
Common Terminology Criteria
for Adverse Events (CTCAE)
Version 5.0
Published: November 27, 2017
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES

Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v5.0
Publish Date: November 27, 2017
Introduction
The NCI Common Terminology Criteria for
Adverse Events is a descriptive terminology which
can be utilized for Adverse Event (AE) reporting. A
grading (severity) scale is provided for each AE
term.
SOC
System Organ Class (SOC), the highest level of the
MedDRA
1
hierarchy, is identified by anatomical or
physiological system, etiology, or purpose (e.g.,
SOC Investigations for laboratory test results).
CTCAE terms are grouped by MedDRA Primary
SOCs. Within each SOC, AEs are listed and
accompanied by descriptions of severity (Grade).
CTCAE Terms
An Adverse Event (AE) is any unfavorable and
unintended sign (including an abnormal
laboratory finding), symptom, or disease
temporally associated with the use of a medical
treatment or procedure that may or may not be
considered related to the medical treatment or
procedure. An AE is a term that is a unique
representation of a specific event used for
medical documentation and scientific analyses.
Each CTCAE v4.0 term is a MedDRA LLT (Lowest
Level Term).
1
CTCAE v5.0 incorporates certain elements of the MedDRA terminology. For further details on MedDRA refer to the MedDRA MSSO Web site (https://www.meddra.org/).
Grades
Grade refers to the severity of the AE. The CTCAE
displays Grades 1 through 5 with unique clinical
descriptions of severity for each AE based on this
general guideline:
Grade 1 Mild; asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or diagnostic
observations only; intervention
not indicated.
Grade 2 Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL*.
Grade 3 Severe or medically significant but not
immediately life-threatening;
hospitalization or prolongation
of hospitalization indicated;
disabling; limiting self care
ADL**.
Grade 4 Life-threatening consequences; urgent
intervention indicated.
Grade 5 Death related to AE.
A Semi-colon indicates ‘or’ within the description
of the grade.
A single dash (-) indicates a Grade is not available.
Not all Grades are appropriate for all AEs.
Therefore, some AEs are listed with fewer than
five options for Grade selection.
Grade 5
Grade 5 (Death) is not appropriate for some AEs
and therefore is not an option.
Definitions
A brief Definition is provided to clarify the
meaning of each AE term. A single dash (-)
indicates a Definition is not available.
Navigational Notes
A Navigational Note is used to assist the reporter
in choosing a correct AE. It may list other AEs that
should be considered in addition to or in place of
the AE in question. A single dash (-) indicates a
Navigational Note has not been defined for the AE
term.
Activities of Daily Living (ADL)
*Instrumental ADL refer to preparing meals,
shopping for groceries or clothes, using the
telephone, managing money, etc.
**Self care ADL refer to bathing, dressing and
undressing, feeding self, using the toilet, taking
medications, and not bedridden.
Table of Contents
Blood and lymphatic system disorders ....................................................................... 4
Cardiac disorders ........................................................................................................ 6
Congenital, familial and genetic disorders ................................................................ 12
Ear and labyrinth disorders ....................................................................................... 13
Endocrine disorders .................................................................................................. 15
Eye disorders ............................................................................................................ 18
Gastrointestinal disorders ........................................................................................ 24
General disorders and administration site conditions .............................................. 44
Hepatobiliary disorders ............................................................................................ 48
Immune system disorders ........................................................................................ 51
Infections and infestations ....................................................................................... 53
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications ....................................................... 70
Investigations ........................................................................................................... 84
Metabolism and nutrition disorders ......................................................................... 91
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders ..................................................... 95
Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified (incl cysts and polyps) ................... 103
Nervous system disorders ...................................................................................... 104
Pregnancy, puerperium and perinatal conditions ................................................... 114
Psychiatric disorders ............................................................................................... 115
Renal and urinary disorders .................................................................................... 119
Reproductive system and breast disorders............................................................. 123
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders .................................................... 131
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders ................................................................. 142
Social circumstances ............................................................................................... 150
Surgical and medical procedures ............................................................................ 151
Vascular disorders .................................................................................................. 152

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 4
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Anemia
Hemoglobin (Hgb) <LLN - 10.0
g/dL; <LLN - 6.2 mmol/L; <LLN
- 100 g/L
Hgb <10.0 - 8.0 g/dL; <6.2 - 4.9
mmol/L; <100 - 80g/L
Hgb <8.0 g/dL; <4.9 mmol/L;
<80 g/L; transfusion indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin in 100 ml of blood. Signs and symptoms of anemia may include pallor of the skin and mucous
membranes, shortness of breath, palpitations of the heart, soft systolic murmurs, lethargy, and fatigability.
Navigational Note: -
Bone marrow hypocellular
Mildly hypocellular or <=25%
reduction from normal
cellularity for age
Moderately hypocellular or
>25 - <50% reduction from
normal cellularity for age
Severely hypocellular or >50 -
<=75% reduction cellularity
from normal for age
Aplastic persistent for longer
than 2 weeks
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the inability of the bone marrow to produce hematopoietic elements.
Navigational Note: -
Disseminated intravascular
coagulation
-
Laboratory findings with no
bleeding
Laboratory findings and
bleeding
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by systemic pathological activation of blood clotting mechanisms which results in clot formation throughout the body. There is an increase in the
risk of hemorrhage as the body is depleted of platelets and coagulation factors.
Navigational Note: -
Eosinophilia
>ULN and >Baseline
-
Steroids initiated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate an increased number of eosinophils in the blood.
Navigational Note: -
Febrile neutropenia
-
-
ANC <1000/mm3 with a single
temperature of >38.3 degrees
C (101 degrees F) or a
sustained temperature of
>=38 degrees C (100.4
degrees F) for more than one
hour
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an ANC <1000/mm3 and a single temperature of >38.3 degrees C (101 degrees F) or a sustained temperature of >=38 degrees C (100.4 degrees
F) for more than one hour.
Navigational Note: -
Hemolysis
Laboratory evidence of
hemolysis only (e.g., direct
antiglobulin test; DAT;
Coombs'; schistocytes;
decreased haptoglobin)
Evidence of hemolysis and
>=2 g decrease in hemoglobin
Transfusion or medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
steroids)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate widespread erythrocyte cell membrane destruction.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 5
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Hemolytic uremic syndrome
-
-
Laboratory findings with
clinical consequences (e.g.,
renal insufficiency, petechiae)
Life-threatening
consequences, (e.g., CNS
hemorrhage or
thrombosis/embolism or renal
failure)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a form of thrombotic microangiopathy with renal failure, hemolytic anemia, and severe thrombocytopenia.
Navigational Note: -
Leukocytosis
-
-
>100,000/mm3
Clinical manifestations of
leucostasis; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate an increased number of white blood cells in the blood.
Navigational Note: -
Lymph node pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in a lymph node.
Navigational Note: -
Methemoglobinemia
-
>ULN
Requiring urgent intervention
Life-threatening consequences
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate increased methemoglobin in the blood.
Navigational Note: -
Thrombotic
thrombocytopenic purpura
-
-
Laboratory findings with
clinical consequences (e.g.,
renal insufficiency, petechiae)
Life-threatening
consequences, (e.g., CNS
hemorrhage or
thrombosis/embolism or renal
failure)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the presence of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenic purpura, fever, renal abnormalities and neurological abnormalities such
as seizures, hemiplegia, and visual disturbances. It is an acute or subacute condition.
Navigational Note: -
Blood and lymphatic system
disorders - Other, specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 6
Cardiac disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Aortic valve disease
Asymptomatic valvular
thickening with or without
mild valvular regurgitation or
stenosis by imaging
Asymptomatic; moderate
regurgitation or stenosis by
imaging
Symptomatic; severe
regurgitation or stenosis by
imaging; symptoms controlled
with medical intervention
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated (e.g.,
valve replacement,
valvuloplasty)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a defect in aortic valve function or structure.
Navigational Note: -
Asystole
Periods of asystole; non-
urgent medical management
indicated
-
-
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia without cardiac electrical activity. Typically, this is accompanied by cessation of the pumping function of the heart.
Navigational Note: -
Atrial fibrillation
Asymptomatic, intervention
not indicated
Non-urgent medical
intervention indicated
Symptomatic, urgent
intervention indicated; device
(e.g., pacemaker); ablation;
new onset
Life-threatening
consequences; embolus
requiring urgent intervention
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia without discernible P waves and an irregular ventricular response due to multiple reentry circuits. The rhythm disturbance
originates above the ventricles.
Navigational Note: -
Atrial flutter
Asymptomatic, intervention
not indicated
Non-urgent medical
intervention indicated
Symptomatic, urgent
intervention indicated; device
(e.g., pacemaker); ablation
Life-threatening
consequences; embolus
requiring urgent intervention
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia with organized rhythmic atrial contractions with a rate of 200-300 beats per minute. The rhythm disturbance originates in the
atria.
Navigational Note: -
Atrioventricular block
complete
-
Non-urgent intervention
indicated
Symptomatic and
incompletely controlled
medically, or controlled with
device (e.g., pacemaker); new
onset
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia with complete failure of atrial electrical impulse conduction through the AV node to the ventricles.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC
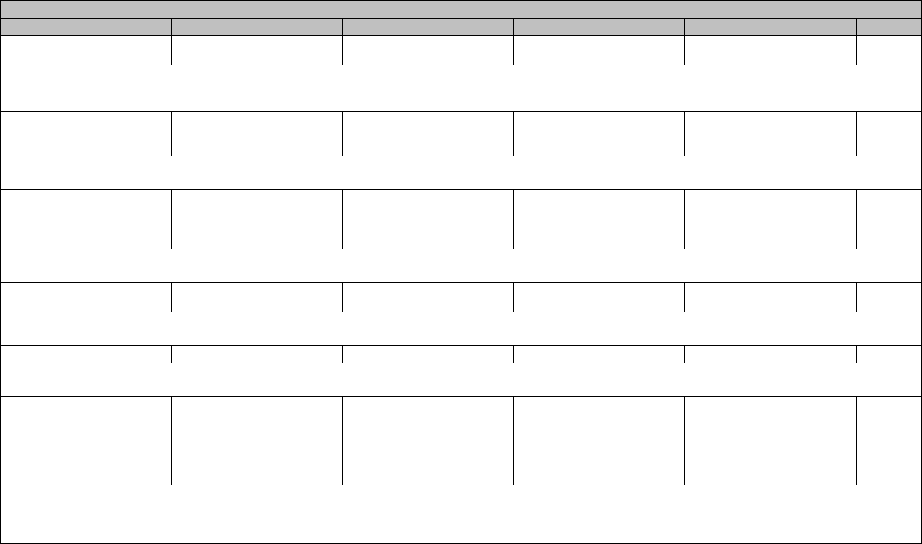
CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 7
Cardiac disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Atrioventricular block first
degree
Asymptomatic, intervention
not indicated
Non-urgent intervention
indicated
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia with a delay in the time required for the conduction of an electrical impulse through the atrioventricular (AV) node beyond 0.2
seconds; prolongation of the PR interval greater than 200 milliseconds.
Navigational Note: -
Cardiac arrest
-
-
-
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by cessation of the pumping function of the heart.
Navigational Note: -
Chest pain - cardiac
Mild pain
Moderate pain; pain on
exertion; limiting instrumental
ADL; hemodynamically stable
Pain at rest; limiting self care
ADL; cardiac catheterization;
new onset cardiac chest pain;
unstable angina
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by substernal discomfort due to insufficient myocardial oxygenation e.g., angina pectoris.
Navigational Note: Also consider Cardiac disorders: Myocardial infarction.
Conduction disorder
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Non-urgent medical
intervention indicated
Symptomatic, urgent
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by pathological irregularities in the cardiac conduction system.
Navigational Note: -
Cyanosis
-
Present
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a bluish discoloration of the skin and/or mucous membranes.
Navigational Note: -
Heart failure
Asymptomatic with laboratory
(e.g., BNP [B-Natriuretic
Peptide ]) or cardiac imaging
abnormalities
Symptoms with moderate
activity or exertion
Symptoms at rest or with
minimal activity or exertion;
hospitalization; new onset of
symptoms
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated (e.g.,
continuous IV therapy or
mechanical hemodynamic
support)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the inability of the heart to pump blood at an adequate volume to meet tissue metabolic requirements, or, the ability to do so only at an
elevation in the filling pressure.
Navigational Note: If left sided use Cardiac disorders: Left ventricular systolic dysfunction; also consider Cardiac disorders: Restrictive cardiomyopathy, Investigations: Ejection fraction
decreased.
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 8
Cardiac disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Left ventricular systolic
dysfunction
-
-
Symptomatic due to drop in
ejection fraction responsive to
intervention
Refractory or poorly
controlled heart failure due to
drop in ejection fraction;
intervention such as
ventricular assist device,
intravenous vasopressor
support, or heart transplant
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by failure of the left ventricle to produce adequate output.
Navigational Note: Also consider Investigations: Ejection fraction decreased.
Mitral valve disease
Asymptomatic valvular
thickening with or without
mild valvular regurgitation or
stenosis by imaging
Asymptomatic; moderate
regurgitation or stenosis by
imaging
Symptomatic; severe
regurgitation or stenosis by
imaging; symptoms controlled
with medical intervention
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated (e.g.,
valve replacement,
valvuloplasty)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a defect in mitral valve function or structure.
Navigational Note: -
Mobitz (type) II
atrioventricular block
Asymptomatic, intervention
not indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Symptomatic and
incompletely controlled
medically, or controlled with
device (e.g., pacemaker); new
onset
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia with relatively constant PR interval prior to the block of an atrial impulse. This is the result of intermittent failure of atrial
electrical impulse conduction through the atrioventricular (AV) node to the ventricles.
Navigational Note: -
Mobitz type I
Asymptomatic, intervention
not indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Symptomatic and
incompletely controlled
medically, or controlled with
device (e.g., pacemaker)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia with a progressively lengthening PR interval prior to the blocking of an atrial impulse. This is the result of intermittent failure of
atrial electrical impulse conduction through the atrioventricular (AV) node to the ventricles.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 9
Cardiac disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Myocardial infarction
-
Asymptomatic and cardiac
enzymes minimally abnormal
and no evidence of ischemic
ECG changes
Severe symptoms; cardiac
enzymes abnormal;
hemodynamically stable; ECG
changes consistent with
infarction
Life-threatening
consequences;
hemodynamically unstable
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by gross necrosis of the myocardium; this is due to an interruption of blood supply to the area.
Navigational Note: -
Myocarditis
-
Symptoms with moderate
activity or exertion
Severe with symptoms at rest
or with minimal activity or
exertion; intervention
indicated; new onset of
symptoms
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated (e.g.,
continuous IV therapy or
mechanical hemodynamic
support)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation of the muscle tissue of the heart.
Navigational Note: -
Palpitations
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Intervention indicated
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an unpleasant sensation of irregular and/or forceful beating of the heart.
Navigational Note: -
Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia
Asymptomatic, intervention
not indicated
Non-urgent medical
intervention indicated
Symptomatic, urgent
intervention indicated;
ablation
Life-threatening
consequences; incompletely
controlled medically;
cardioversion indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia with abrupt onset and sudden termination of atrial contractions with a rate of 150-250 beats per minute. The rhythm disturbance
originates in the atria.
