed certificate (to replace the deleted certificate), simply restart the Enterprise Manager
service.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 37

5 Security considerations
5.2 Setting up HSTS on Enterprise Manager
HSTS is a web security policy mechanism that helps to protect websites against man-in-the-middle attacks
such as protocol downgrade attacks and cookie hijacking. It allows web servers to declare that web browsers
(or other complying Dilqam) should automatically interact with it using only HTTPS connections, which
provide Transport Layer Security (TLS/SSL).
You can force the Enterprise Manager Web UI and/or the Enterprise Manager REST API connections to use
HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security). To do this, run the commands described below.
All commands should be run from as Admin from the product bin folder.
Enabling HSTS
Command syntax
aemctl.exe configuration set --static_http_headers
header_list
--rest_http_headers
header_list
Parameters
Parameter Description
--static_http_headers The headers required to connect to the Enterprise Manager Web UI.
--rest_http_headers The headers required to connect using the API.
Headers should be specified using the following format:
aemctl.exe configuration set --static_http_headers "header1:value1" "header2:value2" --rest_
http_headers "header1:value1" "header2:value2"
Example
aemctl.exe configuration set --static_http_headers "Strict-Transport-Security:max-
age=31536000; includeSubDomains;" --rest_http_headers "Strict-Transport-Security":"max-
age=31536000; includeSubDomains;"
Disabling HSTS
You can also revert to regular HTTPS connections.
Command syntax
aemctl.exe configuration set --static_http_headers ""|--rest_http_headers ""
Parameters
Parameter Description
--static_http_headers Use this parameter to revert the headers required to connect to the
Enterprise Manager Web UI.
--rest_http_headers Use this parameter to revert the headers required to connect using the
API.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 38

5 Security considerations
Example
Disable static_http_headers
aemctl.exe configuration set --static_http_headers ""
Disable rest_http_headers
aemctl.exe configuration set --rest_http_headers ""
5.3 Replacing the self-signed certificate on Windows
The instructions below are intended for organizations who wish to replace the built-in self-signed certificate
automatically generated by the Enterprise Manager UI Server on Windows with their own certificate. This is
achieved by removing the self-signed certificate and then importing the new certificate.
See also Setting up HTTPS for the Enterprise Manager console (page 35).
Before starting, make sure that the following prerequisites have been met:
l
The replacement certificate must be a correctly configured SSL PFX file containing both the private key
and the certificate.
l
The common name field in the certificate must match the name browsers will use to access the
machine.
To remove the self-signed certificate created by Enterprise Manager:
1. Stop the Qlik Enterprise Manager service.
2. Open a command prompt (using the "Run as administrator" option) and change the path to the bin
directory. The default path is:
C:\Program Files\Qlik\Enterprise Manager\bin.
3. Run the following command:
AemCtl.exe certificate clean
To import your own certificate:
1. Run mmc.exe to open the Microsoft Management Console.
2. From the File menu, select Add/Remove Snap-in.
The Add or Remove Snap-ins dialog box opens.
3. In the left pane, double-click Certificates.
The Certificates snap-in wizard opens.
4. Select Computer account and then click Next.
5. In the Select Computer screen, make sure that Local computer is selected and then click Finish.
6. Click OK to close the Add or Remove Snap-ins dialog box.
7. In the left pane, expand the Certificates folder. Then, right-click the Personal folder and select All
Tasks>Import.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 39

5 Security considerations
8. In the File to Import screen, select your PFX certificate file. Note that by default the Open dialog box
displays CER files. In order to see your PFX files, you need to select Personal Information Exchange
from the drop-down list in the bottom right of the dialog box.
9. Click Next and enter the private key password.
10. Continue clicking Next until you reach the Completing the Certificate Import Wizard screen. Then
click Finish to exit the wizard.
11. In the Personal> Certificates folder, double-click the newly imported certificate.
The Certificate dialog box opens.
12. Scroll down the Details tab until you see the Thumbprint details and copy them to the clipboard.
13. Open a command prompt and run one of the following commands:
Syntax:
¢ netsh http add sslcert ipport=0.0.0.0:443 certhash=[YOUR_CERTIFICATE_THUMBPRINT_
WITHOUT_SPACES] appid={4dc3e181-e14b-4a21-b022-59fc669b0914}
Example:
netsh http add sslcert ipport=0.0.0.0:443
certhash=5f6eccba751a75120cd0117389248ef3ca716e61 appid={4dc3e181-e14b-4a21-b022-
59fc669b0914}
Syntax:
¢ netsh http add sslcert ipport=[::]:443 certhash=[YOUR_CERTIFICATE_THUMBPRINT_WITHOUT_
SPACES] appid={4dc3e181-e14b-4a21-b022-59fc669b0914}
Example:
netsh http add sslcert ipport=[::]:443 certhash=5f6eccba751a75120cd0117389248ef3ca716e61
appid={4dc3e181-e14b-4a21-b022-59fc669b0914}
14. Close the command prompt and Microsoft Management Console.
15. Start the Qlik Enterprise Manager service.
5.4 Setting the hostname and changing the SSL port
After installing Qlik Enterprise Manager, you can use the Enterprise Manager CLI to set the hostname and SSL
port for accessing the Enterprise Manager server machine.
Under normal circumstances, you should not need to set the hostname. However, on some systems,
connecting using HTTPS redirects to localhost. If this occurs, set the hostname of the Enterprise Manager
machine by running the command shown below.
To set the hostname:
Run the following command:
<product_dir>\bin\AemCtl.exe configuration set -a
hostAddress
where hostAddress is the address of the Enterprise Manager server machine.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 40

5 Security considerations
When using a Load Balancer, hostAddress should be the Load Balancer host address.
To change the SSL port:
Run the following command:
<product_dir>\bin\AemCtl.exe configuration set -s
httpsPort
where httpsPort is the SSL port number of the Enterprise Manager server machine.
5.5 Replacing the Master User Password
Qlik goes to great lengths to ensure that sensitive information is protected from unauthorized parties, which is
why all passwords and other sensitive information are encrypted (and decrypted) using the Enterprise
Manager Master Key. Enterprise Manager uses only FIPS 140-2 compliant algorithms for hashing and
encryption: SHA256 for hashing and AES256 for encryption.
This topic provides an overview of how the Enterprise Manager Master Key is generated and applied as well as
explaining how to encrypt the User Permissions file.
The Master Key
The following section describes the role the master key and the master user key play in keeping your data
secure.
l
Using the Enterprise Manager CLI, the user provides the system with an alphanumeric password
(Master User Password), which must be at least 32 characters.
By default (i.e. after first time installation), the Master User Password is randomly generated
by Enterprise Manager. It is strongly recommended to change the Master User Password as
soon as possible (especially in a production environment) as this will allow recovery of
backed up data in the event of disk failure. The password should of course be kept in a
secure location for future use.
You can either use your own password or run the
genpassword
utility to generate a password
for you.
l
Enterprise Manager uses a one way hashing functions to generate a key (Master User Key) from the
Master User Password.
The one way hash function guarantees that, given the same Master User Password as input,
the same Master User Key will be generated. This is what happens in high availability
scenarios - the same Master User Password is entered on two different machines.
l
Enterprise Manager encrypts the Master User Key using the local machine’s key (Windows) and stores it
in a file named muk.dat. The muk.dat file can contain several entries (and indeed does in a high
availability environment), with each entry uniquely identifying the machine on which Enterprise
Manager is running.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 41

5 Security considerations
l
Enterprise Manager generates a random Master Key, encrypts it with the Master User Key and stores it
in a common location (e.g. the root repository).
l
On software startup, the following occurs:
l
The Master User Key is read and decrypted (using the local machine’s key)
l
The Master Key is read and decrypted using the Master User Key
Once this process is complete, Enterprise Manager is able to encrypt and decrypt all sensitive information.
For more information on commands related to the master user password, see Commands Related to the
Master User Password.
High Availability mode
In a High Availability environment, Enterprise Manager runs on at least two machines that share the same
data folder. As there are two machines, there will also be two different keys - one for each machine.
As mentioned earlier, the Master User Key file (muk.dat) is constructed of entries, with each entry
corresponding to one machine. Both machines scan the entries searching for an entry they can decrypt.
If no matching entry can be found, an error will be returned. In this case, simply use the Enterprise Manager
CLI to enter the Master User Password again, and create an entry for the new machine.
See also Installing Qlik Enterprise Manager in a Windows cluster (page 327).
5.6 Encrypting the user permissions file
User permissions are stored in the following repository file:
<product_dir>\Data\cfgrepo.sqlite
To prevent unauthorized access of this file, you can encrypt it using the procedure described below. After you
perform the procedure, the repository file will be encrypted with the AES-256 bit cipher.
The length of any passwords specified during the procedure must be at least 32 characters.
To encrypt the repository file:
1. Open a command prompt as administrator and change the working directory to:
<product_dir>\bin
2. Run the following command to set the master user key:
aemctl.exe masterukey set --password your_MasterUserPassword
Example:
aemctl.exe masterukey set --password ANqaGYERP3UKmGLK6UNuMqrkAGxwH8FM
3. Restart the Qlik Enterprise Manager service.
4. Run the following command to set the repository password:
aemctl.exe repository setpassword --master-user-password your_MasterUserPassword --
repository-password your_RepositoryPassword
Example:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 42

5 Security considerations
aemctl.exe repository setpassword --master-user-password
ANqaGYERP3UKmGLK6UNuMqrkAGxwH8FM --repository-password 12345678901234567890123456789000
Steps 1-4 only need to be performed the first time you want to encrypt the repository file. If you
subsequently need to decrypt the repository file and then re-encrypt it, they are not required.
5. Run the following command to encrypt the repository:
aemctl.exe repository secure --on --master-user-password your_MasterUserPassword
Example:
aemctl.exe repository secure --on --master-user-password
ANqaGYERP3UKmGLK6UNuMqrkAGxwH8FM
6. Restart the Qlik Enterprise Manager service.
To disable encryption for the repository:
l
Run the following command:
aemctl.exe repository secure --off --master-user-password your_MasterUserPassword
For information on setting user permission, see User permissions (page 278).
For more information on commands related to the master user password, see Commands Related to the
Master User Password.
5.7 Controlling execution of user-defined commands
Several endpoints support running user-defined commands for pre/post-processing files. In the Operating
System Level Credentials tab shown in SERVER view, you can provide user credentials for user-defined
commands that needs to be executed at operating system level. By default, such commands are executed
under the Replicate Server service account. This may constitute a security risk, as it allows any Replicate user
with Admin or Designer permissions to specify user-defined commands that could lead to a full compromise of
the server.
Note that when Replicate Server is installed on Linux, the External utilities (page 54) tab will be hidden as the
potential security risk is relevant to Windows only.
You can also determine whether to allow user-defined commands to be executed at all.
To do this:
1. On the Replicate Server machine, open the <PRODUCT_DIR>\bin\repctl.cfg file and set
the enable_execute_user_defined_commands parameter to "true" or "false" (the
default) as required.
2. If Another account is selected in the Operating System Level Credentials tab and you
changed the default Attunity Replicate Server service Log On user (see the Replicate
Help for instructions on how to do this):
a. For both admin and non-admin users:
Add the user specified in the Attunity Replicate Server service
Log On tab to the "Replace a process level token" policy in
the "Local Security Policy" settings.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 43

5 Security considerations
b. For non-admin users only:
i. Grant the user full control over the
Replicate data folder.
The default location of the data folder
is C:\Program Files\Qlik\Replicate\data
ii. Grant the user full control over the folder containing
the user-defined command to be executed.
The user must be the same as the non-
admin user specified in the Attunity
Replicate Server service Log On tab.
3. Restart the Qlik Replicate services.
Executing operating system commands as a different user
The load utility of the following target endpoints can run via user-provided credentials instead of the
LocalSystem user:
l
Microsoft APS PDW
l
Google Cloud BigQuery
l
IBM Netezza
l
PostgreSQL-based
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 44

6 Managing servers
6 Managing servers
Servers View is where you manage the Replicate and Compose Servers to be monitored by Enterprise
Manager. This view also provides information about the number of tasks defined on each server as well as
their current status. To switch from Tasks View to Servers View, click the Servers tab in the top left of the
console.
Some of the management options described in this chapter are available for Replicate servers only.
In such cases, a note will clearly indicate that the described management option is not available for
Compose servers.
In this section:
l
Server requirements (page 45)
l
Adding Servers (page 46)
l
Monitoring servers (page 48)
l
Server settings (page 50)
l
Additional server management options (page 60)
l
Registering a license for a monitored server (page 62)
l
Viewing server messages (page 63)
6.1 Server requirements
The following section lists the requirements for connecting to a Replicate or Compose Server.
Qlik Replicate Server requirements
To be able to connect to a Replicate Server, Enterprise Manager requires the following for each Replicate
Server to be monitored:
l
A Replicate administrator user. Enterprise Manager uses this user to connect to the Qlik Replicate
instance. This means:
l
If the connection is made directly to the replication server, you can use the fixed user name
admin. In this case, the default port is 3552. You set the admin user password on the Replicate
server using the repctl setserverpassword command, as follows:
On the Replicate server, run the following command from the bin directory; then restart the
Replicate service:
Repctl.exe setserverpassword <adminPassword>
For more details, see the Replicate documentation.
l
If the connection is made to the Replicate UI server, you must specify a user with Admin role.
This can be the user that installed Replicate, an Active Directory user with the Replicate Admin
role, or a member of the AttunityReplicateAdmins Active Directory group.
The default port is 443. For information on setting user roles within Qlik Replicate, refer to the
Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 45

6 Managing servers
It is recommended that you configure this user with a strong password that does not need to be
changed frequently. If the administrator password changes, you also need to change it in Enterprise
Manager.
If you need to change the password and the associated user is an Active Directory user, you
must stop monitoring all servers with the same user before changing the password in Active
Directory.
l
The port that Enterprise Manager uses for connecting to Qlik Replicate needs to be opened inbound on
the Replicate server machine. Depending on your network architecture (for example a WAN
environment), you may also need to open ports on routers and border firewalls. If you block outbound
traffic from the Enterprise Manager machine, you need to make an exception on the Enterprise
Manager machine for the ports used to connect to the Replicate Server.
For additional information, see Software requirements (page 16).
Qlik Compose Server requirements
To be able to connect to a Compose Server, Enterprise Manager requires the following for each Compose
Server to be monitored:
l
A Compose administrator user. Enterprise Manager uses this user to connect to the Qlik Compose
instance.
It is recommended that you configure this user with a strong password that does not need to be
changed frequently. If the administrator password changes, you also need to change it in Enterprise
Manager
l
The port that Enterprise Manager uses for connecting to Qlik Compose needs to be opened inbound on
the Compose server machine. Depending on your network architecture (for example a WAN
environment), you may also need to open ports on routers and border firewalls. If you block outbound
traffic from the Enterprise Manager machine, you need to make an exception on the Enterprise
Manager machine for the ports used to connect to the Compose Server.
6.2 Adding Servers
You can add both Replicate Servers and Compose Servers to Enterprise Manager. Once a Server is added and
monitoring is enabled, Enterprise Manager establishes a connection to it and automatically discovers and
retrieves all tasks and messages, along with basic information about the server.
You need the admin role to be able to add a server.
To add a server:
1. Open Qlik Enterprise Manager.
2. Click Add Server.
The Add Server dialog box opens.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 46

6 Managing servers
3. Provide the following information:
l
Name: A unique name not exceeding 64 characters. The name can contain Latin characters,
spaces, dots, dashes, and underscores.
l
Description: Optional. Cannot exceed 250 characters.
l
Type:Choose Replicate or Compose according to the server you wish to add.
l
Host: The server’s host name or IP address. The combination of host and port must be unique.
l
Port: The port on which the host listens. The combination of host and port must be unique.
l
Username: The user name for the server. Enterprise Manager uses this user to connect to the
server. The name can contain Latin characters, spaces, dots, dashes, and underscores.
For a domain user, use the following format: <domain>\<user name>
For example: Qlik_LOCAL\JohnMiller
The user must be a user with admin privileges. For more information, see Server
requirements (page 45).
l
Password: The user password for the server.
If you need to change the password and the associated user is an Active Directory
user, you must stop monitoring all servers with the same user before changing the
password in Active Directory.
For details, see Server requirements (page 45).
4. Verify server certificate.
Select this option to ensure the Server certificate is trusted. As a rule, to reduce the chance of "man-in-
the-middle" attacks, this option should always be selected.
l
When connecting directly to an Replicate replication server (default port 3552) with its
automatically generated self-signed certificate, Enterprise Manager is able to validate the
certificate without requiring any additional setup.
l
When connecting to a Replicate Server via the Replicate UI Server (typically using port 443) or
to the Replicate replication server with a user-installed certificate, you must make sure that the
SSL/TLS certificate used by the server is trusted by the Enterprise Manager machine. The same
applies when connecting to a Compose Server with a user-installed certificate. You can easily
verify whether the certificate is trusted by opening a Chrome browser window on the Enterprise
Manager machine and connecting to Replicate. If there are no security warnings, the certificate
is trusted.
For information on the different ways of connecting to Qlik Replicate, see Qlik Replicate Server
requirements (page 45).
5. Select the Monitor this server’s tasks and messages check box if you want Enterprise Manager to
retrieve tasks and messages from this server.
6. Click Test Connection to verify that Qlik Enterprise Manager is able to establish a connection to the
server.
7. Click OK to save your settings.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 47

6 Managing servers
6.3 Monitoring servers
Qlik Enterprise Manager shows server information in table format. The following columns are available. Note
that columns marked with an asterisk (*) are not available for Compose servers.
General columns:
l
State: The current state of the server. When the server is being monitored, the state can be Monitored
(green icon), which means that the Enterprise Manager connected and synchronized successfully, or
Error, including error details (red icon). When the server is not being monitored, the state is Not
Monitored and the connection icon is grayed out.
When a server experiences connection issues, tasks for this server are grayed out in the Tasks
View.
l
Name: The server’s display name
l
Host: The server’s hostname or IP address
l
Port: The port through which the server is accessed
l
Type: The server version (i.e. Compose or Replicate)
l
Version: The server version
l
License Expiration: The expiration date of the server license
l
Last Connection: The date and time of the last successful sync/retrieval of tasks and messages
l
Message: The error message displayed if Qlik Enterprise Manager cannot connect to the server
Not displayed by default:
l
Days to Expiration: Days remaining until the license expires
l
Description: A description of the server
l
Issue Date: When the license was issued
l
License State: The current license state (e.g. valid, expired, etc.)
l
Platform: The operating system on which the server is installed, which will be Windows or Linux for
Replicate servers or Windows for Compose servers.
*Resource utilization columns:
l
*Disk Usage (MB): The amount of disk space that the server is currently consuming. This is the sum of
disk usage of all tasks on this server. For details about a task’s disk usage, see Task progress summary
(page 203).
l
*Memory (MB): The amount of memory that the server is currently consuming. This is the sum of
memory usage of all active tasks on this server, not including stopped tasks. For details about a task’s
memory usage, see Task progress summary (page 203).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 48

6 Managing servers
Not displayed by default:
l
*Qlik CPU (%): The amount of CPU being utilized on the server machine by Replicate and Enterprise
Manager processes only.
l
*Machine CPU (%): The amount of CPU being utilized by all processes on the server machine
(including Replicate and Enterprise Manager processes).
Tasks columns: The number of tasks for each state.
Task State Icon Description
Total N/A The total number of tasks, regardless of state.
Running The number of running tasks
Stopped The number of stopped tasks
Recovering The number of recovering tasks.
Error The number of tasks that encountered a fatal error
Task state columns
Customizing server columns
You can use the Columns Settings dialog box to select the columns to display and to arrange the order in
which they appear. In addition, from the context menu, you can hide a column, export the list to a TSV file, or
sort by column in ascending or descending order. For more information, see Customizing task columns (page
231).
Searching for servers
You can search for specific servers by typing a string into the Search Servers box above the table. Note that
Enterprise Manager searches only textual columns, not numeric columns. The following columns are included
in the search, even if a column is not displayed in the user interface:
l
State
l
Name
l
Host
l
Port
l
Description
l
License Expiration
l
Message
l
Platform
l
Version
You can also restrict a search to a specific column by preceding the search string with the column name and a
colon, as follows: ColumnName:value (for example: Name:john-vm.abc.local). This is applicable to all
available columns, not only the columns listed above.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 49

6 Managing servers
When searching for a number, only enter whole numbers, no commas or special characters. For
example, to search for 2,500, as displayed in the user interface, enter
2500
; to search for 100%, enter
100.
6.4 Server settings
You can modify Replicate and Compose server settings.
This feature requires the monitored Replicate servers to be version 6.0 or later. Currently, only the
logging settings for Compose servers can be modified.
To modify server settings, switch to Servers view and select the desired server. Then, from the Server
Management drop-down menu, select Settings.
The Settings for Server "<Name>" window opens.
The following items are displayed on the left of the window:
l
Global error handling (page 50) (Replicate servers only)
l
Resource Control (page 51) (Replicate servers only)
l
File Transfer Service (page 52) (Replicate servers only)
l
External utilities (page 54)
l
Logging (page 54)
l
More options (page 202)
Global error handling
You can configure how Qlik Replicate responds to specific types of errors. You can define error handling on the
task level or the server level. The configurations you make in the Server Settings affect all tasks created for
this instance of Qlik Replicate unless you define a task to use the definitions you create for that task. For
information on how to configure error handling for a specific task, see Error handling (page 186) in the
Customizing tasks (page 82) chapter.
l
Changes to settings will only take affect after restarting all tasks.
l
Global error handling is not available when the Apply changes using SQL MERGE task setting
is enabled.
The following sub-tabs are available:
l
Environmental Errors: An error that is caused by an environmental problem in the source or target
endpoint or on the network. Environmental errors can be restarted.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 50

6 Managing servers
The information you enter in this tab is the same as the information you enter in the Environmental
Errors tab for tasks. For information about the options available in this tab, see Environmental errors
(page 187).
l
Data Error: An error related to data processing at the record level.
The information you enter in this tab is the same as the information you enter in the Data Error tab for
tasks. For information about the options available in this tab, see Data Errors (page 188) in the
Customizing Tasks chapter.
l
Table Error: An error in processing data or metadata for a specific table. This only includes general
table data and not an error that relates to a specific record.
The information you enter in this tab is the same as the information you enter in the Table Error tab
for tasks. For information about the options available in this tab, see Table Errors (page 191) in the
Customizing Tasks chapter.
l
Apply Conflicts: Errors that occur when the target endpoint is not synchronized with the source
endpoint when processing changes. This can cause duplicate key errors on INSERT operations or zero
rows affected on UPDATE/DELETE operations.
The information you enter in this tab is the same as the information you enter in the Apply Conflicts
tab for tasks. For information about the options available in this tab, see Apply Conflicts (page 191) in
the Customizing Tasks chapter.
Resource Control
You can set high and critical disk space and memory utilization thresholds.
Disk space is checked only for the drive where the data folder resides.
Thresholds are calculated as a percentage of total capacity. So, for example, a disk space utilization threshold
of 80% would mean that 20% of available disk space remains.
After setting the thresholds, you can click the New Notification button to define a notification that will be
sent whenever a given threshold is exceeded and/or returns to normal.
Disk space control
Before you can modify settings, you first need to select the Disk Space check box. To disable Disk Space
resource control, clear the Disk Space check box.
In the High Disk Space Utilization Threshold section, specify the high disk space utilization threshold (in
terms of percentage). When the threshold is reached, a notification will be sent (if defined).
In the Critical Disk Space Utilization Threshold section, specify the critical disk space utilization threshold
(in terms of percentage). When the threshold is reached, all tasks will be stopped and a notification will be
sent (if enabled). Replicate will resume the tasks automatically when there is sufficient disk space to do so.
System memory control
Before you can modify settings, you first need to select the System Memory check box. To disable System
Memory resource control, clear the System Memory check box.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 51

6 Managing servers
Memory utilization is calculated using the following formula (note that “swap file” is used generically to refer
to both page file memory on Windows and swap file memory on Linux):
(used_swap_file + used_physical_memory) /
(total_swap_file + total_physical_memory) * 100
Example:
(5 GB + 5 GB) / (10 GB + 10 GB) * 100 = 50%
In the High System Memory Utilization Threshold section, specify the high system memory utilization
threshold (in terms of percentage). When the threshold is reached, a notification will be sent (if defined).
In the Critical System Memory Utilization Threshold section, specify the critical system memory utilization
threshold (in terms of percentage). When the threshold is reached, Replicate will start stopping tasks and a
notification will be sent (if enabled). The tasks will be resumed automatically when there is sufficient memory
to do so.
File Transfer Service
The Qlik File Transfer Service (FTS) is a robust and reliable file transfer engine designed to efficiently transfer
files over the WAN. This can dramatically improve transfer speeds when the source endpoint and the target
endpoint are located on different LANs.
Changes to settings will only take affect after restarting all tasks.
How it works
A solution using FTS consists of two Qlik Replicate Servers: A local Qlik Replicate Server installed on the
source endpoint LAN and a remote Qlik Replicate Server installed on the target endpoint LAN.
A local task on the local server is defined from the source endpoint to a File Channel target. A remote task on
the remote Qlik Replicate Server is defined from a File Channel source to the target endpoint.
The FTS runs on the remote Qlik Replicate Server only and transfers the File Channel files from the storage
location defined in the local task to the storage location defined in the remote task.
Upon file transfer, and before Compression (page 52) and Encryption (page 53), large files are split into smaller
blocks which form recoverable transport units, and small files are merged into bigger blocks to be sent at the
same time. The blocks are then transferred and reconstructed into File Channel files when received by the FTS
server.
For information on setting up a File Channel source or target to use FTS, refer to the Qlik Replicate Setup and
User Guide.
Compression
File Channel files are compressed upon sending using GZIP. You can disable the compression and control the
compression level.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 52

6 Managing servers
Encryption
After compression, File Channel files are encrypted using a randomly generated AES-256 session key. The
session key is exchanged between the client and server using the Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol which
is authenticated using a secret key that is shared between the client and the server.
The File Transfer Service should be configured on the remote Qlik Replicate Server only.
Defining a File Transfer Service
Define a File Transfer Service as described below.
To add a File Transfer Service:
1. In the File Transfer Service tab, click Add File Transfer Service.
The Add File Transfer Service window opens.
2. Edit the values in the Name, Host and Port columns as follows:
l
Name: The name of the File Transfer Service.
l
Host: The host name or IP address of machine on which the remote Qlik Replicate Server is
installed. The default is 0.0.0.0 (all interfaces). If the server has multiple NICs (Network Interface
Cards), you can define a different File Transfer Service for each card.
l
Port: The port through which the File Channel files are received.
l
Enabled: select the check box to enable the File Transfer Service.
3. Click Save to save your settings.
Editing a File Transfer Service
You can edit a File Transfer Service as described below.
To edit a File Transfer Service:
1. Select the File Transfer Service you want to edit.
2. Edit the values in the Name, Host and Port columns as follows:
a. Click the cell to make it editable.
b. Change the value as required and then click Save.
When you edit a File Transfer Service, make sure that any File Channel targets configured to
use the File Transfer Service are also updated accordingly. For more information on File
Channel Targets, refer to the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
Deleting a File Transfer Service
You can delete File Transfer Services that you no longer want to use.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 53

6 Managing servers
To delete a File Transfer Service:
1. In the File Transfer Services List, select the item you want to delete.
2. Click the Remove button.
External utilities
Several endpoints support running user-defined commands for pre/post-processing files. In this tab, you can
provide user credentials for user-defined commands that needs to be executed at operating system level.
By default, such commands are executed under the Replicate Server service account. This may constitute a
security risk, as it allows any Replicate user with Admin or Designer permissions to specify user-defined
commands that could lead to a full compromise of the server.
Note that when Replicate Server is installed on Linux, this tab will be hidden as the potential security risk is
relevant to Windows only.
Changes to settings will only take affect after restarting all tasks.
Endpoints that support user-defined commands are as follows:
l
Amazon S3 target
l
File source
l
File target
l
Google Cloud Storage target
l
Microsoft Azure ADLS target
IMPORTANTExecution of user-defined commands is blocked by default. To allow execution of user-
defined commands, follow the procedure described in Controlling execution of user-defined
commands (page 43).
To run user-defined commands under the Replicate service (Log On) account (the default):
l
Select Replicate service account.
To run user-defined commands under a different account:
1. Select Another account and then specify a user name and password in the designated fields.
For domain users, the user name should be entered in the following format: Domain/Username
For local users, the Domain is not required.
2. If you changed the default Attunity Replicate Server service Log On user, add the user specified in the
Attunity Replicate Server service Log On tab to the "Replace a process level token" policy in the
"Local Security Policy" settings.
Logging
The following topics describe the log management options:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 54

6 Managing servers
l
Setting Logging Levels for the Server and File Transfer Service
l
Setting Automatic Roll Over and Cleanup
l
Viewing and downloading logs (page 57)
l
Deleting server, task and FTS log files (page 57)
Setting logging levels
You set the logging level for the Replicate Server, File Transfer Service logs, Compose Server and Compose
Agent logs in Server view. The level you set determines what information is written to the logs. The Server
logs provide information about the Qlik Replicate Server instance you are working with as opposed to
individual tasks. For information on configuring the task logs, see Logging (page 192).
The following logging levels are available, ordered from the lowest level to the highest:
1. Errors
2. Warnings
3. Info
4. Trace
5. Verbose
The higher levels always include the messages from the lower levels. Therefore, if you select Error, only error
messages are written to the log. However, if you select Info, informational messages, warnings, and error
messages are included. Selecting Verbose writes all possible messages to the log.
You can set a global logging level for all components or you can set a separate logging level for each
component.
To set the logging levels:
1. To set a global logging level, move the top slider (the slider with the labels) to the log level you want.
Note that all of the sliders for the individual modules move to the same position that you set in the
main slider.
2. Make any changes to the sliders for the individual modules. This is optional. Note that if you change
the main slider, all of the individual sliders are reset to the new position. If you want to maintain a
different logging level for a specific module, you need to reset it.
3. Click Save at the bottom of the window.
Storing trace and verbose logging in memory
This option is relevant to Replicate tasks only.
When the logging level is set to "Trace" or "Verbose", you can instruct Replicate to store the logging
information in memory until an error occurs. On detecting an error, Replicate will begin writing to the physical
logs and continue to do so for a few minutes after the initial occurrence of the error.
If no error occurs before the allocated memory is used up, Replicate will empty the memory buffer and start
afresh.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 55

6 Managing servers
This option is useful for tasks that fail unpredictably and for no obvious reason. The problem with continually
writing large amounts of information to the logs is twofold:
l
Running in "Trace" or "Verbose" logging mode will quickly use up available disk space (unless the
logging settings have been configured to prevent this).
l
Continually writing large amounts of data to the logs will affect performance.
To use this option
1. Select the Store trace/verbose logging in memory, but if an error occurs, write to the logs check
box at the top of the tab.
2. In the Allocate memory up to (MB) field, specify the amount of memory you want to allocate for
storing logging information.
Setting automatic roll over and cleanup
In the Log File Management tab, you can define when to roll over the log files and when to delete old log files
from the system.
Automatic rollover
You can determine when to stop logging to the current log file and begin to log to a new log file. Rolled over
log files are appended with a 12-digit timestamp.
l
Roll over the log if the log file is older than (days): Select the check box and then specify the
maximum number of days the current log file is allowed to exist before being rolled over.
The default value is 7 days.
This option is not available for Compose servers.
l
Roll over the log if the log file is larger than (MB): Select the check box and then specify the
maximum number of megabytes the current log file is allowed to reach before being rolled over.
When the Store trace/verbose logging in memory, but if an error occurs, write to the
logs option is enabled, the actual size of the repsrv.log may reach the sum of the Allocate
memory up to (MB) size and the Roll over the log if the log file is larger than (MB) size,
before it is rolled over.
For more information on the "Store trace/verbose logging in memory" option, see Setting
logging levels (page 55)
The default value is 100 megabytes.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 56

6 Managing servers
l
If you edit this setting while tasks are running, the new setting will not affect the task log files
until the tasks are stopped and then resumed. The server log files are not affected by this
limitation.
l
The scheduled process (
LogFileCleanLogs
) that checks the log file size runs every five
minutes. Consequently, the actual size/age of the rolled over log file may deviate slightly
from the specified value(s).
l
The time of a file is determined by its "modified" time as opposed to its "created" time.
Automatic cleanup
You can determine the maximum number of days old log files (i.e. log files that have been rolled over) are
retained before being deleted.
l
Delete log files that are older than (days): Select the check box and then specify the maximum
number of days to retain a saved log file. Log files that are older than the specified number of days will
be automatically deleted from the system. For example, if you specify 4, then on the fifth day, any log
file older than 4 days will be deleted.
The default value is 45 days.
Viewing and downloading logs
You can view the server or File Transfer Service log files and download them if necessary.
File Transfer Service log files are not relevant for Compose servers.
To view or download log files:
1. In Servers view:
1. Select a server and then select Settings from the Server Management drop-down menu.
2. Select Logging on the left of the Settings for Server <server_name> window.
2. Select the Server Logging Levels or the File Transfer Service Logging Level tab as required.
3. Click the View Logs button.
The Log Viewer window opens.
4. Continue from step 2 in Viewing and downloading log files.
Deleting server, task and FTS log files
You can manually delete task, server, and File Transfer Service log files older than the specified number of
days.
Log files from Compose servers cannot be deleted.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 57

6 Managing servers
To delete the log files:
1. In Servers view:
1. Select a server and then select Settings from the Server Management drop-down menu.
2. Select Logging on the left of the Settings for Server <server_name> window.
2. Click the Delete Logs button in any of the available tabs.
The Delete Logs window opens.
3. Select which logs to delete and, for each log, optionally change the default number of days (45).
4. Click Delete.
Selected logs older than the specified number of days will be deleted.
More options
These options are not exposed in the UI as they are only relevant to specific versions or environments.
Consequently, do not set these options unless explicitly instructed to do so by Qlik Support or product
documentation.
To set an option, simply copy the option into the Add feature name field and click Add. Then set the value or
enable the option according to the instructions you received.
Server management permissions
The following table describes the required permissions for viewing and managing server settings.
Only permissions related to logging settings are relevant for Compose servers.
For information on managing user permissions, see Managing user permissions (page 286).
Permission To
Requires:
Admin
Requires:
Designer
Requires:
Operator
Requires:
Viewer
View Global Error
Handling
All Tasks All Tasks - -
Edit Global Error
Handling
All Tasks All Tasks - -
Global Error Handling setting permissions
Permission To
Requires:
Admin
Requires:
Designer
Requires:
Operator
Requires:
Viewer
View server logging levels
Server Server Server -
Edit server logging levels Server Server Server -
Server Logging Levels setting permissions
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 58
6 Managing servers
Permission To
Requires:
Admin
Requires:
Designer
Requires:
Operator
Requires:
Viewer
View/download server
logs
Server Server Server -
Delete server/FTS logs Server Server Server -
Delete task logs Server Server Server -
Permission To
Requires:
Admin
Requires:
Designer
Requires:
Operator
Requires:
Viewer
View FTS log levels Server Server Server -
Edit FTS log levels Server Server Server -
View/download FTS
logs
Server Server Server -
Delete server/FTS logs Server Server Server -
Delete task logs Server Server Server -
FTS Logging Levels setting permissions
Permission To
Requires:
Admin
Requires:
Designer
Requires:
Operator
Requires:
Viewer
View Compose Agent log levels Server Server Server -
Edit Compose Agent log levels Server Server Server -
View/download Compose Agent
logs
Server Server Server -
Compose Agent Logging setting permissions
Permission To
Requires:
Admin
Requires:
Designer
Requires:
Operator
Requires:
Viewer
View Cleanup/Rollover policy for
server/FTS/Compose Agent
Server Server Server -
View Cleanup/Rollover policy for tasks Server Server Server -
Edit Cleanup/Rollover policy for
server/FTS/Compose Agent
Server Server Server -
Edit Cleanup/Rollover policy for tasks Server Server Server -
Delete server/FTS logs Server Server Server -
Delete task logs Server Server Server -
Log File Management setting permissions
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 59

6 Managing servers
Permission To
Requires:
Admin
Requires:
Designer
Requires:
Operator
Requires:
Viewer
View Resource Control
Server Server Server -
Edit Resource Control Server Server - -
Resource Control setting permissions
Permission To Requires: Admin
Requires:
Designer
Requires:
Operator
Requires:
Viewer
View FTS list Server Server Server -
Add/Edit/Remove
FTS
Server Server - -
File Transfer Service (FTS) setting permissions
6.5 Additional server management options
In addition to adding servers, you can also perform other management tasks, as described in the following
table. Note that before performing any of the actions, you must first select the desired server or servers
(multiple selection is supported for some actions).
To Do this
Edit a server Double-click the server.
OR
Right-click the server and select
Connection Properties.
OR
Select the server and then click the
Connection Properties button on the
toolbar.
Edit the information as described in
Adding Servers (page 46).
Manage Endpoints Connections (Replicate Servers only) Click Manage Endpoints.
Edit the information as described in
Adding an Endpoint.
Server management actions
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 60

6 Managing servers
To Do this
Create a new task on the server (Replicate Servers only) Click New Task.
Edit the information as described in
Setting up Tasks.
View server log files If you need more detailed information
about a server, you can view the log files
directly from within Enterprise Manager.
See Viewing and downloading log files
(page 267).
Start monitoring or stop monitoring a server
Stopping monitoring servers may be useful when a
maintenance window, upgrade, or known outage is coming
up, or when you want to focus on a single server or a set of
servers without being disrupted by messages and tasks from
other servers.
When you stop monitoring a server, the server
appears as disabled in the Servers View, the Tasks
View does not include any tasks for the respective
server, and the Message Center does not show new
messages for the respective server.
You need the admin role to be able to start or stop
monitoring a server.
Right-click the server and select Stop
Monitoring/Start Monitoringaccordingly.
OR
Select the server and then click the Stop
Monitoring or Start Monitoring button
on the toolbar.
Delete a server
Deleting a server deletes the tasks and the
message history for the respective server.
You need the admin role to be able to delete a
server.
Right-click the server and select Delete.
OR
Select the server and then click Delete.
When prompted to confirm the deletion.
click Yes.
Register a server license See Registering a license for a monitored
server (page 62).
Edit user permissions on the server level, for all tasks on the
server, or for all endpoints (relevant to Replicate Servers only)
on the server.
Click Server Permissions. Follow the
instructions in Managing user permissions
(page 286).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 61

6 Managing servers
6.6 Registering a license for a monitored server
You can update an existing Replicate or Compose server license or register a new license directly from Qlik
Enterprise Manager.
To register a license:
1. Copy the license file to your computer or any computer in your network you have access to.
2. Select Register License from the Server Management drop-down menu or right-click the server and
select Server Management > Register License.
The Register License dialog box opens.
3. Do one of the following:
l
Click Load and browse to locate and select the license file.
l
Copy the license text and paste it into the License text field.
The license text is displayed in the dialog box as shown below. Check to be sure that the details are
correct.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 62

6 Managing servers
4. Click Register License to register the license.
A message indicating that the license was registered successfully is displayed.
6.7 Viewing server messages
You can view server messages in the Message Center. The Message Center is located at the bottom of the
console and contains messages about the servers and tasks. For more information, see Messages and
notifications (page 250).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 63

7 Defining and managing tasks
7 Defining and managing tasks
This section describes how to design a replication task. To design a replication task, you must first be sure
that you have configured at least one source endpoint and one target endpoint to work with Qlik Replicate.
The operations described in this section are relevant for Replicate tasks only.
A number of variables affect the amount of tasks that can be run on a single Replicate Server,
including the task configuration (e.g. how many tables are being replicated), the size of the source
tables and the hardware configuration of the Replicate Server machine. Bearing this in mind, the
number of tasks that can be run on a single Replicate Server should not exceed 100 (and may need
to be significantly less depending on the aforementioned variables). Best practice is to perform load
testing in a Test environment before moving to Production.
In this section:
l
Adding tasks (page 64)
l
Defining and managing endpoints (page 69)
l
Adding a source and target endpoint to a task (page 72)
l
Selecting tables and/or views for replication (page 73)
l
Editing a replication task (page 79)
l
Deleting a replication task (page 80)
l
Searching for tasks (page 80)
l
Exporting and importing tasks (page 80)
7.1 Adding tasks
Before you get started with designing the features that you need for a task, you must first define the task's
default behavior.
To add a task:
1. In Tasks view or Servers view, click New Task.
The New Task dialog box opens.
When you open this dialog box from the Servers view, the server is already selected and cannot be
changed.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 64

7 Defining and managing tasks
2. From the Server Name list, select the server for the task.
You can only select the server name when you open the dialog box from the Tasks view. When you
open the dialog box from the Servers view, it opens in context of the selected server.
3. Enter a name for the task. The name should be descriptive to indicate the purpose of the task. The
name cannot exceed 32 characters, contain non-Latin characters, or contain any of the following
characters: | \ / : * ? " < >
4. Optionally, enter a description for the task.
5. Choose one of the following replication profiles:
l
Unidirectional - Choose to replicate between endpoints for the purpose of Unidirectional.
l
Bidirectional - Choose to synchronize records between two endpoints.
For more information, see the instructions on setting up Bidirectional replication (page 66).
l
Log Stream Staging - Log Stream Staging enables a dedicated Replicate task to save data
changes from the transaction log of a single source database and apply them to multiple
targets, without the overhead of reading the logs for each target separately.
For information about Log Stream Staging, refer to the Qlik Replicate online help.
6. Select task options:
l
Full Load: Click to enable or disable Full Load options for this task.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 65

7 Defining and managing tasks
When full load is enabled, Enterprise Manager loads the initial source data to the target
endpoint. By default, a full load is carried out for this task. If you want to change this setting
after you begin working with this task, you make the change in the Task Settings, Full Load
(page 171) tab.
l
Apply Changes: Click to enable or disable Apply Changes (Change Processing).
When this option is enabled, Enterprise Manager keeps the target tables continually up-to-date
with any changes made to the source tables. By default, change processing is carried out for
this task. You can view the change processing in the Monitor view.
For more information, see Monitoring Change Processing replication (page 215). If you want to
change this setting after you begin working with this task, you make the change in the Task
Settings, Change Processing (page 174) tab.
When the Bidirectional replication profile is selected, the Apply Changes option
cannot be disabled.
l
Store Changes: Click this button to enable or disable Store Changes.
If this option is enabled, changes are stored in change tables or in an audit table. By default,
changes are not stored.
For information about storing and applying changes, see the Qlik Replicate online help.
When the Bidirectional replication profile is selected, the Store Changes button will
be unavailable.
7. Click OK to close the New Task dialog box and save your settings.
Bidirectional replication
Bidirectional replication enables organizations to synchronize data between two endpoints (henceforth
referred to as Endpoint A and Endpoint B), ensuring that both endpoints contain identical records. The
endpoints can either be the same type (e.g. Oracle-to-Oracle) or different types (e.g. Microsoft SQL Server-to-
Oracle). To implement bidirectional replication, two Bidirectional Replication tasks need to be defined: one
that captures changes made to Endpoint A and replicates them to Endpoint B (Task 1) and another that
captures changes made to Endpoint B and replicates them to Endpoint A (Task 2). An explanation of how to
set up these tasks is provided in the following sections.
Limitations
The following limitations apply to bidirectional replication tasks:
l
Bidirectional replication does not currently support conflict resolution. To prevent conflicts,
organizations should ensure that the application that updates the endpoints participating in a
bidirectional replication task, does not simultaneously update the same record in both endpoints.
In other words, if a record in Endpoint A was updated, the equivalent record in Endpoint B should only
be updated after the update from Endpoint A is replicated to Endpoint B.
l
Bidirectional replication tasks currently only support DDL statements from one of the sources involved
in the task only. This means that for one of the sources, you must set the Apply Changes DDL Handling
Policy to "Ignore" for all of the options (DROP, TRUNCATE, and ALTER).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 66

7 Defining and managing tasks
The
CREATE TABLE
DDL is not supported.
l
To ensure that the source and target endpoints are identical, transformations and filters should not be
used in bidirectional replication tasks.
l
The Use direct path full load option in the Oracle target endpoint settings is not supported.
l
The Stopping the Task after Full Load options in the task settings' Full Load Settings tab is not
supported.
l
The task's Change Processing Mode must be set to Transactional apply.
Supported endpoints
Bidirectional tasks support the following endpoints:
Source Endpoints:
l
Amazon RDS for MySQL
l
Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL
l
Amazon RDS for SQL Server
l
AWS Aurora Cloud for PostgreSQL
l
File Channel
l
Google Cloud SQL for MySQL
l
Google Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL
l
IBM DB2 for iSeries
l
IBM DB2 for LUW
l
IBMDB2 for z/OS
l
Microsoft Azure SQL (MS-CDC)
l
Microsoft SQL Server
l
Microsoft SQL Server (MS-CDC)
l
MySQL
l
Oracle
l
PostgreSQL
l
SAP Sybase ASE
Target Endpoints:
l
File Channel
l
Google Cloud SQL for MySQL
l
Google Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL
l
IBMDB2 for z/OS
l
Microsoft SQL Server
l
Microsoft Azure SQL Database
l
MySQL
l
ODBC
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 67
7 Defining and managing tasks
l
Oracle
l
PostgreSQL
l
SAP Sybase ASE
Setting up Bidirectional replication
This section describes how to set up a Bidirectional replication task in Enterprise Manager.
To set up Bidirectional Task 1:
1. Define a Bidirectional Replication task that replicates data from Endpoint A to Endpoint B.
In a bidirectional replication task, Full Load replication is not enabled by default since it is
assumed that both endpoints contain identical tables. If this is not the case (for instance, if
Endpoint A contains tables that do not exist in Endpoint B), enable Full Load replication as
well.
2. Specify a source and target Loopback prevention table schema in the task settings’ Loopback
Prevention tab. For more information about loopback prevention settings, see Bidirectional (page
170).
3. Run the task.
To set up Bidirectional Task 2:
1. Define another Bidirectional Replication task that replicates data from Endpoint B to Endpoint A.
2. Specify a source and target Loopback prevention table schema in the task settings’ Loopback
Prevention tab. For more information about loopback prevention settings, see Bidirectional (page
170).
3. If Full Load was enabled when replicating data from Endpoint A to Endpoint B, you must first wait for
the Full Load replication to complete before running the task. Otherwise, run the task immediately.
Using bidirectional replication with the File Channel endpoint
You can use bidirectional replication together with the File Channel endpoint. This is useful if you need to
synchronize two endpoints that are either not able to communicate with each other (i.e. are not physically
connected) or are located in the WAN. The process involves setting up six separate tasks: Two Full Load-only
Unidirectional tasks and four Apply Changes-only Bidirectional tasks.
For information on setting up the File Channel endpoint, see the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
To set up bidirectional replication with File Channel Endpoints:
1. Set up and run two Full Load only Unidirectional tasks.
Example (FC = File Channel):
Task 1: MySQL --> FC Target Task 2: FC Source --> Oracle
2. Wait for the Full Load-only tasks to finish.
3. Set up and run four Apply Changes-only Bidirectional tasks.
Example (FC = File Channel):
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 68

7 Defining and managing tasks
Task 1: MySQL Source --> FC Target Task 2: FC Source 1 --> Oracle Target
Task 3: Oracle Source --> FC Target 2 Task 4: FC Source 2 --> MySQL Target
7.2 Editing and viewing a task description
You can provide a description for specific tasks and then easily view or edit that description as required.
To provide or edit a task description:
1. Open the desired task.
2.
In Designer or Monitor view, click the toolbar button on the left.
3. Enter a description.
4. Click OK.
To view a task's description:
1. Open the desired task.
2.
In Designer or Monitor view, hover your mouse over the toolbar button on the left.
A tooltip will display the description.
7.3 Defining and managing endpoints
Enterprise Manager requires information to connect to the source and target endpoints that you want to use
in a task. For a list of endpoints you can work with in Qlik Replicate, see the Qlik Replicate Setup and User
Guide.
You use the Manage Endpoint Connections window to add endpoints and edit and view the endpoint
connection information.
The name cannot exceed 32 characters, contain non-Latin characters, or contain any of the following
characters: | \ / : * ? " < >
l
Defining an endpoint (page 70)
l
Editing endpoint configuration information (page 70)
l
Viewing endpoint configuration information (page 71)
l
Testing an endpoint connection (page 71)
l
Duplicating endpoints (page 71)
l
Searching for endpoints (page 71)
l
Deleting endpoints (page 72)
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 69

7 Defining and managing tasks
Defining an endpoint
Before you can begin to design a task, you must add endpoints to the Replicate server. To use an endpoint,
you must have access to it somewhere in your system. When you add the endpoint to the Replicate server,
you must provide connection information and proper user credentials.
Once you add endpoints to the Replicate server, you can begin to use them to build a replication task. For
information on how to add an endpoint to a replication task, see Adding a source and target endpoint to a task
(page 72).
To add an endpoint:
1. In the Servers view or on a dedicated task tab, click Manage Endpoint Connections.
The Manage Endpoint Connections window opens. The server is already selected and cannot be
changed.
2. In the Manage Endpoint Connections window, click New Endpoint.
3. Select the type of endpoint you are using. The information that you must enter depends on which
endpoint you select.
For a list of supported endpoints and for more information on setting up a specific endpoint, see the
Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
Editing endpoint configuration information
After you add the endpoint to the Replicate server and provide the connection information, you can make
changes to some of the information.
You cannot change the following information in the endpoint window:
l
The name you provided for the endpoint.
l
The endpoint Type, for example Oracle or Microsoft SQL Server.
l
The endpoint role, either SOURCE or TARGET.
To edit endpoint configuration information:
1. In the Manage Endpoint Connections window, select the endpoint you want to edit.
OR
In the Endpoints list on the left of the Designer view, double-click the endpoint you want to edit. Note
that this option is only available when editing a specific task.
The Manage Endpoint Connections window opens with the selected endpoint settings.
2. Make changes to the information in any of the tabs in the window.
For more information, see the chapter for the specific Qlik Replicate endpoint you are using in the Qlik
Replicate Setup and User Guide. For a list of supported endpoints, see the Qlik Replicate Setup and
User Guide.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 70

7 Defining and managing tasks
Viewing endpoint configuration information
After you add the endpoint to the Replicate server and provide the connection information, you can view the
information in the Manage Endpoint Connections window.
To view endpoint configuration information:
l
Select an endpoint from the Endpoints list in the left pane; then click the tabs to view the information.
Testing an endpoint connection
You can try to contact the endpoint to make sure that you are connected to the endpoint you want to work
with.
To test the endpoint connection:
1. In the Manage Endpoint Connections window, select the endpoint you want to work with.
2. At the bottom of the endpoint’s General tab, click Test Connection.
If the connection is successful, a success message is displayed and a green check mark icon appears
next to the Test Connection button.
If the connection fails, an error message is displayed at the bottom of the dialog box and the View Log
button becomes available.
3. If the connection is successful, click Close.
If the connection fails, click View Log to view the server log entry with information for the connection
failure.
Duplicating endpoints
You can duplicate an endpoint if you need to define a new endpoint with similar settings. Except for the name,
all endpoint settings are duplicated to the new endpoint.
To duplicate an endpoint:
1. In the left panel of the Manage Endpoint Connections window, click the endpoint you want to
duplicate.
2. Click Duplicate.
3. On the General tab, edit the name for the endpoint.
4. Make any other necessary changes.
5. Click Save; then click Close.
Searching for endpoints
You can search for endpoints by typing a sequence of letters in the Filter by box above the endpoints list. For
example, to search for all endpoints whose names contain the string "Oracle", type "or". Only endpoints that
match the search string are displayed.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 71

7 Defining and managing tasks
Deleting endpoints
You can delete endpoints that you no longer require. Note that to delete an endpoint that is defined as a
source or target in a task, you first need to remove the endpoint from the task.
To delete an endpoint:
l
In the left panel of the Manage Endpoint Connections window, Select the endpoint and click Delete.
7.4 Adding a source and target endpoint to a task
Once you have added the endpoints, you can design the replication task. The first step in this process is to
define the source endpoint where your data is currently stored and the target endpoints where you want to
replicate the data. To do this, you just drag one of the endpoints you added into the task map (in Designer
mode).
Once you select the endpoint for your task, you must select the tables from the source endpoint to be
replicated. The next step in creating a replication task is Selecting tables and/or views for replication (page 73).
To add source and target endpoints to a task:
1. Do one of the following:
l
Create a new task. When you click OKin the Create New Task dialog box, the task opens on a
dedicated tab. For more information, see Adding tasks (page 64).
l
In the Tasks view, select the task to which you want to add endpoints and click View Task. The
task opens on a dedicated tab.
2. On the dedicated tab for the task, click Designer to switch to Designer mode.
The Task map is displayed, with the available endpoints listed in the pane on the left, as shown in the
following figure.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 72

7 Defining and managing tasks
3. Drag a source endpoint to the top circle in the task map (that contains the text Drop source endpoint
here). If dragging is not possible, make sure that the endpoint you are using is defined as a source
endpoint.
4. Drag a target endpoint to the bottom circle in the task map (that contains the text Drop target
endpoint here). If dragging is not possible, make sure that the endpoint you are using is defined as a
target endpoint.
5. Click Save.
7.5 Selecting tables and/or views for replication
This procedure describes how to select the source tables or views that you want to replicate. Note that tables
can be selected from any supported endpoint, but views can only be selected from the following endpoints:
l
Teradata
l
Amazon Redshift
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 73

7 Defining and managing tasks
l
PostgreSQL
l
MySQL
l
SAP Sybase ASE
l
IBM DB2 for LUW
l
IBM DB2 for z/OS
l
Oracle
l
Microsoft SQL Server
l
ODBC with CDC
l
ODBC
l
Replication of views is supported in Full Load Only tasks only, except when replicating from
the following sources:
l
Amazon Redshift
l
Teradata
l
ODBC with CDC
l
Views are replicated to the target endpoint as tables
l
When replicating views, the corresponding tables are created without a primary key. This
presents an issue for Apply Changes tasks, which require the target tables to have a primary
key. Therefore, if you are also running Apply Changes tasks (using one of the CDC-capable
endpoints mentioned above), you need to define one or more primary keys for each of the
target tables using a transformation. For an explanation of how to accomplish this, see Using
the Transform tab (page 86) in Defining transformations for a single table/view (page 84).
When working with ODBC with CDC and Teradata source endpoints, any views and tables that you
want to replicate must have the same context field(s). If you only want to replicate views, then all of
the views must have the same context field(s).
For information on setting up context fields, see "Configuring Change Processing Settings" in the Qlik
Replicate Setup and User Guide.
Once you have selected tables/views to replicate, you can run the replication task. However, if you need to
make any changes to the structure of the tables in the target endpoint or only select specific columns, you will
need to carry out one or both of the following procedures:
To select tables/views:
1. Open the task you are working with if it is not already displayed in a dedicated tab.
For information on opening a task, see Editing a replication task (page 79).
2. In Designer mode, on the right side, click Table Selection.
If the source endpoint does not support view selection, the Select Tables dialog box opens. If the
source endpoint supports view selection, the Select Tables/Views dialog box opens.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 74

7 Defining and managing tasks
See the following for information on how to work with the Select Tables/Select Tables/Views dialog
box:
l
Searching for tables/views to use in a replication task (page 75)
l
Selecting specific tables/views for replication (page 76)
l
Creating table/view selection patterns (page 78)
l
Setting load order (page 77)
Searching for tables/views to use in a replication task
This topic walks you through searching for specific tables/views in preparation for including them in a
replication task. You first search for tables that match specific criteria. Then you select the required
tables/views from the search results to include them in the task. You can also carry out another search with
new criteria and then add additional tables/views to the replication task.
After you finish searching, you can select tables/views for replication. Continue with Selecting specific
tables/views for replication (page 76).
To search for tables/views to use in a replication task:
1. In Designer mode, click Table Selection.
2. In the Select Tables dialog box, if the source endpoint supports view selection, select one of the
following:
l
All to search for tables and views
l
Tables to search for tables only
l
Views to search for views only
Otherwise, skip to the next step.
3. From the Schema drop-down list, select a table/view schema.
When working with Microsoft SQL Server, quote characters in schema names - such as "\" or "
[" - must be doubled in order to show the list of tables in the specified schema. For example,
My\Schema should be specified as My\\Schema.
When selecting tables from the SAP Application or SAP Application (DB) endpoint, "Business
Groups" will appear instead of "Schema".
4. Optionally, in the Table/View field, type the name or partial name of a table/view you wish to
replicate. If you do not do this, Replicate will search for all of the tables/views in the selected schema.
You can also include special characters in your search string. For more information, see the
Note in Creating a record selection condition for one or more columns (page 94).
5. Click Search to display a list of tables/views.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 75

7 Defining and managing tasks
When selecting tables from the SAP Application or SAP Application (DB) endpoint, the Table
List will display all of the tables in the selected Business Group. Hovering your mouse cursor
over a table will display a tooltip as shown below.
The Table List field displays any table/view that matches the specified search criteria.
If the source endpoint supports view selection, an additional Type column indicates whether the
database object is a table or a view.
6. Click OK.
See also: Creating table/view selection patterns (page 78).
Selecting specific tables/views for replication
This topic walks you through selecting specific tables/views to replicate.
When you select specific tables/views, all selected tables/views are replicated in full unless you define
transformations or filters for the table/view. If you need to make changes to the table/view structures in the
target endpoint or if you only want to select specific columns, then you need to perform the procedures
described in Defining transformations for a single table/view (page 84) and Using filters (page 92) respectively.
To select specific tables/views:
1. Open the Select Tables/Views dialog box.
2. Select a Schema.
3. Optionally, select the Use exact table name check box. This option is useful if your schema contains
numerous tables as it will save you having to scroll through the entire list to find one specific table.
4. If you selected the Use exact table name check box, type the exact name of the table you want to
replicate in the Table/View field.
5. Click Search.
The table or tables (If you did not select the Use exact table name check box) will be shown in the
search results.
6. Select the table by adding it to the list on the right.
7. To add additional tables from the same schema, repeat steps 3-6. To add additional tables from a
different schema, repeat steps 2-6.
8. Click OK to save your settings.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 76

