
Assessment Report
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 1
CERTIFICATION
Project Number:
23/039
Education Institution:
Coursera Inc.
Courses:
Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate
Google Digital Marketing and E-
Commerce Professional Certifica
Google IT Support Professional Certificate
Google IT Automation with Python Professional Certificate
Google Project Management Professional Certificate
Google UX Design Professional Certificate
To whom it may concern
All information in this report was provided by Coursera and assessed by the FIBAA expert panel.
However, some of the information had to be redacted for one of the following reasons
• Material/information prohibited from disclosing as a public company under U.S.
securities laws
• Proprietary information about internal processes not publicly known
• Level of detail that Coursera generally does not share with the public (e.g. expressly
naming internal tools to support compliance processes). Please see
https://www.coursera.org/about/privacy for relevant public information
• Confidential personal information
For information about redactions, please contact: PR@coursera.org

Assessment Report
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 2
Decision of the FIBAA Accreditation and
Certification Committee
11th Meeting on 20 September 2023
CERTIFICATION
Project Number:
23/039
Education Institution:
Coursera Inc.
Courses:
Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate
Google Digital Marketing and E-Commerce Professional Certificate
Google IT Support Professional Certificate
Google IT Automation with Python Professional Certificate
Google Project Management Professional Certificate
Google UX Design Professional Certificate
The FIBAA Accreditation and Certification Committee has taken the following decision:
Certification with conditions:
According to § 7 (2) in conjunction with § 10 (1) of the “Special Conditions for awarding the FIBAA
Quality Seal for Continuing Education Courses”, the continuing education course(s) are certified
with three conditions.
Period of Certification: September 20, 2023 - September 19, 2028
The FIBAA Quality Seal is awarded.
Condition 1
Coursera and Google provide a deduction of the intended EQF levels of each of the
respective courses.
Condition 2
For each of the six courses, Coursera and Google implement a learners’ workload evaluation
system which includes a systematic control loop from the survey to the analysis of the
results and the taking of appropriate measures.
Condition 3
Coursera and Google ensure correct documentation about the ECTS credit awarding and
recognition on the homepage, in the program descriptions and in the certificates issued
after certification, considering ECTS credit recognition obligations by HEIs, EQF levels
assigned, number of credits awarded, requirements for awarding credits and workload
assigned to the courses.
Proof of meeting these conditions is to be supplied by June 19, 2024.
The FIBAA Quality Seal is awarded.

Assessment Report
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 3
FOUNDATION FOR INTERNATIONAL
BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION ACCREDITATION
Assessment Report
Institution:
Coursera Inc.
Content partner: Google
Continuing Education Course:
● Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate
● Google Digital Marketing and E-Commerce Professional Certificate
● Google IT Support Professional Certificate
● Google IT Automation with Python Professional Certificate
● Google Project Management Professional Certificate
● Google UX Design Professional Certificate

Assessment Report
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 4
Brief description of the continuing education courses:
Coursera Inc.
1
hosts a portfolio of “Professional Certificates” from Google, IBM, Intuit, Meta,
Salesforce, and other industry leaders as MOOCs (Massive open online courses). The Professional
Certificates are issued after completing the respective online course which is designed to help
develop the skills needed to land entry-level digital jobs in business, IT, data science, and design.
Google Professional Certificate Courses
2
belong to this portfolio of Professional Certificates and
are targeted towards individuals worldwide who seek to reskill with Professional Certificates to
move into emerging digital careers. All six Google Professional Certificate Courses of this
certification process comprise a workload of approximately 110 to 230 hours, thus also
representing “microcredentials” as small learning entities. With FIBAA certification, Coursera
proposes ECTS crediting recommendation following the “Recognition of prior learning“ as outlined
in the ECTS Users’ Guide
3
.
All Google Professional Certificate Courses are based on a methodological approach provided by
Coursera and a content conceived, produced, and instructed by Google.
Date of opening of the procedure:
February 2, 2023
Date of filing the self-assessment report:
May 31, 2023
Date of online assessment conference:
July 25-27, 2023
Type of certification:
Certification
Mode of study:
Online, Part-time
Initial start of the Courses:
● Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate: March 2021
● Google Digital Marketing and E-Commerce Professional Certificate: April 2022
● Google IT Support Professional Certificate: January 2018
● Google IT Automation with Python Professional Certificate: January 2020
● Google Project Management Professional Certificate: March 2021
● Google UX Design Professional Certificate: March 2021
Start of course cycle: continuous
Capacity load: not limited
1
Referred to as “Coursera” in this report (except for summary chapter)
2
Referred to as “programs” by Coursera, for terminology see glossary at the end of this report.
3
ECTS Users’ guide 2015, page 46

Assessment Report
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 5
Learner intake by April 2023:
● Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate: 1,526,115 learners
● Google Digital Marketing and E-Commerce Professional Certificate: 330,954 learners
● Google IT Support Professional Certificate: 1,241,033 learners
● Google IT Automation with Python Professional Certificate: 565,027 learners
● Google Project Management Professional Certificate: 1,056,760 learners
● Google UX Design Professional Certificate: 769,380 learners
No. of ECTS credits assigned to the Course:
● Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate: seven ECTS credits
● Google Digital Marketing and E-Commerce Professional Certificate: seven ECTS credits
● Google IT Support Professional Certificate: five ECTS credits
● Google IT Automation with Python Professional Certificate: five ECTS credits
● Google Project Management Professional Certificate: six ECTS credits
● Google UX Design Professional Certificate: nine ECTS credits
Hours (workload) per credit:
25
Date of the Meeting of FIBAA-Certification Commission:
September 20, 2023
Resolution:
Certification under conditions: Panel recommendation: The certification of the course is subject to
three conditions and is valid for five years.
Duration of Certification:
September 20, 2023 – September 19, 2028
Project Manager:
Michael Stephan
Panel Members
4
:
Alina Bülbül
University of Applied Science Munich, Germany
Student of Entrepreneurship and Digital Transformation (M.A.); (graduated: Technische Redaktion
und Kommunikation (B.Eng.))
Prof. Dr.-Ing.Ronald Glasberg
SRH Berlin University of Applied Sciences, Germany
4
The panel is presented in alphabetical order.

Assessment Report
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 6
Professor of International Strategic Management (Business Administration, General Management,
Innovation Management, Computer Science and Strategic Management, International
Management, Entrepreneurship, Digital Business)
Ilja Kogan
Wayfair GmbH, Berlin, Germany
Senior Product Manager (Global Operations, e-Commerce, Project Management, Business
Administration, Economics, Business Informatics, Logistics, Digital Management, Trade
Management, IT and digital Analytics, Big Data, Agile)
Prof. Dr. Wolfgang Renninger
Ostbayerische Technische Hochschule Amberg-Weiden, University of Applied Sciences, Germany
Professor of Organization and Business Informatics
(Business Process Management, Performance Management, Quality Assurance in IT, Business
Informatics, IT & Business Value, Organizational Impacts of Information Technology, Business
Intelligence Systems, IT-supported Teaching)

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 7
List of Tables
Table 1: Entry-level Professional Certificates at Coursera 10
Table 2: Entry-level Professional Certificates: Pathways to digital jobs 11
Table 3: SWOT analysis of Professional Certificates 19
Table 4: Courseraʼs lifelong learning ecosystem 21
Table 5: Entry-Level Professional Certificate Content Specifications 27
Table 6: Credly Sample page 30
Table 7: Sample weekly plan 32
Table 8: Workload calculation and intended ECTS credit assignment 33
Table 9: Google Professional Certificates: Course contents and learning hours 35
Table 10: Coursera Pedagogy Principles 47
Table 11: Google Professional Certificates instructors’ qualifications 49
Table 12: Coursera Professional Certificate Career Resources 55
Table 13: Coursera Quality Assurance System 66
Table 14: Screenshot – Item level feedback 72
Table 15: Screenshot – Course level feedback 73
Table 16: Screenshot – Feedback to the teaching staff 73
Table 17: Course level completion feedback 74

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 8
Summary
The panels’ assessment takes into account the self-assessment and the results of the online
assessment conference as well as the statement of Coursera Inc. to the assessment report dated
September 7, 2023.
Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate; Google Digital Marketing and E-Commerce
Professional Certificate; Google IT Support Professional Certificate; Google IT Automation with
Python Professional Certificate; Google Project Management Professional Certificate; and Google
UX Design Professional Certificate of Coursera Inc. fulfil (with three exceptions) the FIBAA quality
requirements for certified continuing education courses and can be certified by the Foundation for
International Business Administration Accreditation (FIBAA) under three conditions. They may be
recognized as modules within further educational programs and have assigned ECTS credits.
The panel members identify need for action regarding the following aspects: Logic and
transparency of course objectives (see chapter 1.1); Structure (see chapter 3.1) and
Documentation (see chapter 5). Therefore, they recommend the credit recommendation on
condition of meeting the following requirements:
Condition 1 (see chapter 1.1)
Coursera and Google provide a deduction of the intended EQF levels of each of the
respective courses.
Condition 2 (see chapter 3.1)
For each of the six courses, Coursera and Google implement a learners’ workload evaluation
system which includes a systematic control loop from the survey to the analysis of the
results and the taking of appropriate measures.
Condition 3 (see chapter 5)
Coursera and Google ensure correct documentation about the ECTS credit awarding and
recognition on the homepage, in the program descriptions and in the certificates issued
after certification, considering ECTS credit recognition obligations by HEIs, EQF levels
assigned, number of credits awarded, requirements for awarding credits and workload
assigned to the courses.
Proof of meeting these conditions is to be documented by June 19, 2024.
The panel members also identified several areas where the courses could be further developed:
● summarizing the information defined in the ECTS Users’ Guide in one publicly accessible
sheet or course description, the classification of learning objectives in taxonomy levels,
listing recommended literature and communicating to learners and completers that the
combination of the Professional Certificate in combination with proof of relevant
professional experience may also facilitate recognition of ECTS credits. (see chapter 3.1),
● re-evaluating the communication of international and intercultural aspects in the course
descriptions (see chapter 3.2),

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 9
● serving learners’ and completers aspirations by not only listing recommended literature
(see recommendation chapter 3.1), but additionally providing a guided process into the
work with further literature (see chapter 3.2),
● considering enriching the concept of the asynchronous MOOCs by options of synchronous
teaching formats, like live lectures or real-time interactive formats (see chapter 3.4),
● systemizing access to subject-specific databases (see chapter 4.5.),
● communicating current Learner Outcome Reports on the website (see chapter 6).
The measures Coursera and Google take in order to implement the recommendations of the panel
members are to be considered in the context of the re-certification.
On the other hand, there are several criteria that exceed the quality requirements:
● Positioning of the courses in the education and job market, and the professional field (see
chapter 1.3),
● Logic and conceptual coherence of the content (see chapter 3.2),
● Logic and transparency of teaching and learning methodology (see chapter 3.4),
● Internal cooperation (see chapter 4.1),
● Process organization and administrative support for learners and teaching staff (see
chapter 4.2),
Furthermore, there are two criteria which the panel team rates as “exceptional”:
● Skills for employment/Employability (see chapter 3.5),
● Practical experience of the teaching staff (see chapter 4.1),
For the overall assessment please refer to the quality profile at the end of this report.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 10
Details on the institution
Launched in 2012 by two Stanford professors, Andrew Ng, and Daphne Koller, Coursera´s mission
is to provide universal access to world-class learning. Coursera is now one of the largest online
learning platforms, with 118 million registered learners, partnering with over 300 university and
industry partners to offer a broad catalog of content and credentials, including courses,
Specializations, Professional Certificates, Guided Projects, and bachelorʼs and masterʼs degrees.
Institutions worldwide use Coursera to upskill and reskill their employees, citizens, and students
in data science, technology, and business. Coursera became a B Corp
5
in February 2021.
Coursera operates in five essential business units within two models:
1) Coursera for Individual learners
a. Degrees
b. Open Content (Professional Certificates, Specializations & Courses by university and
Industry Partners)
2) Business to Business (Coursera for Enterprise)
a. Coursera for Business
b. Coursera for Campus
c. Coursera for Government
Learners coming to Coursera are offered a broad range of learning offerings, from a two-hour Guided
Project on how to build a website to full study programs. As technology automates more repetitive,
predictable, lower-skilled job tasks, individuals worldwide seek to reskill with Professional
Certificates and college degrees to move into emerging digital careers. Coursera hostsa portfolio
of entry-level Professional Certificates from Google, IBM, Intuit, Meta, Salesforce, and other
industry leaders that help develop the skills needed to land entry-level digital jobs in business, IT,
cybersecurity, data science, marketing, sales, design, and finance without requiring a college
degree or any experience in the field. Coursera also hosts online degrees in data science, computer
science, engineering, business, social science, and public health. The full Coursera catalog
includes
6
:
● 2,200+ Guided Projects: Gain a job-relevant skill in less than two hours
● 5,300+ Courses: Learn something new in four to six weeks
● 625+ Specializations: Gain a job-relevant skill in three to six months
● 75+ Certificates
● 15+ Entry-level Professional Certificates
7
: Earn a certification of job readiness for an in-
demand career in three to nine months
5
https://www.bcorporation.net/en-us/ (certification for sustainability)
6
As of December 31, 2021. The periods noted are intended completion timeframes; actual time to completion
varies.
7
In this report referred to as “courses”, for terminology see glossary at the end of this report.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 11
● 20+ MasterTrack Certificates: In three to twelve months, earn a university-issued certificate
from a module of a university degree and credit that can be applied to that degree in the
future.
● 30+ Degrees: Earn a bachelorʼs or masterʼs degree or a postgraduate diploma entirely
online.
The Coursera platform is designed to enable learners to discover the right content and credentials
by domain (e.g., Business, Technology, Health), by skills (e.g., Python, Statistics, Data
Visualization), and by job role (e.g., Data Analyst, Marketer, Engineer). Once learners enroll in a
course, the unified technology platform is designed to enable them to learn effectively to advance
their careers and earn credentials to signal their learning to prospective employers.
Learners either pay per single guided project, course, certificate, or degree. Coursera Plus is a
subscription pricing model that gives learners access to over 7,000 courses, Guided Projects,
Specializations, and Professional Certificates on Coursera for a monthly or an annual fee.
As part of Coursera´s strategy and focus on supporting individuals with job readiness certificates
in their career planning, certificate offerings have increasing importance in Coursera´s product
catalog. After the first positive experiences with this training offer, Coursera has been able to
expand the number of available entry-level certificates to over 30 (see Table 1: Entry-level
Professional Certificates at Coursera). Coursera systematically derives the needs from a thorough
analysis of data as well as the latest conference and research results. Coursera partners with
companies to integrate subject matter expertise from professional practice and to train the skills
that are needed on the job for the respective tasks. A separate corporate division has dedicated
itself to this topic of industry partnerships.
Table 1: Entry-level Professional Certificates at Coursera