Navigational Note: -
Pericardial effusion
-
Asymptomatic effusion size
small to moderate
Effusion with physiologic
consequences
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by fluid collection within the pericardial sac, usually due to inflammation.
Navigational Note: -
Pericardial tamponade
-
-
-
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an increase in intrapericardial pressure due to the collection of blood or fluid in the pericardium.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 10
Cardiac disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Pericarditis
Asymptomatic, ECG or
physical findings (e.g., rub)
consistent with pericarditis
Symptomatic pericarditis (e.g.,
chest pain)
Pericarditis with physiologic
consequences (e.g.,
pericardial constriction)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by irritation to the layers of the pericardium (the protective sac around the heart).
Navigational Note: -
Pulmonary valve disease
Asymptomatic valvular
thickening with or without
mild valvular regurgitation or
stenosis by imaging
Asymptomatic; moderate
regurgitation or stenosis by
imaging
Symptomatic; severe
regurgitation or stenosis by
imaging; symptoms controlled
with medical intervention
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated (e.g.,
valve replacement,
valvuloplasty)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a defect in pulmonary valve function or structure.
Navigational Note: -
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
Imaging findings only
Symptomatic without signs of
heart failure
Symptomatic heart failure or
other cardiac symptoms,
responsive to intervention;
new onset of symptoms
Refractory heart failure or
other poorly controlled
cardiac symptoms
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an inability of the ventricles to fill with blood because the myocardium (heart muscle) stiffens and loses its flexibility.
Navigational Note: -
Right ventricular dysfunction
Asymptomatic with laboratory
(e.g., BNP [B-Natriuretic
Peptide ]) or cardiac imaging
abnormalities
Symptoms with moderate
activity or exertion
Severe symptoms, associated
with hypoxia, right heart
failure; oxygen indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated (e.g.,
ventricular assist device);
heart transplant indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by impairment of right ventricular function associated with low ejection fraction and a decrease in motility of the right ventricular wall.
Navigational Note: -
Sick sinus syndrome
Asymptomatic, intervention
not indicated
Symptomatic, intervention
not indicated; change in
medication initiated
Symptomatic, intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia with alternating periods of bradycardia and atrial tachycardia accompanied by syncope, fatigue and dizziness.
Navigational Note: -
Sinus bradycardia
Asymptomatic, intervention
not indicated
Symptomatic, intervention
not indicated; change in
medication initiated
Symptomatic, intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia with a heart rate less than 60 beats per minute that originates in the sinus node.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 11
Cardiac disorders
CTCAE Term
Grade 1
Grade 2
Grade 3
Grade 4
Grade 5
Sinus tachycardia
Asymptomatic, intervention
not indicated
Symptomatic; non-urgent
medical intervention indicated
Urgent medical intervention
indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia with a heart rate greater than 100 beats per minute that originates in the sinus node.
Navigational Note: -
Supraventricular tachycardia
Asymptomatic, intervention
not indicated
Non-urgent medical
intervention indicated
Symptomatic, urgent
intervention indicated
Life-threatening consequences
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia with a heart rate greater than 100 beats per minute that originates above the ventricles.
Navigational Note: -
Tricuspid valve disease
Asymptomatic valvular
thickening with or without
mild valvular regurgitation or
stenosis
Asymptomatic; moderate
regurgitation or stenosis by
imaging
Symptomatic; severe
regurgitation or stenosis;
symptoms controlled with
medical intervention
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated (e.g.,
valve replacement,
valvuloplasty)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a defect in tricuspid valve function or structure.
Navigational Note: -
Ventricular arrhythmia
Asymptomatic, intervention
not indicated
Non-urgent medical
intervention indicated
Urgent intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; hemodynamic
compromise
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia that originates in the ventricles.
Navigational Note: -
Ventricular fibrillation
-
-
-
Life-threatening
consequences; hemodynamic
compromise
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia without discernible QRS complexes due to rapid repetitive excitation of myocardial fibers without coordinated contraction of the
ventricles.
Navigational Note: -
Ventricular tachycardia
-
Non-urgent medical
intervention indicated
Symptomatic, urgent
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; hemodynamic
compromise
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia with a heart rate greater than 100 beats per minute that originates distal to the bundle of His.
Navigational Note: -
Cardiac disorders - Other,
specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 12
Congenital, familial and genetic disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Congenital, familial and
genetic disorders - Other,
specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 13
Ear and labyrinth disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Ear pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the ear.
Navigational Note: -
External ear pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the external ear region.
Navigational Note: -
Hearing impaired
Adults enrolled on a
Monitoring Program (on a 1,
2, 4, 3, 6, and 8 kHz
audiogram): Threshold shift of
15 - 25 dB averaged at 2
contiguous test frequencies in
at least one ear;
Adults not enrolled on a
Monitoring Program:
Subjective change in hearing
in the absence of documented
hearing loss;
Pediatric (on a 1, 2, 3, 4, 6,
and 8 kHz audiogram):
Threshold shift >20 dB hearing
loss (HL) (i.e., 25 dB HL or
greater); sensorineural
hearing loss (SNHL) above 4
kHz (i.e., 6 or 8 kHz) in at least
one ear
Adults enrolled on a
Monitoring Program (on a 1,
2, 3, 4, 6, and 8 kHz
audiogram): Threshold shift of
>25 dB averaged at 2
contiguous test frequencies in
at least one ear;
Adults not enrolled on a
Monitoring Program: Hearing
loss with hearing aid or
intervention not indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL;
Pediatric (on a 1, 2, 3, 4, 6,
and 8 kHz audiogram):
Threshold shift >20 dB at 4
kHz in at least one ear
Adults enrolled on a
Monitoring Program (on a 1,
2, 3, 4, 6, and 8 kHz
audiogram): Threshold shift of
>25 dB averaged at 3
contiguous test frequencies in
at least one ear; therapeutic
intervention indicated;
Adults not enrolled on a
Monitoring Program: Hearing
loss with hearing aid or
intervention indicated;
limiting self care ADL;
Pediatric (on a 1, 2, 3, 4, 6,
and 8 kHz audiogram):
Hearing loss sufficient to
indicate therapeutic
intervention, including
hearing aids; threshold shift
>20 dB at 2 to < 4 kHz in at
least one ear
Adults: Decrease in hearing to
profound bilateral loss
(absolute threshold >80 dB HL
at 2 kHz and above);
nonservicable hearing
Pediatric: Audiologic
indication for cochlear
implant; > 40 dB HL (i.e., 45 dB
HL or more); SNHL at 2 kHz
and above
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by partial or complete loss of the ability to detect or understand sounds resulting from damage to ear structures.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 14
Ear and labyrinth disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Middle ear inflammation
Serous otitis
Serous otitis, medical
intervention indicated
Mastoiditis; necrosis of canal
soft tissue or bone
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation (physiologic response to irritation), swelling and redness to the middle ear.
Navigational Note: -
Tinnitus
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by noise in the ears, such as ringing, buzzing, roaring or clicking.
Navigational Note: -
Vertigo
Mild symptoms
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation as if the external world were revolving around the patient (objective vertigo) or as if he himself were revolving in space (subjective
vertigo).
Navigational Note: -
Vestibular disorder
-
Symptomatic; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by dizziness, imbalance, nausea, and vision problems.
Navigational Note: -
Ear and labyrinth disorders -
Other, specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 15
Endocrine disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Adrenal insufficiency
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms;
hospitalization indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the adrenal cortex not producing enough of the hormone cortisol and in some cases, the hormone aldosterone. It may be due to a disorder of
the adrenal cortex as in Addison's disease or primary adrenal insufficiency.
Navigational Note: -
Cushingoid
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms, medical
intervention or hospitalization
indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by signs and symptoms that resemble Cushing's disease or syndrome: buffalo hump obesity, striations, adiposity, hypertension, diabetes, and
osteoporosis, usually due to exogenous corticosteroids.
Navigational Note: -
Delayed puberty
-
No breast development by
age 13 yrs for females; testes
volume of <3 cc or no Tanner
Stage 2 development by age
14.5 yrs for males
No breast development by
age 14 yrs for females; no
increase in testes volume or
no Tanner Stage 2 by age 16
yrs for males; hormone
replacement indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by unusually late sexual maturity.
Navigational Note: -
Growth accelerated
-
>= +2 SD (standard deviation)
above mid parental height or
target height
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by greater growth than expected for age.
Navigational Note: -
Hyperparathyroidism
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an increase in production of parathyroid hormone by the parathyroid glands. This results in hypercalcemia (abnormally high levels of calcium in
the blood).
Navigational Note: -
Hyperthyroidism
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; thyroid
suppression therapy
indicated; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL; hospitalization
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by excessive levels of thyroid hormone in the body. Common causes include an overactive thyroid gland or thyroid hormone overdose.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 16
Endocrine disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Hypoparathyroidism
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; medical
intervention or hospitalization
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease in production of parathyroid hormone by the parathyroid glands.
Navigational Note: -
Hypophysitis
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation and cellular infiltration of the pituitary gland.
Navigational Note: -
Hypopituitarism
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease in production of hormones from the pituitary gland.
Navigational Note: -
Hypothyroidism
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; thyroid
replacement indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL; hospitalization
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease in production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland.
Navigational Note: -
Precocious puberty
Physical signs of puberty with
no biochemical markers for
females <8 years and males <9
years
Physical signs and biochemical
markers of puberty for
females <8 years and males <9
years
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by unusually early development of secondary sexual features; the onset of sexual maturation begins usually before age 8 for girls and before age 9
for boys.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 17
Endocrine disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Testosterone deficiency
Asymptomatic; mild
symptoms with no
intervention indicated
Replacement therapy initiated
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by low testosterone.
Navigational Note: -
Virilization
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by inappropriate masculinization occurring in a female or prepubertal male.
Navigational Note: -
Endocrine disorders - Other,
specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 18
Eye disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Blurred vision
Intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; moderate
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity 20/40
and better or 3 lines or less
decreased vision from known
baseline); limiting
instrumental ADL
Symptomatic with marked
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity worse
than 20/40 or more than 3
lines of decreased vision from
known baseline, up to
20/200); limiting self care ADL
Best corrected visual acuity of
20/200 or worse in the
affected eye
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by visual perception of unclear or fuzzy images.
Navigational Note: -
Cataract
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; moderate
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity 20/40
and better or 3 lines or less
decreased vision from known
baseline); glare symptoms
affecting instrumental ADL
Symptomatic with marked
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity worse
than 20/40 or more than 3
lines of decreased vision from
known baseline, up to
20/200); limiting self care ADL
Best corrected visual acuity of
20/200 or worse in the
affected eye
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by partial or complete opacity of the crystalline lens of one or both eyes. This results in a decrease in visual acuity and eventual blindness if
untreated.
Navigational Note: -
Corneal ulcer
-
-
Corneal ulcer without
perforation in the affected
eye
Perforation in the affected eye
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an area of epithelial tissue loss on the surface of the cornea. It is associated with inflammatory cells in the cornea and anterior chamber.
Navigational Note: -
Dry eye
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
symptoms relieved by
lubricants
Symptomatic; moderate
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity 20/40
and better or 3 lines or less
decreased vision from known
baseline)
Symptomatic with marked
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity worse
than 20/40 or more than 3
lines of decreased vision from
known baseline, up to
20/200); limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by dryness of the cornea and conjunctiva.
Navigational Note: If corneal ulcer is present, grade under Eye disorders: Corneal ulcer.
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 19
Eye disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Extraocular muscle paresis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only
Unilateral paresis without
double vision
Bilateral paresis or unilateral
paresis causing double vision
in peripheral gaze, but not in
central gaze
Bilateral paresis requiring
head turning to see beyond
central 60 degrees or double
vision in central gaze
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by incomplete paralysis of an extraocular muscle.
Navigational Note: -
Eye pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the eye.
Navigational Note: -
Eyelid function disorder
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; nonoperative
intervention indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Limiting self care ADL;
operative intervention
indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by impaired eyelid function.
Navigational Note: -
Flashing lights
Symptomatic but not limiting
ADL
Limiting instrumental ADL
Limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sudden or brief burst of light.
Navigational Note: Also consider Eye disorders: Retinal tear or Retinal detachment
Floaters
Symptomatic but not limiting
ADL
Limiting instrumental ADL
Limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an individual seeing spots before their eyes. The spots are shadows of opaque cell fragments in the vitreous humor or lens.
Navigational Note: Also consider Eye disorders: Retinal tear or Retinal detachment
Glaucoma
Less than 8 mmHg of elevated
intraocular pressure (EIOP);
no visual field deficit
EIOP which can be reduced to
21 mmHg or under with
topical medications and no
visual field deficit
EIOP causing visual field
deficits
Visual field deficit within the
central 10 degrees of the
visual field in the affected eye
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an increase in pressure in the eyeball due to obstruction of the aqueous humor outflow.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 20
Eye disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Keratitis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; moderate
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity 20/40
and better or 3 lines or less
decreased vision from known
baseline)
Symptomatic with marked
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity worse
than 20/40 or more than 3
lines of decreased vision from
known baseline, up to
20/200); corneal ulcer;
limiting self care ADL
Perforation; best corrected
visual acuity of 20/200 or
worse in the affected eye
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation to the cornea of the eye.
Navigational Note: Also consider Eye disorders: Corneal ulcer
Night blindness
Symptomatic but not limiting
ADL
Symptomatic; moderate
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity 20/40
and better or 3 lines or less
decreased vision from known
baseline); limiting
instrumental ADL
Symptomatic with marked
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity worse
than 20/40 or more than 3
lines of decreased vision from
known baseline, up to
20/200); limiting self care ADL
Best corrected visual acuity of
20/200 or worse in the
affected eye
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an inability to see clearly in dim light.
Navigational Note: -
Optic nerve disorder
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only
Moderate decrease in visual
acuity (best corrected visual
acuity 20/40 and better or 3
lines or less decreased vision
from known baseline)
Marked decrease in visual
acuity (best corrected visual
acuity worse than 20/40 or
more than 3 lines of
decreased vision from known
baseline, up to 20/200)
Best corrected visual acuity of
20/200 or worse in the
affected eye
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by involvement of the optic nerve (second cranial nerve).
Navigational Note: -
Papilledema
Asymptomatic; no visual field
deficit
Symptomatic; moderate
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity 20/40
and better or 3 lines or less
decreased vision from known
baseline)
Symptomatic with marked
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity worse
than 20/40 or more than 3
lines of decreased vision from
known baseline, up to 20/200)
Best corrected visual acuity of
20/200 or worse in the
affected eye
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by swelling around the optic disc.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 21
Eye disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Periorbital edema
Soft or non-pitting
Indurated or pitting edema;
topical intervention indicated
Edema associated with visual
disturbance; increased
intraocular pressure,
glaucoma or retinal
hemorrhage; optic neuritis;
diuretics indicated; operative
intervention indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by swelling due to an excessive accumulation of fluid around the orbits of the face.
Navigational Note: -
Photophobia
Symptomatic but not limiting
ADL
Limiting instrumental ADL
Limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by fear and avoidance of light.
Navigational Note: -
Retinal detachment
-
-
Macular sparing
rhegmatogenous detachment
Macula-off rhegmatogenous
retinal detachment
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by the separation of the inner retina layers from the underlying pigment epithelium.