7 Defining and managing tasks
If you rename a table in the database, the Designer tab will still show the original table name. The
Monitor tab, on the other hand, will show the new table name.
Setting load order
You can set the load order for each of the selected tables. This may be useful, for example, if your selected
tables list contains tables of different sizes and you want the smaller tables to be loaded before the larger
tables. When a group of tables are set with the same load order, Replicate will load the tables according to the
table ID.
Load order can be set and modified (see note below) in the following places:
l
The Select Tables window (opened in Designer view by clicking the Table Selection button in the
right of the console).
l
The Patterns and Selected Tables list in the right of the console (in Designer view).
l
Load order cannot be changed while the task is running. If you want to change the load
order, first stop the task, then change the load order as desired, and finally reload the target.
l
Load order cannot be set for "Exclude" patterns.
To set the load order for a specific table:
1. Select the desired table in the Selected Tables list.
2. From the Load Order drop-down list, select one of the available priority levels (Lowest Priority, Low
Priority, Normal Priority, High Priority, and Highest Priority).
3. This step is only relevant if you are setting load order in the Select Tables window. Click OK to save
your settings and close the Select Tables window.
To set the same load order for multiple tables:
1. Select the desired tables in the Selected Tables list.
2. From any of the selected items' Load Order drop-down list, select one of the available priority levels.
3. This step is only relevant if you are setting load order in the Select Tables window. Click OK to save
your settings and close the Select Tables window.
Removing specific tables/views from a replication task
This topic walks you through removing specific tables/views from the replication task.
To remove tables from the Selected Tables list:
1. From the Selected Tables list, select a table that you want to remove from the replication task and
then click the button with a single left-facing arrowhead (Remove).
2. To remove all of the tables/views from the Selected Tables or Selected Tables/Views list, click the
button with two left-facing arrowheads (Remove All).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 77

7 Defining and managing tasks
3. Click OK to close the Select Tables or Select Tables/Views dialog box.
4. Click Save to make sure that Enterprise Manager saves the table information for this task.
Creating table/view selection patterns
This topic walks you through selecting tables/views using patterns. For example, you can include all
tables/views that belong to the HR schema except for one or two tables/views that you exclude. You can also
only exclude one or more table/view schemas or tables/views. This replicates the entire endpoint, except for
those tables/views that you excluded.
The following example shows a pattern that replicates all tables that are members of the dbo schema except
for the dbo.PRODUCT_1% table.
Include dbo.%
Exclude dbo.PRODUCT_1%
You can also use the "_" wildcard character to match a single character. For example, specifying Exclude m_
d% will exclude all tables that begin with m and end with d%, such as model or msdb.
Do not escape wildcard characters as this will instruct Replicate to interpret them as standard
characters. As escape character conventions differ across databases, you should consult your
database Help for guidance about supported escape characters. Some examples (where an
underscore is the wildcard character) are as follows:
l
MySQL and PostgreSQL - \\_
l
Microsoft SQL Server - [_]
l
Oracle - For Oracle, use the escapeCharacter internal parameter to define a custom
escape character.
When you explicitly select tables/views, all selected tables/views are replicated in full unless you define
transformations or filters for the table/view. If you need to make changes to the table/view structures in the
target endpoint or if you only want to select specific columns, then you need to perform the procedures
described in Defining transformations for a single table/view (page 84) and Using filters (page 92) respectively.
To view all of the tables/views included when you use a table selection pattern, click the Full Table
List tab in Designer view. The Full Table List lists all of the tables/views included in any table
pattern you defined as well as all explicitly selected tables/views. To view only patterns and
explicitly selected tables/views, click the Patterns and Selected Tables tab in Designer view.
To create table/view selection patterns:
1. In the Designer view, in the Select Tables/Views dialog box, do any of the following:
l
Select a schema from the Schema drop-down list. All tables/views that belong to that schema
are included in the table/view selection pattern.
l
Type the name or partial name of a table/view in the Table/View field. Any string that you enter
here is included in the table/view selection pattern.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 78

7 Defining and managing tasks
l
If the table/view that you type here is a member of the schema you selected in the Schema
drop-down list, then you only have to type the name of the table/view.
l
If you did not select a schema or the table/view belongs to another schema, include the schema
with the table name in the following format: HR.Employees, where HR is the schema.
2. Click Include to include all of the tables/views that match the selection criteria.
3. Click Exclude to exclude any tables that match the selection criteria.
4. Click OK to close the Select Tables/Views dialog box.
5. Click Save to make sure that Enterprise Manager saves the table/view information for this task.
Excluding specific tables from the replication task
You can easily exclude specific tables from being replicated.
To do this:
1. Open the the Select Tables/Views dialog box.
2. Select a Schema and then click Search.
Any tables in that schema will be shown in the search results.
3. Select the tables by adding them to the list on the right.
4. Click the Include button.
Include <schema_name>.% will be added to the Table Selection Patterns list.
5. Select the Use exact table name check box.
6. Type the name of the table you want to exclude in the Table/View field.
7. Click the Exclude button.
Exclude <schema_name>.<table_name> will be added to the Table Selection Patterns list.
8. To exclude additional tables from the same schema, repeat Steps 6-7. To exclude tables from a
different schema, clear the Use exact table name check box and then repeat Steps 2-7.
9. Click OK to save your settings.
Filters containing wildcard escape characters that excluded/included tables during Full Load will not
exclude/include matching tables added during CDC. For example, if there is an exclude pattern
dbo.pc[_]% and a new table dbo.pc_table2 is created during CDC, the table will be added to
replication task (as opposed to being excluded).
7.6 Editing a replication task
You can make changes to tasks that you previously created. Just open the task and make the changes in the
same way that you did when you created the task.
To edit a task:
1. In Tasks view, select the task and click Open.
The task opens, displaying the source and target endpoints and which tables have been selected for
replication.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 79

7 Defining and managing tasks
2. Continue with any of the following procedures:
l
Adding a source and target endpoint to a task (page 72)
l
Selecting tables and/or views for replication (page 73)
l
Defining transformations for a single table/view (page 84)
l
Using filters (page 92)
l
Task Settings (page 165)
7.7 Searching for tasks
In Tasks view, you can search for tasks by typing a sequence of letters in theSearch Tasks box above the
tasks. For example, to search for all tasks with names that begin with "Oracle-to", type "or". Only tasks that
match the search string are displayed.
7.8 Deleting a replication task
You can delete tasks that you created. To prevent complications, it is recommended not to use the name of a
deleted task for a new task you create. Such a task would be created with the same settings as the deleted
task.
If you use a Microsoft SQL Server endpoint, a Microsoft SQL Server system administrator must delete
the Microsoft SQL Server Replication Publisher definitions for the endpoint that was used in the task
from SQL Server.
For more information, see the "Limitations" section in the Microsoft SQL Server chapter in the Qlik
Replicate Setup and User Guide.
To delete a task:
1. Stop the task that you want to delete.
2. In Tasks view, click Delete Task.
The task is deleted.
7.9 Exporting and importing tasks
This functionality is supported with Replicate tasks only.
The ability to export tasks is useful if you need to migrate tasks between different Enterprise Manager
machines, which may be necessary if you need to decomission a machine or when moving from a test
machine to a production machine, for example. Tasks can be exported with or without endpoints.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 80

7 Defining and managing tasks
Export Task When
With
Endpoints
l
The task's endpoints do not exist in the target environment. This way, the task will
be created with endpoints when it is imported.
l
The endpoints already exist in the target environment but with a different
configuration that you would like to override.
In both of the above cases, after importing the task, you need to edit the
endpoints and re-enter the passwords. This will encrypt the passwords
using the Master User Key of the target machine.
Without
Endpoints
The task's endpoints already exist in the target environment with a suitable configuration.
Task export use cases
For information on what permissions are required to export and import tasks, see Roles and permissions (page
284).
To export a task:
1. In Tasks view, do one of the following:
l
Select or open the task you want to export and then click the Export Task toolbar button.
l
Right-click the task you want to export and select Export Task from the context menu.
2. Select Without Endpoints or With Endpoints accordingly.
Depending on your browser settings, the task JSON file will either be downloaded to your default
Downloads folder or you will be prompted to save it to you preferred location.
The file name format is as follows:
AEM_<ReplicateServerName>_<TaskName>_<Date>_<Time>.json
To import a task:
1. If the task is running on the target server, stop the task.
2. In Servers view, do one of the following:
l
Select the target server (i.e. the server to which you want the task to be imported).
l
Right-click the target server and select Import Task from the context menu.
The Import Task window opens.
3. Either select the task JSON file using the Browse button or drag the file to the window.
4. Click Import.
5. Optionally, when the import completes, start the task.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 81

8 Customizing tasks
8 Customizing tasks
This section describes how to customize a replication task. For example, you can create new tables or
columns for the target endpoint or select only some of the data from each column to be replicated. This is
done using transformations and filters.
Although the descriptions in this section only refer to tables, the procedures described herein are
applicable to views as well. When a transformation is defined for a view, the word "View(s)" appears
in the UI instead of the word "Table(s)".
In this section:
l
Table Settings (page 82)
l
Defining global rules (page 107)
l
Using the Expression Builder (page 137)
l
Task Settings (page 165)
8.1 Table Settings
In the <Table_Name> - Table Settings window, you can define how the data for each individual table/view is
replicated to the target.
Some of the table settings are not available in a Log Stream Staging setup.
For information on the availability of table settings in a Log Stream Staging setup, refer to the Qlik
Replicate Setup and User Guide.
To open the Table Settings window:
1. Open the task you are working with.
For information on opening a task, see Editing a replication task (page 79).
2. In Designer view, select the desired table from one of the following tabs on the right of the console:
l
The Patterns and Selected Tables tab - if the desired table was explicitly selected.
l
The Full Table List tab - if the desired table was selected using a table inclusion pattern.
For information on how to define table selection patterns, see Creating table/view selection
patterns (page 78).
3. Click the Table Settings button above the table list.
The <Table_Name> - Table Settings window opens.
4. In the Table Settings window, perform any of the following tasks:
l
Performing General tasks for a single table/view (page 83)
l
Defining transformations for a single table/view (page 84)
l
Using filters (page 92)
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 82

8 Customizing tasks
l
Parallel Load (page 98)
l
Handling LOB columns (page 103)
l
Message format (page 106)
l
Full Load (page 106)
5. Click OK to close the Table Settings window.
6. Click Save in the main toolbar to preserve the table and column information for this task.
To restore the default table values:
l
Click Restore Table Defaults at the bottom left of the Table Settings window. This option is available
in all tabs.
Any changes you made will be discarded and the table's default settings will be restored.
The names of modified tables will be followed by the word (changed), enabling you to easily identify
which tables have been modified.
Performing General tasks for a single table/view
Although the descriptions in this section only refer to tables, the procedures describe herein are
applicable to views as well. When a task is being performed for a view, the word "View(s)" will
appear in the UI instead of the word "Table(s)"
The General tab in the Table Settings window displays basic information about the selected table and allows
you to define new names for the table/schema on the target as well as override the default tablespace for the
table and its index (Oracle target only).
To edit the general table settings:
1. Open the Table Settings (page 82) window.
2. Click the General tab on the left side of the window, as shown below.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 83

8 Customizing tasks
In the Map to target table section, the following options are available:
l
Table Schema: Specify the schema in which you want the table to be created on the target.
l
Table Name: Specify a new name for the table on the target.
l
Table tablespace: This option is only available when the task is defined with an Oracle target
endpoint.
Specify the name of the tablespace in which you want the table to be created on the target. By
default (i.e. when this field is empty), the table will either be created in the source table
tablespace on the target (when replicating from an Oracle source) or in the default tablespace
(when replicating from any other source).
l
Index tablespace: This option is only available when the task is defined with an Oracle target
endpoint.
Specify the name of the tablespace in which you want the table's index to be created on the
target. By default (i.e. when this field is empty), the index will either be created in the source
table tablespace on the target (when replicating from an Oracle source) or in the default
tablespace (when replicating from any other source).
Defining transformations for a single table/view
Although the descriptions in this section only refer to tables, the procedures describe herein are
applicable to views as well. When a transformation is defined for a view, the word "View(s)" will
appear in the UI instead of the word "Table(s)".
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 84

8 Customizing tasks
This section describes how to define data transformations. Data transformations are performed when the task
is run. They are optional. If you do not define any transformations, the data is replicated "as is" from the
source to the target.
Enterprise Manager lets you make the following changes to the tables and columns:
l
Rename any column for the target table
l
Delete a target column
l
Change the data type and/or the length of any target column
l
Add additional target columns
l
Designate which target columns (i.e. segments) will comprise the Unique Index
l
Recalculate the data
Limitations
Transformations are subject to the following limitations:
l
Calculating columns of right-to-left languages is not supported.
l
Transformations cannot be performed on columns that contain special characters (e.g. #, \, /, -) in their
name.
l
Transformations cannot be performed on columns that have a pound character (#) in their name.
l
The only supported transformation for LOB/CLOB data types is to drop the column on the target.
l
Using a transformation to rename a column and then add a new column with the same name is not
supported.
You can use the method described here for transformations that are specific to a single table or a few tables in
your task. To make a similar change over multiple tables, see Starting the Global Transformation Rules wizard
(page 107).
For an explanation of how to configure transformations, see Using the Transform tab (page 86).
To define a data transformation for a single table:
1. Select the table you want to transform and open the Table Settings (page 82) window.
2. Click Transform on the left side of the window.
The following figure shows the information in the Transform tab of the Table Settings window.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 85

8 Customizing tasks
Using the Transform tab
In the Transform tab, you can define transformations using Replicate's built-in functionality.
Customers that requires functionality not provided by Replicate's built-in transformations can write
their own transformations, and then access them from the Replicate Expression Builder. For an
explanation of how to create user-defined transformations (requires basic programming skills), see
User-defined transformations (page 163).
The Transform tab in the Table Settings window consists of the following elements:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 86
8 Customizing tasks
l
Input: This lists the columns on which you can perform transformations.
When creating a transformation for the SAP Application source endpoint, you can hover your
mouse cursor over an Input column to see a tooltip with the table’s actual name:
l
Output: This table shows the defined output for the columns in the table where you are performing
the transformation(s). See Transformation Options below for information on how to change the default
output.
Limitations and considerations
l
Dropping a column, saving your changes, and then adding a column with the same name and defining
an expression corresponding to the dropped column's data, is not supported. If you mistakenly drop a
column, simply add the column back again without an expression.
l
If you stop a task and define a metadata transformation for one of the tables (such as dropping a
column), make sure the DROP and CREATE table option is selected (the default) in the Task Settings'
Full Load Settings tab before resuming the task.
l
In homogeneous replication tasks (such as Oracle to Oracle), modifying a single table column (by
changing the column data type or length for example), will break the homogeneity for the entire table.
Transformation options
The following table describes the transformation options available in the Transform tab.
To Do This
Rename a column Select the Name column for the table column you want to change. Type in a
new name.
The top right corner turns blue when the name is changed. To view the original
name, hover the mouse pointer over the field and the original name is
displayed.
Set a column as a
primary key/unique key
or disable a column's
primary key/unique key
1. Select the desired row in the Output table and then click the cell in the
Key column.
A key icon will be displayed.
2. Repeat to set primary keys/unique keys for additional columns.
3. To disable the primary key/unique key, click the key icon.
Transform actions
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 87

8 Customizing tasks
To Do This
Change the data type
for a column
Select the Type column for the table column you want to change and select a
new data type from the drop-down list. Make sure that the data type you select
is compatible with the data in that column.
For a description of Qlik Replicate data types, information about data-type
mapping from the native endpoint to Qlik Replicate, and for a list of endpoints
supported by Qlik Replicate, see the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
Change the data
subtype for a column
This option is available for the CLOB, NCLOB, STRING, and WSTRING data
types only.
Select the Subtype column for the table column whose data type you want to
change, and then select either JSON or XML from the drop-down list. Make sure
that the data in the column is compatible with the selected subtype. The
default is Regular, which means that data type in the Type column will be used
with no subtype.
For a description of Qlik Replicate data types, information about data-type
mapping from the source endpoint to Qlik Replicate, and for a list of endpoints
supported by Qlik Replicate, see the Qlik Replicate online help.
Add a new column Click Add Column to add a new column. When you add a column, the Name is
blank and the Type is listed as string(50).
Type a name for the new column in the Name column. If needed (according to
the column data), click in the Type column and select a data type from the list.
Add an existing column From the Input pane, select one or more columns and click the right facing
arrow button.
To add all of the columns, click the right-facing double arrow.
l
By default all tables columns are included in the Output list.
To include only some of the columns clear the By default
include all columns check box at the top of the Transform
tab. This removes all of the columns from the list. You can
then add back any existing column as required.
l
If a column is explicitly added at the table level but then
dropped at the global level (using a global transformation
rule), the column will still be created on the target, but
without any data.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 88
8 Customizing tasks
To Do This
Delete a column From the Output list, select the row with the column you want to delete and
click the left-facing arrow button.
To remove all columns, click the left-facing double arrow. Note that all the
columns except for columns defined as a primary key/unique index are deleted.
Add/Remove a Unique
Index segment to/from
a target column
A key icon indicates which target columns segments of the Unique Index.
To add a Unique Index segment, click in the Key column to the left of target
column to which you want to add the segment. A key icon will appear.
To remove a Unique Index segment, click the key icon to the left of the target
column from which you want to remove the segment. The key icon will
disappear.
Recalculate the data for
a column in the target
endpoint
Click in the Expression column in the row with the table column you want to
change the data for. Enter an expression using SQLite syntax.
See Creating an expression for transformations (page 91) and Using SQLite syntax
with transformations (page 91) for information on creating expressions.
Once you add a calculated expression, you can test the expression. See Using
the Expression Builder (page 137).
Change the data type
for a specific input
column
Supported
with the IBM
DB2 for
iSeries and
IBM DB2 for
z/OS source
endpoints
only.
This is required if a source column is defined as character type but the data
stored in that column is binary or vice versa.
When the source column type is STRING, WSTRING, CLOB, or NCLOB,
you must also select a Character Set, otherwise an error will be
shown and the OK button will be disabled.
In the Input table, click the relevant cell in the Type column and then select
either STRING or BYTES from the drop-down list as required.
If you change a column's Type in the Input table, you also need to
set the same Type for the corresponding column in the Output table.
Note that if you select STRING, you can also change the character set, as
explained below.
Modified cells will display a triangle in the top right corner. To see the
original value, click the triangle.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 89

8 Customizing tasks
To Do This
Change the Character
Set for a specific input
column
Supported
with the IBM
DB2 for
iSeries and
IBM DB2 for
z/OS source
endpoints
only.
This is required if a source character column is wrongly encoded. For example,
if a source character column is described as encoded in CCSID X, but the data
stored in that column is actually encoded in CCSID Y.
You can also set a custom character set as described in Setting a custom
character set (page 90) below.
In the Input table:
1. Click the relevant cell in the Type column and select STRING from the
drop-down list.
2. Click the relevant cell in the Character Set column and then select the
appropriate character set from the drop-down list.
l
Only character sets compatible with the selected Type
will be available for selection.
l
Modified cells will display a triangle in the top right
corner. To see the original value, click the triangle.
Setting a custom character set
The following procedure is supported with the IBM DB2 for iSeries and IBM DB2 for z/OS source endpoints
only.
Perform the steps below if the source table is defined with an incorrect CCSID and the correct definition is
actually in a UCM file.
1. Create a mapping data file with the file extension .ucm.
If you edit an existing UCM file, you must also change the values of the
<code_set_name>
and
<icu:alias>
properties. If the file does not contain an
<icu:alias>
property, then you only
need to change the value of the
<code_set_name>
property.
2. Create a CNV file for the UCM file by running the following command:
<product_dir>\bin\makeconv.exe -v <file_name>.ucm
Example:
"c:\Program Files\Attunity\Replicate\bin\makeconv.exe" -v 1047_EX.ucm
This will create a CNV file with the same name as the UCM file (for example, 1047_EX.cnv).
3. Create a new subfolder named icudt<XX>l under <product_dir>\bin where the XX is the same as the
number in the icudt<XX>.dll file name.
For example, If the DLL file name is icudt69.dll, create a new subfolder named icudt69l.
4. Copy the CNV file to the subfolder you just created (<product_dir>\bin\icudt69l in the example above).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 90

8 Customizing tasks
When using the Replicate File Channel, the file should be copied to the same location on both
Replicate servers.
5. Restart the Qlik Replicate UI Server service.
5. Select the custom character set from the Character Set drop-down list; it will appear as the CNV file
name followed by the word "Custom" e.g. 1047_EX.cnv (Custom).
Using a column's before-image data in a transformation
You can use a column's before-image data in a transformation. This is useful if you need to store the before-
image data on the target.
To do this, simply specify the source column name in Output table's Expression column, in the following
format:
$BI__MyColumn
Where $BI__ is a mandatory prefix (that instructs Replicate to capture the before-image data) and MyColumn
is the source column name.
Although you can store the before-image data in an existing target column, it is recommended to create a new
target column (using the Add Column button) in which to store the before-image data.
Creating an expression for transformations
Use an expression to define the contents of a new or re-calculated column.
To create an expression:
1. In the Transform tab, select the row with the column for which you want to create an expression.
or
Click Add Column to add a new column.
2.
Click the button in the Expression column.
The Expression Builder opens.
3. Build an expression as described in Using the Expression Builder (page 137).
Using SQLite syntax with transformations
The following table lists the SQLite operators that are supported with transformations.
Operator Description
|| Concatenate strings.
FIRST_NAME||LAST_NAME
PHONE_NUMBER||<Office Only> (adds the string Office Only to the telephone number).
SQLITE syntax operators
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 91

8 Customizing tasks
Operator Description
+ Adds two values together.
DEPARTMENT_ID+100 (adds 100 to each ID number). Any column used in an expression with
this operator must be a numeric data type.
- Subtracts a value from another value.
MANAGER_ID-100 (subtracts 100 from each ID number). Any column used in an expression
with this operator must be a numeric data type.
% Uses the remainder of a division expression as the value.
%SALARY/7 (Divides the value of the Salary column by 7 and uses any remainder from the
expression as the column value).
/ Divides one value into another.
SALARY/.16 (Divides the value of the Salary column by .16.
If the two values in the division expression are integers (two NUMERIC columns
with no digits after the decimal) and the result is a fractional value, the result
returned will be 0.
* SALARY*.16 (Multiplies the value of the Salary column by .16. This could be used to calculate
taxes that are subtracted from a salary).
For more information about SQLite syntax, see the SQLite documentation.
Using filters
Filters let you include or exclude records from a replication task based on the value(s) of the source table
columns, thereby allowing you to replicate only the specific data that you need.
In this section:
l
Filter limitations (page 92)
l
Opening the Filter tab (page 93)
l
Creating a filter condition for a specified column (page 94)
l
Creating a record selection condition for one or more columns (page 94)
l
Adding or removing filter ranges (page 96)
l
Using SQLite syntax with filtering (page 97)
Filter limitations
When creating a filter, the following limitations apply:
l
Filters are not supported for calculating columns of Right-to-Left languages.
l
Filters can only be applied to immutable columns.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 92

8 Customizing tasks
l
Filters on mutable columns:
When a filter is created to exclude/include specific rows in a column, the specified rows will always be
excluded/included, even if the rows that were originally excluded/included are later changed. For
example, if you chose to exclude/include rows "1-10" in a column named "Age" and those rows were
later changed to "11-20", the rows will continue to be excluded/included, even though the data is no
longer the same.
Additionally, if a row outside the filter scope was changed (i.e. updated or updated and then deleted)
so that it should now be excluded/included (as defined by the filter), it will not be replicated to the
target. So, for example if you created a filter to exclude/include rows less than 5 and then changed row
6 to -6, it will not be replicated (even though it is included in the filter's criteria range).
l
Filter cannot be applied to LOB columns.
l
When specifying numeric data as a filtering condition, the data preceding the decimal point cannot
exceed int64.
Opening the Filter tab
The Filter Table tab contains the following information:
l
Data Columns list: This list contains a list of the columns for the table where you filtering data. You
can use these to select the columns to use in the filtering operations.
This list has the following tabs:
l
Source: This tab lists the original source columns in the table.
l
Header: This tab lists the available header columns. You can create filters using these columns
and include them in expressions. For information on these header columns, see Headers (page
159).
l
Calculated: This tab lists the columns added to the table. You add columns through
transformations. For more information, see Defining transformations for a single table/view
(page 84).
l
Filter Conditions table: This table has the following columns:
l
Name: The name of the column where you are filtering the data.
l
Type: The data type for the column.
l
Include/Exclude: Indicate whether to include or exclude the filtered data for this column.
l
Ranges: Click the button on the right of the Ranges field to open the Range Builder. For
information on creating a value or ranges with the Range Builder, see Adding or removing filter
ranges (page 96).
For more information on typing in the filter ranges manually, see Using SQLite syntax with
filtering (page 97).
l
Record Selection Condition: Enter a complex condition that can include multiple columns. The
condition must evaluate to TRUE to be accepted. You can create a condition using SQLite operators or
by Using the Expression Builder (page 137). For information on using the SQLite operators, see Creating
a record selection condition for one or more columns (page 94).
The following figure is an example of the information in the Filter tab of the Table Settings window.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 93

8 Customizing tasks
Table Settings: Filter
To open the Filter tab:
1. Select the table you want to filter and then open the Table Settings (page 82) window.
2. Click the Filter tab on the left side of the window.
Creating a filter condition for a specified column
You can create a simple condition for a single column in the table you are working with. You can include any
combination of ranges or specific values in the filter and determine whether to include or exclude the defined
data.
To create a filter condition:
1. Select a column from the data columns list and then click the right-facing arrow next to the Filter
Conditions table.
To remove the column, click on it in the Filter Conditions table and then click the left-facing arrow.
Any data entered for this column in the Include/Exclude or Values columns is also deleted.
2. Click in the Include/Exclude column to select whether to include or exclude the data that meets this
condition.
3. Click the Edit Ranges button in the Ranges column.
4. The <Name> <Include|Exclude> Ranges window opens. Continue from Adding or removing filter
ranges (page 96).
Creating a record selection condition for one or more columns
You can create a record selection condition manually and/or by using the Expression Editor.
When entering a string, you can use the following special characters:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 94

8 Customizing tasks
l
%: Matches any string of zero or more characters. For example, Mc% searches for every name that begins
with Mc or %bob% includes every name that contains bob.
l
_:Matches a single character (as a wildcard). For example: ’Sm_th’ includes names that begin with Sm
and end with th, such as Smith or Smyth. To search for an underscore character, use [_]".
l
[..]: Includes a range or set of characters. For example, [CK]ars[eo] includes names Carsen, Karsen,
Carson, and Karson or [M-Z]inger includes all words that end in inger with the first letter between M
and Z, such as Ringer, Singer, or Zinger.
For more information, see documentation on how to use Transact-SQL.
For information on what SQLite operators can be used to create Record Selection Condition filters, see Using
SQLite syntax with filtering (page 97).
To create a record selection condition:
1. From the Data Columns list, select a source column, header column or calculated column and then
click the arrow to the left of the Record Selection Condition pane.
2. Use SQLite operators, such as < or = to create the condition. Use any amount of strings or columns as
you need to create a condition.
For example $EMPLOYEE_ID < 100 AND $SALARY > 100,000
In this case only rows that satisfy both of these conditions are replicated in the replication task.
The following example provides an example using SQL search pattern strings. Only rows that satisfy
this condition are replicated.
$EMPLOYEE_NAME IS ’Sm_th’
To create a record selection condition using the Expression Builder:
l
Click Open Expression Builder. This button is located directly under the record selection condition
box. Follow the directions for creating an expression in the section Using the Expression Builder (page
137).
Applying updates to specific columns only
You can define an expression that instructs Replicate only to apply UPDATEs when a user-defined condition
has been met, for example, only when specific columns have changed. This is useful in situations when there
are many updates in the source that the user has deemed not relevant for the target, as "irrelevant" updates
will be ignored.
Limitations
l
Does not support columns that do not have Before-Image data (e.g. LOB columns)
l
Does not support the following sources (i.e. sources that do not support Before-Image records):
l
ODBC with CDC
l
Teradata
l
Subject to the existing expression builder and filter limitations
l
Content-based filtering may result in loss of data or data corruption. For example, if the Primary Key
value changes (an UPDATE operation), the expression may ignore the UPDATE if the columns that were
specified in the expression did not change. The result in this case would be that a "phantom" row with
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 95

8 Customizing tasks
the old row contents will remain, even if a change was later applied to the columns specified in the
expression.
How to
Assume that you have a source table named table1 with columns c1-c10 but you are only interested in
updating columns c7, c8 and c9 on the target.
To do this, you would need to:
1. Open the Table Settings for table1 and select the Filter tab.
2. Click the Expression Builder button at the bottom right of the tab.
The Expression Builder opens.
3. Optionally, select the Headers tab.
Although selecting the Headers tab is optional, selecting it will enable you to add
$AR_H_
OPERATION
to your expression (as required in Step 4 below) simply by double-clicking the
column on the left of the tab.
4. Enter the following expression in the Build Expression pane and then click OK:
($AR_H_OPERATION != 'UPDATE') OR
(($AR_H_OPERATION = 'UPDATE') AND (( ifnull($BI__c7,0) != ifnull($c7,0)) OR ( ifnull
($BI__c8,0) != ifnull($c8,0)) OR ( ifnull($BI__c9,0) != ifnull($c9,0))))
The above expression means that changes will be applied to c7, c8 and c9 only if one of the following
is true:
l
The operation is not an UPDATE.
l
The value of c7, c8 or c9 has changed as the result of an UPDATE operation.
When used in an expression, Before-Image columns must be prefixed with
$BI__.
For
operations other than UPDATE, the value of the specified columns will be NULL.
Adding or removing filter ranges
You can add one or more values to the Ranges column using the Range Builder. Values that match any of the
ranges in the list are included in the replication.
You can also delete a filter range using the Range Builder.
Filter ranges that you enter manually are also displayed in the Filter Builder. You can use the Filter
Builder to delete them.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 96

8 Customizing tasks
To use the Range Builder:
1. In the Filter tab of the Table Settings (page 82) window, select a column to filter. For more information,
see Using filters (page 92).
2. Click the button to the right of the Ranges column.
The Ranges Builder opens.
3. Click Add Range. Select any of the following from the drop-down list displayed.
l
Equal to: Select Equal to to enter a single value. The following is displayed in the range list.
Equal to = [N]
Click the [N] and type a value in the field that is displayed.
When the value in the selected column equals the value you enter, the result is included or
excluded in the replication task depending on the option selected in the Include/Exclude
column.
l
Between: Click Between to enter a range of values. The following is displayed in the range list.
Between [N] - [N]
Click each [N] and type a value in the fields that are displayed.
When the column contains the values between the two values entered, the result is included or
excluded in the replication task depending on the option selected in the Include/Exclude
column.
l
Less than or equal to: Select Less than or equal to and enter a maximum value. The following
is displayed in the range list.
Less than or Equal to =< [N]
Click the [N] and type a value in the field that is displayed.
When the value in the selected column is equal to or less than the value you enter, the result is
included or excluded in the replication task depending on the option selected in the
Include/Exclude column.
l
Greater than or equal to: Select Greater than or equal to and enter a minimum value. The
following is displayed in the range list.
Greater than or Equal to => [N]
Click the [N] and type a value in the field that is displayed.
When the value in the selected column is equal to or more than the value you enter, the result
is included or excluded in the replication task depending on the option selected in the
Include/Exclude column.
To delete a filter range from the Range Builder:
1. In the Filter tab of the Table Settings (page 82) window, select the column with the filter condition you
want to delete.
2. Click the button to the right of the Ranges column. The Ranges Builder opens.
3. Click the X next to the range you want to delete. The deleted range is removed from the list.
Using SQLite syntax with filtering
Qlik Replicate supports the following SQLite operators when creating Record Selection Condition filters.
You must put the ($) in front of each input as shown below.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 97

8 Customizing tasks
Operator Description
< Is less than.
$SALARY<100000
<= Is less than or equal to
$SALARY<=100000
> Is greater than
$SALARY>100000
>= Is more than or equal to
$SALARY>=100000
= Is equal to
$SALARY=100000
!= or <> Is not equal to
$SALARY!=100000
IS Is the same as
$HIRE_DATE IS 2014-09-29
IS functions the same as = unless one or both of the operands are NULL. In this case, if both
operands are NULL, then the IS operator evaluates to 1 (true). If one operand is NULL and
the other is not, then the IS operator evaluates to 0 (false).
IS NOT Is not the same as
$HIRE_DATE IS NOT 2014-09-29
IS NOT functions the same as != unless one or both of the operands are NULL. In this case, if
both operands are NULL, the IS NOT operator evaluates to 0 (false). If one operand is NULL
and the other is not, then the IS NOT operator evaluates to 1 (true).
AND Both operands are true.
$MANAGER_ID AND EMPLOYEE ID >100
OR Either operand is true.
$MANAGER_ID OR EMPLOYEE ID >100
SQLITE syntax operators
For more information on how to use the SQLite syntax, see the SQLite documentation.
Parallel Load
In Full Load replication mode, you can accelerate the replication of large tables by splitting the table into
segments and loading the segments in parallel. Tables can be segmented by data ranges, by partitions, or by
sub-partitions.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 98

8 Customizing tasks
Supported endpoints
The task must be defined with a combination of the following source and target endpoints:
Supported source endpoints:
l
Amazon RDS for Microsoft SQL Server
l
IBM DB2 for LUW
l
IBM DB2 for z/OS
Table segmentation by partitions or sub-partitions is not supported with the IBM DB2 for z/OS
source endpoint.
l
Microsoft SQL Server
l
MySQL
l
Oracle
l
PostgreSQL
Table segmentation by partitions or sub-partitions is not supported with the PostgreSQL
source endpoint.
l
SAP Sybase ASE
l
SAP Application
l
SAP Application (DB)
Tables are by default client dependent with the SAP Application (DB) source endpoint. The
MANDT column is automatically taken directly from the endpoint.
l
SAP HANA
l
Teradata
Supported target endpoints:
l
Amazon EMR
l
Amazon MSK
l
Amazon Redshift
l
Amazon S3
l
Cloudera Data Platform (CDP) Private Cloud
l
Databricks (Cloud Storage)
l
File
l
Google Cloud BigQuery
l
Google Cloud SQL for MySQL
l
Google Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 99

8 Customizing tasks
l
Google Cloud Storage
l
Google Dataproc
l
Hadoop (Hortonworks, Cloudera, and MapR)
l
Hortonworks Data Platform (HDP)
l
Kafka
l
Microsoft Azure ADLS
l
Microsoft Azure Database for MySQL
l
Microsoft Azure Database for PostgreSQL
l
Microsoft Azure Data Warehouse
l
Microsoft Azure HDInsight
l
Microsoft Azure SQL Database
l
Microsoft SQL Server
l
MySQL
l
Oracle
l
PostgreSQL
l
Snowflake on Google
l
Snowflake on AWS
l
Snowflake on Azure
l
Sybase ASE
l
Vertica
Setting up Parallel Load
To define segment boundaries by data range:
1. In the Parallel Load tab's Select Parallel Load Method section, select Use Data Ranges.
2. In the Select Details section, click Select Segment Columns.
The Columns window opens
3. For all endpoints, the Unique Index column is automatically selected. Select which additional columns
whose data you wish to use to delineate the ranges and then click OK.
l
Selecting indexed columns will significantly improve performance
l
You can select up to ten columns (multi-selection is supported)
l
Records with null values will not be replicated
l
The following data types cannot be used to define segments by ranges: DOUBLE,
FLOAT, and LOB (BLOB, CLOB, NCLOB)
4. In the Define Segment Boundaries section:
a. Click Add Segment to add a segment.
The columns that you selected will appear as table headings.
b. Enter the upper data range for the segment in the selected columns.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 100

8 Customizing tasks
Values in DATE columns must be entered in the format supported by the source. For
example, for an Oracle source, the correct format would be:
l
ALTER SESSION SET NLS_DATE_FORMAT:
'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS'
(specifying
YYYY-MM-DD
only is also valid)
l
ALTER SESSION SET NLS_TIMESTAMP_FORMAT:
'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS.FF9'
l
ALTER SESSION SET NLS_TIMESTAMP_TZ_FORMAT:
'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS.FF9 TZH:TZM'
c. Add additional segments as required.
d. Click Validate to validate that the specified data corresponds to the source column data type
and that all of the defined segments contain values.
e. To delete a segment, select the desired segment and then click Delete.
5. Click OK to save your settings.
When Use Data Ranges is selected, all of the table data will be replicated, even if data ranges are
not defined for all of the columns.
Usage example
Let's assume that the following segments are defined in the Define Segment Boundaries table:
Column_1 Column_2 Column_3
10 30 105
20 20 120
100 12 99
Example table data
In this case, the following "WHERE" clauses will be created for each load segment:
l
Segment 1: ((COL1 < 10) OR ((COL1 = 10) AND (COL2 < 30)) OR ((COL1 = 10) AND (COL2 = 30)
AND (COL3 < 105)))
l
Segment 2: NOT ((COL1 < 10) OR ((COL1 = 10) AND (COL2 < 30)) OR ((COL1 = 10) AND (COL2 =
30) AND (COL3 < 105))) AND ((COL1 < 20) OR ((COL1 = 20) AND (COL2 < 20)) OR ((COL1 = 20)
AND (COL2 = 20) AND (COL3 < 120)))
l
Segment 3: NOT ((COL1 < 20) OR ((COL1 = 20) AND (COL2 < 20)) OR ((COL1 = 30) AND (COL2 =
20) AND (COL3 < 120))) AND ((COL1 < 100) OR ((COL1 = 100) AND (COL2 < 12)) OR ((COL1 =
100) AND (COL2 = 12) AND (COL3 < 99)))
l
Segment 4: NOT ((COL1 < 100) OR ((COL1 = 100) AND (COL2 < 12)) OR ((COL1 = 100) AND
(COL2 = 12) AND (COL3 < 99)))
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 101

8 Customizing tasks
To define segment boundaries by all of the table partitions:
Only select this method if you are sure that the table is already partitioned.
1. In the Parallel Load tab's Select Parallel Load Method section, select Use Partitions.
2. In the Select Partitions section, select Use all table partitions. This will segment the table according
to partitions that already exist in the source database.
3. Select one the following:
l
Use main partitions
l
Use sub partitions
This option will be disabled if the source database does not support sub-partitions.
4. Click OK.
To define segment boundaries by specific partitions:
Only select this method if you are sure that the table is already partitioned.
1. In the Parallel Load tab's Select Parallel Load Method section, select Use Partitions.
2. In the Select Partitions section, select Specify partitions. This will split the data according to the
specified source partitions.
When Specify partitions is selected, only the specified partitions will be replicated.
3. Click Add Partition.
4. Specify the name of an existing partition or sub-partition.
5. If you specified the name of a sub-partition, select the check box in the Sub-Partition column.
The check box will be disabled if the source database does not support sub-partitions.
6. Add additional partitions/sub-partitions as required.
7. To delete a partition/sub-partition, select the partition/sub-partition and then click Delete.
8. Click OK to save your settings.
Adjusting the number of segments that can be loaded in parallel
You can increase or decrease the number of segments that will be loaded in parallel. For example, if you
selected the Use all table partitions option and the source table has 20 partitions, increasing the default
number of concurrent tasks (5) may improve performance.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 102

8 Customizing tasks
Sub-tasks are allocated for each segment \ partition \ sub partition.
For example: If you select a table with 6 partitions and load the table using the Use Partitions
method, 5 partitions will be loaded in parallel, corresponding with the default number of concurrent
tasks (5). When one of the sub-tasks completes its run, it will be assigned to loading the sixth
partition.
The currently set value is displayed at the bottom of the Parallel Load tab. You can modify this value in the
Maximum number of tables to load in parallel field in the Full Load Tuning (page 173) tab.
Handling LOB columns
You can override the task's LOB settings for individual tables.
This option is only available for tasks defined with any combination of the following source and
target endpoints: Oracle source, Oracle target, PostgreSQL source, PostgreSQL target, Microsoft SQL
Server source, Microsoft SQL Server target, MySQL source, and MySQL target.
l
During CDC or during Full Load when the Allow unlimited LOB size option is enabled, LOB
data types are supported only in tables with a primary key or unique index.
l
When replicating from Microsoft SQL Server, inline LOBS will always be read directly from the
logs (i.e. without lookup).
The following LOB handling options are available:
Option Description
Replicate LOB
columns
When this option is selected (the default), LOB columns will be replicated.
Note that replicating LOBs may impact performance. This is especially true in the case of
the large LOBs which require Replicate to perform a lookup from the source table in order
to retrieve the source LOB value.
Allow
unlimited LOB
size
Select this option - also known as Full LOB mode - to ensure that all LOBs are replicated
without being truncated. This option should be selected when all (or nearly all) of the
LOBs you wish to replicate are large (i.e. exceed 1 GB).
NoteIf the task's Change Processing Mode is set to "Batch optimized apply"
(the default), Replicate will switch to "Transactional apply" mode to apply
tables with LOBs.
LOB handling options
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 103

8 Customizing tasks
Option Description
Optimize
handling when
LOB size is
less than (KB)
Select this option when you need to replicate both small and large LOBs, and most of the
LOBs are small.
This option is supported with the following endpoints only:
l
Sources: Oracle, Microsoft SQL server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, IBM DB2 for
LUW, and Sybase ASE.
l
Targets: Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, IBM DB2 for
z/OS, and Sybase ASE.
When this option is selected, during Full Load, the small LOBs will be replicated "inline"
(which is more efficient), and the large LOBs will be replicated by performing a lookup
from the source table.
During Change Processing, however, both small and large LOBs will be replicated by
performing a lookup from the source table.
When this option is selected, Replicate will check all of the LOB sizes to
determine which ones to transfer "inline". LOBs larger than the specified size
will be replicated using Full LOB mode.
Therefore, if you know that most of the LOBs are larger than the specified
setting, it is better to use the Allow unlimited LOB size option instead.
Chunk size
(KB)
Optionally, change the size of the LOB chunks to use when replicating the data to the
target. The default chunk size should suffice in most cases, but if you encounter
performance issues, adjusting the size may improve performance.
With some databases, data type validation occurs when the data is inserted or
updated. In such cases, replication of structured data types (e.g. XML, JSON,
GEOGRAPHY, etc.) may fail if the data is bigger than the specified chunk size.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 104

8 Customizing tasks
Option Description
Limit LOB size
to (KB)
Select this option if you only need to replicate small LOBs or if the target endpoint does
not support unlimited LOB size. The maximum permitted value for this field is 102400 KB
(100 MB).
When replicating small LOBs, this option is more efficient than the Allow unlimited LOB
size option since the LOBs are replicated "inline" as opposed to via "lookup" from the
source. During Change Processing, small LOBs are usually replicated via "lookup" from
the source.
As the value of the Limit LOB size to is in bytes, the size should be calculated according
to the following formulas:
l
BLOB – The length of the largest LOB.
l
NCLOB – The length of the longest TEXT in characters multiplied by two (as each
character is handled as a double-byte).
If the data includes 4-byte characters, multiply it by four.
l
CLOB – The length of the longest TEXT in characters (as each character is handled
as a UTF8 character).
If the data includes 4-byte characters, multiply it by two.
l
Any LOBs larger than the specified size will be truncated.
l
During Change Processing from Oracle source, inline BLOBs are
replicated inline.
l
Changes to this setting will only affect existing tables after they are
reloaded.
In some scenarios, tasks configured to replicate tables with multiple LOB columns may consume a
large amount of memory. This is because Replicate allocates memory by multiplying the Limit LOB
size to value by the Commit rate during full load value, the sum of which, it multiplies by the
number of LOB columns being replicated. So, for example, if LOB size is limited to 5 MB and the
default commit rate is used (10000 events), a task replicating 6 LOB columns will consume 30 GB of
memory. Note that other factors such as the database type and version may also affect memory
consumption.
Should you encounter memory consumption issues and suspect that a combination of the above
factors may be the cause, stop the task and lower the value in the Commit rate during full load
field. Then resume the task. Repeat this process until acceptable performance/memory levels are
reached.
These instructions apply to Change Processing and Full Load tasks.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 105

8 Customizing tasks
Changes to a column’s LOB size while a task is running will not be reflected in the Change Table,
unless the target tables are created by Qlik Replicate. In such cases, the task must be configured to
drop and create the Change Table (the default) and the target tables need to be reloaded (after the
LOB size has changed).
For more information on the Change Table, see Store Changes Settings (page 175). For information
on reloading target tables, see the Qlik Replicate User Guide and Reference.
Message format
This tab is only available for tasks defined with a supported streaming endpoint.
When a task is defined with such an endpoint, you can specify a custom message format that will override the
default Replicate message format. This may be useful if the consumer application needs to process the
message in a particular format.
The custom message format can be defined at task level and/or at table level. When it is defined at both task
and table level, the message format defined for the table will take precedence over the message format
defined for the task.
To define a custom message at table level:
1. Select a table.
2. Open the Table Settings window as described in Table Settings (page 82).
3. Select the Message Format tab and click the Change to Table Policy button.
4. Configure the message format as described in Message Format (page 196).
5. To use the message format defined for the task, click the Change to Task Policy button.
For information on defining a custom message at task level, see Message Format (page 196).
Full Load
This tab is available for tasks defined with the IBMDB2 for z/OS and IBM DB2 for iSeries source endpoints
only.
Select the Eliminate creation of duplicate records on full load option if you need to prevent duplicate
records from being replicated during Full Load. You can either set the option at task level or per table.
Note that selecting this option could impact performance as Replicate instructs the source database to return
the table records by Primary Key order and then removes any duplicate records.
To prevent creation of duplicate records per table:
1. Select the desired table and then open the Table Settings window as described in Table Settings (page
82).
2. Select the Full Load tab and click the Change to Table Policy button.
3. Select the Prevent creation of duplicate records on the target check box.
For information on preventing creation of duplicate records at task level, see Full Load Settings (page 171).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 106

8 Customizing tasks
8.2 Defining global rules
Global rules are a useful way of making changes across multiple tables and columns in the same task. You can
define transformation rules that modify the source data or metadata before it reaches the target, and/or you
can define filter rules that determine which records will be replicated to the target.
Global rules are not available in a Log Stream Staging setup.
For information on Log Stream Staging, refer to the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
l
Transformations - One way transformations can be used is to change the names of all tables in a task.
You can change the names using wildcards and patterns. For example, you may want to change the
names of the tables from account_% to ac_%. This is helpful when replicating data from a Microsoft SQL
Server endpoint to an Oracle endpoint where the Microsoft SQL Server endpoint has a limit of 128
characters for a table name and the Oracle endpoint has a limit of 31 characters.
You may also need to change a specific data type in the source to a different data type in the target for
many or all of the tables in the task. Global transformation will allow you to accomplish this without
having to define a transformation for each individual table.
Table-specific transformations override global transformations. For example, you can define
a global transformation that changes the data type for all tables from DATE to DATETIME(6)
and then define another transformation for a specific table that changes the data type from
DATE to STRING(50).
For information on defining a transformation for a specific table, see Defining
Transformations for a Single Table/View.
For an explanation of how to create global transformation, see Starting the Global Transformation Rules
wizard (page 107).
l
Filters - Use filter rules to determine which records will be replicated to the target. Filter can be based
on column data (e.g. only replicate records where Age is greater than 18) or record attributes (e.g. only
replicate UPDATED records).
For an explanation of how to create global filters, see Starting the Global Filter Rules wizard (page 131).
Starting the Global Transformation Rules wizard
You define global transformations using the Global Transformation Rules wizard.
To start the Global Transformations wizard:
1. Open the task for which you want to create a global transformations or a global filter.
You can click View Task above the Tasks list or double-click the task.
2. If you are not in the Designer mode, click Designer at the top right of the screen.
For more information on the Designer mode, see Designer mode (page 207).
3. In Designer mode, click Global Rules.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 107

8 Customizing tasks
The Global Rules window opens.
4. Click the New Rule toolbar button and select Transformation.
The New Transformation Rule wizard opens.
5. Enter the information to define a global transformation rule. The first step is selecting the
Transformation type (page 108).
Limitations for global transformations
The following limitations apply to global transformations:
l
Transformations are not supported for columns with Right-to-Left languages.
l
Transformations cannot be performed on columns that contain special characters (e.g. #, \, /, -) in their
name.
l
The only supported transformation for columns that are mapped to BLOB/CLOB data types (by
Replicate) is to drop the column on the target.
l
Expressions must be written using SQLite syntax only.
l
Changing a global transformation value will not reload affected tables automatically. The target must
be reloaded manually for the changes to take effect.
For information on reloading the target, see Using the Run button options (page 235).
Transformation type
In the Transformation type step of the New Transformation Rule wizard, you define the type of
transformation you want to be performed.
You can only create one rule for each transformation type on the same object (e.g. a column). If you
create multiple rules for a single transformation type on the same object, only the last rule you
create will be valid. For example, if you create the following rules (in order) to rename a schema:
Rename Schema: Add Prefix
Rename Schema: Add Suffix
OR
Rename Column: Add Prefix
Rename Column: Add Suffix
Only the second rule (adding a suffix) will be executed.
To select the transformation type:
1. Enter a name for the rule.
The name cannot exceed 32 characters, contain non-Latin characters, or contain any of the following
characters: \/:*?"<>|
2. Select one of the following:
Table or Schema:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 108

8 Customizing tasks
l
Rename schema: Select this to change the schema name for multiple tables. For example, if
you want all HR tables to be renamed PERS.
l
Rename table: Select this to change the name of multiple tables. For example, if you want all
tables named SALARY to be called WAGES.
Tablespace:
l
Change table tablespace: Select this to change the table tablespace on the target. You can
change the table tablespace regardless of what objects it contains or you can specify a
condition for it to be renamed. For example, change all table tablespaces that contain the table
Employees in the schema Company.
By default (i.e. when this option is not selected), the tables will either be created in the source
table tablespace on the target (when replicating from an Oracle source) or in the default
database tablespace (when replicating from any other source).
This option is only available for tasks with an Oracle target endpoint.
l
Change index tablespace: Select this to change the index tablespace on the target. You can
change the index tablespace regardless of what objects it contains or you can specify a
condition for it to be renamed. For example, change all table tablespaces that contain the table
Employees in the schema Company.
By default (i.e. when this option is not selected), the indexes will either be created in the source
table tablespace on the target (when replicating from an Oracle source) or in the default
database tablespace (when replicating from any other source).
This option is only available for tasks with an Oracle target endpoint.
Column:
l
Rename column: Select this to change the name of multiple columns. For example, if you want
to change all columns with word MINIMUM to MIN.
l
Add column: Select this to add a column with a similar name to multiple tables.
l
Drop column: Select this to drop a column with a similar name from multiple tables.
l
Convert data type: Select this if you want to change a specific data type to a different one
across multiple tables. For example, if you want to change all Integer data types to a string.
l
Replace column data: Select this to replace column data across multiple target tables.
In homogeneous replication tasks (such as Oracle to Oracle), modifying a single table column
(by changing the column data type or length for example), will break the homogeneity for the
entire table.
Change Table:
Change Table transformations are only available when the Store Changes replication option is enabled.
For more information on Change Tables, refer to the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
l
Rename Change Table: Select this to rename the Replicate Change Table for all tables or for
any table that matches the specified schema name and/or table name.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 109
8 Customizing tasks
l
Rename Change Table schema: Select this to change the schema under which the Replicate
Change Table will be created, for all tables or for any table that matches the specified schema
name and/or table name.
3. Click Next to proceed to the Transformation scope (page 110) step.
Transformation scope
In the Transformation scope screen, you define which tables will be affected by the transformation. For
example, you can apply the rule to all tables that contain the word SALARY as part of their name.
The options displayed in this screen depend on the selected Transformation Type.
The following table describes all available options. The second column lists the Transformation Type where
the option to be available.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 110

8 Customizing tasks
Option Transformation Type Description
Schema name
is like %
All Leave the % sign to include all schemas in your global
transformation.
Click the % sign to add a filter. In this case you can enter
any name combination to include only that schema in
your global transformation rule.
For example, enter HR to include only tables that have
the schema HR.
You can use the % sign as a wildcard. For example, H%
includes all tables with a schema that begins with the
letter H, such as HR, HELLO, or HQ.
The % wildcard can be used in any position. For example,
if you use it at the beginning, %H, then all table names
that end in H are included in the transformation rule.
The % can also be used in a middle position.
If you are using an Oracle target, you must
enter a schema that exists on the target
endpoint. Qlik Replicate does not create new
schemas on an Oracle endpoint. If you want
to use a new schema for the target, create
the schema on the Oracle endpoint before
running the task. For more information, see
the topic "Configuring an Oracle database as
a Qlik Replicate Target" in the Qlik Replicate
User and Reference Guide.
Transformation conditions
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 111

8 Customizing tasks
Option Transformation Type Description
Table
tablespace is
like %
Change table tablespace
This option is only available if the task is
defined with an Oracle target endpoint.
Leave the % sign to include all table tablespace names in
your global transformation.
Click the % sign to add a filter. In this case, you can enter
any name combination to include only the specified
table tablespace in your global transformation rule.
For example, enter SYSTEM to include only table
tablespaces called SYSTEM.
You can also use the % sign as a wildcard anywhere in
the string. For example, H% includes all table tablespaces
that begin with the letter "H" whereas %H includes all
table tablespaces that end with the letter "H".
Index
tablespace is
like %
Change index tablespace
This option is only available if the task is
defined with an Oracle target endpoint.
Leave the % sign to include all index tablespace names in
your global transformation.
Click the % sign to add a filter. In this case, you can enter
any name combination to include only the specified
index tablespace in your global transformation rule.
For example, enter SYSTEM to include only index
tablespaces called SYSTEM.
You can also use the % sign as a wildcard anywhere in
the string. For example, H% includes all index tablespaces
that begin with the letter "H" whereas %H includes all
index tablespaces that end with the letter "H".
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 112

8 Customizing tasks
Option Transformation Type Description
Table name is
like %
All Leave the % sign to include all table names in your global
transformation rule.
Click the % sign to add a filter. In this case you can enter
any name combination to include only tables with that
specific name in your global transformation rule.
You can use the % sign as a wildcard. For example, J%
includes all tables with a name that begins with the
letter J, such as JOBS, JOBS_HISTORY, or JACKSONVILLE.
The % wildcard can be used in any position. For example,
if you use it at the beginning, %H, then all table names
that end in H are included in the transformation rule.
The % can also be used in a middle position.
Column name
is like %
Rename column
Drop column
Convert data type
Replace column value
Leave the % sign to include all column names in your
global transformation rule.
Click the % sign to add a filter. In this case you can enter
any name combination to include only columns with
that specific name in your global transformation rule.
You can use the % sign as a wildcard. For example, N%
includes all columns with a name that begins with the
letter N, such as NAME, NAME_FIRST, or NAME_LAST.
The % wildcard can be used in any position. For example,
if you use it at the beginning, %IES, then all column
names that end in with the string "IES" are included in
the transformation rule. The % can also be used in a
middle position.
Data type is Convert data type
Replace column value
Select a new data type from the drop-down list. Make
sure that the data type you select is compatible with the
data in that column.
For a description of Qlik Replicate data types,
information about data type mapping from the native
endpoint to Qlik Replicate, or for a list of endpoints
supported by Qlik Replicate, see the Qlik Replicate User
and Reference Guide.
Scope
expression
All Click Advanced options to define a scope expression
using the Expression Builder.
After you complete defining the transformation rule definitions, click Next to go to the Transformation action
(page 114) step.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 113

8 Customizing tasks
If the global transformation type you are defining is Drop Column, you do not need to create a
Transformation Rule. In this case, click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Transformation action
In the Transformation action screen, you define what happens to the objects affected by the transformation
rule. For example, you can define a new name for the affected objects or add a prefix to the table names. Only
objects that fall within the Transformation scope (page 110) will be affected.
The following transformation options are available:
l
Rename Schema (page 114)
l
(page 118)
l
(page 118)
l
Rename Table (page 118)
l
Rename Column (page 121)
l
Add column (page 124)
l
Drop Column (page 124)
l
Convert data type (page 124)
l
Rename Change Table schema (page 129)
l
Rename Change Table (page 126)
When done, click Next.
Limitations for transformation rules
The following limitations apply to transformation rules:
l
Transformations are not supported for columns with Right-to-Left languages.
l
Transformations cannot be performed on columns that contain special characters (e.g. #, \, /, -) in their
name.
l
The only supported transformation for columns that are mapped to BLOB/CLOB data types (by
Replicate) is to drop the column on the target.
l
Expressions must be written using SQLite syntax only.
l
Changing a global transformation value will not reload affected tables automatically. The target must
be reloaded manually for the changes to take effect.
For information on reloading the target, see Using the Run button options (page 235).
The options displayed in this screen depend on the Transformation Type selected.
Rename Schema
If your transformation type is Rename Schema, you can do the following:
l
Rename schema to (string) (page 115)
l
Add a prefix or suffix (page 115)
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 114