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 12
Coursera´s research and internal data analysis shows that career certificates are a significant
opportunity for learners to progress in their jobs and form a path to digital jobs. Many off-platform
demand signals are considered when defining Professional Certificate targets, such as job postings
and job growth in the last twelve months in key countries, percentage of entry-level positions,
percentage of roles not requiring a Bachelorʼs degree, projected growth, median salary, and
difficulty in hiring. The demand signals are further validated once the programs are live by
analyzing on-platform demand signals such as search volume, enrollment numbers, revenue, and
the number of learners with a Professional Certificate that later have proceeded to enroll in a degree
program.
An increasing number of universities worldwide recognize Professional Certificates towards their
degrees, thus making these learning units stackable into full-degree programs. To ease recognition
in Europe and in accordance with the ECTS Users’ Guide’ s intention of Recognition of Prior
Learning
8
, Coursera and Google also aims at ECTS credit recommendation with FIBAA certification.
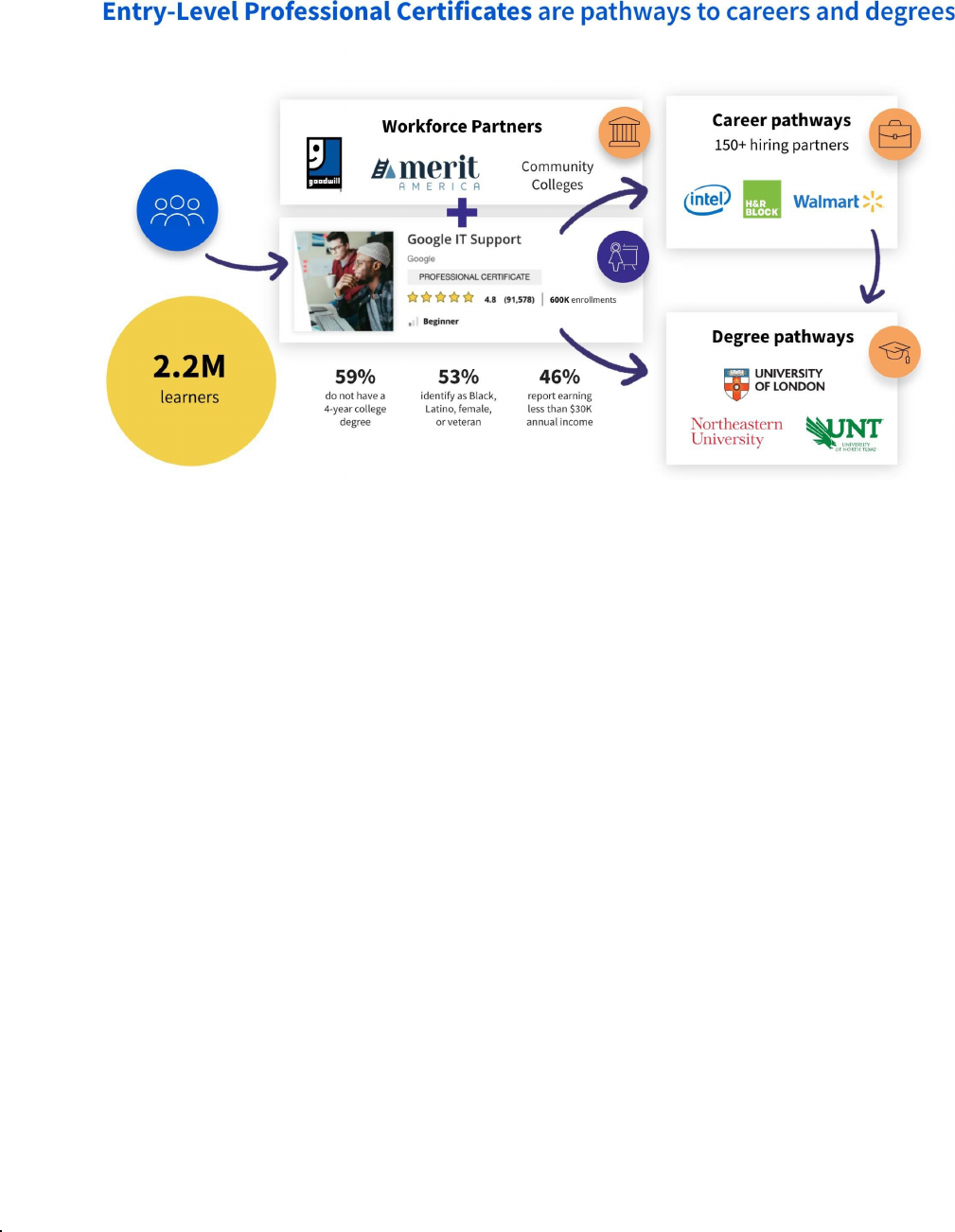
On the other hand, in many cases, entry-level certificates enable learners to start their careers in
various new job opportunities (see Table 2: Entry-level Professional Certificates: Pathways to
digital jobs).
For Coursera hosted Professional Certificates in the areas of business, information technology, data
analytics, and user experience, Coursera has been able to hostGoogle as a content partner. Google
Career Certificates are part of Grow with Google, an initiative that draws on Google’s 20-year
history of building products, platforms, and services that help people and businesses grow.
Through programs like these, Google aims to help those who make up the workforce of today and
the students who will drive the workforce of tomorrow – access the best of Googleʼs training and
tools to grow their skills, careers, and businesses (see self-report p. 8f.).
8
ECTS Users’ guide 2015, page 46
Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 13
Table 2: Entry-level Professional Certificates: Pathways to digital jobs
Although this is the first time the courses in this bundle will be certified according to the ECTS
standards, many learners have already completed the courses. Most of the certification courses
have already been assessed at least once by the American Council on Education and have received
a positive credit recommendation. Comments and recommendations from beta testing and first
learners have been successfully implemented. In addition to these external quality assurance
measures, Coursera continuously and systematically collects, processes, and makes available data
points, including the number of learners, number of completions, star rating, the average time to
completion, average passing score, pass ratios, and learner satisfaction rates in dashboards that
are analyzed at least once a year in a detailed feedback and evaluation meeting between all parties.
In this meeting, areas for improvement are identified, measures derived, and implementation
timetables recorded. It is also reviewed whether changes or updates to the learning content are
necessary (see also chapter 6.).
Appraisal:
The panel acknowledges Coursera as a well-established platform of online courses. Google is a
leader in building products, platforms, and services, and has profound experience in developing
trainings. Moreover, Google provides exceptional practical content knowledge. Thus, the co-
operation to develop and conduct Professional Certificates combines considerable knowledge and
resources for conceiving and designing the courses and provides a considerable number of highly
effective processes as well as outstanding employability (see also chapters 3.2, 3.4, 3.5, 4.1, 4.2).

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 14
Description and appraisal in Detail
1 STRATEGY AND OBJECTIVES
1.1 Logic and transparency of course objectives
Coursera´s general objectives for “Professional Certificates” (entry-level, advanced, experts) offer
an accessible learning experience from top companies and universities. Learners can get started
immediately, study at their own pace, anytime and anywhere. They can create work samples
through the course to demonstrate their skills and earn a career credential.
“Entry-level Professional Certificates” on Coursera are designed to provide a comprehensive and
high-quality approach to preparing learners for an in-demand career. They are targeted at learners
with little prerequisites and no or little previous knowledge. Learners gain practical skills and
knowledge through hands-on projects and, upon completion, can demonstrate job readiness to
potential employers with a Professional Certificate credential.
The Google Professional Certificates are designed to provide learners with subject-specific,
methodological, and social competencies through a holistic qualification concept. Across the
various Google Professional Certificates, the application orientation is represented in the practical
implementation of projects and application of Data Analytics, Project Management, IT Support,
Marketing, E-Commerce, UX Design, and IT Automation procedures in the respective method
courses and labs. Theoretical foundations and explanations always accompany the expertise of
practitioners and subject matter experts.
Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate
Data analytics is the collection, transformation, and organization of data in order to draw
conclusions, make predictions, and drive informed decision making. Learners are supposed to gain
in-demand skills that prepare them for an entry-level job. Skills they are supposed to gain include:
Data cleaning, problem solving, critical thinking, data ethics, and data visualization. Platforms and
tools learners are supposed to gain include: Presentations, Spreadsheets, SQL, Tableau and R
Programming. Learning objectives are:
● Gain an immersive understanding of the practices and processes used by a junior or
associate data analyst in their day-to-day job,
● Learn key analytical skills (data cleaning, analysis, & visualization) and tools
(spreadsheets, SQL, R programming, Tableau),
● Understand how to clean and organize data for analysis, and complete analysis and
calculations using spreadsheets, SQL and R programming,
● Learn how to visualize and present data findings in dashboards, presentations and
commonly used visualization platforms.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 15
Google Digital Marketing and E-Commerce Professional Certificate
Learners are supposed to gain in-demand skills that prepare them for an entry-level job. Skills they
are supposed to gain include: Developing digital marketing and e-commerce strategies; attracting
and engaging customers through digital marketing channels like search and email; measuring
marketing analytics and sharing insights; building e-commerce stores, analyzing e-commerce
performance, and building customer loyalty. Platforms and tools learners are supposed to gain
include: Canva, Constant Contact, Google Ads, Google Analytics, Hootsuite, HubSpot, Mailchimp,
Shopify, and Twitter. Learning objectives are:
● Learn the fundamentals of digital marketing and e-commerce to gain the skills needed to
land an entry-level job,
● Attract and engage customers through digital marketing channels like search and email,
● Measure marketing performance through analytics and present insights,
● Build e-commerce stores, analyze online performance, and grow customer loyalty.
Google IT Support Professional Certificate
Learners are supposed to gain in-demand skills that prepare them for an entry-level job in IT
support. The program covers the fundamentals of IT support, including troubleshooting, customer
service, networking, operating systems, system administration, and security. Skills learners are
supposed to gain include: Network protocols, cloud computing, Windows operating system, Linux
command line, systems administration, encryption algorithms and techniques. Learning objectives
are:
● Learn to perform day-to-day IT support tasks including computer assembly, wireless
networking, installing programs, and customer service,
● Learn how to provide end-to-end customer support, ranging from identifying problems to
troubleshooting and debugging,
● Learn to use systems including Linux, Domain Name Systems, Command-Line Interface, and
Binary Code.
Google IT Automation with Python Professional Certificate
Learners are supposed to gain in-demand skills – including Python, Git, and IT automation – to
advance their career. Knowing how to write a code to solve problems and automate solutions is a
crucial skill for anybody in IT. According to Coursera
9
Python is now the most in-demand
programming language by employers.
This program is designed to teach how to program with Python and how to use Python to automate
common system administration tasks. Learners will also learn to use Git and GitHub, troubleshoot
and debug complex problems, and apply automation at scale by using configuration management
9
Appendix B, page 4

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 16
and the cloud, and practice their technical skills with hands-on projects including a capstone
project. The course is designed to prepare learners for a variety of roles in IT, like more advanced
IT Support Specialist or Junior Systems Administrator positions. Learning objectives are:
● Automate tasks by writing Python scripts,
● Use Git and GitHub for version control,
● Manage IT resources at scale, both for physical machines and virtual machines in the cloud,
● Analyze real-world IT problems and implement the appropriate strategies to solve those
problems.
Google Project Management Professional Certificate
Project managers set the plan, guide teammates, manage changes, risks, and stakeholders.
Learners are supposed to gain in-demand skills that prepare them for an entry-level job. Skills
learners are supposed to gain include: Creating risk management plans; understanding process
improvement techniques; managing escalations, team dynamics, and stakeholders; creating
budgets and navigating procurement; utilizing project management software, tools, and templates;
practicing agile project management, with an emphasis on Scrum. Learners will get introduced to
initiating, planning, and running both traditional and agile projects and develop a toolbox to
demonstrate their understanding of key project management elements, including managing a
schedule, budget, and team. Learning objectives are:
● Gain an immersive understanding of the practices and skills needed to succeed in an entry-
level project management role,
● Learn how to create effective project documentation and artifacts throughout the various
phases of a project,
● Learn the foundations of agile project management, with a focus on implementing Scrum
events, building Scrum artifacts, and understanding Scrum roles,
● Practice strategic communication, problem-solving, and stakeholder management through
real-world scenarios.
Google UX Design Professional Certificate
User experience (UX) designers focus on the interaction that users have with products, like
websites, apps, and physical objects. They make those everyday interactions useful, enjoyable, and
accessible. Learners of this course are supposed to gain in-demand skills that prepare them for an
entry-level job. Participants will learn how to complete the design process from beginning to end,
including: Empathizing with users; defining user pain points; coming up with ideas for design
solutions; creating wireframes, mockups, and prototypes; testing designs through usability
studies; iterating on designs based on feedback. Participants will create designs on paper and in
digital design tools like Figma and Adobe XD. By the end of the certificate program, they will have

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 17
a professional UX portfolio that includes three end-to-end projects, enabling them to apply for jobs.
Learning objectives are:
● Follow the design process: empathize with users, define pain points, ideate solutions,
create wireframes and prototypes, test and iterate on designs
● Understand the basics of UX research, like planning research studies, conducting interviews
and usability studies, and synthesizing research results
● Apply foundational UX concepts, like user-centered design, accessibility, and equity-
focused design
● Create a professional UX portfolio that includes three end-to-end projects: a mobile app, a
responsive website, and a cross-platform experience
According to Coursera and Google, the specifications from the European Qualifications Framework
(EQF) have been taken into account in the design of the learning objectives of the modules and
courses
10
, e.g., “the ability and willingness of the individual to use knowledge and skills as well as
personal, social and methodological abilities and to behave in a thoughtful and individually and
socially responsible manner. Competence is understood in this sense as comprehensive action
competence” (see self-report p. 11).
Appraisal:
The qualification objectives of the courses are explained and convincingly presented in relation to
the target group. They embrace appropriate training of knowledge, skills and competence,
comprehensive employability, as well as the development of the individual learner’s personality
(in relation to the scope of the courses).
The course objectives are based on subject-specific and generic learning outcomes which are in
line with the level of the qualification to be awarded upon completion. However, the panel misses
a clear deduction of the European Qualification Framework (EQF) level, supported by a taxonomy
of the job skills provided in the job task analyses.
Therefore, the panel suggests the following condition:
Coursera and Google provide a deduction of the intended EQF levels of each of the
respective courses.
In order to achieve this the panel suggests taking into account a taxonomy of the intended job
skills, (e.g. based on Bloom, EQF and the e-Competence Framework of the EU
11
).
The panel acknowledges the exceptional employability (see chapter 3.5) of the completersand the
fact that the courses may be recognized as credits for respective courses in undergraduate study
programs (for communication and documentation, see condition chapter 5).
10
See chapter 3.1 Structure
11
e-CF levels, (see p. 42 to align e-CF and EQF levels)

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 18
When defining the learning objectives, the course provider and content partner (Google) also take
into account the findings of course completers-tracking studies (further occupational development
of all Professional Certificate graduates). Coursera does not analyze course-specific completion-
tracking, but a completion-tracking for all Professional Certificates.
Exceptional
Exceeds
quality
requirements
Meets
quality
requirements
Does not meet
quality re-
quirements
n.r.
1.
Strategy and Objectives
1.1*
12
Logic and transparency of course
objectives
Condition
1.2 International orientation of the courses
Coursera and Google prepare its learners with Entry-Level Professional Certificates for jobs in an
international environment. The certificates are intended to facilitate learnersʼ development of an
international perspective on issues and explicitly prepare them for global professional activity. The
language of instruction also supports the certificatesʼ internationality. All courses at this level are
delivered in English, while some are translated into other world languages like Spanish, French, or
German. Additional languages can be added on request and due to identified demand for certain
areas or markets.
If relevant to the learning objectives, international aspects of the respective course content are
integrated into all modules, thus enabling learnersto gain an international perspective on the
problem areas. In addition, when selecting instructors and subject matter experts
13
, greater
importance is attached to ensuring they have foreign language skills and international experience,
e.g., through stays abroad, employment in internationally active companies, and/or internationally
oriented project work (see self-report p. 12).
Any country-specific differences in software, research, and applicability of what has been learned
are addressed. Especially in software training, various formatting, or convention differences are
explicitly highlighted, and workarounds are made available within the framework of toolboxes or
adapted versions.
The learning objectives are designed to provide learners worldwide with the relevant/appropriate
subject knowledge and develop skills that will help them work successfully in an international
environment. The necessary skills are derived from carefully crafted and analyzed JTAs (job tasks
analysis, see chapter 3.5) with leading enterprises and subject matter experts. Emphasis is always
placed on international standards, and common procedural techniques applied worldwide.
12
*: Asterisk Criterion
13
For Coursera terminology of teaching staff, see chapter 4.1 and glossary.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 19
Appraisal:
Within the scope of the courses and with respect to the international availability of the courses, the
intention is to sustainably promote the employability of completers. The panel highlights that
Google assigns teaching staff with a dedicated international background (see also chapter 4.1).
Exceptional
Exceeds quality
requirements
Meets quality
requirements
Does not meet
quality
requirements
n.r.
1.
Strategy and Objectives
1.2
International orientation of the courses
X
1.3 Positioning of the courses
During the Covid19 pandemic, online learning provided educators, businesses, and governments
with the means to respond to a global crisis that fundamentally changed how people learn and
work. The combined forces of online learning and remote work assist to the vision of a world, where
anyone, anywhere, has access to education. By working directly with universities and enterprises
and powering institutional collaboration across the platform, Coursera and Google provide access
to global and affordable education while paving the way for talent to rise from anywhere with
remote, digital jobs.
With the rise of online learning and the increasing demand for skills and qualifications, online
Professional Certificates have become increasingly popular. They offer a way for individuals to gain
new skills, qualifications, and credentials without attending traditional classrooms.
Coursera hostedProfessional Certificates are industry-recognized and can provide a competitive
edge on the job market. In addition, Professional Certificates are becoming a much sought-after
asset for both candidates (job seekers and employees) and employers, as they demonstrate that an
individual has the skills and knowledge necessary to excel in a certain field. They provide
individuals with a convenient and accessible way to gain the necessary skills and qualifications to
pursue a career. As employers and educational institutions become more rigorous in their
requirements, Professional Certificates become an invaluable asset in helping individuals meet
their career goals and objectives.
The development of the Professional Certificates was strongly oriented toward the specifications
and recommendations of business and industry representatives to prepare completers
appropriately for labor market requirements. Concerning the range of qualifications, care was taken
to include the facets and characteristics of the intended occupational fields and to anchor them in
the syllabus (see description Job Task Analysis (JTA) chapter 3.5).

