
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 1 of 80
Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
Version 2.0
18 March 2020
This is a Non-binding Permanent Reference Document of the GSMA
Security Classification: Non-confidential
Access to and distribution of this document is restricted to the persons permitted by the security classification. This document is confidential to the
Association and is subject to copyright protection. This document is to be used only for the purposes for which it has been supplied and
information contained in it must not be disclosed or in any other way made available, in whole or in part, to persons other than those permitted
under the security classification without the prior written approval of the Association.
Copyright Notice
Copyright © 2020 GSM Association
Disclaimer
The GSM Association (“Association”) makes no representation, warranty or undertaking (express or implied) with respect to and does not accept
any responsibility for, and hereby disclaims liability for the accuracy or completeness or timeliness of the information contained in this document.
The information contained in this document may be subject to change without prior notice.
Antitrust Notice
The information contain herein is in full compliance with the GSM Association’s antitrust compliance policy.
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 2 of 80
Table of Contents
1 Introduction 4
1.1 Document Purpose 4
1.2 Business Rational 4
1.3 Intended Audience 5
1.4 Compliance Requirements 5
1.5 Abbreviations 5
1.6 References 6
1.7 Conventions 7
2 VVM Interfaces Overview 7
2.1 Message Retrieval Interface Description 8
2.1.1 Message Retrieval: IMAP4 Command Reference 9
2.1.2 Message Retrieval: Supported Message Types 15
2.1.3 Message Retrieval: Supported Attachment Formats 16
2.1.4 VVM TUI Features Limitations 16
2.1.5 Message Retrieval Header Reference 17
2.2 Message Deposit Interface Description 21
2.2.1 Standard Message Deposit Header Reference 22
2.2.2 VVM Specific Message Deposit Header Reference 25
2.2.3 Message Deposit Attachment Header Reference 25
2.3 VVM Self-care 26
2.3.1 TUI Password Changes Interface Description 26
2.3.2 Change TUI Language Interface Description 27
2.3.3 Generic Feature Change: Interface Description 28
2.4 Close NUT Interface Description 29
2.4.1 Close NUT Request Syntax 30
2.4.2 Close NUT Response Syntax 30
2.5 On Demand Audio Message Transcription Command Services 30
2.5.1 On-Demand Transcription Request Syntax 30
2.5.2 On-Demand Transcription Response Syntax 31
2.5.3 Automatic Transcription Service START/STOP Request Syntax 31
2.5.4 Automatic Transcription Service START/STOP Response Syntax 32
2.6 Guidelines For Greetings And Voice Signature Management 32
2.6.1 Uploading a Greeting or VS 33
2.6.2 Deleting a Greeting or VS 33
2.6.3 Greeting Header Reference 34
2.7 Provisioning Status 35
2.8 VVM SMS Interface Description 37
2.8.1 Server Originated SMS Messages: Overview 39
2.8.2 Client Originated SMS Messages: Overview 40
2.8.3 SYNC SMS (Server Originated) 40
2.8.4 STATUS SMS (Server Originated) 44
2.8.5 OTP SMS Description (Server Originated) 52
2.8.6 STATUS SMS (Client Originated) 52
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 3 of 80
2.8.7 Activate SMS (Client Originated) 53
2.8.8 Deactivate SMS (Client Originated) 55
2.9 VVM Message Commands 56
2.10 VVM REST Interface Description 56
2.10.1 Register 56
2.10.2 ProvideOTP 57
2.10.3 ProvidePassword 58
2.10.4 Unregister 58
2.10.5 UpdateToken 59
2.10.6 Push-based register scenario (option 1) 60
2.10.7 Push-based register scenario (option 2) 60
2.11 VVM Push Notification Interface Description 61
2.11.1 STATUS 62
2.11.2 NEW_MESSAGE 62
2.11.3 PASSWORD 63
2.12 DeviceToken Verification Server Interface 63
2.13 Client Authentication 64
3 RFC Compliance 65
3.1 RFC Compliance Related to Internet Mail 65
3.2 RFC Compliance Related to IMAP4 66
3.3 RFC Compliance Related to SMTP 66
Annex A Examples of VVM Commands and Responses 67
Annex B Security guidelines for Voicemail and VVM 78
B.1 Encryption of OOB SMS and Push Notification payload 78
B.2 Recommendations for password value 79
Annex C Document Management 80
C.1 Document History 80
Other Information 80
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 4 of 80
1 Introduction
1.1 Document Purpose
The aim of this document is to provide a Technical Recommendation for an open and
standardised Visual Voice Mail (VVM) interface protocol which VVM clients may use to interact
with a voice mail server. The key functions of this interface will be support of:
• Message Retrieval
• Message Upload
• VVM Management
• Greeting Management
• Provisioning
• Registration of Push-based VVM clients
The document will not define how a VVM client looks nor will it define the general behaviour
of a client/user interface or the manner in which a user shall interact with the user interface.
The definition of the protocol may however imply certain client and/or user behaviours. The
intention of the document is to ensure that the standard functionality of voice mail servers may
be accessed through a range of VVM clients via a defined interface. This approach leaves
scope for operators and vendors to differentiate their products.
1.2 Business Rational
The growth of VVM services and possible new business models is restrained by the lack of a
standardised client side interface to the voice mail server.
Native support on terminals for a voice mail interface will significantly improve the overall user
experience, which in turn will encourage wider use of voice mail services.
If vendors are able to support a single VVM interface their time to market and associated costs
shall be reduced.
A standardised interface definition shall allow client developers to focus on producing better
clients rather than modifying clients to work with multiple interfaces.
Having only one interface to support will improve the ability of an operator to provide the VVM
service on a variety of terminals, roll out the service more quickly and contain operational
expenditure.
A number of VVM implementations currently exist in the market, however, service deployment
is at a nascent stage and therefore market fragmentation can still be prevented. It is imperative
that vendors and operators achieve quick agreement on the core VVM interface.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 5 of 80
1.3 Intended Audience
The audience for this document includes:
• Network operators who define specific requirements for VVM clients to be delivered on
mobile Terminals which are delivered in accordance with the operators mobile
requirements documents.
• Terminal vendors, i.e. equipment and technology vendors who will deliver VVM clients
on their Terminals.
• Third party providers of VVM clients and servers.
1.4 Compliance Requirements
Conformance to this document does not offer a partial compliance option at the individual
requirements level as is the case with most OMTP requirements documents. Conformance
may only be stated if the vendor is 100% compliant to all aspects of the recommendation.
This document is a Technical Recommendation for an open and standardised VVM
interface protocol. VVM clients may use the interface protocol to interact with a voice mail
server. The compliance statement encompasses only the interface protocol and does not
state compliance to VVM functionalities implemented.
1.5 Abbreviations
Term
Description
AMR
Adaptive Multi-Rate
AT Application Terminated
AUTH authentication
CLI Calling Line Identification
DSN Delivery Status Notification
ECC Empty Call Capture
EVRC Enhanced Variable Rate Codec
EVS Enhanced Voice Services
FQDN Fully Qualified Domain Name
GU Greetings Update
IMAP Internet Message Access Protocol
MBU Mailbox update
MDN Message Disposition Notification
MD5 Message-Digest algorithm 5
MIME Multi-purpose Internet Mail Extension
MSISDN Mobile Subscriber Integrated Services Digital Network Number
NM New Message
NUT New User Tutorial
OMTP
Open Mobile Terminal Platform
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 6 of 80
Term Description
OOB Out Of Band
OS Operating System
OTP One Time Password
PDF Portable Document Format
QCELP
Qualcomm code-excited linear prediction
RCS Rich Communication Services
RFC Request For Change
SMPP Short Message Peer to Peer
SMS Short Message Service
SMSC Short Message Service Centre
SMTP Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
SSL Secure Sockets Layer
TIF Tagged Image Format
TIFF Tagged Image File Format
TLS Transport Layer Security
TUI Telephony User Interface
UDH User Data Header
UI User Interface
UID Unique Identifier
UTC
Coordinated Universal Time
VM Voice Mail
VS Voice Signature
VVM Visual Voice Mail
WAV Waveform audio file format
Table 1 Abbreviations
1.6 References
Ref
Doc Number
Title
[1]
RFC 2119
“Key words for use in RFCs to Indicate Requirement Levels”, S.
Bradner, March 1997. Available at http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2119.txt
[2]
GSMA SG.20 Official Document SG.20 - Voicemail Security Guidelines
[3]
GSMA RCC.14
GSMA PRD RCC.14 Service Provider Device Configuration, Version
7.0, 16 October 2019 (Universal Profile 2.4)
http://www.gsma.com/
[4]
3GPP TS23.040 Technical realization of Short Message Service (SMS)
[5]
RFC 2045
Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) Part One: Format of
Internet Message Bodies
[6]
RFC 2046 Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) Part Two: Media Types
[7]
RFC 2195 IMAP/POP AUTHorize Extension for Simple Challenge/Response

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 7 of 80
Ref Doc Number Title
[8]
RFC 2821 Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
[9]
RFC 2822 Internet Message Format
[10]
RFC 2831 Using Digest Authentication as a SASL Mechanism
[11]
RFC 3458 Message Context for Internet Mail
[12]
RFC 3461
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) Service Extension for Delivery
Status Notifications (DSNs)
[13]
RFC 3798 Message Disposition Notifications
[14]
RFC 2595 Using TLS with IMAP, POP3 and ACAP
[15]
RFC 3501 Internet Message Access Protocol - Version 4rev1
[16]
RFC 2087 IMAP4 QUOTA extension
[17]
RFC 4315 Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) - UIDPLUS extension
[18]
RFC 5464 The IMAP METADATA Extension
[19]
RFC 3207
SMTP Service Extension for Secure SMTP over Transport Layer
Security
[20]
RFC 2554 SMTP Service Extension for Authentication
[21]
RFC 3463 Enhanced Mail System Status Codes
[22]
RFC8174 Ambiguity of Uppercase vs Lowercase in RFC 2119 Key Words
Table 2: References
1.7 Conventions
The key words "MUST", "MUST NOT", "REQUIRED", "SHALL", "SHALL NOT", "SHOULD",
"SHOULD NOT", "RECOMMENDED", "NOT RECOMMENDED", "MAY", and "OPTIONAL" in
this document are to be interpreted as described in BCP 14 (RFC2119) [1] (RFC8174) [22]
when, and only when, they appear in all capitals, as shown here.
2 VVM Interfaces Overview
The VVM service enables third parties to develop terminal client applications for subscribers
to manage their mailbox messages. Subscribers can use the VVM client on their terminals to
listen to messages, delete messages, and compose messages.
Table 3 below gives the outline of this specification:
Section Section Title Category Mandatory (M)/
Optional (O)
2.1 Message Retrieval
Interface Description
Basic Feature M
2.2 Message Deposit Interface
Description
Basic Feature M
2.3 VVM Self-care: TUI
Password Changes,
Change Language
Interface Description and
Self-care Features O

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 8 of 80
Section Section Title Category Mandatory (M)/
Optional (O)
Generic Feature Change:
Interface Description
2.4 Close NUT Interface
Description
Basic Feature O
2.5 On Demand Audio
Message Transcription
Command Services
Basic Feature O
2.6 Guidelines for Greetings
and Voice Signature
Management
Basic Feature O
2.7 Provisioning Status Basic Feature M
2.8 VVM SMS Interface
Description
Authentication, Activation and
Deactivation Feature
M
Triggering Feature
(Triggering for new voicemail
deposits)
M/O
Mandatory if Push
Notification not
implemented
Optional if Push
Notification implemented
2.9 VVM Messages
Commands
Basic Feature
M
2.10 VVM REST Interface
Description
Enhanced Feature
O
2.11 VVM PUSH Notification
Interface Description
Enhanced Feature
O
2.12 Device Token Verification
Server Interface
Enhanced Feature
O
2.13 Client Authentication Authentication, Activation and
Deactivation Feature
M
At least one of the client
authentication methods
must be implemented
Table 3: Outline of this specification
The VVM service complies with Request for Change (RFC) standards referenced as described
in section 3.
Examples of VVM message commands and responses are provided in Annex B.
Security guidelines for Voicemail and VVM are provided in SG.20 [2] and Annex C.
2.1 Message Retrieval Interface Description
The VVM client communicates with the VVM server via a standard IMAP4 protocol for
message retrieval. In addition to the IMAP4 RFC, some extensions have been added to enable