8 Customizing tasks
l
Remove a prefix or suffix (page 115)
l
Replace a prefix or suffix with different characters (page 116)
l
Convert schema name to uppercase (page 117)
l
Convert schema name to lowercase (page 117)
l
Rename schema (Expression) (page 117)
Rename schema to (string)
Use the Rename schema to: [string] option to change the name of all table schemas that you defined in the
Transformation scope (page 110) step to a different name. For example, if you have a schema called Human_
Resources and want to change all instances of this name to HR then enter the string HR. You can enter any
string in this field.
Add a prefix or suffix
Use the Add a prefix or suffix option to add additional characters to the beginning or end of the schema
name for all schemas that fit the definition you created in the Transformation scope (page 110) step. For
example, if the schema name is HR, you can add a suffix, such as TAR or _TAR to the schema name for all
tables with that schema name. In this case, the resulting schema name will be HRTAR or HR_TAR.
If you are using Oracle as your target endpoint, Qlik Replicate does not create a new schema.
Therefore, the schema name that is the result of replacing a prefix or suffix with a different string of
characters must exist in the Oracle target endpoint. If the resulting schema name does not exist, you
must create the schema in the Oracle endpoint before carrying out this task.
For more information, see the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
To globally add a prefix or suffix
1. Select Add <Prefix/Suffix> Insert Characters to matching schema names.
2. Click the word Prefix or Suffix and select one of these two from the list.
3. Click [string] to activate the field.
4. Type the characters you want as the prefix or suffix. If you want to include an underscore or other legal
character to separate the prefix/suffix from the original name, you must add it as part of the character
string.
5. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Remove a prefix or suffix
Use the Remove a prefix or suffix option to remove a string of characters from the beginning or end of a
schema name for all schema that fit the definition you created in the Transformation scope (page 110) step.
For example, you can use this option to remove the letters _REV from the schema name for all tables in the
schema HR_REV. In this case the schema name in the target will be HR.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 115

8 Customizing tasks
If you are using Oracle as your target endpoint, Qlik Replicate does not create a new schema.
Therefore, the schema name that is the result of replacing a prefix or suffix with a different string of
characters must exist in the Oracle target endpoint. If the resulting schema name does not exist, you
must create the schema in the Oracle endpoint before carrying out this task.
For more information, see the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
To globally remove a prefix or suffix
1. Select Remove <Prefix/Suffix> Insert Characters from matching schema names.
2. Click the word Prefix or Suffix and select one of these two from the list.
3. Click [string] to activate the field.
4. Type the characters you want to remove. If you want to remove an underscore or other legal character
from the original name, you must add it as part of the character string.
5. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Replace a prefix or suffix with different characters
Use the Replace a prefix or suffix option to replace a string of characters with a different string of characters.
You determine whether to replace the characters at the beginning or end of a schema name for all schema
that fit the definition you created in the Transformation scope (page 110) step.
For example, you can use this option to replace the letters _ORIG with _REPL in the schema name for all tables
in the schema HR_ORIG. In this case the schema name in the target will be HR_REPL.
If you are using Oracle as your target endpoint, Qlik Replicate does not create a new schema.
Therefore, the schema name that is the result of replacing a prefix or suffix with a different string of
characters must exist in the Oracle target endpoint. If the resulting schema name does not exist, you
must create the schema in the Oracle endpoint before carrying out this task.
For more information, see the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
To globally replace a prefix or suffix
1. Select Replace <Prefix/Suffix> Insert Characters by Insert Characters for all matching schema
names.
2. Click the word Prefix or Suffix and select one of these two from the list.
3. Click the first [string] to activate the field.
4. Type the characters from the existing (source) schema that you want to replace. If you want to include
an underscore or other legal character from the original name in the string that you want to replace,
you must add it as part of the character string.
5. Click the second [string] to activate the field.
6. Type the characters you want to use in the target. These characters replace the original (source)
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 116

8 Customizing tasks
characters in the target.
7. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Convert schema name to uppercase
Use the convert to uppercase option to convert all of the letters in a schema name to upper case. For
example:
l
Schema_cat, becomes SCHEMA_CAT
l
schema_cat, becomes SCHEMA_CAT
l
sChEMa_Cat, becomes SCHEMA_CAT
To globally change the schema name to all uppercase
1. Select Convert schema name to uppercase.
2. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Convert schema name to lowercase
Use the convert to lowercase option to convert all of the letters in a schema name to lower case. For example:
l
Schema_cat, becomes schema_cat
l
SCHEMA_CAT, becomes schema_cat
l
sChEMa_Cat, becomes schema_cat
To globally change the schema name to all uppercase
1. Select Convert schema name to lowercase.
2. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Rename schema (Expression)
Use the Rename schema to [expression] option to change the name of all table schemas that you defined in
the Transformation scope (page 110) step to a different name. For example, if you have a schema called Human_
Resources and want to change all instances of this name to HR.
If you are using Oracle as your target endpoint, Qlik Replicate does not create a new schema.
Therefore, the schema name that is the result of replacing a prefix or suffix with a different string of
characters must exist in the Oracle target endpoint. If the resulting schema name does not exist, you
must create the schema in the Oracle endpoint before carrying out this task.
For more information, see the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
To globally change a schema name
1. Select Rename schema to [expression]
2. Click the button to the right of the Rename schema option to open the Expression Editor. For
information on how to use the Expression Editor, see Using the Expression Builder (page 137). Then go
to step 4.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 117

8 Customizing tasks
or
Click [expression] to activate the field and continue with step 3.
3. Type an SQLite expression or a string (in quotes) to rename the schema. For example:
l
"New_Schema"
l
’PREF_’||$SCHEMA_NAME_VAR||’_SUFF’
You can use the following variables in the SQLite expression:
l
$SCHEMA_NAME_VAR
l
$TABLE_NAME_VAR
l
$COLUMN_NAME_VAR
l
$COLUMN_DATATYPE_VAR
4. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Change table tablespace
If your transformation type is Change table tablespace, you can change the table tablespace on an Oracle
target. You can also set certain conditions that must exist in the source for the table tablespace to be
changed. These include schema name, table name and table tablespace name.
For more information, see the following topics:
l
Transformation type (page 108)
l
Transformation action (page 114)
Change index tablespace
If your transformation type is Change index tablespace, you can change the index tablespace on an Oracle
target. You can also set certain conditions that must exist in the source for the tablespace to be changed.
These include schema name, table name and index tablespace name.
For more information, see the following topics:
l
Transformation type (page 108)
l
Transformation action (page 114)
Rename Table
If your transformation type is Rename Table, you can do the following:
l
Rename table to (string) (page 119)
l
Add a prefix or suffix (page 119)
l
Remove a prefix or suffix (page 119)
l
Replace a prefix or suffix with different characters (page 119)
l
Convert table name to uppercase (page 120)
l
Convert table name to lowercase (page 120)
l
Rename table (expression) (page 120)
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 118

8 Customizing tasks
Rename table to (string)
Use the Rename table to: [string] option to change the name of all tables that you defined in the
Transformation scope (page 110) step to a different name. For example, if you have a table called EMPLOYEE
and want to change all instances of this name to EMP then enter the string EMP. You can enter any string in this
field.
Add a prefix or suffix
Use the Add a prefix or suffix option to add additional characters to the beginning or end of the table name
for all tables that fit the definition you created in the Transformation scope (page 110) step. For example, if the
table name is EMPLOYEES, you can add a suffix, such as TAR or _TAR to the table name for all tables with that
table name. In this case, the resulting table name will be EMPLOYEESTAR or EMPLOYEES_TAR.
To globally add a prefix or suffix:
1. Select Add <Prefix/Suffix> Insert Characters to matching table names.
2. Click the word Prefix or Suffix and select one of these two from the list.
3. Click [string] to activate the field.
4. Type the characters you want as the prefix or suffix. If you want to include an underscore or other legal
character to separate the prefix/suffix from the original name, you must add it as part of the character
string.
5. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Remove a prefix or suffix
Use the Remove a prefix or suffix option to remove a string of characters from the beginning or end of a
table name for all tables that fit the definition you created in the Transformation scope (page 110) step.
For example, you can use this option to remove the letters _REV from the table name for all tables with the
name EMPLOYEES. In this case the table name in the target will be EMPLOYEES.
To globally remove a prefix or suffix:
1. Select Remove <Prefix/Suffix> Insert Characters from matching table names.
2. Click the word Prefix or Suffix and select one of these two from the list.
3. Click [string] to activate the field.
4. Type the characters you want to remove. If you want to remove an underscore or other legal character
from the original name, you must add it as part of the character string.
5. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Replace a prefix or suffix with different characters
Use the Replace a prefix or suffix option to replace a string of characters with a different string of characters.
You determine whether to replace the characters at the beginning or end of a table name for all tables that fit
the definition you created in the Transformation scope (page 110) step.
For example, you can use this option to replace the letters _ORIG with _REPL in the table names for all tables
called EMPLOYEE_ORIG. In this case the table name in the target will be EMPLOYEE_REPL.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 119

8 Customizing tasks
To globally replace a prefix or suffix:
1. Select Replace <Prefix/Suffix> Insert Characters by Insert Characters for all matching schema
names.
2. Click the word Prefix or Suffix and select one of these two from the list.
3. Click the first [string] to activate the field.
4. Type the characters from the existing (source) schema that you want to replace. If you want to include
an underscore or other legal character from the original name in the string that you want to replace,
you must add it as part of the character string.
5. Click the second [sting] to activate the field.
6. Type the characters you want to use in the target. These characters replace the original (source)
characters in the target.
7. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Convert table name to uppercase
Use the convert to uppercase option to convert a table name to all upper case. For example:
l
Table_cat, becomes TABLE_CAT
l
table_cat, becomes TABLE_CAT
l
taBLe_Cat, becomes TABLE_CAT
To globally change the table name to all uppercase:
1. Select Convert table name to uppercase.
2. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Convert table name to lowercase
Use the convert to lowercase option to convert a table name to all lower case. For example:
l
Table_cat, becomes table_cat
l
TABLE_CAT, becomes table_cat
l
taBLe_Cat, becomes table_cat
To globally change the table name to all lowercase:
1. Select Convert table name to lowercase.
2. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Rename table (expression)
Use the Rename table to [expression] option to change the name of all tables that fit the definition you
created in the Transformation scope (page 110) step. For example, if you have a table called EMPLOYEE and
want to change all instances of this name as defined in the previous step it to EMP.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 120

8 Customizing tasks
To change the table name:
1. Select Rename table to: [expression]
2. Click the button to the right of the Rename table option to open the Expression Editor. For
information on how to use the Expression Editor, see Using the Expression Builder (page 137). Then go
to step 4.
or
Click [expression] to activate the field and continue with step 3.
3. Type an SQLite expression or a string (in quotes) to rename the table. For example:
l
"New_Table"
l
’PREF_’||$TABLE_NAME_VAR||’_SUFF’
You can use the following variables in the SQLite expression:
l
$SCHEMA_NAME_VAR
l
$TABLE_NAME_VAR
l
$COLUMN_NAME_VAR
l
$COLUMN_DATATYPE_VAR
Rename Column
If your transformation type is Rename Column, you can do the following:
l
Rename column to (string) (page 121)
l
Add a prefix or suffix (page 121)
l
Remove a prefix or suffix (page 122)
l
Replace a prefix or suffix with different characters (page 122)
l
Convert column name to uppercase (page 122)
l
Convert column name to lowercase (page 123)
l
Rename column (expression) (page 123)
Rename column to (string)
Use the Rename column to: [string] option to change the name of all columns that you defined in the
Transformation scope (page 110) step to a different name. For example, if you have a table called SALARY and
want to change all instances of this name to EMP then enter the string SAL. You can enter any string in this
field.
Add a prefix or suffix
Use the Add a prefix or suffix option to add additional characters to the beginning or end of the column
name for all columns that fit the definition you created in the Transformation scope (page 110) step. For
example, if the column name is SALARY, you can add a suffix, such as TAR or _TAR to the table name for all
tables with that table name. In this case, the resulting table name will be SALARYTAR or SALARY_TAR.
To globally add a prefix or suffix:
1. Select Add <Prefix/Suffix> Insert Characters to matching column names.
2. Click the word Prefix or Suffix and select one of these two from the list.
3. Click the [string] to activate the field.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 121

8 Customizing tasks
4. Type the characters you want as the prefix or suffix. If you want to include an underscore or other legal
character to separate the prefix/suffix from the original name, you must add it as part of the character
string.
5. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Remove a prefix or suffix
Use the Remove a prefix or suffix option to remove a string of characters from the beginning or end of a
column name for all columns that fit the definition you created in the Transformation scope (page 110) step.
For example, you can use this option to remove the letters _REV from the column name for all columns with
the name SALARY. In this case the column name in the target will be SALARY.
To globally remove a prefix or suffix:
1. Select Remove <Prefix/Suffix> Insert Characters from matching column names.
2. Click the word Prefix or Suffix and select one of these two from the list.
3. Click [string] to activate the field.
4. Type the characters you want to remove. If you want to remove an underscore or other legal character
from the original name, you must add it as part of the character string.
5. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Replace a prefix or suffix with different characters
Use the Replace a prefix or suffix option to replace a string of characters with a different string of characters.
You determine whether to replace the characters at the beginning or end of a column name for all columns
that fit the definition you created in the Transformation scope (page 110) step.
For example, you can use this option to replace the letters _ORIG with _REPL in the column names for all
columns called SALARY_ORIG. In this case the column name in the target will be SALARY_REPL.
To globally replace a prefix or suffix:
1. Select Replace <Prefix/Suffix> Insert Characters by Insert Characters for all matching schema
names.
2. Click the word Prefix or Suffix and select one of these two from the list.
3. Click the first [string] to activate the field.
4. Type the characters from the existing (source) column that you want to replace. If you want to include
an underscore or other legal character from the original name in the string that you want to replace,
you must add it as part of the character string.
5. Click the second [string] to activate the field.
6. Type the characters you want to use in the target. These characters replace the original (source)
characters in the target.
7. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Convert column name to uppercase
Use the convert to uppercase option to convert a column name to all upper case. For example:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 122

8 Customizing tasks
l
Column_cat, becomes COLUMN_CAT
l
column_cat, becomes COLUMN_CAT
l
coLUMnM_Cat, becomes COLUMN_CAT
To globally change the table name to all uppercase
1. Select Convert column name to uppercase.
2. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Convert column name to lowercase
Use the convert to lowercase option to convert a column name to all lower case. For example:
l
Column_cat, becomes column_cat
l
column_cat, becomes column_cat
l
coLUMnM_Cat, becomes column_cat
To globally change the column name to all lowercase:
1. Select Convert column name to lowercase.
2. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Rename column (expression)
Use the Rename column to [expression] option to change the name of all tables that fit the definition you
created in the Transformation scope (page 110) step. For instance, if you have a column called SALARY and
want to change it to SAL.
To change the column name:
1. Select Rename column to: [expression]
2. Click the button to the right of the Rename column option to open the Expression Editor. For
information on how to use the Expression Editor, see Using the Expression Builder (page 137). Then go
to step 4.
or
Click [expression] to activate the field and continue with step 3.
3. Type an SQLite expression or a string (in quotes) to rename the column. For example:
l
"New_Column"
l
’PREF_’||$COLUMN_NAME_VAR||’_SUFF’
You can use the following variables in the SQLite expression:
l
$SCHEMA_NAME_VAR
l
$TABLE_NAME_VAR
l
$COLUMN_NAME_VAR
l
$COLUMN_DATATYPE_VAR
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 123

8 Customizing tasks
Add column
When you add a column to multiple tables, you must provide a name, define the data type for the column and
define the data that the column contains. The column that you define here is added to all tables that fit the
definition you created in step Transformation scope (page 110).
The following describes the information you must enter in the transformation rule page for adding a column.
l
Column name: Click the [string] to activate the field. Type the name for the column in the field. A
column with this name is added to all tables that fit the definition you created in step Transformation
scope (page 110).
l
Add to Primary Key: Select to add the column to the target tables' Primary Key.
l
Expression: Click the button to the right of this field to open the Expression Builder or type an
expression using SQLite operators to define the data in the column.
For information on how to use the Expression Editor to create an expression, see Using the Expression
Builder (page 137).
For more information on creating expressions, see Creating an expression for transformations (page 91)
and Using SQLite syntax with transformations (page 91).
l
Set target data type to: Click the drop-down for a list of data types and select a new data type from
the drop-down list. Make sure that the data type you select is compatible with the data in that column.
When BYTES, STRING or WSTRING is selected, specify a Length as well. When NUMERIC is selected,
specify a Precision and Scale as well.
l
Subtype: When CLOB, NCLOB, STRING, or WSTRING data types are selected, you can also set a data
subtype. Select either JSON or XML from the Subtype drop-down list. Make sure that the data in the
new column will be compatible with the selected subtype. The default is Regular, which means that
the regular data type will be used without a subtype.
For a description of the available data types and for a list of endpoints supported by Qlik Replicate,
and for information about data type mapping from source endpoints to Qlik Replicate data types, see
the Qlik Replicate online help
Drop Column
This option does not require a transformation rule. For this option you complete the Global transformation
rule after the Transformation scope (page 110) step.
Convert data type
The data type that you define in this step is applied to all columns and tables that fit the definition you
created in the Transformation scope (page 110) step. Make sure that the data type you select is compatible
with the data in the columns you defined.
l
Set target data type to - If you change the target value type (e.g. string to numeric), you may also
need to change the data type of the target columns as well.
For the BYTES, STRING, and WSTRING data types, you can optionally specify the Length as well. If you
leave the default value ("0"), Replicate will calculate the data type length based on the source column
definition. You can also set the length using an expression. When you click the fx button to the right of
the Length field, the Expression Builder opens showing the Metadata tab. For an explanation of the
variables in this tab, see Metadata (Global transformations only) (page 143).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 124

8 Customizing tasks
Example:
The following expression multiplies the modified data type length by two.
$AR_M_MODIFIED_DATATYPE_LENGTH * 2
For the NUMERIC data type, you can optionally set the Precision and Scale. If you leave the default
value ("0"), Replicate will calculate the precision and/or scale based on the source column value.
l
Subtype: When CLOB, NCLOB, STRING, or WSTRING data types are selected, you can also set a data
subtype. Select either JSON or XML from the Subtype drop-down list. Make sure that the new data in
the column will be compatible with the selected subtype. The default is Regular, which means that the
regular data type will be used without a subtype.
For a description of the available data types and for a list of endpoints supported by Qlik Replicate, and for
information about data type mapping from source endpoints to Qlik Replicate data types, see the Qlik
Replicate online help
Replace column value
Use the Replace column value transformation to replace the values in the source columns (set in the
Transformation scope) with different values in the corresponding target columns.
The following options are available:
l
Replace target value with - Create an expression for replacing the value in the source column values
with a different value in the target columns. When you click the fx button to the right of the field, the
Expression Builder opens showing the Data tab. For an explanation of the variables in this tab, see
Data (global transformations only) (page 142).
Example:
The following expression appends the string "_new" to the original source column values.
$AR_M_SOURCE_COLUMN_DATA || '_new'
l
Set target data type to - If you change the target value type (e.g. string to numeric), you may also
need to change the data type of the target columns as well.
For the BYTES, STRING, and WSTRING data types, you can optionally specify the Length as well. If you
leave the default value ("0"), Replicate will calculate the data type length based on the source column
definition. You can also set the length using an expression. When you click the fx button to the right of
the Length field, the Expression Builder opens showing the Metadata tab. For an explanation of the
variables in this tab, see Metadata (Global transformations only) (page 143).
Example:
The following expression multiplies the modified data type length by two.
$AR_M_MODIFIED_DATATYPE_LENGTH * 2
For the NUMERIC data type, you can optionally set the Precision and Scale. If you leave the default
value ("0"), Replicate will calculate the precision and/or scale based on the source column value.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 125

8 Customizing tasks
l
Subtype: When CLOB, NCLOB, STRING, or WSTRING data types are selected, you can also set a data
subtype. Select either JSON or XML from the Subtype drop-down list. Make sure that the new data in
the column will be compatible with the selected subtype. The default is Regular, which means that the
regular data type will be used without a subtype.
See also: Using the Expression Builder (page 137)
Rename Change Table
This transformation is only available when the Store Changes replication option is turned on.
If your transformation type is Rename Change Table, you can do the following:
l
Rename Change Table to (string) (page 126)
l
Add a prefix or suffix (page 126)
l
Remove a prefix or suffix (page 127)
l
Replace a prefix or suffix with different characters (page 127)
l
Convert Change Table name to uppercase (page 127)
l
Convert Change Table name to lowercase (page 128)
l
Rename Change Table (expression) (page 128)
l
Globally renaming a Change Table will override the Change Table suffix defined in the task
settings.
l
The Change Table name must be different from the source table names. Otherwise, a table
error will occur.
Rename Change Table to (string)
Use the Rename Change Table to: [string] option to change the name of all Change Tables that you defined
in the Transformation scope (page 110) step to a different name. For example, if you have a Change Table
called EMPLOYEE and want to change all instances of this name to EMP then enter the string EMP. You can enter
any string in this field.
Add a prefix or suffix
Use the Add a prefix or suffix option to add additional characters to the beginning or end of the Change
Table name for all Change Tables that fit the definition you created in the Transformation scope (page 110)
step. For example, if the Change Table name is EMPLOYEES, you can add a suffix, such as TAR or _TAR to the
Change Table name for all Change Tables with that name. In this case, the resulting Change Table name will
be EMPLOYEESTAR or EMPLOYEES_TAR.
To globally add a prefix or suffix:
1. Select Add <Prefix/Suffix> <String> to matching Change Table names.
2. Click the word Prefix or Suffix and select one of these two from the list.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 126

8 Customizing tasks
3. Click [string] to activate the field.
4. Type the characters you want as the prefix or suffix. If you want to include an underscore or other legal
character to separate the prefix/suffix from the original name, you must add it as part of the character
string.
5. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Remove a prefix or suffix
Use the Remove a prefix or suffix option to remove a string of characters from the beginning or end of a
Change Table name for all Change Tables that fit the definition you created in the Transformation scope (page
110) step.
For example, you can use this option to remove the letters _REV from the Change Table name for all Change
Tables with the name EMPLOYEES. In this case the Change Table name in the target will be EMPLOYEES.
To globally remove a prefix or suffix:
1. Select Remove <Prefix/Suffix> <String> from matching Change Table names.
2. Click the word Prefix or Suffix and select one of these two from the list.
3. Click [string] to activate the field.
4. Type the characters you want to remove. If you want to remove an underscore or other legal character
from the original name, you must add it as part of the character string.
5. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Replace a prefix or suffix with different characters
Use the Replace a prefix or suffix option to replace a string of characters with a different string of characters.
You determine whether to replace the characters at the beginning or end of a Change Table name for all
Change Tables that fit the definition you created in the Transformation scope (page 110) step.
For example, you can use this option to replace the letters _ORIG with _REPL in the Change Table names for all
Change Tables called EMPLOYEE_ORIG. In this case the Change Table name in the target will be EMPLOYEE_REPL.
To globally replace a prefix or suffix:
1. Select Replace <Prefix/Suffix> <String> by <String> for all matching Change Table names.
2. Click the word Prefix or Suffix and select one of these two from the list.
3. Click the first [string] to activate the field.
4. Type the characters from the existing (source) schema that you want to replace. If you want to include
an underscore or other legal character from the original name in the string that you want to replace,
you must add it as part of the character string.
5. Click the second [sting] to activate the field.
6. Type the characters you want to use in the target. These characters replace the original (source)
characters in the target.
7. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Convert Change Table name to uppercase
Use the convert to uppercase option to convert a Change Table name to all upper case. For example:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 127

8 Customizing tasks
l
Table_cat, becomes TABLE_CAT
l
Change Table_cat, becomes TABLE_CAT
l
taBLe_Cat, becomes TABLE_CAT
To globally change the Change Table name to all uppercase:
1. Select Convert Change Table name to uppercase.
2. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Convert Change Table name to lowercase
Use the convert to lowercase option to convert a Change Table name to all lower case. For example:
l
Table_cat, becomes Change Table_cat
l
TABLE_CAT, becomes Change Table_cat
l
taBLe_Cat, becomes Change Table_cat
To globally change the Change Table name to all lowercase:
1. Select Convert Change Table name to lowercase.
2. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Rename Change Table (expression)
Use the Rename Change Table to [expression] option to change the name of all Change Tables that fit the
definition you created in the Transformation scope (page 110) step. For example, if you have a Change Table
called EMPLOYEE and want to change all instances of this name as defined in the previous step it to EMP.
To change the Change Table name:
1. Select Rename Change Table to: [expression]
2. Click the button to the right of the Rename Change Table option to open the Expression Editor. For
information on how to use the Expression Editor, see Using the Expression Builder (page 137). Then go
to step 4.
or
Click [expression] to activate the field and continue with step 3.
3. Type an SQLite expression or a string (in quotes) to rename the table. For example:
l
"New_Change_Table_Name"
l
’PREF_’||$AR_M_SOURCE_TABLE_NAME||’_SUFF’
You can use the following metadata in the SQLite expression:
l
$AR_M_SOURCE_COLUMN_DATATYPE
l
$AR_M_SOURCE_COLUMN_NAME
l
$AR_M_SOURCE_SCHEMA
l
$AR_M_SOURCE_TABLE_NAME
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 128

8 Customizing tasks
Rename Change Table schema
This transformation is only available when the Store Changes replication option is turned on.
If your transformation type is Rename Change Table schema, you can do the following:
l
Rename Change Table schema to (string) (page 129)
l
Add a prefix or suffix (page 129)
l
Remove a prefix or suffix (page 129)
l
Replace a prefix or suffix with different characters (page 130)
l
Convert Change Table schema name to uppercase (page 130)
l
Convert Change Table schema name to lowercase (page 130)
l
Rename Change Table schema (expression) (page 131)
Rename Change Table schema to (string)
Use the Rename Change Table schema to: [string] option to change the name of all Change Table schemas
that you defined in the Transformation scope (page 110) step to a different name. For example, if you have a
Change Table schema called EMPLOYEE and want to change all instances of this name to EMP then enter the
string EMP. You can enter any string in this field.
Add a prefix or suffix
Use the Add a prefix or suffix option to add additional characters to the beginning or end of the Change
Table schema name for all tables that fit the definition you created in the Transformation scope (page 110)
step. For example, if the Change Table schema name is EMPLOYEES, you can add a suffix, such as TAR or _TAR to
the Change Table schema name for all Change Table schemas with that Change Table schema name. In this
case, the resulting Change Table schema name will be EMPLOYEESTAR or EMPLOYEES_TAR.
To globally add a prefix or suffix:
1. Select Add <Prefix/Suffix> Insert Characters to matching Change Table schema names.
2. Click the word Prefix or Suffix and select one of these two from the list.
3. Click [string] to activate the field.
4. Type the characters you want as the prefix or suffix. If you want to include an underscore or other legal
character to separate the prefix/suffix from the original name, you must add it as part of the character
string.
5. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Remove a prefix or suffix
Use the Remove a prefix or suffix option to remove a string of characters from the beginning or end of a
Change Table schema name for all tables that fit the definition you created in the Transformation scope (page
110) step.
For example, you can use this option to remove the letters _REV from the Change Table schema name for all
Change Table schemas with the name EMPLOYEES. In this case the Change Table schema name in the target
will be EMPLOYEES.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 129

8 Customizing tasks
To globally remove a prefix or suffix:
1. Select Remove <Prefix/Suffix> <String> from matching Change Table schema names.
2. Click the word Prefix or Suffix and select one of these two from the list.
3. Click [string] to activate the field.
4. Type the characters you want to remove. If you want to remove an underscore or other legal character
from the original name, you must add it as part of the character string.
5. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Replace a prefix or suffix with different characters
Use the Replace a prefix or suffix option to replace a string of characters with a different string of characters.
You determine whether to replace the characters at the beginning or end of a Change Table schema name for
all tables that fit the definition you created in the Transformation scope (page 110) step.
For example, you can use this option to replace the letters _ORIG with _REPL in the Change Table schema
names for all Change Table schemas called EMPLOYEE_ORIG. In this case the Change Table schema name in the
target will be EMPLOYEE_REPL.
To globally replace a prefix or suffix:
1. Select Replace <Prefix/Suffix> <String> by <String> for all matching schema names.
2. Click the word Prefix or Suffix and select one of these two from the list.
3. Click the first [string] to activate the field.
4. Type the characters from the existing (source) Change Table schema name that you want to replace. If
you want to include an underscore or other legal character from the original name in the string that
you want to replace, you must add it as part of the character string.
5. Click the second [sting] to activate the field.
6. Type the characters you want to use in the target. These characters replace the original (source)
characters in the target.
7. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Convert Change Table schema name to uppercase
Use the convert to uppercase option to convert a Change Table schema name to all upper case. For example:
l
Table_cat, becomes TABLE_CAT
l
table_cat, becomes TABLE_CAT
l
taBLe_Cat, becomes TABLE_CAT
To globally change the Change Table schema name to all uppercase:
1. Select Convert Change Table schema name to uppercase.
2. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Convert Change Table schema name to lowercase
Use the convert to lowercase option to convert a Change Table schema name to all lower case. For example:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 130

8 Customizing tasks
l
Table_cat, becomes table_cat
l
TABLE_CAT, becomes table_cat
l
taBLe_Cat, becomes table_cat
To globally change the Change Table schema name to all lowercase:
1. Select Convert Change Table schema name to lowercase.
2. Click Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Rename Change Table schema (expression)
Use the Rename Change Table schema to [expression] option to change the name of all tables that fall
within the scoped you defined in the Transformation scope (page 110) step. For example, if you have a Change
Table schema called EMPLOYEE and want to change all instances of the Change Table schema name as defined
in the previous step to EMP.
To rename the Change Table schema:
1. Select Rename Change Table schema to.
2. Click the button to the right of the Rename Change Table schema to option to open the Expression
Editor. For information on how to use the Expression Editor, see Using the Expression Builder (page
137).
or
Click [expression] to activate the field and continue with step 3.
3. Type an SQLite expression or a string (in quotes) to rename the table. For example:
l
"New_Change_Table_Schema"
l
’PREF_’||$AR_M_SOURCE_SCHEMA||’_SUFF’
You can use the following metadata in the SQLite expression:
l
$AR_M_SOURCE_COLUMN_DATATYPE
l
$AR_M_SOURCE_COLUMN_NAME
l
$AR_M_SOURCE_SCHEMA
l
$AR_M_SOURCE_TABLE_NAME
4. When you're done, click Next to see a summary of your rule and replace the default name and
description, or Finish to add the rule to the Global Rules list.
Starting the Global Filter Rules wizard
You define global filters using the Global Filter Rules wizard.
To start the Global Filters wizard:
1. Open the task for which you want to create a global transformations or a global filter.
You can click View Task above the Tasks list or double-click the task.
2. If you are not in the Designer mode, click Designer at the top right of the screen.
For more information on the Designer mode, see Designer mode (page 207).
3. In Designer mode, click Global Rules.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 131

8 Customizing tasks
The Global Rules window opens.
4. Click the New Rule toolbar button and select Filter.
The New Filter Rule wizard opens.
5. Enter the information to define a global transformation rule. The first step is selecting the Filter type
(page 132).
Filter type
In the Filter Type screen of the New Filter Rule wizard, you define the type of filtering you want to be
performed.
l
Filter by columns - Only include records that match specific column data. For example, only include
records where Birth Date is later than 02-Feb-2021.
Filtering by columns containing changeable values (e.g. Age) may result in inconsistent data
on the target.
l
Filter by record attributes - Only include records that match specific record attributes. For example,
only include UPDATE or INSERTED records.
Filter scope
In the Filter Scope screen of the New Filter Rule wizard, you define which tables will be filtered. For example,
you can limit the filter to all tables that contain the word SALARY as part of their name.
The options displayed in this screen depend on selected filter type.
Scope options when filtering by columns
The following table describes the options that are available when filtering by columns.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 132

8 Customizing tasks
Option Description
Schema
name is like
%
Leave the % sign to apply the rule to all source schemas (the default).
Alternatively, enter a custom string. The rule will only be applied to columns in schemas
that match the specified string.
For example, enter HR to include only columns that belong to schema HR.
You can use the % symbol as a wildcard. For example, specifying H% will include all columns
in tables that belong to schemas beginning with the letter H, such as HR, HELLO, or HQ.
The % wildcard can be used in any position. For example, if you use it at the beginning (%H),
then the rule will be applied to all columns in schemas that end with the letter "H". The %
symbol can also be used in the middle of a string.
If you are using an Oracle target, you must enter a schema that exists on the
target endpoint. Qlik Replicate does not create new schemas on an Oracle
endpoint. If you want to use a new schema for the target, create the schema on
the Oracle endpoint before running the task. For more information, see the topic
"Configuring an Oracle database as a Qlik Replicate Target" in the Qlik Replicate
User and Reference Guide.
Table name
is like %
Leave the % sign to apply the rule to all source tables (the default).
Alternatively, enter a custom string. The rule will only be applied to columns in tables that
match the specified string.
You can use the % symbol as a wildcard. For example, specifying J% will include all columns
in tables with names beginning with the letter J, such as JOBS, JOBS_HISTORY, or
JACKSONVILLE.
The % wildcard can be used in any position. For example, if you use it at the beginning (%H),
then the rule will be applied to all columns in tables that end with the letter "H". The %
symbol can also be used in the middle of a string.
Column
name is like
%
Leave the % sign to apply the rule to all source columns (the default).
Alternatively, enter a custom string. The rule will only be applied to columns that match
the specified string.
You can use the % symbol as a wildcard. For example, specifying N% will include all columns
with names beginning with the letter N, such as NAME, NAME_FIRST, or NAME_LAST.
The % wildcard can be used in any position. For example, if you use it at the beginning (%n),
then the rule will be applied to all columns that end with the letter "n". The % symbol can
also be used in the middle of a string.
Columns filtering scope
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 133

8 Customizing tasks
Option Description
Data type is Optionally, select a specific data type from the drop-down list. Make sure the data type you
select is compatible with the data in that column.
For a description of Qlik Replicate data types, information about data type mapping from
the native endpoint to Qlik Replicate, or for a list of endpoints supported by Qlik Replicate,
see the Qlik Replicate User and Reference Guide.
Scope
expression
Click Advanced options to define a scope expression using the expression builder.
Scope options when filtering by record attributes
The following table describes the options that are available when filtering by record attributes.
Option Description
Schema
name is like
%
Leave the % sign to apply the rule to all source schemas (the default).
Alternatively, enter a custom string. The rule will only be applied to columns in schemas
that match the specified string.
For example, enter HR to include only columns that belong to schema HR.
You can use the % symbol as a wildcard. For example, specifying H% will include all columns
in tables that belong to schemas beginning with the letter H, such as HR, HELLO, or HQ.
The % wildcard can be used in any position. For example, if you use it at the beginning (%H),
then the rule will be applied to all columns in schemas that end with the letter "H". The %
symbol can also be used in the middle of a string.
If you are using an Oracle target, you must enter a schema that exists on the
target endpoint. Qlik Replicate does not create new schemas on an Oracle
endpoint. If you want to use a new schema for the target, create the schema on
the Oracle endpoint before running the task. For more information, see the topic
"Configuring an Oracle database as a Qlik Replicate Target" in the Qlik Replicate
User and Reference Guide.
Record attributes filtering scope
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 134

8 Customizing tasks
Option Description
Table name
is like %
Leave the % sign to apply the rule to all source tables (the default).
Alternatively, enter a custom string. The rule will only be applied to columns in tables that
match the specified string.
You can use the % symbol as a wildcard. For example, specifying J% will include all columns
in tables with names beginning with the letter J, such as JOBS, JOBS_HISTORY, or
JACKSONVILLE.
The % wildcard can be used in any position. For example, if you use it at the beginning (%H),
then the rule will be applied to all columns in tables that end with the letter "H". The %
symbol can also be used in the middle of a string.
Scope
expression
Click Advanced options to define a scope expression using the expression builder.
After defining the filter scope, click Next to proceed to the Transformation action (page 114) screen.
Filter action
In the Filter action screen, you create an expression for selecting records based on their column data (when
defining a Filter by columns) or based on their attributes (when defining a Filter by record attributes). Only
records that fall within the Filter scope (page 132) will be affected.
Filter action for columns
Use the Expression Builder to define a record selection expression based on column data. Click the fx button
to open the Expression Builder.
The Expression Builder opens displaying the Data tab. Define an expression using the available parameters.
Example (Assumes that "Age" is the column being filtered):
Create the following expression to select all records for citizens between the age of 50 and 80.
$AR_M_SOURCE_COLUMN_DATA > '60' AND $AR_M_SOURCE_COLUMN_DATA < '70'
Filter action for record attributes
Use the Expression Builder to define a record selection expression based on record attributes. Click the fx
button to open the Expression Builder.
The Expression Builder opens displaying the Headers tab. Define an expression using the available Header
columns.
Header columns are not relevant for Full Load tasks. They are only relevant when the task's Apply
Changes or Store Changes replication options are enabled.
Example:
Create the following expression to select UPDATED records only:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 135

8 Customizing tasks
$AR_H_OPERATION='UPDATE'
See also: Using the Expression Builder (page 137)
Managing global rules
The Global Rules window lists the names and descriptions of all rules that are defined for the Qlik Replicate
instance you are working with. This is where you go to edit, delete, reposition, or activate/deactivate rules.
Editing global rules
You cannot change the name of a transformation rule
To edit a global rule:
1. In the Global Rules window, select the rule you want to edit.
2. Click the Edit button or double-click the rule.
The Edit Existing Transformation Rule wizard or Edit Existing Filter Rule wizard opens.
3. Make any changes you need in the wizard.
For information on how to configure a global transformation, see the following topics:
l
Transformation type (page 108)
l
Transformation scope (page 110)
l
Transformation action (page 114)
For information on how to configure a global filter, see the following topics:
l
Filter type (page 132)
l
Filter scope (page 132)
l
Filter action (page 135)
Deleting global rules
To delete a global rule:
1. In the Global Rules window, select the rule you want to delete.
2. Click the Delete button.
3. When prompted for confirmation, click OK.
The rule is removed from the list and deleted from the system.
Positioning global rules
Rules are applied in the order they appear. To prevent conflicts therefore, ensure that rules are arranged in a
logical order. You can use the up/down arrows to rearrange the rule order.
Activating or deactivating global rules
To activate or deactivate a rule, select or clear the check box in the Activate column as needed.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 136

8 Customizing tasks
8.3 Using the Expression Builder
The Qlik Replicate Expression Builder provides an easy way to build an expression. It provides you with easy
access to the required elements for your expression without having to type out any information manually. You
access the Expression Builder through the dialog boxes where you define Filters, Defining transformations for a
single table/view (page 84), and Global Transformations when you do any of the following:
l
Rename Schema (page 114)
l
Rename Table (page 118)
l
Rename Column (page 121)
The following topics describe the Expression Builder:
l
Overview of the Expression Builder (page 137)
l
Build an expression (page 139)
l
Parse an expression (page 140)
l
Test an expression (page 140)
l
Using elements in the Expression Builder (page 142)
Overview of the Expression Builder
The following is an example of the Expression Builder with its four main parts shown. The Expression Builder
you are working with may look different depending on whether you want to build an expression for a filter, a
transformation, or a global transformation.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 137

8 Customizing tasks
Expression Builder for filters, transformations, and global transformations
The following sections describe the tasks you can perform in each part of the Expression Builder:
l
Elements Pane (on the left): This pane contains elements that you can add to an expression. Select
elements and move them into the Expression Builder box to create the expression. For more
information, see Build an expression (page 139).
The Elements Pane contains the following tabs:
l
Metadata (available only when working with Global transformations)
l
Input (available only when working with transformations or filters)
l
Header (for Global transformations, this tab is available only when you select Add Column)
l
Variables
l
Operators
l
Functions
For more information on these elements, see Using elements in the Expression Builder (page 142).
l
Build Expression Panel: The Build Expression Panel is where you put together the expression you are
building. You move elements, such as columns or operators into the box. You can also type all or part
of an expression in this box.
For more information, see Build an expression (page 139).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 138

8 Customizing tasks
l
Parse Expression Panel: This panel displays the parameters for the expression. After you build the
expression, click Parse Expression to list the expression parameters. You can then enter a value or
argument for each of the parameters. For more information, see Parse an expression (page 140).
The top part of the Expression panel contains the Operator toolbar. This toolbar contains the most
common operators. Click the operator you want to use to add it to the expression. You can also add
operators from the Element Pane, Operators tab.
l
Test Expression Panel: This panel displays the results of a test that you can run after you provide
values to each of the parameters in your expression. For more information, see Test an expression
(page 140).
Build an expression
The first step in using the expression builder is to build an expression. The expression that you build is
displayed in the top section of the right pane. You can open the Expression when:
l
You define Defining transformations for a single table/view (page 84) for a single table.
l
You define Filters for a single table.
l
You use the Global transformations dialog box to Rename Schema (page 114), Rename Table (page
118), Rename Column (page 121), or Add column (page 124).
Note: To add operators to your expression, you can use the Operator tab in the Element pane or the Operator
buttons at the top of the Build Expression panel or any combination of these. See Operators (page 144) and
Operator toolbar (page 139).
For example, to create an expression that will combine the first name and last name, do the following:
1. In the Input Columns tab add the FIRST_NAME column to the Build Expression box.
2. Click the concatenate (||) operator from the Operator bar at the top of the Build Expression box.
3. In the Input Columns tab add the LAST_NAME column into the Build Expression box.
To build an expression:
1. In the Elements Pane, select any element you want to include in your expression. For information on
the elements you can use in an expression, see Functions (page 147).
2. Add an element to the Build Expression panel by selecting it and then clicking the arrow to the right
of the element.
3. Continue to add elements as needed.
Operator toolbar
The Operator toolbar is above the Build Expression box. It contains the most common operators so you can
easily add them to an expression.
The following operators are available in the Operator toolbar: addition, subtraction, multiplication, division,
percentage, not equal, equal, concatenate, AND, OR.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 139

8 Customizing tasks
For information on these operators, see Operators (page 144).
To use the Operator toolbar:
1. Click the place in the Build Expression box where you want to add the operator.
2. Click the operator you want to add. It is added to the expression.
Parse an expression
You can parse an expression to determine its parameters and to determine whether the expression is valid.
To parse an expression:
1. In the Expression Builder window, create an expression as described in Build an expression (page 139).
2. Click Parse Expression.
If the expression is not valid, an error message is written in red at the bottom of the Expression Builder
window.
If the expression is valid, the expression parameters are displayed in the Parameter column in the
Parse Expression section. See the figure under Test an expression (page 140).
3. Type a valid value for each of the parameters in the Value column to Test an expression (page 140).
For example, type John for the FIRST_NAME and Smith for the LAST_NAME in the Value column. Once
you type in values, you can Test an expression (page 140).
Test an expression
You can use the Qlik Replicate Test procedure to display the results of a test expression. The following figure is
an example of a built expression that is evaluated and contains a test result.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 140

8 Customizing tasks
3. View the parameters that are displayed. If your expression is not valid, an error message is displayed.
See Parse an expression (page 140).
4. Type values for each parameter then click Test to see the calculated expression.
For example, type John for FIRST_NAME and Smith for LAST_NAME. The result displayed is JohnSmith.
If you want a space between the words add it to the end of the FIRST_NAME value or the beginning of
the LAST_NAME value.
Note: Testing calls to the source_lookup and target_lookup functions is not supported.
Using elements in the Expression Builder
You can use the following types of elements to build expressions for transformations, filters, and global
transformations. Select the appropriate tab to select the elements.
l
Columns (transformations and filters only) (page 142)
l
Data (global transformations only) (page 142)
l
Metadata (Global transformations only) (page 143)
l
Variables (page 143)
l
Operators (page 144)
l
Functions (page 147)
l
Headers (page 159)
l
User-defined transformations (page 163)
Data (global transformations only)
In this tab, you can create an expression that leverages modified source column data and/or the original
source column data. Modified column data is data that has been replaced or modified using a global
transformation (e.g. Replace column value) whereas the original source column data is the data as it appears
in the source database.
The following options are available:
l
$AR_M_MODIFIED_COLUMN_DATA - Use to specify column data that has been replaced or modified
using a global transformation.
l
$AR_M_SOURCE_COLUMN_DATA - Use to specify the original column data.
Example:
For a source column called "Age", the following expression can be defined to exclude all records for
citizens between the age of 50 and 80.
$AR_M_SOURCE_COLUMN_DATA > '50' AND $AR_M_SOURCE_COLUMN_DATA < '80'
Columns (transformations and filters only)
This tab lists the columns for the table you are working with. The table you are working with is the table you
selected when you opened the Table Settings dialog box.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 142

8 Customizing tasks
Expressions containing a condition for a NUMBER exceeding 19 digits are not valid. For example, the
following expression is not valid:
case when $ID==12345678910111213149 then '1' else '0' end
Metadata (Global transformations only)
The Metadata tab contains the following variables that you can use in an expression. Variables with MODIFIED
in their name can be used to specify metadata that has been replaced or modified using a global
transformation (such as Convert data type) whereas variables names without MODIFIED can be used to
specify the original metadata as it is defined in the source database.
l
AR_M_MODIFIED_SCHEMA - The modified source schema name.
l
AR_M_MODIFIED_TABLE_NAME - The modified source table name.
l
AR_M_MODIFIED_COLUMN_NAME - The modified column name in the source table.
l
AR_M_MODIFIED_COLUMN_SUBTYPE_NAME - The modified data type subtype of a column in the source
table.
l
AR_M_MODIFIED_DATATYPE_NAME - The modified data type of a column in the source table.
l
AR_M_MODIFIED_DATATYPE_LENGTH - The modified data type length of a column in the source table.
l
AR_M_MODIFIED_DATATYPE_PRECISION - The modified data type precision of a column in the source
table.
l
AR_M_MODIFIED_DATATYPE_SCALE - The modified data type scale of a column in the source table.
l
AR_M_SOURCE_SCHEMA - The name of the source schema.
l
AR_M_SOURCE_TABLE_NAME - The name of the source table.
l
AR_M_SOURCE_COLUMN_NAME - The name of a column in the source table.
l
AR_M_SOURCE_DATATYPE_NAME - The data type of a column in the source table.
l
AR_M_SOURCE_DATATYPE_LENGTH - The data type length of a column in the source table.
l
AR_M_SOURCE_DATATYPE_PRECISION - The data type precision of a column in the source table.
l
AR_M_SOURCE_DATATYPE_SCALE - The data type scale of a column in the source table.
Example: Using metadata variables in the Rename Column transformation
To rename all columns named "product" to "source_schema.table_name", enter "product"in the Column
name is like field (in the Transformation scope (page 110) screen) and then enter the following expression in
the Rename column to field (in the Transformation action (page 114) screen):
$AR_M_SOURCE_SCHEMA ||"."|| $AR_M_SOURCE_TABLE_NAME
Variables
Your expression can contain any of the variables (which will be replaced during runtime) described in the table
below.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 143
8 Customizing tasks
Variable Name Description Data Type
AR_V_HOST_NAME The host name of the machine on which Qlik Replicate Server is
installed.
STRING (50)
AR_V_SOURCE_
NAME
The logical name of the source endpoint defined in the endpoint
settings.
STRING (50)
AR_V_TARGET_
NAME
The logical name of the target endpoint defined in the endpoint
settings.
STRING (50)
AR_V_TASK_NAME The task name. STRING (50)
AR_V_TASK_UUID A unique string (Universal Unique Identifier) that identifies the task. STRING (50)
AR_V_RELOAD_
TIME
The time the source tables were reloaded. DATETIME
(6)
AR_V_START_TIME The time the task started. DATETIME
(6)
Variables
Operators
The sections below describe the SQLite operators you can use to build an expression with the Expression
builder. The Expression builder divides the operators into the following categories:
l
Strings (page 144)
l
Logical (page 145)
l
Mathematical (page 147)
With the exception of table-level transformations, all operator symbols must be preceded by a space
and followed by a space. For example, the expression for concatenating a first and last name should
be specified like this:
FIRST_NAME || LAST_NAME
And not like this:
FIRST_NAME||LAST_NAME
Strings
You can use the following string:
||
Name: Concatenate strings.
Examples:
FIRST_NAME || LAST_NAME
PHONE_NUMBER || <Office Only> (adds the string Office Only to the telephone number).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 144

8 Customizing tasks
Logical
The following table describes the logical SQLite operators used by the Qlik Replicate Expression Builder.
Operator Description
!= or <> Is not equal to
$SALARY!=100000
IS Is the same as
$HIRE_DATE IS 2014-09-29
IS functions the same as = unless one or both of the operands are NULL. In this case, if both
operands are NULL, then the IS operator evaluates to 1 (true). If one operand is NULL and
the other is not, then the IS operator evaluates to 0 (false).
IS NOT Is not the same as
$HIRE_DATE IS NOT 2014-09-29
IS NOT functions the same as != unless one or both of the operands are NULL. In this case, if
both operands are NULL, the IS NOT operator evaluates to 0 (false). If one operand is NULL
and the other is not, then the IS NOT operator evaluates to 1 (true).
IN The IN operator takes a single scalar operand on the left and a vector operand on the right
formed by an explicit list of zero or more scalars or by a single subquery. When the right
operand of an IN operator is a subquery, the subquery must have a single result column.
When the right operand is an empty set, the result of IN is false regardless of the left
operand and even if the left operand is NULL.
SQLite allows the parenthesized list of scalar values on the right-hand side of an IN operator
to be an empty list but most other SQL endpoint engines and the SQL92 standard require
the list to contain at least one element.
LIKE The LIKE operator does a pattern matching comparison. The operand to the right of the LIKE
operator contains the pattern and the left operand contains the string to match against the
pattern. A percent symbol ("%") in the LIKE pattern matches any sequence of zero or more
characters in the string. An underscore ("_") in the LIKE pattern matches any single
character in the string. Any other character matches itself or its lower/upper case equivalent.
(By default SQLite only understands upper/lower case for ASCII characters. The LIKE
operator is case sensitive by default for unicode characters that are beyond the ASCII range.
For example, the expression 'a' LIKE 'A' is TRUE but 'æ' LIKE 'Æ' is FALSE.)
LIKE can be preceded by the NOT keyword.
Logical operators
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 145

8 Customizing tasks
Operator Description
CASE Evaluates a list of conditions and returns one of multiple possible result expressions.
Example 1:
WHEN $NEWEST = 'Y' THEN '1' ELSE '0' END
Example 2:
case length($month)
when 2 then $year||$month
when 1 then $year||0||$month end
GLOB The GLOB operator acts in the same way as the LIKE operator but uses the UNIX file
globbing syntax for its wildcards. GLOB is case sensitive.
GLOB can be preceded by the NOT keyword to invert the sense of the test. The infix GLOB
operator is implemented by calling the function glob(Y,X) and can be modified by overriding
that function.
MATCH The MATCH operator is a special syntax for the match() application-defined function. The
default match() function implementation raises an exception and is not really useful for
anything. But extensions can override the match() function with more helpful logic.
REGEXP The REGEXP operator is a special syntax for the regexp() user function. No regexp() user
function is defined by default and so use of the REGEXP operator will normally result in an
error message.
AND Both operands are true.
$MANAGER_ID AND EMPLOYEE ID >100
OR Either operand is true.
$MANAGER_ID OR EMPLOYEE ID >100
<< Bitwise shift left.
x << n
A bitwise shift to the left of x by n bits.
>> Bitwise shift right.
x >> n
A bitwise shift to the right of x by n bits.
& Unary and
| Unary or
< Is less than.
$SALARY<100000
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 146

8 Customizing tasks
Operator Description
<= Is less than or equal to
$SALARY<=100000
> Is greater than
$SALARY>100000
>= Is more than or equal to
$SALARY>=100000
= or == Is equal to
$SALARY=100000
Mathematical
The following table describes the mathematical SQLite operators used by the Expression Builder.
Operator Description
+ Adds two values together.
DEPARTMENT_ID+100 (adds 100 to each ID number). Any column used in an expression with
this operator must be a numeric data type.
- Subtracts a value from another value.
MANAGER_ID-100 (subtracts 100 from each ID number). Any column used in an expression
with this operator must be a numeric data type.
% Uses the remainder of a division expression as the value.
%SALARY/7 (Divides the value of the Salary column by 7 and uses any remainder from the
expression as the column value).
/ Divides one value into another.
SALARY/.16 (Divides the value of the Salary column by .16.
Note: If the two values in the division expression are integers (two NUMERIC columns with
no digits after the decimal) and the result is a fractional value, the result returned will be 0.
* SALARY*.16 (Multiplies the value of the Salary column by .16. This could be used to calculate
taxes that are subtracted from a salary).
Mathematical operators
Functions
The sections below describe the SQLite functions you can use to build an expression with the Expression
builder. The Expression builder divides the functions into the following categories:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 147

8 Customizing tasks
l
Strings (page 148)
l
LOBs (page 149)
l
Numeric (page 149)
l
NULL check (page 150)
l
Date and Time (page 150)
l
Data Enrichment (page 153)
l
Operation (page 156)
l
Other Functions (page 157)
l
Hash (page 158)
l
User-defined transformations (page 163)
Strings
The following table describes the string functions used by the Expression Builder in Enterprise Manager.
Function Description
lower(x) The lower(x) function returns a copy of string x with all characters converted to lower
case. The default built-in lower() function works for ASCII characters only.
ltrim(x,y) The ltrim(x,y) function returns a string formed by removing all characters that appear in y
from the left side of x. If there is no value for y, ltrim(x) removes spaces from the left side
of x.
replace(x,y,z) The replace(x,y,z) function returns a string formed by substituting string z for every
occurrence of string y in string x.
rtrim(x,y) The rtrim(x,y) function returns a string formed by removing all characters that appear in
y from the right side of x. If there is no value for y, rtrim(x) removes spaces from the right
side of x.
substr(x,y,z) The substr(x,y,z) function returns a substring of input string x that begins with the y-th
character and which is z characters long. If z is omitted then substr(x,y) returns all
characters through the end of the string x beginning with the y-th. The left-most
character of x is number 1. If y is negative then the first character of the substring is
found by counting from the right rather than the left. If z is negative then the abs(z)
characters preceding the y-th character are returned. If x is a string then characters
indices refer to actual UTF-8 characters. If x is a BLOB then the indices refer to bytes.
trim(x,y) The trim(x,y) function returns a string formed by removing all characters that appear in y
from both sides of x. If there is no value for y, trim(x) removes spaces from both sides of
x.
String functions
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 148

8 Customizing tasks
Function Description
replaceChars
(X,Y,Z)
The replaceChars(X,Y,Z) function replaces any character in string X that also
exists in string Y (characters to be replaced) with Z (replacement characters) in the same
position. This is especially useful for removing non-valid characters from paths and file
names.
l
If string Z (replacement characters) does not include a character that has
corresponding position in string X, it will be replaced with the first character in
string Z.
l
If string X includes a character that does not exist in string Z, the original
character will be left unchanged.
So, for example, specifying replaceChars("abcde","abcd","123") would return
1231e.
LOBs
The following table describes the LOB functions used by the Expression Builder in Enterprise Manager.
Function Description
hex(x) The hex() function receives an argument as a BLOB and returns an upper-case
hexadecimal string version of the BLOB content.
randomblob
(N)
The randomblob(N) function returns an N-byte BLOB that contains pseudo-random bytes.
If N is less than 1 then a 1-byte random BLOB is returned.
zeroblob(N) The zeroblob(N) function returns a BLOB that consists of N bytes of 0x00.
LOB functions
Numeric
The following table describes the numeric functions used by the Expression Builder in Enterprise Manager.
Function Description
abs(x) The abs(x) function returns the absolute value of the numeric argument X. Abs(x) returns
NULL if x is NULL. Abs(x) returns 0.0 if x is a string or BLOB that cannot be converted to a
numeric value.
random() The random() function returns a pseudo-random integer between -9223372036854775808
and +9223372036854775807.
round(x,y) The round(x,y) function returns a floating-point value x rounded to y digits to the right of the
decimal point. If there is no value for y, it is assumed to be 0.
Numeric functions
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 149

8 Customizing tasks
Function Description
max(x,y...) The multi-argument max() function returns the argument with the maximum value, or
returns NULL if any argument is NULL. The multi-argument max() function searches its
arguments from left to right for an argument that defines a collating function and uses that
collating function for all string comparisons. If none of the arguments to max() define a
collating function, then the BINARY collating function is used. Note that max() is a simple
function when it has two or more arguments but operates as an aggregate function if it has a
single argument.
min(x,y...) The multi-argument min() function returns the argument with the minimum value. The
multi-argument min() function searches its arguments from left to right for an argument that
defines a collating function and uses that collating function for all string comparisons. If
none of the arguments to min() define a collating function, then the BINARY collating
function is used. Note that min() is a simple function when it has two or more arguments but
operates as an aggregate function if it has a single argument
NULL check
The following table describes the NULL check functions used by the Expression Builder in Enterprise Manager.
Function Description
coalesce
(x,y...)
The coalesce() function returns a copy of its first non-NULL argument, it returns NULL if all
arguments are NULL. Coalesce() have at least two arguments.
ifnull(x,y) The ifnull() function returns a copy of its first non-NULL argument, it returns NULL if both
arguments are NULL. Ifnull() must have exactly two arguments. The ifnull() function is the
same as coalesce() with two arguments.
nullif(x,y) The nullif(x,y) function returns a copy of its first argument if the arguments are different and
returns NULL if the arguments are the same. The nullif(x,y) function searches its arguments
from left to right for an argument that defines a collating function and uses that collating
function for all string comparisons. If neither argument to nullif() defines a collating function
then the BINARY is used.
NULL check functions
Date and Time
The following table describes the Date and Time functions used by the Expression Builder in Enterprise
Manager.
Function Description
date(timestring,
modifier,
modifier,...)
Returns the date in the format YYYY-MM-DD.
Date and Time functions
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 150