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 20
Table 3: SWOT analysis of Professional Certificates
Strengths
Weaknesses
Opportunities
Threats
Certificates provide a more
specialized approach to
higher education, allowing
students to gain skills and
knowledge more quickly and
efficiently than traditional
college degrees.
Certificates may not be
recognized or accepted by
certain employers or
educational institutions.
Certificates can provide new
educational and career
opportunities to those who
may not have access to
traditional college degrees.
Certain employers or
educational institutions may
not accept certificates.
Certificates are often
more affordable than
traditional college
degrees, making them
attractive to various
students.
Certificates may not provide
the same prestige or
recognition as traditional
college degrees.
Certificates can provide
employers with a way to
recognize the specialized
skills of their employees.
Certificates may not provide
the same level of recognition
as traditional college
degrees.
Certificates provide
employers with a way to
recognize the specialized
skills and professional
qualifications of their
employees.
Certificates may not provide
the same educational or
career opportunities as
traditional college degrees.
Certificates can help
employers stay competitive
in their respective industries.
Certificates may be seen as a
“quick fix” to gaining skills
and knowledge rather than a
true commitment to higher
education.
Strengths
Weaknesses
Opportunities
● Develop partnerships with employers
and educational institutions to ensure
that Professional Certificates are
accepted and recognized in their
respective industries.
● Develop career counseling services to
assist students in utilizing the skills
and knowledge gained through
Professional Certificates to find
employment.
● Develop marketing campaigns to emphasize
the benefits of Professional Certificates, such
as their affordability and more specialized
approach to higher education.
● Develop promotional campaigns focusing on
the potential educational and career
opportunities that Professional Certificates
can provide.
Threats
● Develop strategies to ensure that
Professional Certificates are seen as
a true commitment to education
rather than a “quick fix” to gaining
skills and knowledge.
● Develop programs that can demonstrate
the value of Professional Certificates in
terms of the specialized skills and
knowledge that they provide.
● Develop strategies to ensure that
Professional Certificates are recognized and
accepted by employers and educational
institutions.
● Develop strategies to ensure that
Professional Certificates are considered a
valid form of education equal to parts of
traditional college degrees.
Coursera conducts regular competitive analyses and performs internal analyses of its strengths,
weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. These analyses provide valuable insights into the
company's positioning compared to its competitors. The sub-areas analyzed are based on detailed
information about various criteria, and the team identifies key learning points from the differences
identified. Based on these learning points, recommendations and alternative courses of action are

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 21
derived and integrated into the strategic development of the company's service and product
offerings.
Coursera is a learner-first and learner-centric platform for career advancement. The key learner
segments for Coursera are Career Starters (15-19%), Career Switchers (24-35%), Career Advancers
(21-34%), and Enthusiasts (8-13%). The first two are composed of job-seekers: Starters want to
learn skills to land their first professional job, and Switchers want to switch to a different role by
developing new skills. Moreover, Starters and Switchers represent most of the learners on
Courseraʼs platform, with the proportion of starters being even higher for other regions outside the
US
14
.
Coursera considers lifelong and lifecycle learning in positioning courses on the Coursera platform.
We aim to reach learners early in their careers and offer them affordable, job-relevant content, skills
learning, and credentials to help them start or advance their careers. Courseraʼs lifelong learning
ecosystem (see Table 4) shows the three pillars of the companyʼs strategy: the connections made
between learners and educators, industry, or university partners, the one between learners and
institutions, and the one between educators and institutions.
In this context, Courseraʼs partnership with Google connects learners and educators to solve a
particular learner problem: learning new skills to either land their first professional job or switch
to different roles. When further assessing the learnerʼs pain points, Coursera has found that entry-
level Professional Certificates from globally renowned brands that are highly job aligned generate
very strong Product-Market-fit (PMF). The internal analysis supports this affirmation, considering
that entry-level Professional Certificates are currently the largest driver of revenue globally (2022).
Extensive research has been conducted to define what partners would be better suited (what
companies learners would want to learn from) and what content is highly demanded on the job
market. Through that process, Google was identified as a thought leader and expert in areas of high
job growth.
14
Sample figures: Career Starters in US approximately 31 %, in India 44%

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 22
Table 4: Courseraʼs lifelong learning ecosystem
Appraisal:
The panel appreciates the very structured and holistic approach of the job market analysis. The
position in the education and job market is reviewed, and the courses’ competitiveness analyzed
and documented. Course completion-tracking studies are undertaken, analyzed and confirm the
desired position of the courses’ completers.
The way in which the courses are integrated into Coursera’s overall strategy and relate to the other
offers of Coursera is plausibly described. The courses pursue qualification objectives which
correspond to the course provider’s concept and strategic planning.
Exceptional
Exceeds
quality
requirements
Meets
quality
requirements
Does not meet
quality re-
quirements
n.r.
1.
Strategy and Objectives
1.3
Positioning of the courses
1.3.1
Positioning of the course in the education
and job market, and the
professional field
(“Employability”)
X
1.3.2
Position of the course within the
institution’s overall strategy
X

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 23
2 ADMISSION
Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate
The target group for the Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate is beginner-level learners
who want to develop job-ready skills, tools, and a portfolio for an entry-level Data Analyst, Junior
Data Analyst, or Associate Data Analyst position. This program does not require any prior
experience.
Google Digital Marketing & E-commerce Professional Certificate
The target group for the Google Digital Marketing & E-commerce Professional Certificate is
beginner-level learners who want to develop job-ready skills, tools, and a portfolio for an entry-
level Marketing Coordinator, E-commerce Associate, Paid Search Specialist position. This program
does not require any prior experience.
Google IT Support Professional Certificate
The target group for the Google IT Support Professional Certificate is beginner-level learners who
want to develop job-ready skills, tools, and a portfolio for an entry-level IT Specialist, or IT Support
Specialist position. This program does not require any prior experience.
Google IT Automation with Python Professional Certificate
The Google IT Automation with Python Professional Certificate is designed to provide IT
professionals with in-demand skills - including Python, Git, and IT automation - that can help
advance their career. The Google IT Automation with Python Professional Certificate can help
prepare learners for a variety of roles in IT, like more advanced IT Support Specialist or Junior
Systems Administrator positions. Familiarity with basic IT concepts, like operating systems, files
and processes, networking and data management will be required in further courses. For learners
with no IT background at all, Coursera recommends taking the Google IT Support Professional
Certificate, but it is not required to enroll in this program. Coursera and Google recommend
participants to have Python installed on their computer. They also need a computer where they can
install Git.
Google Project Management: Professional Certificate
The target group for the Google Project Management Professional Certificate is beginner-level
learners who want to develop job-ready skills, tools, and a portfolio for an entry-level Project
Manager, Project Coordinator, or Project Assistant position. This program does not require any
prior experience.
Google UX Design Professional Certificate
The target group for the Google UX Design Professional Certificate is beginner-level learners who
want to develop job-ready skills, tools, and a portfolio for an entry-level User Experience (UX)
Designer, UI Designer, or Interaction Designer position. This program does not require any prior
experience.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 24
To enroll in each of the Google Professional Certificates, learners must subscribe to the Coursera
platform and enroll in their preferred course from the course description page on the Coursera
website. To enrol, learners must 1) open the page for the course they want to enroll in, 2) click
enroll and 3) choose the preferred payment option
15
. After enrolling, learners must agree that they
will be required to provide a government-issued ID to earn a certificate for completing learning
content, after which learners can navigate to the beginning of the course through the learning
management system and begin learning asynchronously. To enroll in the course, learners must have
access to a computer or mobile device and internet connection. Learners who enroll in the courses
must be proficient in English
16
.
As the online platform provider, Coursera has a contract with Google to host its content. When
enrolling in a course, learners agree to Coursera's terms of use and access hosted content through
the Coursera platform. The learner's parent relationship is with Coursera, and as such, Coursera
holds their data as the controller. Content and instruction are from Google and owned by Google.
Coursera's role is to (a) aid in sharing best practices for teaching online, (b) recruit learners, (c)
foster engagement between learners and the hosted content, and (d) to serve as the main point of
organizational contact to ensure a successful learning experience through learner support services,
educator support services, and technical support.
Legal Relationship between Coursera and Google
Coursera and Google have contractual documentation in place to govern the provision and hosting
of content on the Coursera platform. The documentation sets out the parties' agreement on matters
such as material licensing, intellectual property rights, marketing, content production and content
review responsibilities, course appropriateness rights, functionality and accessibility, and
responsibilities for both the content and platform. There are relevant provisions agreeing on terms
for liability, termination events, and the teach-out to protect learner interests upon termination.
The agreement also contains relevant provisions for data and information security protection to
safeguard the protection of personally identifiable information.
The parties are agreeing on clear permissions for Google to permit participation in creditworthiness
reviews through a participation agreement. These agreements are held on a confidential basis.
Legal relationship between Coursera and Learners
Coursera sets out terms of use in relation to learners that use the platform. The terms contain key
information and provisions on areas such as the extent of a learnerʼs license when using Coursera
services, content offering and credit granting, security standards, the use of third-party content,
and modification permissions. There are also boilerplate terms related to liability and disclaimers.
15
See information on payment in chapter “Details on the institution”
16
English is the default language for all Professional Certificates, although for some courses there are
variants available in other world languages or with subtitles. Learners are informed about the available
language versions on the course page and can choose the one that suits them best.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 25
The terms of use are available online
17
. In addition to the contractual terms of use, the document
also includes key policies which help clarify material terms for learners on the platform:
● Acceptable Use Policy - which sets out activities that learners are and are not allowed to do on
the platform.
● Copyright and Trademark Policy - this protects intellectual property in the content and platform
● Payment and Refund Policy - this policy sets out details on refund, and cancellation in line with
Coursera’s consumer law obligations
● Honor Code - this code is published to protect academic integrity standards and links to a
plagiarism policy. Coursera notes that this Honor Code has undertaken a substantive review
and is about to be updated (see self-report p. 20).
Google and Teaching staff
All instructors are Google employee subject matter experts (SMEs) with a professional background
and expertise in the subject area of instruction with relevant or noteworthy skill sets to the
curriculum they are teaching. They were recommended by VP and Director-level leadership and
vetted by certificate leads through interviews and work product (e.g., case studies, design
portfolios, textbooks authored). In addition, they were supported by instructional designers with
expertise in adult learning and by Coursera's pedagogical training. Google subject matter experts
develop and review all of the material in each certificate program.
Appraisal:
The choice of the specific target group is based on the strategic objectives of the certificate course.
All courses aim at specific target groups with no prior expertise or formal requirements (see also
chapter 5) but targeted at specific career aspirations and job profiles.
Admission guidelines have been defined and are coherent (e.g., proficiency in English). They take
into account the specific characteristics of the target groups (e.g., job seekers and job switchers).
They support the achievement of the course objectives. Admission guidelines also include
information on the requirements in terms of technical equipment.
The contractual relationship between Coursera and the content partner (Google) on the one hand
and the learners on the other hand, as well as between content partner and teaching staff is set
down and documented. Rights and obligations of contractual parties have been established and are
known to all relevant parties. Transparency and legal certainty exist.
Exceptional
Exceeds quality
requirements
Meets quality
requirements
Does not meet
quality
requirements
n.r.
2.
Admission
2.1*
Focus on the target group
X
2.2*
Admission conditions
X
2.3*
Legal relationship
X
17
https://www.coursera.org/about/terms (last call August 7, 2023)

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 26
3 IMPLEMENTATION
3.1 Structure
Entry-Level Professional Certificates require no degree or experience in the area to take the
program or obtain a specified entry-level job role. For example, a learner with a high school diploma
and no degree or work experience can take an Entry-Level Professional Certificate and be
considered for related roles upon completion. Like all content on Coursera, Professional
Certificates include Courseraʼs Pedagogy Principles (see chapter 3.4).
Each Google Professional Certificate program contains “courses”, which contain weekly
“modules”
18
(four to six lessons) that progressively build on concepts taught previously. Each
module contains weekly learning objectives. By completing the weekly content for each module in
order, learners can achieve the learning outcomes required to progress to the subsequent module.
Google Professional Certificates on Coursera:
● Include eight to 13 courses designed to be completed in in three to five months (workload
of ten hours/week).
● Include career-relevant, hands-on projects to showcase to potential employers on the
learnerʼs resume and in interviews.
● Include a partner-branded Professional Certificate, which Coursera issues and the partner
delivers, from the partner dashboard to learners who successfully complete the program.
● Provide career-readiness resources, so the learner knows how to prepare for the job role.
Learners should be expected to complete an Entry-Level Professional Certificate in 80-200 hours
of total engagement time. Each course in the Entry-Level Professional Certificate must include
approximately 10 hours of total learner engagement time per week (e.g., watching videos, reading
materials, completing assessments).
To help learners prepare for an entry-level job, Coursera and Google emphasize that they should
get ample practice and hands-on learning time to learn the skills they need for the role. Each course
should also include a job-relevant project at the end of each course to help learners demonstrate
their skills and build their resumes for potential employers. Coursera summarizes Entry-Level
Professional Certificate Content Specifications as follows:
18
“Course” in Coursera terminology is a learning unit within the certificate program covering a certain
content topic. A course (topic) is split into “modules” (in Coursera terminology) which is a weekly learning
unit, thus “module” being Coursera´s terminology for the smallest learning unit within the “course” and the
“program” (as a whole), see glossary.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 27
Table 5: Entry-Level Professional Certificate Content Specifications
Entry-Level Professional Certificate Content Specifications
Content
Structure
4+ courses per Entry-Level Professional Certificate
4+ modules per course (10-16 hours of total learner engagement time per course)
3+ lessons per module in a course
1 graded assessment at the end of each module
30+ min of hands-on learning in each module (Optional for Course
1) 1 cumulative hands-on project at the end of each course
80-200 hours of total learner engagement time across the Professional Certificate
Learning
Objectives
4+ per Entry-Level Professional Certificate
program 4+ per course
4+ per module
1 per instructional item
1 evaluated by each graded assessment
All course learning objectives are applied through the hands-on project
All learning objectives uploaded to the Coursera platform and incorporated directly into instructional
materials
Assessments
16+ graded per Entry-Level Professional Certificate Program
4+ graded per course, including at least one hands-on
project 1+ graded per module
1+ practice per instructional item
Graded and practice assessments align with a learning objective or career
skills 30 minutes of learner time per practice assessment
30+ minutes of learner time per graded assessment Graded
assessments appear at the end of each module
Graded hands-on project appears at the end of each course
All assessments include detailed feedback
Instructional
materials
Identify the Professional Certificate target audience, prerequisites, related job role, and associated
certification (if applicable) in a video, a reading, and landing pages
Include a “Welcome to the course” in a video and a reading
Include module descriptions on the Coursera platform
1+ hour of video (4-7 min each) per module
30+ minutes of hands-on learning time per
module 1 hour of readings per module
1 discussion prompt per course

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 28
Best Practices
Scaffold the learning path
Promote active learning withpractice
Explain with visuals and metaphors
Provide career information
Google Professional Certificates have been developed from the ground up to ensure employability
for a specific target occupation and to build skills, abilities, and competencies to be job-ready.
1. Learning Outcomes
Derived from the respective JTA (job task analysis, see chapter 3.5), a basic idea of the learning
objectives has been developed by Googleʼs instructional designers and a team of subject matter
experts. Each Professional Certificate has therefore defined learning objectives to be achieved
at the top level, whereby both the EQF recommendations on competence acquisition have been
applied, and the descriptions of the respective learning objectives have been formulated based
on the recommendations of Bloom's taxonomy.
In addition, the overarching learning objectives for the respective certificate are broken down
further toward individual learning outcomes for each “course” and for each weekly “module”.
The quizzes and assessments are aligned with the learning objectives at the weekly “module”,
“course”, and certificate levels.
2. Workload
To determine the workload, each sub-element is analyzed within the pre-structured weekly
learning plans, and the length (e.g., videos or reading) is determined. The learning and
processing times determined in this way are finally summarized at the level of the Professional
Certificate. In this way, learners know the total workload in the respective certificate and the
weekly learning times for each element. It is possible to set individual learning time targets
and days on which Coursera and Google remind the user of their learning goals in the app or
the browser, thus continuously motivating learners to participate. The workload at all levels is
documented and systematically displayed before and during learning.
3. Recommendations for ECTS credit allocation
Referencing the methodology and principles from the ECTS User’s Guide 2015 and utilizing the
application of the workload calculation, Coursera and Google aim to show a defined ECTS credit
recommendation that corresponds appropriately to the workload and learning objectives for
the individual certificates. One ECTS credit should correspond to 25 hours of workload. The
individual workload per module may vary depending on the task and exceed the initially
determined reference time. The workload analyses provide a regular check, but in case of doubt,
a slightly higher effort for a task should be assumed rather than less learning time. Coursera

