
Source:TexasEducationAgenc
y
STAARResources Page1 of2 REV02/03/2014
STAAR Standards Snapshot – Algebra I
(New TEKS – 2015-16)
MathematicalProcessStandards
A.1(A) A.1(B) A.1(C) A.1(D) A.1(E) A.1(F) A.1(G)
apply
mathematics
toproblems
arisingin
everydaylife,
society,and
theworkplace
useaproblem‐solvingmodel
thatincorporatesanalyzing
giveninformation,formulatinga
planorstrategy,determininga
solution,justifyingthesolution,
andevaluatingtheproblem‐
solvingprocessandthe
reasonablenessofthesolution
selecttools,includingreal
objects,manipulatives,paperand
pencil,andtechnologyas
appropriate,andtechniques,
includingmentalmath,
estimation,andnumbersenseas
appropriate,tosolveproblems
communicatemathematical
ideas,reasoning,andtheir
implicationsusingmultiple
representations,including
symbols,diagrams,graphs,
andlanguageasappropriate
createanduse
representations
toorganize,
record,and
communicate
mathematical
ideas
analyze
mathematical
relationships
toconnectand
communicate
mathematical
ideas
display,explain,and
justifymathematical
ideasandarguments
usingprecise
mathematical
languageinwritten
ororal
communication
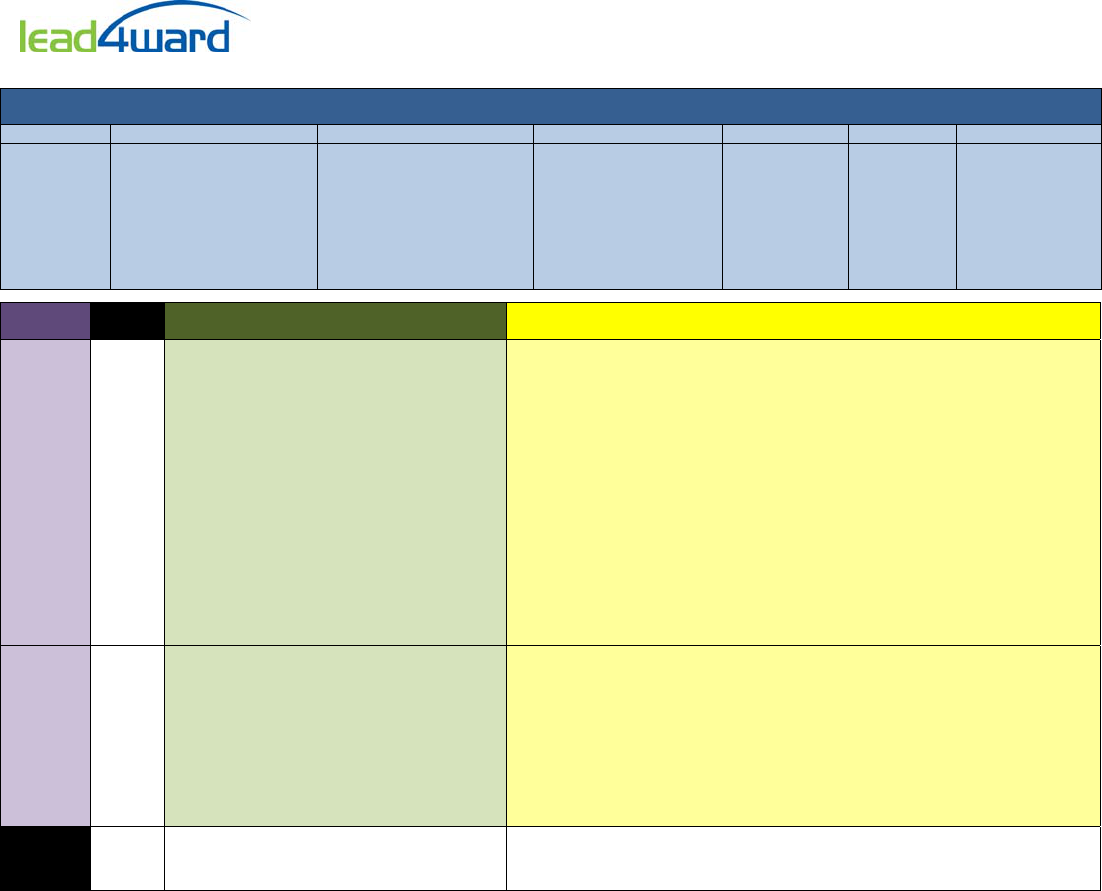
RptgCat STAAR
ReadinessStandards SupportingStandards
1
NumberandAlgebraicMethods
11
A.10(E) factor,ifpossible,trinomialswithrealfactors
intheformax
2
+bx+c,includingperfect
squaretrinomialsofdegreetwo
A.11(B) simplifynumericandalgebraicexpressions
usingthelawsofexponents,including
integralandrationalexponents
A.10(A) addandsubtractpolynomialsofdegreeoneanddegreetwo
A.10(B) multiplypolynomialsofdegreeoneanddegreetwo
A.10(C) determinethequotientofapolynomialofdegreeoneandpolynomialofdegreetwo
whendividedbyapolynomialofdegreeoneandpolynomialofdegreetwowhenthe
degreeofthedivisordoesnotexceedthedegreeofthedividend
A.10(D) rewritepolynomialexpressionsofdegreeoneanddegreetwoinequivalentformsusing
thedistributiveproperty
A.10(F) decideifabinomialcanbewrittenasthedifferenceoftwosquaresand,ifpossible,use
thestructureofadifferenceoftwosquarestorewritethebinomial
A.11(A) simplifynumericalradicalexpressionsinvolvingsquareroots
A.12(A) decidewhetherrelationsrepresentedverbally,tabularly,graphically,andsymbolically
defineafunction
A.12(B) evaluatefunctions,expressedinfunctionnotation,givenoneormoreelementsintheir
domains
A.12(C) identifytermsofarithmeticandgeometricsequenceswhenthesequencesaregivenin
functionformusingrecursiveprocesses
A.12(D) writeaformulaforthen
th
termofarithmeticandgeometricsequences,giventhevalue
ofseveraloftheirterms
A.12(E) solvemathematicandscientificformulas,andotherliteralequations,foraspecified
variable
2
DescribingandGraphingLinearFunctions,
Equations,andInequalities
12
A.3(B) calculatetherateofchangeofalinear
functionrepresentedtabularly,graphically,
oralgebraicallyincontextofmathematical
andreal‐worldproblems
A.3(C) graphlinearfunctionsonthecoordinate
planeandidentifykeyfeatures,including