Navigational Note: -
Retinal tear
No retinal detachment and
treatment not indicated
No retinal detachment and
treatment indicated
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a small laceration of the retina, this occurs when the vitreous separates from the retina. Symptoms include flashes and floaters.
Navigational Note: If retinal detachment is present, grade under Eye disorders: Retinal detachment
Retinal vascular disorder
-
Retinal vascular disorder
without neovascularization
Retinal vascular disorder with
neovascularization
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by pathological retinal blood vessels that adversely affects vision.
Navigational Note: If vitreous hemorrhage is present, report under Eye disorders: Vitreous hemorrhage.
Retinopathy
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only
Symptomatic; moderate
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity 20/40
and better or 3 lines or less
decreased vision from known
baseline); limiting
instrumental ADL
Symptomatic with marked
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity worse
than 20/40 or more than 3
lines of decreased vision from
known baseline, up to
20/200); limiting self care ADL
Best corrected visual acuity of
20/200 or worse in the
affected eye
-
Definition: A disorder involving the retina.
Navigational Note: If vitreous hemorrhage is present, report under Eye disorders: Vitreous hemorrhage.
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 22
Eye disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Scleral disorder
No change in vision from
baseline
Symptomatic; moderate
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity 20/40
and better or 3 lines or less
decreased vision from known
baseline); limiting
instrumental ADL
Symptomatic with marked
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity worse
than 20/40 or more than 3
lines of decreased vision from
known baseline, up to
20/200); limiting self care ADL
Best corrected visual acuity of
20/200 or worse in the
affected eye
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by involvement of the sclera of the eye.
Navigational Note: -
Uveitis
Anterior uveitis with trace
cells
Anterior uveitis with 1+ or 2+
cells
Anterior uveitis with 3+ or
greater cells; intermediate
posterior or pan-uveitis
Best corrected visual acuity of
20/200 or worse in the
affected eye
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation to the uvea of the eye.
Navigational Note: -
Vision decreased
-
Moderate decrease in visual
acuity (best corrected visual
acuity 20/40 and better or 3
lines or less decreased vision
from known baseline)
Marked decrease in visual
acuity (best corrected visual
acuity worse than 20/40 or
more than 3 lines of
decreased vision from known
baseline, up to 20/200)
Best corrected visual acuity of
20/200 or worse in the
affected eye
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease in visual acuity.
Navigational Note: If etiology is known, use a more specific CTCAE term.
Vitreous hemorrhage
Intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; moderate
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity 20/40
and better or 3 lines or less
decreased vision from known
baseline); limiting
instrumental ADL
Symptomatic with marked
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity worse
than 20/40 or more than 3
lines of decreased vision from
known baseline, up to
20/200); limiting self care
ADL; vitrectomy indicated
Best corrected visual acuity of
20/200 or worse in the
affected eye
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding into the vitreous humor.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 23
Eye disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Watering eyes
Intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; moderate
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity 20/40
and better or 3 lines or less
decreased vision from known
baseline)
Marked decrease in visual
acuity (best corrected visual
acuity worse than 20/40 or
more than 3 lines of
decreased vision from known
baseline, up to 20/200)
Best corrected visual acuity of
20/200 or worse in the
affected eye
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by excessive tearing in the eyes; it can be caused by overproduction of tears or impaired drainage of the tear duct.
Navigational Note: -
Eye disorders - Other, specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated; no
change in vision
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting
instrumental ADL; best
corrected visual acuity 20/40
and better or 3 lines or less
decreased vision from known
baseline
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately sight-
threatening; limiting self care
ADL; decrease in visual acuity
(best corrected visual acuity
worse than 20/40 or more
than 3 lines of decreased
vision from known baseline,
up to 20/200)
Sight-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated; best
corrected visual acuity of
20/200 or worse in the
affected eye
-
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 24
Gastrointestinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Abdominal distension
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe discomfort; limiting
self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by swelling of the abdomen.
Navigational Note: -
Abdominal pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the abdominal region.
Navigational Note: -
Anal fissure
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic
Invasive intervention
indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a tear in the lining of the anus.
Navigational Note: -
Anal fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the opening in the anal canal to the perianal skin.
Navigational Note: -
Anal hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the anal region.
Navigational Note: -
Anal mucositis
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by ulceration or inflammation of the mucous membrane of the anus.
Navigational Note: Report Grade 4 and 5 as Gastrointestinal disorders: Anal ulcer
Anal necrosis
-
-
TPN or hospitalization
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the anal region.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 25
Gastrointestinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Anal pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the anal region.
Navigational Note: -
Anal stenosis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function
Symptomatic and severely
altered GI function; non-
emergent operative
intervention indicated; TPN or
hospitalization indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a narrowing of the lumen of the anal canal.
Navigational Note: -
Anal ulcer
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function
Severely altered GI function;
TPN indicated; elective
invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a circumscribed, erosive lesion on the mucosal surface of the anal canal.
Navigational Note: -
Ascites
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by accumulation of serous or hemorrhagic fluid in the peritoneal cavity.
Navigational Note: -
Belching
Increase from baseline
Intervention initiated
(including over the counter
medications)
-
-
-
Definition: To expel gas noisily from the mouth.
Navigational Note: Synonym: Burping
Bloating
No change in bowel function
or oral intake
Symptomatic, decreased oral
intake; change in bowel
function
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by subject-reported feeling of uncomfortable fullness of the abdomen.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 26
Gastrointestinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Cecal hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the cecum.
Navigational Note: -
Cheilitis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL; intervention
indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation of the lip.
Navigational Note: -
Chylous ascites
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
fat-restricted diet);
paracentesis or tube drainage
indicated
Severe symptoms; elective
operative intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by accumulation of milky fluid in the peritoneal cavity.
Navigational Note: -
Colitis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Abdominal pain; mucus or
blood in stool
Severe abdominal pain;
peritoneal signs
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation of the colon.
Navigational Note: -
Colonic fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the large intestine and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Colonic hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the colon.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 27
Gastrointestinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Colonic obstruction
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function
Hospitalization indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by blockage of the normal flow of the intestinal contents in the colon.
Navigational Note: -
Colonic perforation
-
Invasive intervention not
indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a rupture in the colonic wall.
Navigational Note: -
Colonic stenosis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function
Severely altered GI function;
tube feeding or
hospitalization indicated;
elective operative
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a narrowing of the lumen of the colon.
Navigational Note: -
Colonic ulcer
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function
Severely altered GI function;
TPN indicated; elective
invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a circumscribed, erosive lesion on the mucosal surface of the colon.
Navigational Note: -
Constipation
Occasional or intermittent
symptoms; occasional use of
stool softeners, laxatives,
dietary modification, or
enema
Persistent symptoms with
regular use of laxatives or
enemas; limiting instrumental
ADL
Obstipation with manual
evacuation indicated; limiting
self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by irregular and infrequent or difficult evacuation of the bowels.
Navigational Note: -
Dental caries
One or more dental caries,
not involving the root
Dental caries involving the
root
Dental caries resulting in
pulpitis or periapical abscess
or resulting in tooth loss
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by the decay of a tooth, in which it becomes softened, discolored and/or porous.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 28
Gastrointestinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Diarrhea
Increase of <4 stools per day
over baseline; mild increase in
ostomy output compared to
baseline
Increase of 4 - 6 stools per day
over baseline; moderate
increase in ostomy output
compared to baseline; limiting
instrumental ADL
Increase of >=7 stools per day
over baseline; hospitalization
indicated; severe increase in
ostomy output compared to
baseline; limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an increase in frequency and/or loose or watery bowel movements.
Navigational Note: -
Dry mouth
Symptomatic (e.g., dry or
thick saliva) without
significant dietary alteration;
unstimulated saliva flow >0.2
ml/min
Moderate symptoms; oral
intake alterations (e.g.,
copious water, other
lubricants, diet limited to
purees and/or soft, moist
foods); unstimulated saliva 0.1
to 0.2 ml/min
Inability to adequately aliment
orally; tube feeding or TPN
indicated; unstimulated saliva
<0.1 ml/min
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by reduced salivary flow in the oral cavity.
Navigational Note: -
Duodenal fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the duodenum and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Duodenal hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the duodenum.
Navigational Note: -
Duodenal obstruction
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function
Hospitalization indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by blockage of the normal flow of stomach contents through the duodenum.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC
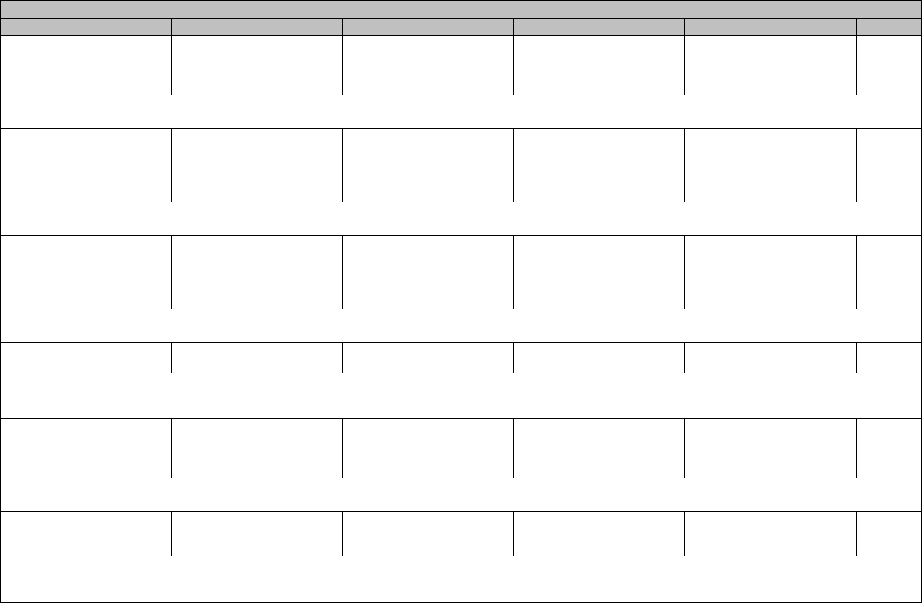
CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 29
Gastrointestinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Duodenal perforation
-
Invasive intervention not
indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a rupture in the duodenal wall.
Navigational Note: -
Duodenal stenosis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function
Severely altered GI function;
tube feeding or
hospitalization indicated;
elective operative
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a narrowing of the lumen of the duodenum.
Navigational Note: -
Duodenal ulcer
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severely altered GI function;
TPN indicated; elective
invasive intervention
indicated; limiting self care
ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a circumscribed, erosive lesion on the mucosal surface of the duodenal wall.
Navigational Note: -
Dyspepsia
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; operative
intervention indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an uncomfortable, often painful feeling in the stomach, resulting from impaired digestion. Symptoms include burning stomach, bloating,
heartburn, nausea and vomiting.
Navigational Note: -
Dysphagia
Symptomatic, able to eat
regular diet
Symptomatic and altered
eating/swallowing
Severely altered
eating/swallowing; tube
feeding, TPN, or
hospitalization indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by difficulty in swallowing.
Navigational Note: -
Enterocolitis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Abdominal pain; mucus or
blood in stool
Severe or persistent
abdominal pain; fever; ileus;
peritoneal signs
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation of the small and large intestines.
Navigational Note: If reporting a known abnormality of the colon, use Gastrointestinal disorders: Colitis. If reporting a documented infection, use Infections and infestations:
Enterocolitis infectious.
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 30
Gastrointestinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Enterovesical fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the urinary bladder and the intestine.
Navigational Note: -
Esophageal fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the esophagus and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Esophageal hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the esophagus.
Navigational Note: -
Esophageal necrosis
-
-
Inability to aliment adequately
by GI tract; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the esophageal wall.
Navigational Note: -
Esophageal obstruction
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function; limiting instrumental
ADL
Hospitalization indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; limiting self care
ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by blockage of the normal flow of the contents in the esophagus.
Navigational Note: -
Esophageal pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the esophageal region.
Navigational Note: -
Esophageal perforation
-
Invasive intervention not
indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a rupture in the wall of the esophagus.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 31
Gastrointestinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Esophageal stenosis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function
Severely altered GI function;
tube feeding or
hospitalization indicated;
elective operative
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus.
Navigational Note: -
Esophageal ulcer
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function; limiting instrumental
ADL
Severely altered GI function;
TPN indicated; elective
invasive intervention
indicated; limiting self care
ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a circumscribed, erosive lesion on the mucosal surface of the esophageal wall.
Navigational Note: -
Esophageal varices
hemorrhage
-
Self-limited; intervention not
indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from esophageal varices.
Navigational Note: -
Esophagitis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered
eating/swallowing; oral
supplements indicated
Severely altered
eating/swallowing; tube
feeding, TPN, or
hospitalization indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation of the esophageal wall.
Navigational Note: -
Fecal incontinence
Occasional use of pads
required
Daily use of pads required
Severe symptoms; elective
operative intervention
indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by inability to control the escape of stool from the rectum.
Navigational Note: -
Flatulence
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate; persistent;
psychosocial sequelae
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a discharge of excessive gas from the lower GI tract.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 32
Gastrointestinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Gastric fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the stomach and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Gastric hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the gastric wall.
Navigational Note: -
Gastric necrosis
-
-
Inability to aliment adequately
by GI tract; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the gastric wall.
Navigational Note: -
Gastric perforation
-
Invasive intervention not
indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a rupture in the stomach wall.
Navigational Note: -
Gastric stenosis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function
Severely altered GI function;
tube feeding or
hospitalization indicated;
elective operative
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a narrowing of the lumen of the stomach.
Navigational Note: -
Gastric ulcer
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function; medical intervention
indicated; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severely altered GI function;
TPN indicated; elective
invasive intervention
indicated; limiting self care
ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a circumscribed, erosive lesion on the mucosal surface of the stomach.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 33
Gastrointestinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Gastritis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function; medical intervention
indicated
Severely altered eating or
gastric function; TPN or
hospitalization indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation of the stomach.
Navigational Note: -
Gastroesophageal reflux
disease
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; operative
intervention indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by reflux of the gastric and/or duodenal contents into the distal esophagus. It is chronic in nature and usually caused by incompetence of the lower
esophageal sphincter, and may result in injury to the esophageal mucosal. Symptoms include heartburn and acid indigestion.
Navigational Note: -
Gastrointestinal fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between any part of the gastrointestinal system and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Gastrointestinal pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the gastrointestinal region.
Navigational Note: -
Gastroparesis
Mild nausea, early satiety and
bloating, able to maintain
caloric intake on regular diet
Moderate symptoms; able to
maintain nutrition with
dietary and lifestyle
modifications; may need
pharmacologic intervention
Weight loss >=20% from
baseline; tube feeding or TPN
indicated; elective operative
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an incomplete paralysis of the muscles of the stomach wall resulting in delayed emptying of the gastric contents into the small intestine.
Navigational Note: -
Gingival pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain interfering
with oral intake
Severe pain; inability to
aliment orally
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the gingival region.
Navigational Note: -
Hemorrhoidal hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the hemorrhoids.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 34
Gastrointestinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Hemorrhoids
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; banding or
medical intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by the presence of dilated veins in the rectum and surrounding area.