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 29
and Google consider this by using the lower end of the range
19
and showing a corresponding
ECTS credit recommendation value.
4. Non-Allocation for single educational components (on module/course level)
Although the Professional Certificate comprises smaller units, the respective “courses” and
“modules”, Coursera and Google refrain from distributing ECTS credits at this level. This
approach follows the application in higher education institutions. For example, a module in the
field of tertiary education, similar to an entire certificate, extends over four to six months. The
ECTS credit allocation assigned to one module at higher education institutions should,
according to many national recommendations
20
, not be less than five ECTS credits as a rule. A
different allocation than full ECTS credits should be avoided unless the general program design
can compensate for the sensible full ECTS credits per semester. In addition, the corresponding
course unit should conclude with an examination performance, which justifies the acquisition
of the ECTS credits. In the case of the Professional Certificate, this is the Final Project, often
also called the Capstone Project.
5. 60 ECTS credits allocation per year
The Professional Certificates are part-time continuing education programs intended to enable
the acquisition of competencies and skills part-time. The weekly learning performance is geared
towards this circumstance, with a maximum workload of approximately ten hours per week for
three to five months.
6. ECTS credit documentation
The use of ECTS credits is facilitated and quality enhanced by supporting documents like the
course catalog and the certificate supplement via Credly. The use of Credly has proven to be an
exceptional fit because learners have the permanent ability to store their achieved digital
credits in one secure place. In addition, Credly provides prospective employers with the ability
to verify that the individual earned the Professional Certificate, thus enabling a certificate
authenticity check. In addition to badges, Credly provides learners with a transcript that
Registration Offices a HEIs can utilize.
19
i.e. the possible range of hours allocated per ECTS credit: 25-30
20
As an example, they refer to the recommendations for action of the University Rectors' Conference in Germany
(HRK), such as the recommendation on "Designing modularization" from February 2016.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 30
Table 6: Credly Sample page
7. Certificate supplements
A Certificate supplement documents the courses and the associated qualifications. The
acquired skills, the earning criteria for the certificate, the learner, the content, the issuer, the
course description, and the certificate details (when and where obtained) are documented
transparently and through Credly in a safe space that still allows for authenticity checks for
external parties.
For each certificate program, Coursera and Google provided a plan including learning objectives of
the program, the “courses”, and the “modules”, the learning projects, and an overview and
biographies of the teaching staff
21
.
After enrolment, learners must agree that they will be required to provide a government-issued ID
to earn a certificate for completing learning content, after which learners can navigate to the
beginning of the course through the learning management system and begin learning
asynchronously.
21
See also chapter 4.1 and glossary

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 31
Learners attend the course by viewing lectures, completing readings and quizzes, responding to
discussion prompts, and completing hands-on labs and programming assignments. Each Google
Professional certificate has a minimum passing score of either 70 % or 80 % that learners must
meet in order to pass graded quizzes and complete the qualification for the Professional Certificate.
All Coursera learners must adhere to the Coursera Code of Conduct, Honor Code, and Terms of Use.
Detailed conditions of participation and assessment regulations, such as quiz attempt rates,
passing grades, and identity verification, are described to learners within each Google Professional
Certificate program at the start of each assignment as they navigate throughout the course content.
In addition, learners are informed where they can go in case of doubt about discrepancies and how
the grading appeal procedure would look like in these cases.
Coursera aims to ensure the feasibility of the programs’ workload by a suitable curriculum design
and a plausible calculation of workload of under ten hours of study a week to complete the course
within the suggested three to five months (see Table 7: Sample weekly plan). Learner enrolment is
voluntary and self-guided. Learners will complete the content asynchronously at a pace that meets
the demands of their personal schedules. Assessment deadlines are generated based on a
personalized schedule that begins when a learner enrolls in a course. If learners miss two
assessment deadlines in a row or an assessment deadline by two weeks, they will see a “reset
deadlines” option in their grades page. Learners can then switch to a new schedule for the course
with updated deadlines and can utilize this option as many times as needed. This does not remove
progress made in the course. If a learner cancels their Coursera subscription and then reactivates
it, their deadlines will automatically reset.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 32
Table 7: Sample weekly plan

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 33
Discussion forums are accessible for enrolled learners, where they benefit from:
● Support from fellow learners which are moderated,
● Interaction with classmates, shared resources, and help answer questions about course
materials or assessments,
● Asking questions, debating ideas, and identifying classmates who share the same goals.
Appraisal:
The courses’ structural elements are convincingly described and motivated. The course structures
serve to promote the objectives and the learner' acquisition of knowledge and competences in line
with the given objectives.
By giving an analysis of the approach towards ECTS credit allocation, Coursera and Google have
proven comprehensive examination of the ECTS guidelines. The following ECTS elements: principle
of modularization, credit points and workload specifications, have mostly been implemented. The
guidelines for workload calculation are clearly and understandably deduced. The course
descriptions provide detailed descriptions of intended learning outcomes and the information
defined in the ECTS Users’ Guide
. Certificate supplements document the courses and the associated
qualifications in a transparent and coherent manner.
As for the workload calculated by Coursera and Google and intended ECTS credits to be awarded,
the conversion would be as follows:
Table 8: Workload calculation and intended ECTS credit assignment
Course Learning
hours
22
Learning
hours/25
ECTS credits
Intended
ECTS credit
assignment
Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate
187 7,48 7
Google Digital Marketing and E-Commerce Professional
Certificate
166 6,64 7
Google IT Support Professional Certificate 137 5,48 5
Google IT Automation with Python Professional Certificate 113 4,52 5
Google Project Management Professional Certificate 152 6,08 6
Google UX Design Professional Certificate
234 9,36 9
22
See chapter 3.2, Table 9: Google Entry-Level Professional Certificates: Course contents and learning hours

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 34
According to the ECTS Users’ Guide
23
, workload is an estimation of the time the individual typically
needs to complete all learning activities such as lectures, seminars, projects, practical work, work
placements and individual study required to achieve the defined learning outcomes in formal
learning environment. Based on the generally valid rounding rules (4,5 equals up to 5 equals up to
5,4) the panel notes that workload calculation and ECTS credit allocation is plausible for all six
programs.
The panel notes that Coursera and Google did not provide proof of a process of reviewing the
workload including taking into account learner feedback and the courses’ success rate. During the
assessment conference learners confirmed that the calculated workload was feasible, however, a
question whether the actual workload of the whole course corresponds with, is lower or higher than
the estimated workload (including teaching time, self-study time and examination) is missing in
the course completer survey.
Therefore, the panel recommends the following condition:
For each of the six courses, Coursera and Google implement a learner workload evaluation
system which includes a systematic control loop from the completion survey to the analysis
of the results and the taking of appropriate measures.
The panel recommends harmonizing learning hours on the basis of the calculation of 25 h per ECTS
credit, by developing respective course structures for 125 h (5 ECTS credits), 150 h (6 ECTS credits),
175 h (7 ECTS credits) or 225 h (9 ECTS credits), also taking into account the panel’s review
recommendations in terms of content (see chapter 3.2) and methodology (see chapter 3.4).
The panel points out that a more coherent allocation of workload hours per ECTS credit throughout
the courses may facilitate ECTS recognition. ECTS recognition and comprehending the assignment
to EQF-levels may also be facilitated by classification of competencies according to taxonomy
levels. The panel also notes that the information defined in the ECTS Users’ Guide is spread across
several pages on the course website only registered users can access. Furthermore, the panel points
out that listings of literature recommendations in module/course descriptions are not mandatory
by regulations of the ECTS Users’ Guide 2015 but have become quite common and therefore may
also add to facilitating ECTS recognition. In order to facilitate the intended ECTS credit recognition,
the panel therefore recommends summarizing the information defined in the ECTS Users’ Guide in
one publicly accessible sheet or course description, the classification of learning objectives in
taxonomy levels, listing recommended literature in the course/module descriptions (see also
recommendation chapter 3.2) and communicating to learners and completers that the combination
of the Professional Certificate in combination with proof of relevant professional experience may
also facilitate recognition of ECTS credits.
There are transparent conditions of participation and assessment regulations. The courses’
characteristic structural features have been implemented.
Apart from the missing implementation of learners’ feedback into the evaluation of the workload
(see condition, second part), the feasibility of the courses’ workload is ensured by a suitable
curriculum design, by a plausible calculation of workload, by an adequate number and frequency
23
ECTS Users’ guide 2015, page 10

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 35
of assessments, by appropriate support services as well as academic and general learner
counselling.
Exceptional
Exceeds quality
requirements
Meets quality
requirements
Does not meet
quality
requirements
n.r.
3.
Implementation
3.1
Structure
3.1.1
Structure of the course
X
3.1.2*
Application of the „European Credit
Transfer and Accumulation System (ECTS)“
and modularization
Condition
3.1.3*
Conditions of participation and
assessment regulations
X
3.1.4*
Feasibility of study workload
X
3.2 Content
The course contents are as follows:
Table 9: Google Professional Certificates: Course contents and learning hours
Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate (8 “courses”
24
)
Module Number
Module Title
Learning Hours
1
Foundations: Data, Data, Everywhere
22
2
Ask Questions to Make Data-Driven Decisions
21
3
Prepare Data for Exploration
25
4
Process Data from Dirty to Clean
23
5
Analyze Data to Answer Questions
26
6
Share Data Through the Art of Visualization
24
7
Data Analysis with R Programming
37
8
Google Data Analytics Capstone: Complete a Case Study
9
Total Learning Hours
187
24
In the following tables, Coursera uses the term “modules” for what is elsewhere called “courses”, see
glossary

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 36
Google Digital Marketing & E-commerce Professional Certificate (7 “courses”
24
)
Module Number
Module Title
Learning Hours
1
Foundations of Digital Marketing & E-commerce
18
2
Attract and Engage Customers with Digital Marketing
21
3
From Likes to Leads: Interact with Customers Online
27
4
Think Outside the Inbox: Email Marketing
25
5
Assess for Success: Marketing Analytics and Measurement
26
6
Make the Sale: Build, Launch, and Manage the E-commerce Stores
23
7
Satisfaction Guaranteed: Develop Customer Loyalty Online
26
Total Learning Hours
166
Google IT Support Professional Certificate (5 “courses”
24
)
Module Number
Module Title
Learning Hours
1
Technical Support Fundamentals
21
2
The Bits and Bytes of Computer Networking
27
3
Operating Systems and You: Becoming a Power User
33
4
System Administration and IT Infrastructure Services
25
5
IT Security: Defense against the digital dark arts
31
Total Learning Hours
137
Google IT Automation with Python Professional Certificate (6 “courses”
24
)
Module Number
Module Title
Learning Hours
1
Crash Course on Python
26
2
Using Python to Interact with the Operating System
25
3
Introduction to Git and GitHub
15
4
Troubleshooting and Debugging Techniques
16
5
Configuration Management and the Cloud
14
6
Automating Real-World Tasks with Python
17
Total Learning Hours
113

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 37
Google Project Management Professional Certificate (6 “courses”
24
)
Module Number
Module Title
Learning Hours
1
Foundations of Project Management
18
2
Project Initiation: Starting a Successful Project
21
3
Project
Planning: Putting It All Together 29
4
Project Execution: Running the Project
26
5
Agile Project Management
25
6
Capstone: Applying Project Management in the Real World
33
Total Learning Hours
152
Google UX Design Professional Certificate (7 “courses”
24
)
Module Number
Module Title
Learning Hours
1
Foundations of User Experience Design
18
2
Start the UX Design Process: Empathize, Define, and Ideate
28
3
Build Wireframes and Low-Fidelity Prototypes
22
4
Conduct UX Research and Test Early Concepts
24
5
Create High
-Fidelity Designs and Prototypes in Figma 39
6
Responsive Web Design in Adobe XD
41
7
Design a User Experience for Social Good & Prepare for Jobs
62
Total Learning Hours
234
Google’s Professional Certificates adhere to Coursera's best practice guidelines for Quality in
Online Learning and other manuals on online teaching pedagogy and course structures. Each week
is comprised of individual content units that incorporate both theoretical and practical
components. The theoretical components include readings and videos, while the practical elements
are always aligned with the previously covered knowledge. This approach enables learners to
assess their progress not only through small quizzes throughout the learning process but also
through practical exercises that allow them to apply what they have learned. For example, learners
will learn how to complete the UX design process from beginning to end, including: Empathizing
with users; defining user pain points; coming up with ideas for design solutions; creating

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 38
wireframes, mockups, and prototypes; testing designs through usability studies; and iterating on
designs based on feedback. Furthermore, learners can discuss their approaches in the forum and
upload their work at the end of each unit. As a result, there is a continuous and effective interplay
between theoretical learning and practical application.
Intercultural content is appropriately included in the courses where necessary (e.g. content on
country specific regulations on data transfer in Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate and
content on international teams and change management in different cultures in Google Project
Management Professional Certificate).
The Professional Certificates courses are targeting at providing participants with the essential
knowledge and skills required to perform well in their intended job role, including proficiency in
relevant software, programming languages, tools, and systems. The Professional Certificates also
offer an overview of current industry trends. Through practical, hands-on exercises, learners will
develop their methodological competence and practical experience using various business tools
and industry best practices.
The courses adopt a methodological approach to learning, enabling learners to acquire practical
skills through exercises and projects. Learners will have the opportunity to apply their newly
acquired skills in practical settings, preparing them for entry-level positions in the workforce.
The in-depth methods build on the basic knowledge acquired earlier in the course and enable the
planning and use of complex methods for evaluation and assessment. Learners will deepen their
knowledge through projects and practical exercises, including the final capstone projects.
The following types of assessments and examinations are included in Google Professional
Certificates to assess learning outcomes:
● Discussion prompts (formative): Discussion prompts allow for active reflection and
engagement among learners in a public forum on Coursera. Discussion prompts offer a low-
stakes opportunity for learners to reflect on what they have learned, connect new
knowledge to prior understanding, and benefit from discussions and feedback.
● Practice Quizzes (formative): Ungraded quizzes, or practice quizzes, are used to help
leaners monitor their own learning. They answer the question: Is this learner successfully
learning what he or she is expected to learn? When a new concept is introduced, it is
typically tested in an ungraded quiz.
● Self-Review (formative): The self-review activities allow learners to put the course concepts
they are learning into practice by doing an activity or solving a problem. Learners can check
their own work using an Exemplar (an expert-created version of the activity introduced in
the self-review); this helps learners develop insights and check their own understanding.
● Peer-reviewed assessments (formative): The peer review activities allow learners to put the
course concepts they are learning into practice by doing an activity or solving a problem.
In a peer review, learners complete an artifact, review, and grade each otherʼs work, and
receive qualitative and quantitative feedback from other learners. During the assessment
conference Coursera and Google specified the concept of peer review, which is a two-sided
process: In a peer review all learners are obliged to assess and to let their project be

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 39
assessed (by at least three peers). The quality of the assessment is also evaluated by the
learners.
● In-video Quizzes (IVQ, formative): In-video quizzes are ungraded quiz questions that
appear while learners watch a video. IVQs reinforce key concepts, serve as a check-in with
the learner, and review video content with a question that is not difficult or surprising. IVQs
typically appear close to the content they reference and are not grouped at the end of a
video.
● Plugins (formative): Plugins are interactive, hands-on activities that encourage learners to
practice specific tasks and help them apply knowledge they have gained in the course.
There are five main types of plugin activities: drag & drop, multiple choice, infographic,
matching, and flip card.
● Graded quizzes (summative): Graded quizzes are used to monitor educational outcomes.
They answer the question: Has this learner demonstrated that he or she can complete this
task?
Learners are given transparent information about established plagiarism standards and regulations
regarding the conduct of digital assessments on the Coursera platform (Coursera Honor Code).
Appraisal:
The curricula adequately reflect the qualification objectives of the courses. The contents of the
courses are well-balanced, logically connected, and oriented towards the intended learning
outcomes. The lectures and seminars on offer are related in such a manner, that they help the
learners to achieve a great development in their qualification. They are systematically oriented
towards the requirements of a dynamic job market.
In the courses, theory and practice are linked. Knowledge delivery and practical contributions
complement each other to develop the learners’ competences.
Within the limited scope of the courses in terms of workload, international contents are
appropriately integrated according to the courses’ qualification objectives and strategy. The panel
states that intercultural aspects are lived by the instructors. The practical training of intercultural
aspects contributes to the learners’ capacity to act in an intercultural environment. As Coursera
and Google rated international and intercultural contents as “not applicable” (see self-report, p.
32), the panel recommends re-evaluating the communication of international and intercultural
aspects in the course descriptions.
The acquisition of methodological competences is ensured. It is set down as a learning objective
in the module descriptions.
Due to the limited duration and the focus of the programs the integration of academic work and
science-based teaching was rated by Coursera and Google as not applicable. However, during the
assessment conference, learners and completers revealed remarkable aspirations as to further
qualifications and the possibilities of aiming at (further) academic qualifications throughout their
career. The panel therefore recommends serving those aspirations by not only listing recommended