x‐intercept,y‐intercept,zeros,andslope,in
mathematicalandreal‐worldproblems
A.3(D) graphthesolutionsetoflinearinequalitiesin
twovariablesonthecoordinateplane
A.3(A) determinetheslopeofalinegivenatableofvalues,agraph,twopointsontheline,and
anequationwritteninvariousforms,includingy=mx+b,Ax+By=C,and
y–y
1
=m(x–x
1
)
A.3(E) determinetheeffectsonthegraphoftheparentfunctionf(x)=xwhenf(x)isreplacedby
af(x),f(x)+d,f(x–c),f(bx)forspecificvaluesofa,b,c,andd
A.3(F) graphsystemsoftwolinearequationsintwovariablesonthecoordinateplaneand
determinethesolutionsiftheyexist
A.3(G) estimategraphicallythesolutionstosystemsoftwolinearequationswithtwovariables
inreal‐worldproblems
A.3(H) graphthesolutionsetofsystemsoftwolinearinequalitiesintwovariablesonthe
coordinateplane
A.4(A) calculate,usingtechnology,thecorrelationcoefficientbetweentwoquantitative
variablesandinterpretthisquantityasameasureofthestrengthofthelinearassociation
A.4(B) compareandcontrastassociationandcausationinreal‐worldproblems
A.4(C) write,withandwithouttechnology,linearfunctionsthatprovideareasonablefittodata
toestimatesolutionsandmakepredictionsforreal‐worldproblems
3
WritingandSolvingLinearFunctions,
Equations,andInequalities
14
A.2(A) determinethedomainandrangeofalinear
functioninmathematicalproblems;
determinereasonabledomainandrange
valuesforreal‐worldsituations,both
continuousanddiscrete;andrepresent
domainandrangeusinginequalities
A.2(C) writelinearequationsintwovariablesgiven
atableofvalues,agraph,andaverbal
description
A.2(I) writesystemsoftwolinearequationsgivena
tableofvalues,agraph,andaverbal
description
A.5(A) solvelinearequationsinonevariable,
includingthoseforwhichtheapplicationof
thedistributivepropertyisnecessaryandfor
whichvariablesareincludedonbothsides
A.5(C) solvesystemsoftwolinearequationswith
twovariablesformathematicalandreal‐
worldproblems
A.2(B) writelinearequationsintwovariablesinvariousforms,includingy=mx+b,Ax+By=C,
andy–y
1
=m(x–x
1
),givenonepointandtheslopeandgiventwopoints
A.2(D) writeandsolveequationsinvolvingdirectvariation
A.2(E) writetheequationofalinethatcontainsagivenpointandisparalleltoagivenline
A.2(F) writetheequationofalinethatcontainsagivenpointandisperpendiculartoagiven
line
A.2(G) writeanequationofalinethatisparallelorperpendiculartothex‐ory‐axisand
determinewhethertheslopeofthelineiszeroorundefined
A.2(H) writelinearinequalitiesintwovariablesgivenatableofvalues,agraph,andaverbal
description
A.5(B) solvelinearinequalitiesinonevariable,includingthoseforwhichtheapplicationofthe
distributivepropertyisnecessaryandforwhichvariablesareincludedonbothsides
Source:TexasEducationAgenc
y
STAARResources Page2 of2 REV02/03/2014
STAAR Standards Snapshot – Algebra I
(New TEKS – 2015-16)
MathematicalProcessStandards
A.1(A) A.1(B) A.1(C) A.1(D) A.1(E) A.1(F) A.1(G)
apply
mathematics
toproblems
arisingin
everydaylife,
society,and