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 9 of 80
the client to perform certain mailbox configuration actions, such as changing the Telephony
User Interface (TUI) password and language.
The number of concurrent IMAP4 sessions for a single client has a configurable limit. The
client must log out at the end of a session.
Commands used during the IMAP4 message retrieval sessions are described in section 2.1.1
The headers included in the messages retrieved via the VVM service are described in section
2.1.5
Message types and attachment formats supported by the VVM message retrieval sessions
are described in sections 2.1.2 and 2.1.3
Some TUI features are limited by the VVM service, as described in section 2.1.4.
2.1.1
Message Retrieval: IMAP4 Command Reference
The VVM service supports the IMAP4 commands listed in Table 4 below with some
restrictions described in this section. Other IMAP4 extensions are not supported, unless
specifically stated.
Command Name
RFC Reference
APPEND
RFC3501
AUTHENTICATE
RFC3501 for the DIGEST- MD5
algorithm (RFC 2831) only
CAPABILITY
RFC3501
CHECK
RFC3501
CLOSE
RFC3501
EXAMINE
RFC3501
EXPUNGE
RFC3501
FETCH
RFC3501
GETMETADATA
RFC5464
GETQUOTAROOT
RFC2087
GETQUOTA
RFC2087
LIST
RFC3501
LOGIN
RFC3501
LOGOUT
RFC3501
NOOP
RFC3501
SEARCH
RFC3501
SELECT
RFC3501
SETMETADATA
RFC5464
STARTTLS
RFC3501
STATUS
RFC3501
STORE
RFC3501
UID
RFC3501
Table 4: Supported IMAP4 Commands
When a server receives a command that is not listed in Table 4 and which the server does not
support, it will respond with the following error message:
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 10 of 80
No command not allowed
2.1.1.1 Append
The VVM service supports the APPEND command, as described in RFC3501.
The APPEND command is not supported on the Inbox folder. The APPEND command can be
used only to append a new greeting to the Greetings folder.
If the APPEND command is performed on the Inbox folder, the system returns the following
error message:
No command not allowed
The APPENDUID response code described in RFC4315 is supported. However, commands
described in RFC4315 are not supported.
2.1.1.2 Authenticate
The VVM service supports the AUTHENTICATE command described in RFC3501 for the
DIGEST-MD5 algorithm (RFC2831) only.
The AUTHENTICATE command includes the following credentials:
Username: Defines the subscriber’s IMAP4 user name as received in the STATUS SMS
Password: Defines the VVM service password and is either the subscriber’s IMAP4 password
or the TUI password, depending on the system setup.
The IMAP4 password is sent in the STATUS SMS message. If a TUI password is used, it must
be set by the user.
Table 5 below describes error messages that can be returned for the AUTHENTICATE
command.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 11 of 80
Error
Description
NO unknown user
The subscriber cannot be located in the system.
NO unknown client
The Client Type or Protocol Version is unknown.
NO invalid password
The password received from the client does not match the
password defined in the subscriber's profile.
NO mailbox not initialized
The subscriber's mailbox has not yet been initialised via the
TUI (the VVM server can, by configuration, reject login
attempts if the subscriber has not changed the default
password/greeting via the TUI).
NO service is not provisioned
The subscriber has not been provisioned for the VVM
service.
NO service is not activated
The subscriber is provisioned for the VVM service but the VVM
service is currently not active (the VVM server can, by
configuration, reject login attempts in such cases also)
NO user is blocked
The Voice Mail Blocked flag in the subscriber's profile is set to
YES.
No application error
There is a system error preventing authentication
Table 5: AUTHENTICATE Command Error Messages
2.1.1.3 Capability
The VVM service supports the CAPABILITY command, as described in RFC3501.
Note: The untagged response returned by the server indicates which authentication
mechanisms are supported. Currently AUTH=DIGEST-MD5 and STARTTLS
LOGINDISABLED are returned.
The QUOTA IMAP4 extension (RFC2087) and the IMAP METADATA extension (RFC5464)
are also supported, as indicated in the CAPABILITY response.
2.1.1.4 Fetch
The VVM service supports the FETCH command, as described in RFC3501.
Note: The Fetch item RFC822.SIZE, in addition to ALL, FAST, and FULL Fetch macros, return
an inaccurate size value.
Upon receiving the Fetch Body content, the attachment is transcoded to the format supported
by the client. The size returned with the Fetch item RFC822.SIZE command is the size of the
original attachment format, as stored in the server and not necessarily the size of the content
sent to the client after the server performed any transcoding.
A Partial Body Fetch, such as BODY[<section>]<<partial>> is not currently supported. If a
partial fetch command is performed, the system returns the following error message:
No command not allowed
If the user has no credit, the system may return the following error message:

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 12 of 80
No reservation failed
2.1.1.5 Getmetadata
The GETMETADATA command, as defined in RFC5464, is used for the client to query the
VVM server about some information. The "depth" and "maxsize" command options are not
supported.
All parameter names are defined in a namespace, with the following prefix: “/private/VVM/”
Table 6 below lists the parameters to be managed by the GETMETADATA command. It is
envisaged that any new parameters included in this protocol will be managed via the
METADATA extension rather than via SMS.
Variable
Values
Comment
GreetingTypesAllowed
Comma Separated List of zero or more of:
personal
voiceSignature
busyGreeting
noAnswerGreeting
extendedAbsenceGreeting
This parameter
defines the list of
the greeting
announcements
supported by the
VVM server.
Table 6: Parameters supported by GETMETADATA
Example of usage for the allowed greeting:
The possible error responses are:
If the GETMETADATA command is used with parameters not defined in RFC5464 or not
supported by the server, the error response will be:
C: a GETMETADATA "" /private/VVM/GreetingTypesAllowed S: * METADATA ""
(/private/VVM/GreetingTypesAllowed personal,voiceSignature,busyGreeting)
S: a OK GETMETADATA complete
S: a BAD GETMETADATA invalid parameter
S: a NO GETMETADATA application error
S: a BAD GETMETADATA invalid command
S: a BAD GETMETADATA command not allowed

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 13 of 80
2.1.1.6 Getquotaroot and Getquota Command
The VVM service supports the GETQUOTAROOT and GETQUOTA commands, as described
in RFC2087. All other commands in the quota extension are not supported.
Both the GETQUOTAROOT and GETQUOTA responses include the total quota and the quota
per media types for all mailbox folders. The following is the GETQUOTA response syntax:
Where:
• The media type returned in the GETQUOTAROOT or GETQUOTA responses
depends on the media types supported in the system, including the following:
o Voice
o Fax
o Video
o Greeting
o Empty Call Capture
o NUMBER message
Additional media types might be returned in the response. Such media types shall be
ignored by the client.
• The soft quota represents the quota on which the subscriber is being notified.
• The returned units depend on system initial setup. The default setup is as follows:
o Voice messages = Length in seconds
o Video messages = Length in seconds
o Fax messages = Number of pages
o Greetings messages = Length in seconds
o STORAGE = Size in KB
o Empty Call Capture and NUMBER messages = number of messages
QUOTA "" (STORAGE [occupied] [total] MESSAGE [occupied] [total] MESSAGE-soft
[occupied] [total] empty-call-capture [occupied] [total] empty-call-capture-soft [occupied]
[total] number [occupied] [total] number-soft [occupied] [total] fax [occupied] [total] fax-soft
[occupied] [total] voice [occupied] [total] voice-soft [occupied] [total] video [occupied] [total]
video-soft [occupied] [total] x-voice-greeting [occupied] [total] x-voice-greeting-soft
[occupied] [total])

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 14 of 80
The VVM service can be configured to return total storage only or a specific media type, such
as voice only, fax only, video only, or greeting only. In this case the response syntax is as
follows:
* QUOTA "" (STORAGE [occupied][total])
2.1.1.7 Login
The VVM service supports the LOGIN command, as described in RFC3501.
For the error messages that can be returned for the LOGIN command, refer to Table 5
AUTHENTICATE Command Error Messages.
2.1.1.8 Search
The VVM service supports the SEARCH command, as described in RFC3501.
Note: The BODY, LARGER, SMALLER, and TEXT search criteria must not be used. SEARCH
commands performed with one of these attributes can respond with incorrect results, due to
the differences between the media format stored in the server and the format returned to the
client upon the Body Fetch command.
2.1.1.9 Setmetadata
The SETMETADATA command, as defined in the RFC5464, is used for the client to set
annotations, and it is only available in authenticated or selected states.
All parameter names for this command are defined in a namespace, with the following prefix:
“/private/VVM/”. It is envisaged that any new parameters included in the protocol will be
managed via the METADATA extension rather than via SMS.
Table 7 lists the parameters which are supported for the VVM service:
Variable Values Comment
Accept
A list of the media formats
supported by the VVM
client.
Legal values:
List of one or more
voice media types
listed in Table 8
separated by a comma
(,).
This parameter defines the
media formats supported by
the client.
A SETMETADATA
command shall be issued by
the client at the beginning of an
IMAP session, right after a
successful authentication with
the VVM server.
Table 7: Parameters supported by SETMETADATA

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 15 of 80
Example of usage for the allowed greeting:
Possible error responses are:
2.1.1.10 Starttls
The VVM service supports the STARTTLS command, as described in RFC3501.
2.1.1.11 Status
The VVM service supports the STATUS command, as described in RFC3501.
The client application must not perform the STATUS command on the Greetings folder. The
VVM server synchronises the greetings in the Greetings folder with the greeting in the TUI
storage upon a SELECT Greetings command. If the STATUS command is performed on the
greeting folder, the system returns the following error message:
No command not allowed
2.1.1.12 Supported IMAP4 Flags
The following standard IMAP4 flags are supported by the VVM service:
• \Seen: Indicates that the message was played
• \Deleted: Indicates that the message was deleted
• \Recent: Indicates that the message is "recently" arrived in this mailbox
Note: Other standard or non-standard IMAP4 flags, must not be set by the client, except for
the $CNS-Greeting-On flag (see section 2.6 ).
If non-supported flags are set by the client, the system returns the following error message:
No command not allowed
2.1.2
Message Retrieval: Supported Message Types
The following message types can be retrieved via the VVM service:
C: a SETMETADATA "" (/private/VVM/Accept "audio/amr,audio/wav;
codec=g711a")
S: a OK SETMETADATA complete
S: a BAD invalid parameter (wrong parameters) S: a NO application error (server
error)
S: a BAD SETMETADATA unrecognized IMAP4 command (for backward compatibility in
case of new client working against old server)

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 16 of 80
• Voice
• Video
• Fax
• ECC (Empty Call Capture): An empty voice message.
• Number Message: An empty voice message including the number to which the reply
is sent.
• MDN (Message Disposition Notification): A system message advising the
subscriber whether the message has been displayed, deleted, dispatched, or denied
• DSN (Delivery Status Notification): A system message notifying the subscriber of
the message delivery status (Delivered, Failed, or Delayed).
• Infotainment: A voice message deposited directly to the subscriber mailbox by an
external application.
2.1.3
Message Retrieval: Supported Attachment Formats
Upon a Fetch Body command, the VVM server transcodes the message attachment to a
format supported by the client. A message may have multiple attachments or components.
Depending on how the TUI formats forwarded messages, a component may also encapsulate
multiple components.
All attachments are encoded in base64.
Table 8 below lists the file formats supported by the protocol.
Attachment Type
File Formats
MIME Types
Voice and
Greeting
attachments
AMR 12200
AMR WB
audio/amr
audio/amr-wb
WAV g711a
WAV g711u
audio/wav; codec=“g711a” audio/wav;
codec=“g711u”
QCELP 13300
EVRC, 13000
EVS 3GPP TS 26.441
audio/qcelp
audio/evrc
audio
Video
attachments
3gpp h263_amr
video/3gpp; codec=“h263_amr”
Fax attachments
PDF
TIF/TIFF
application/pdf
image/tiff
Scripted Text
Text
plain/text
Table 8: Supported Attachment Formats
2.1.4
VVM TUI Features Limitations
The VVM service has the following limitations relating to specific TUI features:

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 17 of 80
• Re-save: When a message is re-saved via the TUI, the original message is deleted
and the internal date of the new message reflects the last date in which the message
was re-saved. The original message deposit date can be obtained from the message
Date header.
• ECC from the same Calling Line Identification (CLI) Aggregation: When ECC
messages from the same CLI are aggregated, the internal date of the resulted
message reflects the last missed call date. The date in which the ECC was first issued
can be obtained from message Date header.
Note: When these TUI features are used, the UID of the message on which the action was
executed changes.
2.1.5
Message Retrieval Header Reference
The following types of headers are returned to the VVM client during message retrieval
sessions:
• Standard Root Level Message Retrieval Header Reference: Describes the
standard message headers returned in the root level of the message
• VVM Specific Root Level Message Retrieval Header Reference: Describes the
VVM specific message headers returned in the root level of the message
• Attachment Message Retrieval Header Reference: Describes the message header
returned at the attachment level of the message
For examples of MIME messages, see VVM Message Command Examples.
2.1.5.1 Root Level Message Retrieval Header Reference
The following headers are returned to the VVM client during message retrieval sessions at the
root level:
From
Description: Defines the message originator.
This header is mandatory.
Note: In case of a restricted CLI, the VVM client should not rely on the
From field, because the default value can change depending on the
voice mail deployment.
Legal Values: The phone number of the message originator, including the domain, in
the following format:
<phone-number>@<domain name>
Default Value: In case of a restricted CLI, Unknown@<domain name>
The client recognizes that the CLI is restricted if the left side of the
email address is not a numeric phone number.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 18 of 80
To
Description: Defines the phone line numbers associated with the message. Multiple
addresses are separated by commas. This header is mandatory.
Legal Values: <main-phone>@<domain name>
Default Value: N/A
Date
Description: Defines the date that the message was sent.
This header is mandatory.
Note: It is the responsibility of the client to display dates in the time-
zone of the client. The message received date is accessed from the
internal date message attribute. The Internal date may not reflect the
actual received time of the message when the Re- save or ECC
aggregation features are used via the TUI (see VVM TUI Features
Limitations).
Legal Values: As defined in RFC2822.
Default Value: N/A
Example:
Sun, 2 Sep 2007 07:36:05 +0000 (UTC)
Subject
Description: Determines the message subject.
This header is optional.
Note: The VVM client should not rely on the Subject header to detect
the message type. The message type should be detected according to
the Message-Context header.
Legal Values: Alphanumeric string (maximum length 90 characters).
Default Value: N/A
Message-Context
Description: Determines the message context.
This header is mandatory.
For MDN and DSN message types, this header specifies the original
message type.
Legal Values: Voice-message