8 Customizing tasks
Function Description
time(timestring,
modifier,
modifier,...)
Returns the time in the format HH:MM:SS.
datetime
(timestring,
modifier,
modifier,...)
Returns the date and time in the format YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS.
julianday
(timestring,
modifier,
modifier,...)
The julianday() function returns the number of days since noon in Greenwich on
November 24, 4714 B.C.
unixepoch(time-
value, modifier,
modifier,...)
The unixepoch() function returns a unix timestamp - the number of seconds since
1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC. The unixepoch() always returns an integer, even if the
input time-value has millisecond precision.
strftime(format,
timestring,
modifier,
modifier...)
The strftime() routine returns the date formatted according to the format string
specified as the first argument. It supports the following variables:
%d: day of month
%H: hour 00-24
%f: ** fractional seconds SS.SSS
%j: day of year 001-366
%J: ** Julian day number
%m: month 01-12
%M: minute 00-59
%s: seconds since 1970-01-01
%S: seconds 00-59
%w: day of week 0-6 sunday==0
%W: week of year 00-53
%Y: year 0000-9999
%%: %
Examples
The expression builder provides you with a variety of options to build your own expression. You can use the
regular operators with a date as well:
$HIRE_DATE < '2022-02-28'
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 151

8 Customizing tasks
Note that the right operand of the operator is contained between single quotes to prevent it being treated as
a mathematical expression ( 2022 minus 2 minus 28).
Advanced examples using SQLite functions, modifiers and other operators
$HIRE_DATE < date('2022-02-28')
$DATE_1 < '2022-03-01' OR $DATE_1 > '2022-08-01'
$DATE_2 >= date('2022-03-01') AND $DATE_2 <= date('2022-08-01')
$HIRE_DATE < date('now','localtime','-1 year')
$HIRE_DATE <= date('now','utc')
$HIRE_DATE <= date('2022-02-28','+1 months')
$DATE_1 <= date($DATE_2,'+1 months')
List of valid modifiers in SQLite
The 'now' time string is the current date/datetime. You can specify an explicit date '2022-02-28' or you can use
the date from a table column.
You can also apply multiple modifiers such as datetime('now', '-3 hours','+1 months'), for
example.
Modifier Example Result
datetime('now') 2020-04-26 00:53:53
NNN days date('now', '+3 days') 2020-04-29
NNN hours datetime('now', '-3 hours') 2020-04-26 03:53:53
NNN minutes datetime('now', '+3 minutes') 2020-04-26 00:56:53
NNN.NNNN seconds datetime('now', '-30 seconds') 2020-04-26 00:54:23
NNN months date('now', '+3 months') 2020-07-26
NNN years date('now', '-3 years') 2017-04-26
start of month date('now', 'start of month') 2020-04-01
start of year date('now', 'start of year') 2020-01-01
start of day datetime('now', 'start of day') 2020-04-26 00:00:00
weekday N date('now', 'weekday 6') 2020-05-02
unixepoch datetime('1588965525', 'unixepoch') 2020-05-08 19:18:45
localtime datetime('now', 'localtime') 2020-04-26 10:53:53
utc datetime('now', 'utc') 2020-04-25 08:53:53
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 152

8 Customizing tasks
Data Enrichment
Data Enrichment functions allow the selected source tables to be augmented with data from other records
located in either the source or target endpoints. Practical applications of data enrichment functions include
code lookup or master record lookup (e.g. social security number lookup to find a person’s name).
You can enrich the target tables with supplemental data retrieved from the source or target endpoint by
defining a transformation on the table. For more information about defining transformations on a single table,
see Defining transformations for a single table/view (page 84).
Limitations
Amazon Redshift is not supported.
Data Enrichment functions
The table below describes the source and target lookup functions, which can be used both for table
transformations and for global transformations. For a description of the parameters available for these
functions, see Input Parameters below.
Function Description
source_lookup
(TTL,'SCHM','TBL','EXP','COND',
COND_PARAMS)
Use to retrieve additional data from the source
endpoint.
target_lookup
(TTL,'SCHM','TBL','EXP','COND',
COND_PARAMS)
Use to retrieve additional data from the target
endpoint.
Data Enrichment functions
Input parameters
The possible input parameters for the lookup functions are described in the table below. For a usage example,
see Data Enrichment example (page 155).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 153

8 Customizing tasks
Function Description
TTL
TTL (Time to Live) is the amount of time the 'COND' return value will be cached. Caching
the 'COND' return value improves performance by reducing the frequency that Enterprise
Manager needs to access the source/target endpoint. As there is no default, you must specify
a TTL value, which can be one of the following:
<SECONDS> - The time to cache the 'COND' return value in seconds. Specify a short
caching time (e.g. 3) for data that is frequently updated or a long caching time for data that
rarely changes.
'NO_CACHING'- Specify 'NO_CACHING' if you do not want to cache the 'COND' return
value. This is recommended for data that is constantly updated (e.g. share prices).
'NO_EXPIRATION'- For data that is never updated (e.g. a street name), specify 'NO_
EXPIRATION' to store the Functions (page 147) return value permanently in the cache.
'SCHM'
The schema name.
'TBL'
The table on which to perform the lookup.
'EXP'
The expression to retrieve data from the lookup table.
Note: The expression syntax must be native to the endpoint it accesses.
The result should be a single column. Possible expressions include: col1, col1+5, max
(col1).
Note: Full LOB columns are not supported. For information on including Limited-size LOB
columns in the replication, see the description of the Metadata (page 166) tab.
Columns (transformations and filters only) (page 142), Headers (page 159), and Metadata
(Global transformations only) (page 143) can also be used in the expression and are evaluated
before the lookup statement is performed against the endpoint.
'COND'
The condition for the lookup statement.
Note: The condition syntax must be native to the endpoint it accesses.
The COND is a single field referencing all required fields.
Example if the lookup table is located in Oracle:
'Fieldname1=:1 and Fieldname2=:2 and Fieldname3 =:3'
Example if the lookup table is located in Microsoft SQL Server:
'Fieldname1=? and Fieldname2=? and Fieldname3=?'
Columns (transformations and filters only) (page 142), Headers (page 159), and Metadata
(Global transformations only) (page 143) can also be used in the expression and are evaluated
before the lookup statement is performed against the endpoint.
Data Enrichment input parameters
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 154

8 Customizing tasks
Function Description
COND_
PARAMS
Any parameters required by the COND parameter.
The COND_PARAMS (condition parameters) is not a single field, but a list of fields.
Syntax:
$FIELDNAME1 , $FIELDNAME2 , $FIELDNAME3
Full example:
source_lookup(
10000 ,
'HR' ,
'DEPARTMENTS' ,
'DEPARTMENT_NAME’ ,
'COMPANY_ID=? and DIVISION_ID=? and DEPT_ID=?' ,
$COMP_ID , $DIV_ID , $DEPT_ID )
To improve efficiency, the source/target lookup tables should be indexed for the specified lookup fields.
Data Enrichment example
In the following example, Mike needs to add the DEPARTMENT_NAME column to the HR.JOB_HISTORY
table. The DEPARTMENT_NAME column is located in the HR.DEPARTMENTS table in the source endpoint.
This is how the HR.JOB_HISTORY table appears before the column is added:
This is how the HR.JOB_HISTORY table appears after the Full Load completes:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 155

8 Customizing tasks
To add the DEPARTMENT_NAME column, Mike needs to:
1. Create a new task and select the HR.JOB_HISTORY table for replication.
2. Apply a “New Column” transformation to the HR.JOB_HISTORY table. For more information on
defining transformations, see Defining transformations for a single table/view (page 84).
3. Open the Expression Builder and choose Data Enrichment from the Functions tab. For more
information on the Expression Builder, see Using the Expression Builder (page 137).
4. Select the source_lookup function and configure it as follows (using the native syntax of the source
endpoint):
If the lookup table is located in Oracle:
source_lookup(10000,'HR','DEPARTMENTS','DEPARTMENT_NAME',
'DEPARTMENT_ID=:1',$DEPARTMENT_ID)
If the lookup table is located in Microsoft SQL Server:
source_lookup
(10000,'HR','DEPARTMENTS','[DEPARTMENT_NAME]',
'[DEPARTMENT]=?',$DEPARTMENT_ID)
Where:
l
10000 is the TTL parameter.
l
HR is the schema name.
l
DEPARTMENTS is the table name.
l
DEPARTMENT_NAME is the expression.
l
DEPARTMENT_ID=:1 (or ? on Microsoft SQL Server) is the condition.
l
$DEPARTMENT_ID is the condition parameter.
5. Run the task.
Operation
The following table describes the Operation functions used by the Expression Builder in Enterprise Manager.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 156

8 Customizing tasks
Function Description
operation_
indicator
(value_on_
delete,
value_on_
update,
value_on_
insert)
When the operation_indicator function is invoked on its own or as part of an
expression, records deleted from the source table will not be deleted from the
corresponding target table. Instead, the corresponding target record will be flagged
(with a user-provided value) to indicate that it was deleted from the source. The
operation_indicator function also requires you to provide values to indicate
records that were inserted or updated in the source endpoint.
l
The operation_indicator function is not supported on tables that do
not have a Primary Key.
l
It is recommended to add a dedicated column for the flag values, for
example, OPERATION. For an explanation of how to add a column,
see Using the Transform tab (page 86).
l
This function is not supported when:
l
The Apply Conflicts error handling policy is set to No record
found for applying an update: INSERT the missing target
record.
l
The Apply changes using SQL MERGE task setting is enabled.
To specify the function values:
Replace value_on_delete, value_on_insert and value_on_update with the
values that you want to appear in the target endpoint.
Values should be formatted according to the corresponding column type.
Example when the column type is INT4:
operation_indicator(’1’, ’0’, ’0’)
Example when the column type is STRING:
operation_indicator(’Deleted’, ’Updated’, ’Inserted’)
Operation functions
Other Functions
The following table describes additional functions used by the Expression Builder in Enterprise Manager.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 157

8 Customizing tasks
Function Description
length(x) For a string value x, the length(x) function returns the number of characters (not bytes) in x
before to the first NULL character.
If x is NULL then length(x) is NULL. If x is numeric then length(X) returns the length of a string
representation of X.
like(x,y,z) The like() function is used to implement the "Y LIKE X [ESCAPE Z]" expression. The
ESCAPE (z) clause is optional. If there is a z clause, then the like() function is invoked with
three arguments. Otherwise, it is invoked with two arguments.
typeof(x) The typeof(x) function returns a string that indicates the datatype of the expression x: null,
integer, real, text, or BLOB.
Other functions
Hash
The Hash function generates a hash value for an inputted column (using the SHA-256 algorithm) and then
returns the hex value of the generated hash value.
To use the function in an expression, add the hash_sha256(x) function to the Build Expression pane and
then replace the "x" with the desired source column name (from the Input Columns tab).
The function is especially useful for masking sensitive information. In the expression below, for example, the
Hash function has been used to obfuscate employees' email addresses.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 158

8 Customizing tasks
Headers
By default, headers for source tables are not replicated to the target. You can determine which, if any, headers
to replicate when you define a transformation by creating an expression that includes the header.
You can create a filter using header values. Header filters are applied during change processing. See Using
filters (page 92) for additional information.
l
The Headers tab in the Expression builder is available for filters and transformations. It is
available for Global transformations only when you select Add Columns. See Transformation
type (page 108).
l
Header columns are supported by all endpoints, except where explicitly stated to the
contrary.
The available headers are described below.
AR_H_CHANGE_SEQ
Value in Change Processing
A monotonically increasing change sequencer that is common to all Change tables of a task. The Change
sequence has the following format (with time being the UTC time on Replicate Server):
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 159

8 Customizing tasks
YYYYMMDDHHmmSShhxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Where:
l
YYYY is the four-digit year (such as 2012)
l
MM is the two-digit month (range from 01-12)
l
HH is the hour in the day (range from 00-23)
l
mm is the minute in the hour (range from 00-59)
l
SS is the second in the minute (range from 00-59)
l
hh is the hundredth of the second (range from 00-99)
l
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx is a 19-digit, zero prefixed change number (global per task).
The time part usually refers to the commit time of the transaction that includes the change record. Qlik
Replicate contains logic that maintains the monotonicity of the sequence number so modifying or adjusting
the endpoint time may result in multiple changes to seem that they are within the same timestamp but with
increasing change number.
The xxx...xxx is usually the internal change number from the data record except that for BEFORE-IMAGE
records it is the same as the change number of the matching UPDATE record (for example, if the change
number of BEFORE-IMAGE is 1000 and that of the UPDATE is 1001, then both have 1001). This allows a simple
left-outer-join between the table and itself where on the left we scan until the point in time but filter out
operation=before-image, and on the right we join on the same change_seq with the change_oper being 'B' .
Value in Full Load
Empty
Data type
VARCHAR(35)
AR_H_STREAM_POSITION
Value in Change Processing
The stream position value on the source - usually the SCN or LSN - which allows Replicate tasks to resume
from the last processed event.
Value in Full Load
Empty string
Data type
STRING
AR_H_TIMESTAMP
Value in Change Processing
The timestamp of the Change operation, which is represented as the local time on Replicate Server. If your
database and Replicate Server are located in the same timezone, the timestamp will be approximately
representative of the actual Change operation.
Value in Full Load
Current timestamp
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 160

8 Customizing tasks
Data type
DATETIME
AR_H_TRANSACTION_ID
Value in Change Processing
The ID of the transaction to which the Change record belongs. The actual value is a hex-string of the 128-bit
transaction ID. Depending on the source endpoint type, the ID may either be similar to the transaction ID in
the source database or identical to it.
The transaction ID is not guaranteed to be unique and therefore should not be used to create reports
or any other operation that relies upon its uniqueness.
Value in Full Load
Empty
Data type
VARCHAR (32)
AR_H_COMMIT_TIMESTAMP
Value in Change Processing
The source database commit timestamp, according to Replicate Server time. When the source database and
Replicate Server are in the same timezone, the timestamp will be the approximate time of the actual commit
on the source database.
Value in Full Load
Current timestamp
Data type
DATETIME
AR_H_DB_COMMIT_TIMESTAMP
Value in Change Processing
The source database commit timestamp, according to the database server time.
Relevant for the following source endpoints only: Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, IBM DB2 for z/OS,
Microsoft Azure SQL Managed Instance, and Amazon RDS for SQL Server.
Value in Full Load
NULL
Data type
DATETIME
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 161

8 Customizing tasks
AR_H_OPERATION
Value in Change Processing
Can be one of the following: INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE.
Value in Full Load
INSERT
Data type
STRING
AR_H_USER
Value in Change Processing
The user that made the change to the source database.
Relevant for the following source endpoints only:
l
Microsoft SQL Server
l
Microsoft Azure SQL Managed Instance
l
Amazon RDS for SQL Server
l
IBM Informix
l
IBM DB2 for z/OS
l
IBM DB2 for LUW
l
Oracle
l
File
l
AIS-based sources
l
SAP Sybase ASE
Value in Full Load
Empty
Data type
STRING
AR_H_JOB_NAME
Value in Change Processing
The iSeries job that made the change to the source database.
Relevant for the IBM DB2 for iSeries source endpoint only.
Value in Full Load
Empty
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 162

8 Customizing tasks
Data type
STRING
AR_H_PROGRAM_NAME
Value in Change Processing
The iSeries program that made the change to the source database.
Relevant for the IBM DB2 for iSeries source endpoint only.
Value in Full Load
Empty
Data type
STRING
User-defined transformations
Customers that requires functionality not provided by Replicate's built-in transformations can write their own
transformations, and then access them from the Replicate Expression Builder.
It is also recommended to use the Replicate Add-ons API which allows you to take advantage of Replicate's
memory management and logging capabilities, while eliminating the need to create independent memory and
logging routines.
The procedure below is based on the sample files located in:
<INSTALL_DIR>\addons\samples\MyTransformation
The path is the same on Linux, but with slashes (/)instead of backslashes (\). Similarly, although the
explanation below refers to a DLL file (Windows), on Linux this should be an SO file.
Changing the default addon name
You can change the default addon name (MyTransformation) simply by renaming the <INSTALL_
DIR>\addons\samples\MyTransformation\MyTransformation.dll file as desired. Note that if you rename the DLL,
you may also need to specify the new name when editing the addons_def.json.sample file described below
(depending on which parameters you use).
Creating a user-defined transformation
To create a user-defined transformation:
1. Create a shared library that implements the following exported initialization function:
typedef int AR_ADDON_INIT_FUNC(AR_ADDON_CONTEXT *context);
All of the types and prototypes are defined in the ar_addon.h and
ar_addon_transformation.h files located under <INSTALL_DIR>\addons\include.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 163

8 Customizing tasks
2. Make sure your shared library is in the following location:
<INSTALL_DIR>\addons\samples\addon_name
When setting up Qlik Replicate in a Cluster Environment, the created binaries should be
installed on all of the cluster instances.
3. Compile the transformation.
The DLL is automatically created in the following location:
<installation_dir>\addons\addon_name\addon_name.dll
4. Register the library in the addons_def.json.sample file located under <INSTALL_DIR>\addons.
{
"addons": [{
"name": "MyTransformation",
"type": "STARTUP",
//"lib_path": "C:\\Program Files\\Attunity
Replicate\\addons\\samples\\MyTransformation\\MyTransformation.dll",
//"lib_path":
"/opt/attunity/replicate/addons/samples/MyTransformation/MyTransformatio
n.so",
"init_function": "my_transformation_init_func"
}]
}
Where:
l
name is the logical name of the DLL (can be any name). If you do not use the lib_path
parameter to specify the DLL path (see below), then the DLL file must reside in <INSTALL_
DIR>\addons\<addon_name>. On Linux, the <addon_name> folder needs to be created
manually and should either be the default addon name (MyTransformation) or its new name (if
you changed it).
l
type is an optional parameter that specifies when to load the DLL. The only value that is
currently supported is STARTUP.
l
lib_path is the full path of your DLL (e.g. C:\Transformations\MyManipulator.dll). This is
required only if the DLL does not reside in <INSTALL_DIR>\addons\<addon_name> (as
mentioned in the description of the name parameter above).
l
init_function is the function name, as it appears in the C file used to generate the DLL.
5. Save the file as addons_def.json.
6. Register the new function in the addon initialization function (mentioned in Step 1) as in the following
example:
USER_DEFINED_TRANSFORMATION_DEF *transdef = GET_AR_AO_TRANSFORMATION_DEF
();
transdef->displayName = "prefix_with(X, Y)";
transdef->functionName = "prefix_with";
transdef->description = "prefix_with adds the prefix <Y_> to a given
string X";
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 164

8 Customizing tasks
transdef->func = trans_prefix_with;
transdef->nArgs = 2;
AR_AO_REGISRATION->register_user_defined_transformation(transdef);
7. Restart the Qlik Replicate Server service.
The new "prefix_with" function will be available in the Expression Builder under Functions->User Defined.
8.4 Task Settings
Task-specific replication settings can be configured in the <Task Name> - Settings dialog box.
Some of the task settings are not available in a Log Stream Staging setup.
For information on the availability of task settings in a Log Stream Staging setup, refer to the Qlik
Replicate Setup and User Guide.
To open the <Task Name> - Settings dialog box:
1. Open the desired task.
For information on opening a task, see Editing a replication task (page 79).
2. Click the Task Settings toolbar button.
The <Task Name> - Settings dialog box opens, displaying the following tabs:
l
Metadata (page 166)
l
Target metadata (page 166)
l
Control tables (page 169)
l
Bidirectional (page 170)
l
Full Load (page 171)
l
Full Load Settings (page 171)
l
Full Load Tuning (page 173)
l
Change Processing (page 174)
l
Apply Changes Settings (page 174)
l
Store Changes Settings (page 175)
l
Change Processing Tuning (page 181)
l
Error handling (page 186)
l
Error Handling settings (page 187)
l
Environmental errors (page 187)
l
Data Errors (page 188)
l
Table Errors (page 191)
l
Apply Conflicts (page 191)
l
Logging (page 192)
l
Character substitution (page 194)
l
File uploads (page 195)
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 165

8 Customizing tasks
l
Message Format (page 196)
l
Transformations and Filters (page 201)
l
More options (page 202)
Metadata
Clicking the Metadata tab in the Task Settings window reveals the following sub-tabs:
l
Target metadata (page 166)
l
Control tables (page 169)
Target metadata
Target table schema: The schema on the target to which the source tables will be replicated if you do not
want to use the source table schema (or if there is no schema in the source database).
When replicating to Hadoop-based targets, the value specified in this field will be interpreted as a
database name (as opposed to a schema name).
LOB handling options
For information on how to override these settings for individual tables, see Handling LOB columns (page 103).
l
During CDC or during Full Load when the Allow unlimited LOB size option is enabled, LOB
data types are supported only in tables with a primary key or unique index.
l
When replicating from Microsoft SQL Server, inline LOBS will always be read directly from the
logs (i.e. without lookup).
The following LOB handling options are available:
Option Description
Replicate LOB
columns
When this option is selected (the default), LOB columns will be replicated.
Note that replicating LOBs may impact performance. This is especially true in the case of
the large LOBs which require Replicate to perform a lookup from the source table in order
to retrieve the source LOB value.
LOB handling options
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 166

8 Customizing tasks
Option Description
Allow
unlimited LOB
size
Select this option - also known as Full LOB mode - to ensure that all LOBs are replicated
without being truncated. This option should be selected when all (or nearly all) of the
LOBs you wish to replicate are large (i.e. exceed 1 GB).
NoteIf the task's Change Processing Mode is set to "Batch optimized apply"
(the default), Replicate will switch to "Transactional apply" mode to apply
tables with LOBs.
Optimize
handling when
LOB size is
less than (KB)
Select this option when you need to replicate both small and large LOBs, and most of the
LOBs are small.
This option is supported with the following endpoints only:
l
Sources: Oracle, Microsoft SQL server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, IBM DB2 for
LUW, and Sybase ASE.
l
Targets: Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, IBM DB2 for
z/OS, and Sybase ASE.
When this option is selected, during Full Load, the small LOBs will be replicated "inline"
(which is more efficient), and the large LOBs will be replicated by performing a lookup
from the source table.
During Change Processing, however, both small and large LOBs will be replicated by
performing a lookup from the source table.
When this option is selected, Replicate will check all of the LOB sizes to
determine which ones to transfer "inline". LOBs larger than the specified size
will be replicated using Full LOB mode.
Therefore, if you know that most of the LOBs are larger than the specified
setting, it is better to use the Allow unlimited LOB size option instead.
Chunk size
(KB)
Optionally, change the size of the LOB chunks to use when replicating the data to the
target. The default chunk size should suffice in most cases, but if you encounter
performance issues, adjusting the size may improve performance.
With some databases, data type validation occurs when the data is inserted or
updated. In such cases, replication of structured data types (e.g. XML, JSON,
GEOGRAPHY, etc.) may fail if the data is bigger than the specified chunk size.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 167

8 Customizing tasks
Option Description
Limit LOB size
to (KB)
Select this option if you only need to replicate small LOBs or if the target endpoint does
not support unlimited LOB size. The maximum permitted value for this field is 102400 KB
(100 MB).
When replicating small LOBs, this option is more efficient than the Allow unlimited LOB
size option since the LOBs are replicated "inline" as opposed to via "lookup" from the
source. During Change Processing, small LOBs are usually replicated via "lookup" from
the source.
As the value of the Limit LOB size to is in bytes, the size should be calculated according
to the following formulas:
l
BLOB – The length of the largest LOB.
l
NCLOB – The length of the longest TEXT in characters multiplied by two (as each
character is handled as a double-byte).
If the data includes 4-byte characters, multiply it by four.
l
CLOB – The length of the longest TEXT in characters (as each character is handled
as a UTF8 character).
If the data includes 4-byte characters, multiply it by two.
l
Any LOBs larger than the specified size will be truncated.
l
During Change Processing from Oracle source, inline BLOBs are
replicated inline.
l
Changes to this setting will only affect existing tables after they are
reloaded.
In some scenarios, tasks configured to replicate tables with multiple LOB columns may consume a
large amount of memory. This is because Replicate allocates memory by multiplying the Limit LOB
size to value by the Commit rate during full load value, the sum of which, it multiplies by the
number of LOB columns being replicated. So, for example, if LOB size is limited to 5 MB and the
default commit rate is used (10000 events), a task replicating 6 LOB columns will consume 30 GB of
memory. Note that other factors such as the database type and version may also affect memory
consumption.
Should you encounter memory consumption issues and suspect that a combination of the above
factors may be the cause, stop the task and lower the value in the Commit rate during full load
field. Then resume the task. Repeat this process until acceptable performance/memory levels are
reached.
These instructions apply to Change Processing and Full Load tasks.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 168

8 Customizing tasks
Changes to a column’s LOB size while a task is running will not be reflected in the Change Table,
unless the target tables are created by Qlik Replicate. In such cases, the task must be configured to
drop and create the Change Table (the default) and the target tables need to be reloaded (after the
LOB size has changed).
For more information on the Change Table, see Store Changes Settings (page 175). For information
on reloading target tables, see the Qlik Replicate User Guide and Reference.
Control tables
Control Tables provide information about the replication task as well as useful statistics that can be used to
plan and manage both the current replication task and future replication tasks. Aside from the Apply
Exceptions table which is always created, you can choose which Control Tables to create on the target.
Create target control tables in schema: Enter the endpoint schema for the target Control Tables. If you do
not enter any information in this field, then the tables will be created in the default location in the endpoint.
When this field is left empty, the target endpoint is MySQL, and the Multiple Endpoints option is
enabled, a default database named
attrep_control
will be created on the MySQL server. The
selected control tables will be created in this database.
For more information on the Multiple Endpoints option, see the Qlik Replicate User and Reference
Guide.
When replicating to a Hadoop target endpoint, the value specified in this field will be interpreted as
a database name (as opposed to a schema name).
Create target control tables in tablespace: When the target endpoint is Oracle, specify the tablespace where
you want the target control tables to be created. If you do not enter any information in this field, the tables
will be created in the default tablespace in the target database.
Create target control table indexes in tablespace: When the target endpoint is Oracle, specify the
tablespace where you want the control table indexes to be created. If you do not enter any information in this
field, the indexes will be created in the same tablespace as the control tables.
Replication history time slot (minutes): The length of each time slot in the Replication History table. The
default is 5 minutes.
Table selection
In addition to the Apply Exceptions table (required), select which of the following Control Tables you want
Qlik Replicate to create on the target endpoint:
l
Replication Status: Provides details about the current task including task status, amount of memory
consumed by the task, number of changes not yet applied to the target and the position in the source
endpoint from which Qlik Replicate is currently reading.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 169

8 Customizing tasks
l
Suspended Tables: Provides a list of suspended tables as well as the reason they were suspended.
l
Replication History: Provides information about the replication history including the number and
volume of records processed during a replication task, latency at the end of a CDC task, among others.
l
Change Data Partitions: The attrep_cdc_partitions table contains records of partitions created on
the target database when Change Data Partitioning (page 176) is enabled for a Replicate task. You can
use this information to identify partitioned data that needs to be further processed.
l
DDL History: The attrep_ddl_history table contains a history of all supported DDL changes that
occurred during a task.
For a list of DDL changes supported by Replicate, refer to the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
Note that DDL changes written to this Control Table are also subject to the limitations described in the
section in the Limitations when Capturing DDL Changes" section in the Qlik Replicate Setup and User
Guide.
The DDLHistory table is currently supported with the following target endpoints only:
l
Amazon EMR
l
Cloudera Data Platform (CDP) Private Cloud
l
Databricks (Cloud Storage)
l
Google Cloud Pub/Sub
l
Google Dataproc
l
Hadoop
l
Hortonworks Data Platform
l
Microsoft Azure Databricks
l
Microsoft Azure HDInsight
l
Snowflake on Google
For a detailed description of these tables, see the Qlik Replicate User and Reference Guide.
Bidirectional
This tab is only applicable to bidirectional replication tasks. When you click Bidirectional in the Task Settings
dialog box, the Loopback Prevention tab is displayed. In bidirectional replication, loopback prevention is a
mechanism that prevents the same data from being replicated back and forth in an endless loop. To enable
loopback prevention, you need to specify a source and target Loopback prevention table schema.
Bidirectional replication consists of two separate tasks: Task 1 captures changes made to Endpoint A and
replicates them to Endpoint B. Task 2 captures changes made to Endpoint B and replicates them to Endpoint
A. When configuring Task 1 of a bidirectional replication setup, the source loopback prevention table schema
must be identical to the target loopback prevention table schema specified in the Loopback Prevention
settings of Task 2.
Likewise, when configuring Task 2 of a bidirectional replication setup, the source loopback prevention table
schema must be identical to the target loopback prevention table schema specified in the Loopback
Prevention settings of Task 1.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 170

8 Customizing tasks
Oracle schemas are case-sensitive. Therefore, when specifying an Oracle table schema, make sure to
use the correct case in the Loopback Prevention settings in both Tasks.
For instructions on setting up bidirectional replication, see Bidirectional replication (page 66).
Full Load
Clicking the Full Load tab in the Task Settings window reveals the following sub-tabs:
l
Full Load Settings (page 171)
l
Full Load Tuning (page 173)
Full Load Settings
Click the Full Load Settings sub-tab to configure the following:
Full Load Processing is ON/OFF.
Click this button to toggle full load on or off. The initial setting is determined when Adding tasks (page 64).
When full load is ON, Qlik Replicate loads the initial source data to the target endpoint.
Full load can be turned on or off at any stage even if change processing is on. Once the task begins
to process changes, the full load on/off switch is used only as additional protection against
accidental or unauthorized reload.
Target table preparation
If target table already exists: Select one of the following from the list to determine how you want to handle
loading the target at full-load start up:
The option to drop or truncate the target tables is relevant only if such operations are supported by
the source endpoint.
l
DROP and Create table: The table is dropped and a new table is created in its place.
Replicate Control Tables will not be dropped. However, any suspended tables that are
dropped will also be deleted from the attrep_suspended_tables Control Table if the
associated task is reloaded.
l
TRUNCATE before loading: Data is truncated without affecting the table metadata. Note that when
this option is selected, enabling the Create primary key or unique index after full load completes
option will have no effect.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 171

8 Customizing tasks
l
ARCHIVE and CREATE table: A copy of the existing table will be saved to the same schema before the
new table is created. The archived table name will be appended with a timestamp, indicating when the
archiving operation occurred (e.g. Customers_20170605175601).
Currently this option is only available for the Hadoop target endpoint .
l
Do nothing: Existing data and metadata of the target table will not be affected. New data will be
added to the table.
Replicate expects the source column data types to be compatible with the corresponding target
column data types. If you choose either TRUNCATE before loading or Do nothing and one or more
target data types are different than the data types for the corresponding source columns, use a
transformation to convert the data types as required.
For information on creating data type transformations, see Defining transformations for a single
table/view (page 84).
Primary Key or Unique Index Creation
Create primary key or unique index after full load completes: Select this option if you want to delay
primary key or unique index creation on the target until after full load completes.
Stopping the Task after Full Load
After Full Load completes, stop the task: You can set the task to stop automatically after Full Load
completes. This is useful if you need to perform DBA operations on the target tables before the task’s Apply
Changes (i.e. CDC) phase begins.
During Full Load, any DML operations executed on the source tables are cached. When Full Load completes,
the cached changes are automatically applied to the target tables (as long as the Before/After cached
changes have been applied option(s) described below are disabled).
This feature is not available for bidirectional replication tasks.
Select Before cached changes have been applied to stop the task before the cached changes are applied
and/or After cached changes have been applied to stop the task after the cached changes are applied.
Selecting the Before cached changes have been applied option will stop the task after Full Load completes.
Selecting the After cached changes have been applied option will stop the task as soon as data is consistent
across all tables in the task.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 172

8 Customizing tasks
When configuring Replicate to stop the task after Full Load completes, note the following:
l
The task does not stop the moment Full Load completes. It will be stopped only after the first
batch of changes has been captured (as this is what triggers the task to stop). This might
take a while depending on how frequently the source database is updated. After the task
stops, the changes will not be applied to the target until the task is resumed.
l
The task will stop after Full Load completes, even if there are no cached changes to apply.
l
The After cached changes have been applied option is not supported with all file-based and
Hadoop-based target endpoints, namely:
l
File-based: File, Amazon S3, Microsoft Azure ADLS, and Google Storage.
l
Hadoop-based: Hadoop, Hortonworks Data Platform, Amazon EMR, Microsoft Azure
HDInsight , Google Dataproc, Cloudera Data Platform (CDP) Private Cloud, and
Microsoft Azure Databricks.
l
Choosing to stop the task before cached changes have been applied may adversely affect
performance, since the cached changes will only be applied to tables (even those that have
already completed Full Load) after the last table completes Full Load.
l
When the Before/After cached changes have been applied option is selected and a DDL is
executed on one of the source tables during the Full Load process (in a Full Load and Apply
Changes task), Replicate will reload the table. This effectively means that any DML
operations executed on the source tables will be replicated to the target before the task
stops.
l
When working with the File Channel endpoint, these options should be set in the remote File
Channel task and not in the local File Channel task.
For more information on the File Channel endpoint, see the Qlik Replicate Setup and User
Guide.
Duplicate Record Prevention
Supported when using the IBM DB2 for z/OS and IBM DB2 for iSeries source endpoints only.
Select the Eliminate creation of duplicate records on full load option if you need to prevent duplicate
records from being replicated during Full Load. You can either set the option at task level or per table.
Note that selecting this option could impact performance as Replicate instructs the source database to return
the table records by Primary Key order and then removes any duplicate records.
For information on preventing creation of duplicate records at table level, see Full Load (page 106).
Full Load Tuning
Click the Full Load Tuning sub-tab to configure the following:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 173

8 Customizing tasks
Tuning settings:
l
Maximum number of tables to load in parallel: Enter the maximum number of tables to load into
the target at one time. The default value is 5.
l
Transaction consistency timeout (seconds): Enter the number of seconds that Qlik Replicate waits
for transactions to close, if they are open when the task starts, before beginning the Full Load
operation. The default value is 600 (10 minutes). Qlik Replicate will begin the full load after the timeout
value is reached even if there are open transactions.
To replicate transactions that were open when Full Load started but were only committed
after the timeout value was reached, you need to reload the target tables.
l
Commit rate during full load: The maximum number of events that can be transferred together. The
default value is 10000.
Change Processing
Clicking the Change Processing tab in the Task Settings window reveals the following sub-tabs:
l
Apply Changes Settings (page 174)
l
Store Changes Settings (page 175)
l
Change Processing Tuning (page 181)
Apply Changes Settings
Click the Apply Changes Settings sub-tab to configure the following:
Apply Changes is ON/OFF:
Click this button to toggle Apply Changes (Change Processing) on or off. The initial setting is determined when
Adding tasks (page 64).
When Apply Changes is ON, Qlik Replicate processes the changes. You can view the change processing in the
Monitor. For more information, see the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
When you turn on apply changes you must reload the task or position back to the point of the
previous reload.
DDL handling policy: Determine how to handle the target table for the change capture:
l
Executing a DDL on a source table during the Full Load process in a Full Load and Apply
Changes task will cause Replicate to reload the table.
l
The option to drop or truncate the target tables is relevant only if such operations are
supported by the source endpoint.
l
Executing the Rename Table DDL with "Ignore ALTER" selected will cause events to continue
being delivered until you stop and then resume the task.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 174

8 Customizing tasks
l
When source table is dropped, select one of the following:
l
DROP target table
l
Ignore DROP
l
When source table is truncated, select one of the following:
l
TRUNCATE target table
l
Ignore TRUNCATE
l
When source table is altered, select one of the following:
l
ALTER target table
l
Ignore ALTER
Store Changes Settings
When you click Store Changes in the Task Settings dialog box, you can configure the Store Changes Settings
for a replication task.
Store changes processing is ON/OFF:
Click this button to toggle Store Changes on or off. The initial setting is determined when Adding tasks (page
64). If this option is ON, changes are stored in either Change Tables or an Audit Table.
For more information about storing and applying changes, see the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
Store Changes can be turned on or off at any time without affecting anything in the task. Changes
that are processed and not stored as a result of change storage being turned off can be recovered
only by setting the task to an earlier point in time.
If Store Changes is ON, use the following options to determine how to store changes. Changes can be stored
in Change Tables or in a single Audit table. From the Store changes in drop-down list, choose either Change
tables or Audit table according to your needs.
Storing changes in Change Tables
The following section describes the options that are available when storing changes in Change Tables.
l
Suffix: Type a string to use as the suffix for all Change Tables. The default value is __ct.
The Change Table names are the name of the target table with the suffix appended. For example, if you
have a table called HR and use the default value, the name of the Change Table will be HR__ct.
For more information, see the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
l
Header column prefix: Type a string to use as the prefix for all of the Change Table header columns.
The default value is header__.
For example, the header column stream_position when using the default value is called header__
stream_position.
For more information, see the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
l
DDL options: Select one of the following options to determine how to handle DDL operations on the
source tables:
l
Apply to change table - DDL operations to the source tables (such as a column being added)
will be applied to the corresponding Replicate Change Tables only.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 175

8 Customizing tasks
l
Ignore - All DDL operations to source tables will be is ignored.
l
Apply to change table and target table
This is the default option. When this option is selected, DDL operations to the source tables will
be applied both to the Replicate Change Tables and to the corresponding target tables.
l
On UPDATE: Select one of the following options to determine how to store UPDATEs to the source
tables:
l
Store before and after image - To store both the pre-UPDATE data and the post-UPDATE data.
l
Store after image only - To store only the post-UPDATE data.
Change table creation:
If Change Table exists when full load starts: Select one of the following to determine how you want to
handle loading the Change Tables when Full Load replication starts:
l
DROP and CREATE Change Table: The table is dropped and a new table is created in its place.
l
ARCHIVE and CREATE Change Table:A copy of the existing table will be saved to the same schema
before the new table is created. The archived table name will be appended with a timestamp,
indicating when the archiving operation occurred (e.g. Customers___ct_20170605175601).
Currently this option is only available for the Hadoop target endpoint.
l
Delete old changes and store new changes in existing Change Table: Data is truncated and added
without affecting the table metadata.
l
Keep old changes and store new changes in existing Change Table: Data and metadata of the
existing Change table are not affected.
Change Data Partitioning
This feature is supported with the following target endpoints only:
l
Hadoop (Hortonworks, Cloudera, and MapR)
l
File
l
Amazon S3
l
Databricks (Cloud Storage)
l
Microsoft Azure HDInsight
l
Google Cloud Storage
l
Microsoft Azure ADLS
l
Cloudera Data Platform (CDP) Private Cloud
l
Google Data Proc
l
Amazon EMR
l
Hortonworks Data Platform (HDP)
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 176
8 Customizing tasks
In a standard replication task, changes are replicated to the target in no particular order. Change Data
Partitioning enables processing of Change Data from many tables in a consistent fashion. You can define the
duration of partitions as well as the partitioning base time, thereby ensuring overall consistency of the
partitioned data (i.e. no partial transactions, no order headers without order lines, and so on.)
The partitioned data is stored in the Replicate Change Tables. When the Change Data Partitions table is
selected (in the Control tables (page 169) tab), information about the partitions will be recorded in the attrep_
cdc_partitions Control Table on the target database. This information can be used to identify partitioned data
that needs to be further processed.
The partitioning options are as follows:
l
Off - Replicate Change Data without partitioning.
l
Partition every - Specify the length (in hours and minutes) of each partition.
It is recommended to specify a partition length in excess of one hour. Although specifying a
partition length less than one hour may improve latency, creating many partitions on the
target may also impact (target) performance (especially in systems with large volumes of
changes).
If you resume a task from BEFORE the time that the last partition was created, Replicate will
write to a partition that has already been closed.
l
Partition base time - Partitions are created during a 24 hour time period, which is calculated
according to the specified “Partitioning base time” on the source database (in UTC time). For example,
a partition interval of 8 hours with a “Partitioning base time” time of 02:00 will create the following
partitions: 02:00-10:00, 10:00-18:00, 18:00-02:00 - but not necessarily in that order. For instance, if a
task started at 01:00, then the timeframe of the first partition will be 18:00-02:00. Additionally, if a task
started in the middle of a partition (e.g. at 04:00), its Change Data will be inserted into the 02:00-10:00
partition (even though no changes were captured before 04:00).
l
Speed partition mode
This feature is supported with Hadoop-based target endpoints only.
By default, Change Data Partitions for all tables in a replication task are registered on the target at the
same time. As soon as the partitions are registered, information about them (such as a partition's start
and end time) is also published to the Replicate Change Data Partitions Control Table. This ensures
data consistency across all of the replicated tables.
In Speed partition mode, rather than waiting for all Change Data files to be uploaded (for all tables),
Replicate creates and registers a partition per-table as soon as the partition’s first data file is uploaded
(to its table). Creating and registering partitions before all the Change Data has been uploaded is
especially useful for consuming applications such as Qlik Compose that need to process changes with
a minimum of delay, as the Change Data rapidly becomes available for consumption, even if it is
incomplete.
For example, if an endpoint is configured to upload Change Data files every five minutes, each batch of
changes can be processed immediately, even if the Partition every interval is set to six hours.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 177

8 Customizing tasks
However, despite significantly reducing latency, working in this mode may have some possible
drawbacks:
l
Accumulation of a large number of files per partition, which may impact performance on the
target.
It is therefore strongly recommended to clean up old partitions using the Partition Retention
options (see below) provided for this purpose.
l
Inconsistent results may be encountered when querying several tables due to the Change Data
arriving on the target at different times.
Change Tables that were created before Change Data Partitioning was enabled need to be dropped
or renamed so that they can be recreated with the additional "partition_name" column.
Deleting old partitions periodically
Over time, Change Data Partitioning can result in a large number of files and partitions accumulating on the
target system, which may significantly impact performance. Therefore, to ensure optimal performance, best
practice is to delete old partitions from time to time.
There are two ways of deleting processed partitions: periodically and ad-hoc. This topic explains how to set up
periodic partition deletion. For information on ad-hoc partition deletion, refer to "Deleting Old Partitions
Manually" in the Replicate Help.
Currently, this feature is supported with the Microsoft Azure Databricks endpoint only.
Setting up periodic deletion is a two-phase process which involves specifying a deletion interval in the UI, and
setting a partition retention barrier using the Enterprise Manager API.
To do this:
1. Enable the Partition Retention option.
Any partitions created while this option is disabled will not be deleted when deletion is initiated (either
periodic or manual). Therefore, the Partition Retention option should only be disabled if you are
absolutely certain that periodic deletion will not be initiated at any point in the future.
2. Specify a partition deletion interval in Day, Hours or Minutes.
To prevent the deletion of open partitions or recently closed partitions, the partition deletion interval
must be at least double the Partition every value.
3. Set a retention barrier date by calling the relevant Enterprise Manager API method.
To ensure that only old (i.e. processed) partitions will be deleted, periodic deletion requires a retention
barrier date to be set. The retention barrier date should be set by the consuming application each time
it finishes processing a partition. A consuming application can be any application (Qlik or otherwise)
tasked with processing the partitioned data. There may be several consuming applications, each of
which sets its own retention barrier. In this case, partitions will be deleted up to the earliest retention
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 178

8 Customizing tasks
barrier. For example, if Application A sets July 7th, 2020 as a barrier, Application B sets August 7th,
2020 as a barrier, and Application C sets September 7th, 2020 as a barrier, partitions will be deleted up
to July 7th, 2020.
As soon as a retention barrier is set, periodic deletion will start to run according to the defined interval,
until any of the following occurs:
l
The Partition Retention option is disabled
l
An API call removes the retention barrier
l
All partitions until the retention barrier have been deleted
For more information on setting and removing a partition retention barrier using the API, refer to the
Enterprise Manager Developer's Guide.
Limitations and considerations
l
If a connection error occurs during the partition deletion operation, the operation will fail (with a
warning). The operation will continue from the point of failure the next time that deletion is performed
(either periodically or manually).
l
If a specific object (partition or storage) cannot be deleted due to other errors (i.e. not connection
errors), a warning will be written to the log and deletion of the remaining objects will continue.
Partitions that cannot be deleted due to such errors must be deleted directly from the database by the
DBA.
l
To prevent deletion of open partitions, the last partition in a table will not be deleted, even if meets
the criteria for deletion.
l
Deletion of partitions in renamed tables is not supported.
l
Reloading a target with the Drop and Create tables option (the default) will delete both the tables and
their partitions, regardless of any partition deletion policy. However, reloading a target with the Do
nothing option, will leave the partitions untouched. In this case, partitions created prior to the target
reload cannot be deleted using the Replicate partition deletion tools.
Selecting Change Table header columns
The Change Table header columns provide information about the Change Processing operation such as the
type of operation (e.g. INSERT), the commit time, and so on. If you do not need this information, you can
configure Replicate to create the Change Tables without some or all of the header columns, thereby reducing
their footprint in the target database. To do this, clear the check boxes next to the header columns that you
wish to exclude.
Note that you cannot remove additional columns or restore columns while a task is running. To change your
initial selection, you first need to stop the task, then modify your selection, and finally reload the target tables.
When Change Data Partitioning is enabled, an extra header column named "
partition_name
" is
added to the Change Tables and automatically selected in the UI. As this column is required, it
cannot be excluded.
For a description of the header columns, refer to the Qlik Replicate User Guide and Reference .
Storing changes in an Audit table
The following section describes the options that are available for storing changes in an Audit table.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 179
8 Customizing tasks
l
If your source tables contain records exceeding 4096 characters, to prevent truncation of
these records, you must turn on the Task Settings' Replicate LOB columns option (even if the
source tables do not contain any LOB columns).
l
LOB columns with unlimited size are not supported in the CHANGE_RECORD and BU_
CHANGE_RECORD columns. The other fields will be recorded but the LOB will have a NULL
value.
l
For a description of the audit table structure, see the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
l
Audit table schema: Specify a schema if you do not want the Audit table to be created under the
target endpoint's default schema.
The default schema are as follows:
Endpoint Default Schema
Pivotal Greenplum Public
Amazon Redshift Public
Oracle The connected user’s user name.
Teradata The endpoint name.
All others The user’s default schema.
Default schema by endpoint
l
Audit table tablespace: This option is only available when the task's target endpoint is Oracle. Enter
the tablespace name on the target where you want the Audit table to be created. If you do not enter
any information in this field, then the tables will created in the default permanent tablespace.
l
Audit table name: Specify a name for the Audit table.
The default value is attrep__audit_table.
Audit table creation:
If audit table exists when the target is reloaded: Select one of the following to determine how you want to
handle the Audit table when the target is reloaded:
l
DROP and CREATE audit table: The Audit table is dropped and a new table is created in its place.
l
ARCHIVE and CREATE audit table: A copy of the existing table will be saved to the same schema
before the new table is created. The archived table name will be appended with a timestamp,
indicating when the archiving operation occurred (e.g. attrep_audit_table_20170605175601).
Currently this option is only available for the Hadoop target endpoint.
l
Delete old changes and store new changes in existing audit table: Data is truncated and added
without affecting the Audit table metadata.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 180

8 Customizing tasks
l
Keep old changes and store new changes in existing audit table: Data and metadata of the existing
Audit table are not affected.
For a description of the audit table structure, see the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
Change Processing Tuning
Click the Change Processing Tuning sub-tab to fine-tune the Apply Changes settings.
Change Processing Mode
Determine which method will be used to apply changes.
Changes to tables without a Unique Index or Primary Key will always be applied in Transactional
apply mode.
l
Transactional apply: Select this to apply each transaction individually, in the order it is committed. In
this case, strict referential integrity is ensured for all tables.
Applying cached events in transactional mode to endpoints that do not enforce constraints
(such as Vertica and IBM Netezza), may result in duplicate records on the target. This is
because such endpoints do not return duplicate errors.
l
Batch optimized apply: Select this to commit the changes in batches. In this case, a pre-processing
action occurs to group the transactions into batches in the most efficient way. This may affect
transactional integrity. Therefore, you must select one of the following to determine how the system
will handle referential integrity issues:
In the event of a recoverable error during the Batch optimized apply process, multiple
attrep_changes (Net Changes) tables might be created in the target database (each with a
unique name). These tables will need to be deleted manually as the automatic cleanup
process will not delete them.
l
Preserve transactional integrity
This option is only supported when replicating to an Oracle target.
l
Allow temporary lapses in transactional integrity to improve performance
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 181

8 Customizing tasks
These options are not displayed in bidirectional tasks since such tasks always use the "Preserve
transactional integrity" option.
The following target endpoints do not support applying binary data types in Batch optimized apply
mode:
ODBC, SAP Sybase IQ, SAP Sybase ASE, Vertica, IBM Netezza, Teradata, and Amazon Redshift.
When LOB columns are included in the replication, Batch optimized apply can only be used with the
Limit LOB size to option. For more information about including LOB columns in the replication, see
Metadata (page 166).
Using Batch optimized apply to apply changes to tables with foreign keys is not supported.
Batch tuning
The following options are available when Batch optimized apply is selected as the Change Processing
Mode:
l
Apply batched changes in intervals:
l
Longer than: The minimum amount of time to wait between each application of batch
changes. The default value is 1.
Increasing the Longer than value decreases the frequency with which changes are applied to
the target while increasing the size of the batches. This can improve performance when
applying changes to target endpoints that are optimized for processing large batches, such as
Teradata, Vertica, and Pivotal Greenplum.
l
But less than: The maximum amount of time to wait between each application of batch
changes (before declaring a timeout). In other words, the maximum acceptable latency. The
default value is 30. This value determines the maximum amount of time to wait before applying
the changes, after the Longer than value has been reached.
l
Force apply a batch when processing memory exceeds (MB): The maximum amount of memory to
use for pre-processing in Batch optimized apply mode. The default value is 500.
For maximum batch size, set this value to the highest amount of memory you can allocate to Qlik
Replicate. This can improve performance when applying changes to target endpoints that are
optimized for processing large batches, such as Teradata, Vertica, and Pivotal Greenplum.
l
Apply batched changes to multiple tables concurrently: Selecting this option should improve
performance when applying changes from multiple source tables.
l
Maximum number of tables: The maximum number of tables to apply batched changes to
concurrently. The default is five, the maximum is 50, and the minimum is two.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 182

8 Customizing tasks
Limitations:
When the Apply batched changes to multiple tables concurrently option is enabled, the
following limitations apply:
l
Supported by the following target endpoints only: Snowflake on Azure, Snowflake on
AWS, Snowflake on Google, Microsoft SQL Server, Amazon Redshift, Microsoft Azure
Databricks Delta, Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics, and Microsoft Azure SQL
Database.
l
Error handling limitations:
The global error handling policy will be unavailable.
The task error handling policy defaults will be unchanged for Environmental and
Table errors, but the defaults for Data errors and Apply Conflicts errors will be as
follows:
Data Errors:
l
Data truncation errors: Ignore record
l
Other data errors: Suspend table
Apply Conflicts Errors:
l
Deletes: Ignore record
l
Inserts: UPDATE the existing target record
Note that this is not relevant for a Snowflake target (as Snowflake does not
support Primary Keys).
l
Updates: Ignore record
Escalation Action:
l
The Escalation action for both Data errors and Apply Conflicts is not
supported.
l
Control Table limitations:
l
The attrep_apply_exception Control Table is not supported. For information
on this table, refer to the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
l
Limit the number of changes applied per change processing statement to: To limit the number of
changes applied in a single change processing statement, select this check box and then optionally
change the default value. The default value is 10,000.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 183

8 Customizing tasks
This option is not available for tasks configured with the following target endpoints:
l
Microsoft SQL Server
l
Microsoft Azure SQL Database
l
Databricks Lakehouse (Delta) (When using Microsoft Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS)
Gen2 storage)
l
Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics
l
Google Cloud SQL for SQL Server
l
Amazon Redshift
l
Snowflake on AWS
l
Snowflake on Azure
l
Snowflake on Google
The following options are available when Transactional apply is selected as the Change Processing Mode:
l
Minimum number of changes per transaction: The minimum number of changes to include in each
transaction. The default value is 1000.
Replicate applies the changes to the target either when the number of changes is equal to or
greater than the Minimum number of changes per transaction value OR when the batch
timeout value is reached (see below) - whichever occurs first. Because the frequency of
changes applied to the target is controlled by these two parameters, changes to the source
records may not immediately be reflected in the target records.
l
Maximum time to batch transactions before applying (seconds): The maximum time to collect
transactions in batches before declaring a timeout. The default value is 60.
Transaction offload tuning
The following tuning options are available, regardless of which Change processing mode is selected:
l
Offload transaction in progress to disk if:
Qlik Replicate usually keeps transaction data in memory until it is fully committed to the source and/or
target. However, transactions that are larger than the allocated memory or that are not committed
within the specified time limit will be offloaded to disk.
l
Transaction memory size exceeds (MB): The maximum size that all transactions can occupy
in memory before being offloaded to disk. The default value is 1000.
l
Transaction duration exceeds (seconds): The maximum time that each transaction can stay in
memory before being offloaded to disk. The duration is calculated from the time that Qlik
Replicate started capturing the transaction. The default value is 60.
Miscellaneous tuning
l
Statements cache size (number of statements): The maximum number of prepared statements to
store on the server for later execution (when applying changes to the target). The default is 50. The
maximum is 200.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 184

8 Customizing tasks
l
Store task recovery data in target database: Select this option to store task-specific recovery
information in the target database. When this option is selected, Replicate creates a table named
attrep_txn_state in the target database. This table contains transaction data that can be used to
recover a task in the event that the files in the Data folder are corrupted or if the storage device
containing the Data folder has failed.
For more information about this option, see Recovering from data folder loss or corruption (page 241).
l
DELETE and INSERT when updating a primary key column: For tasks configured with streaming
target endpoints (for example, Kafka), the DELETE+INSERT statements will be executed on the actual
target. For all other target endpoints, they will be executed in the associated Change Tables. This
option requires full supplemental logging to be turned on in the source database.
l
Apply changes using SQL MERGE - When this option is not selected, the Batch optimized apply
operation executes separate bulk INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE statements for each of the different
change types in the Replicate Net Changes table.
The Replicate Net Changes table is created on the target when working in Batch optimized
apply mode and contains records that were changed on the source. It is truncated each time
the source changes are applied to the target. For more information on the Net Changes
table, see Net Changes table (page 14)
While this method is highly efficient, enabling the Apply changes using SQL MERGE option is even
more efficient when working with endpoints that support this option.
This is due to the following reasons:
l
It reduces the number of SQL statements run per table from three to one. Most UPDATE
operations in large, immutable, file-based cloud databases (such as Google Cloud BigQuery),
involve rewriting of affected files. With such operations, the reduction of per-table SQL
statements from three to one is very significant.
l
The target database only needs to scan the Replicate net changes table once, significantly
reducing I/O.
l
Optimize inserts: When Apply changes using SQL MERGE is selected together with
this option and the changes consist of INSERTs only, Replicate will perform INSERTs
instead of using SQL MERGE. Note that while this will usually improve performance and
thereby reduce costs, it might also result in duplicate records in the target database.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 185

8 Customizing tasks
l
The Apply changes using SQL MERGE and Optimize inserts options are available for
tasks configured with the following target endpoints only:
l
Google Cloud BigQuery
l
Databricks Lakehouse (Delta)
l
Snowflake on Azure, Snowflake on Google, and Snowflake on Amazon
l
The Apply changes using SQL MERGE and Optimize inserts options are not
supported with the following source endpoints:
l
Salesforce
l
Oracle
For more information, see the "Limitations and Considerations" topic for these
endpoints.
l
When the Apply changes using SQL MERGE option is enabled (either alone or
together with the Optimize inserts option):
l
Non-fatal data errors or data errors that cannot be recovered will be handled
as table errors
l
The Global error handling policy will not be available
l
The Apply Conflicts error handling policy will be preset and read-only. If the
Optimize inserts option is also selected, the Duplicate key when applying
INSERT Apply Conflicts error-handling option will be set to Allow duplicates
in the target.
l
Some of the Data error handling policy options will not be available.
l
The operations will only be performed on the final target tables. For Change
Tables or the Audit Table, INSERTs will be performed.
Error handling
Qlik Replicate handles different types of errors during its operation. The way the system should respond to
these errors depends on several aspects, including the component where the error occurred, the type of error,
and the scope of the error. Because different sites may have different requirements for error behavior, Qlik
Replicate lets you configure the error handling.
You can also add an environment variable that instructs Replicate to create dump files in the event of a crash.
The dump files can then be used by Qlik Support to troubleshoot the cause of the crash. For more
information, refer to the Qlik Replicate setup and User Guide.
You can determine whether or not to override the global error handling settings. For more information, see
Error Handling Settings.
The option to set a Global Error Handling policy is not available when the Apply batched changes
to multiple tables concurrently option is selected in the Task Settings' Change Processing Tuning
tab.
Clicking the Error Handling tab in the Task Settings window reveals the following sub-tabs:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 186