Navigational Note: -
Ileal fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the ileum and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Ileal hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the ileal wall.
Navigational Note: -
Ileal obstruction
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function; limiting instrumental
ADL; naso-gastric tube
indicated
Hospitalization indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; limiting self care
ADL; long intestinal tube
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by blockage of the normal flow of the intestinal contents in the ileum.
Navigational Note: -
Ileal perforation
-
Invasive intervention not
indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a rupture in the ileal wall.
Navigational Note: -
Ileal stenosis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function
Severely altered GI function;
tube feeding or
hospitalization indicated;
elective operative
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a narrowing of the lumen of the ileum.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 35
Gastrointestinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Ileal ulcer
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function
Severely altered GI function;
TPN indicated; elective
invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a circumscribed, erosive lesion on the mucosal surface of the ileum.
Navigational Note: -
Ileus
Asymptomatic and radiologic
observations only
Symptomatic; altered GI
function; bowel rest indicated
Severely altered GI function;
TPN indicated; tube
placement indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by failure of the ileum to transport intestinal contents.
Navigational Note: -
Intra-abdominal hemorrhage
-
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding in the abdominal cavity.
Navigational Note: -
Jejunal fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the jejunum and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Jejunal hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the jejunal wall.
Navigational Note: -
Jejunal obstruction
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function; limiting instrumental
ADL
Hospitalization indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; limiting self care
ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by blockage of the normal flow of the intestinal contents in the jejunum.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 36
Gastrointestinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Jejunal perforation
-
Invasive intervention not
indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a rupture in the jejunal wall.
Navigational Note: -
Jejunal stenosis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function
Severely altered GI function;
tube feeding or
hospitalization indicated;
elective operative
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a narrowing of the lumen of the jejunum.
Navigational Note: -
Jejunal ulcer
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function
Severely altered GI function;
TPN indicated; elective
invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a circumscribed, erosive lesion on the mucosal surface of the jejunum.
Navigational Note: -
Lip pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort of the lip.
Navigational Note: -
Lower gastrointestinal
hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the lower gastrointestinal tract (small intestine, large intestine, and anus).
Navigational Note: -
Malabsorption
-
Altered diet; oral intervention
indicated
Inability to aliment
adequately; TPN indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inadequate absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. Symptoms include abdominal marked discomfort, bloating and diarrhea.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 37
Gastrointestinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Mucositis oral
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; intervention not
indicated
Moderate pain or ulcer that
does not interfere with oral
intake; modified diet
indicated
Severe pain; interfering with
oral intake
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by ulceration or inflammation of the oral mucosal.
Navigational Note: -
Nausea
Loss of appetite without
alteration in eating habits
Oral intake decreased without
significant weight loss,
dehydration or malnutrition
Inadequate oral caloric or
fluid intake; tube feeding,
TPN, or hospitalization
indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a queasy sensation and/or the urge to vomit.
Navigational Note: -
Obstruction gastric
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function; limiting instrumental
ADL
Hospitalization indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; limiting self care
ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by blockage of the normal flow of the contents in the stomach.
Navigational Note: -
Oral cavity fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the oral cavity and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Oral dysesthesia
Mild discomfort; not
interfering with oral intake
Moderate pain; interfering
with oral intake
Disabling pain; tube feeding or
TPN indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a burning or tingling sensation on the lips, tongue or entire mouth.
Navigational Note: -
Oral hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the mouth.
Navigational Note: -
Oral pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the mouth, tongue or lips.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 38
Gastrointestinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Pancreatic duct stenosis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function
Severely altered GI function;
tube feeding or
hospitalization indicated;
elective operative
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a narrowing of the lumen of the pancreatic duct.
Navigational Note: -
Pancreatic fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the pancreas and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Pancreatic hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the pancreas.
Navigational Note: -
Pancreatic necrosis
-
-
Tube feeding or TPN
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the pancreas.
Navigational Note: -
Pancreatitis
-
Enzyme elevation; radiologic
findings only
Severe pain; vomiting;
medical intervention indicated
(e.g., analgesia, nutritional
support)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation of the pancreas with no documented pancreas infection.
Navigational Note: -
Periodontal disease
Gingival recession or
gingivitis; limited bleeding on
probing; mild local bone loss
Moderate gingival recession
or gingivitis; multiple sites of
bleeding on probing;
moderate bone loss
Spontaneous bleeding; severe
bone loss with or without
tooth loss; osteonecrosis of
maxilla or mandible
-
-
Definition: A disorder in the gingival tissue around the teeth.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 39
Gastrointestinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Peritoneal necrosis
-
-
Tube feeding or TPN
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the peritoneum.
Navigational Note: -
Proctitis
Rectal discomfort,
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic (e.g., rectal
discomfort, passing blood or
mucus); medical intervention
indicated; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; fecal
urgency or stool incontinence;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation of the rectum.
Navigational Note: -
Rectal fissure
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic
Invasive intervention
indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a tear in the lining of the rectum.
Navigational Note: -
Rectal fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the rectum and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Rectal hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the rectal wall and discharged from the anus.
Navigational Note: -
Rectal mucositis
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by ulceration or inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rectum.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 40
Gastrointestinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Rectal necrosis
-
-
Tube feeding or TPN
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the rectal wall.
Navigational Note: -
Rectal obstruction
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function; limiting instrumental
ADL
Hospitalization indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; limiting self care
ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by blockage of the normal flow of the intestinal contents in the rectum.
Navigational Note: -
Rectal pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the rectal region.
Navigational Note: -
Rectal perforation
-
Invasive intervention not
indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a rupture in the rectal wall.
Navigational Note: -
Rectal stenosis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function
Severely altered GI function;
tube feeding or
hospitalization indicated;
elective operative
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a narrowing of the lumen of the rectum.
Navigational Note: -
Rectal ulcer
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function (e.g., altered dietary
habits, vomiting, diarrhea)
Severely altered GI function;
TPN indicated; elective
invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a circumscribed, erosive lesion on the mucosal surface of the rectum.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 41
Gastrointestinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Retroperitoneal hemorrhage
-
Self-limited; intervention
indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the retroperitoneal area.
Navigational Note: -
Salivary duct inflammation
Slightly thickened saliva;
slightly altered taste (e.g.,
metallic)
Thick, ropy, sticky saliva;
markedly altered taste;
alteration in diet indicated;
secretion-induced symptoms;
limiting instrumental ADL
Acute salivary gland necrosis;
severe secretion-induced
symptoms (e.g., thick
saliva/oral secretions or
gagging); tube feeding or TPN
indicated; limiting self care
ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation of the salivary duct.
Navigational Note: -
Salivary gland fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between a salivary gland and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Small intestinal mucositis
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe pain; interfering with
oral intake; tube feeding, TPN
or hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by ulceration or inflammation of the mucous membrane of the small intestine.
Navigational Note: -
Small intestinal obstruction
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function; limiting instrumental
ADL
Hospitalization indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; limiting self care
ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by blockage of the normal flow of the intestinal contents of the small intestine.
Navigational Note: -
Small intestinal perforation
-
Invasive intervention not
indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a rupture in the small intestine wall.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 42
Gastrointestinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Small intestinal stenosis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function
Symptomatic and severely
altered GI function; tube
feeding, TPN or
hospitalization indicated; non-
emergent operative
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a narrowing of the lumen of the small intestine.
Navigational Note: -
Small intestine ulcer
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function; limiting instrumental
ADL
Severely altered GI function;
TPN indicated; elective
invasive intervention
indicated; limiting self care
ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a circumscribed, erosive lesion on the mucosal surface of the small intestine.
Navigational Note: -
Stomach pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the stomach.
Navigational Note: -
Tooth development disorder
Asymptomatic; hypoplasia of
tooth or enamel
Impairment correctable with
oral surgery
Maldevelopment with
impairment not surgically
correctable; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a pathological process of the teeth occurring during tooth development.
Navigational Note: -
Tooth discoloration
Surface stains
-
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a change in tooth hue or tint.
Navigational Note: -
Toothache
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the tooth.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 43
Gastrointestinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Typhlitis
-
-
Symptomatic (e.g., abdominal
pain, fever, change in bowel
habits with ileus); peritoneal
signs
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by necrotizing enterocolitis in neutropenic patients.
Navigational Note: Also report Investigations: Neutrophil count decreased
Upper gastrointestinal
hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract (oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, and stomach).
Navigational Note: -
Visceral arterial ischemia
-
Brief (<24 hrs) episode of
ischemia managed medically
and without permanent
deficit
Prolonged (>=24 hrs) or
recurring symptoms and/or
invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; evidence of
end organ damage; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease in blood supply due to narrowing or blockage of a visceral (mesenteric) artery.
Navigational Note: -
Vomiting
Intervention not indicated
Outpatient IV hydration;
medical intervention indicated
Tube feeding, TPN, or
hospitalization indicated
Life-threatening
consequences
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the reflexive act of ejecting the contents of the stomach through the mouth.
Navigational Note: -
Gastrointestinal disorders -
Other, specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 44
General disorders and administration site conditions
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Chills
Mild sensation of cold;
shivering; chattering of teeth
Moderate tremor of the entire
body; narcotics indicated
Severe or prolonged, not
responsive to narcotics
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of cold that often marks a physiologic response to sweating after a fever.
Navigational Note: -
Death neonatal
-
-
-
Neonatal loss of life
-
Definition: Newborn death occurring during the first 28 days after birth.
Navigational Note: -
Death NOS
-
-
-
-
Death
Definition: Death that cannot be attributed to a CTCAE term associated with Grade 5.
Navigational Note: If death is due to an AE (ex., Cardiac disorders: Cardiac arrest), report as a Grade 5 event under that AE.
Disease progression
-
-
-
-
Death
Definition: Death due to disease progression that cannot be attributed to a CTCAE term associated with Grade 5.
Navigational Note: If death is due to an AE (ex., Cardiac disorders: Cardiac arrest), report as a Grade 5 event under that AE.
Edema face
Localized facial edema
Moderate localized facial
edema; limiting instrumental
ADL
Severe swelling; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by swelling due to excessive fluid accumulation in facial tissues.
Navigational Note: -
Edema limbs
5 - 10% inter-limb discrepancy
in volume or circumference at
point of greatest visible
difference; swelling or
obscuration of anatomic
architecture on close
inspection
>10 - 30% inter-limb
discrepancy in volume or
circumference at point of
greatest visible difference;
readily apparent obscuration
of anatomic architecture;
obliteration of skin folds;
readily apparent deviation
from normal anatomic
contour; limiting instrumental
ADL
>30% inter-limb discrepancy
in volume; gross deviation
from normal anatomic
contour; limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by swelling due to excessive fluid accumulation in the upper or lower extremities.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 45
General disorders and administration site conditions
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Edema trunk
Swelling or obscuration of
anatomic architecture on
close inspection
Readily apparent obscuration
of anatomic architecture;
obliteration of skin folds;
readily apparent deviation
from normal anatomic
contour; limiting instrumental
ADL
Gross deviation from normal
anatomic contour; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by swelling due to excessive fluid accumulation in the trunk area.
Navigational Note: -
Facial pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the face.
Navigational Note: -
Fatigue
Fatigue relieved by rest
Fatigue not relieved by rest;
limiting instrumental ADL
Fatigue not relieved by rest,
limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a state of generalized weakness with a pronounced inability to summon sufficient energy to accomplish daily activities.
Navigational Note: -
Fever
38.0 - 39.0 degrees C (100.4 -
102.2 degrees F)
>39.0 - 40.0 degrees C (102.3 -
104.0 degrees F)
>40.0 degrees C (>104.0
degrees F) for <=24 hrs
>40.0 degrees C (>104.0
degrees F) for >24 hrs
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by elevation of the body's temperature above the upper limit of normal.
Navigational Note: -
Flu like symptoms
Mild flu-like symptoms
present
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a group of symptoms similar to those observed in patients with the flu. It includes fever, chills, body aches, malaise, loss of appetite and dry
cough.
Navigational Note: Synonym: Flu, Influenza
Gait disturbance
Mild change in gait (e.g.,
wide-based, limping or
hobbling)
Moderate change in gait (e.g.,
wide-based, limping or
hobbling); assistive device
indicated; limiting
instrumental ADL
Limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by walking difficulties.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 46
General disorders and administration site conditions
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Generalized edema
Noted on exam; 1+ pitting
edema
Interfering with instrumental
ADLs; oral therapy initiated
Interferes with self care ADL;
intravenous therapy
indicated; skin breakdown
Life-threatening consequences
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by fluid accumulation in the tissues of the body including the skin.
Navigational Note: -
Hypothermia
-
35 - >32 degrees C; 95 - >89.6
degrees F
32 - >28 degrees C; 89.6 -
>82.4 degrees F
<=28 degrees C; 82.4 degrees
F; life-threatening
consequences (e.g., coma,
hypotension, pulmonary
edema, acidemia, ventricular
fibrillation)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormally low body temperature. Treatment is required when the body temperature is 35C (95F) or below.
Navigational Note: -
Infusion site extravasation
Painless edema
Erythema with associated
symptoms (e.g., edema, pain,
induration, phlebitis)
Ulceration or necrosis; severe
tissue damage; operative
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by leakage of the infusion into the surrounding tissue. Signs and symptoms may include induration, erythema, swelling, burning sensation and
marked discomfort at the infusion site.
Navigational Note: -
Injection site reaction
Tenderness with or without
associated symptoms (e.g.,
warmth, erythema, itching)
Pain; lipodystrophy; edema;
phlebitis
Ulceration or necrosis; severe
tissue damage; operative
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an intense adverse reaction (usually immunologic) developing at the site of an injection.
Navigational Note: -
Localized edema
Localized to dependent areas,
no disability or functional
impairment
Moderate localized edema
and intervention indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe localized edema and
intervention indicated;
limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by swelling due to excessive fluid accumulation at a specific anatomic site.
Navigational Note: Prior to using this term consider specific edema areas: General disorders and administration site conditions: Edema face, Edema limbs, Edema trunk, or Edema neck;
Nervous system disorders: Edema cerebral; Reproductive system and breast disorders: Genital edema; Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Laryngeal edema or Pulmonary
edema; Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Periorbital edema; Vascular disorders: Lymphedema
Malaise
Uneasiness or lack of well
being
Uneasiness or lack of well
being limiting instrumental
ADL
Uneasiness or lack of well
being limiting self-care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a feeling of general discomfort or uneasiness, an out-of-sorts feeling.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 47
General disorders and administration site conditions
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Multi-organ failure
-
-
Shock with azotemia and acid-
base disturbances; significant
coagulation abnormalities
Life-threatening consequences
(e.g., vasopressor dependent
and oliguric or anuric or
ischemic colitis or lactic
acidosis)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by progressive deterioration of the lungs, liver, kidney and clotting mechanisms.
Navigational Note: -
Neck edema
Asymptomatic localized neck
edema
Moderate neck edema; slight
obliteration of anatomic
landmarks; limiting
instrumental ADL
Generalized neck edema (e.g.,
difficulty in turning neck);
limiting self care ADL
Vascular or respiratory
impairment requiring urgent
intervention
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by swelling due to an accumulation of excessive fluid in the neck.
Navigational Note: -
Non-cardiac chest pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the chest unrelated to a heart disorder.
Navigational Note: -
Pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by the sensation of marked discomfort, distress or agony.