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 19 of 80
Video-message Fax-message
X-empty-call-capture-message X-number-message
X-voice-infotainment-message
Default Value: N/A
Content-Duration
Description: Defines the length of the message, and is returned only for voice and
video messages.
This header is mandatory for voice and video messages.
Legal Values: Length of voice or video content, in seconds.
Default Value: N/A
Content-Type
Description: The message content type. This header is used to recognize MDN and
DSN messages.
This header is mandatory.
Note: The VVM client can use this header value to distinguish
between MDN or DSN messages and other messages.
Legal Values: For voice messages: Multipart/voice-message or Multipart/mixed
For fax messages: Multipart/fax-message or Multipart/mixed
For video messages: Multipart/video-message or Multipart/mixed
For ECC and number messages: Text/Plain
For DSN messages: Multipart/report: report- type=delivery-status
For MDN messages: Multipart/report; report- type=receipt-disposition-
notification (or report- type=disposition-notification)
For Infotainment messages: multipart/mixed
Default Value: N/A
MIME-Version
Description: Determines the MIME version.
This header is mandatory.
Legal Values: 1.0 (Voice Version 2.0)
Default Value: 1.0 (Voice Version 2.0)

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 20 of 80
Importance
Description: Determines the message priority.
This header is optional.
Legal Values: Normal
High
Default Value: Normal
Sensitivity
Description: Determines the message sensitivity.
This header is optional.
Legal Values: Private
Confidential Personal
Default Value: N/A
X-Content-Pages
Description: Defines the number of fax pages in a fax message, and is relevant only for
fax messages.
This header is mandatory for fax messages.
Legal Values: Integer
Default Value: N/A
X-Original-Msg-UID
Description: Used in case the message is the result of on-demand (asynchronous)
transcription that replaced an original voice message. It contains the UID of that original
voice message which no longer exists in the voice mail system (and may exist in the client
cache).
This header is optional.
Note: The current message contains both voice message and the text transcription.
Legal Values: UID as defined in RFC 3501
Default Value: N/A
2.1.5.2 Attachment Message Retrieval Header Reference
The following header is returned to the VVM client during message retrieval sessions per
attachment:

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 21 of 80
Content-Type
Description: Determines the attachment content type.
The name and application parameters can optionally be added to
this header.
This header is mandatory.
Legal Values: For Voice Messages: audio/wav; codec=g711a audio/wav;
codec=g711u audio/amr; audio/qcelp
For Fax Messages: application/pdf
For Video Messages: video/3gpp; codec="h263_amr"
For Scripted Voice Messages: text/plain
For nested messages: Message/rfc822
Default Value: N/A
X-Transcription
Description: This header is added to text attachments (transcription result). It contains
the content ID of the transcript attachment.
This header is optional.
Legal Values: Source-ID= <id>, id value MUST equal to the value of Content-ID header
of the transcript body part (Content-ID header legal value is according to RFC 2111)
Default Value: N/A
2.2 Message Deposit Interface Description
The VVM service supports voice message deposit via the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
(SMTP) protocol as described in RFC2821. SMTP authentication uses the AUTH mechanism
command as described in RFC 2554.
The client may optionally use STARTTLS from RFC2595, RFC3207, RFC4642 for session
encryption.
In the SMTP AUTH (Digest MD5) command, the client is authenticated with a predefined
username and password, supplied as part of the STATUS SMS.
For an example of an SMTP authentication command, see SMTP MD5 Authentication
Example.
Note: Only voice messages can be deposited via the VVM service.
Only the Digest-MD5 algorithm is supported in the AUTH mechanism command.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 22 of 80
Delivery Status Notification (DSN) messages are deposited in the sender’s mailbox if one of
the message recipients was not located. See Voice DSN Message Example for an example
of DSN.
For details about the headers included in deposited messages, see:
• Standard Message Deposit Header Reference (section 2.2.1): Describes message
deposit headers that require specific values
• VVM Specific Message Deposit Header Reference (section 2.2.2): Describes
additional headers that can be added to the deposited message
• Message Deposit Attachment Header Reference (section 2.2.3): Describes
attachment headers that require specific values
When forwarding or replying, the original should be attached as a message [RFC822] mime
component. Putting the original as a message [RFC822] component in the reply/forward
preserves all the header information of the original message. The TUI might need this
information. The VVM server might have to reformat the message to the format that the TUI
expects.
2.2.1
Standard Message Deposit Header Reference
The following RFC2822 message deposit headers require specific values:
From
Description: The Phone number and domain of the message sender.
This header is mandatory.
Legal Values: <phone-number>@<domain name>
Default Value: N/A
Example: [email protected]
To
Description: Defines the message addressee. Multiple addresses are separated by
commas.
This header is mandatory.
Note: RCPT TO envelope headers are used to resolve the destination. The
VVM client must set the RCPT TO envelope header in addition to the
message TO field.
Legal Values: <main-phone>@<domain name>
Default Value: N/A

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 23 of 80
Date
Description: Defines the date that the message was sent.
This header is mandatory.
Legal Values: Date and time as defined by RFC2822
Default Value: N/A
Example:
Sun, 2 Sep 2007 07:36:05 +0000 (UTC)
Subject
Description: Defines the message subject.
This header is optional.
Note: The subject header is not available via TUI sessions, and can
be displayed through web UI access.
The subject set by the client may be overridden by the VVM system
with default values.
Legal Values: Alphanumeric string (maximum length 90 characters)
Default Value: N/A
Message-Context
Description: Defines the standard header for message presentation, based on
RFC 3458.
This header is mandatory.
Legal Values: Voice-message
Default Value: N/A
Content-Duration
Description: Defines the length of the message in seconds.
This header is mandatory.
Legal Values: Integer
Default Value: N/A
Content-Type
Description: Determines the message content-type.
This header is mandatory.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 24 of 80
Legal Values: Multipart/mixed
Default Value: N/A
MIME-Version
Description: Defines the MIME version.
This header is mandatory.
Legal Values: 1.0
Default Value: N/A
Importance
Description: Defines the message importance.
This header is optional.
Legal Values: High
Normal (including Low importance)
Default Value: Normal
Sensitivity
Description: Determines the message sensitivity.
This is an optional header.
Legal Values: Private
Confidential Personal
Default Value: N/A
Expires
Description: Determines the message expiration date, after which the message is
automatically purged by the server periodic process.
This is an optional header.
Legal Values: Date in the following format:
DAY, D MMM YYYY HH:MM:SS (+-)TTTT
Default Value: N/A
Example:
Sun, 10 Mar 2005 18:16:02 +0200

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 25 of 80
2.2.2 VVM Specific Message Deposit Header Reference
The following additional header fields can be added to the deposited message:
X-CNS-Messaging-Action
Description: Determines the messaging action of the message.
This header is relevant only for messages using a messaging service
and is applicable only to some VVM systems.
This header is optional.
Legal Values: reply = Indicates that the message is a reply to a subscriber’s message
forward = Indicates that the message was forwarded to the subscriber by another
subscriber
Default Value: N/A
2.2.3
Message Deposit Attachment Header Reference
The following headers must be set by the VVM client in the attachment level:
Content-Type
Description: Determines the attachment content-type.
This header is mandatory.
Legal Values: message/rfc822
Multipart/mixed
See Table 8 Supported Attachment Formats for list of content-types.
Default Value: N/A
Content-Transfer-Encoding
Description: Determines the content transfer encoding.
This header is mandatory.
Legal Values: base64
Default Value: N/A
Content-Disposition
Description: Determines the attachment, along with the filename.
The voice mail system ignores the path for the file.
This header is mandatory.
Legal Values: attachment; filename="<file name>"

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 26 of 80
Default Value: N/A
Example:
attachment; filename="test.wav"
Content-Duration
Description: Defines the length of the voice attachment in seconds.
This header is mandatory.
Legal Values: Integer
Default Value: N/A
2.3 VVM Self-care
2.3.1 TUI Password Changes Interface Description
The VVM service enables the client to change the subscriber’s TUI password via a custom
IMAP4 command. The change password command can be invoked only in the authenticated
state, meaning that the user must be in the authenticated IMAP4 session.
The password must be made up of numeric digits only.
The password minimum and maximum length will be sent to the client in the STATUS SMS
message (see STATUS SMS Description (Server Originated)).
For details about the command syntax used to change TUI passwords, see:
• Change Password Request Syntax (section 2.3.1.1)
• Change Password Response Syntax (section 2.3.1.2)
2.3.1.1 Change Password Request Syntax
The change password request syntax is as follows:
CNS1 XCHANGE_TUI_PWD PWD=<Value> OLD_PWD=<Value>
The change password request syntax uses the following parameters:
PWD
Description: Defines the new TUI password.
This parameter is mandatory.
Legal Values: Integer
Default Value: N/A
OLD_PWD
Description: The current TUI password that is being replaced.
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 27 of 80
This parameter is mandatory.
Legal Values: Integer
Default Value: N/A
In case of invalid command syntax, the following error is returned:
No Unknown Command
2.3.1.2 Change Password Response Syntax
Upon successfully changing the password, the following response is returned:
CNS1 OK password changed successfully
The following errors can also be returned in the change password response:
CNS1 NO password too short
CNS1 NO password too long
CNS1 NO password too weak
CNS1 NO old password mismatch
CNS1 NO password contains invalid characters
CNS1 NO system error
2.3.2
Change TUI Language Interface Description
The VVM service enables the client to change the subscriber’s voice mail language via a
custom IMAP4 command. The change language command can be invoked only in the
authenticated state, meaning that the user must be in the authenticated IMAP4 session.
The system supported languages is sent to the client in the STATUS SMS message (see
STATUS SMS Description (Server Originated))
For details about the command syntax used to change TUI languages, see:
• Change Language Request Syntax (section 2.3.2.1)
• Change Language Response Syntax (section 2.3.2.2)
2.3.2.1 Change Language Request Syntax
The change language request syntax is as follows:
CNS2 XCHANGE_VM_LANG LANG=<Language number>
The change language request syntax includes the following parameter:

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 28 of 80
Lang
Description: Determines the new language, and is one of the system supported
languages as returned in the STATUS SMS (see STATUS SMS Description (Server
Originated)).
This parameter is mandatory.
Legal Values: String maximum 5 digits in the following format:
<lang code>.<variant>
The "lang code" is an ISO 639-2 value, 3 characters max
The "variant" is optional and is one (values 0 to 9) digit indicating a
speech characteristic or accent extension (for example a male or
female voice). The definition of the variant value will be configured in
the VVM client and server sides according to the operator policies and
requirements.
Examples of valid values: Lang=eng
Lang=eng.1
Default Value: N/A
In case of invalid command syntax, the following error message is
returned:
No unknown command
2.3.2.2 Change Language Response Syntax
Upon a successful language change, the following response is returned:
CNS2 OK language changed successfully
The following possible errors can also be returned in the change language response:
CNS2 NO invalid language
CNS2 NO system problem
2.3.3
Generic Feature Change: Interface Description
The VVM service enables the client to configure operator specific services on the Voicemail
Server. This could be for example toggling on/off the possibility for the mailbox to receive
voicemail deposits (so called “box mode”).
The VVM service enables the client to send a 2-byte generic options string via a custom IMAP4
command. For the example above, the operator could define that the first bit of the options
string defines whether the voice mailbox should accept incoming messages.
The generic feature change command can be invoked only in the authenticated state, meaning
that the user must be in the authenticated IMAP4 session.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 29 of 80
For details about the command syntax used for the generic feature change, see:
• Change Generic Options String Request Syntax (section 2.3.3.1)
• Change Generic Options String Response Syntax (section 2.3.3.2)
2.3.3.1 Change Generic Options String Request Syntax
The change generic options string syntax is as follows:
CNS6 XCHANGE_GEN_OPTIONS_STRING OPTIONSSTRING=<optionsstring>
The change options string request syntax includes the following parameter:
optionsstring
Description: Determines the value of the operator specific options string.
This parameter is mandatory.
Legal Values: HexString 4 characters :
Examples of valid values: option string = ”aaff”
Default Value: N/A
In case of invalid command syntax, the following error message is
returned:
No unknown command
2.3.3.2 Change Generic Options String Syntax
Upon a successful options string change, the following response is returned:
CNS6 OK optionsstring changed successfully
The following possible errors can also be returned in the options string change response:
CNS6 NO invalid value
CNS6 NO system problem
2.4 Close NUT Interface Description
If available, the New User Tutorial (NUT) is implemented in the client. It is usually played the
first time the user uses the VVM application if the subscriber status is “new subscriber” (see
STATUS SMS Description (Server Originated)). The VVM service enables the client to disable
the New User Tutorial (NUT) flag in the server via a custom IMAP4 command to change the
provisioning status of the customer in order for the server to avoid re-playing the TUI NUT.
The CLOSE NUT command can be invoked only in the authenticated state, meaning that the
user must be in the authenticated IMAP4 session.
For details about the command syntax used to change TUI languages, see:
• CLOSE NUT Request Syntax (2.4.1)