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 40
literature (see recommendation chapter 3.1), but additionally providing a guided process into the
work with further literature. With respect to the condition in chapter 1.1, the panel would like to
point out that a there is also a relationship between EQF level and ability for academic reflection.
All assessments, as they are defined for the courses, are suited in format and content to ascertain
the intended learning outcomes as well as the identity of the examinees. The requirements are in
accordance with the desired qualification level. The course provider has established plagiarism
rules and regulations regarding the conduct of digital assessments. Leaners are given transparent
information about these regulations. During the assessment conference learners and completers
expressed criticism of the current implementation of the peer review assessments. They felt that
safety mechanisms do not work in the case where a learner rates a peer-assessment to be unfair.
The panel therefore suggests considering implementing additional feedback tools for learners
regarding the peer-reviews.
Exceptional
Exceeds quality
requirements
Meets quality
requirements
Does not meet
quality
requirements
n.r.
3.
Implementation
3.2
Content
3.2.1*
Logic and conceptual coherence
X
3.2.2
Integration of theory and practice
X
3.2.3
International and intercultural contents
X
3.2.4
Methodological competence
X
3.2.5
Academic work and science-based
teaching
X
3.2.6*
Examinations
X
3.3 Transdisciplinary qualifications and soft skills
The Professional Certificates cover guidelines for collecting, presenting, analyzing, and
interpreting data using appropriate methods. The programs cover various methods such as
analyzing processes, assessing data, and measuring success. Content covers content on how to
visualize and present data findings in dashboards, presentations and commonly used visualization
platforms, how to provide end-to-end customer support (ranging from identifying problems to
troubleshooting and debugging), how to gain skills required to succeed in an entry-level IT job,
how to practice strategic communication, problem-solving, and stakeholder management through
real-world scenarios. And – following design processes – empathize with users, define pain points,
ideate solutions, create wireframes and prototypes, test and iterate on designs.
In the Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate, for example, learners are also taught how to
communicate results to different stakeholders. In the Google Digital Marketing and E-Commerce
Professional Certificate learners are taught how to build e-Commerce stores, analyze online
performance and grow customer loyalty.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 41
Appraisal:
Although Coursera and Google considered this criterion as “not applicable“, the panel would like
to emphasize that they see evidence of fulfillment of this criterion in all courses. Within the limited
scope of the courses in terms of workload, the learners acquire appropriate transdisciplinary
qualifications in accordance with the qualification objectives. This is supported by means of
suitable didactical and methodological measures.
Exceptional
Exceeds quality
requirements
Meets quality
requirements
Does not meet
quality
requirements
n.r.
3.
Implementation
3.3
Transdisciplinary qualifications and soft
skills
X
3.4 Didactics and Methodology
Courseraʼs platform is built for Mastery Learning, a pedagogical model that allows and requires
learners to demonstrate mastery of learning objectives before moving forward to learn subsequent
information. The platform organizes content into modules, setting scheduled milestones for their
completion, which requires learners to demonstrate mastery of the learning objectives over time.
According to Coursera, Data analysis from thousands of courses shows that well-designed, high-
quality content includes both formative and summative assessments with elaborative feedback to
support learners as they work toward mastery of the defined learning objectives (see self-report,
p.35).
Courseraʼs platform structures content to facilitate Mastery Learning by requiring instructors to set
key learning objectives at the program level, course level, and modular levels.
The practical application of Courseraʼs “learners first” strategy begins with effective content and
program development. Coursera strives to partner with leading content providers to help learners
succeed by completing individual courses or certificate programs. Its real time monitoring of
learner progress is an essential element to support all content providers and learners enrolled in
hosted content of all its courses and programs. As defined by Coursera Professional Certificate
Content Specifications (see chapter 3.1, table 5), the six Google Professional Certificates include
hands-on projects that help learners hone and apply the concepts learned throughout each course
in the asynchronous video lectures, readings, discussion posts, and quizzes.
For example, in the Google Project Management Professional Certificate, learners are instructed
through various teaching methods, including discussion prompts, lectures, peer reviews, practice
and graded quizzes, readings, and hands-on projects. Learners are encouraged to actively
participate in the learning process and engage with other learners through discussion prompts,
peer reviews, and applied learning projects. In the final capstone course of the Google Project

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 42
Management Certificate, learners practice applying the project management knowledge and skills
acquired so far through completing a project management capstone.
Through the Project Management Capstone course, learners will:
● Complete a project charter, filling out key information including a project summary,
SMART goals, scope, benefits, and costs.
● Examine project documentation and conduct research to identify tasks for a project and
organize those project tasks and milestones in a project plan.
● Develop effective stakeholder reports by applying storytelling strategies to describe data.
● Determine quality standards and evaluate against those standards to ensure that the
project is achieving the required level of quality.
By the end of the Google Project Management program, learners will have developed a portfolio of
project management artifacts that will demonstrate the skills learned throughout the entire
program, such as the ability to manage stakeholders and teams, organize plans, and communicate
project details. These artifacts can exhibit career readiness when applying for jobs in the field. To
further prepare learners to interview for project management jobs, learners will reflect on past
projects, develop an “elevator pitch,” and anticipate common interview questions.
Formative and summative assessments with feedback-corrective features are used to measure
progression towards those objectives. Instructors can embed practice and feedback directly in the
learning path using various proprietary tools, including in-video questions, quizzes, technical labs,
and other exercises. Providing frequent opportunities for feedback and active learning helps the
learners track their progress towards mastery. Feedback is also used for summative graded
assessments, which are available to learners at the end of each course module. Whereas practice
assessments are low-stakes formative opportunities that provide feedback explaining why a
response is correct or incorrect, learners demonstrate mastery of the learning objectives by passing
each weekʼs summative assessment. Mastery learning embraces “failure as feedback” to the
learning process; allowing multiple attempts on graded assessments. A learner cannot earn a
completion certificate until they demonstrate mastery of the learning objectives by passing all
graded assessments in a course or program.
All course materials for Google Professional Certificates are included within the course content on
the Coursera Platform. Learners do not need to purchase supplementary literature that Google has
not produced and provided itself, therefore, no external content is integrated in the course
structure. Datasets for hands-on labs are provided in the “Resources” section of the LMS in CSV
format for learners to export to their desktops and use for analysis in practical exercises. Welcome,
and learning/lecture videos for each week are hosted under the “Course Material” section of the
LMS with transcriptions. Under “Course Materials”, learners will also find readings, practice
quizzes, and graded assignments in the order they should be reviewed. Within the LMS, there is a
section for learner notes and discussion forums.
Within the LMS, each week of course material begins with a module description and a clear outline
of learning objectives that should be met throughout the week of study. The lectures, readings,
hands-on projects, and quizzes in each week help learners meet the weekly learning objectives.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 43
Appraisal:
The didactic concept of the courses is systematically oriented towards the course objectives. It is
orientated towards the learning outcomes of each course, module, and towards the target group.
A mix of different teaching and learning methods (Videos, quizzes, labs), depending on the
contents and curricular requirements, is applied in the courses/single modules. The panel
appreciates the innovative and creative approaches Google uses in line with Coursera’s
methodological standards to enable the learners to progress faster and more intensely in their
learning, as well as support them during the self-study phases. Leaners are encouraged to take an
active role in the learning process (e.g., by peer-review).
The accompanying course and learning materials are oriented towards the intended learning
outcomes and correspond to the required qualification level. They are up to date easily accessible
for the learners. The course and learning materials are very user-friendly, but do not encourage
learners to engage in further independent studies (see recommendation chapter 3.2). General
standards for materials guide the teaching staff and support the quality of the lecture.
During the assessment conference, learners and completers expressed that as course contents were
highly inspirational and useful, they felt the demand to interact with instructors aside from the
provided custom forums and discussion prompts (see chapter 4.1). The panel therefore
recommends considering enriching the concept of the asynchronous MOOCs by options of
synchronous teaching formats, like live lectures or real-time interactive formats.
Exceptional
Exceeds
quality
requirements
Meets quality
requirements
Does not meet
quality
requirements
n.r.
3.
Implementation
3.4
Didactics and methodology
3.4.1*
Logic and transparency of teaching and
learning methodology
X
3.4.2*
Course and learning materials
X
3.5 Skills for employment / Employability (Asterisk Criterion)
75 % of Google certificate graduates report a positive career outcome (e.g., new job, promotion, or
raise, see self-report p.38) within six months of completion.
To ensure course instruction aligns with job market demands and promotes course graduatesʼ
employability in the professional field, Coursera and Google align on job role requirements to
create learning outcomes in a subject area that leverages Googleʼs areas of expertise as an
organization. This is formally done through a Job Task Analysis (JTA) in the curriculum development
phase of creating a course. Within the Job Task Analysis, Courseraʼs Teaching and Learning, Content
Strategy, and Content Production Services teams work with Google to identify target job titles to

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 44
identify the primary job title that the Professional Certificate prepares learners for, as well as
alternative titles that can be used to describe the target role. In addition, they estimate the number
of entry-level job openings available on the market that do not require a college degree, along with
the average starting salary of an entry-level candidate entering the targeted role. The Coursera
Teaching and Learning team and the Google team staff conducted a gap analysis and an
environmental scan together, and reviewed audience research, jobseeker insights, and market
analysis data to inform course and program development decisions.
The content team of Google conducts job field and learner analysis and creates research-based
learner personas. The content development team at Google held curriculum design sessions in
partnership with SMEs to align on learning outcomes, create learning objectives, and build syllabi
for each course in the Professional Certificate programs.
The nature of self-responsible online learning also promotes the individual development of
organizational skills, specifically concerning time management. These essential skills are integral
to asynchronous online learning experiences; due to structure and learning methods, learners are
guided in this process to reach the intended level of competence. Analyzing problems and making
decisions are competencies that learners require and develop in different course units of the “Entry-
level Professional Certificates”.
Through labs, interactive practice activities, and/or final capstone projects, learners' skills are
further developed through ongoing practical application of the theories and models learned.
Completers of the Professional Certificates are intended to have up-to-date specialist knowledge
and methodological skills in the corresponding qualification areas of the job requirements on which
the certificates are based. They already have practical experience in the application of this
knowledge. They have demonstrated their reliability through their self-motivated and committed
learning and successful completion of the courses. The completers practical experience facilitates
their entry into the world of work or support their career switch into a new industry or job type
upon completion of the certificate. Detailed work samples or portfolios could already be built up in
some certificates.
Example: Job-Task Analysis methodology: Google UX Design Professional Certificate
Coursera and Google performed a Job Task Analysis (JTA) in the curriculum development phase of
the UX Design Professional Certificate. Through the JTA, Coursera and Google identified and
assessed role descriptions and key required skills of the entry-level roles of User Experience (UX)
Designer, UI Designer, Interaction Designer, which informed course learning outcomes. In addition
to identifying learning outcomes through in-demand skills and job-relevant role descriptions, the
teams took into account the number of job openings in the past twelve months, the number of job
openings not requiring a college degree, the number of job openings requiring zero to two years of
work experience, and the number of job openings not requiring a college degree. The role
description for an entry-level UX/UI Designer is as follows:
● Assist with technology design to make products easier for people to use.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 45
● Determine user preferences and assess the process that users follow to access product
functions; develop and test new design models, and incorporate findings into improved
product design.
● Research the behavior of internet users and consumers, compile information about the
target audience for a site, and develop website layout, design and technology features that
improve accessibility and value for users.
● Partners with internal departments to develop an understanding of concepts and business
requirements.
● Applies user centered design methodology to develop an understanding of and serve as
the advocate for the end user.
● Consults with software and content developers to understand and accommodate technical
constraints and reflect appropriate content format and search functionality in the designs.
● Develops wireframes, sitemaps and other design renderings which define the user
interface form, function, navigation, interaction, and basic screen layout.
● Work closely with internal departments to bring products to market, develop and grow
business opportunities, and enhance the customer experience.
● Must have a portfolio demonstrating relevant experience.
This course is designed to ensure that graduates are employable by teaching and assessing key
learning outcomes for skills required by the User Experience Design profession. This includes the
skills of UX Wireframes, Prototyping, Website Design, Graphic Design, User Research, Interaction
Design, Project Management, Web Application Development, Process Design, Product Management,
UI Design, JavaScript, Visual Design, and Adobe Suite. In addition, once learners complete this
course, they have access to job placement support through the Completer Community on Coursera.
This includes a suite of resume and interview prep videos, downloadable resume templates, free
virtual interview practice, a job board with relevant local, regional and national roles, and forums
to connect with other learners and inspiring learner stories.
A similar methodology to this example was applied for the other courses. Coursera provided JTA for
all programs under consideration, utilized to align the learning objectives of Professional
Certificates to required skills for related job openings.
Learners completing Google Professional Certificates on Coursera can also avail no charge access
to Googleʼs employer consortium with more than 150 companies - like Bank of America, Walmart,
Hulu, Intel, GE Digital, PNC Bank, and Google- that consider Google Career Certificate graduates
for their roles. In addition to expert-led training and hands-on projects designed to prepare
learners for a job, learners get access to
an interview practice tool, mock interviews and resume
building workshops, and career coaching sessions.
In addition, once learners complete the courses, they have access to job placement support through
the Completer Community (“Professional Certificate Career Resources”) on Coursera. This includes
a suite of resume and interview prep videos, downloadable resume templates, free virtual interview

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 46
practice, a job board with relevant local, regional and national roles, and forums to connect with
other learners and inspiring learner stories.
Appraisal:
The contents focus on achieving the qualification objectives and have a clear profile. Employability
in accordance with the qualification objectives and the defined learning outcomes is promoted,
adding a benefit for course completersin the respective occupational field.
In addition, the courses are systematically aligned with the expected requirements of a dynamic
labor market. For this purpose, the course provider uses evaluation results (course completers,
employers). The panel highlights that the development of specific job market related skills by a
content partner (Google) that itself sets global standards for the application of these skills, is a
unique selling proposition. The panel also highlights that the Professional Certificate Career
Resources also provide country specific profiles (e.g. Job Search Guide).
Exceptional
Exceeds quality
requirements
Meets quality
requirements
Does not meet
quality
requirements
n.r.
3.
Implementation
3.5*
Skills for employment / Employability
X

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 47
4 RESOURCES AND SERVICES
4.1 Teaching Staff of the courses
Courseraʼs Pedagogy Principles incorporate findings from peer-reviewed educational research
and learning science. Coursera bases its platform technology and education philosophy on
Mastery Learning (see chapter 3.4), which focuses on the importance of feedback in learning
and promotes the mastery of a topic before moving on to more advanced materials.
Quality education that supports Mastery Learning requires the tight alignment of learning
objectives, instructional materials, and assessments. Instructors and curriculum developers
use backward design by creating learning objectives and assessments before content and
instructional materials. All content on Coursera must include these Pedagogy Principles:
Table 10: Coursera Pedagogy Principles
A Google Senior Instructional Designer (equivalent to the program manager) oversees content
production from end to end and partners with internal Google SMEs and stakeholders to ensure
quality of learning materials. Each Google Professional Certificate is developed by a team of subject
matter experts, teaching experts, content creation experts/staff, technical content writers, and
program managers and instructional designers. Subject Matter experts and Instructors of the
programs are selected based on their professional working experience and academic expertise with
regards to curriculum design. They also need technical competencies to create certificate content.
Google instructional designers partner closely with subject matter experts (SMEs) with direct
experience working in the job field of the certificate. Together they identify key skills and job-
related outcomes, best practices, tools commonly used in the profession, and opportunities for
hands-on practice.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 48
The Google team of SMEs, teaching experts, content creation and instructional designers work
collaboratively within the framework of the general project management to operationalize the
predefined learning objectives, divide them into units and logically sequenced learning elements,
and collect and prepare the corresponding materials through internal cooperation. They prepare
materials in the form of videos, reading units, discussion boards, quizzes, and activities as outlined
by the Coursera Pedagogy Principles. On the Coursera platform within the course description page
learners find information on instructor’s backgrounds and qualifications.
Instructors for the Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate include eight subject matter
experts and course developers/instructional designers with expertise in data analytics, finance
analytics, program management and research. Instructors for the Google Digital Marketing and E-
commerce Professional Certificate include seven subject matter experts and course
developers/instructional designers with experience in product marketing, digital marketing and
sales. Instructors for the Google IT Support and IT Automation with Python Professional Certificates
include 13 subject matter experts and course developers/instructional designers with expertise in
site reliability engineering, technical risk, privacy engineering, program management, privacy,
security and compliance, and technical solutions architecture. Instructors for the Google Project
Management Professional Certificate include six subject matter experts and course
developers/instructional designers with expertise in program management and technical program
management. Instructors for the Google UX Design Professional Certificate include eight subject
matter experts and course developers/instructional designers with expertise in user experience
design, user experience research, and interaction design.
According to Coursera and Google (see self-report p. 43), the teaching staff members' and subject
matter expertise, practical experience, and pedagogical and didactic qualifications have undergone
thorough assessment and documentation, thus supporting the certificate's quality profile and
practical orientation. Significant emphasis is placed on the practical experience of the teaching
staff, the instructors have accumulated years of professional experience, averaging twelve years.
As a provider of application-oriented education, Coursera and Google recognize the value of
practical experience in teaching the required practice-oriented knowledge credibly. Therefore,
instructors are continuously assessed through the feedback mechanisms (see chapter 6.2).
All instructors for the Google Professional Certificates are subject matter experts by training, job
role, or research for each topic at Google. Google selects instructors that provide a global presence
and have a range of real-life experience. Instructors have provided evidence of previous academic
training, such as a diploma or bachelor's degree.
Coursera also offers further staff development and qualification measures, including training and
best practices through the Coursera Classroom teaching and learning opportunities.
To provide transparency, the following table displays the qualification and expertise distribution
among instructors for the Google certificates:

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 49
Table 11: Google Professional Certificates instructors’ qualifications
Qualification
Number
Percentage
as Diploma or Bachelor
29
69%
as Master
11
26%
as Ph.D.
2
5%
as professional experts
42/42
100%
The Coursera Teaching and Learning team includes pedagogy experts with graduate degrees in
Cognitive Science, Computer Science & Engineering, Education, Instructional Design, and
Neuroscience as well as AI engineers, software developers and marketing professionals. This team
has developed extensive resources on best practices for online education, based on Courseraʼs own
data from millions of learners and learning science research.
The Coursera Teaching and Learning team is available from the second project phase, the start of
course development, with advice and practical help as well as many useful tips, manuals, and best
practice tips, is involved in intensive QA work to ensure the quality of the learning units and, in
case of doubt, checks each learning element individually for quality and function. Even though the
function is more of an advisory nature, there are explicit veto rights during implementation and
before go-live to initiate changes before the first learners come into contact with the materials. The
Teaching and Learning Team is involved in all phases of the project.
If Google decides to work with third parties, the tasks will be carried out in regular consultation
between the three parties. In the event that the provider does not yet have the appropriate
resources internally or has contact with third party providers, Coursera has a preferred vendor list
to recommend providers who have already gained experience with Coursera and the necessary
didactic concepts and to carry out the development together with them.
Both in terms of the content provided and via cross-checking with Coursera's internal subject
matter experts and the experts from Google, regular checks and reviews are carried out to ensure
that only qualified personnel are working and that the result is subject to standard quality control.
In addition, Coursera Classroom resources are available to all content providers. In addition to the
numerous manuals and guidelines, systematic onboarding about Coursera, the use of the platform,
the available tools and much more takes place here. There are courses such as "Getting Started
with Coursera", "Coursera Administrator Training", "Build and Enterprise Guided Project", and
"Technical Assessment Basics".
Learners are supported and coached by instructors and teaching staff through a variety of
proprietary tools in the learning path, including in-video questions, quizzes, technical labs, and
other exercises. Providing frequent opportunities for feedback and active learning helps the learner
track their progress towards mastery. Feedback is also used for summative graded assessments,
which are available to learners at the end of each module of a course. Whereas practice assessments
are low-stakes formative opportunities that provide feedback explaining why a response is correct

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 50
or incorrect, learners demonstrate mastery of the learning objectives by passing each weekʼs
summative assessment. Outside of feedback related to formative and summative assessments,
instructors can create engagement opportunities with learners through custom forums where
learners can engage with instructors by asking questions and answering discussion prompts.
Learners and instructors can also engage via email messaging in the “Messages” section of the
Learning Management System.
Appraisal:
The qualifications and experience of the course management as represented by the Google Senior
Instructional Designer correspond with the requirements of the course. Google’s course
management is responsible for the quality of the course as a whole (content and methodology),
following Coursera’s Content Specifications and Pedagogy Principles and in close co-operation with
Coursera.
The subject-specific, pedagogical and didactic qualifications of the teaching staff correspond with
the requirements of the courses. Special characteristics of the target group are considered. The
teaching staff has above-average business experience (evidences in their CVs) and according to
learners and completers, uses it in a clearly visible and valuable way in their teaching activities.
Having checked the biographies of the teaching staff and talked to representatives during the
assessment conference, the panel highlights the relevant practical experience of all teaching staff
within Google of five to 20 years as a unique selling proposition. The panel also highlights that
Google assigns teaching staff with a dedicated international background.
By providing assessment procedures for the pedagogical training of the content partner’s (Google)
instructors, Coursera verifies the pedagogical qualifications and competence of the teaching staff
by means of established procedures. Coursera also provides pedagogical training opportunities for
the content partner’s (Google) instructors.
It is systematically ensured that the teaching staff cooperate internally for the purpose of tuning
the course components towards the overall qualification objectives (see also chapter 6). There are
regular meetings of all those teaching in the course. In addition, projects are conducted
cooperatively. An integrative approach is practiced.
The structure and number of teaching staff (instructors) correspond with the requirements of the
courses. Support of the learners is an integral part of the services provided by the teaching staff.
Support is offered on a regular basis and serves to help participants learn successfully. Due to the
nature of the MOOC approach, the role of an instructor focusses on the development of course
content and interaction within the course (videos, in-video questions, quizzes, assessments,
technical labs, discussion forums, etc.). The support of the learners during the course is mainly
limited to technical and legal aspects regarding the course organization of the course environment
(although instructors can create engagement opportunities with learners through custom forums or
via email). As already mentioned in chapter 3.4 the panel has gained the impression from learners
and completers that they would appreciate some more active interaction with on-screen-instructors
(see recommendation chapter 3.4).

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 51
Exceptional
Exceeds quality
requirements
Meets quality
requirements
Does not meet
quality
requirements
n.r.
4.
Resources and Services
4.1
Teaching Staff of the courses
4.1.1*
Course management
X
4.1.2*
Structure and number of teaching staff in
relation to curricular requirements
X
4.1.3*
Teaching staff’s qualifications
X
4.1.4*
Teaching staff’s pedagogical /didactic
qualifications
X
4.1.5
Practical experience of the teaching staff
X
4.1.6
Internal cooperation
X
4.1.7*
Learner support and coaching
X
4.2 Process organization and administrative support for learners and
teaching staff (Asterisk Criterion)
Coursera offers learner support and educator support designed to empower learners, educators,
and administrators to do what they need to do on the Coursera platform. The Learner Help Center
aims to help learners with questions they have on the Coursera platform from finding courses to
take, to participating in their chosen course, to troubleshooting technical issues as needed. The
Learner Help Center is exclusively for Coursera learners before, during, and after their course
participation and completion. Learners can reach the Learner Help Center 24/7 (includes 24-hours
live chat support and clientsupport@coursera.org responding within one hour) and get assistance
in the following areas:
● Account settings, login issues, and notification preferences. Here, learners can get help
with setting up their Coursera account, changing account settings and password
troubleshooting, changing email notifications, and using the Coursera mobile app.
● Payments and subscriptions. Here, learners can receive help with payments for their
courses, apply for financial aid or scholarships, learn about their subscription details, and
receive information about promotions and free trials.
● Enrollment options. Learners can receive help enrolling or un-enrolling in a course and
finding courses to take.
● Grades, peer reviews, assignments, and labs. Learners can receive help with
troubleshooting the submission of peer-reviewed assignments, taking quizzes and
assignments, checking grade details, understanding how to complete programming
assignments, in-browser coding, and common issues with Coursera Labs.
● Sharing and verifying Course Certificates. Learners can access guides on how to

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 52
download and share course certificates, verify their identity, and solve problems with
course certificates.
● Coursera Policies and Program Terms. Learners can access accessibility statements
25
,
accommodations for learners with disabilities, third-party policies, code of conduct, honor
code, age restrictions, General Data Protection Regulations, and more.
● Course content, including videos, discussion forums, and common course issues.
Learners can receive help troubleshooting problems with the Coursera platform, learn about
recommended browsers and devices, receive assistance with video settings and subtitles,
report problems within a course, and receive help with course content in discussion forums.
Learners can also report abuse in forums here.
Learners receive a first response in chat support in under two minutes, with a full resolution in
under 15 minutes.
The Coursera Educator Resource Center, exclusive to Coursera instructors, is a place for both self-
service and on-demand support to ensure the success of the digital classroom. Instructors can reach
the Educator Resource Center 24/7 and get support in the following areas:
● Platform onboarding & best practices. View articles, instructional videos, and frequently
asked questions on Coursera terminology, production milestones, partner communication
channels, recommended browsers, and Coursera Pedagogy Principles.
● Creating course content. View resources on creating and organizing instructional material
in lessons and modules through course authoring tools, digital course content management,
templates for importing and exporting course outlines, video recording, and formatting
guidelines, importing and exporting content assistance, reading item management, and
more.
● Developing effective assessments and managing learner submissions. Learn how
assessments on Coursera work, how to set and adjust grading formulas, how to add new
assessment items, auto-graded questions, and question variations, peer review
assignments, how to manage quizzes, staff graded assignments, and discussion prompt
management. This section also includes information on programming assignments, team
assignments, high-touch grading features, question banks, proctored assignments, and
academic integrity.
● Building custom learning content and programming assignments. Instructors can learn
about how to create custom programming assignments, lab activities, and coding labs.
Learn about developing, managing, and adding plugins, in-browser coding, and managing
and configuring code blocks.
● Viewing tips for launching, branding, and marketing content. Through this resource,
instructors can learn how to launch a new course, set a target launch date, marketing
recommendations, improve search engine optimization, how to beta test, and how to reach
25
https://www.coursera.support/s/article/360050668591-Accessibility-Statement?language=en_US (last
call August 7, 2023)

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 53
new learners in the Coursera community.
● Managing their course staff, landing pages, and other settings. Instructors can learn
how to manage staff roles and permissions, how to copy a course, how to invite group
members, manage landing pages and brand assets, update and manage course certificates,
and how to create and manage private sessions.
● Interacting with learners through discussion forums and announcements. Here,
instructors can learn how to leverage Coursera discussion forums, send course
announcements and messages, recruit mentors to help support learners, and schedule live
events.
● Tracking content performance with data dashboards and exports. Instructors can learn
how to leverage course dashboards, download grade books, manage organization
dashboards, and export data.
● Finding content and accessibility policies. Here, instructors can review content policies,
platform changes, sharing and research policies, data privacy information, and copyright
guidelines.
All employees have access to all learning opportunities on the platform, and partners, like
employees, have additional access to Coursera Classroom Resources and Coursera Administrator
Training.
Appraisal:
The panel was impressed by the feedback management in terms of process organization and
administrative support. The main processes and responsibilities are described. The administrative
staff operates as service provider for both learners and teaching staff, contributes to the further
development of the course in cooperation with the relevant groups and prepares for the learner’s
needs in advance. The administrative contact is regularly available to help with enquiries and acute
problems and questions. The course provider offers continuous professional development for the
administrative staff. Opportunities of electronic service-support are intensively and effectively
applied.
Exceptional
Exceeds quality
requirements
Meets quality
requirements
Does not meet
quality
requirements
n.r.
4.
Resources and Services
4.2*
Process organization and administrative
support for learners and teaching staff
x

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 54
4.3 Networking
Learners are supported in creating and maintaining networks through discussion forums monitored
by Google subject matter experts. In discussion forums, learners receive support from one another
on course-related topics and create and maintain networking opportunities. Discussion forums
benefit learners by providing a space for interaction with classmates, sharing resources, and help
to answer questions about course materials or assessments. They are used for asking questions,
debating ideas, and identifying other classmates who share the same goals so they can pursue
networking opportunities and conversations.
In addition, all Professional Certificate completers receive access to the Professional Certificate
Community, which not only provides further peer support, but also offers a range of career services,
resume support and interview practice.
Google Career Certificates also include content that teaches learners how to set up a professional
network and maintain connections that will be helpful to their career, such as professional social
media profiles, elevator pitches, and personal portfolios and websites.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 55
Table 12: Coursera Professional Certificate Career Resources
Appraisal:
Promoting networks is part of the didactical approach of Mastery Learning. The learners are
supported in creating and maintaining networks by measures Coursera and Google provide to them
like peer review assessments. The panel points out that the felt/subjective unjustified grading
during peer-review assessments (see chapter 3.2) may lead to impeding network creating and
maintaining.
Exceptional
Exceeds
quality
requirements
Meets quality
requirements
Does not meet
quality
requirements
n.r.
4.
Resources and Services
4.3
Networking
X

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 56
4.4 Cooperation with academic institutions or enterprises (Asterisk
Criterion for cooperation courses)
Cooperation of Coursera with all content partners for Professional Certificates (i.e. Google in this
case) follows a general pattern Coursera has developed:
Coursera´s content strategy teamʼs core initiatives are divided into a three-pronged approach:
1. Identify: Identify in-demand jobs and skills, and translate them into relevant content and
credentials, and a sourcing strategy to meet learners’ needs,
2. Advise: Leverage data and domain knowledge to advise other internal teams and external
partners on content to add to Coursera, and
3. Innovate: Collaborate on or incubate new content types (e.g., projects), emergent domains
(e.g., health), and launch strategic efforts to ensure continuous content output. The content
strategy team utilizes relevant databases (both public and private) while simultaneously
working closely together with a network of enterprises and organizations as well as with
academic institutions and university partners to analyze needed skill sets and
qualifications that have an impact on the career readiness of learners. The knowledge and
competencies acquired in the course are mutually recognized and confirmed through
intensive on-platform and off-platform analysis and form the initial set of required learning
objectives.
Cooperation with the content partners:
Having established the foundation for the in-demand course the content strategy team assesses
potential partners to provide the respective course with the help of an established evaluation
process and judging the readiness of the potential partner to deliver the required learning contents.
Moreover, part of this iteration is researching the right topic to be matched with the right content
partner. For that, brand perception, international reach, the companyʼs overall strategy,
employability, size, among other metrics, are taken into consideration. To ensure that the courses
provided by Coursera and the content partner fulfill set quality standards (blueprint), both maintain
active cooperation with relevant networks, enterprises, and other organizations. Target and
outcomes are fixed in a Course Term sheet and later form the basis of the contractual agreements
between Coursera and the content partner.
Quality Assurance in Implementation:
During implementation, either the key account manager (program responsibility) or a dedicated
implementation success manager ensures that all work streams according to Coursera’s blueprint
for high-quality courses, are being well informed, kicked off, have their relevant action items and
keep their deadlines in order to complete the production process of the course to a level where the
beta testing can start (see also chapter 6).
Initial launch and further cooperation:

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 57
Feedback from the beta testing is discussed with Google and changes are recommended. After the
last QA test has successfully been achieved, content can go live on the platform. The cooperation
is followed up by Coursera’s Industry or University Partner success teams and enables Coursera to
stay abreast of current trends and technologies and to develop courses and teaching materials
accordingly. In addition, Coursera participates in research projects and events to gain valuable
insights and further enhance teaching and learning quality. All cooperation is documented in detail
and regularly evaluated. The course provider regularly reviews and updates the agreements to
ensure that all activities contribute to developing the learnersʼ qualifications and skills. After the
initial start yearly success meetings are conducted between Coursera and its partners and past
performance as well as goals for the next year are discussed and action items agreed upon that will
then again feed the PDCA quality cycle of the Coursera QA process (see also chapter 6).
Feedback loop:
After the content is launched, Coursera starts receiving feedback from learners and from the content
partner (Google) itself. Therefore, both the quantitative performance data as well as the qualitative
information received is taken into consideration for future content mapping by Coursera’s content
strategy team making sure that they can collaboratively learn from their mistakes and celebrate
their successes (see also chapter 6).
Appraisal:
The panel acknowledges an effective and professional co-operation between Coursera and Google.
Cooperation with the content partner (i.e. Google) is aligned with the strategy of the course and
actively promoted for example, by means of regular project work involving those who contribute to
the courses in responsible positions to discuss the further development of the programs. The
cooperation is actively pursued and has a clear impact on the conception and implementation of
the courses. Such cooperation has a formative impact on the curricular contents and on the profile
of the completers.
The agreements forming the basis of the cooperation with Google are documented. All such
activities contribute to the development of the learners’ qualifications and skills. Coursera ensures
that the quality standards are met. Processes to enable this are coordinated closely with Google.
Exceptional
Exceeds quality
requirements
Meets quality
requirements
Does not meet
quality re-
quirements
n.r.
4.
Resources and Services
4.4(*)
Cooperation with academic institutions or
enterprises (asterisk
criterion for
cooperation courses)
X