8 Customizing tasks
l
Environmental Errors: An error that is caused by an environmental problem in the source or target
endpoint or on the network. Some examples of environmental errors are loss of communication with
the source or target endpoint, restarting a database, or network problems.
l
Data Errors: An error related to data processing at the record level. Some examples of data errors are
conversion errors, errors in transformations, or bad data.
l
Table Errors: An error in processing data or metadata for a specific table. This only includes general
table data and not an error that relates to a specific record.
l
Apply Conflicts: Errors that occur when the target endpoint is not synchronized with the source
endpoint when processing changes.
This can cause duplicate key errors on INSERT operations or zero rows affected on UPDATE/DELETE
operations.
Error Handling settings
The option to switch between the Global Error Handling policy and a Task Error Handling policy is available in
each of the Error Handling sub-tabs. However, the policy you enable will be applied to all error types,
regardless of where it was enabled. For example, you cannot enable a Task Error Handling policy for Data
Errors and then enable the Global Error Handling policy for Table Errors and Environmental Errors.
For information on setting the global error handling policy, see the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
To set a Task-Specific Error Handling policy:
l
Click the Change to Task Policy button in any of the Error Handling sub-tabs.
To revert to the Global Error Handling policy:
1. Click the Change to Global Policy button in any of the Error Handling sub-tabs.
2. Click OK when prompted to confirm your action.
Environmental errors
Click the Environmental Errors sub-tab and then click Change to Task Policy to configure the following:
l
Maximum retry count: Select this option and then specify the maximum number of attempts to retry
a task when a recoverable environmental error occurs.
1. To never retry a task, clear the check box or specify "0".
2. To retry the task an infinite number of times, specify "-1" (the global error handling default).
When the system attempts to retry the task the designated number of times, the task is stopped and
manual intervention is required.
l
Interval between retry attempts: Use the counter to select or type the number of seconds that the
system waits between attempts to retry a task.
Valid values are 0-2,000.
l
Increase retry interval for long outages: Select this check box to increase the retry interval for long
outages. When this option is enabled, Replicate doubles the interval between each retry attempt and
the next, until the Maximum retry interval is reached (and continues retrying according to the
specified maximum interval).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 187

8 Customizing tasks
l
Maximum retry interval: Use the counter to select or type the number of seconds to wait between
attempts to retry a task when the Increase retry interval for long outages option is enabled. Valid
values are 0-2,000.
Data Errors
Click the Data Errors sub-tab and then click Change to Task Policy.
Data truncation errors
l
For a data truncation error: Click the triangle to open the list and select what happens when an
truncation occurs in one or more specific records. You can select one of the following from the list:
l
Ignore record: The task continues and the error is ignored.
l
Log record to the exceptions table (default): The task continues and the error is written to the
exceptions table.
l
Suspend table: The task continues, but data from the table with the error record is moved into
an error state and its data is not replicated
l
Stop task: The task is stopped and manual intervention is required.
Data truncation error handling is only supported in the following cases:
l
Replication is to the following target endpoints: MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, Microsoft SQL
Server, SAP Sybase ASE, File, Amazon Redshift, Microsoft Azure Database for PostgreSQL,
Google Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL, Microsoft Azure Database for MySQL, Google Cloud SQL for
MySQL, and Microsoft Azure SQL Database
l
Change Processing replication only (i.e. not Full Load)
NOT NULL constraint violations
For source tables, Replicate can explicitly check for NULL values in each data column of each record, and
whether the same column in the corresponding target table is marked as NOT NULL. In such cases, applying
the record to the target will trigger a NOT NULL constraint violation that will be difficult to recover from if the
task is running in Batch Optimized Apply mode. Therefore, the record is not applied to the target. Instead, the
record is handled as an error (see below) without affecting other records in the batch being applied. While this
way of handling NOT NULL constraint violation is very effective, it can impact performance, and if the target
database does not actually enforce NOT NULL constraint violations, Replicate can be configured to skip that
check in order to save CPU time and improve performance. Because Replicate generally knows what target
databases enforce NOT NULL constraint violations, it is safe to always let Replicate activate this protection
based on the target endpoint type. Still, Replicate gives you the option to override this default and either force
a check (with its slight overhead) or disable the check and risk NOT NULL constraint violations.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 188

8 Customizing tasks
When a batch update fails due to a NOT NULL constraint violation, Replicate has no way of knowing
which of the records in the batch caused that violation. Consequently, Replicate switches to a "one-
by-one" strategy of applying changes. While this strategy is acceptable for OLTP databases
(although even with those databases, it is much slower than Batch optimized apply), it is not
practical for analytical data warehouses, specifically those that use columnar storage in files or
micro-partitions (for example, Snowflake, Azure Synapse Analytics, Google BigQuery, and
Databricks). As such databases are not designed for one-by-one record updates, performing such
updates might take an unreasonable amount of time and consume excessive resources. Moreover, If
the target database is a cloud data warehouse that charges based on activity, the one-by-one error
handling strategy could result in extremely high costs.
For NOT NULL constraint violations, select one of the following:
l
Endpoint-determined: This means that the endpoint type (which can be an OLTP database or
an analytical data warehouse) determines whether Replicate checks for NOT NULL constraint
violations.
Some target endpoints do not support checking for NOT NULL constraint violations. In
such cases, the tooltip next to the Endpoint-determined option will indicate that the
current target endpoint does not allow checking for NOT NULL constraints.
For OLTP-based target endpoints, the default is not to check for NOT NULL constraint violations
as it is less critical (from a cost perspective) if a NOT NULL constraint violation occurs during
the task. However, if a NOT NULL constraint violation occurs on any of the tables during the
task, Replicate will switch to one-by-one mode, which will impact performance to a certain
degree (depending on the number and size of the tables being replicated).
You can override the endpoint-determined handling by selecting either the Check or Don't
check options described below.
The string (Check) or (Don't check) will appear after Endpoint-determined
according to the selected target endpoint type.
l
Check: Select this if you always want Replicate to check for NOT NULL constraint violations.
This might be useful if you know beforehand that some of the source table columns contain
NULL values and the corresponding target table columns are configured with NOT NULL
constraints. In this case, Replicate will not switch to one-by-one mode, but will continue change
processing in Batch Optimized Apply mode. If a source table that will violate a NOT NULL
constraint is detected during the check, Replicate will take the action described below. The
default action is to suspend the table.
l
Don't check: Select this if you never want Replicate to check for NOT NULL constraint
violations. This is recommended if you are confident that no such violations will occur during
the task or if you do not mind Replicate switching to one-by-one mode if a NOT NULL constraint
violation occurs.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 189

8 Customizing tasks
Handling options when a NOT NULL constraint violation is discovered during a check:
For the Endpoint-determined and Check options, you can select how Replicate will handle the NOT
NULL constraint violation:
l
Suspend table: This is the default. The task continues, but tables with NULL values are
suspended and their data is not replicated.
l
Ignore record: The task continues and the error is ignored.
l
Log record to the exceptions table: The task continues, but records with NULL values are
written to the exceptions table.
l
Stop task: The task is stopped and manual intervention is required.
Other data errors
l
For other data errors: Click the triangle to open the list and select what happens when an error
occurs in one or more specific records. You can select one of the following from the list:
l
Ignore record: The task continues and the error is ignored.
l
Log record to the exceptions table (default): The task continues and the error is written to the
exceptions table.
l
Suspend table: The task continues, but data from the table with the error record is moved into
an error state and its data is not replicated
l
Stop task: The task is stopped and manual intervention is required.
Escalating error handling
l
Escalate error handling when other data errors reach (per table): Select this check box to escalate
error handling when the number of non-truncation data errors (per table) reaches the specified
amount. Valid values are 1-10,000.
The escalation options are not available when the Apply changes using SQL MERGE task
setting is enabled.
l
Escalation action: Choose what action Replicate should perform when error handling is
escalated. Note that the available actions are dependent on the action selected from the For
other data errors drop-down list described above.
l
Log record to the exceptions table: The task continues, but the record with the error is
written to the exceptions table.
l
Suspend table (default): The task continues, but data from the table with the error
record is moved into an error state and its data is not replicated.
The behavior differs according to the Change Processing Mode:
l
In Transactional apply mode, the last changes will not be replicated
l
In Batch optimized apply mode, a situation is possible where there
will be no replication of data or data replication will occur in part
l
Stop task: The task is stopped and manual intervention is required.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 190

8 Customizing tasks
Table Errors
Click the Table Errors sub-tab and then click Change to Task Policy to configure the following:
When encountering a table error: Select one of the following from the drop-down list:
l
Suspend table (default): The task continues but data from the table with the error record is moved
into an error state and its data is not replicated
l
Stop task: The task is stopped and manual intervention is required.
Escalate error handling when table errors reach (per table): Select this check box to escalate error
handling when the number of table errors (per table) reaches the specified amount. Valid values are 1-10,000.
l
Escalation action: The escalation policy for table errors is set to Stop task and cannot be changed.
Apply Conflicts
The Apply Conflicts error handling policy will be preset and uneditable when the Apply changes
using SQL MERGE task setting is enabled.
Click the Apply Conflicts sub-tab and then click Change to Task Policy to configure the following:
No record found for applying a DELETE: Click the triangle to open the list and select what happens when
there is a conflict with a DELETE operation. You can select one of the following from the list:
l
Ignore record (default): The task continues and the error is ignored.
l
Log record to the exceptions table: The task continues and the record is written to the exceptions
table.
l
Suspend table: The task continues but data from the table with the error record is moved into an error
state and its data is not replicated.
l
Stop task: The task is stopped and manual intervention is required.
Duplicate key when applying an INSERT: Click the triangle to open the list and select what happens when
there is a conflict with an INSERT operation. You can select one of the following from the list:
l
Ignore record: The task continues and the error is ignored.
l
Log record to the exceptions table (default): The task continues and the record is written to the
exceptions table.
l
Suspend table: The task continues but data from the table with the error record is moved into an error
state and its data is not replicated.
l
Stop task: The task is stopped and manual intervention is required.
l
Update the existing target record: The target record with the same primary key as the INSERTED
source record is updated.
l
Allow duplicates in the target: Allows duplicate primary key records to be added to the target table.
When Optimize inserts is enabled, this is the only option that is available at task level error handling.
For more information on the Optimize inserts option, see Change Processing Tuning (page 181).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 191
8 Customizing tasks
No record found for applying an UPDATE: Click the triangle to open the list and select what happens when
there is a conflict with an UPDATE operation. You can select one of the following from the list:
l
Ignore record: The task continues and the error is ignored.
l
Log record to the exceptions table (default): The task continues and the record is written to the
exceptions table.
l
Suspend table: The task continues but data from the table with the error record is moved into an error
state and its data is not replicated
l
Stop task: The task is stopped and manual intervention is required.
l
Insert the missing target record: The missing target record will be inserted into the target table.
When the source endpoint is Oracle, selecting this option requires supplemental logging to be enabled
for all the source table columns.
Escalate handling when apply conflicts reach (per table): Select this check box to escalate error handling
when the number of apply conflicts (per table) reaches the specified amount. Valid values are 1-10,000.
l
When this option is selected and the number of conflicts reaches the specified number,
l
Apply Conflicts errors are counted for each table separately when a task is run. When a task
stops, the error count reverts to zero. When a task is resumed/reloaded, the number of errors
for all the tables are reset.
l
When working in Batch optimized apply Change Processing mode, the calculation of the
Apply Conflicts amount does not include DELETE and UPDATE conflicts that were ignored (as
a result of enabling the Ignore Record option described above).
Escalation action: Choose what action Replicate should perform when handling is escalated. Note that the
available actions are dependent on the action selected in the drop-down lists described above.
When this option is selected and the number of conflicts reaches the specified number, only the
escalation action will be performed (i.e. the original action set for the Apply conflict will not be
performed).
l
Log record to the exceptions table (default): The task continues and the error is written to the task
log and to the exceptions table.
l
Suspend table: The task continues but data from the table with the error record is moved into an error
state and its data is not replicated.
l
Stop task: The task is stopped and manual intervention is required.
Logging
You can set the logging level for task logs by selecting the Logging tab in the Task Settings dialog box and
then selecting the Logging Level sub-tab.The level you set determines what information is written to the log.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 192

8 Customizing tasks
You can also set the task logging level from the Tools menu in Monitor view.
For more information, see Monitor mode (page 208) and Logging (page 244).
For more information on monitoring, see Monitor mode (page 208). For more information on setting
the task logging level in Qlik Replicate, see the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
The following are the available logging levels. The list is in order from the lowest level to the highest level.
1. Error
2. Warning
3. Info
4. Trace
5. Verbose
The higher levels always include the messages from the lower levels. Therefore, if you select Error, only error
messages are written to the log. However, if you select Info, informational messages, warnings, and error
messages are included. Selecting Verbose writes all possible messages to the log.
For information on how to set the logging level in Qlik Replicate, see the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
Storing trace and verbose logging in memory
This option is relevant to Replicate tasks only.
When the logging level is set to "Trace" or "Verbose", you can instruct Replicate to store the logging
information in memory until an error occurs. On detecting an error, Replicate will begin writing to the physical
logs and continue to do so for a few minutes after the initial occurrence of the error.
If no error occurs before the allocated memory is used up, Replicate will empty the memory buffer and start
afresh.
This option is useful for tasks that fail unpredictably and for no obvious reason. The problem with continually
writing large amounts of information to the logs is twofold:
l
Running in "Trace" or "Verbose" logging mode will quickly use up available disk space (unless the
logging settings have been configured to prevent this).
l
Continually writing large amounts of data to the logs will affect performance.
To use this option
1. Select the Store trace/verbose logging in memory, but if an error occurs, write to the logs check
box at the top of the tab.
2. In the Allocate memory up to (MB) field, specify the amount of memory you want to allocate for
storing logging information.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 193

8 Customizing tasks
Character substitution
You can substitute or delete source characters in the target database and/or you can substitute or delete
source characters that are not supported by a selected character set.
l
All characters must be specified as Unicode code points.
l
Character substitution will also be performed on Replicate Control Tables.
l
Invalid values will be indicated by a red triangle in the top right of the table cell. Hovering
your mouse cursor over the triangle will show the error message.
l
Any table-level or global transformations defined for the task will be performed after the
character substitution has been completed.
l
Substitutions actions defined in the Substitute or Delete Source Characters table are
performed before the substitution action defined in the Substitute or Delete Source
Characters Unsupported by the Selected Character Set table.
l
Character substitution does not support LOBdata types.
Substituting or deleting Source Characters
Use the Substitute or Delete Source Characters table to define replacements for specific source characters.
This may be useful, for example, when the Unicode representation of a character is different on the source
and target platforms. For example, on Linux, the minus character in the Shift_JIS character set is
represented as U+2212, but on Windows it is represented as U+FF0D.
To Do This
Define substitution actions. 1. Click the Add Character button above the table.
2. Specify a source character and a target character in the Source
Character and Substitute Character fields respectively.
For example to replace the letter "a" with the letter "e", specify 0061
and 0065 respectively.
To delete the specified source character, enter
0
in the
Substitute Character column.
3. Repeat steps 1-2 to replace or delete additional characters.
Edit the specified source or
target character
Click anywhere in the relevant column and change the character as required.
Delete entries from the
table
Select the desired entry or entries and click the Delete button.
Substitution actions
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 194
8 Customizing tasks
Substituting or deleting Source Characters unsupported by the selected character
set
Use the Substitute or Delete Source Characters Unsupported by the Selected Character Set table to
define a single replacement character for all characters not supported by the selected character set.
To Do This
Define or edit a
substitution
action.
1. Select a character set from the Character Set drop-down list in the table.
Any characters not supported by the selected character set will be replaced on
the target by the character specified in step 2 below.
2. In the Substitute Character column, click anywhere in the column and specify
the replacement character. For example, to replace all unsupported characters
with the letter "a", enter 0061.
To delete all unsupported characters, enter
0
.
Disable the
substitution
action.
Select the blank entry from the Character Set drop-down list.
Unsupported character substitution actions
File uploads
Note that the File Uploads tab will only be shown if the task is defined with an endpoint that supports this
feature.
Click the Optimize File Uploads button to improve performance when replicating to file-based targets such
as Amazon S3 and Hadoop. When this feature is enabled, the button text changes to Disable File Upload
Optimization. Click the Disable File Upload Optimization button to disable file upload optimization.
The upload mode depends on the task type:
l
Full Load - Multiple files created from the same table are transferred in parallel, in no particular order.
l
Apply Changes - Files created from multiple tables are transferred in parallel. Files created from the
same table are transferred sequentially according to creation time.
l
Change Data Partitioning - Files created from multiple tables and files created from the same table
are transferred in parallel.
Note that disabling this option after the task has already started will require you to do one of the following:
l
If the task is in the Full Load stage, reload the target using the Reload Target Run option.
l
If the task is in the Change Processing stage, resume the task using the Start processing changes
from Run option.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 195

8 Customizing tasks
l
Supported by the following target endpoints only: Amazon S3, Hadoop (Hortonworks,
Cloudera, and MapR) Microsoft Azure ADLS, Databricks (Cloud Storage), Microsoft Azure
HDInsight, Hortonworks Data Platform (HDP), Google Cloud Storage, Google Cloud Dataproc,
Amazon EMR, and Cloudera Data Platform (CDP) Private Cloud.
l
General Limitations and Considerations:
l
Post Upload Processing endpoint settings are not supported.
l
Hadoop - Limitations and Considerations:
l
When replicating to a Hadoop target, only Text and Sequence file formats are
supported.
l
Hive jobs are not supported as they will prevent the file upload.
l
Append is not supported when using Text file format.
l
Amazon S3 and Microsoft Azure ADLS - Limitations and Considerations:
l
When working with Reference Files, a new entry is added to the Reference File
immediately after the data file is uploaded (even if the DFM file has not been
uploaded yet).
l
The existence of the DFM file does not necessarily mean that the associated data file
has also been uploaded.
Message Format
The Message Format tab will only be shown if the task is defined with a streaming target endpoint that
supports this feature.
When a task is defined with such an endpoint, you can specify a custom message format that will override the
default Replicate message format. This may be useful if the consumer application needs to process the
message in a particular format.
The custom message format can be defined at task level and/or at table level. When it is defined at both task
and table level, the message format defined for the table will take precedence over the message format
defined for the task.
For information on defining a custom message format at table level, see Message format (page 106).
l
Supported by the Kafka target endpoint only
l
The custom message format feature cannot be used in conjunction the Attunity Avro Message
Decoder SDK
l
Hierarchical structured messages are not supported.
General rules and usage guidelines
When defining a custom message, it is import to consider the rules and usage guidelines listed below.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 196

8 Customizing tasks
Section names:
The following naming rules apply:
l
Section names must start with the characters a-z, A-Z, or _ (an underscore) and can then be followed
by any of the following characters: a-z, A-Z, 0-9, _
l
With the exception of the Record name and Key name sections (that do not end with a slash),
removing the slash from section names will flatten the hierarchy of the associated section (see Slashes
below).
l
All section names except Record name and Key name can be deleted (see Deletion: (page 198) below)
l
The Data name and Include record Before-data section names cannot both be deleted
l
The Data name and Include record Before-data section names cannot be the same
Slashes:
Some of the section names in the UI end with a slash (e.g. beforeData/). The purpose of the slash is to
maintain a hierarchy of the different sections within the message. If the slash is removed, the following will
occur:
l
The hierarchical structure of that section will be flattened, resulting in the section name being
removed from the message
l
The section name will be prefixed to the actual metadata, either directly or using a separator character
(e.g. an underscore) that you appended to the name
Example of a data message when headers/ is specified with a slash:
"message":{
"data":{
"COL1": "159",
"COL2": "159"
},
"beforeData": null,
"headers": {
"operation": "INSERT",
"changeSequence": "2018100811484900000000233",
Example of a data message when headers_ is specified with an underscore instead of a slash:
"message":{
"data":{
"COL1": "159",
"COL2": "159"
},
"beforeData": null,
"headers_operation": "INSERT",
"headers_changeSequence": "2018100811484900000000233",
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 197

8 Customizing tasks
Deletion:
Deleting a section name from the message will flatten the hierarchical structure of that section. This will result
in all of that section's data appearing immediately below the content of the preceding section.
Example of a data message with the headers section name:
"message":{
"data":{
"COL1": "159",
"COL2": "159"
},
"headers": {
"operation": "INSERT",
"changeSequence": "2018100811484900000000233",
Example of a data message without the headers section name:
"message":{
"data":{
"COL1": "159",
"COL2": "159"
},
"beforeData": null,
"operation": "INSERT",
"changeSequence": "2018100811484900000000233",
Variables
You can add variables to names by clicking the button at the end of the row. The following variables are
available:
l
SERVER_NAME - The host name of the Replicate Server
l
TARGET_TABLE_NAME - The name of the table
l
TARGET_TABLE_OWNER - The table owner
l
TASK_NAME - The name of the Replicate task
The TARGET_TABLE_OWNER variable is not available for the Record name and Key name options
(described in the table below).
Defining a custom message format
To define a custom message format, click the Custom Message Format button and configure the options as
described in the table below.
To revert to the default message format, click the Default Message Format button.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 198
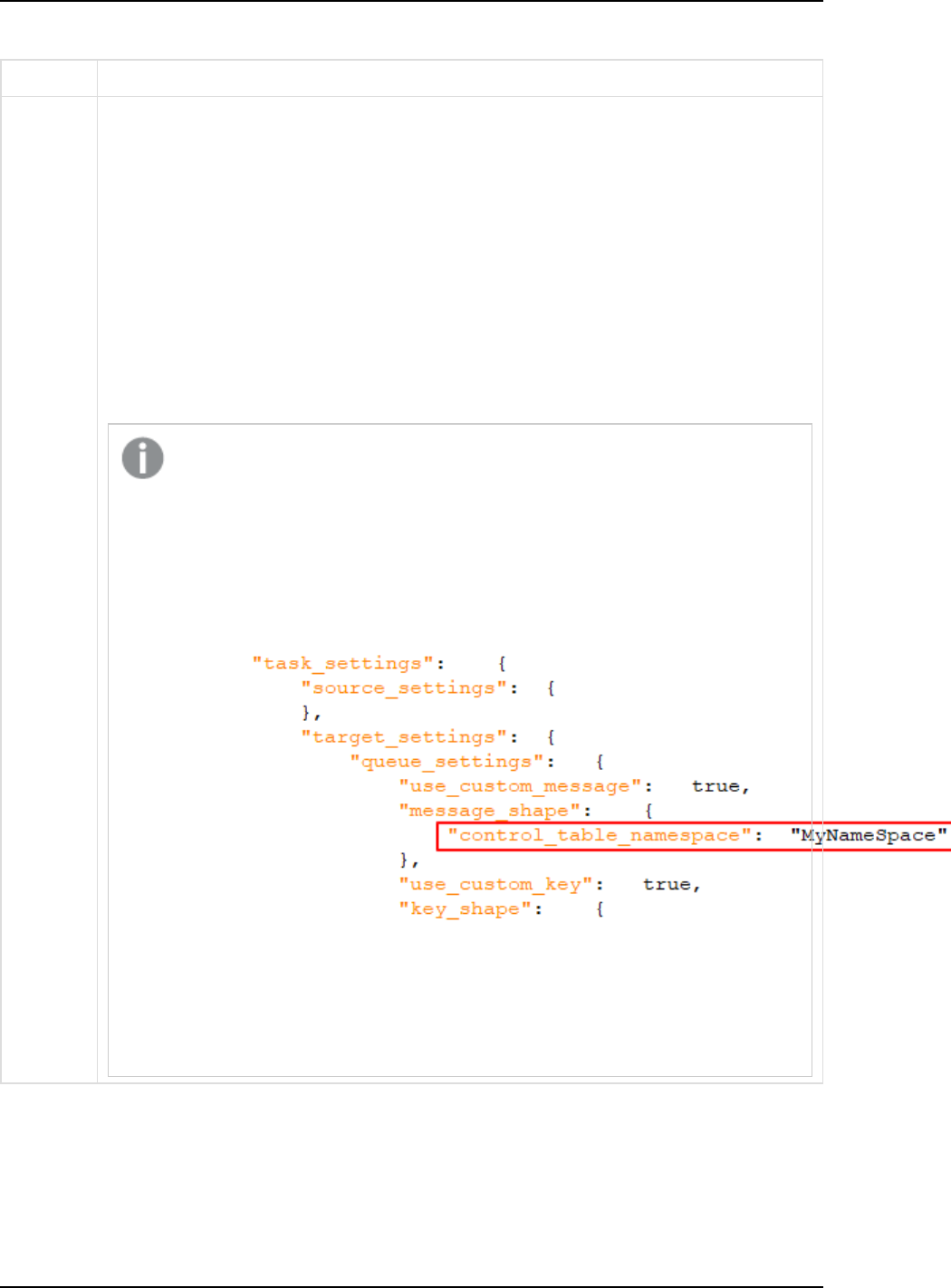
8 Customizing tasks
Option Description
Include
Namespa
ce
A unique identifier for the message. This should be a string, separated by periods. Note that
the Namespace will be included in both the message and the message key.
Example:
mycompany.queue.msg
Default name:
com.attunity.queue.msg.{{TASK_NAME}}.{{TARGET_TABLE_OWNER}}.{{TARGET_TABLE_NAME}}
Default name for Control Tables:
com.attunity.queue.msg.{{TARGET_TABLE_NAME}}
The default Control Table Namespace cannot be changed via the UI. You can,
however, change the default Control Table Namespace as follows:
1. In the Task Settings Message Format tab, click the Custom Message
Format button and then click OK.
2. Save the task and then export it using the Export Task toolbar button.
3. Open the exported JSON file and add the
control_table_namespace
parameter as follows (replacing
MyNameSpace
with your own value):
4. Save the JSON file and then import it to Replicate using the Import Task
toolbar button.
For instructions on exporting/importing tasks, see Exporting and importing tasks
(page 80).
Message format options
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 199

8 Customizing tasks
Option Description
Record
name
The name of the record (i.e. message).
Default name:
DataRecord
Data
name
All of the data columns included in the record.
Default name:
data/
Include
Headers
Header columns provide additional information about the source operations.
For more information, see Include the following headers (page 200) below.
Include
headers
namespa
ce
A unique identifier for the header columns section. This should be a string, separated by
periods.
Example:
headers.queue.msg
Default name:
com.attunity.queue.msg
Headers
name
The name of the section containing the Replicate column headers.
Default name:
headers/
Include
the
following
headers
For a description of the available header columns, refer to Data Messages in the Qlik Help.
Default:
All columns are included by default, except the External Schema ID column.
Include
record
Before-
data
When this check box is selected (the default), both pre and post UPDATE data will be included
in UPDATE messages.
To include only the post UPDATE data in messages, clear the check box.
Default name:
beforeData/
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 200

8 Customizing tasks
Option Description
Key name The name of the section containing the message key.
Default name:
keyRecord
This option is only applicable when:
l
The Encode the message key in Avro format option is enabled
l
The Metadata Publishing Method is set to Publish data schemas to Confluent
Registry Schema or Publish data schemas to Hortonworks Schema Registry
l
The Message key is not set to None
Transformations and Filters
Click the Transformations and Filters tab to show the Expression defaults tab. Expressions can be used in
global transformations and filter rules as well as in table-level transformations and filters.
This option can be set globally for all tasks or individually for a specific task. To set the option for a specific
task, click the Change to Task Policy button and set the option as required. If you want to use the global
policy set in the server settings'Transformations and Filters tab, click the Change to Global Policy button.
l
Support special characters in column names used in expressions: Enable this option if you want to
include source column names with special characters in expressions defined for this task. An example
of such a column name would be special#column.
A condition for enabling this option is that all table and global transformations must use strict SQL
syntax. Specifically, all string literals must use single quotes (') rather than double quotes. If any of
the transformations on any task on the server uses double quotes (") to quote literals, then you
should not enable this option.
Before enabling this option, you must fix any use of double quotes in string literals. For example, a
transformation such as:
CASE age WHEN age < 18 THEN "adult" ELSE "minor" END)
must be rewritten as:
CASE age WHEN age < 18 THEN 'adult' ELSE 'minor' END)
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 201

8 Customizing tasks
See also:
l
Defining global rules (page 107)
l
Using filters (page 92)
l
Defining transformations for a single table/view (page 84)
l
Using the Expression Builder (page 137)
More options
These options are not exposed in the UI as they are only relevant to specific versions or environments.
Consequently, do not set these options unless explicitly instructed to do so by Qlik Support or product
documentation.
To set an option, simply copy the option into the Add feature name field and click Add. Then set the value or
enable the option according to the instructions you received.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 202

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
By default, Qlik Enterprise Manager opens in Tasks View. Tasks View is where you monitor and control your
Replicate and Compose tasks. To switch between Servers View and Tasks View, click the Tasks tab in the top
left of the console.
Currently, the following options are not available for Compose tasks:
l
Task drill-down
l
Deleting tasks
l
Enabling/disabling scheduling
l
Generating task instructions
l
Monitoring of Command tasks
For information on managing user permissions for all tasks on a server or for a specific task, see Managing
user permissions (page 286).
In this section:
l
Monitoring Replicate tasks (page 203)
l
Monitoring Compose tasks and workflows (page 222)
l
Searching for tasks (page 230)
l
Customizing task columns (page 231)
l
Grouping tasks (page 232)
l
Running a task (page 234)
l
Error handling (page 243)
l
Using the monitor tools (page 244)
l
Scheduling jobs (page 247)
9.1 Monitoring Replicate tasks
In this section:
l
Task progress summary (page 203)
l
Viewing specific tasks (page 207)
l
Monitoring Full Load replication (page 209)
l
Monitoring Change Processing replication (page 215)
Task progress summary
The Tasks View displays a list of tasks in tabular format in the middle pane.
For each task, Enterprise Manager can display the following columns:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 203

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
General columns
l
State: The current state of a task. Possible states are described in the table below.
You can filter the table by state by selecting or clearing the respective check box in the States pane
above the table.
Task State Icon Description
Running The task is running.
A spinning circle icon will be shown when the task is in a
"Starting" state.
Stopped The task has not been run yet or when the task has stopped at some
point during the replication.
A spinning circle icon will be shown when the task is in a
"Stopping" state.
Error The task has stopped due to a fatal error.
Recovering The task is recovering from a recoverable error.
Task states
l
Server: The name of the server
l
Task: The name of the task
l
Stage: The current stage of the task: Loading or Change Processing.
l
Tables with Error:The number of tables with error.
Not displayed by default:
l
Reason: An explanation for the current state
l
Description: A description of the task, as entered by the user
l
Data Errors: The total number of data errors in all tables involved in the task. The count is affected by
data errors and the Reset Data Errors option available when you drill down to a task.
l
Profile: The task profile, which can be either unidirectional or bidirectional
l
Log Stream Staging: The name of the Log Stream Staging task, both for the actual Log Stream
Staging task and for any tasks associated with the Log Stream Staging task. For more information
about the Log Stream Staging feature, refer to the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
l
Type: The type of task, such as Full Load, CDC, or Full Load & CDC
l
Loading Ended: Indicates whether loading has completed. This refers to completion of the Full Load
stage in Replicate tasks and completion of the Full Load and/or Change Processing stage in Compose
tasks.
l
Source Name: The name of the source
l
Source Type: The database type of the source
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 204

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
l
Target Name: The name of the target
l
Target Type: The target’s database type
l
Memory (MB): The current utilization of memory, in MB. A task’s memory utilization is sampled
approximately every 10 seconds. When the task is not running, the value is set to zero (0).
l
Disk Usage (MB): The current utilization of disk space, in MB. A task’s disk utilization is sampled
approximately every minute.
l
CPU (%): The amount of CPU being used by a specific task. The CPU sampling rate is approximately 10
seconds.
l
Tags: The tags associated with a task
Loading columns
l
Progress (%): The percentage of loading completed
l
Target Throughput (rec/sec): The current target throughput, in rec/sec
Not displayed by default:
l
Started: The date and time the loading started
l
Ended: The date and time the loading ended
l
Load Duration: The duration of the load process, in hh:mm:ss
l
Total Tables: The total number of tables
l
Tables Completed: The number of completed tables
l
Tables Left: The number of tables remaining to be loaded
l
Tables Loading: The number of tables currently loading
l
Tables Queued: The number of tables in queue
l
Records Completed: The number of completed records
l
Records Left: The number of records remaining to be loaded
l
Source Throughput (kbyte/sec): The current source throughput, in kbyte/sec
l
Source Throughput (rec/sec): The current source throughput, in rec/sec
l
Table Notes: Table notes, such as "0 tables failed loading"
l
Target Throughput (kbyte/sec): The current target throughput, in kbyte/sec
l
Total Records: The total number of records
With Compose tasks, canceled tables are reflected in the Total Tables counter but not in the
Completed/Loading/Queued/Error counters. Therefore, when one or more tables is canceled in a
task, the sum of these counters will be less than the Total Tables.
Change Processing columns
l
Incoming Changes: The number of changes currently being processed
l
Applied Changes: The number of changes applied
l
Apply Throughput (rec/sec): The apply throughput, in rec/sec
l
Apply Latency: The apply latency
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 205

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
l
Apply Throughput (kbyte/sec): The apply throughput, in kbyte/sec
l
Changes for Apply - In Memory (Target): The number of changes in memory during apply and until
target commit
l
Changes for Apply - On Disk (Target): The number of changes on disk during apply and until target
commit
l
Changes In Memory (Source): The number of changes accumulated in memory until source commit
l
Changes on Disk (Source): The number of changes accumulated on disk until source commit
l
COMMIT Change Records: The number of COMMIT change records
l
COMMIT Change Volume: The number of COMMIT change volume, in MB
l
COMMIT Transactions: The number of COMMIT transactions
l
DDLs: The total number of applied DDLs
l
DDLs (%): The percentage of applied DDLs
l
DELETEs: The total number of DELETEs applied
l
DELETEs (%): The percentage of DELETEs applied
l
Incoming Transactions: The number of incoming transactions
l
INSERTs: The total number of INSERTs applied
l
INSERTs (%): The total percentage of INSERTs applied
l
ROLLBACK Change Records: The number of ROLLBACK change records
l
ROLLBACK Change Volume: The number of ROLLBACK change volume, in MB
l
ROLLBACK Transactions: The number of ROLLBACK transactions
l
Source Latency: The current source latency, in hh:mm:ss
l
Source Throughput (kbyte/sec): The current source throughput, in kbyte/sec
l
Source Throughput (rec/sec): The current source throughput, in rec/sec
l
Total Latency: The overall latency, in hh:mm:ss
l
Transactions (Source): The number of transactions accumulated until source commit
l
Transactions for Apply (Target): The number of transaction during apply and until target commit
l
UPDATES: The total number of UPDATEs applied
l
UPDATES (%): The percentage of UPDATEs applied
Status summary
The Status Summary at the bottom of the window provides a quick overview of the current status of all
monitored tasks and servers. It lists the following information:
l
For tasks: The total number of monitored tasks as well as the number of tasks that are running (green
icon), stopped (gray icon), recovering (orange icon), and encountered an error (red icon)
The "running" state also includes "starting" tasks. Similarly, the "stopped" state also
includes "stopping" tasks.
You can double-click the task counters to open the corresponding Tasks View.
Note: The task counters do not consider tasks on servers that are not currently monitored. For more
information, see Additional server management options (page 60).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 206
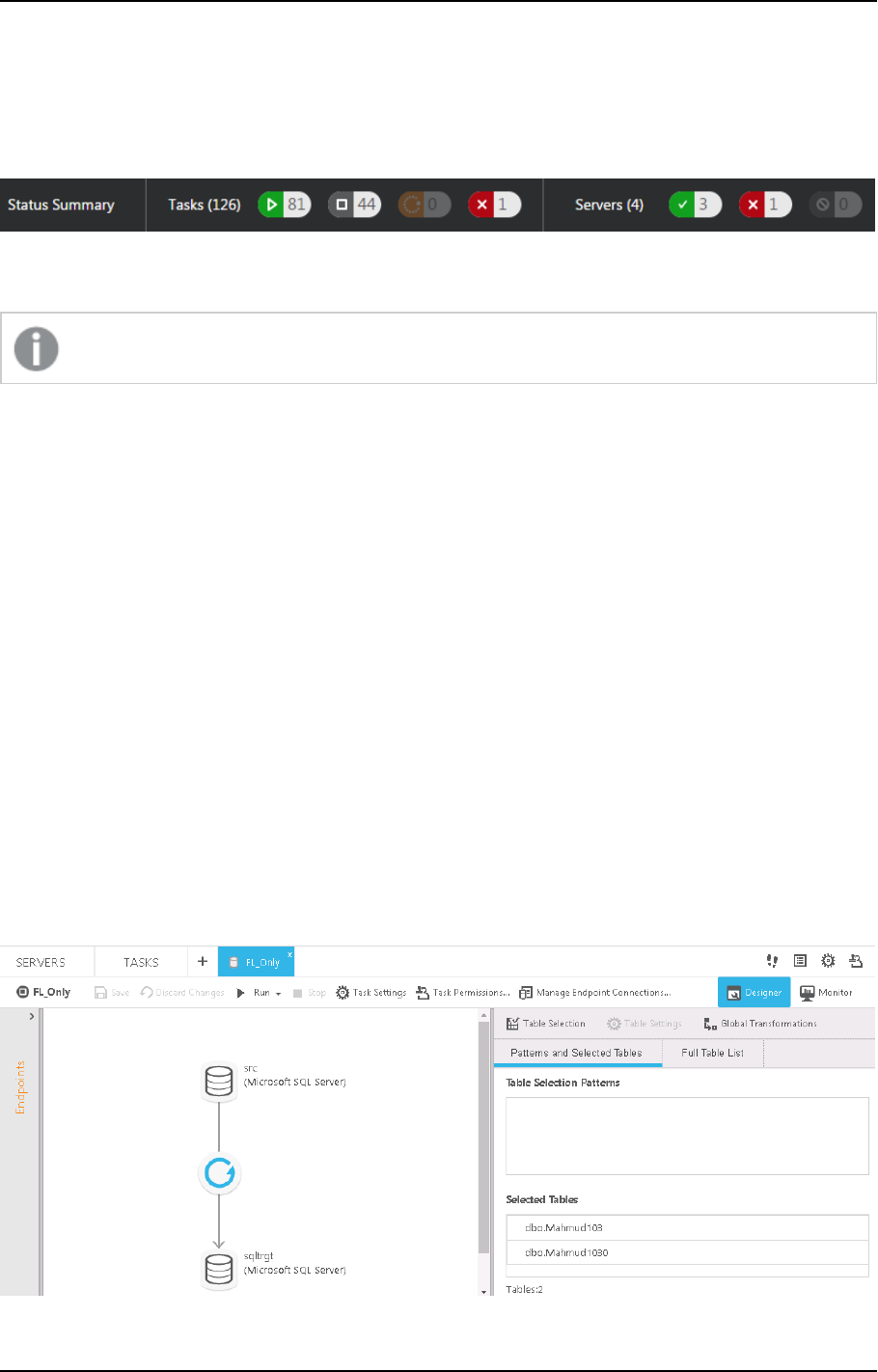
9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
l
For servers: The total number of servers, the number of servers that are running and successfully
monitored (green icon), the number of faulty servers that Enterprise Manager cannot monitor (red
icon), and the number of servers that are not being monitored (gray icon)
Status Bar Example
Viewing specific tasks
Currently, this functionality is available for Replicate tasks only.
From the Tasks view, you can drill down to an individual task, provided you have already created at least one
task (see Defining and managing tasks (page 64) for more information). Two modes display different sets of
information for each task:
l
Designer mode (page 207): Here you define endpoints, select tables, modify table settings (including
filters and transformations), and create global transformation rules.
l
Monitor mode (page 208): Default mode when you open a task. Here you view replication task activities
in real time, along with log messages and notifications.
To view a specific task:
1. In the Tasks view, select the task you want to work with.
The right pane displays the task diagram on the right side of the page.
2. On the Tasks view toolbar, click Open.
Designer mode
In Designer mode, you define endpoints, select tables to be replicated, modify table settings (including filters
and transformations), and create global transformation rules.
Viewing a task in Designer mode
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 207

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
The Designer mode includes the following elements:
l
Endpoints list: Lists the source and target endpoint connections that you added to Qlik Replicate. For
more information, see Defining and managing endpoints (page 69). The figure shows the Endpoints List
in a collapsed state, hiding the endpoints. To expand the list, click the right arrow at the top or
anywhere below it. To close the panel, click the left arrow.
l
Endpoints map: Illustrates the connection between the source and target endpoints for the task. The
round icon between the endpoints represents the task type, which can indicate Full Load only, Full
Load and Apply Changes, or Apply Changes only.
l
When you create a task, you can drag the endpoints to the source and target drop spots as required.
For more information, see Adding a source and target endpoint to a task (page 72).
l
Monitor and Designer buttons: Switch between Monitor mode and Designer mode. See also Monitor
mode (page 208).
l
Run button: Lets you run the task at hand.
l
Task Settings button: Opens the Task Settings dialog box. For more information, see Task Settings
(page 165).
l
Manage Endpoint Connections button: Lets you view the endpoints defined, edit them, or add new
endpoints. For more information, see Defining and managing endpoints (page 69).
l
Select and Define Tables: Lets you select the tables you want to include in your replication task. In
addition, you can use transformation and filter operations to create new tables or to replicate parts of
tables. For more information, Selecting tables and/or views for replication (page 73), Using filters (page
92), and Defining transformations for a single table/view (page 84).
l
Global Transformations option: Lets you create transformations for all tables in a task. For more
information, see Starting the Global Transformation Rules wizard (page 107).
To display a task in Designer mode:
l
On the right side of the toolbar, click Designer.
Monitor mode
In Monitor mode, you view the replication task activities in real time. This is the default mode when you open
a task.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 208

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
Viewing a task in Monitor mode
The Monitor mode includes the following elements:
l
Run button: Lets you run the task at hand.
l
Manage Endpoint Connections button: Lets you view the endpoints defined, edit them, or add new
endpoints. For more information, see Defining and managing endpoints (page 69).
l
Monitor and Designer buttons: Switch between Monitor mode and Designer mode. See also Designer
mode (page 207) and Defining and managing tasks (page 64).
l
Tools list: Provides access to history, log management, and status information.
l
Change Processing/Full Load tabs: Lets you select the information you want to focus on. By default,
Enterprise Manager displays the Change Processing view.
l
Task Map: Illustrates the connection between the source and target endpoints for the task. The round
icon between the endpoints represents the task type, which can indicate Full Load only, Full Load and
Apply Changes, or Apply Changes only.
l
Message Center: Displays notifications and logging messages. By default, the Message Center is
minimized to a message tray at the bottom left of the console. For more information, see Messages
and notifications (page 250).
To display a task in Monitor mode:
l
On the right side of the toolbar, click Monitor.
Monitoring Full Load replication
You can view general information on the progress of a Replicate Full Load operation in the Loading tab, which
is located in the Task Dashboard to the right of the Task List. You can also drill down to more detailed
information in a dedicated tab for the task by clicking a bar or gauge in the Task Dashboard, or by double-
clicking the task in the table.
In this section:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 209

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
l
General information for loading replication (page 210)
l
Detailed information for Full Load replication (page 210)
General information for loading replication
The Loading tab in the right pane shows the following general progress information:
l
Source: The name and type of the source endpoint.
l
Target: The name and type of the target endpoint.
l
Loading and Change Processing tabs containing the information described below.
l
Load Duration: The duration of the loading operation
l
Ended: When the loading operation completed
l
Overall Progress bar: The overall progress of the loading operation
l
Table bars: The status of the tables being loaded, which can be:
l
Completed - The number of tables that have been loaded into the target.
l
Loading - The number of tables that are currently being loaded into the target.
l
Queued - The number of tables that are waiting to be loaded into the target.
l
Error - The number of tables that could not be loaded due to an error
See Messages and notifications (page 250) and Data error handling (page 243) for more
information about error messages.
l
Tables: The number of total tables, the number of tables that have completed loading into the target,
and the number of tables remaining to be loaded into the target.
l
Records: The number of total records, records that have completed loading into the target endpoint,
and records remaining to be loaded into the target endpoint
l
Throughput gauge: The current throughput, which is the number/volume of records being retrieved
from the source and applied to the target at any given time
For more information, see Setting the unit of throughput measurement (page 214).
Detailed information for Full Load replication
This functionality is currently available for Replicate tasks only.
You can view more detailed information about the Full Load status by double-clicking a status bar or about
throughput by double-clicking the throughput gauge. This opens the task in the <task name> tab, in the
context of the bar or gauge that you clicked. The information that is displayed is the same information that
you would see if you were monitoring the task in Replicate.
In this section:
l
Information about the overall progress (page 211)
l
Information about all tables that are being loaded (page 211)
l
Information about tables that Replicate has finished loading (page 212)
l
Information about tables that are being loaded (page 213)
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 210

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
l
Information about tables that are waiting to be loaded (page 214)
l
Information about tables with errors (page 214)
l
Information about throughput (page 214)
l
Setting the unit of throughput measurement (page 214)
Information about the overall progress
To view additional details about the overall progress, in the <task name> tab, click the Total Completion bar.
The Progress Details area displays a grid with the following information:
Category Total Completed Remaining Notes
Tables The total number of
tables that are
included in the task.
The total number of
tables that completed
loading at the current
time.
The total number
of tables waiting to
be loaded.
Additional
information, such as
how many tables
failed loading.
Records The total records
that are included in
the task the current
time.
The total number of
records that completed
loading at the current
time.
The total number
of records waiting
to be loaded.
Additional
information.
Time The estimated time
to load all of the
selected tables in
the task.
The total elapsed time. The estimated
amount of time to
load the remaining
tables.
Additional
information.
Progress information
Information about all tables that are being loaded
To view additional details about the tables, or to reload data to selected tables, in the <task name> tab, click
Select All.
The Tables - All area displays a grid with the following information:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 211

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
l
Table Name: The name of the source table that is included in the task
l
Status: The task status, which can be any of the following:
l
Queued - The table is in the queue waiting to be loaded to the target endpoint.
l
Loading - The table is being processed but is not finished loading.
l
Completed - All of the table records are loaded to the target.
l
Error - The table stopped loading due to an error.
See Messages and notifications (page 250) and Data error handling (page 243) for more
information about error messages.
With Compose tasks, canceled tables are reflected in the Total Tables counter but not in the
Completed/Loading/Queued/Error counters. Therefore, when one or more tables is canceled
in a task, the sum of these counters will be less than the Total Tables.
l
Estimated Count: The estimated number of records that have been loaded to the target
l
Elapsed Time: The total elapsed time since Replicate started processing the records
l
Progress: The loading progress in terms of percentage
l
Reload: To reload selected tables, select the tables you want to reload and then click Reload above
the table list. When prompted to confirm the operation, click OK. The data in the selected tables will
be reloaded to the target endpoint. Note that this option is not available for Apply Changes Only
tasks.
You can also:
l
Reload tables. To reload selected tables, select the tables you want to reload and then click Reload
above the table list. When prompted to confirm the operation, click OK. The data in the selected tables
will be reloaded to the target endpoint. Note that this option is not available for Apply Changes Only
tasks.
l
Use the Columns Settings dialog box to select which columns to display and to arrange the order in
which they appear. For more information, see Customizing task columns (page 231).
l
Hide a column, export the list to a TSV file, or sort by column in ascending or descending order. For
more information, see Customizing task columns (page 231).
Information about tables that Replicate has finished loading
To view more information about tables that Replicate has finished loading, or to reload data to selected
tables, in the <task name> tab, click the Completed bar. The Tables - Completed area displays a grid with the
following information:
l
Table name: The name of the source table that has completed loading.
l
Loaded On: The time that the table completed loading all of its records to the target.
l
Transferred Count: The number of records loaded to the target.
l
Transferred Volume (MB): The volume of the records (in KB) loaded to the target.
l
Load Duration: The amount of time that it took for all records to load to the target.
l
Throughput Records: The average throughput rate for the table. Throughput describes the number of
records read per second. See also Setting the unit of throughput measurement (page 214).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 212

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
l
Throughput Volume (KB/sec): The average throughput rate for the table. Throughput describes the
volume of records (in KB) read per second. See also Setting the unit of throughput measurement (page
214).
You can also:
l
Reload tables. To reload selected tables, select the tables you want to reload and then click Reload
above the table list. When prompted to confirm the operation, click OK. The data in the selected tables
will be reloaded to the target endpoint. Note that this option is not available for Apply Changes Only
tasks.
l
Use the Columns Settings dialog box to select which columns to display and to arrange the order in
which they appear. For more information, see Customizing task columns (page 231).
l
Hide a column, export the list to a TSV file, or sort by column in ascending or descending order. For
more information, see Customizing task columns (page 231).
Information about tables that are being loaded
To view more information about tables that Replicate is currently loading, or to reload data to selected tables,
in the <task name> tab, click the Loading bar. The Tables - Loading area displays a grid with the following
information:
l
Table Name: The names of the source tables that are currently loading.
l
Load Duration: The amount of time that it took for all records to load to the current point in time.
l
Estimated Count: The estimated number of rows that are waiting to be loaded in the full load
operation.
l
Transferred Count: The number of records that are loaded to the target endpoint.
l
Current Throughput: The current throughput rate for the table. Throughput describes the number of
records read per second. For more information about throughput, see also Setting the unit of
throughput measurement (page 214).
l
Cached Changes: The number of changes that were cached during full load when the source tables
changed. Cached changes are typically applied to tables after the last table completes full load.
l
Estimated Finish Time: The approximate date and time the task will finish loading the tables.
l
Progress: The table status and the time the table entered that status.
You can also:
l
Reload tables. To reload selected tables, select the tables you want to reload and then click Reload
above the table list. When prompted to confirm the operation, click OK. The data in the selected tables
will be reloaded to the target endpoint. Note that this option is not available for Apply Changes Only
tasks.
l
Use the Columns Settings dialog box to select which columns to display and to arrange the order in
which they appear. For more information, see Customizing task columns (page 231).
l
Hide a column, export the list to a TSV file, or sort by column in ascending or descending order. For
more information, see Customizing task columns (page 231).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 213

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
Information about tables that are waiting to be loaded
To view more information about tables in the loading queue, in the <task name> tab, click the Queued bar.
The Tables - Queued area displays a grid with the following information:
l
Table Name: The names of the source tables that are currently in the queue waiting to be loaded.
l
Estimated Count: The estimated number of rows that are waiting to be loaded in the full load
operation.
You can also:
l
Use the Columns Settings dialog box to select which columns to display and to arrange the order in
which they appear. For more information, see Customizing task columns (page 231).
l
Hide a column, export the list to a TSV file, or sort by column in ascending or descending order. For
more information, see Customizing task columns (page 231).
Information about tables with errors
To view more information about tables that could not be loaded due to an error, in the <task name> tab, click
the Error bar. The Tables - Error area displays a grid with the following information:
l
Table Name: The names of the source tables that could not be loaded to the target.
l
Failed On: The time that the error occurred.
l
Loaded Count: The number of records loaded when the error occurred.
You can also:
l
Reload tables. To reload selected tables, select the tables you want to reload and then click Reload
above the table list. When prompted to confirm the operation, click OK. The data in the selected tables
will be reloaded to the target endpoint. Note that this option is not available for Apply Changes Only
tasks.
l
Use the Columns Settings dialog box to select which columns to display and to arrange the order in
which they appear. For more information, see Customizing task columns (page 231).
l
Hide a column, export the list to a TSV file, or sort by column in ascending or descending order. For
more information, see Customizing task columns (page 231).
For more information, see Data error handling (page 243).
Information about throughput
To view a graph representing the number or volume of records (depending on the selected measurement unit)
processed during the Full Load operation, click the Throughput gauge. The Throughput Details area displays
a graph illustrating the source and target throughput rate. This rate indicates how fast the table records are
being replicated to the target endpoint.
Setting the unit of throughput measurement
You can set the throughput measurement values either to the number of records replicated per second or to
the number of kilobytes replicated per second. The display is always based on the current load operation.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 214

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
To set the unit of throughput measurement:
l
From the list above the Throughput gauge, select rec/sec or kbyte/sec.
Monitoring Change Processing replication
You can view general information on the progress of Change Data Capture (CDC) processing in the Change
Processing tab, which is located in the Task Dashboard to the right of the Task List. You also have the option
to drill down to more detailed information in a dedicated tab for the task by clicking a bar, graph, or gauge in
the Task Dashboard, or by double-clicking the task in the table.
This functionality is currently relevant to Replicate tasks only.
In this section:
l
General Change Processing information (page 215)
l
Detailed Change Processing information (page 218)
General Change Processing information
General information about change processing is presented in a graphical format, as shown in the following
figure.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 215

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
Task Dashboard - Change Processing Status
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 216

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 217

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
This following information is displayed:
l
Overall Progress bar: The overall progress of the task.
l
Incoming Changes: The number of records that were processed for the task.
l
Transactions: The number of transactions that were processed for the task.
l
Applied Changes: A pie chart showing information about the processed changes:
l
The number of INSERT operations processed. Roll over the Inserts section with your mouse to
see the number and percentage of the accumulated inserts.
l
The number of UPDATE operations processed. Roll over the Updates section with your mouse
to see the number and percentage of the accumulated updates.
l
The number of DELETE operations processed. Roll over the Deletes section with your mouse to
see the number and percentage of the accumulated deletes.
l
The number of metadata changes (DDL) processed. DDL changes include information about
events like changes to table names or to column names.
l
Commit: The number of committed transactions and change records as well as the change volume, in
MB.
l
Rollback: The number of rolled back transactions and change records as well as the change volume, in
MB.
l
Apply Throughput: A gauge that describes the number of change events read per second. For
additional details, see Information about Change Processing throughput (page 221).
l
Apply Latency: A gauge that displays latency information.
The latency values in Qlik Enterprise Manager measure the time delay (latency) between the time when
a change is visible to the source (and committed), and the time when this same change is visible to the
target. The display is always based on the current change being applied.
For additional details, see Information about Change Processing latency (page 221).
Detailed Change Processing information
You can view more detailed information about the Change Processing status by double-clicking the status bar,
the pie chart, or a gauge, or by double-clicking the task in the table. This opens the task in the <task name>
tab, in context of the bar, chart, or gauge that you clicked (if any). The information that displays is the same
information that you would see if you were monitoring the task in Replicate.
In this section:
l
Information about incoming changes (page 218)
l
Information about applied changes (page 220)
l
Information about Change Processing throughput (page 221)
l
Information about Change Processing latency (page 221)
Information about incoming changes
To view more information about incoming changes, in the Change Processing tab, double-click the Incoming
Changes bar. A dedicated tab opens for the task, displaying at the top the Incoming Changes bar and at the
bottom the Incoming Changes Details area with bar graphs that show the following information:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 218

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
l
Accumulating: Two bars indicating the number of records currently being read from the source
endpoint. These records are accumulated in a queue until they are applied to the target.
l
In Memory: The number of accumulating records that are currently in the computer memory.
l
On Disk: The number of accumulating records that are currently stored on disk.
l
Applying: Two bars indicating he number of records currently being written to the target. These are
the applied changes.
l
In Memory: The number of records being applied that are currently in the computer memory.
l
On Disk: The number of records being applied that are currently stored on disk.
Incoming Changes Bar
Incoming Changes Details Area
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 219

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
Information about applied changes
To view more information about applied changes, in the <task name> tab, click the Applied Changes pie
chart. The Applied Changes pie chart displays two grids, each in its own tab, with information about the
applied changes.
Recent Activity
The grid in the Recent Activity tab includes information about which changes occurred in each table:
l
Table Name: The names of the source tables that are included in the task.
l
Update: The number of UPDATE operations processed for the specific table.
l
Insert: The number of INSERT operations processed for the specific table.
l
Delete: The number of DELETE operations processed for the specific table.
l
DDL: The number of metadata changes (DDL) processed. DDL changes include information about
events like changes to table names or to column names.
l
Total Applied: The total number of changes applied to the target.
l
Data Errors: The number of errors related to data processing at the record level, such as conversion
errors, errors in transformations, or bad data.
l
Last Modified: The time the last change occurred for the specific table.
You can also:
l
Filter the grid by entering a string in the Filter By box. This allows you to focus on specific tables.
l
Reload tables. To reload selected tables, select the tables you want to reload and then click Reload
above the table list. When prompted to confirm the operation, click OK. The data in the selected tables
will be reloaded to the target endpoint. Note that this option is not available for Apply Changes Only
tasks.
l
Reset data errors for a specific table. For details, see Data error handling (page 243).
l
Use the Columns Settings dialog box to select which columns to display and to arrange the order in
which they appear. For more information, see Customizing task columns (page 231).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 220

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
l
Hide a column, export the list to a TSV file, or sort by column in ascending or descending order. For
more information, see Customizing task columns (page 231).
Aggregates
The grid on the Aggregates tab includes information about the total number of changes (for all tables) per
change type (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, DDL) and transaction type (COMMIT, ROLLBACK).
Information about Change Processing throughput
To view information about how fast change records are loaded to the target endpoint during a change
processing operation, in the <task name> tab, click the Apply Throughput gauge. The Apply Throughput
Details area displays a graph illustrating the source and target throughput rate.
See also Setting the unit of throughput measurement (page 214).
Information about Change Processing latency
To view information about the time delay (latency) between the time when a change is visible to the source
(and committed) and the time when this same change is visible to the target, in the <task name> tab, click the
Apply Latency gauge. The Apply Latency Details area displays a graph illustrating the source and target
latency. The display is always based on the current change being applied.
You should take the following into consideration:
l
Latency when applying large transactions:
For example, when the most recent latency value was 10 seconds and now a transaction of one million
rows gets committed at the source endpoint, Qlik Enterprise Manager starts to apply that transaction
to the selected target and it will take some time to write all the changes to the target (for example 60
seconds). During the next 60 seconds, the latency value gradually grows to 70 seconds for the last
change in the transaction. Once the transaction is committed, the latency drops back to the 'regular'
latency (10 seconds in this case).
l
Latency when no transactions are being applied:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 221