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 30 of 80
• CLOSE NUT Response Syntax (section 2.4.2)
2.4.1
Close NUT Request Syntax
The CLOSE NUT request syntax is as follows:
CNS3 XCLOSE_NUT
In case of invalid command syntax, the following error is returned:
No unknown command
2.4.2
Close NUT Response Syntax
Upon successful NUT CLOSE, the following response is returned:
CNS3 OK NUT closed
Note: A successful CLOSE NUT command changes the VVM subscriber provisioning status
and triggers a STATUS SMS message (see STATUS SMS Description (Server Originated)).
The following error can also be returned as part of the CLOSE NUT response:
CNS3 NO system error
2.5 On Demand Audio Message Transcription Command Services
The VVM service enables the client to order an audio message transcription via a custom
IMAP4 command. It allows also START/STOP the transcription service.
For details about the command syntax used to trigger the transcription, see:
• On-demand transcription Request Syntax (section 2.5.1)
• On-demand transcription response Syntax (section 2.5.2)
For details about the command syntax used to START/STOP the service, see:
• START/STOP service request Syntax (section 2.5.3)
• START/STOP service response Syntax (section 2.5.4)
2.5.1
On-Demand Transcription Request Syntax
The on-demand transcription request syntax is as follows:
CNS4 XTRANSCRIBE_ UID=< UID>
The on-demand transcription request syntax includes the following parameter:
UID
Description: Determines UID of the audio message to be transcribed on-demand
This parameter is mandatory.
Legal Values: UID as defined in RFC 3501

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 31 of 80
Default Value: N/A
In case of invalid command syntax, the following error message is returned:
No unknown command
2.5.2
On-Demand Transcription Response Syntax
Upon a successful on-demand transcription request, the following response is returned:
CNS4 OK Transcription order sent successfully
The following possible errors can also be returned in the on-demand transcription response:
CNS4 NO invalid UID
CNS4 NO transcription service not available
CNS4 NO system error
2.5.3
Automatic Transcription Service START/STOP Request Syntax
The VVM service allows the VVM client to control the automatic transcription service status.
While the automatic transcription service is enabled, every new voice message deposited to
the mailbox will be transcribed.
The automatic transcription START/STOP request syntax is as follows:
CNS5 XTRANSCRIPTION_SERVICE_ STATE=<START|STOP> EXP_DATE=<date>
SUB_DURATION=<duration>
The command includes the following parameter:
STATE
Description: Determines the requested state of the automatic transcription service.
Legal Values: "START" or "STOP" strings
Default Value: N/A
In case of invalid command syntax, the following error message is returned:
No unknown command
EXP_DATE
Description: Determines the requested expiration date of the automatic transcription
service. This header is optional.
Legal Values: A date in the format YYYY-MM-DD (e.g. 2019-01-25)
Default Value: N/A
In case of invalid command syntax, the following error message is returned:

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 32 of 80
No unknown command
SUB_DURATION
Description: Determines the requested subscription duration (expressed in months) of
the automatic transcription service. This header is optional.
Legal Values: Numeric value from "1" to" 24"
Default Value: N/A
In case of invalid command syntax, the following error message is returned:
No unknown command
2.5.4
Automatic Transcription Service START/STOP Response Syntax
Upon a successful automatic transcription state change request, the following response is
returned:
CNS5 OK Transcription service is now <state>. Validity <EXP_DATE>.
Where <state> is either "stopped" or "started".
Where <EXP_DATE> is the value of the expiration date of the service in the format of YYYY-
MM-DD (e.g. 2019-01-25).
The following possible errors can also be returned in the response:
CNS5 NO Transcription service remains unchanged
CNS5 NO Transcription service unreachable
CNS5 NO system error
2.6 Guidelines For Greetings And Voice Signature Management
The VVM service enables the client to manage personalised greetings and voice signatures.
Not all voice mail users want to leave a fully personalised greeting. The Voice Signature (VS)
option allows users to leave a very short recording typically a couple of seconds long. The
Voice Mail System would use this message, the voice signature, to replace the phone number
in the default system voice mail greeting that a user hears when the call is diverted to the voice
mail system. Thus, for example, instead of hearing the response "You have reached the
mailbox of 12345678910, please leave a message after the beep", one would hear "You have
reached the mailbox of Michel Arnaud, please leave a message after the beep".
Greetings (personalised and VS) are stored in the server in the subscriber’s Greetings Folder,
in the format of a multipart-mixed message with an audio attachment. Personalised greetings
and VS are distinguished by a specific header, as described in section 2.6.3
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 33 of 80
Several personalised greetings or VS can be flagged as “ON”. This flag indicates to the server
that these messages are to be used by the voice mail system in the TUI session, according to
the voice mail logic.
If several greetings of the same type are simultaneously flagged as ($CNS- Greeting-On) the
voice mail system will play the one with the smallest message-sequence. If no personalised
greeting or VS are flagged as ($CNS- Greeting-On) then the default system voice mail greeting
will be played by the voice mail system.
Greeting headers that require specific values and are set by the VVM client are described in
section 2.6.3
See the following for details about how to upload or delete greetings or VSs from the
Greetings Folder on the VVM server:
• Uploading a Greeting or VS section 2.6.1
• Deleting a Greeting or VS section 2.6.1
Note:
Greeting management error responses are formatted according to the IMAP4 standard.
In order to perform actions on the Greetings folder, the client application must issue the
SELECT GREETINGS command.
The client application must not perform STATUS command on the Greetings Folder.
2.6.1
Uploading a Greeting or VS
This procedure describes how to upload a personalised greeting or VS to the Greetings
Folder.
How:
1. Use the IMAP4 APPEND command to append the message to the Greetings Folder.
2. In order to activate a greeting, set the $CNS-Greeting-On flag.
Note:
The VVM client can append several personalised greetings and several VS to the Greetings
folder, up to the quota limit.
The flag can be set as part of the APPEND command or with a dedicated store command.
The client must limit the recorded greeting or VS length according to the maximum greeting
or VS length received in the STATUS SMS message (see STATUS SMS Description (Server
Originated)).
2.6.2
Deleting a Greeting or VS
This procedure describes how to delete a greeting or VS from the Greetings Folder.
How:

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 34 of 80
1. Flag the greeting or VS as deleted.
2. Send the Expunge command.
Note:
Deleted greetings or VS flagged as ($CNS-Greeting-On) are not played by the VVM system,
and the default greeting is played instead.
2.6.3
Greeting Header Reference
The following greeting and VS headers require specific values, and must be set by the client.
X-CNS-Greeting-Type
Description: Determines the greeting type. This header is mandatory.
Legal Values: normal-greeting For Personalised greeting
voice-signature For VS (Name greeting)
busy-greeting For a personalised greeting when busy. If not recorded,
normal greeting is used. If recorded, the normal greeting is used for the
“no-answer” case, and the busy-greeting used for the “busy” case.
extended-absence-greeting If this greeting is flagged “on”, it takes
precedence over “normal” and “no-answer” greetings.
Default Value: N/A
From
Description: The phone number@Domain of the message sender.
This header value is ignored by the server.
Legal Values: N/A
Default Value: N/A
Subject
Description: Defines the message subject.
This header value is ignored by the server.
Legal Values: N/A
Default Value: N/A
Content-Type
Description: Determines the message content type.
This header is mandatory and appears in the message header and in
the MIME part header.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 35 of 80
The greeting must include a single voice attachment at the root level
only.
Legal Values: Message header content-type: multipart/mixed;
[boundary=<boundary -string>]
MIME part content-type (must be encoded in base64):
The valid values are the audio MIME types in Table 8 Supported
Attachment Formats
Default Value: N/A
To
Description: Defines the message addressee.
This header value is ignored by the server.
Legal Values: N/A
Default Value: N/A
MIME-Version
Description: Defines the MIME version.
This header is mandatory.
Legal Values: 1.0
Default Value: N/A
Content-Transfer-Encoding
Description: Defines the content transfer encoding.
This header is mandatory.
Legal Values: base64
Default Value: N/A
2.7 Provisioning Status
The provisioning status of a subscriber determines their access level to VVM services.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 36 of 80
Figure 1: VVM Provisioning Status Transitions
Table 9 below describes the possible status of VVM provisioning.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 37 of 80
VVM
Provisioning
Status
Description
VVM Service Impact
Subscriber
Unknown
The subscriber is not
provisioned to the VVM
service or does not have
a
mailbox in the voice
mail
system
VVM service is not active:
•
SYNC SMS will not be sent from the server.
•
The server may send legacy notifications for voice
mail deposit.
•
STATUS SMS may be sent from the server.
•
The client must not initiate IMAP4 sessions.
•
The server will block IMAP4 session initiation
attempts.
Subscriber
Provisioned
The subscriber is
provisioned to the VVM
service, while the VVM
service is not activated
yet.
VVM service is temporarily not active:
•
SYNC SMS will not be sent from the server.
•
The server may send legacy notifications for voice
mail deposit.
•
STATUS SMS may be sent from the server.
•
The VVM server will block IMAP4 session
initiation attempts.
•
The VVM client may send activate SMS to change
provisioning status to New or Ready.
Subscriber
New
The subscriber is
provisioned to the VVM
service, and the VVM
service is active, while
the
subscriber has not
gone
through NUT
(New User
Tutorial)
session.
VVM service is active:
•
SYNC SMS may be sent from the server.
•
The server may send legacy notifications for voice
mail deposit.
•
STATUS SMS may be sent from the server.
•
The VVM server allows IMAP4 session initiation
attempts.
•
The VVM client may issue CLOSE_NUT
command (to change provisioning status to
READY).
•
The VVM client may send de-activate SMS to
change the provisioning status to Provisioned.
Subscriber
Ready
The subscriber is
provisioned to the VVM
service, and the VVM
service is active, while
the
subscriber has
already
gone through
NUT
session.
VVM service is active:
•
SYNC SMS may be sent from the server.
•
The server may send legacy notifications for voice
mail deposit.
•
STATUS SMS may be sent from the server.
•
The VVM server allows IMAP4 session initiation
attempts.
•
The VVM client may send de-activate SMS to
change the provisioning status to Provisioned
Subscriber
Blocked
The subscriber mailbox
is
Blocked
VVM service is temporarily not active:
•
SYNC SMS may be sent from the server.
•
The server may send legacy notifications for voice
mail deposit.
•
STATUS SMS may be sent from the server.
•
The VVM server will block IMAP4 session
initiation attempts.
Table 9: VVM Provisioning States
2.8 VVM SMS Interface Description
The VVM makes use of SMS for various reasons, e.g. authentication, activation,
deactivation, notification of the client of a new unread messages and notification of the
server for change in provisioning status.
Technically, this is implemented by using the following types of SMS messages:

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 38 of 80
• “Server Originated” SMS Messages: SMS messages sent to the VVM client to
notify the client about a specific event in the subscriber’s mailbox or profile. Note:
“Mobile Terminated SMS (MT-SMS)” from a mobile network point of view;
• “Client Originated” SMS Messages: SMS messages that enable the client to query
the system about the subscriber’s status, activate and deactivate the service, as well
as to set the service notifications on or off. Note: “Mobile Originated SMS (MO-SMS)”
from a mobile network point of view.
Altogether, there are the following SMS message types (Table 10 below).
No
Name
Type
Name Name
1
SYNC SMS
Server
Originated
Notifies the client that the status of a
message or greeting in the mailbox may
have been changed (Triggering)
.
2
STATUS SMS
Server
Originated
Notifies the client that the VVM
subscriber’s provisioning status was
changed (Triggering)
.
3
OTP SMS
Server
Originated
Provides the client with the One-Time-
Password (OTP) that is needed for the
registration of the Push-based VVM client
(Authentication)
4
STATUS SMS
Client Originated
Query the provisioning status of the
subscriber
5
ACTIVATE
SMS
Client Originated
Activate the service (Authentication)
6
DEACTIVATE
SMS
Client Originated
Deactivate the service
Table 10: SMS Message Types
The SMS format is based on the Terminal type, which is stored in the subscriber’s profile either
during the service activation process (see Activate SMS (Client Originated)) or by the
operator’s customer support.
The VVM service sends the VVM notifications to the client’s VVM application port. The
notifications have specific characteristics, as described in section 2.8.1
Note: Depending on the Terminal type, it is possible to configure the VVM service to send
legacy notifications in addition to the VVM notifications, in order to support a scenario in which
the VVM subscriber SIM is switched to a non-VVM enabled Terminal that cannot process VVM
notifications.
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 39 of 80
If regular notifications are sent in addition to VVM notifications, it is the responsibility of the
client to filter out the regular notifications according to the SMS source address or SMS
Protocol Identifier.
2.8.1
Server Originated SMS Messages: Overview
The VVM service sends the following SMS messages to the client:
• SYNC SMS: Notifies the client that the status of a message or greeting in the mailbox
may have been changed.
For details see SYNC SMS Description (Server Originated).
• STATUS SMS: Notifies the client that the VVM subscriber’s provisioning status was
changed.
For details see STATUS SMS Description (Server Originated).
• OTP SMS: Provides the client with the One-Time-Password (OTP) that is needed for
the registration of the Push-based VVM client.
For details see OTP SMS Description (Server Originated) in section 2.8.5
Server Originated SMS Message Characteristics:
• The maximum length for Server Originated SMS messages is 160 characters for 7bit
encoding and 140 characters for 8bit encoding. It is recommended not to exceed the
maximum SMS message length.
• If the SMS message exceeds the maximum message length, the Short Message
Service Centre (SMSC) for both the operator and the client must support SMS
concatenation.
• The outgoing SMS can be configured on the server according to the client type.
• For example, the default SMS configuration of a binary message sent by the server is
according to 3GPP TS23.040. An example of such a message is:
• ESM class = 64 (for using UDH),
• Data coding = 4 (8-bit encoding),
• Protocol ID = 64 (Type 0 message indicating the mobile to acknowledge the
message silently),
• Application Port Addressing scheme in UDH = 5 (16bit address)
• Destination Application Port Address = client’s listening port on the Terminal
by client as defined in 2.8.8
• Replace flag = 1 (replace) for the following service types:
o For SYNC SMS messages due to Inbox change,
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 40 of 80
o For STATUS and deactivate response SMS messages,
o For SYNC SMS messages due to Greeting change.
These SMS parameters can be customised on the server.
2.8.2
Client Originated SMS Messages: Overview
The client can send SMS messages to the server to do the following:
• Query the provisioning status of the subscriber, using a STATUS SMS message (see
STATUS SMS (Client Originated)),
• Activate the service (see Activate SMS (Client Originated), section 2.8.7
• Deactivate the service (see Deactivate SMS (Client Originated), section 2.8.8
The VVM client sends the SMS messages to a destination number that is configured into the
VVM client (see also the field dn in section 2.8.4.2). Upon receiving the VVM client SMS
message, the SMSC finds the relevant VVM system and transfers the received SMS as an AT
message. The VVM service then sends a response to the VVM client that sent the original
message.
Note: The client must not depend on reliable delivery and may retry a command that has not
returned a response.
2.8.3
SYNC SMS (Server Originated)
2.8.3.1 SYNC SMS Description (Server Originated)
SYNC SMS messages are sent from the system to the client in order to notify the client that
the status of a message or greeting in the mailbox may have changed. A SYNC SMS message
will be sent when:
• A new message has been deposited in the subscriber’s mailbox,
Additionally, a SYNC SMS may be sent when one or more of the following events occur:
• Message purge due to retention time exceeded,
• TUI session logout,
• Greeting changed via the TUI, including a personalised greeting or VS recorded or
deleted.
In the SYNC SMS message, both the Client prefix and Prefix fields are followed by a colon (:),
and all other fields are followed by semicolons (;). Each field is represented by the field name,
an equal sign (=), and a legal value. Spaces are not allowed between parameters, although
parameter values may include spaces.
For details about SYNC SMS notification messages see SYNC SMS Field Reference and
SYNC SMS Notification Examples.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 41 of 80
2.8.3.2 SYNC SMS Field Reference
The following fields are used in SYNC SMS text that is sent to the VVM client:
Client prefix
Description: The definition is dependent on the client.
Also see Client prefix in Activate SMS section 2.8.7
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: Configurable string, unlimited length, always followed by a colon (:)
Default Value: //VVM
Prefix
Description: Determines the SMS type.
This field is always followed by a colon (:).
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: String, maximum four characters
SYNC
Default Value: SYNC
ev
Description: Determines the event that triggered the SYNC SMS.
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: String, maximum three characters;
NM = New message deposit, or update of a message with a text
transcription,
MBU = Mailbox update, including TUI session end or message purge,
GU = Greetings/VS update.
Default Value: N/A
id
Description: Defines the message UID.
This field is returned for new message events only, and the value can
be used by the client for the IMAP4 FETCH command, used to
retrieve the message.
This field is mandatory.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 42 of 80
Legal Values: New message UID, maximum 21 digits.
Default Value: N/A
c
Description: Defines the number of new messages in the inbox.
The client may use this field to show the number of new messages.
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: Integer, maximum five digits.
Default Value: N/A
t
Description: Determines the message type. This field is returned for new message
events only.
The client may use this field to show the type of message.
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: Maximum length one character;
v = Voice,
o = Video,
f = Fax,
i = Infotainment,
e = ECC.
Default Value: N/A
s
Description: Defines the message sender (message originator Mobile Subscriber
Integrated Services Digital Network Number (MSISDN)).
This field is returned for new message events only. This field is not
returned if the CLI is restricted.
The client may use this field to show the Message sender before
initiating IMAP communication.
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: Numeric string (phone number in E164 format), maximum length 29
digits (30 including the null terminator).

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 43 of 80
Default Value: N/A
dt
Description: Defines the deposit date and time, in the time zone of the VM server. This
field is returned for new message events only.
The client may use this field to show the deposit time before initiating
IMAP communication.
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: Date and time in DD/MM/YYYY HH:MM TZ format.
Maximum length 22 characters.
Default Value: N/A
Example:
02/08/2008 12:53 +0200
I
Description: Determines the message length.
This field is returned for new message events only.
This field is dependent on system configuration, and is used in the
default setup. The client may use this field to show the length of
message before initiating IMAP communication.
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: Numeric string, maximum five digits, as follows:
Voice, Video, and Infotainment messages: Length in seconds,
Fax messages: Number of pages,
Number and ECC messages: 0.
Default Value: 0
2.8.3.3 SYNC SMS Notification Examples
The following is an example of Server Originated SYNC SMS notifications:
Fields used in the SYNC SMS messages are described in SYNC SMS Field Reference.
//VVM:SYNC:ev=NM;id=3446456;c=1;t=v;s=01234567898;dt=02/08/2008 12:53 +0200;l=30

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 44 of 80
2.8.4 STATUS SMS (Server Originated)
2.8.4.1 STATUS SMS Description
STATUS SMS messages are sent from the system to the client to notify the client about
provisioning status changes. The VVM client is also able to query the VVM service for the
current status.
For details about provisioning status, see section 2.7
In the STATUS SMS message, the mandatory Client prefix field is following by a colon (:), as
well as the mandatory Prefix field. All other fields are followed by semicolons (;). Each field is
represented by the field name, an equal sign (=), and a legal value. Spaces are not allowed.
For details about STATUS SMS notification messages see STATUS SMS Field Reference
and STATUS SMS Field Examples.
2.8.4.2 STATUS SMS Field Reference
The following fields are used in the STATUS SMS text that is sent to the VVM client:
Client prefix
Description: The definition is dependent on the client.
Also see Client prefix in Activate SMS section 2.8.7
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: Configurable string, unlimited length, always followed by a colon (:).
Default Value: //VVM
Prefix
Description: Determines the SMS type.
This field is always followed by a colon (:)
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: String, maximum six characters
STATUS
Default Value: STATUS
st
Description: Determines the subscriber’s provisioning status.
For details about provisioning status transitions, see section 2.7
This field is mandatory.
Note: Depending on system configuration, the st value may appear
between quotation marks.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 45 of 80
For example: st="N"
Legal Values: Maximum length one character
N = Subscriber New
R = Subscriber Ready
P = Subscriber Provisioned
U = Subscriber Unknown
B = Subscriber Blocked
Default Value: N/A
rc
Description: Determines the return code. When the VVM provisioning status is
unknown one of the following codes is returned:
Mailbox unknown: The user is unknown by the voice mail system, he
does not have any voice mail box provisioned, even with a non- VVM
service.
VVM not provisioned: The user has a voice mail box provisioned on the
voice mail system, but he does not belong to a class of service allowing
him to use the VVM service.
VVM not activated: The user has been provisioned with a VVM service
on the system but the VVM service activation has failed.
VVM client unknown: The Client Type or Protocol Version is unknown.
VVM mailbox not initialised: The subscriber's mailbox has not yet been
initialized via the TUI, so the VVM service cannot be activated.
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: Maximum length one character;
0 = Success,
1 = System error,
2 = Subscriber error,
3 = Mailbox unknown,
4 = VVM not activated,
5 = VVM not provisioned,
6 = VVM client unknown,

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 46 of 80
7 = VVM mailbox not initialised.
Default Value: N/A
rs
Description: Provide a URL.
This URL may be used by the client to reach a server, in order for the
user to subscribe to the VVM service.
This field may be returned when the return code (rc) is "VVM not
provisioned".
Legal Values: String, maximum 100 characters
Default Value: N/A
srv
Description: Determines the IMAP4/SMTP server IP address or Fully Qualified Domain
Name.
This field is mandatory, but is not returned for U and B events (see st).
Legal Values: Prefix followed by VVM server IP address or Fully Qualified Domain
Name, maximum length 30 characters.
1:<IP address>
2:<FQDN>
Default Value: N/A
tui
Description: Determines the TUI access number.
This field is mandatory.
The client may use this field to show the visual voicemail TUI number.
Legal Values: A telephone number, up to 16 digits.
Default Value: N/A
dn
Description: Determines the destination number used for addressing the VVM service.
The destination number is used for a client originating SMS. This number is also
configured in the Terminal but may be different in value. The VVM client must always use
the latest number received from the server.
This field is not returned for U and B provisioning status (i.e. st=U or st=B).

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 47 of 80
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: destination number, maximum length 30 characters.
Default Value: N/A
ipt
Description: Determines the IMAP4 listening port.
This field is not returned for U and B events (see st).
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: IMAP4 port, maximum length 10 digits.
Default Value: N/A
spt
Description: Determines the SMTP listening port.
The client may use this field for SMTP deposits.
This field is not returned for U and B provisioning status (i.e. st=U or
st=B).
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: SMTP port, maximum length 10 digits.
0 in case the server does not support SMTP protocol
Default Value: N/A
“space”
Description: Determines the IMAP4 user name that is used upon LOGIN, including
domain.
This field is not returned for U and B events (see st).
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: IMAP4 username, maximum length 50 characters.
Default Value: N/A
pw
Description: Determines the IMAP4 password that is used upon login.
This field is mandatory, but is not returned for U and B events (see st).
Legal Values: IMAP4 password, maximum length 30 characters.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 48 of 80
Default Value: N/A
lang
Description: Determines the list of languages supported by the VVM system.
This field is used together with the change language command (see
section 2.3.2).
This field is not returned for U and B provisioning status (i.e. st=U or
st=B).
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: String, maximum length 36 characters.
Multiple values are separated by a pipe (|).
A language value will be in the following format:
<lang code>.<variant>
The "lang code" is an ISO 639-2 value, 3 characters max
The "variant" is one digit indicating a speech characteristic or accent
extension (for example a male or female voice). The variant is optional.
The definition of the variant value will be configured in the VVM client
and server sides according to the operator policies and requirements.
Example of valid value:
lang=eng.1|eng.2|fre|ita|ger.1|ger.2
Default Value: N/A
g_len
Description: Defines the maximum greeting length allowed, in seconds.
This field is not returned for U and B provisioning status (i.e. st=U or
st=B).
The client may use the field for the Record Greeting feature (see
Guidelines for Greetings and VS Management).
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: Integer, maximum three digits.
Default Value: N/A
vs_len
Description: Defines the maximum VS length allowed, in seconds.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 49 of 80
This field is not returned for U and B provisioning status (i.e. st=U or
st=B).
The client may use the field for the Record VS feature (see Guidelines
for Greetings and VS Management).
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: Integer, maximum three digits.
Default Value: N/A
pw_len
Description: Defines the minimum and maximum TUI password length allowed.
This field is used together with the change Password command (see
section 2.3.1).
This field is not returned for U and B provisioning status (i.e. st=U or
st=B).
The client may use the field for the TUI Password feature (see TUI
Password Changes Interface Description).
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: String, maximum five characters, in the following format:
<min length>-<max length>
Default Value: N/A
smtp_u
Description: Defines the username used upon SMTP authentication.
The client may use it for SMTP deposits.
This field is not returned for U and B provisioning status (i.e. st=U or
st=B).
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: String, unlimited length.
0 in case the server does not support SMTP protocol
Default Value: N/A
smtp_pw
Description: Defines the SMTP password used upon SMTP authentication.
The client may use it for SMTP deposits.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 50 of 80
This field is not returned for U and B provisioning status (i.e. st=U or
st=B).
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: String, unlimited length.
0 in case the server does not support SMTP protocol
Default Value: N/A
pm
Description: Defines if the pin code must be reset by the user at the VVM service
activation.
This field is sent only for new provisioning status.
This parameter, if set to Yes, does not prevent the client to activate the
VVM service, but is an indication which may be used by the client as a
condition to close the NUT.
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: String, Maximum 1 character:
Y
N
Default Value: N
gm
Description: Defines if a personal greeting or a voice signature must be reset by the
user at the VVM service activation.
This field is sent only for new provisioning status.
If this parameter is set to Yes, it does not prevent the client activating
the VVM service, but it is an indication which may be used by the client
as a condition to close the NUT.
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: String, Maximum 1 character;
G = normal greeting,
V = voice signature,
B = Both the normal greeting and the voice signature,
N = Neither.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 51 of 80
Default Value: N
vtc
Description: Defines the VVM server capabilities for a text transcription of a voice
message.
This field is not returned for U and B provisioning status (i.e. st=U or
st=B).
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: String, Maximum 1 character;
N = none (no voice to text capabilities),
D = on user demand,
A = automatic (for all messages),
B = both automatic and on demand.
Default Value: N
vt
Description: Defines the current state of the text transcription service for voice
messages.
This field is not returned for U and B provisioning status (i.e. st=U or
st=B).
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: String, Maximum 1 character;
0 = OFF,
1 = ON.
Default Value: 0
2.8.4.3 STATUS SMS Field Examples
The following are examples of STATUS SMS notifications:
//VVM:STATUS:st=N;rc=0;srv=1:10.115.67.251;tui=123;dn=999;ipt=143; spt=25;
u=78236487@wirelesscarrier.com;pw=32u4yguetrr34; lang=eng|fre;g_len=25;vs_len=15;pw_len=4-6;
smtp_u=super_user@wirelesscarrier.com; smtp_pw=48769463wer;pm=Y;gm=N;vtc=D;vt=1
//VVM:STATUS:st=B;rc=0

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 52 of 80
The fields used in STATUS SMS notifications are described in STATUS SMS Field
Reference.
2.8.5
OTP SMS Description (Server Originated)
OTP SMS messages are sent from the system to the active paging device of the user in order
to verify that he is the owner of the SIM card with MSISDN that he is trying to register for the
Push-based VVM client. An OTP SMS message will be sent when:
• A new Push-based VVM client is trying to register to the server.
The OTP SMS message shall be sent as a normal visible SMS message and normally shall
be visible in the default SMS application on the client’s device. The text of the SMS shall be
easy to understand.
The following is the example of OTP SMS.
Your requested code for Voicemail App is: 123456.
The code is valid for 10 minutes.
More information. www.youroperator.com/voicemail
The server shall support several languages for the OTP SMS. The specific language shall be
used according to the “language” parameter provided in the Register REST command
(section 2.10.1)).
2.8.6
STATUS SMS (Client Originated)
The VVM client can send a STATUS SMS message to query the system about the provisioning
status of the subscriber and the VVM server service settings.
The following is an example of a client originated STATUS SMS message:
STATUS:pv=<value>;ct=<value>;pt=<value>;<Clientprefix>
ct
Description: Determines the client type.
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: String, (up to 30 characters).
Default Value: N/A
Client prefix
Description: This field may be used by the VVM client to change the default client prefix
value “//VVM” which is included in the SYNC and STATUS SMS (see sections 2.9.1.2 and
2.9.1.5). If not used by the client in the Activate SMS, the client prefix value sent in SYNC
and STATUS SMS will remain as default. As an example, some VVM clients may need
the client prefix to include a specific keyword and port number for client wakeup (instead
of UDH).