Navigational Note: Prior to using this term consider using a specific body part pain term found throughout the CTCAE (over 40 different pain terms).
Sudden death NOS
-
-
-
-
Death
Definition: An unexpected death that cannot be attributed to a CTCAE term associated with Grade 5.
Navigational Note: If death is due to an AE (ex., Cardiac disorders: Cardiac arrest), report as a Grade 5 event under that AE.
Vaccination site
lymphadenopathy
Local lymph node
enlargement
Localized ulceration;
generalized lymph node
enlargement
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by lymph node enlargement after vaccination.
Navigational Note: -
General disorders and
administration site conditions
- Other, specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 48
Hepatobiliary disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Bile duct stenosis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function; IV fluids indicated
<24 hrs
Severely altered GI function;
invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a narrowing of the lumen of the bile duct.
Navigational Note: -
Biliary fistula
-
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the bile ducts and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Budd-Chiari syndrome
-
Medical management
indicated
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
asterixis; mild encephalopathy
Life-threatening
consequences; moderate to
severe encephalopathy; coma
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by occlusion of the hepatic veins and typically presents with abdominal pain, ascites and hepatomegaly.
Navigational Note: -
Cholecystitis
-
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation involving the gallbladder. It may be associated with the presence of gallstones.
Navigational Note: -
Gallbladder fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the gallbladder and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Gallbladder necrosis
-
-
-
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent invasive
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the gallbladder.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 49
Hepatobiliary disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Gallbladder obstruction
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; altered GI
function; IV fluids indicated
<24 hrs
Symptomatic and severely
altered GI function; tube
feeding, TPN or
hospitalization indicated; non-
emergent operative
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by blockage of the normal flow of the contents of the gallbladder.
Navigational Note: -
Gallbladder pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the gallbladder region.
Navigational Note: -
Gallbladder perforation
-
-
-
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a rupture in the gallbladder wall.
Navigational Note: -
Hepatic failure
-
-
Asterixis; mild
encephalopathy; drug-
induced liver injury (DILI);
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; moderate to
severe encephalopathy; coma
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the inability of the liver to metabolize chemicals in the body. Laboratory test results reveal abnormal plasma levels of ammonia, bilirubin, lactic
dehydrogenase, alkaline phosphatase, aminotransferase, and/or prolongation of prothrombin time (INR.) Drug-induced liever injury (DILI) as defined by Hy's Law.
Navigational Note: -
Hepatic hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the liver.
Navigational Note: -
Hepatic necrosis
-
-
-
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent invasive
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the hepatic parenchyma.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 50
Hepatobiliary disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Hepatic pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the liver region.
Navigational Note: -
Perforation bile duct
-
-
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a rupture in the wall of the extrahepatic or intrahepatic bile duct.
Navigational Note: -
Portal hypertension
-
Decreased portal vein flow
Reversal/retrograde portal
vein flow; associated with
varices and/or ascites
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an increase in blood pressure in the portal venous system.
Navigational Note: -
Portal vein thrombosis
-
Intervention not indicated
Medical intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the formation of a thrombus (blood clot) in the portal vein.
Navigational Note: -
Sinusoidal obstruction
syndrome
-
Blood bilirubin 2-5 mg/dL;
minor interventions required
(i.e., blood product, diuretic,
oxygen)
Blood bilirubin >5 mg/dL;
coagulation modifier indicated
(e.g., defibrotide); reversal of
flow on ultrasound
Life-threatening
consequences (e.g.,
ventilatory support, dialysis,
plasmapheresis, peritoneal
drainage)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by severe hepatic injury as a result of the blood vessels of the liver becoming inflamed and/or blocked.
Navigational Note: -
Hepatobiliary disorders -
Other, specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 51
Immune system disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Allergic reaction
Systemic intervention not
indicated
Oral intervention indicated
Bronchospasm;
hospitalization indicated for
clinical sequelae; intravenous
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an adverse local or general response from exposure to an allergen.
Navigational Note: If related to infusion, use Injury, poisoning and procedural complications: Infusion related reaction. Do not report both.
Anaphylaxis
-
-
Symptomatic bronchospasm,
with or without urticaria;
parenteral intervention
indicated; allergy-related
edema/angioedema;
hypotension
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an acute inflammatory reaction resulting from the release of histamine and histamine-like substances from mast cells, causing a hypersensitivity
immune response. Clinically, it presents with breathing difficulty, dizziness, hypotension, cyanosis and loss of consciousness and may lead to death.
Navigational Note: -
Autoimmune disorder
Asymptomatic; serologic or
other evidence of
autoimmune reaction, with
normal organ function;
intervention not indicated
Evidence of autoimmune
reaction involving a non-
essential organ or function
(e.g., hypothyroidism)
Autoimmune reactions
involving major organ (e.g.,
colitis, anemia, myocarditis,
kidney)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by loss of function or tissue destruction of an organ or multiple organs, arising from humoral or cellular immune responses of the individual to his
own tissue constituents.
Navigational Note: Prior to using this term consider specific autoimmune AEs
Cytokine release syndrome
Fever with or without
constitutional symptoms
Hypotension responding to
fluids; hypoxia responding to
<40% O2
Hypotension managed with
one pressor; hypoxia requiring
≥ 40% O2
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by fever, tachypnea, headache, tachycardia, hypotension, rash, and/or hypoxia caused by the release of cytokines.
Navigational Note: Also consider reporting other organ dysfunctions including neurological toxicities such as: Psychiatric disorders: Hallucinations or Confusion; Nervous system
disorders: Seizure, Dysphasia, Tremor, or Headache
Serum sickness
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate arthralgia; fever,
rash, urticaria, antihistamines
indicated
Severe arthralgia or arthritis;
extensive rash; steroids or IV
fluids indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; pressor or
ventilatory support indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction to foreign proteins derived from an animal serum. It occurs approximately six to twenty-one days
following the administration of the foreign antigen. Symptoms include fever, arthralgias, myalgias, skin eruptions, lymphadenopathy, chest marked discomfort and dyspnea.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 52
Immune system disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Immune system disorders -
Other, specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 53
Infections and infestations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Abdominal infection
-
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the abdominal cavity.
Navigational Note: -
Anorectal infection
Localized, local intervention
indicated
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the anal area and the rectum.
Navigational Note: -
Appendicitis
-
-
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by acute inflammation to the vermiform appendix caused by a pathogenic agent.
Navigational Note: -
Appendicitis perforated
-
-
Medical intervention
indicated; operative
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by acute inflammation to the vermiform appendix caused by a pathogenic agent with gangrenous changes resulting in the rupture of the
appendiceal wall. The appendiceal wall rupture causes the release of inflammatory and bacterial contents from the appendiceal lumen into the abdominal cavity.
Navigational Note: -
Arteritis infective
-
-
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving an artery.
Navigational Note: -
Bacteremia
-
Blood culture positive with no
signs or symptoms
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by the presence of bacteria in the blood stream.
Navigational Note: Consider Infections and infestations: Sepsis (Grades 3, 4 & 5)
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 54
Infections and infestations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Biliary tract infection
-
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the biliary tract.
Navigational Note: -
Bladder infection
-
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the bladder.
Navigational Note: -
Bone infection
-
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the bones.
Navigational Note: -
Breast infection
-
Local infection with moderate
symptoms; oral intervention
indicated (e.g., antibiotic,
antifungal, or antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; severe infection;
axillary adenitis
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the breast.
Navigational Note: -
Bronchial infection
-
Moderate symptoms; oral
intervention indicated (e.g.,
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the bronchi.
Navigational Note: -
Catheter related infection
-
Localized; local intervention
indicated; oral intervention
indicated (e.g., antibiotic,
antifungal, or antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process that arises secondary to catheter use.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 55
Infections and infestations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Cecal infection
-
Localized; oral intervention
indicated (e.g., antibiotic,
antifungal, or antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the cecum.
Navigational Note: -
Cervicitis infection
-
Localized; local intervention
indicated (e.g., topical
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the uterine cervix.
Navigational Note: -
Conjunctivitis
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; moderate
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity 20/40
and better or 3 lines or less
decreased vision from known
baseline)
Symptomatic with marked
decrease in visual acuity (best
corrected visual acuity worse
than 20/40 or more than 3
lines of decreased vision from
known baseline, up to
20/200); limiting self care ADL
Best corrected visual acuity of
20/200 or worse in the
affected eye
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation, swelling and redness to the conjunctiva of the eye.
Navigational Note: Consider Infections and infestations: Conjunctivitis infective if caused by infection
Conjunctivitis infective
-
Localized; local intervention
indicated (e.g., topical
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the conjunctiva. Clinical manifestations include pink or red color in the eyes.
Navigational Note: -
Corneal infection
-
Localized; local intervention
indicated (e.g., topical
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the cornea.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 56
Infections and infestations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Cranial nerve infection
-
-
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving a cranial nerve.
Navigational Note: -
Cytomegalovirus infection
reactivation
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated; IV
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated;
blindness
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the reactivation of cytomegalovirus (CMV).
Navigational Note: Synonym: CMV
Device related infection
-
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the use of a medical device.
Navigational Note: -
Duodenal infection
-
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
oral antibiotics)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the duodenum.
Navigational Note: -
Encephalitis infection
-
-
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; severe changes in
mental status; self-limited
seizure activity; focal
neurologic abnormalities
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the brain tissue.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC
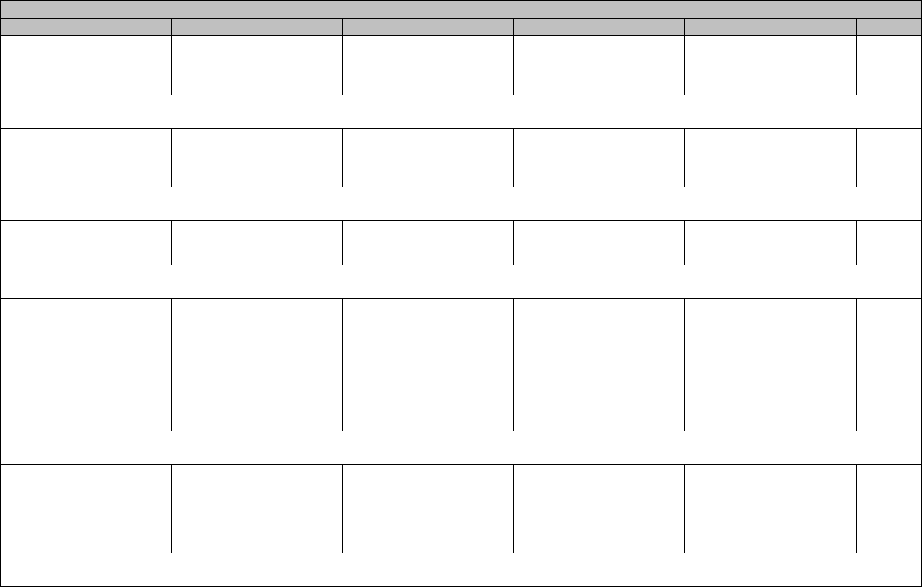
CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 57
Infections and infestations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Encephalomyelitis infection
-
-
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the brain and spinal cord tissues.
Navigational Note: -
Endocarditis infective
-
-
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the endocardial layer of the heart.
Navigational Note: -
Endophthalmitis
-
Local intervention indicated
Systemic intervention;
hospitalization indicated
Best corrected visual acuity of
20/200 or worse in the
affected eye
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the internal structures of the eye.
Navigational Note: -
Enterocolitis infectious
-
Passage of >3 unformed stools
per 24 hrs or duration of
illness >48 hrs; moderate
abdominal pain; oral
intervention indicated (e.g.,
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated;
profuse watery diarrhea with
signs of hypovolemia; bloody
diarrhea; fever; severe
abdominal pain;
hospitalization indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the small and large intestines.
Navigational Note: Includes Clostridium difficile (c. diff, c. difficile).
Epstein-Barr virus infection
reactivation
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated; IV
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the reactivation of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).
Navigational Note: Synonym: EBV
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 58
Infections and infestations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Esophageal infection
-
Local intervention indicated
(e.g., oral antibiotic,
antifungal, antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the esophagus.
Navigational Note: -
Eye infection
-
Localized; local intervention
indicated (e.g., topical
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated;
enucleation
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the eye.
Navigational Note: -
Folliculitis
Covering <10% of the body
surface area; no intervention
indicated
Covering 10-30% of the body
surface area; topical
intervention initiated
>30% BSA; systemic
intervention indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation or infection of the hair follicles.
Navigational Note: -
Fungemia
-
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by the presence of fungus in the blood stream.
Navigational Note: -
Gallbladder infection
-
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the gallbladder.
Navigational Note: -
Gum infection
Local therapy indicated (swish
and swallow)
Moderate symptoms; oral
intervention indicated (e.g.,
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the gums.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 59
Infections and infestations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Hepatic infection
-
Moderate symptoms; oral
intervention indicated (e.g.,
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the liver.
Navigational Note: -
Hepatitis B reactivation
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated; IV
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated; severe
decompensated liver function
(e.g., coagulopathy,
encephalopathy, coma)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the reactivation of hepatitis B virus.
Navigational Note: -
Hepatitis viral
Asymptomatic, intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
Symptomatic liver
dysfunction; fibrosis by
biopsy; compensated
cirrhosis; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; severe
decompensated liver function
(e.g., coagulopathy,
encephalopathy, coma)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a viral pathologic process involving the liver parenchyma.
Navigational Note: -
Herpes simplex reactivation
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated; IV
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the reactivation of Herpes simplex virus.
Navigational Note: -
Infective myositis
-
Localized; local intervention
indicated (e.g., topical
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the skeletal muscles.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 60
Infections and infestations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Joint infection
-
Localized; local intervention
indicated; oral intervention
indicated (e.g., antibiotic,
antifungal, or antiviral);
needle aspiration indicated
(single or multiple)
Arthroscopic intervention
indicated (e.g., drainage) or
arthrotomy (e.g., open
surgical drainage)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving a joint.
Navigational Note: -
Kidney infection
-
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the kidney.
Navigational Note: -
Laryngitis
-
Moderate symptoms; oral
intervention indicated (e.g.,
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an inflammatory process involving the larynx.
Navigational Note: For symptoms and no intervention, consider Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Sore throat or Hoarseness.
Lip infection
Localized, local intervention
indicated
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the lips.
Navigational Note: -
Lung infection
-
Moderate symptoms; oral
intervention indicated (e.g.,
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the lungs, including pneumonia.
Navigational Note: If infection is due to aspiration, consider reporting Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Apiration
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 61
Infections and infestations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Lymph gland infection
-
Localized; oral intervention
indicated (e.g., antibiotic,
antifungal, or antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the lymph nodes.
Navigational Note: -
Mediastinal infection
-
-
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the mediastinum.
Navigational Note: -
Meningitis
-
-
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated; focal
neurologic deficit
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by acute inflammation of the meninges of the brain and/or spinal cord.
Navigational Note: -
Mucosal infection
Localized, local intervention
indicated
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving a mucosal surface.
Navigational Note: -
Myelitis
Asymptomatic; mild signs
(e.g., Babinski's reflex or
Lhermitte's sign)
Moderate weakness or
sensory loss; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe weakness or sensory
loss; limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation involving the spinal cord. Symptoms include weakness, paresthesia, sensory loss, marked discomfort and incontinence.