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
When a time period passes with no changes applied to the target, the latency calculation is based on
the time difference between the current time and the timestamp of the last change event read from
the transaction log. This could happen if, for example, there is high activity on tables that are not
selected for replication in the current task.
9.2 Monitoring Compose tasks and workflows
This section explains how to monitor Compose tasks and workflows in Enterprise Manager.
In this section:
l
Task progress summary (page 222)
l
Monitoring Data Lake tasks (page 225)
l
Monitoring Data Warehouse tasks (page 226)
l
Monitoring workflows (page 227)
Task progress summary
To see Compose tasks, you need to start the task directly in Compose.
Switch to Tasks View to see a list of tasks. Expand the left pane and select the Compose Task Profile options
according to the tasks or processes that you want to monitor.
Compose task profiles
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 222

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
Data Warehouse tasks:
l
Data Warehouse
l
Data Mart
Data Lake tasks:
l
Data Storage
Compose Workflows:
l
Workflows
For each task, the following columns are available.
General columns
l
State: The current state of a task. Possible states are described in the table below. You can filter the
task list using the States check boxes above the list.
Task State Icon Description
Running The task is running.
A spinning circle icon will be shown when the task is in a
"Starting" state.
Stopped The task has not been run yet, the task was stopped, or the task
completed successfully.
Starting The task is starting (indicated by a spinning circle)
Error The task has stopped due to a fatal error.
Recovering The task is recovering from a recoverable error.
Task states
l
Server: The name of the server on which the task is running.
l
Task: The name of the task
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 223

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
l
Stage: The current stage of the task: Loading or Change Processing.
The stage will remain "Loading", regardless of whether the task is actually loading data or
not.
l
Tables with Error:The number of tables in error state.
Not displayed by default:
l
Description: A description of the task, as entered by the user in Compose.
l
Loading Ended: Indicates whether loading has completed. This refers to completion of the Full Load
stage in Replicate tasks and completion of the Full Load and/or Change Processing stage in Compose
tasks.
l
Project - The name of the Compose project.
l
Source Name: The display name of the source database
l
Server type:Compose
l
Source Type: The source database type (e.g. Microsoft SQL Server)
l
Target Name: The display name of the target database
l
Target Type: The target database type
l
Tags: The tags associated with a task
l
Type: The type of task, which can be: Full Load only, CDC only, or Full Load & CDC
Loading columns
l
Progress (%): The percentage of loading completed
Not displayed by default:
l
Started: The date and time the loading started
l
Ended: The date and time the loading ended
l
Load Duration: The duration of the load process, in hh:mm:ss
l
Total Tables: The total number of tables
l
Tables Completed: The number of completed tables
l
Tables Left: The number of tables remaining to be loaded
l
Tables Loading: The number of tables currently loading
l
Tables Queued: The number of tables in queue
l
Total Commands: The number of commands executed in a Compose Task
l
Commands Completed: The number of commands completed in a Compose Task
With Compose tasks, canceled tables are reflected in the Total Tables counter but not in the
Completed/Loading/Queued/Error counters. Therefore, when one or more tables is canceled in a
task, the sum of these counters will be less than the Total Tables.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 224

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
Status summary
The Status Summary at the bottom of the window provides a quick overview of the current status of all
monitored tasks and servers. It lists the following information:
l
For tasks: The total number of monitored tasks as well as the number of tasks that are running (green
icon), stopped (gray icon), recovering (orange icon), and in error state (red icon)
The "running" state also includes "starting" tasks. Similarly, the "stopped" state also
includes "stopping" tasks.
You can double-click the task counters to open the corresponding Tasks View.
Note: The task counters do not reflect tasks on servers that are not currently monitored. For more
information, see Additional server management options (page 60).
l
For servers: The total number of servers, the number of servers that are running and successfully
monitored (green icon), the number of servers that Enterprise Manager cannot monitor due to
connectivity issues (red icon), and the number of servers that are not being monitored (gray icon)
Status Bar Example
Monitoring Data Lake tasks
You can view general information on the progress of Compose Full Load or Change Processing operations in
the Task Dashboard, located to the right of the task list.
Use the arrow to collapse or expand the Task Dashboard.
The top of the dashboard provides buttons for stopping and starting task(s), and viewing task log files. The
following information about the task is also provided:
l
The task name and state
l
A link to the Compose project
l
Source: The Landing Zone name and type in a Data Storage task or the project name and Landing
Zone type in a Provisioning task.
l
Target: The task name and target type in a Provisioning task or the project name and Landing Zone
type in a Data Storage task.
The Loading tab in the right pane shows the following general progress information:
l
Load Duration: The duration of the loading operation.
l
Ended: When the loading operation completed.
l
Overall Progress bar: The overall progress of the loading operation.
l
Table bars: The status of the tables being loaded, which can be:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 225

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
l
Completed - The number of tables that have been loaded into the target.
l
Loading - The number of tables that are currently being loaded into the target.
l
Queued - The number of tables that are waiting to be loaded into the target.
l
Error - The number of tables that could not be loaded due to an error
See Messages and notifications (page 250) and Data error handling (page 243) for more
information about error messages.
With Compose tasks, canceled tables are reflected in the Total Tables counter but not in the
Completed/Loading/Queued/Error counters. Therefore, when one or more tables is canceled
in a task, the sum of these counters will be less than the Total Tables.
l
The number of Commands Completed out of the Total Commands.
Monitoring Data Warehouse tasks
You can view general information on the progress of Compose Full Load or Change Processing operations in
the Task Dashboard, located to the right of the task list.
Use the arrow to collapse or expand the Task Dashboard.
The top of the dashboard provides buttons for stopping and starting task(s), and viewing task log files. The
following information about the task is also provided:
l
The task name and state
l
A link to the Compose project
l
Source: The display name and type of the source database
l
Target: The display name and type of the target database. Note that as the target database does not
have a display name in Compose, the project name is displayed instead.
The Loading tab in the right pane shows the following task information:
l
Load Duration - Load duration time
l
Ended - Load end time
l
Overall progress bar
l
<n> out of <n> commands completed - The total number of ETL statements executed
l
Total Tables - Total number of tables loaded
l
Total Records - Total number of records loaded (also represented in a pie graph)
l
Total number of INSERToperations
l
Total number of UPDATE operations
l
Error Marts (Not displayed for Data Mart tasks as Data Quality rules are run in the Data Warehouse
only)
l
Total number of tables with errors
l
Total number of data errors
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 226

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
Data Warehouse task dashboard example
Monitoring workflows
In order to see your Compose workflows, expand the left pane, and make sure that the Workflow Task
Profile is selected:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 227

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
To see which Compose project a workflow is associated with, expand the right pane to see the project name.
If you want to select other Compose task profiles (not just workflows), then it's a good idea to add the Profile
column to the monitoring grid. This will allow you to easily differentiate between the different Compose task
profiles, as shown in the following image:
For an explanation of how to add or remove columns, see Customizing task columns (page 231).
Limitations and considerations
l
The Stage column will always show Loading regardless of the actual workflow stage. If you are not
monitoring Replicate tasks (in which case this column might be useful), then it might be a good idea to
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 228

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
hide it as described in Customizing task columns (page 231).
l
The Type column will always show Full Load & CDC even if the workflow contains Full Load tasks
only. This column is not displayed by default.
l
While failed workflows are indicated with a icon, workflows that completed successfully are
indicated with a icon. This might cause some confusion as the same icon ( ) can also indicate
that the workflow has not been run yet (which ceases to be an issue after it has been run once), or that
it was stopped. Thus, the only way to be certain that a workflow completed successfully is by opening
the Compose monitor as described in Verifying that a workflow completed successfully (page 229)
below.
Controlling workflows and viewing logs
You can perform the action described below on several workflows simultaneously. To do this, you
first need to select the workflows for which you want to perform the desired action and then either
right-click the list and select the relevant option or click the relevant toolbar button.
Running and stopping workflows
You can run and stop workflows using any of the following methods:
l
Right-click the workflow and select Run or Stop as appropriate.
l
Select the workflow and click the Run or Stop toolbar buttons as appropriate.
The Run button is not available for workflows that have not been validated or that contain elements
that no longer exist in the Compose project.
Viewing logs
You can view the workflow log files using any of the following methods:
l
Right-click the workflow and select View Logs.
l
Select the workflow and click the View Logs toolbar button.
See also: Viewing and downloading log files (page 267).
Verifying that a workflow completed successfully
As mentioned above, it is currently not possible to be certain that a workflow completed successfully just by
looking at the State, as the (stopped) state could also mean that the workflow was stopped manually or
has not been run yet.
To verify that a workflow did indeed complete successfully, expand the right-pane and click the project name
link.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 229

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
This will open the workflow in the Compose monitor, where you will be able to see its current state:
9.3 Searching for tasks
You can search for specific tasks by typing a string into the Search Tasks box above the table. Enterprise
Manager searches only textual columns, not numeric columns. The following columns are included in the
search, even if a column is not displayed in the user interface:
l
State
l
Reason
l
Server
l
Task
l
Profile
l
Type
l
Stage
l
Loading Ended
l
Source Name
l
Source Type
l
Target Name
l
Target Type
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 230

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
l
Tags
l
Project (relevant for Compose tasks only)
You can also restrict a search to a specific column by preceding the search string with the column name and a
colon, as follows: ColumnName:value (for example: Server:john-vm.abc.local). This is applicable to all available
columns, not only the columns listed above.
When searching for a number, only enter whole numbers, no commas or special characters. For
example, to search for 2,500, as displayed in the user interface, enter
2500
; to search for 100%, enter
100.
9.4 Customizing task columns
You can choose to display or hide certain columns as well as sort columns as desired.
To Do this
Hide a column Right-click the heading of the column you want to hide and select Hide Column.
Note that once you hide a column, if you want to display it again, you need to select it in
the Column Settings dialog box (see below).
Select which
columns to
display
1. Right-click a column heading and select Column Settings.
The Column Settings dialog box opens.
2. To display additional columns, in the left pane, select the columns you want to
display and click the right arrow to move them to the right pane.
3. To hide columns, select them in the right pane and use the left arrow to move
them to the left pane.
4. To change the column order, select a column in the right pane and use the up or
down arrow to move it to the required position.
5. To reset column selection and order, click Restore Defaults.
6. Click OK.
Restore
default
columns
1. Right-click a column heading and select Column Settings.
The Column Settings dialog box opens.
2. To reset the column selection and order, click Restore Defaults.
3. Click OK.
Sort by
column
Click anywhere in the column heading to change the sorting order.
OR
Right-click the column and select Sort Ascending or Sort Descending as desired.
An upward facing arrow indicates ascending order whereas a downward facing arrow
indicates descending order.
Column customization actions
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 231

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
To Do this
Export the list
to a TSV file
Right-click any of the column headings and select Export to TSV file. When prompted,
save the file in your desired location. Note that only currently displayed columns will be
exported.
9.5 Grouping tasks
In the Tasks View, the left side (expanded by default) represents the Tags pane. It displays all available tags.
Tags serve as attributes that you can attach to tasks to arrange them in Enterprise Manager. Tags allow you to
group tasks that have a common denominator, and to filter by them, too. For example, you can organize tasks
by flavor, such as all tasks that are part of a particular distribution process, by organization structure, by
environment, by location, by application, by customer, and so on.
All tags:
l
Are static: They remain constant during a task’s life time. For example, the task type (CDC, FL, or
both), source database type, or region of a task do not change as long as the task exists.
l
Are public: All tags are available to all Enterprise Manager users.
l
Can be associated with any number of tasks: You can associate a task with more than one tag.
Enterprise Manager comes with built-in tag categories as well as built-in tags. The following table lists all
categories that are built in:
Category Tag
Custom
l
Untagged
Task Type
l
Full Load Only
l
CDC Only
l
Full Load & CDC
Task Profile
l
Bidirectional
l
Unidirectional
l
Log Stream Staging - For more information about the Log Stream Staging feature,
refer to the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
Source
Database
Type
If more than one source database type is available in your task list, one tag for each
available source database type.
Target
Database
Type
If more than one target database type is available in your task list, one tag for each available
target database type.
Replicate
Servers
One tag for each managed Replicate server
Task categories
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 232

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
Category Tag
Log Stream
Staging
One tag for each Log Stream Staging task. Selecting a tag in this category will show all tasks
that are associated with the Log Stream Staging task (i.e. the Log Stream Staging task and
all tasks that read from the same Log Stream staging folder).
Selecting Other Tasks will show tasks that are not reading from Log Stream or tasks that
are defined as Log Stream Staging tasks but that do not currently have a Log Stream target
endpoint.
Enterprise Manager automatically associates built-in tags with a task based on the task’s characteristics, as
derived from its definition. You cannot change the association of tasks with such tags.
In addition, you can create your own custom tags and assign tasks to them. You can delete such tags at any
time. All tag names must:
l
Be unique.
l
Not exceed 64 characters.
l
Only contain Latin characters, digits, spaces, dots (.), dashes (-), and underscores (_).
l
Start with a digit or character.
Deleting a custom tag does not delete its associated tasks, and vice versa.
For each tag, Enterprise Manager displays the following information:
l
The tag name
l
The total number of tasks associated with this tag
l
An icon that indicates when any associated task experiences a problem
If a task with a problem is associated with more than one tag, all corresponding tags indicate a
problem.
The Tags column in the Tasks view presents a quick way to identify which tags are associated with each task.
The following table describes all options for viewing and managing tags.
To Do this
Add a custom tag In the Tags pane on the left, under Custom, in the New tag text box, enter
a name for the tag and click the check mark to the right (or press Enter).
Delete a custom tag
Note: Deleting a tag does
not delete the tasks
associated with it.
In the Tags pane, under Custom, right-click the tag you want to delete and
select Delete.
When prompted for confirmation, click Yes.
The tag is removed from the list.
Tag management options
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 233

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
To Do this
Filter by tags In the Tags pane, do one of the following:
l
Select the check boxes of tags you want to include in the Tasks
View.
l
Clear the check boxes of tags you want to exclude from the Tasks
View.
When you select different tags:
l
Within the same category, Enterprise Manager uses the logical OR
operator. For example, if you select both Oracle and Netezza in the
Target DB Type category, Enterprise Manager displays tasks to
Oracle or Netezza targets.
l
In different categories, Enterprise Manager uses the logical AND
operator. For example, if you select the Oracle tag in the Target DB
Type category and the Finance tag in the Custom category,
Enterprise Manager displays only task to an Oracle target that are
also associated with the Finance tag.
Assign custom tags to a task
or remove tag assignments
Note: This is only possible
for custom tags. Built-in tags
are assigned by default.
Those assignments cannot
be removed.
1. In the task list, select one ore more tasks to which you want to
assign a tag and click Assign Tags.
2. In the Assign Tags window, select the required tag(s) or enter a
new tag name in the New tag text box and click the check mark.
3. Click OK.
9.6 Running a task
Currently, this functionality is available for Replicate tasks only.
After you design a task (see Defining and managing tasks (page 64)), you can run and monitor its progress with
one click in Enterprise Manager. This simple Click-2-Replicate function is described in this section. In addition,
the various types of run options available are also described.
In this section:
l
How to run a task (page 235)
l
Using the Run button options (page 235)
l
Advanced Run Options (page 236)
l
Recovering from data folder loss or corruption (page 241)
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 234
9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
The task run buttons area available in the toolbar at the top of the console in the following views:
l
Tasks View (in both Designer mode (page 207) and Monitor mode (page 208))
l
When Viewing specific tasks (page 207)
How to run a task
Click the Run button to execute a replication task. The task process continues to run until you click the Stop
button to stop the task.
When you click Run, the following occurs:
l
If this is the first time that a task is run, the Start Processing operation is run.
l
If the task has been started and stopped, the Resume Processing operation described in
Using the Run button options (page 235) is run.
l
If changes were made to the endpoint, change processing takes place after the full load
operation. If you do not want change processing to occur or if you want to start change
processing from a predetermined point, you must make the appropriate Advanced Run
Options (page 236) selection.
In some cases, task replication may stop due to an error although the task process is still running.
See Task progress summary (page 203)for information on the task status and how Qlik Replicate displays
information on the current task status.
The Run button is available in the following views:
l
The Tasks view when you select a task from the Task List.
l
For the individual task, both the Designer mode and Monitor mode have the Run and Stop buttons
available.
You must be in the Monitor mode to view the task progress.
Using the Run button options
Clicking the Run button runs a full-load replication task from the source to the target. This is a first time task
that creates the target endpoints and loads the source data to the target according to your task definitions.
Subsequent runs allow you to resume processing from a specific point and process changes. In addition, you
can also specify from what point you want the replication to start.
The following options are available:
l
Start Processing - This is available the first time you run the task only. This will execute the initial full
load operation. If Change Processing is also enabled for the task or if it is an Apply Changes only task
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 235

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
type, change processing will start as soon as any changes are made to the source endpoint.(switches
to Resume Processing after the task has started)
l
Resume Processing - Resumes task execution from the point that it was stopped. You can also resume
processing by clicking the Run button if the task has been stopped.
If the schema or a filter was changed after the task stopped, the task should be reloaded as
opposed to resumed (see below).
l
Reload Target (Only available when the Full Load or Full Load and Apply Changes replication
options are enabled) - Starts the Full Load and Change Processing (if enabled) from the beginning.
Tables that have already been processed are handled according to the relevant "Target table
preparation" setting.
To replicate tables that were added to the local file channel task after the initial full load,
you need to reload both the local and the remote file channel tasks.
l
Advanced run options - Advanced options for controlling task execution. For more information, see
Advanced Run Options (page 236)
Start Processing
This is available the first time you run the task only. This will execute the initial full load operation. If Change
Processing is also enabled for the task or if it is an Apply Changes only task type, change processing will start
as soon as any changes are made to the source endpoint.
Reload target
Starts the Full Load and Change Processing (if enabled) from the beginning. Tables that have already been
processed are handled according to the relevant "Target table preparation" setting.
To replicate tables that were added to the local file channel task after the initial full load, you need
to reload both the local and the remote file channel tasks.
Advanced Run Options
Advanced Run Options provide you with additional options for resuming and restarting tasks.
Some of the advanced run options are not available in a Log Stream Staging setup.
For information on the availability of advanced run options in a Log Stream Staging setup, refer to
the Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
To use Advanced Run Options, click the triangle next to the Run button and select Advanced Run Options.
The Advanced Run Options dialog box opens.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 236

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
The Advanced Run Options dialog box lets you do the following:
l
**Restart task and start processing changes from current time: This starts the Apply Changes
replication task from the beginning (as if the task has not run before).
**Only available for Apply Changes replication tasks.
l
Tables are already loaded. Start processing changes from:
Metadata changes performed on the source tables while a task is stopped (for example,
DROP COLUMN) will not be captured when the task is resumed from an earlier time or
position (SCN/LSN). In such a case, the metadata that exists when the task is resumed will be
captured.
l
Date and Time: Select the date and time from where you want to Replicate to start processing
changes.
l
When logs are deleted from the database (e.g. due to a purge policy), a log
matching the specified date and time may not exist. In this case, Replicate will
resume the task from the earliest point possible, after the specified date and
time.
l
With the IBM DB2 for LUW source endpoint, this option cannot be used to start
Apply Changes tasks from a point before the original start time of the Apply
Changes task. Or, to put it another way, it can only be used to start tasks from
any time after the original start time of the Apply Changes task.
l
The timestamp uses the local time of the browser machine.
l
This option is not relevant for the File Source endpoint.
l
Source change position (e.g. SCN or LSN): Specify the position in the log from where to
resume change processing. The source change position format differs according to your source
endpoint. For more information, see How to Find the Source Change Position (page 240).
The Source change position option is supported with the following source endpoints
only:
l
Oracle
l
Microsoft SQL Server
l
MySQL
l
PostgreSQL
l
IBM DB2 for z/OS
l
IBM Informix
l
IBM DB2 for LUW
Metadata Only:
The "Metadata only" options described below allow you to:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 237

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
l
Create empty tables on the target and then manually edit them.
l
Create tables during a task.
Enabling the options will also ensure that supplemental logging is set up correctly on the source tables before
starting the actual replication task.
The "Metadata only" feature is not supported when the task is defined with the Apply Changes only
task option. any of the following task options:
l
ApplyChanges only
l
Store Changes only
l
ApplyChanges and Store Changes
l
Recreate all tables and stop: Select this option to recreate the target tables as defined in the Full
Load Settings tab. When "Store Changes" is enabled, the Change tables/Audit table will be created as
defined in the Store Changes Settings tab. To use this option, stop the existing task, run the task with
this option enabled (the task will stop automatically) and finally, resume the task.
l
Create missing tables and stop: Select this option to create missing target tables including Change
Tables. You can use this option to create Change Tables on the target after enabling the "Store
Changes" option (in the Store Changes Settings tab) for an existing task. To use this option, stop the
existing task, run the task with this option enabled (the task will stop automatically) and finally,
resume the task.
The table below shows which tables are created in the target database when the Metadata only option is
enabled for a unidirectional task. As the table shows, when certain task options are enabled, Control tables
and the Audit table will not be created on the target.
Enabled Task Options Tables Created on the Target
Full Load All tables except for Control tables
Full Load and Apply Changes All tables except for Control tables
Full Load, Apply Changes and Store Changes - When changes are
stored in Change tables
All tables except for Control tables
Full Load and Store Changes - When changes are stored in an
Audit table
All tables except for Control tables and
the Audit table
Full Load, Apply Changes and Store Changes - When changes are
stored in an Audit table
All tables except for Control tables and
the Audit table
Recovery:
l
Recover using locally stored checkpoint: Use this option if recovery is not possible using the
Resume Processing or Start process changes from options (due to corrupt swap files, for example).
When this option is selected, Replicate uses the checkpoint data stored in <Data_Folder_
Path>\data\tasks\<task_name>\StateManager to recover the task.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 238

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
When using this option, the following limitations apply:
l
The following source endpoints are supported only:
l
Oracle
l
Microsoft SQL Server
l
MySQL
l
PostgreSQL
l
IBM DB2 for z/OS
l
SAP HANA
l
Tasks can only be recovered during Change Processing (i.e. after Full Load
Completes)
l
With the exception of the File Channel endpoint, all target endpoints are supported.
The following limitations apply:
l
In Transactional apply Change Processing mode: All target endpoints that
support transactions are supported.
l
In Batch optimized apply Change Processing mode: Oracle target endpoint
only is supported. Also requires the Preserve transactional integrity option
to be enabled.
l
For all other target endpoints or Change Processing modes, recovery is
supported, but may cause duplicates on the target.
l
Recover using checkpoint stored on target: Select to recover a task using the CHECKPOINT value from
the attrep_txn_state table (created in the target database).
When using this option, the following limitations apply:
l
Only the following source and target endpoints are supported:
l
Oracle
l
Microsoft SQL Server
l
Tasks can only be recovered during Change Processing (i.e. after Full Load
Completes)
l
The task Change Processing mode must be set to either:
Batch optimized apply with the Preserve transactional integrity option enabled.
Note that this mode is only supported with the Oracle target endpoint.
OR
Transactional apply
For information about setting the Change Processing mode, see Changes Processing
Tuning.
This option will only be available if the Store task recovery data in target database option was
enabled in the Task Settings' Change Processing Tuning (page 181) tab before Change Processing
completed.
Select this option (as opposed to the Recover using locally stored checkpoint option) if the files in
the Data folder are corrupted or if the storage device containing the Data folder has failed.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 239

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
For a detailed explanation of how to set up and implement recovery using the attrep_txn_state
table, see Recovering from data folder loss or corruption (page 241).
How to Find the Source Change Position
The following topic explains how to locate the source change position for each of the supported databases.
MySQL
OPTION 1:
1. Execute:
SHOW BINARY LOGS;
2. Choose a binlog file (e.g. log.000123).
3. Execute:
SHOW BINLOG EVENTS IN 'binlog_filename';
Example:
SHOW BINLOG EVENTS IN 'log.000123';
4. Locate the position of a BEGIN or DDL statement (e.g. 1777888).
MySQL does not support a "start from position" located in the middle of a transaction, which
is why you must select either BEGIN or DDL.
5. Set the internal parameter:
StartFromPosition = binlog_filename:begin_or_ddl_position
Example:
StartFromPosition = log.000123:1777888
OPTION 2:
1. Execute:
SHOW MASTER STATUS;
2. Set the "Start from position" as:
firstColumnValue:secondColumnValue
Example:
mysql.007472:775
Microsoft SQL Server
Execute:
SELECT MAX([Current LSN]) FROM fn_dblog(null,null);
Example: 00002717:00000e08:0003
Oracle
Execute:
SELECT current_scn FROM V$DATABASE;
Example: 1471212002
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 240

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
PostgreSQL
Note that the command differs according to your PostgreSQL version.
PostgreSQL 9.6
Execute:
SELECT * FROM pg_current_xlog_location();
PostgreSQL 10 and later
Execute:
SELECT * FROM pg_current_wal_lsn();
IBM DB2 for z/OS
Specify the LSN, which is the RBA in a non data sharing environment, and the LRSN in a data sharing
environment
IBM DB2 for LUW
1. Execute db2pd to find the correct log name.
2. Execute db2flsn with the returned log name and use the current LRI value.
For more information, refer to "Resuming or Starting a Task from LRI in a pureScale Environment" in
the Replicate Help.
Recovering from data folder loss or corruption
During normal operation, Qlik Replicate maintains the replication state in the following location:
<Data_Folder_Path>\data\tasks\<task_name>\StateManager
This enables tasks that cannot be resumed normally (due to corrupt swap files, for example) to be recovered
using the Recover using locally stored checkpoint option described in Advanced Run Options (page 236).
However, if the files in the data folder become corrupted or if the storage device containing the data folder
fails, tasks must be recovered using the means described below.
This option is supported when replicating between the following endpoints only:
Supported source endpoints Supported target endpoints
Supported source and target endpoints
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 241

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
l
Amazon RDS for MySQL
l
Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL
l
Amazon RDS for SQL
l
AWS Aurora Cloud for PostgreSQL
l
Google Cloud SQL for MySQL
l
Google Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL
l
IBM DB2 for z/OS
l
Microsoft Azure Database for MySQL
l
Microsoft Azure SQL Managed Instance
l
Microsoft SQL Server
l
MySQL
l
Oracle
l
PostrgreSQL
l
SAP HANA
l
Amazon Redshift
l
Google Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL
l
Microsoft Azure Database for MySQL
l
Microsoft Azure Database for PostgreSQL
l
Microsoft SQL Server
l
MySQL
l
Oracle
l
PostgreSQL
l
Snowflake on Azure
l
Snowflake on Google
l
Snowflake on AWS
Setting up and initiating task recovery
For recovery to be successful, the source database transaction logs must be available from the time the task
failed.
To set up a task for recovery
1. Design a task. Make sure to enable the Store task recovery data in target database option in the
Task Settings' Change Processing Tuning (page 181) tab. This option can be enabled at any time during
Change Processing, although it must be enabled before Change Processing completes.
2. Export the task definitions as described in the Qlik Replicate User Guide and Reference.
3. Run the task.
In addition to the selected source tables, the task will write the checkpoint data to the following table in the
target database (and automatically create the table if it has not already been created by another task):
attrep_txn_state
To initiate recovery
1. Import the task definition exported when you set up the task.
2. Enter the passwords in the endpoint connection settings.
3. Access the attrep_txn_state table on the target database and locate the failed task in the TASK_NAME
column. If there are tasks with the same name running on multiple Replicate Servers, you will also
need to locate the appropriate server in the SERVER_NAME column. After locating the relevant task, copy
the value in the corresponding CHECKPOINT column.
4. Select the Recover using checkpoint stored on target option and then provide the CHECKPOINT value
(preferably by pasting) as described in Advanced Run Options (page 236).
5. Click OK to start the recovery.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 242

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
During recovery, Replicate does not write anything to the target database until it identifies the commit event
corresponding to the CHECKPOINT value. Once it identifies the CHECKPOINT commit event, recovery is
performed and the task reverts to standard operation.
9.7 Error handling
The following sections describe how to best handle task and data errors:
l
Task error handling (page 243)
l
Data error handling (page 243)
The descriptions in this section are relevant to Replicate tasks only.
Task error handling
When a tasks fails with an error, Tasks View displays a red error icon in the State column. The following flow
suggests a proper action path for handling task errors.
1. Move the pointer over the error icon to display a tooltip with a high-level error message and a time
stamp.
2. For more information on the problem, do one of the following:
l
Open the Messages and notifications (page 250) to view all messages for the task.
If you do not see any relevant messages, you may need to:
Select Selected Item to only view messages for the selected task.
Change the time frame.
The Message Center only displays the last 20,000 messages.
l
Click View Logs to find the error message in the log files.
l
Click View Task to see more detailed information about the current state of the task.
3. If possible, fix the error based on the information provided in the message.
For more information on error handling in Qlik Replicate, see the Qlik Replicate User Guide and Reference.
Data error handling
Data errors are errors related to data processing at the record level. When Qlik Replicate encounters a data
error during replication, it issues an error warning. Enterprise Manager indicates when a task has data errors
in any of its tables. For each task in the task list, Enterprise Manager shows its data error count, which is the
sum of all data errors that occurred in the task’s tables.
You can drill down to the task to view this information per table. You have the option to reset the counter per
table when the data errors are no longer of interest to you. To view this information per task in the task list,
you can display the Data Errors column. For information on column selection, see Customizing task columns
(page 231).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 243

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
Take the following into account:
l
Reloading a table automatically resets the corresponding counter.
l
Resetting has no effect on the task’s exception table.
l
The error handling behavior of escalation handling for repeating data errors is affected by
counter reset.
9.8 Using the monitor tools
The monitor tools let you view additional information about the task. The following topics describe the
information available through these tools:
l
Setting the logging levels (page 244)
l
Viewing and downloading logs (page 245)
l
Deleting logs (page 246)
l
Downloading a diagnostics package (page 246)
l
Downloading a memory report (page 246)
Logging
In the Logging <Task_Name> window, you can set the logging level for the task you are currently monitoring
as well as view, download, and delete log files.
l
Any changes to the task logging levels take effect immediately without needing to restart the
task.
l
The logging level can also be set in the Logging Level sub-tab in the Task Settings dialog
box. For more information, see Logging (page 192).
Setting the logging levels
To set logging levels:
1. Drill-down to Monitor View as described in Viewing specific tasks (page 207).
2. Then, click the Tools toolbar button and select Logging.
The <Task_Name> Logging window opens.
3. At the top of the <Task_Name> Logging window, set the Component Logging Level slider to the log
level you want. This sets the logging level for all log modules. Note that all of the sliders for the
individual modules move to the same position that you set in the main slider.
4. Make any changes to the sliders for the individual modules. This is optional. Note that if you change
the main slider, all of the individual sliders are reset to the new position. If you want to maintain a
different logging level for a specific module, you need to reset it.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 244

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
Storing trace and verbose logging in memory
This option is relevant to Replicate tasks only.
When the logging level is set to "Trace" or "Verbose", you can instruct Replicate to store the logging
information in memory until an error occurs. On detecting an error, Replicate will begin writing to the physical
logs and continue to do so for a few minutes after the initial occurrence of the error.
If no error occurs before the allocated memory is used up, Replicate will empty the memory buffer and start
afresh.
This option is useful for tasks that fail unpredictably and for no obvious reason. The problem with continually
writing large amounts of information to the logs is twofold:
l
Running in "Trace" or "Verbose" logging mode will quickly use up available disk space (unless the
logging settings have been configured to prevent this).
l
Continually writing large amounts of data to the logs will affect performance.
To use this option
1. Select the Store trace/verbose logging in memory, but if an error occurs, write to the logs check
box at the top of the tab.
2. In the Allocate memory up to (MB) field, specify the amount of memory you want to allocate for
storing logging information.
Viewing and downloading logs
To view and download logs
1. Drill-down to Monitor View as described in Viewing specific tasks (page 207).
2. Then, click the Tools toolbar button and select Logging.
The <Task_Name> Logging window opens.
3. Select the log file you want to view or download from the list in the Log Files pane. If you want to
download the file, skip to Step 7.
4. The contents of the log file will be displayed in the right pane. When you select a row in the log file, a
tooltip will be display the full message of the selected row.
5. You can browse through the log file using the scroll bar on the right and the navigation buttons at the
top of the window.
6. To search for a specific string in the log file, enter the search string in the search box at the top of the
window.
Any terms that match the specified string will be highlighted blue.
7.
To download the log file, click the toolbar button.
Depending on your browser settings, one of the following will occur:
l
The task JSON file will be automatically downloaded to the default download location
l
You will be prompted for a download location. In this case, save the JSON file to your preferred
location.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 245

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
Deleting logs
To delete logs
1. Drill-down to Monitor View as described in Viewing specific tasks (page 207).
2. Then, click the Tools toolbar button and select Logging.
The <Task_Name> Logging window opens.
3. Click the Delete Logs button.
The Delete Logs window opens.
4. Optionally change the default number of days (45) and then click the Delete button.
All log files older than the specified number of days will be deleted.
Downloading a memory report
The memory report is a diagnostics tool that can be used to diagnose memory-related issues, such as
unusually high memory consumption by a specific task.
Usually, multiple memory reports showing the gradual increase in memory consumption will need to be
generated.
To download a memory report:
1. Drill-down to Monitor View as described in Viewing specific tasks (page 207).
2. Click the Tools toolbar button and then select Support > Download Memory Report.
Depending on your browser settings, the following file will either be automatically downloaded to your
designated download folder or you will be prompted to download it:
File name:
<task_name>__diagnostics__<timestamp>.memp
Example:
MyTask__diagnostics__20180109161333.memp
3. Send the report to Qlik.
Downloading a diagnostics package
You can generate a task-specific diagnostics package for Support to review. The diagnostics package contains
the task log files and various debugging data that may assist in troubleshooting task-related issues.
To download a diagnostics package:
1. Drill-down to Monitor View as described in Viewing specific tasks (page 207).
2. Click the Tools toolbar button and then select Support > Download Diagnostics Package.
Depending on your browser settings, the following file will either be automatically downloaded to your
designated download folder or you will be prompted to download it:
File name:
<task_name>__diagnostics__<timestamp>.zip
Example:
MyTask__diagnostics__20180109161333.zip
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 246

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
9.9 Scheduling jobs
Use the Scheduler to schedule a one-time job or a recurrent job for specific Replicate task operations. A job is
essentially an operation that can be scheduled to occur once, daily, weekly or monthly.
The following operations can be scheduled:
l
Run/Resume a task
l
Stop a task
l
Reload a task
l
Changes to settings will only take affect after restarting all tasks.
l
Compose tasks are not supported.
To schedule a new job:
1. Switch to Servers view.
2. Click the Scheduler toolbar button.
The Scheduler for <server_name> window opens.
The window is divided into two tabs: Scheduled Jobs and Executed Jobs. The Scheduled Jobs tab
contains a list of jobs that are scheduled to run periodically or once only while the Executed Jobs tab
contains a list of jobs that have already run.
The Executed Jobs tab will only show executed jobs that were scheduled to run once only. In
other words, jobs scheduled to run periodically (e.g. Daily, Weekly, Monthly) will not be
shown.
3. Click the New Scheduled Job toolbar button.
The New Scheduled Job window opens.
4. Specify a Job Name and then, from the Select scheduled job type drop-down list, select one of the
following:
l
Run task to run or resume the task(s) at the scheduled time.
For Full Load only tasks, it is preferable to select Reload target rather than Run task
when the scheduling is set to Daily, Weekly or Monthly. This will update the table’s
data whereas Run task will replace the existing table.
l
Stop task
l
Reload target
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 247

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
Selecting Reload target will execute the task according to the task's replication
settings. For example, if the task's Full Load and Apply Changes options are
enabled, Reload target will reload the target tables and apply any subsequent
changes.
5. Select one of the following time conventions:
l
Use server local time - When this option is selected (the default), the job will run when the
specified time is reached in the server's location.
See also: Impact of DST Change on Qlik Replicate.
l
Use universal time (UTC) - When this option is selected, the job will run at the specified UTC
time. So, for example, if the server is located in a UTC + 2 timezone, a job scheduled to run at
13:00 UTC time will actually run at 15:00 local server time. Scheduling a job to run in UTC mode
may be useful if you need tasks on several Replicate servers (located in different timezones) to
run concurrently.
For reference, both the server local time and the UTC time are displayed to the right of the
Scheduled Time heading.
6. Select and define one of following scheduling options:
l
Once (Run the job once on the specified day and at the specified time)
l
Daily - (Run the job every day at the specified time)
l
Weekly - (Run the job on the specified days and at the specified time)
l
Monthly - (Run the job on the specified day of the month)
To run the job on the last day of evey month, select Last day of every month from
the Day of month drop-down list.
7. For the Apply to tasks option, select which tasks to schedule. Select either All tasks to apply the job
to all current and future tasks or Selected tasks to apply the job to specific tasks. If you choose
Selected tasks, a list of currently defined tasks is displayed. Select which tasks to apply the job to.
8. Click OK to save your settings.
To enable or disable a scheduled job:
l
In the Scheduled Jobs tab, select or clear the check box in the Enabled column as required.
To edit a scheduled job:
1. Select the job in the Scheduled Jobs or Executed Jobs list.
2. Click the Open toolbar button and edit the job as required.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 248

9 Monitoring and controlling tasks
To delete a scheduled job:
1. Select the job in the Scheduled Jobs or Executed Jobs list.
2. Click the Delete toolbar button.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 249

10 Messages and notifications
10 Messages and notifications
The Message Center is located at the bottom of the console and contains messages about monitored servers
and tasks. This topic describes the various options for viewing and handling messages.
In this section:
l
Message Center overview (page 250)
l
Customizing the Message Center (page 252)
l
Viewing additional information (page 253)
l
Notifications (page 253)
l
Viewing and downloading log files (page 267)
10.1 Message Center overview
By default, the Message Center is minimized to a message tray at the bottom left of the console. The message
tray notifies you of how many messages were received, during which time-period they were received, and the
highest severity of all the messages (indicated by a color-coded callout icon). It is always global in scope,
showing information for all servers and tasks.
The Message Center will not show log messages reported by Compose servers and tasks. However,
messages reported by Enterprise Manager such as when monitoring has started /stopped for a
Compose server or when a server has been deleted, will appear.
In the message tray, the message severity icon indicates the highest severity of the received messages. For
example, if 11 messages were received but only one of them was an error message, the severity icon is red.
Other callout colors are orange for warning messages and blue for informational messages.
Message Tray Example
To open or close the Message Center:
l
Click the diagonal arrows to the right of the message summary.
To maximize the Message Center:
l
When the Message Center is half-way open, click the Maximize icon in the top right corner.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 250

10 Messages and notifications
To reduce the size of the Message Center:
l
When the Message Center is fully open, click the Restore Down icon to the right of the message
summary.
The following types of messages can be displayed: Info, Notification, Warning and Error. The actual message
types that Qlik Enterprise Manager displays as well as the display time period depend on your Message Center
preferences.
Each message type has its own icon, as shown below:
For each message, the following information is available:
l
Severity Icon: Info, notification, warning or error
l
Info: circular blue "i" icon
l
Notification: circular yellow bell icon
l
Warning: triangular orange exclamation mark icon
l
Info: circular red "x" icon
l
Time: When the event occurred
l
Reported By: The display name of the Replicate server. For messages reported by Enterprise Manager,
this field has a value of Qlik Enterprise Manager.
l
Server: The name of the server in Enterprise Manager
l
Task: The task that generated the message
l
Type: The event that generated the message, such as TASK_START
l
Message: The actual message as issued by the Replicate Server or Enterprise Manager
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 251

10 Messages and notifications
l
Error Code: Shows the error code of task errors. You can set a task notification that will be sent
whenever specific error codes are returned. For more information, see Setting a task notification (page
254).
Note that only error codes for tasks running on Replicate versions 6.2 or later will be shown.
Not displayed by default:
l
Table: The table name when the message is related to a particular table. Will appear after the Task
column if added.
l
ID: A unique ID that serves as a reference number. You can copy the ID to the clipboard for easy
reference, for example to paste it into an email when you need to refer to a specific message or to
search for the message later. Will appear after the Error Code column if added.
10.2 Customizing the Message Center
You can customize the Message Center according to your business needs. The table below describes the
available options.
To Do this
Display messages for all
tasks
Under Showing Messages for, select All.
Display messages only
for the selected tasks or
servers
Under Showing Messages for, select Selected Tasks or Selected Servers,
respectively.
Hide current messages Click Hide Current Messages above the message list to only show new
messages coming in. Note that this option is only available when you view all
system tasks.
To bring back all messages, click Show All Messages.
Change the time period
From the drop-down list at the top left of the Message Center, select one of the
available time periods: Last 6 hours, Last 12 hours, Last day, Last 3 days, or
Last week.
Filter message severity Select or clear the Errors, Warnings, Notifications or Info check boxes above
the message list as desired.
Message Center customization options
The Message Center also includes buttons to view log files, open the Task tab to view a task, or view server
information. In addition, you can:
l
Customize the columns to display. For more information, see Customizing task columns (page 231).
l
Configure the message purge policy. For more information, see Message Center purge settings (page
271).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 252

10 Messages and notifications
Searching for messages
You can search for specific messages by typing a string into the Search messages box above the table. Note
that Enterprise Manager searches only textual columns, not numeric columns. The following columns are
included in the search, even if a column is not displayed in the user interface:
l
Severity
l
Reported By
l
Server
l
Task
l
Message
l
Error Code
l
ID
You can also restrict a search to a specific column by preceding the search string with the column name and a
colon, as follows: ColumnName:value (for example: Type:TASK_STOP). This is applicable to all available
columns, not only the columns listed above.
10.3 Viewing additional information
From the Message Center, you can directly open the task or server for a particular message or view its log file.
Click To View
Log information: See Viewing and downloading log files (page 267).
Task information: See Monitoring Full Load replication (page 209) and Monitoring Change
Processing replication (page 215).
Server information: See Monitoring servers (page 48).
Message Center icon actions
These buttons are only available at a certain window size. If the window is too small, they do not
display. In this case, these options are only available from the context menu that appears when you
right-click a table row.
10.4 Notifications
You can configure Enterprise Manager to notify you on the occurrence of a task and/or server event.
Notifications defined in Enterprise Manager do not conflict with notifications defined in Replicate.
Although Replicate notifications cannot be managed via Enterprise Manager, Replicate notification
messages will be shown in the Enterprise Manager Message Center.
Instructions for setting up notifications are provided in the following sections:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 253

10 Messages and notifications
l
Setting a task notification (page 254)
l
Setting a server notification (page 261)
Setting a task notification
Task notifications apply to Replicate tasks only.
Notifications can be set for the following events:
l
Processing status changes
l
Excessive task latency
l
Excessive memory usage
l
Excessive disk usage
l
Processing errors
l
Other errors
To set a task notification:
1.
Click the toolbar button on the right of the console.
The Notification Rules window opens.
2. Click the Tasks tab and then click New.
The New Task Notification wizard opens.
3. Provide a name for the notification.
4. Select a notification in one of the available categories and, where applicable, set the time/size
threshold for sending the notification.
Processing Status:
l
Task was started manually or by the Scheduler: To send the notification when the task is
started manually or by the Scheduler.
l
Task was stopped manually or by the Scheduler: To send the notification when the task is
stopped manually or by the Scheduler.
l
Task was stopped after Full Load: Cached changes were not applied: To send the
notification when the task is stopped after Full Load completes but before cached changes
(changes to the source tables that occurred during Full Load) are applied to the target.
l
Task was stopped after Full Load: Cached changes were applied: To send the notification
when the task is stopped after Full Load completes and cached changes (changes to the source
tables that occurred during Full Load) have been applied to the target.
l
Full Load started: To send the notification when the Full Load process starts.
l
Full Load completed: To send the notification when the Full Load process completes.
Performance/Resources:
l
Latency is higher than [N] seconds
Specify the desired threshold value and unit of measurement (seconds or minutes).
l
Memory usage exceeds [N] GB
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 254

10 Messages and notifications
Specify the desired threshold value and unit of measurement (GB or MB).
l
Disk usage exceeds [N] GB
Specify the desired threshold value and unit of measurement (GB or MB).
Errors and Warnings:
l
Any Error: Select this to receive a notification when any error occurs in the system. Note that
notification will not be sent for the following error types:
l
Recoverable errors. Recoverable errors are printed as INFO in the log (unless the task
logging is set to TRACE, in which case they will be printed as ERROR).
l
Certain user-defined error handling policies. For example, if the Duplicate key when
applying INSERT Apply Conflicts handling option is set to Log record to the
exceptions table, no notification will be sent. However, if it set to Stop task, a
notification will be sent.
Setting this option may result in a large volume of notifications, depending on the
number of tasks running and their current status. It is therefore recommended to
define this notification for selected tasks rather than for all tasks.
l
Any Warning: Select this to receive a notification when a warning is issued in the system.
l
No changes were captured in the last <n> minutes:As this notification requires Replicate May
2022 or later, it will not be available if the monitored Replicate Server is an incompatible
version. Select this notification if you want to be alerted about delays in capturing changes
from the source database. With most databases, receiving this notification will usually indicate
a connectivity problem. However, with the following databases, it could simply mean that no
changes occurred during the specified period.
l
Microsoft SQL Server
l
IBM DB2 for LUW
l
IBM DB2 for iSeries
When the task resumes capturing changes, a notification that change capture has resumed will
be sent, and the notification timer will be reset.
l
Table processing was suspended due to errors: Select this to receive a notification when an
error causes a table to stop processing during a full-load operation or suspend CDC. In this
case, the table process stops, but the task continues.
l
Task stopped due to a non-recoverable error: Select this to receive a notification when an
error that cannot be retried is returned and the task is stopped due to this error.
An additional notification will be sent when the Performance/Resource threshold
returns to normal (where "normal" is 10% below the defined threshold).
l
Errors containing one of these codes
When this option is selected, a notification will be sent whenever an error matching one of the
specified error codes occurs. Error codes for tasks that ended with an error are shown in the
Message Center. You can copy the desired codes from the Message Center and paste them into
this field.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 255

10 Messages and notifications
l
Multiple error codes can be specified. In this case, error codes should be
separated by a comma.
l
Error codes must contain numeric values only.
5. Click Next.
The Associate dialog is displayed.
6. Choose whether to associate the notification with Selected Tasks or with All Current and Future
Tasks.
Note that when you complete the Task Notification wizard, the Associated with column in the
Notification Rules window will display either Selected Tasks or All Current and Future Tasks
depending on which of these options you selected.
If you chose Selected Tasks, from the Server drop-down list, select All Servers or a specific server.
Then, select the desired tasks using the arrow buttons in the middle of the screen (multiple selection is
supported).
The Server drop-down list only displays servers:
l
That are monitored
l
For which the user who defines the notification has View permission
The Tasks list only displays tasks:
l
That are running on monitored servers (that are not in an error state)
l
For which the user who defines the notification has View permission
7. Click Next.
The Recipients dialog is displayed.
8. Notifications will always be displayed in the Message Center. If you also want the notification to be
sent to the Windows Event Log and/or specified Email Recipients, select their respective check
boxes.
See also Replicate Event IDs in Windows Event Log.
If you selected Email Recipients, specify a list of email recipients (separated by semi-colons) in the To,
Cc and/or Bcc fields.
Sending notifications to email recipients requires your organization's outgoing mail server
settings to be defined.
9. Click Next.
The Message dialog displays a default email subject and email/Windows Event Log message for the
selected notification. You can change the default subject and/or message and make use of any of the
variables listed to the right of the message.
The message shown in the Message Center is system generated and cannot be edited.
10. Click Finish to add the notification to Enterprise Manager.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 256

10 Messages and notifications
A summary of the notification settings will be displayed in the Tasks tab in the Notification Rules
window.
New notifications are always created as enabled and are active immediately without any
need to stop/resume tasks.
Task notification variables
In addition to allowing you to edit the default messages, the Message window also provides a list of variables
that you can insert into the notification message. These are described in the table below.
To insert a variable:
1. Select the desired variable.
2. Place the cursor in the message where you want the variable to be inserted.
3. Click the arrow to the left of the variable list.
The table below describes all of the message variables. However, the variables available for
selection in the Message window will vary according to the notification event you select.
Variable Description
${CDC_APPLIED_CHANGES_COUNT} The number of changes applied to the target tables
during Change Processing.
${CDC_APPLY_LATENCY} The overall Change Processing latency.
${CDC_APPLY_THROUGHPUT_KB_SEC} The Change Processing throughput speed in kilobytes
per second.
${CDC_APPLY_THROUGHPUT_REC_SEC} The Change Processing throughput speed in records per
second.
${CDC_CHANGES_FOR_APPLY_IN_MEMORY_
UNTIL_TARGET_COMMIT}
The number of change records in memory waiting to be
committed to the target database.
${CDC_CHANGES_FOR_APPLY_ON_DISK_UNTIL_
TARGET_COMMIT}
The number of change records on disk waiting to be
committed to the target database.
${CDC_CHANGES_IN_MEMORY_UNTIL_SOURCE_
COMMIT}
The number of change records in memory until the next
source commit.
${CDC_CHANGES_ON_DISK_UNTIL_SOURCE_
COMMIT}
The number of change records on disk until the next
source commit.
${CDC_COMMIT_CHANGE_RECORDS_COUNT} The total number of committed change records.
${CDC_COMMIT_CHANGE_VOLUME_MB} The total volume of committed change records in MB.
Task notification variables
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 257

10 Messages and notifications
Variable Description
${CDC_COMMIT_TRANSACTIONS_COUNT} The total number of transactions committed during
Change Processing.
${CDC_DDLS_COUNT} The number of DDLs (metadata) applied during Change
Processing.
${CDC_DDLS_PERCENTAGE} The percentage of changes applied during Change
Processing in terms of DDLs.
${CDC_DELETES_COUNT} The number of DELETEs applied during Change
Processing.
${CDC_DELETES_PERCENTAGE} The percentage of changes applied during Change
Processing in terms of DELETEs.
${CDC_INCOMING_CHANGES_COUNT} The number of incoming changes (from the source
endpoint).
${CDC_INCOMING_TRANSACTIONS_COUNT} The number of incoming transactions (from the source
endpoint).
${CDC_INSERTS_COUNT} The number of INSERTs applied during Change
Processing.
${CDC_INSERTS_PERCENTAGE} The percentage of changes applied during Change
Processing in terms of INSERTs.
${CDC_OPEN_TRANSACTIONS_IN_SOURCE} The number of open transactions in the source
database during Change Processing.
${CDC_ROLLBACK_CHANGE_RECORDS_COUNT} The number of change records rolled back during
Change Processing.
${CDC_ROLLBACK_CHANGE_VOLUME_MB} The volume of change records rolled back during
Change Processing.
${CDC_ROLLBACK_TRANSACTIONS_COUNT} The number of transactions rolled back during Change
Processing.
${CDC_SOURCE_LATENCY} The source latency during Change Processing.
${CDC_SOURCE_THROUGHPUT_KB_SEC} The Change Processing throughput from the source
endpoint in kilobytes per second.
${CDC_SOURCE_THROUGHPUT_REC_SEC} The Change Processing throughput from the source
endpoint in records per second.
${CDC_TRANSACTIONS_FOR_APPLY_ON_
TARGET}
The number of transactions pending apply on the target
${CDC_UPDATES_COUNT} The number of UPDATEs applied during Change
Processing.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 258

10 Messages and notifications
Variable Description
${CDC_UPDATES_PERCENTAGE} The percentage of changes applied during Change
Processing in terms of UPDATEs.
${TIME_SINCE_LAST_CHANGE} The time that has elapsed in minutes since changes
were last captured from the source database.
${CPU_USAGE_PERCENTAGE}
Only available for Replicate 6.2 or
later. For earlier Replicate versions,
this variable will appear as -1 in the
notification message.
The percentage of CPU utilized by the task.
${DISK_USAGE_MB} The total disk usage in MB.
${EVENT_TIME} When the notification event occurred (e.g. when latency
exceeded N MB, when latency returned to normal, and
so on).
${FL_END_TIME} When the Full Load operation ended.
${FL_LOAD_DURATION} The duration of the Full Load operation.
${FL_PROGRESS_PERCENTAGE} The percentage of the Full Load operation already
completed.
${FL_RECORDS_COMPLETED_COUNT} The current number of processed records during Full
Load replication.
${FL_RECORDS_LEFT_COUNT} The current number of records awaiting processing
during Full Load replication.
${FL_SOURCE_THROUGHPUT_KB_SEC} The Full Load throughput from the source endpoint in
kilobytes per second.
${FL_SOURCE_THROUGHPUT_REC_SEC} The Full Load throughput from the source endpoint in
records per second.
${FL_TABLES_COMPLETED_COUNT} The current number of tables loaded to the target
during Full Load replication.
${FL_TABLES_LEFT_COUNT} The current number of tables still waiting to be loaded
during Full Load replication.
${FL_TABLES_LOADING_COUNT} The number of tables currently being loaded during Full
Load replication.
${FL_TABLES_QUEUED_COUNT} The current number of queued tables during Full Load
replication.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 259
10 Messages and notifications
Variable Description
${FL_TARGET_THROUGHPUT_KB_SEC} The Full Load throughput to the target endpoint in
kilobytes per second.
${FL_TARGET_THROUGHPUT_REC_SEC} The Full Load throughput to the target endpoint in
records per second.
${FL_TOTAL_RECORDS_COUNT} The total number of records replicated during Full Load.
${FL_TOTAL_TABLES_COUNT} The total number of tables replicated during Full Load.
${FULL_LOAD_ENDED} A boolean indicating whether or not Full Load has
completed.
${HOST_NAME} The host name of the Replicate Server machine.
${MEMORY_USAGE_MB} The total amount of memory being used.
${SERVER_NAME} The Replicate server display name, specified by the user
when the server was added to Enterprise Manager.
${SOURCE_NAME} The name of the source endpoint.
${SOURCE_TYPE} The source endpoint type (e.g. Microsoft SQL Server).
${TABLES_WITH_ERROR_COUNT} The number of tables with errors.
${TAGS} The name of any tags applied in Enterprise Manager at
the time of the notification.
${TARGET_NAME} The name of the target endpoint.
${TARGET_TYPE} The target endpoint type (e.g. Microsoft SQL Server).
${TASK_DATA_ERRORS_COUNT} The number of data errors encountered by the task.
${TASK_DESCRIPTION} The task description (entered by the user when the task
was defined).
${TASK_NAME} The task name.
${TASK_PROFILE} The task profile (unidirectional or bidirectional).
${TASK_STAGE} The current processing stage of the task.
${TASK_STATE_REASON} The reason for the current task status.
${TASK_STATE} The current task status (stopped, running, etc.).
${TASK_TYPE} The task type (Full Load only, Apply Changes only, or
Full Load and Apply Changes)
${NOTFICATION_NAME} The name of the notification.
${ERROR_DETAILS} Error details related to tasks that encountered an error.
(currently relevant only for the "Task has stopped due
to a non-recoverable error" event).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 260

10 Messages and notifications
Setting a server notification
Notifications can be set for the following events:
l
Excessive disk space usage (Replicate servers only)
l
Excessive memory usage (Replicate servers only)
l
State changes/errors (Replicate and Compose servers)
Currently, it is not possible to configure notifications for individual servers. In other words, any
notification that you define will apply to all current and future servers.
To set a server notification:
1.
Click the toolbar button on the right of the console.
The Notification Rules window opens.
2. Click the Servers tab and then click New.
The New Server Notification wizard opens.
3. Provide a name for the notification.
4. Select and define one of the following:
In the Disk Space section, you can determine the disk usage event that triggers the notification.
Select one of the following:
l
Disk usage reaches the high threshold: The notification will be triggered when disk usage
reaches the percentage defined for the high threshold.
l
Disk usage reaches the critical threshold: The notification will be triggered when disk usage
reaches the percentage defined for the critical threshold.
l
Disk usage returns to normal: The notification will be triggered when disk usage returns to
normal percentage (i.e. not high or critical).
l
Disk usage reaches any of the defined thresholds or returns to normal: The notification will
be triggered in any of the following scenarios:
l
Disk usage increases from normal to the high threshold
l
Disk usage increases from normal to the critical threshold
l
Disk usage increases from the high threshold to the critical threshold
l
Disk usage returns to normal from the high threshold
l
Disk usage returns to normal from the critical threshold
l
Disk usage returns to the high threshold from the critical threshold
In the System Memory section, you can determine the system memory usage event that triggers the
notification.
Select one of the following:
l
System memory usage reaches the high threshold: The notification will be triggered when
system memory usage reaches the percentage defined for the high threshold.
l
System memory usage reaches the critical threshold: The notification will be triggered when
system memory usage reaches the percentage defined for the critical threshold.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 261