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 53 of 80
Legal Values: Configurable string (up to 30 characters), always followed by a colon (:).
Default Value: N/A
pt
Description: Application port 16 bit address (as described in 3GPP TS 23.040 [4]). This
is the destination Terminal port number which the client is listening. The server may use
this value for the destination application port address in the system-originated SMS
message (see example in Section 2.8.1
In case the value is set to 0, the server may not send a binary message but either a legacy
message or a different network specific message. The value of which is dependent on the
client.
This is a mandatory field.
Legal Values: Configurable string, maximum length = 30 characters.
1 – 16999: Application port addressing for GSM-networks.
0: Non-GSM networks and legacy notifications.
Default Value: N/A
pv
Description: Determines the protocol version. For example, version 1.3 of the protocol
takes the value 13.
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: 10-99
Default Value: 13
Upon receiving a STATUS query from the client, a STATUS SMS response is returned, as
described in STATUS SMS Description (Server Originated).
Note: The STATUS SMS message is case-sensitive.
2.8.7
Activate SMS (Client Originated)
The client can send an Activate SMS in the following situations:
• To activate the service (change the VVM provisioning status from Subscriber
Provisioned to Subscriber New or Subscriber Ready). Once the service is activated,
VVM notifications are sent to the client.
• To inform the server about a new client type, that is specified in the SMS and is saved
in the subscriber profile.
• Every time the user puts a new SIMCARD in the mobile to inform the server about the
client capabilities.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 54 of 80
The following is the Activate SMS message syntax:
Activate:pv=<value>;ct=<value>;pt=<value>;<Clientprefix>
An Activate SMS message updates the subscriber’s VVM provisioning status and some Client
information and results in a STATUS SMS, as described in STATUS SMS Description (Server
Originated).
If the Activate SMS message is not successful, the following failure response is sent:
//VVM:STATUS:st=U;rc=<error code>
ct
Description: Determines the client type.
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: String, (up to 30 characters).
Default Value: N/A
Client prefix
Description: This field may be used by the VVM client to change the default client prefix
value “//VVM” which is included in the SYNC and STATUS SMS (see sections 2.8.2 and
2.8.4). If not used by the client in the Activate SMS, the client prefix value sent in SYNC
and STATUS SMS will remain as default. As an example, some VVM clients may need
the client prefix to include a specific keyword and port number for client wakeup (instead
of UDH).
Legal Values: Configurable string (up to 30 characters), always followed by a colon (:).
Default Value: N/A
pt
Description: Application port 16 bit address (as described in 3GPP TS 23.040 [4]). This
is the Terminal destination port number where the client is listening. The server may use
this value for the destination application port address in the system-originated SMS
message (see example in Section 2.8.1).
In case the value is set to 0, the server may not send a binary message
but either a legacy message or a different network specific message.
The value is dependent on the client.
This is a mandatory field.
Legal Values: Configurable string, maximum length = 30 characters:
1 – 16999: Application port addressing for GSM-networks,

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 55 of 80
0: Non-GSM networks and legacy notifications.
Default Value: N/A
pv
Description: Determines the protocol version without a decimal point. For example
version 1.3 of the protocol takes the value 13.
This field is mandatory
Legal Values: 10-99
Default Value: 13
2.8.8
Deactivate SMS (Client Originated)
The client can send a Deactivate SMS message to deactivate the service. No VVM SYNC
notifications are sent to the client after service deactivation.
The following is the Deactivate SMS message syntax:
Deactivate:pv=<value>;ct=<string>
A Deactivate SMS message updates the subscriber VVM provisioning status and results in a
STATUS SMS, as described in STATUS SMS Description (Server Originated).
If the Deactivate SMS message is not successful, the following failure response is sent:
//VVM:STATUS:st=U;rc=<error code>
ct
Description: Determines the client type.
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: String, up to 30 characters.
Default Value: N/A
pv
Description: Determines the protocol version without the decimal point.
For example version 1.3 takes the value 13.
This field is mandatory.
Legal Values: 10-99
Default Value: 13
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 56 of 80
2.9 VVM Message Commands
The following are VVM commands and responses:
A. IMAP4 MD5 Authentication,
B. SMTP MD5 Authentication,
C. Voice Message,
D. Video Message,
E. Fax Message,
F. ECC Message,
G. Number Message,
H. Voice DSN Message,
I. Voice Message Disposition Notification Message,
J. Deposit Voice Message,
K. Greeting Message,
L. VS Message.
Examples of VVM commands and responses are further detailed in Annex B.
2.10 VVM REST Interface Description
In order to support Push-based clients running on multiple and/or SIM-less devices VM server
shall support new type of REST interface with push-based VVM clients.
The REST interface consists of several requests/methods that are always push-based VVM
client originated. VM servers communicates with push-based VVM client via Push Notification
messages (Section 2.11)). Push-based client uses URL (e.g. vvm.youroperator.com/rest-
method1) for communication with the VM server.
2.10.1
Register
The method used to trigger the registration of push-based VVM client for IP Push-based
VVM Service.
The VM server shall verify the validity of the DeviceToken (either using DeviceToken
Verification Server or by Password Push Notification) and check that the MSISDN belongs to
the configured range. After successful registration the DeviceToken value shall be used as an
identification in the IP Push notification.
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 57 of 80
Request:
Attribute Mandatory (M)/
Optional (O)
Description
Msisdn M
The MSISDN of the voice mailbox
DeviceToken M DeviceToken obtained by VVM client
Os O
Operating system, e.g. “android” or “ios”.
Language O The language which shall be used for the
OTP SMS.
Table 11: Register Message Specification
Response Codes:
Response code
Description
200 Successful registration request
400 Bad request
403 Forbidden (Unknown MSISDN, invalid DeviceToken, OS or
language)
500 Internal server error
Table 12: Response codes for Register Message
2.10.1.1 Multi-device support
The VM Server shall store more DeviceToken values for a single MSISDN value. The
number of the DeviceToken values shall be configurable.
In case more devices are registered for a single MSISDN value, the New Message Push
Notification shall be sent to all registered DeviceToken values.
2.10.1.2 Multi-account support
The VM Server shall store more MSISDN values for a single DeviceToken value. The
number of the MSISDN values shall be configurable.
2.10.2
ProvideOTP
The method used to return the OTP value received in MT SMS OTP back to the VM server.
VM Server shall compare the provided OTP value with the original OTP value.
Request:
Attribute Mandatory (M)/
Optional (O)
Description
Msisdn M The MSISDN of the voice mailbox
DeviceToken M DeviceToken obtained by VVM client
OTP M One Time Password, previously sent to
active paging device in OTP SMS.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 58 of 80
Table 13: ProvideOTP Message Specification
Response Codes:
Response code Description
200 User authenticated
400 Bad request
403 Forbidden (Unknown MSISDN, invalid token or wrong OTP)
500 Internal server error
Table 14: Response codes for ProvideOTP
2.10.3 ProvidePassword
The request is used during registration of a new device. Using this command the VVM client
provides Password received in Password Push notification. This logic is used to verify the
authenticity of the push-based VVM client using IP Push channel.
Request:
Attribute Mandatory (M)/
Optional (O)
Description
Msisdn M The MSISDN of the voice mailbox
registrationToken M DeviceToken obtained by VVM client
Password M Random password that has been received
via IP push notification before.
Table 15: ProvidePassword Message Specificaiton
Response Codes:
Response code
Description
200 Previous request authorized and processed successfully
400 Bad request
403 Forbidden (Unknown MSISDN, invalid DeviceToken, wrong
password or wrong OS)
500 Internal server error
Table 16: Response codes for ProvidePassword
2.10.4
Unregister
The method used to unregister from the IP Push-based VVM service. The VM server shall
delete the DeviceToken and start to notify the client using visible SMS notifications.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 59 of 80
Request:
Attribute Mandatory (M)/
Optional (O)
Description
Msisdn M The MSISDN of the voice mailbox
registrationToken Mandatory DeviceToken obtained by VVM client
Table 17: Unregister Message Specification
Response Codes:
Response code Description
200 Successful unregistration
400 Bad request
403 Forbidden (Unknown MSISDN, invalid token)
500 Internal server error
Table 18: Response codes for Unregister
2.10.5 UpdateToken
The method used to update DeviceToken on the VM server once it changes on the VVM client
site. The VM server shall update DeviceToken and use the new value for IP Push notifications.
The value of the old DeviceToken shall be deleted from both push-based VVM client and VM
server.
Request:
Attribute Mandatory (M)/
Optional (O)
Description
Msisdn M The MSISDN of the voice mailbox
oldDeviceToken M DeviceToken obtained by VVM client
newDeviceToken M New DeviceToken obtained Push-based
client
Table 19:Update Token Message Specification
Response Codes:
Response code
Description
200 Token updated
400 Bad request
403 Forbidden (Unknown MSISDN, invalid DeviceTokens)
500 Internal server error
Table 20: Response Codes for Update Token
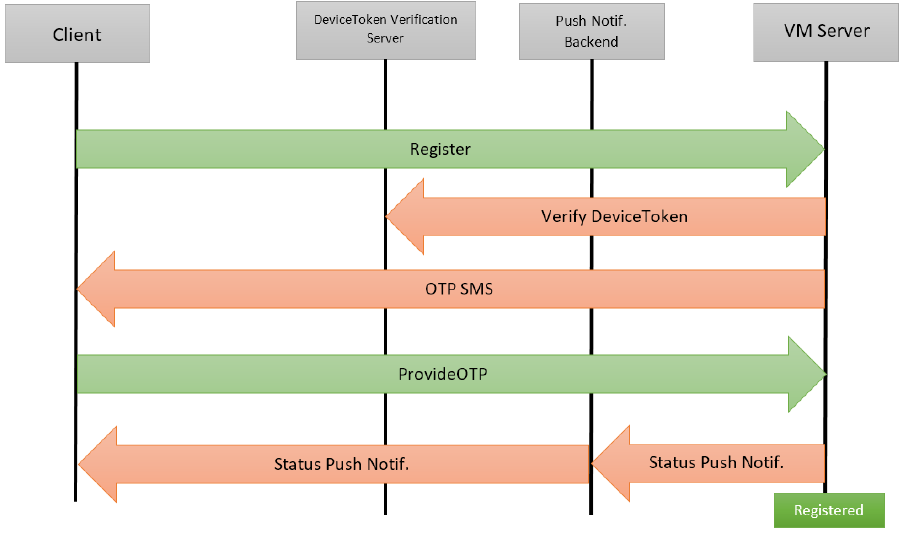
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 60 of 80
2.10.6 Push-based register scenario (option 1)
The scenario where the DeviceToken Verification Sever is available is depicted in the figure
below.
After the Register request is received by the VM server, the VM server must execute the
following two steps:
• Verify the DeviceToken against DeviceToken Verification Sever;
• Send OTP SMS and wait for ProvideOTP request.
Figure 2 :Push Based Register option 1
2.10.7
Push-based register scenario (option 2)
The scenario where the DeviceToken Verification Sever is not available is depicted in the
figure below.
After the Register request is received to the VM server, the VM server must execute the
following two steps:
• Verify the DeviceToken by sending Password Push Notification and wait for
ProvidePassword request;
• Send OTP SMS and wait for ProvideOTP request.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 61 of 80
Figure 3: Push Based Register option 2
2.11 VVM Push Notification Interface Description
All used Push Notification messages are Server Originated. The Push Notification includes
the following types of messages:
• STATUS: Notifies the VVM client that the VVM subscriber’s provisioning status was
changed.
• NEW_MESSAGE: Notifies the client in case new message has been deposited in the
subscriber’s mailbox.
• PASSWORD (optional): Is used in case there is needed to verify identity
(DeviceToken) of the Push-based client.
The target device of the Push Notification message is defined by the unique identified called
DeviceToken that is provided in the register request (2.10.1). The value of the DeviceToken
is created by the OS platform provider. There can be more devices registered for one MSISDN
so the VM server shall send Push Notification messages to all registered DeviceToken values
at the same time.
Depending on the “os” type provided in register request (section 2.10.1), the appropriate Push
Notification server shall be used. The Push Notification servers are usually defined by different
URLs, ports and login credentials or certificates.
The payload of the all Push Notification messages shall be encrypted in the way that only
Push-based client is able to decrypt it.
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 62 of 80
2.11.1 STATUS
The Status Push Notification message shall be sent by the VM server in same cases as the
STATUS SMS (sections 2.8.4, 2.8.4.2, 2.8.4.3). Also the payload of the Push Notification shall
contain same parameters as the STATUS SMS.
In case it is supported by the Push Notification Server, it is recommended to send Status Push
Notification message as a silent notification. This will ensure that the notification is not visible
to customers, but it is handled by the push-based VVM client in the background.
The exact names of used parameters in the Push Notification message may vary depending
on used Push Notification Server type, but following parameters shall be used:
• DeviceToken: Unique identifier of the Device
• Method: e.g. Status, New_Message, Password
• Type (optional): silent
• Payload: the content of the Push Notification
Example:
DeviceToken: 123456789abcd
Method: Status
Type: Silent
Payload: <encrypted value of //VVM:STATUS:st=B;rc=0>
2.11.2
NEW_MESSAGE
The New Message Push Notification message shall be sent by the VM server in same cases
as the SYNC SMS (sections 2.8.2, 2.8.3.2, 2.8.3.3). Also the payload of the Push Notification
shall contain same parameters as the SYNC SMS.
It is recommended to send the New Message Push Notification message as a visible
notification. This will ensure that the notification is visible to customers.
The exact names of used parameters in the Push Notification message may vary depending
on used the Push Notification Server type, but following parameters shall be used:
• DeviceToken: Unique identifier of the Device
• Method: e.g. Status, New_Message, Password
• Payload (Optional): The content of the Push Notification
• Badge (Optional): Number of new messages
Note: Payload and Badge parameters might not supported by all Push Notification servers,
therefore these parameters are optional.
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 63 of 80
Example1:
DeviceToken: 123456789abcd
Method: New_Message
Payload: <encrypted value of //VVM:SYNC:ev=NM;id=3446456;c=1;
t=v;s=01234567898;dt=02/08/2008 12:53 +0200;l=30>
Example2:
DeviceToken: 123456789abcd
Method: New_Message
Badge: <number of new messages>
2.11.3
PASSWORD
The Password Push Notification message shall be sent by the VM server in cases when there
is no interface for DeviceToken verification available (section 2.12). This is the behaviour of
the Apple/APNS. The payload of the Password Push Notification message shall contains
password that shall be returned by the Push-based client in the ProvidePassword method
(section 2.10.3). The value of the password will be handled by the Push-based Client, without
any interaction of the customer.
In case it is supported by the Push Notification Server, it is recommended to send Password
Push Notification message as a silent notification. This will ensure that the notification is not
visible to customers, but it is handled by the Push-based client in the background.
The exact names of used parameters in the Push Notification message may vary depending
on used Push Notification Server type, but following parameters shall be used:
• DeviceToken: Unique identifier of the Device
• Method: e.g. Status, New_Message, Password
• Type (optional): silent
• Payload: the content of the Push Notification
Example:
DeviceToken: 123456789abcd
Method: New_Message
Payload: <Encrypted value of 123456789aBcDeFgHiJxYz>
2.12 DeviceToken Verification Server Interface
Some OS platform providers (e.g. Google) provide a service for verification of provided
DeviceToken value in register request (section 2.10.1). This service shall be used by the VM
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 64 of 80
server in case of registration of new Push-based client (new DeviceToken). The new value of
DeviceToken shall be sent to the verification server. The server shall return list of parameters
for the DeviceToken. At least one of these parameters shall match configured value in VM
Server – in this case the DeviceToken is trusted.
Depending on the “os” type provided in register request (section 2.10.1), the appropriate
DeviceToken Verification server shall be used. Servers are usually defined by different URL,
port and login credentials or certificates.
Example of response (Google):
JavaScript Object Notation: application/json
Object
Member Key: applicationVersion
String value: 1
Key: applicationVersion
Member Key: attestStatus
String value: ROOTED
Key: attestStatus
Member Key: application
String value: de.telekom.vvmapp
Key: application
Member Key: authorizedEntity
String value: 969076060574
Key: authorizedEntity
Member Key: appSigner
String value: bd9599d1cac616e4804f85c6aae58670fec903dc
Key: appSigner
Member Key: platform
String value: ANDROID
2.13 Client Authentication
The VVM client shall authenticate against the VVM server using one of the following methods:
• STATUS SMS as described in 2.8.4,
• OTP SMS followed by Push Notification with credentials as described in 2.8.5.