theworkplace
useaproblem‐solvingmodel
thatincorporatesanalyzing
giveninformation,formulatinga
planorstrategy,determininga
solution,justifyingthesolution,
andevaluatingtheproblem‐
solvingprocessandthe
reasonablenessofthesolution
selecttools,includingreal
objects,manipulatives,paperand
pencil,andtechnologyas
appropriate,andtechniques,
includingmentalmath,
estimation,andnumbersenseas
appropriate,tosolveproblems
communicatemathematical
ideas,reasoning,andtheir
implicationsusingmultiple
representations,including
symbols,diagrams,graphs,
andlanguageasappropriate
createanduse
representations
toorganize,
record,and
communicate
mathematical
ideas
analyze
mathematical
relationships
toconnectand
communicate
mathematical
ideas
display,explain,and
justifymathematical
ideasandarguments
usingprecise
mathematical
languageinwritten
ororal
communication
RptgCat STAAR
ReadinessStandards SupportingStandards
4
QuadraticFunctionsandEquations
11
A.6(A) determinethedomainandrangeof
quadraticfunctionsandrepresentthe
domainandrangeusinginequalities
A.7(A) graphquadraticfunctionsonthecoordinate
planeandusethegraphtoidentifykey
attributes,ifpossible,includingx‐intercept,
y‐intercept,zeros,maximumvalue,minimum
values,vertex,andtheequationoftheaxis
ofsymmetry
A.7(C) determinetheeffectsonthegraphofthe
parentfunctionf(x)=x
2
whenf(x)isreplaced
byaf(x),f(x)+d,f(x–c),f(bx)forspecific
valuesofa,b,c,andd
A.8(A) solvequadraticequationshavingreal
solutionsbyfactoring,takingsquareroots,
completingthesquare,andapplyingthe
quadraticformula
A.6(B) writeequationsofquadraticfunctionsgiventhevertexandanotherpointonthegraph,
writetheequationinvertexform(f(x)=a(x–h)
2
+k),andrewritetheequationfrom
vertexformtostandardform(f(x)=ax
2
+bx+c)
A.6(C) writequadraticfunctionswhengivenrealsolutionsandgraphsoftheirrelatedequations
A.7(B) describetherelationshipbetweenthelinearfactorsofquadraticexpressionsandthe
zerosoftheirassociatedquadraticfunctions
A.8(B) write,usingtechnology,quadraticfunctionsthatprovideareasonablefittodatato
estimatesolutionsandmakepredictionsforreal‐worldproblems
5
ExponentialFunct i onsand
Equations
6
A.9(C) writeexponentialfunctionsintheform
f(x)=ab
x
(wherebisarationalnumber)to
describeproblemsarisingfrommathematical
andreal‐worldsituations,includinggrowth
anddecay
A.9(D) graphexponentialfunctionsthatmodel
growthanddecayandidentifykeyfeatures,
includingy‐interceptandasymptote,in
mathematicalandreal‐worldproblems
A.9(A) determinethedomainandrangeofexponentialfunctionsoftheformf(x)=ab
x
and
representthedomainandrangeusinginequalities
A.9(B) interpretthemeaningofthevaluesofaandbinexponentialfunctionsoftheform
f(x)=ab
x
inreal‐worldproblems
A.9(E) write,usingtechnology,exponentialfunctionsthatprovideareasonablefittodataand
makepredictionsforreal‐worldproblems
#Items
54
(5Griddable)
32‐35questionsfromReadinessStandards 19‐22questionsfromSupportingStandards