10 Messages and notifications
l
System memory usage returns to normal: The notification will be triggered when system
memory usage returns to normal percentage (i.e. not high or critical).
l
System memory usage reaches any of the defined thresholds or returns to normal: The
notification will be triggered in any of the following scenarios:
l
System memory usage increases from normal to the high threshold
l
System memory usage increases from normal to the critical threshold
l
System memory usage increases from the high threshold to the critical threshold
l
System memory usage returns to normal from the high threshold
l
System memory usage returns to normal from the critical threshold
l
System memory usage returns to the high threshold from the critical threshold
In the State/Errors section, select the Server state has changed notification to receive a notification
whenever any of the following occurs:
l
Enterprise Manager starts monitoring a Compose/Replicate server
l
Enterprise Manager stops monitoring a Compose/Replicate server
l
A connection error to any of the monitored Compose/Replicate servers occurs
5. Click Next.
The Recipients screen is displayed.
6. Notifications will always be displayed in the Message Center. If you also want the notification to sent to
the Windows Event Log and/or specified Email Recipients, select their respective check boxes.
For more information about Windows Event Log IDs, see Replicate Event IDs in Windows Event Log
If you selected Email Recipients, specify a list of email recipients (separated by semi-colons) in the To,
Cc and/or Bcc fields.
Sending notifications to email recipients requires your organization's outgoing mail server
settings to be defined.
7. Click Next.
The Message screen displays a default email subject and email/Windows Event Log message for the
selected notification. You can change the default subject and/or message and make use of any of the
variables listed to the right of the message.
The message shown in the Message Center is system generated and cannot be edited.
8. Click Finish to add the notification to Enterprise Manager.
A summary of the notification settings will be displayed in the Servers tab in the Notification Rules
window.
New notifications are always created as enabled and are active immediately without any
need to stop/start monitoring servers.
Server notification variables
In addition to allowing you to edit the default messages, the Message window also provides a list of variables
that you can insert into the notification message. These are described in the table below.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 262

10 Messages and notifications
To insert a variable:
1. Select the desired variable.
2. Place the cursor in the message where you want the variable to be inserted.
3. Click the arrow to the left of the variable list.
The table below describes all of the message variables. However, the variables available for
selection in the Message window varies according to the notification event you select.
Variables related to Disk, Memory, Qlik CPU, and Machine CPU usage are not available for Compose
servers. If defined, these variables will appear as -1 in the notification message.
Variables related to Qlik CPU and Machine CPU usage are only available for Replicate 6.2 or later.
For earlier Replicate versions, these variables will appear as -1 in the notification message.
${ATTUNITY_CPU_USAGE_
PERCENTAGE}
Total percentage of CPUutilized by the Replicate Server's services and
tasks.
${MACHINE_CPU_USAGE_
PERCENTAGE}
Total percentage of CPU utilized by the machine on which the server is
installed.
${DISK_TOTAL_GB} The total size of the disk on which the Replicate "Data" folder is installed.
${DISK_USAGE_GB} The total amount of disk space(in GB) utilized by the Replicate "Data"
folder.
${DISK_USAGE_MB} The total amount of disk space(in MB) utilized by the Replicate "Data"
folder.
${DISK_USAGE_PERCENTAGE} The total percentage of disk space utilized by the Replicate "Data" folder.
${DISK_USAGE_PREV_STATE} The previous disk usage state (Normal, High, or Critical)
${DISK_USAGE_STATE} The current disk usage state (Normal, High, or Critical)
${ERROR_DETAILS} Information about server connection errors.
${ERROR_TASKS_COUNT} The total number or tasks in an "Error" state.
${EVENT_TIME} When the notification event occurred.
${HOST_NAME} The host name of the server machine.
${LAST_CONNECTION} The last successful connection to the server.
${LICENSE_DAYS_TO_
EXPIRATION}
The number of days left until the license expires.
${LICENSE_EXPIRATION} When the license is due to expire.
${LICENSE_ISSUE_DATE} When the license was issued.
${LICENSE_STATE} The current license state.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 263

10 Messages and notifications
${MEMORY_TOTAL_GB} The total amount of memory available on the Replicate Server machine.
${MEMORY_USAGE_GB} The amount of memory (in GB) consumed by Replicate tasks on the
Replicate Server machine.
${MEMORY_USAGE_MB} The amount of memory (in MB) consumed by Replicate tasks on the
Replicate Server machine.
${MEMORY_USAGE_
PERCENTAGE}
The percentage of total memory consumed by Replicate tasks on the
Replicate Server machine.
${MEMORY_USAGE_PREV_
STATE}
The previous memory state (Normal, High, or Critical)
${MEMORY_USAGE_STATE} The current memory state (Normal, High, or Critical)
${PLATFORM} The platform on which the server machine is installed (Linux or Windows)
${PORT} The server port.
${RECOVERING_TASKS_
COUNT}
The total number of tasks with a "Recovering" status.
${RUNNING_TASKS_COUNT} The total number of tasks with a "Running" status.
${SERVER_DESCRIPTION} The server description in Enterprise Manager.
${SERVER_NAME} The server name in Enterprise Manager.
${SERVER_PREV_STATE} The previous server state (Not Monitored, Monitored, or Error)
${SERVER_STATE} The current server state (Not Monitored, Monitored, or Error)
${STOPPED_TASKS_COUNT} The total number of tasks with a "Stopped" status.
${TASKS_TOTAL_COUNT} The total number of tasks, regardless of state.
${USER_NAME} The user name for accessing the server.
${VERSION} The server version.
Managing notifications
You can manage task and server notification in their respective tabs.
The following management options are available:
All of the actions described below can also be performed via the context menu.
To Do this
Delete a notification Select the desired notification(s) and then click the Delete toolbar button.
When prompted to confirm your action, click Yes.
Notification actions
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 264

10 Messages and notifications
To Do this
Edit a notification Select the desired notification(s) and then click the Open toolbar button.
Enable a notification Select the desired notification(s) and then click the Enable toolbar button.
Disable a notification Select the desired notification(s) and then click the Disable toolbar button.
Search for a notification Use the search box to perform a search on all the columns in the notification list.
OR
Search by column value by specifying the column name as a prefix.
Example 1:
To find all enabled notifications specify:
Enabled: true
Example 2:
To find all notifications where "Jeff" is one of the recipients, specify:
Recipients: Jeff
Required permissions
Notifications have their own set of permissions which are inherited from Enterprise Manager by default.
These are as follows:
l
Admin: Can view notifications, enable/disable notifications, add/edit/delete notifications, and change
the notification permissions.
l
Designer: Can view notifications, enable/disable notifications, and add/edit/delete notifications.
l
Operator: Can view notifications as well as enable/disable notifications.
l
Viewer: Can only view notifications.
For more information on setting user permissions, see Managing user permissions (page 286)
Event IDs in Windows Event Log
The table below lists the Event IDs for tasks and server events in Windows Event Log.
Some events share the same ID. With these events, the recommended way of identifying the event is
to parse the notification subject. This is especially recommended if you are using third-party tools to
detect and report events.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 265

10 Messages and notifications
Event ID Description
261 Any error.
262 Any warning.
263 Errors containing the specified codes.
Other Event IDs
Event ID Description
300 Server disk usage has changed.
300 Disk utilization has changed
300 Server disk usage has reached the high threshold.
300 Server disk usage has reached the critical threshold.
300 Server disk usage has returned to normal.
320 Server system memory usage has changed.
320 Memory utilization has changed.
320 Server system memory usage has reached the high threshold.
320 Server system memory usage has reached the critical threshold.
320 Server system memory usage has returned to normal.
340 Server state has changed.
ServerEvent IDs
Event ID Description
400 Task has started.
401 Full load has started.
402 Full load has completed.
403 Task has stopped after Full Load – cached changes were applied.
404 Task has stopped after Full Load – cached changes were not applied.
405 Task has stopped (other cases).
406 Task has stopped due to a non-recoverable error.
261 Task latency has exceeded the set limit.
261 Task latency is back to normal.
432 Task memory usage has exceeded the set limit.
433 Task memory usage is back to normal.
Task Event IDs
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 266

10 Messages and notifications
434 Task disk usage has exceeded the set limit.
435 Task disk usage is back to normal.
Event ID Description
502 Table processing was suspended due to errors.
Table Event IDs
10.5 Viewing and downloading log files
In Enterprise Manager, you can view different types of log files:
l
Replicate Server log files (repsrv.log): Retrieved from the monitored Replicate server.
l
Replicate Task log files (reptask_<task_name>.log): Retrieved from the monitored Replicate server.
l
Compose Server log files (Compose.log): Retrieved from the monitored Compose server.
l
Compose Agent log files (Compose.log): Retrieved from the monitored Compose server. When
selecting a task associated with a Compose for Spark project, you can also view the Compose job files
in the Spark History Server as described below.
l
Compose task log files (<n>.log): Retrieved from the monitored Compose server.
l
Operations log files (EnterpriseManager.log): Created by and managed in Enterprise Manager.
l
Analytics log files (aemanalytics.log): Created by the Enterprise Manager Analytics processes.
To view a log file:
1. Do one of the following to open the Log Viewer:
l
For server log files: In the Servers list, select a server and click View Logs above the list.
This option is only available for servers that are connected.
l
For Compose and Replicate task log files: In the Tasks list, select a task and click View Logs
above the list.
This option is only available for tasks associated with connected servers.
When selecting a task associated with a Compose for Spark project, a View Spark History
Server link appears at the bottom of the window. Clicking the link will open a window
displaying the Compose Spark jobs.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 267

10 Messages and notifications
If you encounter an access error when clicking the View Spark History Server link,
try one or both of the following:
l
Add an entry to the client host file that maps the Spark History Server host
name to its externally accessible IP address.
l
Open the necessary firewall ports to allow Enterprise Manager to access the
Spark History Server.
l
For Operations log files: Click the View Logs icon in the top right corner. Then select
Operations from the Log Files drop-down list in the top left of the window.
You can also view log files for messages in the Message Center. The View Logs option
is available for all messages reported by Enterprise Manager, for messages reported
by a server that is connected, and for tasks pertaining to a server that is connected.
l
For Analytics log files: Click the View Logs icon in the top right corner. Then select Analytics
from the Log Files drop-down list in the top left of the window.
2. In the Log Viewer window, in the Log Files pane on the left, select the log file you want to view.
The content of the log file is displayed in the right pane. When you select a row in the log file, a tooltip
displays the full message of the selected row.
3. Browse through the log file using the scroll bar on the right.
4. To search for a specific string in the log file, enter the search string in the search box at the top of the
window.
Any terms that match the specified string are highlighted blue. The number of matches is displayed
next to the search box. You can use the navigation errors to move to the first, next, previous, or last
occurrence of the search string.
5. To start a new log file, click Roll Log File.
The log file gets saved with a 12-digit timestamp appended to its name, such as EnterpriseManager_
160619073410.log or repsrv_160703131920.log.
This option is not available for Compose log files.
This option is not available when you open the Log Viewer window from the Message Center.
6. Click Close.
To download a log file:
l
In the Log Viewer window, select the log file you want to download and click the Download Log File
icon at the top right.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 268

11 Administration
11 Administration
This section describes how to configure message purge and logging settings in Qlik Enterprise Manager.
For information on setting up and using Analytics, see Analytics (page 305).
In this section:
l
Enterprise Manager settings (page 269)
l
Enterprise Manager logging settings (page 269)
l
Message Center purge settings (page 271)
l
Repository connection settings (page 272)
l
Qlik Catalog Server connection (page 273)
l
Analytics - Data collection and purge settings (page 273)
l
Configuring mail server settings (page 275)
l
Registering and managing licenses (page 276)
l
User permissions (page 278)
l
Creating an audit trail (page 289)
11.1 Enterprise Manager settings
In the Settings window you can configure the following:
l
Enterprise Manager logging settings (page 269)
l
Message Center purge settings (page 271)
l
Repository connection settings (page 272)
l
Analytics - Data collection and purge settings (page 273)
l
Configuring mail server settings (page 275)
l
Registering and managing licenses (page 276)
To open the Settings window, click the toolbar button in the top right of the console.
Enterprise Manager logging settings
In Enterprise Manager, you can modify the logging settings for system log files. This includes specifying:
l
Logging levels (page 270)
l
Automatic log rollover and cleanup (page 270)
To modify logging settings for server and task log files, you need to access the web console for the respective
monitored Replicate server.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 269

11 Administration
Logging levels
The logging level you set determines what information is written to the system log file, EnterpriseManager.log,
and whether information is written to the Attunity.WebLog.log file. The system log file provides information
about events, warnings, and errors occurring in Enterprise Manager, but not for the monitored Replicate
servers and their respective tasks. The WebLog file captures requests and responses between the client and
server, but only when the logging level for the WebLog component is set to Trace or Verbose.
Because the WebLog file grows quickly in size, it is recommended that you only set the logging level
for the WebLog component to Trace or Verbose for short periods of time, such as when
troubleshooting an issue.
The following logging levels are available, from the lowest to the highest:
l
Error: Include only error messages.
l
Warning: Include error and warning messages.
l
Info: Include error, warning, and info messages.
l
Trace: In addition to error, warning, and info messages, include debug data.
l
Verbose: In addition to error, warning, and info message, include detailed debug data.
Within the log file, the logging level is indicated by the initial letter: E for error, W for warning, and so on. The
higher levels always include the messages from the lower levels. Therefore, if you select Error, only error
messages are written to the log. However, if you select Info, informational messages, warnings, and error
messages are included. Selecting Verbose writes all possible messages to the log.
You can set a global logging level for all log components or separate logging levels for each component. For
example, you can define a logging level of Info for Message Center logs and a logging level of Warning for
Replicate tasks.
To set the logging level:
1. In the top right corner, click the gear icon.
2. In the Settings window, in the Logging Levels tab, move the top slider to the log level you want.
This sets the log level for all components. Note that the sliders for all components move along to the
same position.
3. Optionally, modify the individual logging level for any component.
4. Click OK.
Automatic log rollover and cleanup
You can define when Enterprise Manager should roll over the system log file and WebLog file and when to
purge old log files. The current log files are called EnterpriseManager.log and Attunity.WebLog.log, respectively.
Rolled over log files have a 12-digit timestamp appended to their name, such as EnterpriseManager_
160407111842.log or Attunity.WebLog_160717115348.log.
Automatic rollover is enabled by default. You can also perform rollover manually if needed. See Manual log
rollover (page 271).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 270

11 Administration
To configure automatic rollover and cleanup:
1. In the top right corner, click the gear (settings) icon.
2. In the Settings window, in the Logging|Log File Management tab:
l
Select the Enable automatic rollover check box to have log files rolled over at the default size
of 100 MB. By default, this check box is selected.
l
If you prefer a different cutoff size for rollover, select the check box Roll over the log if the log
file is larger than (MB): and specify a different file size. When the log file reaches the specified
size, the old log is saved with a timestamp appended to its name and a new log file is started.
The maximum file size is 1,024 MB.
l
Under Maximum number of newest log files to keep, specify the maximum number of log
files to keep. By default, this is 45 files. The maximum number of files cannot exceed 100.
Enterprise Manager keeps the newest log files and removes any files beyond the specified
number.
3. Click OK.
Manual log rollover
If you need to start a new system log file or WebLog file before the current file has reached the size specified
for automatic rollover, or if you want to start a new server or task log file, you can do this manually. Manual
rollover is only available for active log files and for log files pertaining to tasks that are currently running.
To manually roll over a log file:
1. In the top right corner, click the View Logs icon.
2. In the Log Viewer window, select the current log file and click Roll Log File.
Enterprise Manager starts logging to a new log file. Rolled over log files have a 12-digit timestamp
appended to their name, such as EnterpriseManager_160407111842.log or Attunity.WebLog_
160717115348.log.
3. Click Close.
Message Center purge settings
Enterprise Manager pulls error, warning, information, and notification messages from all managed Replicate
Servers and stores them locally on the machine where Enterprise Manager is installed. The Enterprise Manager
console then retrieves these messages from the local storage and displays them in the Message Center as
described in Messages and notifications (page 250).
To avoid storage issues, you can specify the interval at which Enterprise Manager should purge messages from
the Message Center and the maximum number of messages to be stored. By default, Enterprise Manager
purges messages after 14 days and when the number of messages exceeds 200,000. Purged messages are no
longer available for retrieval.
The message purge policy you define in Enterprise Manager does not affect any log purge policy of
the monitored Replicate servers.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 271

11 Administration
To modify Message Center purge settings:
1. Click the gear icon in the top right corner.
The Settings window opens.
2. In the Message Center tab, specify:
l
After how many days or weeks to purge messages. The default value is 14 days; the maximum
value 91 days (13 weeks). You can enter any value between 1 and 91.
l
The maximum number of messages to be stored in Enterprise Manager. The default value is
200,000. The maximum value is 1,000,000; the minimum 100. You can enter any value between
100 and 1,000,000.
Enterprise Manager purges messages at 12:00 PM and 00:00 AM only. As such, it is
possible that the number of actual messages may occasionally exceed the value
specified in the Store no more than field.
3. Click OK.
Repository connection settings
The repository is used to store data from the Analytics module. Once PostgreSQL is installed, you need to
configure the connection settings to the repository.
To set up connectivity:
1. Switch to Operations View and then click the Settings button in the top right corner.
2. In the Settings window, click the Repository Connection tab.
3. Enter the following information:
Field Value
Repository host The IP address or host name of the PostgreSQL machine.
Port The port through which the PostgreSQL machine is accessed.
Database The name of the PostgreSQL database where you want the analytics data to be
stored.
User name The user name for accessing the PostgreSQL database.
Password The password for accessing the PostgreSQL database.
Maximum
number of
connections
The number of concurrent connections to the specified PostgreSQL database.
You may need to increase the number of connections based on task activity.
Repository connection fields
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 272

11 Administration
Field Value
Additional
connection
properties
Enter any additional connection properties for the PostgreSQL database.
Properties should be formatted as follows:
"key=value;key=value"
For a description of JDBC connection properties, visit:
https://jdbc.postgresql.org/documentation/use/
4. To test the settings (recommended), click Test Connection.
5. If the connection test is successful, click Save. Note, after clicking Save, if you have specified a new
database, you will also need to click Initialize Analytics Repository to enable the Analytics module.
Clicking Initialize Analytics Repository will delete all data from an existing Repository.
Therefore, you should only initialize them if you are configuring connectivity to a new
database.
6. Configure the data collection and purging settings for Analytics as described in Analytics - Data
collection and purge settings (page 273).
Qlik Catalog Server connection
For information on these settings, please refer to Cataloging tasks in Qlik Catalog (page 300).
Analytics - Data collection and purge settings
When working with the Analytics module, after configuring the connection settings to your repository, you
then need to configure data collection and purge settings.
You can also change the log level and management settings if desired.
Defining data collection and purging settings
To set up and start the collector:
1. Select the Analytics tab.
2. In the Collector properties section, optionally change the following information:
Field Value
Collect data
every
The number of minutes to wait between data collection operations.
Store data up to The number of days to store data from the moment it is collected.
Collector property fields
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 273

11 Administration
Field Value
If the repository
is unavailable,
store data in
memory for up to
The number of minutes of data that should be stored in memory if the Analytics
repository is unavailable for any reason.
Analyze database
tables during
data collection
When selected (the default), the Collector process will analyze the tables in the
Analytics repository during each run. If unchecked, the Collector process will
not analyze the tables and the customer should ensure that statistics are being
updated periodically.
As the size of the database gets larger, it is less important to update statistics
frequently and it may start to impact the performance of the Collector, so it is
recommended to disable if you notice the Analytics dashboards being updated
less frequently.
3. Click Start Collector.
To stop the collector:
l
Click the Stop Collector button in the Collector properties section.
To resume data collection, click the Start Collector button.
To start and stop the purger:
l
Click the Start Purger button. Data will be purged according to the value specified in the Store data
up to field described above.
To prevent data from being purged, click the Stop Purger button.
Setting logging levels
In the Logging Levels sub-tab, you can set the logging levels for the log files generated by the Analytics
service. The level of information in the log files is determined by the logging level set in this tab. Analytics log
files can be viewed in the Log Viewer as described in Viewing and downloading log files (page 267).
Because the WebLog file grows quickly in size, it is recommended that you only set the logging level
for the WebLog component to Trace or Verbose for short periods of time, such as when
troubleshooting an issue.
The following logging levels are available, from the lowest to the highest:
l
Error: Include only error messages.
l
Warning: Include error and warning messages.
l
Info: Include error, warning, and info messages.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 274

11 Administration
l
Trace: In addition to error, warning, and info messages, include debug data.
l
Verbose: In addition to error, warning, and info message, include detailed debug data.
Within the log file, the logging level is indicated by the initial letter: E for error, W for warning, and so on. The
higher levels always include the messages from the lower levels. Therefore, if you select Error, only error
messages are written to the log. However, if you select Info, informational messages, warnings, and error
messages are included. Selecting Verbose writes all possible messages to the log.
You can set a global logging level for all log components or separate logging levels for each component. For
example, you can define a logging level of Info for Message Center logs and a logging level of Warning for
Replicate tasks.
To set the logging level:
1. Move the top slider to the log level you want.
This sets the log level for all components. Note that the sliders for all components move along to the
same position.
2. Optionally, modify the individual logging level for any component.
3. Click OK.
Automatic rollover and cleanup
You can define when Enterprise Manager should roll over the Analytics log file and when to purge old log files.
The current log file is called aemanalytics.log. Rolled over log files have a 12-digit timestamp appended to
their name, such as aemanalytics_180407111842.log.
Automatic rollover is enabled by default. If needed, you can also perform rollover manually as described in
Viewing and downloading log files (page 267).
To configure automatic rollover and cleanup:
1. Select the Log File Management sub-tab.
2. In the Settings window, in the Logging|Log File Management tab:
l
Select the Enable automatic rollover check box to have log files rolled over at the default size
of 100 MB. By default, this check box is selected.
l
If you prefer a different cutoff size for rollover, select the check box Roll over the log if the log
file is larger than (MB): and specify a different file size. When the log file reaches the specified
size, the old log is saved with a timestamp appended to its name and a new log file is started.
The maximum file size is 1024 MB.
l
Under Maximum number of newest log files to keep, specify the maximum number of log
files to keep. By default, this is 45 files. The maximum number of files cannot exceed
100.Enterprise Manager keeps the newest log files and removes any files beyond the specified
number.
3. Click OK.
Configuring mail server settings
Mail server settings are required for sending Enterprise Manager notifications.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 275

11 Administration
To configure the mail server settings:
1.
Click toolbar button in the right of the console.
The Settings window opens.
2. Select the Mail Server Settings tab and enter the following information:
l
Mail server: The host name or IP address of your organization's outgoing mail server.
Example: smtp.example.com
l
Port: The port used to communicate with the mail server. The default value is 25.
l
Use SSL: Select to connect to the mail server (for sending notifications) using SSL.
l
Verify peer: Select if you want the mail server to send a certificate proving its identity. On
Windows, the certificate will be authenticated using the default CA certificates.
l
CA Path: On Linux, specify the location of the server CA certificate.
l
Verify host:Select to verify that the host name in the certificate matches the host name of the
mail server.
l
Anonymous login: Select this to allow users to receive notifications without having to provide
login credentials.
l
User name: The user name for the email user account that is sending notifications.
l
Password: The password for the email user account that is sending notifications.
l
Sender email address: The email address from which notifications will be sent. The address
will appear in the From field of the email notification.
3. To send a test mail, specify an email address in the Send to field and then click the Send Test Mail
button.
If the mail server settings are correct, an email will be sent to the specified email recipient. Otherwise,
an error will be shown at the top of the console.
4. Click OK to save your settings.
Registering and managing licenses
In the Licenses tab, you can view and register licenses for each of the Qlik Enterprise Manager modules.
Currently, the following modules require a license:
l
Replication Management - Enables design, customization, monitoring, and control of Replicate tasks
as well as Replicate Server management.
l
Replication Analytics - Provides measurements of server and task metrics over a specific time-period.
When the Replication Analytics license expires, data collection will no longer occur. However,
the Analytics dashboards will continue to show the analytics that were collected before the
license expired. Additionally, the Analytics tab will also remain available.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 276

11 Administration
Registering a license
To register a license:
1. Do one of the following:
l
Click the Register License link in the Register License message that is displayed when you
open Qlik Enterprise Manager, or that is displayed in the main Analytics tab (after you have
already registered a Replication Management license).
The Register <Module Name> License window opens.
Continue from Step 5 below.
l
Click the toolbar button in the right of the console.
2. The Settings window opens.
3. Select the Licenses tab.
The following sub-tabs are displayed (one for each module):
l
Replication Management
l
Replication Analytics
4. To register a license, select the relevant tab, and then click the Register License button at the top of
the tab.
The Register <Module Name> License window opens.
5. Click Load to load the license from a file, or copy the license text (e.g. from an email message) into the
License text area.
If the license you loaded or pasted is for a different module (e.g. you intended to load a
Replication Management license, but mistakenly loaded a Replication Analytics license), a
warning will appear at the top of the Register <Module Name> License window.
In such a case, you can either register the license anyway (since you may have intended to
register that license later) or load/paste another the license (i.e. the license that you
originally intended to register).
6. Click the Register License button at the bottom of the window.
If the license is valid, a confirmation that the license was registered successfully will be shown at the
top of the Settings window. Otherwise, an appropriate error message will be shown.
Viewing licenses
You can view the properties of registered licenses (such as when the license is due to expire).
To view a license:
1.
Click the toolbar button in the right of the console.
The Settings window opens.
2. Select the Licenses tab.
3. Select the Replication Management or Replication Analytics sub-tab accordingly.
A list of properties will be shown.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 277

11 Administration
Showing/hiding the Analytics Dashboards
The main Analytics tab is shown by default, regardless of whether or not you have registered a Replication
Analytics license. If you do not intend to use the Replication Analytics module, you can hide the tab by
either clicking the Hide Analytics Dashboards link in the Analytics tab or by following the procedure
described below.
To show/hide the main Analytics tab:
1.
Click the toolbar button in the right of the console.
The Settings window opens.
2. Select the Licenses tab.
3. Select the Replication Analytics sub-tab.
4. Clear or select the Hide Analytics Dashboards check box as required.
This option is only available when no Replication Analytics license has been registered.
5. Click Save.
License alerts
If any of the Enterprise Manager licenses are invalid, due to expire, or have already expired, a License Alerts
link will appear at the top of the console. Clicking the link will list the issue(s) and provide links to resolve
them (e.g. Register License).
Permissions
For information on permissions required to perform the various the license-related operations (i.e. registering
licenses, viewing licenses, and hiding the Analytics tab) see Roles and permissions (page 284).
11.2 User permissions
You can grant Qlik ReplicateEnterprise Manager users different roles according to the tasks you want them to
perform. Qlik ReplicateEnterprise Manager comes with the following predefined security roles: Admin,
Designer, Operator and Viewer. Each role has its own set of permissions, as described in Roles and permissions
(page 284). For more information on permissions, seeGranular access control (page 279)
You can associate a user with a security role by adding the user to the appropriate Active Directory group or
by assigning a role directly to the user. By default, the user under whose account you install Enterprise
Manager is associated with the Admin role. In addition, you can fine-tune access control per user or group. For
more information, see Granular access control (page 279).
As a user with the relevant permissions, you can view and change the permissions for existing users or groups,
or add users or groups that do not yet exist in Enterprise Manager.
The advantage of adding groups over users is that you can assign a security role to a group as a whole, instead
of to individual users, and any new user that gets added to an existing group automatically acquires the
security role granted to that group.
You can also:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 278

11 Administration
l
Add users as domain users that are not related to an active directory group.
l
Add local groups. However, this is not possible by default. To set up Enterprise Manager to work with
local groups, perform the steps in Working with local groups (page 286).
To set user permissions using Active Directory groups, you can either create Active Directory groups with the
names listed in the table below, or you can create Active Directory groups with different names. Then, add
users to the groups according to the role you want them to perform.
If you create your own Active Directory groups, you need to add them to the User Permissions tab in the
Settings window and set their permissions as described in Managing user permissions (page 286).
Role Active Directory Group
Administrator AttunityEnterpriseManager Admin
Designer AttunityEnterpriseManager Designers
Operator AttunityEnterpriseManager Operators
Viewer AttunityEnterpriseManager Viewer
Roles and ADgroups
Effective permissions are the permissions that take effect when a user is part of more than one group, or when
there is a conflict between the user's permission and the group's permission, or in the hierarchy. For details,
see Inheritance and overrides (page 280).
Encrypting the User Permissions File
User permissions are stored in the following repository file:
<product_dir>\Data\cfgrepo.sqlite
To prevent unauthorized access of this file, you can encrypt it using the procedure described in Replacing the
Master User Password (page 41).
Granular access control
For each user, Enterprise Manager lets you set granular access permissions for different hierarchy levels in the
system and for different objects at the same hierarchy level. This granular access control facilitates
decentralization of control, effectively preventing the same user from, for example, accessing endpoints and
defining and running tasks. As such, granular access control lets you create a buffer between those who can
create and access endpoints (DBAs) and those who can create and run tasks.
Enterprise Manager handles permission management as follows:
l
Admins can add, remove, and change permissions.
l
Designers and Operators can view permissions.
l
Viewers cannot view permissions.
By default, each object inherits its permissions from its parent. The following hierarchy is in place, where:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 279

11 Administration
l
Enterprise ManagerRoot refers to all Enterprise Manager server settings and all Replicate servers
monitored by Enterprise Manager.
Changes to Enterprise Manager root permissions will affect all levels that inherit those
permissions.
l
All Servers refers to all Replicate servers monitored by Enterprise Manager. This level does not have
access to Enterprise Manager server settings.
l
Specific Server refers to a server monitored by Enterprise Manager and all its child objects (server
settings, tasks, and endpoints).
l
All Tasks refers to all tasks that run on a specific Replicate server.
l
Specific Task refers to all parameters of the particular task.
To make a user a designer on a task, the user must be at least a viewer on All Endpoints.
l
All Endpoints refers to all endpoints connected to a specific Replicate server.
Inheritance and overrides
Group permission may contradict the permission that a particular user was granted. In this case, the higher
permission overrides the lower permission, as illustrated in the following figure:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 280

11 Administration
Group vs. user permissions
By default, the permission of a user or group object is inherited from the access control list (ACL)of the
object's parent. However, a lower or higher permission may override this permission. In this case, the
overriding higher permission is the effective permission for the object, stopping inheritance from the parent.
As a result, any changes to the parent no longer affect this user or group.
The following figures illustrate these concepts:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 281
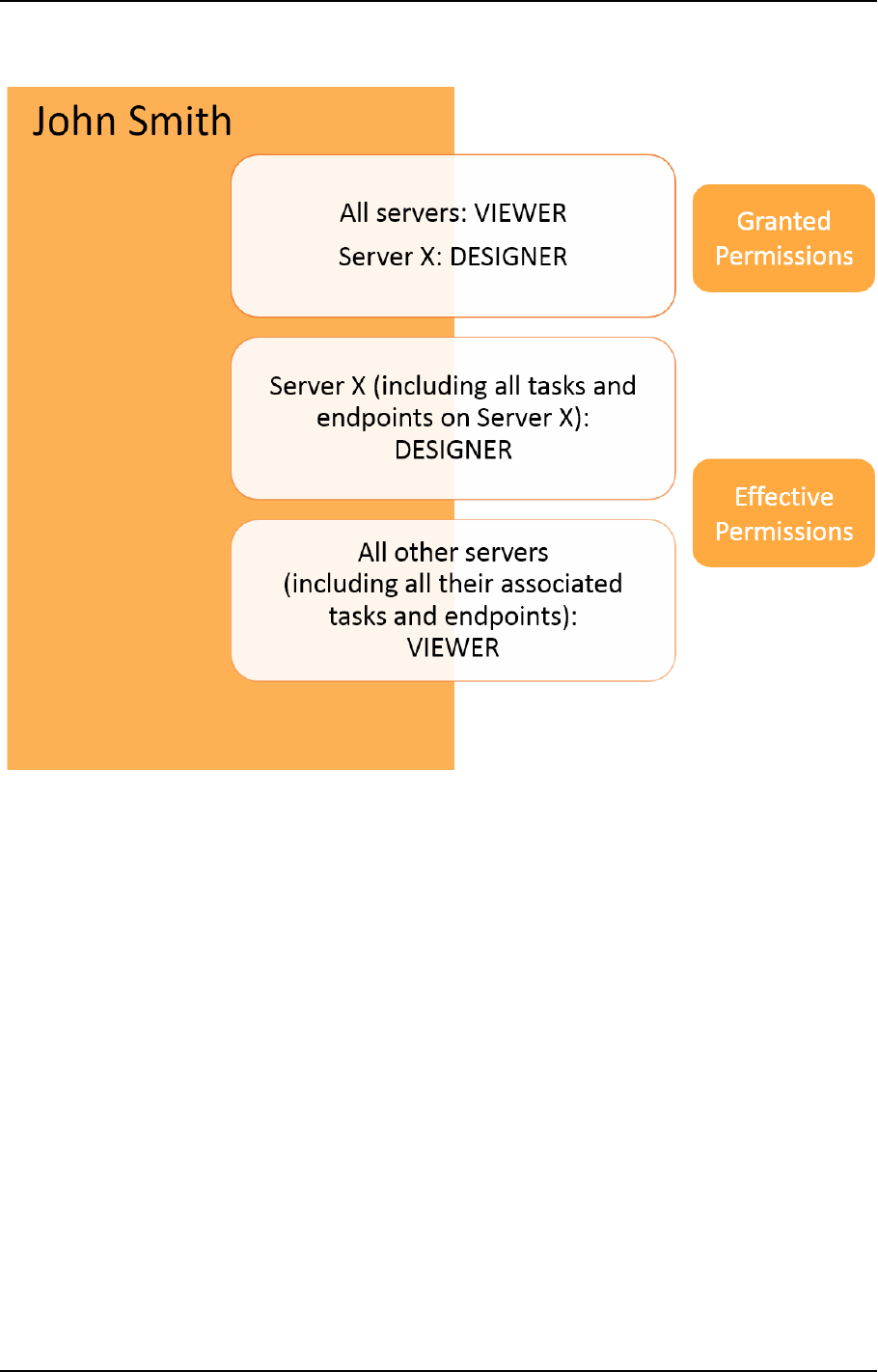
11 Administration
Inheritance overriden by higher permission
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 282

11 Administration
Inheritance overriden by lower permission
In the User Permissions window, inheritance is indicated by a checkmark in the Inherited column. By default,
inheritance is enabled for all users and groups on any level. Changing permissions by using the slider
automatically stops inheritance for the selected user or group. Enterprise Manager also lets you disable
inheritance by disconnecting the entire authorization level from the parent level. For information on how to
do this, see Managing user permissions (page 286).
Override exceptions
When a user or group is granted any permission higher than None on an object (except an endpoint), it
automatically receives Viewer permission on all parent objects in the hierarchy. However, the Viewer
permission granted to the parent objects does not enable the user or group to see items in the hierarchy that
they were not permitted to see before they received Viewer permission. For clarification, see the example in
the following table:
- Granted Permission Effective Permission
Server X None Viewer
All Tasks on Server X None Viewer (limited to Task Z)
Task Z on Server X Designer Designer
Permission override example
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 283

11 Administration
Roles and permissions
This topic explains how user roles affect the availability of console elements as well as which roles are
required in order to perform Enterprise Manager operations.
Availability of console elements according to role
In the Enterprise Manager Console, you see menu items and buttons based on your particular security role.
For example:
l
The Servers view is available to all roles, but Designers only have read access to user permissions, and
operators cannot add servers and can only view the different settings, but not edit them. Viewers do
not see the options to view logs, edit settings, add, edit, or delete a server, register a license, or
start/stop monitoring.
l
The Server dialog box is available to Admins, Designers, and Operators. Operators can test the
connection, but they cannot edit any fields. Viewers do not have access to this dialog box.
l
In the Tasks view, Operators see the Open, Run, and Stop options, but Viewers only see Open option.
Operators can search and assign tags, but they cannot add new tags or delete tags.
l
In the dedicated Task tab, Operators see all available options (Run, Stop, Reload, Resume, Reset
data errors, and so on) as well as the Monitor tab, but they do not see the Designer tab. Viewers only
see the Monitor tab. They do not have access to any actions.
l
In the Message Center, Viewers do not see the option to view logs.
Roles required for Enterprise Manager operations
The following table lists which user role is required to perform the available Enterprise Manager operations.
Some of the task operations are not available/relevant for Qlik Compose tasks. To find out if a
particular permission applies to Qlik Compose, refer to the Help topic explaining how to perform the
associated operation.
Permissions defined in Enterprise Manager take precedence over the permissions required for
performing the correspondng operation directly in Replicate or in Qlik Compose.
Permission/Operation Admin Designer Operator Viewer
Servers view Yes Read-Only Read-Only Read-
Only
Add and delete server Yes No No No
View server connection properties Yes Yes Yes No
Edit server connection properties Yes Read-Only Read-Only No
Test server connection Yes Yes Yes No
Edit column settings in the server list, search for
servers, and access the context menu for a specific
server.
Yes Yes Yes Yes
Server operation roles
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 284

11 Administration
Permission/Operation Admin Designer Operator Viewer
Access Design view (Replicate only) Yes Yes No No
Access Monitor view (Replicate only) Yes Yes Yes Yes
Add and design tasks Yes Yes No No
Add and design endpoints Yes Yes No No
Import Task
When a task with the same name already exists
on the target server.
Yes Yes* (see note
below)
No No
Import Task
When a task with the same name does not exist
on the target server.
Yes Yes* (see note
below)
No No
Export task without endpoints Yes Yes Yes No
Export task with endpoints Yes Yes Yes* (see note
below)
No
Task operation roles
For both of the Import Task permissions mentioned above, if the the exported JSON includes
endpoints, then the Enterprise Manager user must also have the role of Designer on All Endpoints
on the target server.
For the 'Export Task with endpoints' permissions mentioned above, the Enterprise Manager user
must have the role of Operator on the task as well as on both endpoints.
Permission/Operation Admin Designer Operator Viewer
Set logging levels, set log file
cleanup/rollover, and edit Message Center
settings
Yes Yes Read-Only No
Edit user permissions Yes Read-Only Read-Only No
View logs Yes Yes Yes No
Perform runtime operations (such as start,
stop, or reload targets)
Yes Yes Yes No
Delete tasks Yes Yes No No
Search for and assign tags Yes Yes Yes No
Other operation roles
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 285

11 Administration
Permission/Operation Admin Designer Operator Viewer
Add and delete tags Yes Yes No No
Perform Tools menu actions (in Monitor
view)
Yes Yes Yes
Note: The Operator
must be for a specific
task.
No
Access Message Center Yes Yes Yes Yes
Register license Yes No No No
View licenses Yes Yes Yes No
View the Enterprise Manager machine
name in the Licenses tab
Yes Yes Yes No
Hide the main Analytics tab Yes Yes No No
View license alerts Yes Yes Yes Yes
Working with local groups
By default, Enterprise Manager only supports working with domain users and groups. To set up support for
local groups, you must update the aemctl.exe.config file, which is located in the bin folder of your Enterprise
Manager installation directory (by default, this is C:\Program Files\Attunity\Enterprise Manager\bin).
To set up support for local groups:
1. Stop the Qlik Enterprise Manager service.
2. Open the following file in a text editor: installation directory\bin\aemctl.exe.config
3. Under <appSettings>, add the following row:
<add key="UseLocalGroups" value="true"/>
Example:
<appSettings>
<!-- LogOverwrite: comma seperated list of loggers ot '*' for enabling global debug -->
<!-- Loggers: Root,Service,Repository,Host,Command,Security,WebLog-->
<add key="LogDebugOverwrite" value=""/>
<add key="AssemblyList" value="AemGlobals,RepuiGlobals"/>
<add key="ClientSettingsProvider.ServiceUri" value=""/>
<add key="DisableToken" value="false"/>
</appSettings>
4. Save and close the file.
5. Restart the service.
Managing user permissions
This section explains how to edit user permissions, add and remove users or groups, disable or enable
inheritance, restore inherited permissions if they were overridden, and view effective permissions for a user.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 286

11 Administration
By default, inheritance is enabled for all objects (users and groups). This means that permissions are
automatically carried over from the parent object. You can turn inheritance on or off for all objects at the
current level.
Effective permissions are the permissions that are in effect for a user at any particular level.
For more information on the underlying concepts, see Granular access control (page 279) and Inheritance and
overrides (page 280).
To access user permissions at the Enterprise Manager, Analytics, Notifications or All Servers level:
1.
Click the User Permissions icon in the top right corner.
2. In the Enterprise Manager User Permissions window, select one of the following tabs:
l
Enterprise Manager to specify Enterprise Manager-wide user permissions.
NoteChanges to Enterprise Manager permissions will affect all levels that inherit
those permissions.
l
Analytics to specify Analytics permissions.
l
Notifications to specify notification permissions.
l
All Servers to specify permissions for all monitored servers.
To access user permissions for a specific Server, All Tasks, or All Endpoints:
1. In Servers view, select the desired server and then select Permissions from the Server Management
toolbar drop-down menu.
2. In the User Permissions for server: '{server name}' window, select one of the following tabs:
l
Server to specify server-wide user permissions.
l
All Tasks to specify permissions for all tasks on this server.
l
All Endpoints to specify permissions for all endpoints on this server.
To access user permissions for a specific Task:
l
In the tab for a specific task, click the task permissions icon in the task toolbar.
The User Permissions for task: {task name} windowopens.
To disable inheritance:
1. In the User Permissions window, click Disable Inheritance.
This option disconnects the entire authorization level from the parent level.
2. In the Disable Inheritance dialog box, select whether you want to:
l
Convert inherited permissions on this object into explicit permissions: This option changes
inherited permissions to explicit permissions. Any new users or groups will not inherit
permissions from the parent.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 287

11 Administration
l
Remove all inherited permissions from this object: This option removes all existing
permissions inherited from the parent level. Any new users or groups will not inherit
permissions from the parent.
3. Click Disable.
If you chose to convert inherited permissions, the check mark in the Inherited column changes into an
X. If you chose to remove inherited, all users and groups disappear from the list.
4. Click Save or OK to accept the changes, or Discard Changes or Cancel to undo them.
To enable inheritance:
1. In the User Permissions window, click Enable Inheritance.
This option enables inheritance for all users and groups on this level.
2. In the Enable Inheritance dialog box, select whether you want to:
l
Inherit all permissions from parent and override any definition manually made at this
level: This option reinstates inherited permissions for all users and groups that are already
defined, and new users and groups will inherit their permissions from the parent level.
l
Inherit all permissions from parent but keep definitions manually made at this level: This
option preserves the permissions already defined for the existing users and groups and adds all
permissions from the parent level. New users and groups will inherit permissions from the
parent level.
3. Click Enable.
4. Click Save or OK to accept the changes, or Discard Changes or Cancel to undo them.
To edit user permissions:
1. In the User Permissions window, adjust the permission slider for a user or group as desired.
Adjusting the slider stops inheritance from the parent object.
2. Click Save or OK to accept the changes, or Discard Changes or Cancel to undo them.
To add a user or group:
1. In the User Permissions window, click Add.
2. In the Add User/Group dialog box, select User or Group.
3. Enter the name for the new user or group in the following format:
l
NetBIOS_name\user (for example:qa\qa)
l
machine_name/local_user (for example: re2008r2js1\JohnMil1)
l
username - This format is supported with SAML authentication only. The user/group name can
contain any Unicode character up to 255 characters and must be a valid Identity Provider user
(Okta or Microsoft Azure).
4. Click OK to add the group and close the dialog box.
5. Click Save or OK to accept the changes, or Discard Changes or Cancel to undo them.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 288

11 Administration
To remove a user or group:
1. In the User Permissions window, select the user or group you want to remove.
2. Click Remove.
3. When prompted, click Yes to confirm.
4. Click Save or OK to accept the changes, or Discard Changes or Cancel to undo them.
To restore inherited permissions for a single user or group if they were overridden:
1. In the User Permissions window, select the user or group.
2.
Click Restore Inheritance .
The check mark returns to the Inherited column to indicate that permissions for this user or group are
inherited from the parent.
To view effective permissions for a user:
1. In the User Permissions window, do one of the following:
l
Select a user in the list on the left.
l
If a user does not appear in the list but exists in the system and is part of a group, enter the
user name in the text field in the Effective Permissions pane on the right.
Make sure to use the following format:
l
NetBIOS_name\user (for example: qa\qa)
l
machine_name/local_user (for example: re2008r2js1\JohnMil1)
2. Click Get Effective Permissions.
The effective permissions for the user you entered appear below the button.
Managing Personal Access Tokens
In the Personal Access Tokens tab, you can view the status of all Personal Access Tokens in the system and
revoke a user's Personal Access Token. Note that if you revoke a user's Personal Access Token, it will no
longer be possible to use the Enterprise Manager API to log in with that token.
The Personal Access Tokens tab is only visible to Enterprise Manager admins.
To revoke a user's token
1. Select the user and click Revoke.
2. When promoted to confirm the operation, click Yes.
11.3 Creating an audit trail
An audit trail provides you with information about the transactions executed in Enterprise Manager. Enterprise
Manager traces operations that require a minimum role of operator. For these operations, the audit trail
shows who did what, when, and on which objects. By default, the audit trail is enabled. Audit trail files are
located in the following folder: <Enterprise Manager installation folder>\data\AuditTrail\audit_service.
The audit trail is secure. Audit files are compressed and protected by checksum.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 289

11 Administration
Do not edit or delete the audit files. Any changes to these files might cause the system to crash.
Enterprise Manager retains audit files for two weeks or until they reach a total size of 100 MB (10 files). You can
configure these settings through the command line interface (CLI). For more information, see Configuring
Enterprise Manager using the CLI (page 293), in particular the aemctl.exe audit_trail control command.
In addition, you can manually download an audit trail file in .csv format. This file includes filtered actions for a
specific time frame or a custom time range.
Audit trail files may contain all or some of the following information, depending on whether the object exists
in Enterprise Manager:
l
Timestamp (UTC)
l
User
l
Node
l
Requested Action
l
Required Permission
l
Effective Permission
l
Security Result
l
Action Result
l
Error Message
l
Server
l
Task
l
Endpoint
l
Notification
l
Enable
l
Delete_task_logs
l
Tag
l
Schema
l
Table
l
Delete_fts_logs
l
FTS (File Transfer Service)
l
Payload
To view payload information, you can copy the link in the Payloadcolumn and paste it into the
address bar of a browser window.
For information on decoding stream payloads, see Decoding an encoded stream payload (page 291).
The REST information listed in the following table is not presented in the audit trail columns.
It is only accessible via the payload.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 290

11 Administration
REST Info Access From
puterrorbehavior payload - taskname
tablecontrol payload - taskname
test_database_async payload - endpoint name
browse_connection_async payload - endpoint name
action=test_async_complete payload - endpoint name
action=browse_connection_async payload - endpoint name
REST access points
To manually download an audit trail file:
1.
Click the Audit Trail icon in the top right corner.
2. In the Audit Trail dialog box, from the Time Range list, select a time range.
3. If you select Custom, also specify the From date and time and the To date and time.
The time you select is the local machine time. This gets converted to coordinated universal time (UTC)
in the resulting CSV file.
4. Click Generate.
The AuditTrail.csv file is created and downloaded. Depending on your browser, you should see it at the
bottom of your browser window or in a separate window.
Decoding an encoded stream payload
Some audit records (e.g. RegisterLicenses) may contain an encoded stream payload. Encoded payloads are
displayed as byte arrays and need to be decoded using Base64.
To decode an encoded stream payload:
1. Locate the payload URL in the audit record.
2. Copy the URL into your browser's address bar and press [Enter].
A byte array will be displayed.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 291

11 Administration
3. Copy the byte array into a Base64 decoder and decode it.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 292

12 Configuring Enterprise Manager using the CLI
12 Configuring Enterprise Manager using the CLI
You can use the Enterprise Manager command line interface (CLI) to modify the data directory, change the
default configuration settings, and manage the Qlik Enterprise Manager service during installation or when
configuring Enterprise Manager to run on a cluster.
All commands should be run from <PRODUCT_INSTALLATION_DIRECTORY>\bin
To get help when using the command line, you can run the Help command. For example, for help about the
parameters available with the service command, run the following command (shown with the default
installation path):
C:\Program Files\Attunity\Enterprise Manager\bin>aemctl.exe service help
This brings up the list of help parameters.
Or, for a list of the available commands, run:
aemctl.exe help
When the Enterprise Manager data directory is installed in a non-default location, the -d <data_
directory> parameter must be included in all commands, where data directory is the
location of the data directory.
Running CLIcommands requires the admin role. For more information, see User permissions (page
278).
The login authentication method is also set using the CLI. For more information, see Setting the login
authentication method (page 25).
12.1 Setting the Enterprise Manager host address
To set the host address, run the following command:
aemctl.exe configuration set --address
hostAddress
where hostAddress is the address of the Enterprise Manager server machine.
When using a Load Balancer, hostAddress should be the Load Balancer host address.
Abbreviated parameter: -a
12.2 Setting the Enterprise Manager HTTP port
To set the HTTP port, run the following command:
aemctl.exe configuration set --http_port
port
Abbreviated parameter: -p
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 293

12 Configuring Enterprise Manager using the CLI
Default: 80
12.3 Setting the Enterprise Manager HTTPS port
To set the HTTPS port, run the following command:
aemctl.exe configuration set --https_port
port
Abbreviated parameter: -s
Default: 443
12.4 Setting the Enterprise Manager root URL
To set the root URL, run the following command:
aemctl.exe configuration set --root_url
url
Abbreviated parameter: -r
12.5 Showing the Enterprise Manager version
To show the version, run the following command:
aemctl.exe configuration set --version
12.6 Showing the Enterprise Manager CLI Help
To show the Help, run the following command:
aemctl.exe configuration set --help
12.7 Service Commands
To stop the Qlik Enterprise Manager service, run the following command:
aemctl.exe service stop --name
servicename
[--timeout seconds]
Where:
servicename is the name of the Enterprise Manager service
seconds is the time to wait in seconds before stopping the service
To start the Qlik Enterprise Manager service, run the following command:
aemctl.exe service start --name
servicename
[--timeout seconds]
Where:
servicename is the name of the Enterprise Manager service
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 294

12 Configuring Enterprise Manager using the CLI
seconds is the time to wait in seconds before starting the service
To bring up a list of other service-related parameters, run the following command:
aemctl.exe service
12.8 Cleaning the self-signed certificate
To clean (i.e. clear) the self-signed certificate, run the following command:
aemctl.exe cerificate clean
12.9 Setting the audit trail retention size and age
To see the audit trail size and/or age limit, run the following command:
aemctl.exe audit_trail control [--age hours] [--size megabytes]
Where:
hours is the number of hours to retain the audit trail file. The default is 168 hours, which is one week.
megabytes is the maximum size of the audit file to retain. The default is 500 MB.
12.10 Master User Password commands
The following section describes commands that can be used to generate a Master User Password, set the
Master User Key, and change the Master User Key.
For more information on the role of the master user password and the master user key, see Replacing the
Master User Password (page 41).
Generating a random Master User Password
To generate a random master user password, run the following command:
aemctl.exe utils genpassword
Setting or changing the MUK (Master User Key)
Run this command to set the Enterprise Manager MUK (Master User Key) as part of the corporate security
policy or when configuring Enterprise Manager to work in a cluster.
For information on installing Enterprise Manager on a cluster, see Installing Qlik Enterprise Manager in a
Windows cluster (page 327)
The password must be at least 32 characters.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 295

12 Configuring Enterprise Manager using the CLI
If you add the --prompt parameter to the command and omit the -p and -c parameters, the CLI will prompt
you for the password. When you enter the password, it will be obfuscated. This is especially useful if you do
not want passwords to be retained in the command prompt history.
Syntax:
aemctl.exe [-d
data_directory
] masterukey set --prompt
To set the MUK, run the following command:
aemctl.exe [--data
data_directory
] masterukey set --password
password
Where:
--data (or -d in its abbreviated form) is used to specify the location of the Enterprise Manager data folder,
but is only required if the data folder is not on the same drive as the bin folder.
To change the MUK, run the following command:
aemctl.exe [--data
data_directory
] masterukey set --password
new_password
--current-password
old_password
Where:
--data (or -d in its abbreviated form) is used to specify the location of the Enterprise Manager data folder,
but is only required if the data folder is not on the same drive as the bin folder.
Setting or changing the Java MUK (Master User Key)
Run this command to set the Enterprise Manager MUK (Master User Key) as part of the corporate security
policy or when configuring Enterprise Manager to work in a cluster.
For information on installing Enterprise Manager on a cluster, see Installing Qlik Enterprise Manager in a
Windows cluster (page 327)
The password must be at least 32 characters.
To set the Java MUK, run the following command:
atajs.bat [--data JavaDataFolderFullPath] masterukey set
password
Where:
--data (or -d in its abbreviated form) is used to specify the location of the Enterprise Manager data folder,
but is only required if the data folder is not on the same drive as the bin folder.
To change the Java MUK, run the following command:
atajs.bat [--data JavaDataFolderFullPath] masterukey set new_password
old_password
Where:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 296

12 Configuring Enterprise Manager using the CLI
l
--data (or -d in its abbreviated form) is used to specify the location of the Enterprise Manager data
folder, but is only required if the data folder is not on the same drive as the bin folder.
l
new_password is the new password.
l
old_password is the current password.
12.11 Showing the connectivity and login settings
To show the current connectivity and login settings, run the following command:
aemctl configuration show
The output will be as shown below.
Connectivity settings
l
-a, --address - The Enterprise Manager host address.
l
-p, --http_port - The HTTP port through which Enterprise Manager is accessed.
l
-s, --https_port - The HTTPS port through which Enterprise Manager is accessed.
l
-r, --root_url - The Enterprise Manager URL root.
l
-u, --user_timeout - The user idle timeout (minutes).
l
-m, --domain - The Enterprise Manager domain name.
l
--authentication_method - FORM, SSO or SAML.
SAML settings
If SAML was configured in the past, these parameters will always be shown (even if SAML is not the
current authentication method).
l
--idp_url - The SAML IdP URL.
l
--idp_issuer - The unique identity of the SAML IdP.
l
--idp_certificate_file - A file containing the certificate from the SAML IdP.
l
--idp_username_attribute - The user name specified in the SAML assertion document.
l
--idp_user_displayname_attribute - The user display name specified in the SAML assertion
document.
l
--idp_user_groups_attribute - The group name specified in the SAML assertion document.
For information on setting up SAML and other types of authentication, see Setting the login authentication
method (page 25).
12.12 Fine tuning performance
This section describes various parameters that you can set to tweak performance.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 297

12 Configuring Enterprise Manager using the CLI
Turning off the Analytics Server
If you have configured the Analytics module and you are running multiple instances of Enterprise Manager, for
each Enterprise Manager instance there will be a corresponding Analytics Server instance. As only one
Analytics Server instance is required, you can turn off the other instances to improve performance.
To do this:
1. Run the following command:
aemctl analytics set --noserver
2. Restart the Qlik Enterprise Manager service.
To turn the Analytics Server back on:
1. Run the following command:
aemctl analytics set --runserver
2. Restart the Qlik Enterprise Manager service.
Changing the update intervals
If you are encountering performance issues due to a large number of monitored tasks or servers (Replicate or
Compose), increasing the update intervals should significantly improve performance.
Changing the server update interval
The server update interval determines how often Enterprise Manager queries all of the monitored servers for
updated statistics on tasks, views, and tags.
To change the interval, run the following command (replacing
your-interval
with the desired interval in
seconds):
aemctl manager set --server_update_interval
your-interval
Abbreviated parameter: -u
Default: 5 seconds
Changing the web console refresh interval for servers
The web console update interval for servers determines how often the browser queries Enterprise Manager in
order to refresh the associated pages.
To change the interval, run the following command (replacing
your-interval
with the desired interval in
seconds):
aemctl manager set --web_update_server_interval
your-interval
Abbreviated parameter: -s
Default: 3 seconds
Changing the web console refresh interval for tasks
The web console update interval for tasks determines how often the browser queries Enterprise Manager in
order to refresh the associated pages.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 298

12 Configuring Enterprise Manager using the CLI
To change the interval, run the following command (replacing
your-interval
with the desired interval in
seconds):
aemctl manager set --web_update_task_interval
your-interval
Abbreviated parameter: -t
Default: 5 seconds
Changing the data tree cache interval
The data tree cache interval determines how often a cache of Enterprise Manager's data is created. When set,
the web console will read from the cached copy instead of the main data tree according to the specified
interval. Usually, this parameter does not need to be changed. However, if changing the other performance
parameters does not resolve your performance issues, adjusting this parameter might help.
The minimum interval that can be set is five seconds.
To change the interval, run the following command (replacing
your-interval
with the desired interval in
seconds):
aemctl manager set --data_tree_cache_interval
your-interval
Abbreviated parameter: -c
To turn off data tree caching, set
your-interval
to
-1
Default: Off
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 299

13 Cataloging tasks in Qlik Catalog
13 Cataloging tasks in Qlik Catalog
Leveraging Qlik Catalog's powerful cataloging capabilities allows you to gain insights into your data assets
and take appropriate action. You can select any Replicate task in Enterprise Manager and catalog all of the
target table metadata.
In this section:
l
Terminology (page 300)
l
Prerequisites (page 301)
l
Setting up connectivity to Qlik Catalog (page 301)
l
Limitations and considerations (page 301)
l
Catalog operations (page 302)
13.1 Terminology
Leveraging Qlik Catalog's powerful cataloging capabilities allows you to gain insights into your data assets
and take appropriate action. You can select any Replicate task in Enterprise Manager and catalog all of the
target table metadata.
Replicate users may find some of the Qlik Catalog terminology a little confusing at first; for instance, the
Replicate target endpoint is referred to as the Source Connection in Qlik Catalog. To lessen the potential for
confusion, some of the cataloging terms used in Enterprise Manager differ from those used in Qlik Catalog.
While this may seem counter-intuitive at first, it is hoped that using terms that are appropriate within the
specific context of each application will actually create a far more intuitive user experience.
Before getting started then, it's important to understand how the cataloging and replication terminology used
in Enterprise Manager is reflected in Qlik Catalog.
The table below lists the terms in use by Enterprise Manager and the equivalent term in Qlik Catalog.
Enterprise Manager
Term
Catalog Term Enterprise Manager Default Value
N/A Source <ReplicateServer>_<TargetEndpoint>_<Schema>
Datastore Source
Connection
<ReplicateServer>_<TargetEndpoint>
Location Source
Hierarchy
Replicate.<ReplicateServer>_<ReplicateTask>
Data Asset Datasets <ReplicateServer>_<ReplicateTask>
Catalog AD Group Group <The Active Directory group defined in the Qlik Catalog
connection settings>
Column Field N/A
Table Entity N/A
Equivalent terms and values
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 300