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 58
4.5 Technology and Facilities
4.5.1 Technical organizational unit
For the work of the technical organizational unit to enable and support the implementation of
digital teaching see description of the Coursera Educator Resource Center in chapter 4.2. Coursera
regularly maintains and updates the Educator Resource Center and the Coursera platform with
guides on various innovative technologies and tools for teaching, digital classroom management,
assessment management, and learner management so that instructors can create a seamless digital
learning experience for learners.
4.5.2 Teaching and Learning platform (Asterisk Criterion)
The Coursera platform is designed to enable learners to discover the right content and credentials
by domain (e.g., business, technology, health), by skill (e.g., Python, statistics, data visualization),
and by job role (e.g., data analyst, marketer, engineer). Once learners enroll in a course, the unified
technology platform is designed to enable them to learn more effectively to advance in their careers
and earn credentials to signal their learning to prospective employers.
The learning experience includees:
● Courses with video-based lectures, in-video quizzes, notes and highlights, readings,
assessments, peer reviews, and group projects;
● AI-driven learning features such as In-course Coach, Smart Review Material, and Goal
Setting to help learners stay motivated and making progress;
● Coursera Labs with hands-on projects that teach practical skills using real-world tools such
as Python, Jupyter Notebooks, VS Code, R-Studio, and many other desktop and cloud-based
applications fully in-browser with no software or data downloads;
● A mobile app that is designed to enable course downloads for offline learning, regarded to
be especially important for leaners with limited or intermittent internet connectivity or
power; and
● Localized learning experiences including localized homepage, payment options, local
partnership, and content discovery.
Learners enroll in their preferred course by clicking “Enroll” and subscribing to Coursera through
the course description page. After enrolling, learners can view all course
26
content by module and
week, continue to the course and begin navigating the Coursera platform. Within the platform, there
is a navigation bar that contains sections including Course Material, Grades, Notes, Discussion
Forums, Messages, and Course Information. All tools and multimedia files are integrated into the
Coursera platform, and the entirety of teaching and learning activities in Coursera courses occurs
within the Coursera platform.
● Course Material: In this section, learners can navigate throughout the weekly learning
material. Each week begins with a summary overview, introductory videos, an overview of
the learning objectives, video lecture, readings, and assignments, and ends with a summary
26
For Coursera terminology program/course/module, see chapter 3.1 and glossary.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 59
of the week.
● Grades: In this section, learners can view the quiz or assessment item, their completion
status, the due date, the weight of the quiz or assessment item, and their grades.
● Notes: Learners can utilize the Notes section as a digital notebook, where notes are
collected throughout the duration of their study.
● Discussion Forums: Instructors can create custom forums to provide a space for learners
to interact with one another. Learners can share resources and help answer questions about
course materials or assessments. This section holds all discussion forums for the course by
week, where learners can discuss the weekʼs modules or respond to assigned prompts.
Discussion forums can also be used to ask questions, debate ideas, and find classmates
who share their goals. Forum guidelines are available for reference in the Discussion
Forums section of the LMS.
● Messages: In the Messages section, learners can read messages from the instructor,
organization, or Coursera support. Instructors can send messages to learners to
communicate important updates and information. They can send course announcements to
all learners who meet certain criteria, like those who are currently enrolled or have
completed the course. Instructors can also send announcements only to learners in a
specific private course instance.
● Course Information: In the Course Information section, learners can view a course
description and course details, view instructor information, and review the syllabus.
In addition to the above features of the Coursera platform, learners can access the Learner Help
Center, and Instructors are able to access the Educator Resource Center, directly through their
respective LMS instance.
In order to enable learning outside the homepage, i.e., without constant access to the internet,
learners have the possibility to download all videos, the corresponding transcripts and toolboxes
to their own computers and to read and edit the materials offline.
In addition, Coursera offers a learning app for download via all common app stores. Learners can
keep track of their current learning status, view and download the relevant elements of the current
week or the entire course, and watch videos directly in the app. The app also offers the possibility
to receive learning reminders as a notification and to be reminded of learning at self-determined
times. Only the software-supported labs require learning on a computer.
Another feature was made available with the last update. With the new "audio only" mode,
participants can now listen to only the audio track of selected videos.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 60
Accessibility
Coursera’s mission is to provide universal access to the world's best education. They are committed
to achieve the goal of maintaining access to the website and mobile applications to all learners,
including those with disabilities via the following:
● Coursera strives to comply with the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (“WCAG”) 2.1 AA
published by World Wide Web Consortium.
● All course lecture videos offer closed captioning. Learners may flag issues while watching
lecture videos and are encouraged to submit support tickets for content that is not
captioned appropriately. Coursera is committed to address the matter promptly.
● Courseraʼs videos are available to learners at any time which allows learners to get a head
start on the course.
● An independent accessibility consultant periodically reviews the platform. Potential
accessibility issues are identified so that Coursera can address such issues and take any
remedial actions deemed necessary.
● Coursera developers engage in training and projects relating to accessibility that both
educate and improve the accessibility of their products as they are being developed.
● Coursera has published accessibility guidelines for content providers and contractually
requires that content providers comply with their independent obligations under
applicable accessibility laws.
● Coursera manages an email alias where incoming accessibility support tickets from
learners are addressed.
The Learner Help Center has resources for learners with disabilities
27
.
Data Protection
Data is collected by Coursera from the learning management system and platform in a variety of
ways for learning analytics and course performance. Large amounts of data can be processed, as
Coursera courses are open to unlimited learners. Coursera has built product features that give
learners more control over their data. Coursera has also contracted with third-party vendors to
perform certain specialized tasks, including processing personal data.
These vendors fall into the following categories:
● Hosting. The Coursera platform is hosted on third-party servers.
● Analytics/Marketing. To improve Coursera and the content offered, Coursera uses various
third-party analytics and marketing tools to refine offerings, understand learner habits,
optimize the platform, and tailor marketing efforts.
27
https://www.coursera.support/s/article/208280056-Accommodations-for-learners-with-
disabilities?language=en_US (last call August 7, 2023)

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 61
● Customer Support/Communication. To provide customer support, Coursera uses third-party
tools and services to communicate and respond to questions promptly.
Coursera has implemented a series of changes to bring policies and procedures into GDPR
compliance. Coursera has updated the Terms of Use and Data Protection Addendum, Privacy
Policies, and Cookies Policy
28
to be more transparent about how Coursera uses learner data. In
accordance with GDPR, Coursera has changed the age of consent for residents of EEA (European
Economic Area) to use the services
29
.
4.5.3 Data Analysis System
Data is collected by Coursera from the learning management system and platform in a variety of
ways for learning analytics and course performance. Large amounts of data can be processed, as
Coursera courses are open to unlimited learners. Some ways Coursera collects learner feedback
include:
● Numeric course ratings
● Thumbs-up or thumbs-down feedback (likes and dislikes)
● Problem reports on individual content items in the course
● Written feedback (e.g., content reviews and post-course stories)
Ratings and stories provide instructors with direct feedback from learners. This is especially
valuable in helping instructors improve the learner experience. Based on this feedback, instructors
can revise materials and fix errors.
Coursera collects data and summarizes feedback in the form of self-service dashboards. Instructors
can view a variety of dashboards to assess course performance, learner performance, and
organizational performance. Below are examples of what kind of data is collected within the various
dashboards:
● Course summary dashboard: The Course Summary Dashboard is the first-course dashboard in
the Analytics tab of the Course Overview page. It provides a snapshot of some key metrics for
the course, such as basic retention, daily and monthly engagement, feedback and ratings, and
more. This data can help Coursera and Google staff (Senior Instructional Designer, subject
matter experts, instructors) to gain more insight into the learner experience of the course to
make improvements to the course content. Data in the Course Summary Dashboard starts being
captured after a course's description page is launched and as soon as visitor information is
available.
● Course content feedback dashboard: The Course Content Feedback Dashboard is where one
can find comments from learners in a live course, see feedback that learners have submitted for
specific course items, and investigate any problem reports. Dashboard data becomes available
about 15 days after a course opens to learners. Learner feedback data (such as likes or dislikes
28
Terms of Use; Data Protection Addendum; Privacy Policies; Cookies Policy (last call August 7, 2023)
29
https://www.coursera.support/s/global-search/age%20restrictions?dataCategory=LHC (last call August
7, 2023)

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 62
on course items) and problem report data (such as comments and reports on problems on
course items related to technical issues, content improvement flags, and offensive content
flags) are included in course content feedback dashboards.
● Quiz grades dashboard: The quiz grades dashboard includes an overview of basic quiz metrics,
including graph distribution and submission data, as well as detailed question-level data for
learner quiz responses.
● Institution dashboard: The institution dashboard provides comprehensive data across an
institution or organizationʼs Coursera content so that the Google can track and analyze the
performance of the content Google has on the Coursera platform. Institution dashboards
include an overview of key metrics such as enrollments, completions, and engagement,
institution reach and demographic data, and revenue disbursement.
● Gradebook exports: Gradebook exports supplement the grading data in the quiz grades
dashboard and the Gradebook Manager. They come in the form of a CSV file containing rows for
learners per course and columns for information like the grades learners have received on their
assessments, their submission times, their overall course grade, and whether learners have
earned a Course Certificate. Course-level grade book exports include grading data for an entire
course across all sessions and course versions. All required assessments in a course are
included in the exports, and hashed identifiers are shown in place of any personally identifiable
information (PII) to protect learner privacy. Group-level grade book exports include grading
data for learners in a group or private session. Grading data for all required assessments in a
course are included in group-level exports, as well as the names and email addresses of
learners.
4.5.4 Technical support for learners (Asterisk Criterion)
Apart from the administrative support that learners receive from the Coursera Learner Help Center
(see chapter 4.2) learners can also reach the same hotline for technical support
30
. The Learner Help
Center includes 24-hour, live chat support for immediate issues. Learners can email
clientsupport@coursera.org or submit a form through the Learner Help Center “Contact Customer
Support” portal to receive help over email. Coursera technical support usually responds to requests
by email within 24 hours and responds to chat support immediately.
Coursera supports learners in using technologies and tools to enable digital learning and increase
digital skills through the various articles, tutorials, videos, and help resources available in the
Learner Help Center. The Learner Help Center aims to help learners with questions they have on the
Coursera platform from finding courses to take, to participating in their chosen course, to
troubleshooting technical issues as needed.
4.5.5. Access to required literature
By enrolling in the course content through the Coursera platform, learners receive access to a
number of course items, including lecture videos, readings and labs. Materials are aligned with the
30
https://www.coursera.support/s/learner-help-center-contact-us?language=en_US (last call August 7,
2023)

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 63
course content and learning objectives and are kept up to date within the Coursera learning
management system.
Appraisal:
The technical organizational unit enables and supports the implementation of digital teaching.
Teachers have sufficient advisory and support services available. The technical organizational unit
follows trends and enables teachers to implement innovative technologies and tools in teaching
beyond the standard.
The teaching platform is clearly structured and designed to be user-friendly. It is stable and
scalable and there are no disruptive impulses when using it. It offers sufficient possibilities for
embedding text, audio, images, graphics, animation, multimedia files and social media. Leaners
can navigate smoothly through the teaching units. The teaching platform offers sufficient
opportunity for collaborative learning.
Coursera has access to a data analysis system and sufficient technology or resources to process
large amounts of data.
Learners can reach the technical support of Coursera easily. Questions regarding digital teaching
and the teaching platform are answered quickly. Coursera ensures that learners are able to handle
the technologies and tools.
Coursera provides access to all necessary literature, articles and information within the course. The
information is aligned with the course content and up to date. A concept for the course’s continuing
development (update) is available. To further develop the courses and serve learners’ aspirations
31
,
the panel recommends systematizing access to subject-specific databases like IEEE (Institute of
Electrical and Electronics Engineers).
Exceptional
Exceeds quality
requirements
Meets quality
requirements
Does not meet
quality re-
quirements
n.r.
4.
Resources and Services
4.5
Technology and Facilities
4.5.1
Technical organizational unit
X
4.5.2*
Teaching and Learning platform
X
4.5.3
Data analysis system
X
4.5.4*
Technical support for learners
X
4.5.5
Access to required literature
X
31
see also recommendation in chapter 3.2 for a guided process into the work with further literature.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 64
5 DOCUMENTATION
The Google Professional Certificates are documented and publicized through the Coursera platform.
Learners can access the entirety of the course description and learning objectives before enrolling
in the course through the course description pages. Learners can access all course data and content
by enrolling in Professional Certificates at the following points of registration:
● Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate:
https://www.coursera.org/professional-certificates/google-
data-analytics
● Google Digital Marketing & E-Commerce Professional Certificate:
https://www.coursera.org/professional-certificates/google-digital-marketing-
ecommerce
● Google IT Automation with Python Professional Certificate:
https://www.coursera.org/professional-certificates/google-it-
automation
● Google IT Support Professional Certificate:
https://www.coursera.org/professional-
certificates/google-it-support
● Google Project Management Professional Certificate:
https://www.coursera.org/professional-certificates/google-project-
management
● Google UX Design Professional Certificate:
https://www.coursera.org/professional-certificates/google-ux-
design
32
All course content, including lectures, projects, readings, assessments, and assignments are
accessible for interested parties within the Coursera platform. The coursesʼ content, curricula, and
assessment schemes are documented on the course and module description pages accessible by
the stated web address.
In addition to course documentation through the Coursera platform, Coursera’s academic policies
and procedures related to accommodations for learners with disabilities, age restrictions,
accessibility, honor code, general data protection regulations, international restrictions, and third-
party tools are constantly updated and made publicly available .
33
It is planned that after successful initial certification, additional information will also be made
available on the course homepages about ECTS credit documentation.
32
Last call August 7, 2023
33
https://www.coursera.support/s/learner-help-center-coursera-policies?language=en_US, last call August
7, 2023

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 65
Appraisal:
The courses’ contents, curricula, and assessment schemes have been suitably documented and
published. Therefore, the basic quality requirements as described in the assessment guide are met
regarding the current state of documentation.
However, for the planned documentation on the program homepages about ECTS documentation
the panel team emphasizes the following issues to observe:
1. Documentation of ECTS crediting has to be included on the respective course description
and include: number of credits awarded
34
, requirements for awarding credits and workload
assigned to the course (see condition chapter 3.2).
2. Documentation of ECTS crediting has also to be included on the respective certificate
issued by Coursera and Google. Documentation has to include number of credits awarded
34
and workload assigned to the course (see condition chapter 3.2).
3. The EQF level assignment must not communicate EQF levels others than what has been
confirmed by the FIBAA certification committee after condition chapter 1.1 has been met.
4. When course completers apply for recognition of ECTS credits at a HEI, the HEI is obliged
to examine recognition and to justify if ECTS credits are not or only partially accepted.
However, the HEI is not obliged to the recognition of ECTS credits. Documentation on the
Coursera Homepage therefore must not evoke the impression that HEIs are obliged to give
(full) recognition. The panel also points out that as there are no formal admission
requirements for the Professional Certificates, course completersmay also be required to
catch up on formal admission requirements of the HEI (e.g. school-leaving certificate
level).
Based on these requirements, the panel team recommends the following condition for the planned
documentation of ECTS credit award of the Coursera hosted Professional Certificates from Google:
Coursera and Google ensure correct documentation about the ECTS credit recommendation
and recognition on the homepage, in the program descriptions and in the certificates issued
after certification, considering ECTS credit recognition obligations by HEIs, EQF levels
assigned, number of credits, requirements for achieving credits and workload assigned to
the courses.
Exceptional
Exceeds quality
requirements
Meets quality
requirements
Does not meet
quality
requirements
n.r.
5.*
Documentation
Condition
34
For the sake of readability, “awarded” is used here. Coursera does not “award” credits, but issues an
ECTS credit recommendation

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 66
6 QUALITY ASSURANCE
Coursera´s quality assurance system follows the systematics of the closed control loop
according to the PDCA model (Plan, Do, Check, Act) and along the content life cycle. Coursera
designed a system to ensure that content on the platform is high quality, relevant, accurate,
and up-to-date and that the learning platform and technology are reliable and accessible to all
learners.
Table 13: Coursera Quality Assurance System
Quality means
● Coursera aims to systematically include learners' needs and wishes and the labor
market's demands in the offerings' content and organizational design.
● Coursera aims to break down its mission statement (see chapter “Details on the
institution”) and educational profile to the level of the individual course utilizing
subject-specific content standards for teaching.
● Coursera aims to develop the products strictly following its pedagogical
requirements and policies to allow customers the best possible learning outcomes.
● Coursera aims to constantly improve its offerings by subjecting newly developed
products to a yearly review with the university or industry partners.
● Coursera aims to develop mutually beneficial relationships with cooperation
partners and other interested parties like governments, learners, companies, and
universities.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 67
Google Professional Certificates
The Coursera-led Teaching and Learning team partners with Google to use a data-driven multi-step
research and development process to ensure content is aligned with best practices for successful
online delivery. The Google staff, including subject matter experts, teaching and learning experts,
and behavioral scientists, a program manager/instructional designer and assessment creation
subject matter expert, led the program creation process by selecting and guiding specific subject
matter experts with relevant skills globally to create content and provide recommended resources
to map to the overall Coursera blueprint (see chapter 4.1) and Job Task Analysis (JTA, see chapter
3.5). Each SME provided new or existing content that would teach the learner the skill required to
meet the learning objectives of each course/module and also provided feedback on the graded
assessments and knowledge checks to test each learnerʼs knowledge.
Together, the Coursera Teaching and Learning team and the Google staff worked to conduct a gap
analysis and an environmental scan, and reviewed audience research, jobseeker insights, and
market analysis data to inform course and program development decisions.
Extensive internal cooperation is required between Coursera stakeholders and Google stakeholders
in preliminary research for in-demand content, curriculum development, content production,
testing, and instruction. Google and Coursera collaborate closely across the following phases:
Research, Course Development, Production, Beta Testing, and Evaluation and Improvement.
Phase 1: Research
Courseraʼs Content Strategy team identifies content topics to host on the platform based on learner
demand, labor market data, and global workforce needs. The Coursera Content Strategy team works
cross-functionally to generate target content lists for different learner audiences by developing
roadmaps to provide an end-to-end content strategy approach and key strategic content
recommendations to improve metrics such as enrollments, learner retention and completion, and
career outcomes.
Content Strategy categorizes content based on product definitions (entry-level or advanced
Professional Certificates) as they relate to job roles. The criteria for the job role include:
● Target role with role summary and minimum qualified candidate description
● Target audience
● Key certification(s) if any
● number of jobs total
● number of jobs openings not requiring undergraduate degree
● number of jobs openings requiring zero to two years’ experience
● percentage of workers in the role without a four-year undergraduate degree