Navigational Note: -
Nail infection
Localized, local intervention
indicated
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the nail.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 62
Infections and infestations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Otitis externa
Localized, local intervention
indicated
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the outer ear and ear canal. Contributory factors include excessive water exposure (swimmer's ear infection) and
cuts in the ear canal. Symptoms include fullness, itching, swelling and marked discomfort in the ear and ear drainage.
Navigational Note: Changes associated with radiation to external ear (pinnae) are graded under Injury, poisoning and procedural complications: Dermatitis radiation
Otitis media
-
Localized; oral intervention
indicated (e.g., antibiotic,
antifungal, or antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the middle ear.
Navigational Note: -
Ovarian infection
-
Localized; oral intervention
indicated (e.g., antibiotic,
antifungal, or antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the ovary.
Navigational Note: -
Pancreas infection
-
-
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the pancreas.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC
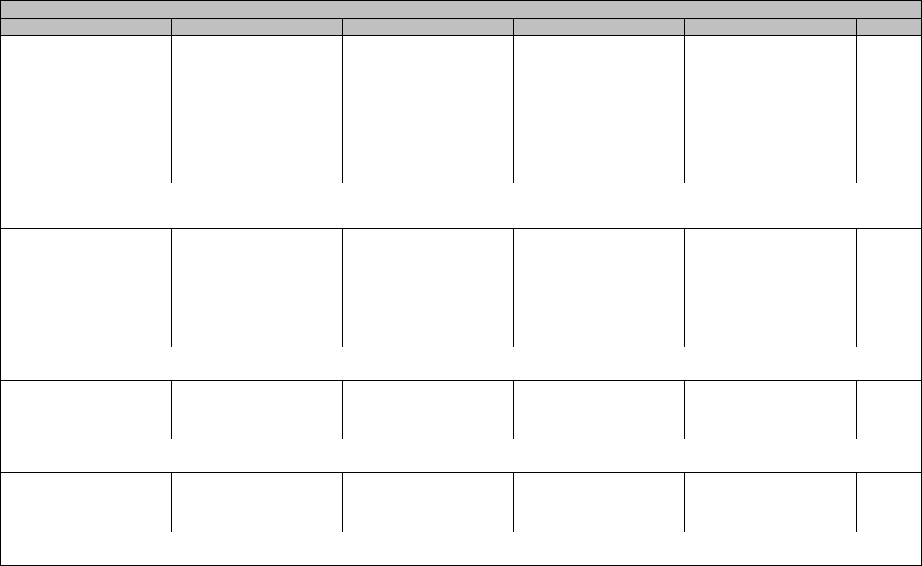
CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 63
Infections and infestations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Papulopustular rash
Papules and/or pustules
covering <10% BSA, which
may or may not be associated
with symptoms of pruritus or
tenderness
Papules and/or pustules
covering 10-30% BSA, which
may or may not be associated
with symptoms of pruritus or
tenderness; associated with
psychosocial impact; limiting
instrumental ADL; papules
and/or pustules covering >
30% BSA with or without mild
symptoms
Papules and/or pustules
covering >30% BSA with
moderate or severe
symptoms; limiting self-care
ADL; IV antibiotics indicated
Life-threatening
consequences
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an eruption consisting of papules (a small, raised pimple) and pustules (a small pus filled blister), typically appearing in face, scalp, and upper
chest and back. Unlike acne, this rash does not present with whiteheads or blackheads, and can be symptomatic, with itchy or tender lesions.
Navigational Note: -
Paronychia
Nail fold edema or erythema;
disruption of the cuticle
Local intervention indicated;
oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal,
antiviral); nail fold edema or
erythema with pain;
associated with discharge or
nail plate separation; limiting
instrumental ADL
Operative intervention
indicated; IV antibiotics
indicated; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the soft tissues around the nail.
Navigational Note: -
Pelvic infection
-
Moderate symptoms; oral
intervention indicated (e.g.,
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the pelvic cavity.
Navigational Note: -
Penile infection
Localized, local intervention
indicated
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the penis.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 64
Infections and infestations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Periorbital infection
-
Localized; local intervention
indicated (e.g., topical
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the orbit of the eye.
Navigational Note: -
Peripheral nerve infection
-
Localized; local intervention
indicated (e.g., topical
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the peripheral nerves.
Navigational Note: -
Peritoneal infection
-
-
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the peritoneum.
Navigational Note: -
Pharyngitis
-
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation of the throat.
Navigational Note: For Grade 1 Consider Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Sore throat
Phlebitis infective
Localized, local intervention
indicated
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the vein. Clinical manifestations include erythema, marked discomfort, swelling, and induration along the course
of the infected vein.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 65
Infections and infestations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Pleural infection
-
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the pleura.
Navigational Note: -
Prostate infection
-
Moderate symptoms; oral
intervention indicated (e.g.,
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the prostate gland.
Navigational Note: -
Rash pustular
-
Localized; local intervention
indicated (e.g., topical
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a circumscribed and elevated skin lesion filled with pus.
Navigational Note: Synonym: Boil
Rhinitis infective
-
Localized; local intervention
indicated
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the nasal mucosal.
Navigational Note: -
Salivary gland infection
-
Moderate symptoms; oral
intervention indicated (e.g.,
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the salivary gland.
Navigational Note: -
Scrotal infection
Localized, local intervention
indicated
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the scrotum.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 66
Infections and infestations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Sepsis
-
-
Blood culture positive with
signs or symptoms; treatment
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the blood stream that cause a rapidly progressing systemic reaction that may lead to shock.
Navigational Note: Includes SIRS. Also consider Infections and infestations: Bacteremia (Grade 2)
Shingles
Localized, local intervention
indicated
Local infection with moderate
symptoms; oral intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated; IV
intervention indicated;
limiting self-care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the reactivation of herpes zoster virus.
Navigational Note: Synonym: Herpes zoster
Sinusitis
-
Localized; oral intervention
indicated (e.g., antibiotic,
antifungal, or antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the mucous membranes of the paranasal sinuses.
Navigational Note: -
Skin infection
Localized, local intervention
indicated
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the skin such as cellulitis.
Navigational Note: -
Small intestine infection
-
Moderate symptoms; oral
intervention indicated (e.g.,
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the small intestine.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 67
Infections and infestations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Soft tissue infection
-
Localized; oral intervention
indicated (e.g., antibiotic,
antifungal, or antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving soft tissues.
Navigational Note: -
Splenic infection
-
-
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the spleen.
Navigational Note: -
Stoma site infection
Localized, local intervention
indicated
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving a stoma (surgically created opening on the surface of the body).
Navigational Note: -
Thrush
Asymptomatic; local
symptomatic management
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antifungal)
IV antifungal intervention
indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a suspected candidal infection involving an oral mucosal surface.
Navigational Note: -
Tooth infection
-
Localized; local intervention
indicated (e.g., topical
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving a tooth.
Navigational Note: -
Tracheitis
-
Moderate symptoms; oral
intervention indicated (e.g.,
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the trachea.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 68
Infections and infestations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Upper respiratory infection
-
Moderate symptoms; oral
intervention indicated (e.g.,
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the upper respiratory tract (nose, paranasal sinuses, pharynx, larynx, or trachea).
Navigational Note: -
Urethral infection
-
Localized; oral intervention
indicated (e.g., antibiotic,
antifungal, or antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the urethra.
Navigational Note: -
Urinary tract infection
-
Localized; oral intervention
indicated (e.g., antibiotic,
antifungal, or antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the urinary tract, most commonly the bladder and the urethra.
Navigational Note: -
Uterine infection
-
Moderate symptoms; oral
intervention indicated (e.g.,
antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the endometrium. It may extend to the myometrium and parametrial tissues.
Navigational Note: -
Vaginal infection
Localized, local intervention
indicated
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the vagina.
Navigational Note: -
Viremia
-
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by the presence of a virus in the blood stream.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 69
Infections and infestations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Vulval infection
Localized, local intervention
indicated
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the vulva.
Navigational Note: -
Wound infection
Localized, local intervention
indicated
Oral intervention indicated
(e.g., antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral)
IV antibiotic, antifungal, or
antiviral intervention
indicated; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the wound.
Navigational Note: -
Infections and infestations -
Other, specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 70
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Ankle fracture
Mild; non-operative
intervention indicated
Limiting instrumental ADL;
outpatient operative
intervention indicated
Limiting self care ADL; elective
operative intervention
indicated requiring
hospitalization
-
-
Definition: A finding of damage to the ankle joint characterized by a break in the continuity of the ankle bone. Symptoms include marked discomfort, swelling and difficulty moving the
affected leg and foot.
Navigational Note: -
Aortic injury
-
Operative intervention not
indicated
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL; repair or revision
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; evidence of
end organ damage; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to the aorta.
Navigational Note: -
Arterial injury
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; repair or
revision not indicated
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL; repair or revision
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; evidence of
end organ damage; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to an artery.
Navigational Note: -
Biliary anastomotic leak
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of leakage of bile due to breakdown of a biliary anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures).
Navigational Note: -
Bladder anastomotic leak
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of leakage of urine due to breakdown of a bladder anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures).
Navigational Note: -
Bruising
Localized or in a dependent
area
Generalized
-
-
-
Definition: A finding of injury of the soft tissues or bone characterized by leakage of blood into surrounding tissues.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 71
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Burn
Minimal symptoms;
intervention not indicated
Medical intervention; minimal
debridement indicated
Moderate to major
debridement or
reconstruction indicated
Life-threatening
consequences
Death
Definition: A finding of impaired integrity to the anatomic site of an adverse thermal reaction. Burns can be caused by exposure to chemicals, direct heat, electricity, flames and
radiation. The extent of damage depends on the length and intensity of exposure and time until provision of treatment.
Navigational Note: -
Dermatitis radiation
Faint erythema or dry
desquamation
Moderate to brisk erythema;
patchy moist desquamation,
mostly confined to skin folds
and creases; moderate edema
Moist desquamation in areas
other than skin folds and
creases; bleeding induced by
minor trauma or abrasion
Life-threatening
consequences; skin necrosis
or ulceration of full thickness
dermis; spontaneous bleeding
from involved site; skin graft
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of cutaneous inflammatory reaction occurring as a result of exposure to biologically effective levels of ionizing radiation.
Navigational Note: Synonym: Radiation induced skin toxicities (CTCAE v3.0 )
Esophageal anastomotic leak
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of an esophageal anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures).
Navigational Note: -
Fall
Minor with no resultant
injuries; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; noninvasive
intervention indicated
Hospitalization indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated
-
-
Definition: A finding of sudden movement downward, usually resulting in injury.
Navigational Note: -
Fallopian tube anastomotic
leak
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a fallopian tube anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures).
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 72
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Fallopian tube perforation
-
Invasive intervention not
indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated (e.g., organ
resection)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a rupture of the fallopian tube wall.
Navigational Note: -
Fracture
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic but non-
displaced; immobilization
indicated
Severe symptoms; displaced
or open wound with bone
exposure; limiting self care
ADL; operative intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of traumatic injury to the bone in which the continuity of the bone is broken.
Navigational Note: Prior to using this term consider specific fracture areas: Injury, poisoning and procedural complications: Ankle fracture, Hip fracture, Spinal fracture, or Wrist
fracture
Gastric anastomotic leak
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a gastric anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures).
Navigational Note: -
Gastrointestinal anastomotic
leak
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a gastrointestinal anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures).
Navigational Note: -
Gastrointestinal stoma
necrosis
-
Superficial necrosis;
intervention not indicated
Severe symptoms;
hospitalization indicated;
elective operative
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the gastrointestinal tract stoma.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 73
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Hip fracture
-
Hairline fracture; mild pain;
limiting instrumental ADL;
non-operative intervention
indicated
Severe pain; hospitalization or
intervention indicated for pain
control (e.g., traction);
operative intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; symptoms
associated with neurovascular
compromise
-
Definition: A finding of traumatic injury to the hip in which the continuity of either the femoral head, femoral neck, intertrochanteric or subtrochanteric regions is broken.
Navigational Note: -
Infusion related reaction
Mild transient reaction;
infusion interruption not
indicated; intervention not
indicated
Therapy or infusion
interruption indicated but
responds promptly to
symptomatic treatment (e.g.,
antihistamines, NSAIDS,
narcotics, IV fluids);
prophylactic medications
indicated for <=24 hrs
Prolonged (e.g., not rapidly
responsive to symptomatic
medication and/or brief
interruption of infusion);
recurrence of symptoms
following initial improvement;
hospitalization indicated for
clinical sequelae
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by adverse reaction to the infusion of pharmacological or biological substances.
Navigational Note: -
Injury to carotid artery
-
Repair or revision not
indicated
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL (e.g., transient
cerebral ischemia); repair or
revision indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to the carotid artery.
Navigational Note: -
Injury to inferior vena cava
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; repair or
revision not indicated
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL; repair or revision
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to the inferior vena
cava.
Navigational Note: -
Injury to jugular vein
-
Repair or revision not
indicated
Symptomatic limiting self care
ADL; repair or revision
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to the jugular vein.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 74
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Injury to superior vena cava
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; repair or
revision not indicated
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL; repair or revision
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to the superior vena cava.
Navigational Note: -
Intestinal stoma leak
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of leakage of contents from an intestinal stoma (surgically created opening on the surface of the body).
Navigational Note: -
Intestinal stoma obstruction
-
Self-limited; intervention not
indicated
Severe symptoms; IV fluids,
tube feeding, or TPN indicated
>=24 hrs; elective operative
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by blockage of the normal flow of the contents of the intestinal stoma.
Navigational Note: -
Intestinal stoma site bleeding
Minimal bleeding identified
on clinical exam; intervention
not indicated
Moderate bleeding; medical
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the intestinal stoma.