13 Cataloging tasks in Qlik Catalog
13.2 Prerequisites
Before you begin to work with Qlik Catalog, make sure the following prerequisites have been met:
l
Replicate 7.0 or later installed in your network
l
Make a note of your Qlik Catalog access information (hostname, username, password, etc.). You will
need it to configure connectivity to the Qlik Catalog Server.
13.3 Setting up connectivity to Qlik Catalog
To catalog Replicate tasks in Qlik Catalog, Enterprise Manager needs to establish and maintain a connection
with the Qlik Catalog server.
To provide your Qlik Catalog connection details:
1. Open the Settings window and select Qlik Catalog Server Connection on the left.
2. Enter the following information:
l
Host: The host name of the Qlik Catalog server machine.
l
Port: The port over which the connection will be established. The default port is 8443.
l
User name: The user name for connecting to the Qlik Catalog server machine.
l
Password: The password for connecting to the Qlik Catalog server machine.
l
Web app name: qdc
l
URL: The URL link is created automatically from the host name, the port and the Web app
name.
l
Default catalog AD group: The Active Directory group in Qlik Catalog under which tasks will be
cataloged. This will be the default group when cataloging tasks.
3. Optionally, click Test Connection to verify your connection settings.
4. Click Save to save your setting or Discard Changes to revert to your previous settings.
Catalog columns
After you configure connectivity to a Qlik Catalog server, the following columns become visible in Tasks View.
l
Cataloged - Indicates whether or not the task is cataloged.
l
Name - The task's data asset (dataset) name in Qlik Catalog.
l
Location - The task's location in the Qlik Catalog hierarchy.
l
Datastore - The task's datastore (source connection) name in Qlik Catalog.
l
AD Group - The Active Directory group in Qlik Catalog under which the task is cataloged.
13.4 Limitations and considerations
Working with Qlik Catalog is subject to the following limitations:
l
Compose tasks are not supported.
l
Cataloging a task with a large number of source tables might take some time.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 301

13 Cataloging tasks in Qlik Catalog
l
Replicate streaming target endpoints (such as Kafka) are not supported. For a full list of streaming
endpoints, see the Replicate Support Matrix.
l
Replicate file-based target endpoints (e.g. Amazon S3) are not supported.
l
Operations performed directly in Qlik Catalog on cataloged Replicate tasks and sources will not be
synced back to Enterprise Manager. For example, if you delete a source in Qlik Catalog, the task will
still appear as cataloged in Enterprise Manager.
l
Tasks that are deleted in Enterprise Manager when a server is not being monitored will not be deleted
in Qlik Catalog when monitoring is resumed for that server. Such tasks will need to be manually
deleted in Catalog.
l
After upgrading to Enterprise Manager 7.0, existing tasks need to be stopped and then resumed in
order to be eligible for cataloging.
l
Data cannot currently be ingested from the Replicate target tables (entities) into Qlik Catalog.
13.5 Catalog operations
You can catalog, recatalog, and uncatalog tasks. This topic describes how and when such operations should
be performed.
Cataloging tasks
To catalog a task:
1. In Tasks view, select the task you want to catalog and then click the Catalog toolbar button and select
Catalog.
A window displaying the following auto-generated properties opens:
l
Data asset name in catalog: This is a combination of the Replicate server and task name. So,
for example, if the server name is RepServer and the task name is SQLtoAWS, the data asset
name will be RepServer_SQLtoAWS.
l
Catalog data asset under: By default, all data assets are cataloged under Replicate. For
example, a data asset named RepServer_SQLtoAWS would appear as Replicate.RepServer_
SQLtoAWS. You can create additional hierarchies (or sub-locations using Enterprise Manager
terminology), using dots as separators. For example, to add a top-level container called QDI to
Replicate.RepServer_SQLtoAWS, you would need to enter the following:
QDI.Replicate.RepServer_SQLtoAWS
l
Datastore in catalog: This is a combination of the Replicate server name and the target
endpoint name.
l
Catalog AD group: The name of the Active Directory Group defined in Qlik Catalog under which
the task will be cataloged.
You can edit these properties as required.
2. Click Catalog.
If the cataloging operation is successful, a confirmation will be displayed at the top of the page and a
new Catalog tab with the cataloging properties (described in step 1 above) will be added to the
monitoring dashboard in the right pane.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 302

13 Cataloging tasks in Qlik Catalog
Cataloging example
In the following example, a Replicate task has copied the following tables (shown as schema.table) from a
PostgreSQL on-premises database to a PostgreSQL in the cloud (AWS): HumanResources.Department,
HumanResources.Employee, Purchasing.ShipMethod, Purchasing.Vendor, Sales.Customer, and
Sales.Store. The customer needs to ensure the validity and integrity of these tables for the purpose of
analytics. To this end, the customer has decided to catalog the Replicate task.
After cataloging the Replicate task, the associated target tables immediately become visible in Qlik Catalog:
Clicking the Source tab shows the list of schemas to which the tables belong.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 303

13 Cataloging tasks in Qlik Catalog
For a detailed description of the tasks that can be performed within Qlik Catalog, refer to the Qlik Catalog
Help.
Uncataloging tasks
You can uncatalog a task by simply selecting the desired task, clicking the Catalog toolbar button and then
selecting Uncatalog.
When you delete a cataloged task from Enterprise Manager, the task is automatically removed from
Qlik Catalog as well.
Recataloging tasks
Recataloging task uncatalogs and then catalogs a task in a single operation. Recataloging can be used to
remedy out-of-sync situations resulting from actions performed directly in Catalog (such as deleting a source).
You can recatalog a task by simply selecting the desired task, clicking the Catalog toolbar button and then
selecting Recatalog.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 304
14 Analytics
14 Analytics
Enterprise Manager Analytics can be used to measure server and task metrics over a specific time-period.
Examples of server metrics that can measured include memory consumption and disk usage. Examples of task
metrics that can measured include the number of tables and records processed, throughput, and the number
of changes applied.
You can also filter the information according to server, source database, target database, and task type.
Analytics is currently provided for Replicate tasks only.
Analytics information is useful in the following cases:
l
Capacity Planning
l
Sizing of Replicate Servers
l
Replicate Performance Monitoring
l
Historical Trend Analysis
In this section:
l
Prerequisites (page 305)
l
Permissions (page 307)
l
Analytics dashboards (page 307)
l
Exporting to TSV (page 315)
l
Creating filters (page 315)
l
Using the Pivot Menu (page 317)
l
Analytics repository schema (page 317)
14.1 Prerequisites
This section describes the prerequisites for working with the Enterprise Manager Analytics module.
Install PostgreSQL
Enterprise ManagerAnalytics data is stored in a PostgreSQL database. Therefore, prior to using Enterprise
ManagerAnalytics, make sure that PostgreSQL 12.16 or later is installed either on the Enterprise Manager
machine or on a machine that is accessible from Enterprise Manager.
For your convenience, the PostgreSQL setup file is included with Enterprise Manager. If you would like to
install PostgreSQL on the Enterprise Manager machine and did not do so during the Enterprise Manager
installation, you can find the PostgreSQL installer in the following location:
<Enterprise_Manager_INSTALLATION_FOLDER>\postgresqlkit
For instructions on installing and maintaining PostgreSQL, refer to the PostgreSQL Help.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 305

14 Analytics
Create a dedicated database and assign the required privileges
l
Create a dedicated database and user in PostgreSQL that will own the tables accessed by the
Enterprise ManagerAnalytics module.
l
Recommended: Create a dedicated tablespace for the Enterprise Manager tables and allocate it as the
default tablespace for the Enterprise Manager database.
l
The Enterprise Manager user will need ALL PRIVILEGES on the Enterprise Manager database.
Configure connectivity to PostgreSQL
Configure connectivity to the PostgreSQL repository as described in Repository connection settings (page 272).
Set up data collection and purging from PostgreSQL
Configure data collection and purging settings as described in Analytics - Data collection and purge settings
(page 273).
Register a license
A Replication Analytics license is required in order to use Analytics. If no license is detected, a Register
License message will be displayed in the main Analytics tab.
If you have a license, you can register it by following the procedure described in Registering a license (page
277).
If you do not intend to use the Analytics feature, you can hide the main Analytics tab by clicking the
Hide Analytics Dashboards link in the Register License message.
Obtaining a license
The procedure below does not apply when installing Enterprise Manager in a High Availability
Cluster. To obtain a Replication Analytics license for Enterprise Manager in a High Availability
Cluster, you must provide your Qlik Sales Representative with the following information, depending
on which Windows version the cluster is running:
l
Windows Server 2016: The official cluster FQDN.
l
Windows Server 2012 R2: The FQDN of each of the cluster nodes and the official cluster
FQDN.
If you do not have a license, you can obtain one as follows:
1. Copy the Enterprise Manager machine name from either of the following locations:
l
The Register License message that is displayed in the main Analytics tab.
l
The bottom of the Licenses tab in the Settings window.
2. Request a license from your Qlik Sales Representative, making sure to include the Enterprise Manager
machine name in your request.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 306

14 Analytics
Port
Make sure that the PostgreSQL port (5432 by default) is open for outbound communication.
Hardware
If the PostgreSQL database is installed on the Enterprise Manager server and there are less than 1000 tasks,
then the Enterprise Manager hardware guidelines should be enough for the PostgreSQL database as well.
If you wish to install PostgreSQL on a different server, then the following minimum system requirements are
recommended:
l
8 GB RAM
l
4 CPU Cores
l
10 GB disk space database tablespace
14.2 Permissions
Analytics has its own set of permissions which are inherited from Enterprise Manager by default.
These are as follows:
l
Viewers, Operators and Designers can access the Analytics dashboards and run reports.
l
Administrators can access the Analytics dashboards and also access the Analytics settings to configure
the PostgreSQL repository, control how much data is stored in the Repository and start/stop the
Analytics processes.
14.3 Analytics dashboards
In the Analytics tab, you can review server and task trends over a specific time period. For each graph, you
can choose whether to display weekly, hourly, daily (the default), monthly, or by minute data. You can also
filter the data to show information for a particular timeframe and for particular tasks, Replicate servers,
source databases, and target databases.
Dashboards can be accessed either by selecting the desired dashboard from the drop-down list on the left of
the toolbar, or by expanding the pivot menu on the right of the Analytics tab and clicking the desired
dashboard link.
The following dashboards are available:
l
Trends
l
Trends by Server
l
Trends by Task
l
Top Servers
l
Top Tasks
l
Capacity Planning
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 307

14 Analytics
Trends
The Trends dashboard plots key performance and activity metrics for the given time frame. Below each chart,
you can toggle to view the trending data by hour, by day, by week, by month, or by minute.
For the specified filters, the Trends dashboard displays the following charts:
l
Server utilization (page 308)
l
Full load (page 308)
l
Change processing (page 308)
l
Errors (page 309)
Server utilization
The Server Utilization section contains the following graphs:
l
Memory - Shows the average and maximum memory consumption across all specified servers and
tasks.
l
Disk Utilization - Shows the average and maximum disk space utilization across all specified servers
and tasks.
l
Qlik CPU - Shows the average and maximum Qlik CPU per server (as a percentage) across all specified
servers and tasks.
l
Machine CPU - Shows the average and maximum machine CPU per server (as a percentage) across all
specified servers and tasks.
l
Task CPU - Shows the average and maximum CPU per task (as a percentage of server CPU) across all
specified servers and tasks.
Full load
The Full Load section contains the following graphs:
l
Throughput - Shows the average source and target throughput (in rec/sec) per task.
l
Tables - Shows the total number of completed, loading, queued and error tables across all specified
servers and tasks.
l
Records - Shows the total number of completed and remaining records across all specified servers and
tasks.
For the Full Load charts, the data is not aggregated and cannot be viewed by hour, by day, by week,
by month, or by minute. Rather, data is displayed for key points in time for the given time frame.
Change processing
The Change Processing section contains the following graphs:
l
Applied Changes - Shows the total number of changes applied, grouped by INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
and DDLs across all specified servers and tasks.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 308

14 Analytics
l
Throughput and Latency- Shows the average source and target throughput (in rec/sec) and the
average source and apply latency (in seconds) per task.
l
Change Volume - Shows the total COMMIT change volume across all servers and tasks.
l
Changes in Memory and Disk - Shows the average number of changes accumulated in memory and
on disk until source commit as well as the average number of changes in memory and on disk during
apply, and until target commit per task.
Errors
The graph in the Errors sections shows the total number of data errors across all specified servers and tasks,
including both Full Load and Change Processing tasks.
Trends by server
The Trends by Server dashboard plots key performance and activity metrics for the given time frame,
according to server. Trends for the top 10 servers will be displayed based on the selected Rank By metric. If
necessary, narrow your filter set to investigate a specific set of servers.
Below each chart, you can toggle to view the trending data by hour, by day, by week, by month, or by minute.
For the specified filters, the Trends by Server dashboard displays the following charts:
l
Server utilization (page 309)
l
Full load (page 309)
l
Change processing (page 309)
l
Data errors (page 310)
Server utilization
The Server Utilization section contains the following graphs:
l
Average Memory - The average memory consumed by all tasks on a server.
l
Average Disk Utilization - The average disk space utilization by all tasks on a server.
l
Average Qlik CPU - The average CPU utilization per server by Replicate and Enterprise Manager
processes only.
l
Average Machine CPU - The average CPU utilization per server by all processes (including Replicate
and Enterprise Manager processes).
l
Average Task CPU - The average CPU utilization per task (as a percentage of server CPU) for each
server.
Full load
The Full Load section contains the following graph:
l
Average Throughput - The average target throughput (in rec/sec) per task for each server
Change processing
The Change Processing section contains the following graphs:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 309

14 Analytics
l
Total Applied Changes - The total number of applied changes for all tasks on a server.
l
Average Target Throughput - The average target throughput (in rec/sec) per task for each server.
l
Average Apply Latency- The average apply latency (in seconds) per task for each server.
l
Total Change Volume - The total COMMIT change volume for all tasks on a server.
Data errors
The total number of data errors across all tasks on a server, including both Full Load and Change Processing
tasks.
Trends by tasks
The Trends by Task dashboard plots key performance and activity metrics for the given time frame,
according to task. Trends for the top 10 tasks will be displayed based on the selected Rank By metric. If
necessary, narrow your filter set to investigate a specific set of tasks.
Below each chart, you can toggle to view the trending data by hour, by day, by week, by month, or by minute.
For the specified filters, the Trends by Task dashboard displays the following charts:
l
Server utilization (page 310)
l
Full load (page 310)
l
Change processing (page 310)
l
Data errors (page 310)
Server utilization
The Server Utilization section contains the following graphs:
l
Average Memory - The average memory consumed by each task.
l
Average Disk Utilization - The average disk space utilized by each task.
l
Average Task CPU - The average CPU (as a percentage of server CPU) consumed by each task.
Full load
The Full Load section contains the following graph:
l
Average Throughput - The average target throughput (in rec/sec) for each task.
Change processing
The Change Processing section contains the following graphs:
l
Total Applied Changes - The total number of applied changes for each task.
l
Average Target Throughput - The average target throughput (in rec/sec) for each task.
l
Average Apply Latency- The average apply latency (in seconds) for each task.
l
Total Change Volume - The total COMMIT change volume for each task.
Data errors
The total number of data errors for each task, including both Full Load and Change Processing tasks.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 310

14 Analytics
Top servers
The Top Servers dashboard provides a summary of activity and performance metrics for the given time frame
and filter set. It also provides a bubble chart comparing three key metrics for your top servers together with a
corresponding data grid. You can customize the bubble chart by selecting the number of servers to view and
the three metrics to plot, including the Rank By metric, the X-Axis metric and the Y-Axis metric. The Rank By
selection in the bubble chart will also control the sorting of the data in the grid below. You can also choose
whether to rank the bubble chart data in Ascending or Descending order. The grid can be further customized
as described in Customizing task columns (page 231).
For the specified filters, the Top Servers dashboard displays the following key metrics:
l
Server utilization (page 311)
l
Full load (page 311)
l
Change processing (page 311)
Server utilization
The Server Utilization section contains the following metrics:
l
Average Memory - The average memory consumed by all tasks on a server.
l
Average Disk Utilization - The average memory consumed by all tasks on a server.
l
Average Qlik CPU - The average Qlik CPU (as a percentage) for each server.
l
Average Machine CPU - The average machine CPU (as a percentage) for each server.
l
Average Task CPU - The average CPU per task (as a percentage of server CPU) for each server.
Full load
The Full Load section contains the following metrics:
l
Total Tables: The total number of tables for all tasks on a server.
l
Total Records: The total number of records for all tasks on a server.
l
Max Load Duration: The longest duration of the load process (in seconds).
l
Average Load Duration: The average duration of the load process for all completed tasks on a server
(in seconds).
l
Average Source Throughput (rec/sec): The average source throughput (in rec/sec) per task.
l
Average Source Throughput (kb/sec): The average source throughput (in kb/sec) per task.
l
Average Target Throughput (rec/sec): The average target throughput (in rec/sec) per task.
l
Average Target Throughput (kb/sec): The average target throughput (in kb/sec) per task.
Change processing
The Change Processing section contains the following metrics:
l
Total Applied Changes: The total number of applied changes for all tasks on a server.
l
Total INSERTs: The total number of INSERTs applied.
l
Total UPDATEs: The total number of UPDATEs applied.
l
Total DELETEs: The total number of DELETEs applied.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 311

14 Analytics
l
Total DDLs: The total number of DDLs applied.
l
Total COMMIT Change Volume: The total COMMIT change volume for all tasks on a server.
l
Total COMMIT Change Records: The total number of COMMIT change records for all tasks on a server.
l
Total Applied Transactions: The total number of COMMIT transactions for all tasks on a server.
l
Average Changes in Memory (Source): The average number of changes accumulated in memory until
source commit per task.
l
Average Changes on Disk (Source): The average number of changes accumulated on disk until source
commit per task.
l
Average Changes for Apply in Memory (Target): The average number of changes in memory during
apply and until target commit per task.
l
Average Changes for Apply on Disk (Target): The average number of changes on disk during apply
and until target commit per task.
l
Average Source Throughput (rec/sec): The average source throughput (in rec/sec) per task.
l
Average Source Throughput (kb/sec): The average source throughput (in kb/sec) per task.
l
Average Target Throughput (rec/sec): The average target throughput (in rec/sec) per task.
l
Average Target Throughput (kb/sec): The average target throughput (in kb/sec) per task.
l
Average Apply Latency (secs): The average apply latency (in seconds) per task.
l
Average Source Latency (secs): The average source latency (in seconds) per task.
Top tasks
The Top Tasks dashboard provides a summary of activity and performance metrics for the given time frame
and filter set. It also provides a bubble chart comparing three key metrics for your top tasks together with a
corresponding data grid. You can customize the bubble chart by selecting the number of tasks to view and the
three metrics to plot, including the Rank By metric, the X-Axis metric and the Y-Axis metric. You can also
choose whether to rank the bubble chart data in Ascending or Descending order. The grid can be further
customized as described in Customizing task columns (page 231).
For the specified filters, the Top Tasks dashboard displays the following key metrics:
l
Server utilization (page 312)
l
Full load (page 312)
l
Change processing (page 313)
Server utilization
The Server Utilization section contains the following metrics:
l
Average Memory - The average memory consumed by a task.
l
Average Disk Utilization - The average disk space utilization by a task.
l
Average Task CPU - The average CPU (as a percentage of server CPU) consumed by each task.
Full load
The Full Load section contains the following metrics:
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 312

14 Analytics
l
Total Tables: The total number of tables for a task.
l
Total Records: The total number of records for a task.
l
Max Load Duration: The longest duration of the load process (in seconds).
l
Average Load Duration: The average duration of the load process for a completed task (in seconds).
l
Average Source Throughput (rec/sec): The average source throughput (in rec/sec) for a task.
l
Average Source Throughput (kb/sec): The average source throughput (in kb/sec) for a task.
l
Average Target Throughput (rec/sec): The average target throughput (in rec/sec) for a task.
l
Average Target Throughput (kb/sec): The average target throughput (in kb/sec) for a task.
Change processing
The Change Processing section contains the following metrics:
l
Total Applied Changes: The total number of applied changes for a task.
l
Total INSERTs: The total number of INSERTs applied.
l
Total UPDATEs: The total number of UPDATEs applied.
l
Total DELETEs: The total number of DELETEs applied.
l
Total DDLs: The total number of DDLs applied.
l
Total COMMIT Change Volume: The total COMMIT change volume for a task.
l
Total COMMIT Change Records: The total number of COMMIT change records for a task.
l
Total Applied Transactions: The total number of COMMIT transactions for a task.
l
Average Changes in Memory (Source): The average number of changes accumulated in memory until
source commit for a task.
l
Average Changes on Disk (Source): The average number of changes accumulated on disk until source
commit for a task.
l
Average Changes for Apply in Memory (Target): The average number of changes in memory during
apply and until target commit for a task.
l
Average Changes for Apply on Disk (Target): The average number of changes on disk during apply
and until target commit for a task.
l
Average Source Throughput (rec/sec): The average source throughput (in rec/sec) for a task.
l
Average Source Throughput (kb/sec): The average source throughput (in kb/sec) for a task.
l
Average Target Throughput (rec/sec): The average target throughput (in rec/sec) for a task.
l
Average Target Throughput (kb/sec): The average target throughput (in kb/sec) for a task.
l
Average Apply Latency (secs): The average apply latency (in seconds) for a task.
l
Average Source Latency (secs): The average source latency (in seconds) for a task.
Capacity planning
The Capacity Planning dashboard is meant to be run for a small number of representative servers and Change
Processing tasks to help you forecast sizing requirements. It provides an overview of key metrics related to
activity and performance as well as providing a summary of key capacity indicator metrics.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 313

14 Analytics
Charts related to Server Utilization and Change Processing Performance are also shown for the given time
frame. Below each chart, you can toggle to view the trending data by hour, by day, by week, by month, or by
minute. For the specified filters, the Capacity Planning dashboard displays the following information and
charts:
Overall activity
l
Time Frame Start and End: The start and end time for the tasks that were run.
l
Total Tasks: The total number of tasks that were run.
l
Total Tables: The total number of tables for all tasks.
l
Total INSERTs: The total number of INSERTs applied.
l
Total UPDATEs: The total number of UPDATEs applied.
l
Total DELETEs: The total number of DELETEs applied.
l
Total DDLs: The total number of DDLs applied.
l
Total Applied Changes: The total number of applied changes for all tasks.
l
Total COMMIT Change Volume: The total COMMIT change volume for all tasks.
l
Total COMMIT Change Records: The total number of COMMIT change records for all tasks.
l
Total Applied Transactions: The total number of COMMIT transactions for all tasks.
l
Applied Changes by Task: Pie chart showing the total number of applied changes by task.
l
Applied Transactions by Task: Pie chart showing the total number of COMMIT transactions by task.
l
COMMIT Change Records by Task: Pie chart showing the total number of COMMIT change records by
task.
l
COMMIT Change Volume by Task: Pie chart showing the total COMMIT change volume by task.
Overall performance
l
Average Memory: The average memory per task.
l
Average Disk Usage: The average disk space utilization per task.
l
Avg Qlik CPU - The average Qlik CPU (as a percentage) per server.
l
Avg Machine CPU - The average machine CPU (as a percentage) per server.
l
Throughput: The average, minimum and maximum target throughput (in rec/sec) per task.
l
Latency: The average, minimum and maximum apply latency (in seconds) per task.
Capacity indicators
l
Average Tables per Task: The average number of tables per task.
l
Average Applied Changes per Task: The average number of applied changes per task.
l
Average Applied Transactions per Task: The average number of COMMIT transactions per task.
l
Average Transaction Size: The average COMMIT change volume per COMMIT transaction.
l
Average Number of Changes per Transaction: The average number of applied changes per COMMIT
transaction.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 314

14 Analytics
Server utilization
l
Average Memory: The area chart shows the average memory consumed by all tasks. The lines show
the average memory for each task that was run.
l
Average Task CPU: The area chart shows the average task CPU (as a percentage). The lines show the
average CPU for each task that was run.
l
Total Applied Changes and Change Volume: The total number of applied changes as well as the total
COMMIT change volume for all tasks.
l
Average Disk Usage: The area chart shows the average disk space utilization for all tasks. The lines
show the average disk usage for each task that was run.
l
Changes in Memory and Disk: The average number of changes accumulated in memory and on disk
until source commit as well as the average number of changes in memory and on disk during apply
and until target commit per task.
Change processing performance
l
Applied Changes: The total number of applied changes for all tasks.
l
Throughput and Latency: The average source and target throughput (in rec/sec) and the average
source and apply latency (in seconds) per task.
14.4 Exporting to TSV
For each dashboard, you can export the data to a TSV file.
To export Trends, Trends by Server, Trends by Task and Capacity Planning data:
1. Click the Export to TSV button to the right of the Filters button.
The Export to TSV window opens.
2. Optionally, move the slider to change the default resolution level.
3. Select which charts to export. A separate file will be created for each of the selected charts.
4. Click Export.
Depending on your browser settings, the file will either be exported (downloaded) to your browser's
default "Downloads" location or you will be pompted to save the file to your preferred location.
To export Top Servers and Top Tasks grid data:
l
Click the Export to TSV button to the right of the Filters button.
Depending on your browser settings, the file will either be exported (downloaded) to your browser's
default "Downloads" location or you will be pompted to save the file to your preferred location.
14.5 Creating filters
You can filter the dashboards to only show data for a particular timeframe and/or for particular objects (tasks,
Replicate servers, source endpoints, and target endpoints).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 315

14 Analytics
To create a timeframe filter:
1.
Click the icon to the right of the From field and select a "from" date using the calendar
control.
OR
Enter the date manually.
2.
Specify a "from" time in the two fields to the right of the icon.
3.
Click the icon to the right of the To field and select a "to" date using the calendar control.
OR
Enter the date manually.
4.
Specify a "to" time in the two fields to the right of the icon.
5. Click the Apply toolbar button.
To create an object filter
1. Click the Filters toolbar button.
The Filters window opens.
2. From the left pane, choose one of the following object types:
l
Servers
l
Source endpoints
l
Target endpoints
l
Tasks
By default, all instances of the selected object type are shown.
3. To search for a specific object, in the Name field, enter all or part of the object name and then click
Search.
4. If you selected Source endpoints or Target endpoints, optionally filter the search results by Type as
well.
If you do not select an endpoint type, all endpoints will be shown in the Source Endpoint List/Target
Endpoint List.
5. If you selected Tasks, optionally filter the search results by Task Type and/or Status as well.
If you do not select a type, all tasks will be shown in the Task List.
6. To exclude a specific object, select the object(s) and click the Exclude button (multiple selection is
supported). The object is added to the list on the right.
7. To include a specific object, select the object(s) and click the Include button (multiple selection is
supported). The object is added to the list on the right.
8. To include or exclude all objects that match a pattern, type the pattern in the Name field and then
click the Include or Exclude button accordingly.
For example, to include all task names that start with Bus, type Bus*.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 316

14 Analytics
The pattern is added to the <Object_Name> Selection Patterns list on the right.
The patterns list can contain both include and exclude patterns.
9. Click OK to save your settings and then click Apply to apply the filter.
14.6 Using the Pivot Menu
The Pivot Menu is located on the right of the Analytics tab. You can select any item in a chart or any row from
a grid, and the pivot menu will open up allowing you to pivot, or drill, to another dashboard. When you
pivot/drill to another dashboard, the selected item(s) will be applied as filters to the selected dashboard.
14.7 Analytics repository schema
In addition to the data provided by the Enterprise Manager Analytics dashboards, organizations can also use
their own BI tools to generate reports based on the available metrics. To assist with this, the following topic
provides a description of the Analytics repository schema together with a couple of sample queries.
The Analytics repository contains the following tables:
l
aem_endpoint_type (page 317)
l
aem_meta_source_database (page 318)
l
aem_meta_target_database (page 318)
l
aem_server
l
aem_source_database
l
aem_target_database
l
aem_target_processes
l
aem_task
l
aem_task_name
l
aem_task_previous_metrics
l
aem_task_profile
l
aem_task_state
l
aem_task_stop_reason
aem_endpoint_type
The aem_endpoint_type table provides lookup information about the Replicate endpoints.
Column Data Type Description
endpoint_type_id Integer The endpoint type ID.
endpoint_type_name Character varying(1024) The endpoint type.
Available table columns
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 317

14 Analytics
aem_meta_source_database
The aem_meta_source_database table provides lookup information about the source endpoint.
Column Data Type Description
meta_source_database_id Integer The source endpoint ID.
meta_source_database_name Character varying(1024) The source endpoint name.
endpoint_type_id Integer The endpoint type ID.
Available table columns
aem_meta_target_database
The aem_meta_target_database table provides lookup information about the target endpoint.
Column Data Type Description
meta_target_database_id Integer Target Endpoint ID
meta_target_database_name Character varying(1024) Target Endpoint Name
endpoint_type_id Integer Endpoint Type ID
Available table columns
aem_server
The aem_server table provides lookup information about the Replicate server.
Column Data Type Description
server_id Integer The Replicate server ID.
server_name Character varying(1024) The Replicate server name.
Host Character varying(1024) The host name or IP address.
port Integer The Replicate port.
platform Character varying(1024) The Replicate server platform.
version Character varying(1024) The Replicate version.
Available table columns
aem_source_database
The aem_source_database table provides information about the source endpoint used in a specific task.
Column Data Type Description
task_id Integer The task run ID.
Available table columns
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 318

14 Analytics
Column Data Type Description
source_database_id Integer The source endpoint ID.
source_database_name Character varying(1024) The source endpoint name.
endpoint_type_id Integer The endpoint Type ID.
aem_target_database
The aem_target_database table provides information about the target endpoint used in a specific task.
Column Data Type Description
task_id Integer The task run ID.
target_database_id Integer The target endpoint ID.
target_database_name Character varying(1024) The target endpoint name.
endpoint_type_id Integer The target endpoint type ID.
Available table columns
aem_target_processes
The aem_target_processes table is used internally to monitor the Enterprise Manager Analytics processes
such as the Collector and the Purger.
aem_task
This is a fact table for each run or instance of a Replicate task.
Column Data Type Description
task_id Integer The task run ID.
target_database_id Integer The target endpoint ID.
target_database_name Character
varying(1024)
Target endpoint name.
endpoint_type_id Integer The endpoint type ID.
retrieval_time Timestamp
without time
zone
The time that the information about the task was retrieved.
server_id Integer The Replicate server ID.
task_name_id Integer The task name ID.
task_state_id Integer The task state ID.
task_stop_reason_id Integer The task stop Reason ID.
Available table columns
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 319

14 Analytics
Column Data Type Description
task_profile_id Integer The task profile ID.
cdc_evt_applied_
insert_count
Integer The number of INSERTs since the last retrieval time or since the
task was started.
cdc_evt_applied_
update_count
Integer The number of UPDATEs since the last retrieval time or since
the task was started.
cdc_evt_applied_
delete_count
Integer The number of DELETEs since the last retrieval time or since the
task was started.
cdc_evt_applied_ddl_
count
Integer The number of DDLs since the last retrieval time or since the
task was started.
full_load_tables_
completed_count
Integer The number of completed tables loaded to the Target at
retrieval time.
full_load_tables_
loading_count
Integer The number of tables being loaded to the target at retrieval
time.
full_load_tables_
queued_count
Integer The number of tables waiting to be loaded to the target at
retrieval time.
full_load_tables_with_
error_count
Integer The number of tables that could not be loaded to the target at
retrieval time due to an error.
full_load_total_
records_transferred
Integer The total number of records that have completed loading to the
target at retrieval time.
full_load_est_records_
count_for_all_tables
Integer The estimated number of records to be loaded to the target.
full_load_completed Integer Indicates if the Full Load has completed.
full_load_start Timestamp
without time
zone
The start time of the Full Load.
full_load_finish Timestamp
without time
zone
The finish time of the Full Load.
full_load_thrput_src_
thrput_records_count
Integer The Full Load source throughput (in rec/sec) at retrieval time.
full_load_thrput_src_
thrput_volume
Integer The Full Load source throughput (in kb/sec) at retrieval time.
full_load_thrput_trg_
thrput_records_count
Integer The Full Load target throughput (in rec/sec) at retrieval time.
full_load_thrput_trg_
thrput_volume
Integer The Full Load target throughput (in kb/sec) at retrieval time.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 320

14 Analytics
Column Data Type Description
cdc_thrput_src_thrput_
records_count
Integer The Change Processing source throughput (in rec/sec) at
retrieval time.
cdc_thrput_src_thrput_
volume
Integer The Change Processing source throughput (in kb/sec) at
retrieval time.
cdc_thrput_trg_thrput_
records_count
Integer The Change Processing target throughput (in rec/sec) at
retrieval time.
cdc_thrput_trg_thrput_
volume
Integer The Change Processing target throughput (in kb/sec) at
retrieval time
cdc_trans_read_
rollback_count
Integer The number of ROLLBACK transactions since the last retrieval
time or since the task was started.
cdc_trans_read_
records_rollback_count
Integer The number of ROLLBACK change records since the last
retrieval time or since the task was started.
cdc_trans_rollback_
change_volume
Integer The volume of ROLLBACK changes (in bytes).
cdc_trans_applied_
transactions_in_
progress_count
Integer The number of transactions in progress at retrieval time.
cdc_trans_applied_
records_in_progress_
count
Integer The number of records for all transactions in progress at
retrieval time.
cdc_trans_applied_
comitted_transaction_
count
Integer The number of transactions committed since the last retrieval
time or since the task was started.
cdc_trans_applied_
records_comitted_
count
Integer The number of records for all committed transactions since the
last retrieval time or since the task was started.
cdc_trans_applied_
volume_comitted
Integer The volume of change for all committed transactions (in bytes)
since the last retrieval time or since the task was started.
cdc_trans_read_
memory_events_count
Integer The number of changes accumulated in memory until source
commit at retrieval time.
cdc_trans_read_
swapped_events_count
Integer The number of changes accumulated on disk until source
commit at retrieval time.
cdc_trans_applied_
memory_events_count
Integer The number of changes in memory during apply and until
target commit at retrieval time
cdc_trans_applied_
swap_events_count
Integer The number of changes on disk during apply and until target
commit at retrieval time.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 321

14 Analytics
Column Data Type Description
cdc_source_latency Integer The average time gap between the original change in the
source endpoint and capturing it (in seconds) at retrieval time.
cdc_apply_latency Integer The overall latency (in seconds) at retrieval time.
memory_usage_kb Integer The memory usage for the task (in kilobytes) at retrieval time.
disk_usage_kb Integer The utilization of disk space for the task (in kilobytes) at
retrieval time.
cpu_percentage Integer The CPU consumption of the task (as a percentage of server
CPU with a value of 0-100) at retrieval time.
data_error_count Integer The total number of data errors at retrieval time for all tables
involved in a task.
task_option_full_load_
enabled
Integer Indicates if Full Load is enabled.
task_option_apply_
changes_enabled
Integer Indicates if Apply Changes is enabled.
task_option_store_
changes_enabled
Integer Indicates if Store Changes is enabled.
task_option_audit_
changes_enabled
Integer Indicates if Audit Changes is enabled.
task_option_recovery_
enabled
Integer Indicates if Recovery is enabled.
server_cpu_percentage Integer The CPU percentage being utilized by the Replicate server
process running on the server machine at retrieval time.
machine_cpu_
percentage
Integer The total CPU percentage being utilized by all processes (i.e.
not just Qlik processes) running on the server machine at
retrieval time.
tasks_cpu_percentage Integer The total CPU percentage being utilized by all Replicate task
processes running on the server machine at retrieval time.
aem_task_name
The aem_task_name table provides lookup information about the task name.
Column Data Type Description
server_id Integer The Replicate server ID.
task_name_id Integer The task name ID.
task_name Character varying(1024) The task name.
Available table columns
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 322

14 Analytics
aem_task_previous_metrics
Used internally to calculate differences between the current run of a task and the previous run.
aem_task_profile
The aem_task_profile table provides lookup information about the task profile.
Column Data Type Description
task_profile_id Integer The task profile ID.
name Character varying(1024) The task profile name.
description Character varying(1024) The task profile description.
Available table columns
aem_task_state
The aem_task_state table provides lookup information about the task state.
Column Data Type Description
task_state_id Integer The task state ID.
name Character varying(1024) The task state dame.
description Character varying(1024) The task state description.
Available table columns
aem_task_stop_reason
The aem_task_stop_reason table provides lookup information about the reason that a task stopped.
Column Data Type Description
task_stop_reason_id Integer The stop reason ID.
name Character varying(1024) The stop reason name.
description Character varying(1024) The stop reason description.
Available table columns
Sample Queries
The following sample queries demonstrate how useful information can be extracted from the schema.
Query 1:
Provides a sampling of Full Load and Change Processing metrics for all tasks with a source endpoint named
"Teradata DB" for the month of August 2017.
SELECT
AEM_SERVER.SERVER_NAME AS "Server"
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 323

14 Analytics
,AEM_TASK_NAME.TASK_NAME AS "Task"
,AVG(AEM_TASK.MEMORY_USAGE_KB / 1024::float) AS "Avg Memory"
,AVG(AEM_TASK.DISK_USAGE_KB) / 1024::float AS "Avg IO"
,MAX((CASE WHEN AEM_TASK.FULL_LOAD_TABLES_COMPLETED_COUNT IS NULL THEN 0
ELSE AEM_TASK.FULL_LOAD_TABLES_COMPLETED_COUNT END)+(CASE WHEN AEM_TASK.FULL_
LOAD_TABLES_LOADING_COUNT IS NULL THEN 0 ELSE AEM_TASK.FULL_LOAD_TABLES_
LOADING_COUNT END)+(CASE WHEN AEM_TASK.FULL_LOAD_TABLES_QUEUED_COUNT IS NULL
THEN 0 ELSE AEM_TASK.FULL_LOAD_TABLES_QUEUED_COUNT END)+(CASE WHEN AEM_
TASK.FULL_LOAD_TABLES_WITH_ERROR_COUNT IS NULL THEN 0 ELSE AEM_TASK.FULL_
LOAD_TABLES_WITH_ERROR_COUNT END)) AS "Full Load Total Tables"
,MAX(FULL_LOAD_TOTAL_RECORDS_TRANSFERRED) AS "Full Load Total Records"
,MAX(AEM_TASK.FULL_LOAD_FINISH-AEM_TASK.FULL_LOAD_START) AS "Full Load Max
Load Duration"
,AVG(AEM_TASK.FULL_LOAD_FINISH-AEM_TASK.FULL_LOAD_START) AS "Full Load Avg
Load Duration"
,AVG((CASE WHEN AEM_TASK.FULL_LOAD_THRPUT_TRG_THRPUT_RECORDS_COUNT IS NULL
THEN 0 ELSE AEM_TASK.FULL_LOAD_THRPUT_TRG_THRPUT_RECORDS_COUNT END)) AS "Full
Load Avg Target Throughput Records per Second"
,SUM((CASE WHEN AEM_TASK.CDC_EVT_APPLIED_INSERT_COUNT IS NULL THEN 0 ELSE
AEM_TASK.CDC_EVT_APPLIED_INSERT_COUNT END)+(CASE WHEN AEM_TASK.CDC_EVT_
APPLIED_UPDATE_COUNT IS NULL THEN 0 ELSE AEM_TASK.CDC_EVT_APPLIED_UPDATE_
COUNT END)+(CASE WHEN AEM_TASK.CDC_EVT_APPLIED_DELETE_COUNT IS NULL THEN 0
ELSE AEM_TASK.CDC_EVT_APPLIED_DELETE_COUNT END)+(CASE WHEN AEM_TASK.CDC_EVT_
APPLIED_DDL_COUNT IS NULL THEN 0 ELSE AEM_TASK.CDC_EVT_APPLIED_DDL_COUNT
END)) AS "CDC Total Applied Changes"
,SUM((CASE WHEN AEM_TASK.CDC_TRANS_APPLIED_COMITTED_TRANSACTION_COUNT IS
NULL THEN 0 ELSE AEM_TASK.CDC_TRANS_APPLIED_COMITTED_TRANSACTION_COUNT END))
AS "CDC Total Applied Transactions"
,AVG((CASE WHEN AEM_TASK.CDC_THRPUT_TRG_THRPUT_RECORDS_COUNT IS NULL THEN 0
ELSE AEM_TASK.CDC_THRPUT_TRG_THRPUT_RECORDS_COUNT END)) AS "CDC Avg Target
Throughput Records per Second"
,AVG((CASE WHEN AEM_TASK.CDC_APPLY_LATENCY IS NULL THEN 0 ELSE AEM_
TASK.CDC_APPLY_LATENCY END)) AS "CDC Avg Apply Latency"
FROM
AEM_TASK
INNER JOIN AEM_SERVER ON (AEM_TASK.SERVER_ID = AEM_SERVER.SERVER_ID)
INNER JOIN AEM_TASK_NAME ON (AEM_TASK.TASK_NAME_ID = AEM_TASK_NAME.TASK_
NAME_ID)
INNER JOIN AEM_SOURCE_DATABASE ON (AEM_TASK.ID = AEM_SOURCE_DATABASE.TASK_
ID)
WHERE
(AEM_TASK.RETRIEVAL_TIME >= TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE '2017-08-01
00:00:00.00000+00')
AND (AEM_TASK.RETRIEVAL_TIME < TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE '2017-09-01
00:00:00.00000+00')
AND (AEM_SOURCE_DATABASE.SOURCE_DATABASE_NAME = 'Teradata DB')
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 324

14 Analytics
GROUP BY
AEM_SERVER.SERVER_NAME
,AEM_TASK_NAME.TASK_NAME
Query 2:
Provides a trend throughout the day of the number of Completed, Queued, Loading and Error tables related to
Full Load for the month of August 2017 and for a Replicate server named "rep-server1-prod".
SELECT
SUM((CASE WHEN AEM_TASK.FULL_LOAD_TABLES_COMPLETED_COUNT IS NULL THEN 0
ELSE AEM_TASK.FULL_LOAD_TABLES_COMPLETED_COUNT END)) AS "Full Load Tables
Completed"
,SUM((CASE WHEN AEM_TASK.FULL_LOAD_TABLES_LOADING_COUNT IS NULL THEN 0 ELSE
AEM_TASK.FULL_LOAD_TABLES_LOADING_COUNT END)) AS "Full Load Tables Loading"
,SUM((CASE WHEN AEM_TASK.FULL_LOAD_TABLES_QUEUED_COUNT IS NULL THEN 0 ELSE
AEM_TASK.FULL_LOAD_TABLES_QUEUED_COUNT END)) AS "Full Load Tables Queued"
,SUM((CASE WHEN AEM_TASK.FULL_LOAD_TABLES_WITH_ERROR_COUNT IS NULL THEN 0
ELSE AEM_TASK.FULL_LOAD_TABLES_WITH_ERROR_COUNT END)) AS "Full Load Tables
Error"
,AEM_TASK.RETRIEVAL_TIME AS "Date and Time"
FROM
AEM_TASK
INNER JOIN AEM_SERVER ON (AEM_TASK.SERVER_ID = AEM_SERVER.SERVER_ID)
WHERE
(AEM_TASK.RETRIEVAL_TIME >= TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE '2017-08-01
00:00:00.00000+00')
AND (AEM_TASK.RETRIEVAL_TIME < TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE '2017-09-01
00:00:00.00000+00')
AND (AEM_SERVER.SERVER_NAME IN ('rep-server1-prod'))
GROUP BY
AEM_TASK.RETRIEVAL_TIME
ORDER BY
"Date and Time" ASC
Query 3:
Provides an daily trend of Average Throughput and Latency metrics related to Change Processing for the
month of August 2017 and for a Replicate server named "rep-server1-prod".
SELECT
AVG((CASE WHEN AEM_TASK.CDC_THRPUT_SRC_THRPUT_RECORDS_COUNT IS NULL THEN 0
ELSE AEM_TASK.CDC_THRPUT_SRC_THRPUT_RECORDS_COUNT END)) AS "CDC Avg Source
Throughput Records"
,AVG((CASE WHEN AEM_TASK.CDC_THRPUT_TRG_THRPUT_RECORDS_COUNT IS NULL THEN 0
ELSE AEM_TASK.CDC_THRPUT_TRG_THRPUT_RECORDS_COUNT END)) AS "CDC Avg Target
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 325

14 Analytics
Throughput Records"
,AVG((CASE WHEN AEM_TASK.CDC_SOURCE_LATENCY IS NULL THEN 0 ELSE AEM_
TASK.CDC_SOURCE_LATENCY END)) AS "CDC Avg Source Latency"
,AVG((CASE WHEN AEM_TASK.CDC_APPLY_LATENCY IS NULL THEN 0 ELSE AEM_
TASK.CDC_APPLY_LATENCY END)) AS "CDC Avg Apply Latency"
,EXTRACT(YEAR from AEM_TASK.RETRIEVAL_TIME) AS "Year"
,EXTRACT(MONTH from AEM_TASK.RETRIEVAL_TIME) AS "Month"
,EXTRACT(DAY from AEM_TASK.RETRIEVAL_TIME) AS "Day"
FROM
AEM_TASK
INNER JOIN AEM_SERVER ON (AEM_TASK.SERVER_ID = AEM_SERVER.SERVER_ID)
WHERE
(AEM_TASK.RETRIEVAL_TIME >= TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE '2017-08-01
00:00:00.00000+00')
AND (AEM_TASK.RETRIEVAL_TIME < TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE '2017-09-01
00:00:00.00000+00')
AND (AEM_SERVER.SERVER_NAME IN ('rep-server1-prod'))
GROUP BY
EXTRACT(YEAR from AEM_TASK.RETRIEVAL_TIME)
,EXTRACT(MONTH from AEM_TASK.RETRIEVAL_TIME)
,EXTRACT(DAY from AEM_TASK.RETRIEVAL_TIME)
ORDER BY
"Year", "Month", "Day"
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 326

A Setting up High Availability
A Setting up High Availability
This section describes how to set up Enterprise Manager in a Windows High Availability Cluster.
l
When the Enterprise Manager data directory is installed in a non-default location, the -d
<data_directory> parameter must be included in all commands, where data
directory is the location of the data directory.
l
To obtain a Replication Management license for Enterprise Manager in a High Availability
Cluster, you must provide your Qlik Sales Representative with the official cluster FQDN.
l
Throughout this chapter "Node 1" and "Node 2" are used to refer to the primary and
secondary clustering nodes respectively.
When building failover cluster solutions with Replicate using Windows Server Failover Cluster (WSFC)
or a Linux failover cluster software, Qlik recommends using a block device (physical, virtual or iSCSI-
based) for the shared Replicate DATA folder. Using NFS or SMB-based storage is not supported due
to the associated latency which could greatly degrade the data transfer performance, as well as due
to reduced reliability and compatibility issues. When building a cloud-based high availability
solution that needs to span different availability zones, it is recommended to use a Storage-as-a-
Service solution that can handle the block-level replication of the storage and that is integrated with
the chosen failover clustering software.
In this section:
l
Installing Qlik Enterprise Manager in a Windows cluster (page 327)
l
Upgrading Qlik Enterprise Manager in a Windows cluster (page 330)
l
Uninstalling Qlik Enterprise Manager from a Windows cluster (page 332)
A.1 Installing Qlik Enterprise Manager in a Windows cluster
This topic explains how to install Enterprise Manager in a Windows cluster.
l
For information on obtaining a license for Enterprise Manager in a Windows cluster, see Replication
Management license (page 17).
l
For information on upgrading and uninstalling Enterprise Manager in/from a Windows cluster, see
Upgrading Qlik Enterprise Manager in a Windows cluster (page 330) and Uninstalling Qlik Enterprise
Manager from a Windows cluster (page 332) respectively.
l
For more information on the Master User Key commands mentioned in this section, see Replacing the
Master User Password (page 41) and Configuring Enterprise Manager using the CLI (page 293).
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 327

A Setting up High Availability
Unless specified otherwise, all commands should be run from the Enterprise Manager bin folder. The
default location is:
C:\Program Files\Attunity\Enterprise Manager\bin
To install Enterprise Manager in a Windows cluster:
1. Open Failover Cluster Manager and connect to a network that contains the cluster nodes and a
clustered disk (for the Enterprise Manager "data" folder).
2. Install Enterprise Manager on Node 1. This node should be the Cluster Disk owner. You can specify any
Destination Location, but the "data" folder must be installed on a clustered disk (i.e. a disk that is
accessible to the other cluster node).
The "data" folder contains a "java" subfolder. At various points in the cluster setup, you will
need to specify the location of both the "data" folder and the "java" folder. It is therefore
recommended to make a note of the "data" folder location.
3. Set the Enterprise Manager Master User Key by opening a command prompt and running the following
command:
aemctl.exe -d data_folder_path masterukey set -p password
where -d data_folder_path is the path to the shared Enterprise Manager data folder.
4. Set the Java Master User Key by opening a command prompt and running the following command
from the Java bin folder (<INSTALL_DIR>\Enterprise Manager\java\bin by default):
atajs.bat -d java_data_folder_path masterukey set password
where -d java_data_folder_path is the path to the shared Enterprise Manager data\java folder.
5. On Node 1, open the Windows Services console and stop the Enterprise Manager service.
6. Move the shared Cluster Disk to Node 2.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 328

A Setting up High Availability
7. Install Enterprise Manager on Node 2. The Destination Location can be any local folder, but make sure
to install the "data" folder on the same clustered disk specified in step 2 above.
8. Make sure the Enterprise Manager service is stopped on Node 2.
9. Set the Enterprise Manager Master User Key by opening a command prompt and running the following
command:
aemctl.exe -d data_folder_path masterukey set -p password
where -d data_folder_path is the path to the shared Enterprise Manager data folder.
10. Set the Java Master User Key by opening a command prompt and running the following command
from the Java bin folder (<INSTALL_DIR>\Enterprise Manager\java\bin by default):
atajs.bat -d java_data_folder_path masterukey set password
where -d java_data_folder_path is the path to the shared Enterprise Manager data\java folder.
11. Configure the Enterprise Manager cluster role as follows:
a. Right click on Roles and select Configure Role.
b. In the Select Role: Choose "Generic Service" and then click Next.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 329

A Setting up High Availability
c. In the Select Service screen, choose "Enterprise Manager". Click Next.
d. In the Client Access Point screen, enter the Enterprise Manager host name without the domain
information (e.g. mycompany and not mycompany.qa.int). Click Next.
e. In the Select Storage, select the location on the clustered disk where the Enterprise Manager
"data" folder was installed. Click Next.
f. Continue clicking Next until the Finish button is displayed and then click Finish.
12. Configure the host name by opening a command prompt and running the following command:
aemctl.exe -d data_folder_path configuration set -a host_name
where -d data_folder_path is the path to the shared Enterprise Manager data folder.
The host name must be specified as a FQDN (e.g.
mycompany.qa.int
and not
mycompany
)
13. Enterprise Manager Cluster Role Dependencies: Verify that the Enterprise Manager cluster role has
set dependency on the clustered disk and the Enterprise Manager service. You can view the
dependencies in the role properties.
Your Enterprise Manager cluster should now be ready for use.
A.2 Upgrading Qlik Enterprise Manager in a Windows cluster
This topic explains how to upgrade Enterprise Manager in a Windows cluster.
To upgrade Enterprise Manager in a Windows cluster:
1. Open Failover Cluster Manager on the active cluster node.
2. Stop the Enterprise Manager service on both nodes.
3. Verify that the Enterprise Manager Cluster Role status is "Failed".
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 330

A Setting up High Availability
4. Run the upgrade on Node 1.
5. Move the Enterprise Manager Role to Node 2.
6. Stop the Enterprise Manager service on both nodes.
7. Verify that the Enterprise Manager Cluster Role status is "Failed".
8. Run the upgrade on Node 2.
9. Start the Enterprise Manager Cluster Role.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 331

A Setting up High Availability
The upgrade should now be complete.
A.3 Uninstalling Qlik Enterprise Manager from a Windows
cluster
This topic explains how to uninstall Enterprise Manager from a Windows cluster.
To uninstall Enterprise Manager from a Windows cluster:
1. Open Failover Cluster Manager on the active cluster node.
2. On each of the cluster nodes, open the Windows Services console and stop the Enterprise Manager
service.
3. Verify in Failover Cluster Manager that the status of the Enterprise Manager cluster role is "Failed".
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 332

A Setting up High Availability
4. Go to Node 1 that should be owner to Enterprise Manager Cluster Role and Cluster Disk. Uninstall the
service.
5. Move the Enterprise Manager Role to Node 2.
6. Uninstall Enterprise Manager on Node 2.
7. Remove the Enterprise Manager Cluster Role.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 333

A Setting up High Availability
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 334

B Impact of DST change on Qlik Replicate
B Impact of DST change on Qlik Replicate
This topic describes the impact of Daylight Saving Time (DST) on Qlik Replicate and provides guidelines for
handling changes brought about by DST.
Tasks that move from Full Load to Change Processing when DST comes into effect may encounter data loss.
However, such data loss can be prevented by adhering to the guidelines outlined in this appendix.
Additionally, the times displayed in the Replicate Console may not be synced with the server. Should you
encounter any time discrepancy issues, either restart the Qlik Replicate Server service or stop and resume the
tasks.
There are two types of DST changes:
l
DST On - Occurs approximately when Summer starts (actual date is country specific). Its impact on
local time is that local time is moved one hour forward (so, for example, 01:00 AM becomes 02:00 AM).
This DST change does not impact Qlik Replicate because it does not result in time overlap.
l
DST Off - Occurs approximately when Winter starts (actual date is country specific). Its impact on local
time is that local time is moved back one hour (so, for example, 02:00 AM becomes 01:00 AM). This DST
change results in time overlap where local time travels over the same hour twice in a row.
The comments below assume that the customer has not changed the time but rather the timezone or the DST
setting. Changing the actual time (not for minor time adjustments) is a sensitive operation and is best done
when Qlik Replicate is stopped.
Running Qlik Replicate tasks do not depend on the timezone or DST for correctly scanning and processing the
transaction logs. Internally, Qlik Replicate timers use UTC.
Still, there are several places where DST may have an effect:
1. Timestamps in logs and audit messages are in local time. As a result, when Winter time starts, the logs
will show the time going back an hour; conversely, when Summer time starts, the logs may appear to
be missing one hour.
2. Scheduled jobs as well as the global and table manipulation variables timestamp and commit_
timestamp use local time so these will also be affected. The impact of this depends on the
manipulation done and on the intended use of the timestamp based data.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 335

B Impact of DST change on Qlik Replicate
To prevent timestamp and scheduling anomalies resulting from DST starting or ending, the
following best practices should be observed:
l
DST Off (summer to winter): Do not schedule a task to start from the time the clock
changes until the following hour. For example, if DST ends at 02:00 am, do not
schedule a task to run between 02:00 and 02:59, as the task will run twice.
l
DST On (winter to summer): Do not schedule a task to start from the time the clock
changes until the following hour. For example, if DST starts at 02:00 am, do not
schedule a task to run between 02:00 and 02:59 as this hour does not exist.
l
The initial Full Load of tables or reloading of tables should not be done during the
DST change window. It is recommended to perform such operations either an hour
before or an hour after DST.
If you have existing jobs scheduled to start at the overlap time and you do not want to
modify them, then you need to stop the Qlik Replicate Server. Going in to Winter time, for
example, if at 02:00 AM the clock is to be set back to 01:00 AM then when the time is 00:55 AM
the Qlik Replicate Server should be stopped and, after an hour and ten minutes (at 01:05 AM),
should be started again.
If you forget to do this, all scheduled jobs will run an hour earlier than intended. You can
rectify this by setting the desired scheduling time and then restarting the Qlik Replicate
Server service.
3. Statistics shown on the console are also sensitive to local time and thus may also show
confusing/inaccurate data in the overlap period (going in to Winter time) or for the skipped period
(going into Summer time).
4. If the clock on Qlik Replicate Server machine is one hour behind the clock on the Qlik Replicate
Console (UI) machine, the following issues are known to occur:
l
The Applied Changes circle graph will be updated as the changes are applied, but the
information in the Recent Activity tab will not be updated.
l
Scheduled jobs will start according to the Qlik Replicate Server time (as expected), but will
remain in the Active Jobs list after execution instead of moving to the Expired Jobs tab.
For more information on scheduling jobs, see Scheduling jobs (page 247).
In general, it is recommended to avoid non-critical task design changes during the first overlap period (going
in to Winter time) so as to prevent confusion about when the changes took place.
In addition to Qlik Replicate, other components are also involved including:
l
The source endpoint system
l
The target endpoint system
l
The local operating system
l
The task design (specifically using timestamp based variables)
Given the complexity of the topic and the involvement of many independent components and settings, Qlik
generally recommends that customers first verify the impact of DST changes in their test environment.
Setup and User Guide - Enterprise Manager, May 2023 336