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 65 of 80
Both authentication methods can be combined in the multi-client setup, i.e. when more than
one client is provisioned with a single mailbox credentials or a single client is provisioned with
a more than one mailbox.
V VM Server 2
VVM
Client 1
V VM Server 1
VVM
Client 2
VVM
Client 3
VVM
Client 4
VVM
Mailbox 1
VVM
Mailbox 2
VVM
Mailbox 3
VVM
Mailbox 4
Figure 4: Multi-client setup
Except for support of the VVM client authentication by means of the OTP mechanism and
STATUS SMS, the VVM client and server should also support alternative authentication
mechanisms as described in RCS RCC.14 [3], section HTTP(S) based client configuration
mechanism with GBA Authentication and section Support of OpenID Connect.
3 RFC Compliance
The VVM service complies with the following RFC standards:
• RFC Compliance Related to Internet Mail,
• RFC Compliance Related to IMAP4,
• RFC Compliance Related to SMTP.
Also refer to 3GPP TS23.040 Technical realization of Short Message Service (SMS).
3.1 RFC Compliance Related to Internet Mail
The VVM service complies with the following RFCs related to Internet Mail:
• RFC 2045: Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) Part One: Format of
Internet Message Bodies (renders obsolete RFCs 1521, 1522, 1590),
• RFC 2046: Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) Part Two: Media
Types,
• RFC 2195: IMAP/POP AUTHorize Extension for Simple Challenge/Response,
• RFC 2821: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (renders obsolete RFCs 821, 974,
1869),
• RFC 2822: Internet Message Format,
• RFC 2831: Using Digest Authentication as a SASL Mechanism,
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 66 of 80
• RFC 3458: Message Context for Internet Mail,
• RFC 3461: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) Service Extension for
Delivery Status Notifications (DSNs),
• RFC 3798: An Extensible Message Format of MIME content-type for
Message Disposition Notifications.
3.2 RFC Compliance Related to IMAP4
The VVM service complies with the following RFCs related to IMAP4:
• RFC 2595: STARTTLS Plain text communication protocol to an encrypted
TLS or SSL connection
• RFC 3501: Internet Message Access Protocol: Version 4, rev. 1,
• RFC 2087: IMAP4 QUOTA extension,
• RFC 4315: Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) - UIDPLUS extension,
• RFC 5464: The IMAP METADATA Extension.
3.3 RFC Compliance Related to SMTP
The VVM service complies with the following RFCs related to SMTP:
• RFC 3207: STARTTLS Plain text communication protocol to an encrypted
TLS or SSL connection
• RFC 2554: SMTP Service Extension for Authentication,
• RFC 3463: Enhanced Mail System Status Codes for Delivery Reports.
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 67 of 80
Annex A Examples of VVM Commands and Responses
Example A: IMAP4 MD5 AUTHENTICATION EXAMPLE
The following example illustrates the use of the required IMAP4 authentication command:
Client: a0001 authenticate digest-md5
cmVhbG09ImVzdTFiLm1zdW5nLnRlc3QiLG5vbmNlPSIyNzIzN
TU4Q0YwQzVGO
UI3NjRFRDJCMkU0RDcwNzY
MjExN0ExIixhbGdvcml0aG09Im1kNS1zZXNzIixxb3A9ImF1dG gi
Client:
dXNlcm5hbWU9InZsYWRAdmxhZC5jb20iLHJlYWxtPSJlc3Ux
Yi5tc3VuZy50ZXN
0Iixub25jZT0iMjcyMzU1OE
1RjlCNzY0RUQyQjJFNEQ3MDc2MkVDMjIxMTdBMSIsY25vbm NlPSJNVGs1T1R
Fek1UTTVMakV3TkRnMk1UTXdPVFk9IixuYz
wMDAwMSxxb3A9YXV0aCxkaWdlc3QtdXJpPSJpbWFwL2Vzd TFiLm1zdW5nLnR
lc3QiLHJlc3BvbnNlPWU0Y2NhZDJkYTZiNW 1ODZlZTEzOWY0OTY3ZmU0
Server: +
cnNwYXV0aD1kYjQ0Y2U0ZjdjYzVkZTNlYzkyZmViZWRjOGNlZD YyMQ==
Client:
Server:
a0001 OK login successful
For more information about IMAP4, see RFC 2195.
Example B: SMTP MD5 AUTHENTICATION EXAMPLE
The following example illustrates the use of the required SMTP authentication command:
Client: ehlo mta.example.com Server: 250-esu1c.example.com 250-DSN
250-8BITMIME
250-PIPELINING
250-HELP
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 68 of 80
250-AUTH DIGEST-MD5
250-DELIVERBY 300
250-MEDIASIZE text:0Kb voice:0sec fax:0pages number:0bytes empty-call-
capture:0bytes voice-infotainment:0sec
250-SIZE OK
Client: auth digest-md5
Server: 334
cmVhbG09ImVzdTFjLmljb212ZXJzZS5jb20iLG5vbmNlPSJBNz
Q3NTJEOEIwNzE2MzlDN0QzQzBCNkNDMjE1Mz
QzMzgwNjQzMTZGIixhbGdvcml0aG09Im1kNS1zZXNzIixxb3A9I mF1dGgi
Client:
dXNlcm5hbWU9InVzZXIxQGguaCIscmVhbG09ImVzdTFjLmljb 212ZXJzZS5
jb20iLG5vbmNlPSJBNzQ3NTJEOEIwNzE2MzlDN0Qz
QzBCNkNDMjE1MzQzMzgwNjQzMTZGIixjbm9uY2U9Ik1UazVP VEV6TVRNNU
xqRXdORGcyTVRNd09UWT0iLG5jPTAwMDAwMDAxLHFv
cD1hdXRoLGRpZ2VzdC11cmk9ImltYXAvZXN1MWMuaWNvbX ZlcnNlLmNvbSIs
cmVzcG9uc2U9MDQ5ZmRlODI4OTFjMmJhZTE2OTg1 Y2FlYjRmOWRjNTY=
Server: 334 ...
Server: 235 digest-md5 authentication successful
Example C: VOICE MESSAGE EXAMPLE
The following example illustrates the use of voice message commands:
Return-Path: <>
Received: from msuic1 (10.106.145.31) by MIPS.SITE1 (MIPS Email Server)
id 45879DD300000196 for [email protected]; Tue, 19 Dec 2006 12:12:09 +0200
subject: voice mail
MIME-Version: 1.0 (Voice Version 2.0)
Message-Id: <31.24.2326006@msu31_24>
Content-Type: Multipart/ voice-message; boundary="------------
Boundary-00=_90NIQYRXFQQMYJ0CCJD0"

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 69 of 80
From: [email protected]
Message-Context: voice-message
Date: Tue, 19 Dec 2006 10:12:09 +0000 (UTC)
--------------Boundary-00=_90NIQYRXFQQMYJ0CCJD0
Content-Type: Text/Plain Content-Transfer-Encoding: 7bit click on attachment
--------------Boundary-00=_90NIQYRXFQQMYJ0CCJD0
Content-Type: audio/amr
Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64
Content-Disposition: attachment; filename="vm.amr"
Content-Duration: 17
[message attachment]
--------------Boundary-00=_90NIQYRXFQQMYJ0CCJD0—
Example D: VIDEO MESSAGE EXAMPLE
The following example illustrates the use of video message commands:
Return-Path: <>
Received: from msuic196 (10.119.37.197) by MIPS.SITE1
(MIPS Email Server)
id 4545A1DF00039933 for [email protected]
;
Wed, 20 Dec 2006 12:13:48 +0200
Subject: video message
MIME-Version: 1.0 (Voice Version 2.0)
Message-Id: <197.195.3706011@msu197_195>
Content-Type: Multipart/Mixed; boundary="------------
Boundary-00=_7XAKIOLYA1UMYJ0CCJD0"
From: [email protected]