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 68
Phase 2: Course Development
Entry-level Professional Certificates that are hosted on the Coursera platform are assigned a Senior
Program Manager and a Technical Account Manager from Coursera to provide project management,
content production, and launch support to assist in course development. Entry-level certificates
also benefit from additional pedagogical support from the Coursera Teaching and Learning team
(see chapter 4.1).
Googleʼs learning design team uses the ADDIE (Analyze, Design, Develop, Implement, and Evaluate)
model. After the job-task (JTA) and learner analysis (see chapter 3.5) the team hosts a multi–day
design sprint with the goal of defining the key skills and concepts to be taught in the certificate
and the learning outcomes. Skills are aligned to the JTA and industry standard, then mapped to
courses. Once skills mapping is complete, the content team develops learning objectives and
designs a detailed syllabus that outlines the topic areas and assets that will be included in the
certification. This syllabus and the learning objectives are used throughout the content building
process to guide the content team in development of all course assets. All content undergoes a
thorough review by SMEs and specialized SMEs for topics such as DEI (Diversity, Equity and
Inclusion) and accessibility. Assessments are aligned to learning objectives and designed in
accordance with best practices for assessment design.
During the content creation process, the Coursera Teaching and Learning team and Courseraʼs
product teams worked alongside Google to develop learning objectives, create the syllabi for each
of the modules in the Professional Certificate programs, and align learning outcomes and platform
features.
Mastery learning is followed by mapping instruction and assessments (formative and summative)
to these established learning objectives. To ensure completeness and alignment to specific job
roles, the learner objectives are validated against the skills in the Jobs Task Analysis (JTA, see
chapter 3.5).
Phase 3: Production
The Coursera and Google course team included several SMEs from Google, including:
● Instructors, who teach the course. They need to fill out a public "instructor" profile.
● An instructional designer, who helps transform the curriculum into an online learning
experience. They design learning activities that support mastery of the course topic(s).
● Subject matter experts who work in the fields for which the certificate program is
preparing learners.
The team decides which goals and outcomes learners need to achieve by the end of each module
which includes the design of the graded assessments that measure whether learners achieved the
learning objectives. Coursera's platform supports many assessment types that measure course
topic mastery such as graded quizzes and final examinations.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 69
Coursera and Google used a variety of modalities in its courses to teach and interact with learners
including:
● Video with in-video questions,
● Ungraded assessments to provide practice opportunities for learners to apply their newly
learned skills,
● Discussion forums,
● Supplemental readings.
Phase 4: Beta Testing
When the course is ready, Coursera conducts beta testing and the technical quality assurance (QA)
process. After a week of technical QA, the course will launch to millions of learners around the
world.
During beta testing, a defined group of learners gain free early access to an unlaunched program.
In exchange, they review course materials and leave comments, flags, suggestions, and feedback.
Coursera’s Teaching and Learning team analyzes the feedback and sends a report with concrete
recommendations. This provides a specific learners’ perspective for course teams and
opportunities for improvement in the courses before it reaches millions of learners. It is also seen
as opportunity to test new methods, materials, and creative assessments.
Coursera recruits beta testers from a pool of dedicated Coursera learners who are part of Coursera’s
beta testing community. They voluntarily give their time to provide feedback to content providers.
Learners can join the beta testing community in two ways:
● Invitation: Top learners who complete a course in a relevant or related topic are invited
to become beta testers.
● Signing up: Learners can sign up on their own through the Coursera platform and join
the beta testing community.
The beta testing community receives a weekly update with a list of courses being tested that week.
Testers choose courses they are interested in, and receive early access to those courses. On
average, a single course attracts between 25-100 beta testers.
Beta testing runs for one week. After that, the Coursera Teaching and Learning team analyzes the
feedback to create a comprehensive report, which helped Google identify and address content
quality issues specific to the course. The report was sent to Google within 1-3 business days after
the test ends and is divided into three sections:
● High Priority: these must be addressed prior to course launch (e.g., errors in quiz
answers, clarifying peer review instructions)
● Quick Fix: small improvements that should be made before launch (e.g., typos, adding
a discussion prompt, adding a sub-forum)

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 70
● Deeper Dive: in-depth or labor-intensive changes that can be incorporated after launch
(e.g., making changes to videos)
Beta testers also provided reliable predictions of the course rating, which helps to benchmark plans
for future improvements to ensure positive learner experiences.
Phase 5: Evaluation and Improvement
Courseraʼs real-time monitoring of learner progress is an essential element to support all content
providers and learners enrolled in hosted content of all its programs. It is common for the Coursera
Teaching and Learning team to provide partners feedback with pedagogical recommendations
during quarterly business reviews.
Coursera collects program feedback from learners in several ways (see below): All collected course
feedback is reflected in the course dashboards which only Google and their instructors can view.
Based on this feedback, materials are revised, and errors fixed. This direct feedback from learners
is valuable in helping to improve the learner experience in the course.
Coursera collaborates closely with Google to execute on a number of items related to student
services. These services include but are not limited to: monitoring all course forums and Slack
channels on a regular basis to answer student technical questions, reviewing student progress in
certificate progression, identifying at-risk students, or students that may demonstrate behaviors
that indicate they may not be on a path to being successful in pursuit of their program, and
generating automated and personalized communications to support successful engagement and
completion. These include in-course pop-ups, learning reminder and nudge emails, and app
notifications. They generally fall into categories such as motivation help, pain-point help, and
dropout intervention. By providing timely response to student inquiries through Courseraʼs scaled
services communication tool within one business day, Coursera is able to support the learner
community with their diverse needs and questions.
In addition to automated in-product retention support, Coursera provides staff support via:
● Program Support Dashboards, which are created using learner behavior data (e.g.,
assignments attempted/passed, activity in course, and platform behavior) and by
highlighting students at risk of not progressing successfully through a course, term, or
program; and
● Student Support Dashboards, which enable course staff to track student progress within a
specific course.
Prior to publishing programs Google conducts QA reviews and beta testing to ensure high quality
standards are met and any problems are ironed out before courses go live. Google also monitors
course ratings and learner reviews on an ongoing basis and endeavors to update courses annually.
In addition, the Google team gains further insights about how the content is being interpreted and
identifies ways to improve the content by monitoring discussion forums on the Coursera platform,
listening to organic social conversation from learners, and gathering feedback from ecosystem
partners like nonprofits, universities, and employers who offer the Google Career Certificates.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 71
Content life-cycle-management
The quality assurance process starts with identifying highly in-demand skills and job requirements.
It is followed by a rigorous vetting process for the instructors and content creators to ensure they
are SMEs with the appropriate qualifications and experience.
Once the content has been created, it is reviewed by a team of SMEs, instructional designers, and
quality assurance professionals to ensure that it meets the standards set by the learning provider.
Feedback from learners is incorporated into the process to identify improvement areas and ensure
that the content meets their needs.
Coursera claims its quality assurance system ensures that the learning platform and technology are
reliable, user-friendly, and accessible to all learners. This ongoing evaluation includes regular
testing and updates to address any issues or bugs that may arise.
Coursera's "learners first" strategy emphasizes effective content and program development to help
learners succeed in completing individual courses or certificate programs. To achieve this, Coursera
provides real-time monitoring of learner progress to support all learners and Google. For
information on the various learning analytics data collection, see chapter 4.5.
Coursera collects course feedback from learners in several ways:
● In-course
○ Thumbs-up or thumbs-down feedback (likes and dislikes) in the course and
○ Problem reports on individual content items in the course.
● After Program completion
○ Numeric program ratings and
○ Written feedback (e.g., content reviews and post-course stories).
To aid the content development and instructional team in acting on feedback and data, Coursera
has provided the following prompts:
● Do any items have a large number of reports or dislikes? These likely show points of
learner confusion or frustration. Try iterating on these items to improve the learner
experience.
● Do any items have a large number of likes and positive reviews? What do learners love
about these items? Can these aspects be incorporated into other items or throughout
the course?
● Are learners sharing more insight about these content items on the discussion forums?
As part of this approach, the Coursera Teaching and Learning Team conducts quarterly business
reviews with Google to provide pedagogical feedback and recommendations based on the learner
results, course performance, and feedback received on the different levels. Each course element is
linked to a discussion forum, allowing learners to engage with other participants or directly pose
questions to the Google or Coursera team. Learners can provide feedback at the end of each learning
unit, including the option to report errors or flag content issues such as problems with video, audio,

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 72
offensive content, or subtitles. They may also suggest improvements or additions to the content.
This flagging option opens a dialogue box:
Table 14: Screenshot - Item level feedback
At the end of each course, learners are encouraged to rate the module on a 5-star scale and
provide individual feedback to the teacher. If the learner does not provide feedback directly,
an email is sent with a gentle reminder to encourage them to contribute to improvement.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 73
Table 15: Screenshot – Course level feedback
Table 16: Screenshot – Feedback to the teaching staff
Upon certificate completion, learners are asked to evaluate the entire program, including all
courses. All evaluations and feedback are made available to Google and discussed in quarterly
sessions with all relevant stakeholders from Google and Coursera to identify necessary
measures for improvement.
35
Additionally, learners are asked to identify the relevant skills they have learned in the program,
selecting from a provided list, or adding their own. This information is used to improve future
program offerings and ensure learners are gaining the desired skills and knowledge.
35
Proprietary information not publicly known about internal processes

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 74
Table 17: “Course”
36
level completion feedback
During the quarterly meeting mentioned above, the Google SMEs also discuss suggestions for
updating content, adding exercises or other adjustments. All participants have the same data basis
through the collected student feedback. The SMEs then can suggest and address improvements in
36
„course“ meaning program according to Coursera terminology, see glossary

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 75
discussions with the Teaching and Learning Team at Coursera. The points discussed in this meeting
are documented, worked through, and implemented within the framework of a defined project plan.
Completers are surveyed after six months to determine their overall satisfaction with the course
and whether it met their individual career goals and expectations. Evaluations are carried out
across all product areas to gauge whether learners' career aspirations and desired changes are
being realized. While an employer survey on a large scale is currently unfeasible due to the vast
number of learners, feedback is solicited and channeled to the relevant teams, enabling valuable
input to be collected.
37
Coursera employs external quality assurance measures to guarantee the quality of its courses.
Professional Certificates have been subject to quality assurance and recertification by the American
Council on Education for several years. Feedback and recommendations are incorporated into the
PDCA cycle, scrutinized in quarterly feedback meetings, and serve as a springboard for individual
course improvements and adjustments. The Content Strategy Team leverages this data to identify
skillset gaps and develop additional certificates based on the needs of companies, universities,
governments, and the external environment.
Appraisal:
There is a quality assurance and development procedure, which systematically and continuously
monitors and develops the quality of the courses with respect to its contents, processes, technology
and outcomes. Sufficient staff recourses are available and responsibilities are clearly defined.
Teaching staff and learners’ contribution to quality assurance and development procedures is
ensured (For the learner workload evaluation see condition chapter 3.1).
Evaluation by learners is carried out on a regular basis and in accordance with a prescribed
procedure; the outcomes are communicated and provide input for the quality development process.
Coursera collects a lot of feedback information and processes this into the “Learner Outcome
Report”. However, it has not become clear to the panel whether and how information of the Learner
Outcome Report is provided to the learners and completers. The panel therefore recommends
communicating current Learner Outcome Reports on the website.
Quality controls by the teaching staff and external evaluation are carried out on a regular basis and
in accordance with a prescribed procedure; the outcomes are communicated to the learners and
provide input for the quality development process. The panel suggests increasing participation of
the instructors in course development by conceiving an instructors’ feedback survey. The panel is
convinced that the procedure of the job task analysis (JTA) is an effective alternative to the
traditional method of assigning expert advisory boards for course and overall program
development.

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 76
Exceptional
Exceeds
quality
requirements
Meets quality
requirements
Does not meet
quality
requirements
n.r.
6.
Quality Assurance
6.1*
Quality assurance and development of
course content, processes, and outcomes
X
6.2
Instruments of quality assurance
6.2.1
Evaluation by learners
X
6.2.2
Quality assurance by teaching staff
X
6.2.3
External evaluation by course completers,
employers and others
X

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 77
● Quality Profile
Institution: Coursera Inc.
Content partner: Google
Continuing Education Courses:
● Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate
● Google Digital Marketing and E-Commerce Professional Certificate
● Google IT Support Professional Certificate
● Google IT Automation with Python Professional Certificate
● Google Project Management Professional Certificate
● Google UX Design Professional Certificate
Quality Ratings
Exceptional
Exceeds
quality
requirements
Meets quality
requirements
Does not meet
quality
requirements
n.r.
1.
Strategy and Objectives
1.1*
38
Logic and transparency of course
objectives
Condition
1.2
International orientation of the courses
X
1.3
Positioning of the courses
1.3.1
Positioning of the courses in the education
and job market, and
the professional field
(“Employability”)
X
1.3.2
Position of courses within the course
provider’s overall strategy
X
2.
Admission
2.1*
Focus on the target group
X
2.2*
Admission conditions
X
2.3*
Legal relationship
X
3.
Implementation
3.1
Structure
3.1.1
Structure of the courses
X
3.1.2*
Application of the „European Credit
Transfer and Accumulation System (ECTS)“
and modularization
Condition
3.1.3*
Conditions of participation and
assessment regulations
X
3.1.4*
Feasibility of study workload
X
3.2
Content
3.2.1*
Logic and conceptual coherence
X
3.2.2
Integration of theory and practice
X
3.2.3
International and intercultural contents
X
38
*: Asterisk Criterion

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 78
Quality Ratings
Exceptional
Exceeds
quality
requirements
Meets quality
requirements
Does not meet
quality
requirements
n.r.
3.2.4
Methodological competence
X
3.2.5
Academic work and science-based
teaching
X
3.2.6*
Examinations
X
3.3
Transdisciplinary qualifications and
softskills
X
3.4
Didactics and methodology
3.4.1*
Logic and transparency of teaching and
learning methodology
X
3.4.2
Course and learning materials
X
3.5*
Skills for employment/Employability
X
4.
Resources and Services
4.1
Teaching staff of the courses
4.1.1*
Course management
X
4.1.2*
Structure and number of teaching staff in
relation to curricular requirements
X
4.1.3*
Teaching staff’s qualifications
X
4.1.4*
Teaching staff’s pedagogical/teaching
qualifications
X
4.1.5
Practical experience of the teaching staff
X
4.1.6
Internal cooperation
X
4.1.7*
Learner support and coaching
X
4.2*
Process organization and administrative
support for learners and teaching staff
X
4.3
Networking
X
4.4(*)
Cooperation with
academic institutions or
enterprises (asterisk criterion for
cooperation courses)
X
4.5
Technology and Facilities
4.5.1
Technical organizational unit
X
4.5.2*
Teaching and learning platform
X
4.5.3
Data analysis system
X
4.5.4*
Technical support for learners
X
4.5.5
Access to required literature
X
5.*
Documentation
Condition
6.
Quality Assurance
6.1*
Quality assurance and development of
course content, processes and outcomes
X
6.2
Instruments of quality assurance
6.2.1
Evaluation by learners
X
6.2.2
Quality assurance by teaching staff
X
6.2.3
External evaluation by course completers,
employers and others
X

Description and appraisal in Detail
© FIBAA Certification Report Page 79
● Glossary
Coursera and report terminology
description
Professional Certificate (program);
Program
Course (entity that is subject to certification)
Course Content entity covering one topic within the program
Module Weekly learning entity, smallest learning entity
Subject Matter Expert Employee of Google (Coursera content partner) or third party
assigned by Google (Coursera content partner), who is
qualified for content development
Instructor Teaching staff that is part of the team that conceives, designs,
and produces the course