Navigational Note: -
Intraoperative arterial injury
Primary repair of injured
organ/structure indicated
Partial resection of injured
organ/structure indicated
Complete resection or
reconstruction of injured
organ/structure indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to an artery during a surgical procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Intraoperative breast injury
Primary repair of injured
organ/structure indicated
Partial resection of injured
organ/structure indicated
Complete resection or
reconstruction of injured
organ/structure indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to the breast parenchyma during a surgical procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 75
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Intraoperative cardiac injury
-
-
Primary repair of injured
organ/structure indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to the heart during a surgical procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Intraoperative ear injury
Primary repair of injured
organ/structure indicated
Partial resection of injured
organ/structure indicated
Complete resection or
reconstruction of injured
organ/structure indicated;
limiting self care ADL (e.g.,
impaired hearing; impaired
balance)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to the ear during a surgical procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Intraoperative endocrine
injury
Primary repair of injured
organ/structure indicated
Partial resection of injured
organ/structure indicated
Complete resection or
reconstruction of injured
organ/structure indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to the endocrine gland during a surgical procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Intraoperative gastrointestinal
injury
Primary repair of injured
organ/structure indicated
Partial resection of injured
organ/structure indicated
Complete resection or
reconstruction of injured
organ/structure indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to the gastrointestinal system during a surgical procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Intraoperative head and neck
injury
Primary repair of injured
organ/structure indicated
Partial resection of injured
organ/structure indicated
Complete resection or
reconstruction of injured
organ/structure indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to the head and neck during a surgical procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Intraoperative hemorrhage
-
-
Postoperative invasive
intervention indicated;
hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of uncontrolled bleeding during a surgical procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 76
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Intraoperative hepatobiliary
injury
Primary repair of injured
organ/structure indicated
Partial resection of injured
organ/structure indicated
Complete resection or
reconstruction of injured
organ/structure indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to the hepatic parenchyma and/or biliary tract during a surgical procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Intraoperative
musculoskeletal injury
Primary repair of injured
organ/structure indicated
Partial resection of injured
organ/structure indicated
Complete resection or
reconstruction of injured
organ/structure indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to the musculoskeletal system during a surgical procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Intraoperative neurological
injury
Primary repair of injured
organ/structure indicated
Partial resection of injured
organ/structure indicated
Complete resection or
reconstruction of injured
organ/structure indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to the nervous system during a surgical procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Intraoperative ocular injury
Primary repair of injured
organ/structure indicated
Partial resection of injured
organ/structure indicated
Complete resection or
reconstruction of injured
organ/structure indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to the eye during a surgical procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Intraoperative renal injury
Primary repair of injured
organ/structure indicated
Partial resection of injured
organ/structure indicated
Complete resection or
reconstruction of injured
organ/structure indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to the kidney during a surgical procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Intraoperative reproductive
tract injury
Primary repair of injured
organ/structure indicated
Partial resection of injured
organ/structure indicated
Complete resection or
reconstruction of injured
organ/structure indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to the reproductive organs during a surgical procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 77
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Intraoperative respiratory
injury
Primary repair of injured
organ/structure indicated
Partial resection of injured
organ/structure indicated
Complete resection or
reconstruction of injured
organ/structure indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to the respiratory system during a surgical procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Intraoperative splenic injury
-
Primary repair of injured
organ/structure indicated
Resection or reconstruction of
injured organ/structure
indicated; limiting self care
ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to the spleen during a surgical procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Intraoperative urinary injury
Primary repair of injured
organ/structure indicated
Partial resection of injured
organ/structure indicated
Complete resection or
reconstruction of injured
organ/structure indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to the urinary system during a surgical procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Intraoperative venous injury
Primary repair of injured
organ/structure indicated
Partial resection of injured
organ/structure indicated
Complete resection or
reconstruction of injured
organ/structure indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to a vein during a surgical procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Kidney anastomotic leak
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of leakage of urine due to breakdown of a kidney anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures).
Navigational Note: -
Large intestinal anastomotic
leak
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of an anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures) in the large intestine.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 78
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Pancreatic anastomotic leak
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a pancreatic anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures).
Navigational Note: -
Pharyngeal anastomotic leak
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a pharyngeal anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures).
Navigational Note: -
Postoperative hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate bleeding requiring
transfusion < 2 units (10 cc/kg
for pediatrics) of pRBCs
Transfusion indicated of >=2
units (10 cc/kg for pediatrics)
pRBCs; invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding occurring after a surgical procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Postoperative thoracic
procedure complication
-
Extubated within 24 - 72 hrs
postoperatively
Extubated >72 hrs
postoperatively, but before
tracheostomy indicated
Life-threatening airway
compromise; urgent
intervention indicated (e.g.,
tracheotomy or intubation)
Death
Definition: A finding of a previously undocumented problem that occurs after a thoracic procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Prolapse of intestinal stoma
Asymptomatic; reducible
Recurrent after manual
reduction; local irritation or
stool leakage; difficulty to fit
appliance; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; elective
operative intervention
indicated; limiting self care
ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of protrusion of the intestinal stoma (surgically created opening on the surface of the body) above the abdominal surface.
Navigational Note: -
Prolapse of urostomy
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Local care or maintenance;
minor revision indicated
Dysfunctional stoma; elective
operative intervention or
major stomal revision
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of displacement of the urostomy.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 79
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Radiation recall reaction
(dermatologic)
Faint erythema or dry
desquamation
Moderate to brisk erythema;
patchy moist desquamation,
mostly confined to skin folds
and creases; moderate edema
Moist desquamation in areas
other than skin folds and
creases; bleeding induced by
minor trauma or abrasion
Life-threatening
consequences; skin necrosis
or ulceration of full thickness
dermis; spontaneous bleeding
from involved site; skin graft
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of acute skin inflammatory reaction caused by drugs, especially chemotherapeutic agents, for weeks or months following radiotherapy. The inflammatory reaction
is confined to the previously irradiated skin and the symptoms disappear after the removal of the pharmaceutical agent.
Navigational Note: -
Rectal anastomotic leak
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a rectal anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures).
Navigational Note: -
Seroma
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; simple
aspiration indicated
Symptomatic, elective
invasive intervention
indicated
-
-
Definition: A finding of tumor-like collection of serum in the tissues.
Navigational Note: -
Small intestinal anastomotic
leak
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of an anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures) in the small bowel.
Navigational Note: -
Spermatic cord anastomotic
leak
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a spermatic cord anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures).
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 80
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Spinal fracture
Mild back pain;
nonprescription analgesics
indicated
Moderate back pain;
prescription analgesics
indicated; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe back pain;
hospitalization or intervention
indicated for pain control
(e.g., vertebroplasty); limiting
self care ADL; disability
Life-threatening
consequences; symptoms
associated with neurovascular
compromise
Death
Definition: A finding of traumatic injury to the spine in which the continuity of a vertebral bone is broken.
Navigational Note: -
Stenosis of gastrointestinal
stoma
-
Symptomatic; IV fluids
indicated <24 hrs; manual
dilation at bedside
Severely altered GI function;
tube feeding, TPN or
hospitalization indicated;
elective operative
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of narrowing of the gastrointestinal stoma (surgically created opening on the surface of the body).
Navigational Note: -
Stomal ulcer
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; elective
operative intervention
indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a circumscribed, erosive lesion on the jejunal mucosal surface close to the anastomosis site following a gastroenterostomy procedure.
Navigational Note: -
Tracheal hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the trachea.
Navigational Note: -
Tracheal obstruction
Partial asymptomatic
obstruction on examination
(e.g., visual, radiologic or
endoscopic)
Symptomatic (e.g., noisy
airway breathing), no
respiratory distress; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
steroids); limiting
instrumental ADL
Stridor or respiratory distress
limiting self care ADL; invasive
intervention indicated (e.g.,
stent, laser)
Life-threatening airway
compromise; urgent
intervention indicated (e.g.,
tracheotomy or intubation)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by blockage of the lumen of the trachea.
Navigational Note: -
Tracheostomy site bleeding
Minimal bleeding identified
on clinical exam; intervention
not indicated
Moderate bleeding; medical
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the tracheostomy site.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 81
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Ureteric anastomotic leak
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a ureteral anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures).
Navigational Note: -
Urethral anastomotic leak
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a urethral anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures).
Navigational Note: -
Urostomy leak
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of leakage of contents from a urostomy.
Navigational Note: -
Urostomy obstruction
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; dilation or
endoscopic repair or stent
placement indicated
Altered organ function (e.g.,
sepsis or hydronephrosis, or
renal dysfunction); elective
operative intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; organ failure;
urgent operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by blockage of the urostomy.
Navigational Note: -
Urostomy site bleeding
Minimal bleeding identified
on clinical exam; intervention
not indicated
Moderate bleeding; medical
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the urostomy site.
Navigational Note: -
Urostomy stenosis
-
Symptomatic but no
hydronephrosis, sepsis, or
renal dysfunction; dilation or
endoscopic repair or stent
placement indicated
Symptomatic (e.g.,
hydronephrosis, or renal
dysfunction); elective
operative intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of narrowing of the opening of a urostomy.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 82
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Uterine anastomotic leak
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a uterine anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures).
Navigational Note: -
Uterine perforation
-
Invasive intervention not
indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a rupture in the uterine wall.
Navigational Note: -
Vaccination complication
Mild pain; erythema 2.5-5cm;
induration/swelling 2.5-5cm;
does not interfere with
activity
Moderate pain; Erythema 5.1-
10 cm; Induration/swelling
5.1-10 cm; lipodystrophy;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe pain; Erythema > 10
cm; Induration/swelling > 10
cm; necrosis; limiting self care
ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
-
Definition: A disorder that occurs after the injection of a substance with antigenic properties, administered to activate the immune system.
Navigational Note: For systemic vaccination complications, consider Immune system disorders: Allergic reaction or Anaphylaxis.
Vaginal anastomotic leak
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a vaginal anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures).
Navigational Note: -
Vas deferens anastomotic leak
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a vas deferens anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures).
Navigational Note: -
Vascular access complication
TPA administration into line
with no intent for systemic
therapy indicated
Device dislodgement,
blockage, leak, or malposition;
device replacement indicated
Pulmonary embolism, deep
vein or cardiac thrombosis;
intervention indicated (e.g.,
anticoagulation, lysis, filter,
invasive procedure)
Life-threatening
consequences with
hemodynamic or neurologic
instability
Death
Definition: A finding of a previously undocumented problem related to the vascular access site.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 83
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Venous injury
Asymptomatic diagnostic
finding; intervention not
indicated
Symptomatic (e.g.,
claudication); repair or
revision not indicated
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL; repair or revision
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; evidence of
end organ damage; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of damage to a vein.
Navigational Note: -
Wound complication
Observation only; topical
intervention indicated
Bedside local care indicated
Operative intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences
Death
Definition: A finding of development of a new problem at the site of an existing wound.
Navigational Note: Prior to using this term consider Injury, poisoning and procedural complications: Wound dehiscence or Infections and infestations: Wound infection
Wound dehiscence
Incisional separation,
intervention not indicated
Incisional separation, local
care (e.g., suturing) or medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
analgesic)
Fascial disruption or
dehiscence without
evisceration; revision by
operative intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; symptomatic
hernia with evidence of
strangulation; fascial
disruption with evisceration;
major reconstruction flap,
grafting, resection, or
amputation indicated
Death
Definition: A finding of separation of the approximated margins of a surgical wound.
Navigational Note: Also consider Infections and infestations: Wound infection
Wrist fracture
Mild; non-operative
intervention indicated
Limiting instrumental ADL;
outpatient operative
intervention indicated
Limiting self care ADL; elective
operative intervention
indicated requiring
hospitalization
-
-
Definition: A finding of traumatic injury to the wrist joint in which the continuity of a wrist bone is broken.
Navigational Note: -
Injury, poisoning and
procedural complications -
Other, specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 84
Investigations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Activated partial
thromboplastin time
prolonged
>ULN - 1.5 x ULN
>1.5 - 2.5 x ULN
>2.5 x ULN; bleeding
-
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results in which the partial thromboplastin time is found to be greater than the control value. As a possible indicator of coagulopathy, a
prolonged partial thromboplastin time (PTT) may occur in a variety of diseases and disorders, both primary and related to treatment.
Navigational Note: -
Alanine aminotransferase
increased
>ULN - 3.0 x ULN if baseline
was normal; 1.5 - 3.0 x
baseline if baseline was
abnormal
>3.0 - 5.0 x ULN if baseline
was normal; >3.0 - 5.0 x
baseline if baseline was
abnormal
>5.0 - 20.0 x ULN if baseline
was normal; >5.0 - 20.0 x
baseline if baseline was
abnormal
>20.0 x ULN if baseline was
normal; >20.0 x baseline if
baseline was abnormal
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate an increase in the level of alanine aminotransferase (ALT or SGPT) in the blood specimen.
Navigational Note: Also consider Hepatobiliary disorders: Hepatic failure
Alkaline phosphatase
increased
>ULN - 2.5 x ULN if baseline
was normal; 2.0 - 2.5 x
baseline if baseline was
abnormal
>2.5 - 5.0 x ULN if baseline
was normal; >2.5 - 5.0 x
baseline if baseline was
abnormal
>5.0 - 20.0 x ULN if baseline
was normal; >5.0 - 20.0 x
baseline if baseline was
abnormal
>20.0 x ULN if baseline was
normal; >20.0 x baseline if
baseline was abnormal
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate an increase in the level of alkaline phosphatase in a blood specimen.
Navigational Note: -
Aspartate aminotransferase
increased
>ULN - 3.0 x ULN if baseline
was normal; 1.5 - 3.0 x
baseline if baseline was
abnormal
>3.0 - 5.0 x ULN if baseline
was normal; >3.0 - 5.0 x
baseline if baseline was
abnormal
>5.0 - 20.0 x ULN if baseline
was normal; >5.0 - 20.0 x
baseline if baseline was
abnormal
>20.0 x ULN if baseline was
normal; >20.0 x baseline if
baseline was abnormal
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate an increase in the level of aspartate aminotransferase (AST or SGOT) in a blood specimen.
Navigational Note: Also consider Hepatobiliary disorders: Hepatic failure
Blood antidiuretic hormone
abnormal
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Hospitalization indicated
-
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate abnormal levels of antidiuretic hormone in the blood specimen.
Navigational Note: -
Blood bicarbonate decreased
<LLN and no intervention
initiated
-
-
-
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate a decrease in levels of bicarbonate in a venous blood specimen.
Navigational Note: Also consider Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Acidosis or Alkalosis
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 85
Investigations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Blood bilirubin increased
>ULN - 1.5 x ULN if baseline
was normal; > 1.0 - 1.5 x
baseline if baseline was
abnormal
>1.5 - 3.0 x ULN if baseline
was normal; >1.5 - 3.0 x
baseline if baseline was
abnormal
>3.0 - 10.0 x ULN if baseline
was normal; >3.0 - 10.0 x
baseline if baseline was
abnormal
>10.0 x ULN if baseline was
normal; >10.0 x baseline if
baseline was abnormal
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate an abnormally high level of bilirubin in the blood. Excess bilirubin is associated with jaundice.
Navigational Note: Also consider Hepatobiliary disorders: Hepatic failure
Blood corticotrophin
decreased
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Hospitalization indicated
-
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate an decrease in levels of corticotrophin in a blood specimen.
Navigational Note: -
Blood gonadotrophin
abnormal
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate abnormal levels of gonadotrophin hormone in a blood specimen.
Navigational Note: -
Blood lactate dehydrogenase
increased
>ULN
-
-
-
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate increased levels of lactate dehydrogenase in the blood specimen.
Navigational Note: -
Blood prolactin abnormal
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
-
-
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate abnormal levels of prolactin hormone in a blood specimen.
Navigational Note: -
Carbon monoxide diffusing
capacity decreased
3 - 5 units below LLN; for
follow-up, a decrease of 3 - 5
units (ml/min/mm Hg) below
the baseline value;
asymptomatic and
intervention not indicated
6 - 8 units below LLN; for
follow-up, an asymptomatic
decrease of >5 - 8 units
(ml/min/mm Hg) below the
baseline value; symptomatic
and intervention not indicated
Asymptomatic decrease of >8
units drop; >5 units drop
along with the presence of
pulmonary symptoms (e.g.,
>Grade 2 hypoxia or >Grade 2
dyspnea); intervention
indicated
-
-
Definition: A finding based on lung function test results that indicate a decrease in the lung capacity to absorb carbon monoxide.