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 70 of 80
Content-Duration: 11
Message-Context: video-message
Date: Wed, 20 Dec 2006 07:46:19 +0000 (UTC)
--------------Boundary-00=_7XAKIOLYA1UMYJ0CCJD0
Content-Type: Text/Plain
Content-Transfer-Encoding: 7bit
Double-click on the attached video file
-------------- Boundary-00=_7XAKIOLYA1UMYJ0CCJD0
Content-Type: video/3gpp; codec="h263_amr"
Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64
Content-Disposition: attachment; filename="fffff2df.3gp"
Content-Duration: 11
[message attachment]
-------------- Boundary-00=_7XAKIOLYA1UMYJ0CCJD0
EXAMPLE E: FAX MESSAGE EXAMPLE
The following example illustrates the use of fax message commands:
Return-Path: <>
Received: from msuic1 (10.106.145.31) by MIPS.SITE1 (MIPS Email Server)
id 458E1FCB0000183B for [email protected]
;
Mon, 25 Dec 2006 17:02:06 +0200
subject: fax mail
MIME-Version: 1.0 (Voice Version 2.0)
Message-Id: <31.24.2326073@msu31_24>
Content-Type: Multipart/fax-message; boundary="------------
Boundary-00=_IF4U6KM71OVNTT4D7TH0"
From: [email protected]

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 71 of 80
Message-Context: fax-message
Date: Mon, 25 Dec 2006 15:02:06 +0000 (UTC)
--------------Boundary-00=_IF4U6KM71OVNTT4D7TH0
Content-Type: Text/Plain
Content-Transfer-Encoding: 7bit
click on attachment
--------------Boundary-00=_IF4U6KM71OVNTT4D7TH0
Content-Type: Application/pdf
Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64
Content-Disposition: attachment; filename="fax123.pdf"
X-Content-Pages: 3
[message attachment]
--------------Boundary-00=_IF4U6KM71OVNTT4D7TH0--
EXAMPLE F: ECC MESSAGE EXAMPLE
The following example illustrates the use of ECC message commands:
Return-Path: <>
Received: from msuic196 (10.119.37.197) by MIPS.SITE1
(MIPS Email Server)
id 4545A1DF00039C1E for [email protected]
;
Wed, 20 Dec 2006 16:07:41 +0200
subject: empty message
MIME-Version: 1.0 (Voice Version 2.0)
Message-Id: <197.195.3706023@msu197_195>
Content-Type: Text/Plain; boundary="------------ Boundary-
00=_ZQLK6RB00M3NTT4D7TH0"
From: [email protected]
Message-Context: x-empty-call-capture-message

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 72 of 80
Date: Wed, 20 Dec 2006 11:40:11 +0000 (UTC)
4504
EXAMPLE G: NUMBER MESSAGE EXAMPLE
The following example illustrates the use of Number message commands:
Received: from aplus2 (172.17.5.44) by mips.system.com
(MIPS Email Server)
id 43EB428D00001AFD for [email protected]
;
Fri, 10 Feb 2006 13:57:21 +0200
subject: number message
MIME-Version: 1.0 (Voice Version 2.0)
Message-Id: <9.6.4252201@msu9_6>
Content-Type: Text/Plain; boundary="------------ Boundary-
00=_R5EK7W5NTEPOO49D7TH0"
From: message@system.com
Message-Context: x-number-message
Date: Fri, 10 Feb 2006 09:58:39 +0200 (IST)
523
EXAMPLE H: VOICE DSN MESSAGE EXAMPLE
The following example illustrates the use of Delivery Status Notification (DSN):
Return-Path: <>
Received: from msuic1 (10.106.145.31) by MIPS.SITE1
(MIPS Email Server)
id 458A530000000D39 for [email protected]
;
Fri, 22 Dec 2006 05:02:28 +0200
Message-ID: <[email protected]> (added by

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 73 of 80
postmaster@MIPS.SITE1) subject: voice mail
Content-Type: Multipart/report; report-type=delivery-status;
boundary="------------Boundary-
00=_44NNCQ75B3NNTT4D7TH0"
From: [email protected]
Date: Fri, 22 Dec 2006 01:02:28 -0200
This multi-part MIME message contains a Delivery Status Notification. If you
can see this text, your mail client may not be able to understand MIME
formatted messages or DSNs (see RFC 2045 through 2049 for general MIME
information and RFC 3461, RFC 3463 DSN specific information).
--------------Boundary-00=_44NNCQ75B3NNTT4D7TH0
Content-Type: Text/Plain
--------------Boundary-00=_44NNCQ75B3NNTT4D7TH0
Content-Type: Message/Delivery-Status
Reporting-MTA: smtp; msung.example.com
Final-Recipient: [email protected]
Action: Failed
Status: 5.4.3 (routing server failure)
--------------Boundary-00=_44NNCQ75B3NNTT4D7TH0
Content-Type: Message/rfc822
subject: voice mail
MIME-Version: 1.0 (Voice Version 2.0)
Message-Id: <31.24.2326058@msu31_24>
Content-Type: Multipart/voice-message; boundary="------------
Boundary-00=_44NNHG35B3NNTT4D7TH0"
From: [email protected]
Content-Duration: 78
Message-Context: voice-message

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 74 of 80
Date: Tue, 19 Dec 2006 15:02:26 +0000 (UTC)
--------------Boundary-00=_44NNHG35B3NNTT4D7TH0
Content-Type: Text/Plain
Content-Transfer-Encoding: 7bit
--------------Boundary-00=_44NNHG35B3NNTT4D7TH0
Content-Type: audio/vnd.cns.inf1
Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64
Content-Disposition: attachment; filename="3ec6c(null).sbc"
Content-Duration: 78
[message attachment]
--------------Boundary-00=_44NNHG35B3NNTT4D7TH0--
EXAMPLE I: VOICE MESSAGE DISPOSITION NOTIFICATION MESSAGE EXAMPLE
The following example illustrates the use of Message Disposition Notification (MDN)
messages:
Return-Path: <>
Received: from aplus2 (172.17.5.44) by mips.system.com
(MIPS Email Server)
id 43EF8A6E00000668 for [email protected]
;
Mon, 13 Feb 2006 14:54:28 +0200
Message-ID: [email protected]
(added by [email protected])
subject: voice mail
Content-Type: Multipart/report; report-type=receipt-
disposition-notification; boundary="------------Boundary-
00=_XGBMBU3XFQQMYJ0CCJD0"
From: [email protected]
Date: Wed, 8 Feb 2006 10:55:45 -2200

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 75 of 80
This multi-part MIME message contains a Message Disposition Notification. If
you can see this text, your mail client may not be able to understand MIME
formatted messages or MDNs (see RFC 2045 through 2049 for general MIME
information and RFC 3798 for MDN specific information).
--------------Boundary-00=_XGBMBU3XFQQMYJ0CCJD0
Content-Type: Text/Plain
--------------Boundary-00=_XGBMBU3XFQQMYJ0CCJD0
Content-Type: Message/disposition-notification
Final-Recipient: [email protected]
Disposition: manual-action/MDN-sent-automatically; displayed
--------------Boundary-00=_XGBMBU3XFQQMYJ0CCJD0
Content-Type: Message/rfc822
subject: voice mail
MIME-Version: 1.0 (Voice Version 2.0)
Message-Id: <9.6.4278007@msu9_6>
Content-Type: Multipart/voice-message; boundary="------------
Boundary-00=_XGBMGJZXFQQMYJ0CCJD0"
From: [email protected]
Content-Duration: 2
Message-Context: voice-message
Date: Mon, 13 Feb 2006 10:44:36 +0200 (IST)
--------------Boundary-00=_XGBMGJZXFQQMYJ0CCJD0
Content-Type: Text/Plain
Content-Transfer-Encoding: 7bit
--------------Boundary-00=_XGBMGJZXFQQMYJ0CCJD0
Content-Type: audio/vnd.cns.inf1
Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64
Content-Disposition: attachment; filename="48f36.sbc"
Content-Duration: 2

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 76 of 80
[message attachment]
--------------Boundary-00=_XGBMBU3XFQQMYJ0CCJD0—
EXAMPLE J: DEPOSIT VOICE MESSAGE EXAMPLE
The following example illustrates the use of a Deposit Voice Message command. In this
example, the client deposits an 18-second message.
Message-ID:
10545552.1131961091850.JavaMail.icassagn@I20050329
Date: Wed, 21 Dec 2005 16:34:50 +0100 (CET)
From: [email protected]
MIME-Version: 1.0
Content-Type: multipart/mixed; boundary="----
=_Part_6_16713087.1135179290661"
Importance: Normal
Message-Context: voice-message
Content-Duration: 18
Expires: Sat, 31 Dec 2005 00:00:00 +0100 (CET)
------=_Part_6_16713087.1135179290661
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=us-ascii
Content-Transfer-Encoding: 8bit
Open the attached file
------=_Part_6_16713087.1135179290661
Content-Type: Audio/wav; codec=g711a
Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64
Content-Disposition: attachment;
filename="wav_00000002.wav"
Content-Duration: 18
[message attachment]
------=_Part_6_16713087.1135179290661—

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 77 of 80
EXAMPLE K: GREETING MESSAGE EXAMPLE
The following example illustrates the use of a greeting message:
X-CNS-Greeting-Type: normal-greeting
Message-ID: 1232456789.example4u@MGU_5
Date: Thu, 27 Mar 2008 17:37:02 +0200
From: [email protected]
Subject: append personalised greeting
Mime-Version: 1.0
Content-Type: multipart/mixed;
boundary="----=_Part_10_6838114.1062660453543"
Content-Duration: 8
------=_Part_10_6838114.1062660453543
Content-Type: Audio/AMR;
name="greeting.amr"
Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64
Content-Disposition: attachment; size=3724;
filename="greeting.amr"
[message attachment]
------=_Part_10_6838114.1062660453543—
EXAMPLE L: VS MESSAGE EXAMPLE
The following example illustrates the use of a VS message:
X-CNS-Greeting-Type: voice-signature
Message-ID: 1232456789.example4u@MGU_5
Date: Thu, 27 Mar 2008 17:37:02 +0200
From: [email protected]
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 78 of 80
Subject: append VOICE SIGNATURE
Mime-Version: 1.0
Content-Type: multipart/mixed;
boundary="----=_Part_10_6838114.1062660453543"
Content-Duration: 8
------=_Part_10_6838114.1062660453543
Content-Type: audio/qcelp; name=vs.qcp
Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64
Content-Disposition: attachment;
filename=vs.qcp [message attachment]
------=_Part_10_6838114.1062660453543—
Annex B Security guidelines for Voicemail and VVM
B.1 Encryption of OOB SMS and Push Notification payload
The VVM server shall encrypt Mobile Terminated (MT) Out Of Band (OOB) messages or push
notification payload, so that the receiver will not be able to read the IMAP access data (e.g.
credentials) in the inbox of the mobile device.
For sake of simplicity the following encryption algorithm should be sufficient to reach the
desired goal.
Encryption
The leading User Data Header (UDH) is removed from the shortMessage of the Protocol Data
Unit (PDU). The first byte of the shortMessage contains the length of the remaining UDH
(without the length byte itself). The remaining cleartext is encrypted using the DESede (3DES,
TripleDES) algorithm in Electronic CookBook mode (ECB) using PKCS5PADDING.
In short the encryption is specified by DESede/ECB/PKCS5PADDING. The final
shortMessage consists of the original UDH and the ciphertext (encrypted cleartext). The
dataCoding of the PDU is changed to 8-bit binary (0x04).
The DESede requires a 24 byte password where the leading 8 bytes are used for the first
encryption (e), the middle 8 bytes for the following decryption (d) and the tailing 8 bytes for the
final encryption (e).
In contrast to different modes (e.g. CBC) ECB is less safe but requires no Initialization Vector
(IV). The cipher blocks are not manipulated so that two identical 8 byte blocks of cleartext
result in identical blocks of ciphertext.
GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 79 of 80
PKCS5PADDING appends 1 to 8 bytes of data before encryption so that the cleartext reaches
a full 8 byte block boundary. The padding is unambiguous because each appended byte
contains the number of appended bytes (01, 0202, 030303, …, 0808080808080808). In the
worst cast the short message length will increase by 8 bytes.
Decryption
Decryption of the encrypted shortMessage works just the same as the encryption using the
same 24 byte password. After removing the User Data Header (UDH) the remaining ciphertext
is decrypted using DESede/ECB/PKCS5PADDING. The resulting cleartext is appended to the
original UDH so that the original shortMessage is restored.
B.2 Recommendations for password value
The value of the password should be created by the VM server using the following
conditions:
• 128 x randomly generated bits:
o Create a 128 Bit (16 Byte) string out of 0 and 1. To store and transmit, this
string should be base64-encoded.
o Create a 38 characters string out of 0-9.
o Create a 22 characters string out of 0-9, a-z, A-Z.
• Password expiry – 1 minute

GSM Association Non-confidential
Official Document TS.46 - Visual Voicemail Interface Specification
V2.0 Page 80 of 80
Annex C Document Management
C.1 Document History
Version Date Brief Description of Change Approval
Authority
Editor /
Company
This Specification was originally published as an OMTP Document.
The last version published was v1.3 11
th
June 2010
2.0 March
2020
The OMTP document has been
updated to make it compatible
with Android. The document is
now published as a GSMA
Terminal Steering Group PRD at
v2.0
TSG39a Daniel Kolivoska /
T-Mobile
Vaclav Pechacek/
T-Mobile
Elena Mancevska /
KPN
Hans van
Oortmarssen / KPN
Other Information
Type
Description
Document Owner Terminal Steering Group
Editor / Company Daniel Kolivoska / T-Mobile
Vaclav Pechacek/ T-Mobile
Elena Mancevska / KPN
Hans van
Oortmarssen / KPN
It is our intention to provide a quality product for your use. If you find any errors or omissions,
please contact us with your comments. You may notify us at prd@gsma.com
Your comments or suggestions & questions are always welcome.