Navigational Note: Also consider Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Respiratory failure or Dyspnea
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 86
Investigations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Cardiac troponin I increased
Levels above the upper limit
of normal and below the level
of myocardial infarction as
defined by the manufacturer
-
Levels consistent with
myocardial infarction as
defined by the manufacturer
-
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate increased levels of cardiac troponin I in a biological specimen.
Navigational Note: Also consider Cardiac disorders: Heart failure or Cardiac disorders: Myocardial infarction. Report Cardiac disorders: Heart failure or Cardiac disorders: Myocardial
infarction if same grade event.
Cardiac troponin T increased
Levels above the upper limit
of normal and below the level
of myocardial infarction as
defined by the manufacturer
-
Levels consistent with
myocardial infarction as
defined by the manufacturer
-
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate increased levels of cardiac troponin T in a biological specimen.
Navigational Note: Also consider Cardiac disorders: Heart failure or Cardiac disorders: Myocardial infarction. Report Cardiac disorders: Heart failure or Cardiac disorders: Myocardial
infarction if same grade event.
CD4 lymphocytes decreased
<LLN - 500/mm3; <LLN - 0.5 x
10e9 /L
<500 - 200/mm3; <0.5 - 0.2 x
10e9 /L
<200 - 50/mm3; <0.2 x 0.05 -
10e9 /L
<50/mm3; <0.05 x 10e9 /L
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate an decrease in levels of CD4 lymphocytes in a blood specimen.
Navigational Note: -
Cholesterol high
>ULN - 300 mg/dL; >ULN -
7.75 mmol/L
>300 - 400 mg/dL; >7.75 -
10.34 mmol/L
>400 - 500 mg/dL; >10.34 -
12.92 mmol/L
>500 mg/dL; >12.92 mmol/L
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate higher than normal levels of cholesterol in a blood specimen.
Navigational Note: -
CPK increased
>ULN - 2.5 x ULN
>2.5 x ULN - 5 x ULN
>5 x ULN - 10 x ULN
>10 x ULN
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate an increase in levels of creatine phosphokinase in a blood specimen.
Navigational Note: Also consider Cardiac disorders: Heart failure or Cardiac disorders: Myocardial infarction. Report Cardiac disorders: Heart failure or Cardiac disorders: Myocardial
infarction if same grade event.
Creatinine increased
>ULN - 1.5 x ULN
>1.5 - 3.0 x baseline; >1.5 - 3.0
x ULN
>3.0 x baseline; >3.0 - 6.0 x
ULN
>6.0 x ULN
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate increased levels of creatinine in a biological specimen.
Navigational Note: Also consider Renal and urinary disorders: Acute kidney injury
Back to TOC
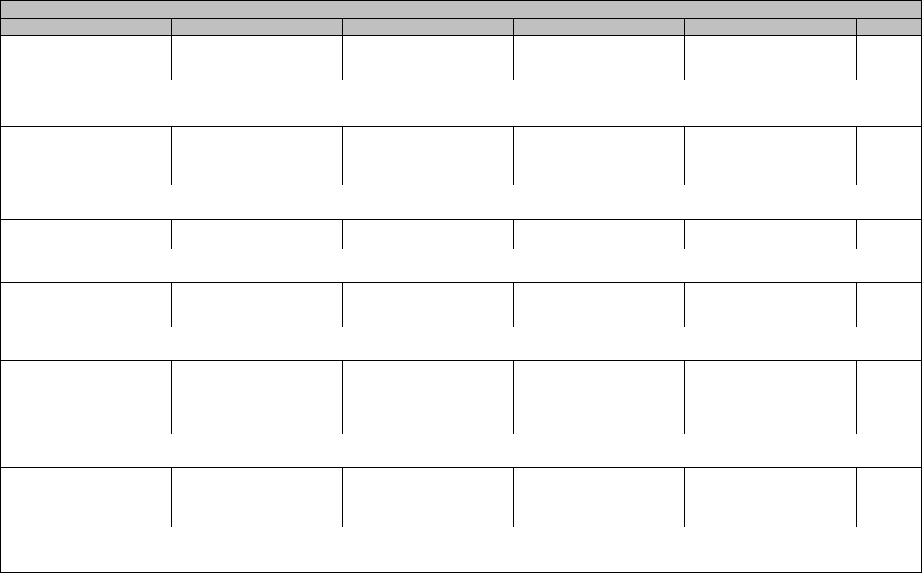
CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 87
Investigations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Ejection fraction decreased
-
Resting ejection fraction (EF)
50 - 40%; 10 - 19% drop from
baseline
Resting ejection fraction (EF)
39 - 20%; >=20% drop from
baseline
Resting ejection fraction (EF)
<20%
-
Definition: The percentage computed when the amount of blood ejected during a ventricular contraction of the heart is compared to the amount that was present prior to the
contraction.
Navigational Note: Also consider Cardiac disorders: Left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Report Cardiac disorders: Left ventricular systolic dysfunction if same grade event.
Electrocardiogram QT
corrected interval prolonged
Average QTc 450 - 480 ms
Average QTc 481 - 500 ms
Average QTc >= 501 ms; >60
ms change from baseline
Torsade de pointes;
polymorphic ventricular
tachycardia; signs/symptoms
of serious arrhythmia
-
Definition: A finding of a cardiac dysrhythmia characterized by an abnormally long corrected QT interval.
Navigational Note: -
Electrocardiogram T wave
abnormal
T wave flattening
Nonspecific ST segment
change
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by Electrocardiogram T wave amplitude changes.
Navigational Note: -
Fibrinogen decreased
<1.0 - 0.75 x LLN; if abnormal,
<25% decrease from baseline
<0.75 - 0.5 x LLN; if abnormal,
25 - <50% decrease from
baseline
<0.5 - 0.25 x LLN; if abnormal,
50 - <75% decrease from
baseline
<0.25 x LLN; if abnormal, 75%
decrease from baseline;
absolute value <50 mg/dL
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate an decrease in levels of fibrinogen in a blood specimen.
Navigational Note: -
Forced expiratory volume
decreased
FEV1% (percentages of
observed FEV1 and FVC
related to their respective
predicted values) 99 - 70%
predicted
FEV1 60 - 69%
50 - 59%
<= 49%
-
Definition: A finding based on test results that indicate a relative decrease in the fraction of the forced vital capacity that is exhaled in a specific number of seconds.
Navigational Note: Also consider Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Respiratory failure or Dyspnea
GGT increased
>ULN - 2.5 x ULN if baseline
was normal; 2.0 - 2.5 x
baseline if baseline was
abnormal
>2.5 - 5.0 x ULN if baseline
was normal; >2.5 - 5.0 x
baseline if baseline was
abnormal
>5.0 - 20.0 x ULN if baseline
was normal; >5.0 - 20.0 x
baseline if baseline was
abnormal
>20.0 x ULN if baseline was
normal; >20.0 x baseline if
baseline was abnormal
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate higher than normal levels of the enzyme gamma-glutamyltransferase in the blood specimen. GGT (gamma-
glutamyltransferase ) catalyzes the transfer of a gamma glutamyl group from a gamma glutamyl peptide to another peptide, amino acids or water.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 88
Investigations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Growth hormone abnormal
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
-
-
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate abnormal levels of growth hormone in a biological specimen.
Navigational Note: -
Haptoglobin decreased
<LLN
-
-
-
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate an decrease in levels of haptoglobin in a blood specimen.
Navigational Note: -
Hemoglobin increased
Increase in >0 - 2 g/dL
Increase in >2 - 4 g/dL
Increase in >4 g/dL
-
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate increased levels of hemoglobin above normal.
Navigational Note: -
INR increased
>1.2 - 1.5; >1 - 1.5 x baseline if
on anticoagulation;
monitoring only indicated
>1.5 - 2.5; >1.5 - 2.5 x baseline
if on anticoagulation; dose
adjustment indicated
>2.5; >2.5 x baseline if on
anticoagulation; bleeding
-
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate an increase in the ratio of the patient's prothrombin time to a control sample in the blood.
Navigational Note: -
Lipase increased
>ULN - 1.5 x ULN
>1.5 - 2.0 x ULN; >2.0 - 5.0 x
ULN and asymptomatic
>2.0 - 5.0 x ULN with signs or
symptoms; >5.0 x ULN and
asymptomatic
>5.0 x ULN and with signs or
symptoms
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate an increase in the level of lipase in a biological specimen.
Navigational Note: -
Lymphocyte count decreased
<LLN - 800/mm3; <LLN - 0.8 x
10e9/L
<800 - 500/mm3; <0.8 - 0.5 x
10e9 /L
<500 - 200/mm3; <0.5 - 0.2 x
10e9 /L
<200/mm3; <0.2 x 10e9 /L
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate a decrease in number of lymphocytes in a blood specimen.
Navigational Note: -
Lymphocyte count increased
-
>4000/mm3 - 20,000/mm3
>20,000/mm3
-
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate an abnormal increase in the number of lymphocytes in the blood, effusions or bone marrow.
Navigational Note: -
Neutrophil count decreased
<LLN - 1500/mm3; <LLN - 1.5 x
10e9 /L
<1500 - 1000/mm3; <1.5 - 1.0
x 10e9 /L
<1000 - 500/mm3; <1.0 - 0.5 x
10e9 /L
<500/mm3; <0.5 x 10e9 /L
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate a decrease in number of neutrophils in a blood specimen.
Navigational Note: -
Pancreatic enzymes
decreased
<LLN and asymptomatic
Increase in stool frequency,
bulk, or odor; steatorrhea
Sequelae of absorption
deficiency
-
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate an decrease in levels of pancreatic enzymes in a biological specimen.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC
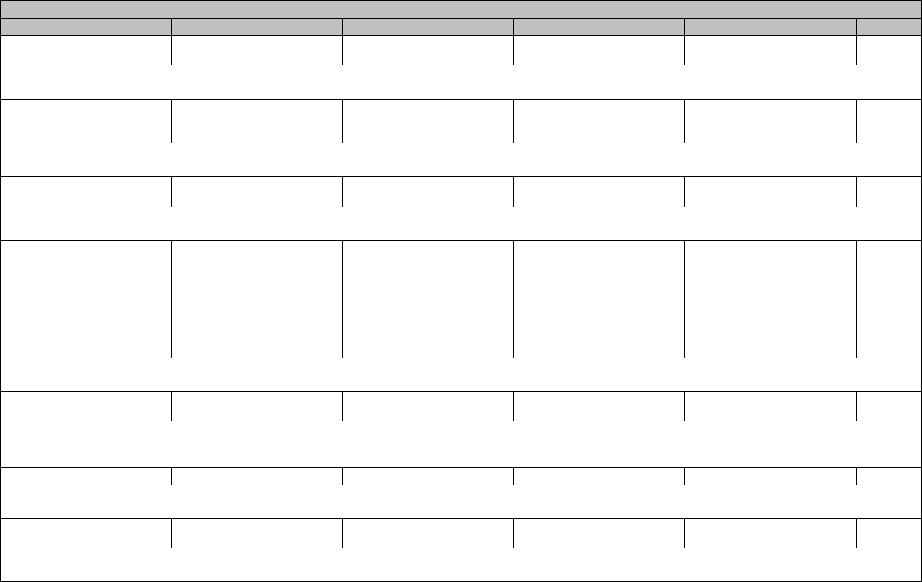
CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 89
Investigations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Platelet count decreased
<LLN - 75,000/mm3; <LLN -
75.0 x 10e9 /L
<75,000 - 50,000/mm3; <75.0
- 50.0 x 10e9 /L
<50,000 - 25,000/mm3; <50.0
- 25.0 x 10e9 /L
<25,000/mm3; <25.0 x 10e9 /L
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate a decrease in number of platelets in a blood specimen.
Navigational Note: -
Serum amylase increased
>ULN - 1.5 x ULN
>1.5 - 2.0 x ULN; >2.0 - 5.0 x
ULN and asymptomatic
>2.0 - 5.0 x ULN with signs or
symptoms; >5.0 x ULN and
asymptomatic
>5.0 x ULN and with signs or
symptoms
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate an increase in the levels of amylase in a serum specimen.
Navigational Note: -
Thyroid stimulating hormone
increased
TSH increased and no
intervention initiated
-
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an increase in thyroid stimulating hormone.
Navigational Note: If intervention initiated or symptomatic, report as Endocrine disorders: Hypothyroidism.
Urine output decreased
-
-
Adult: Oliguria (<80 ml in 8
hr);
Infants: < 0.5 mL/kg per hour
for 24 hours;
Children: < 500 mL/1.73 m2
body surface area per day
Adult: Anuria (<240 ml in 24
hr);
Pediatric: No urine output
over 12 hours
-
Definition: A finding based on test results that indicate urine production is less relative to previous output.
Navigational Note: -
Vital capacity abnormal
90 - 75% of predicted value
<75 - 50% of predicted value;
limiting instrumental ADL
<50% of predicted value;
limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A finding based on pulmonary function test results that indicate an abnormal vital capacity (amount of exhaled after a maximum inhalation) when compared to the
predicted value.
Navigational Note: Also consider Investigations: Forced Expiratory Volume; Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Respiratory failure or Dyspnea
Weight gain
5 - <10% from baseline
10 - <20% from baseline
>=20% from baseline
-
-
Definition: A finding characterized by an unexpected or abnormal increase in overall body weight; for pediatrics, greater than the baseline growth curve.
Navigational Note: Do not use Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Obesity, this term is being retired.
Weight loss
5 to <10% from baseline;
intervention not indicated
10 - <20% from baseline;
nutritional support indicated
>=20% from baseline; tube
feeding or TPN indicated
-
-
Definition: A finding characterized by a decrease in overall body weight; for pediatrics, less than the baseline growth curve.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 90
Investigations
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
White blood cell decreased
<LLN - 3000/mm3; <LLN - 3.0 x
10e9 /L
<3000 - 2000/mm3; <3.0 - 2.0
x 10e9 /L
<2000 - 1000/mm3; <2.0 - 1.0
x 10e9 /L
<1000/mm3; <1.0 x 10e9 /L
-
Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate an decrease in number of white blood cells in a blood specimen.
Navigational Note: -
Investigations - Other, specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 91
Metabolism and nutrition disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Acidosis
pH <normal, but >=7.3
-
pH <7.3
Life-threatening
consequences
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by abnormally high acidity (high hydrogen-ion concentration) of the blood and other body tissues.
Navigational Note: -
Alcohol intolerance
-
Present
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an increase in sensitivity to the adverse effects of alcohol, which can include nasal congestion, skin flushes, heart dysrhythmias, nausea,
vomiting, indigestion and headaches.
Navigational Note: -
Alkalosis
pH >normal, but <=7.5
-
pH >7.5
Life-threatening
consequences
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by abnormally high alkalinity (low hydrogen-ion concentration) of the blood and other body tissues.
Navigational Note: -
Anorexia
Loss of appetite without
alteration in eating habits
Oral intake altered without
significant weight loss or
malnutrition; oral nutritional
supplements indicated
Associated with significant
weight loss or malnutrition
(e.g., inadequate oral caloric
and/or fluid intake); tube
feeding or TPN indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a loss of appetite.
Navigational Note: -
Dehydration
Increased oral fluids indicated;
dry mucous membranes;
diminished skin turgor
IV fluids indicated
Hospitalization indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by excessive loss of water from the body. It is usually caused by severe diarrhea, vomiting or diaphoresis.
Navigational Note: -
Glucose intolerance
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; dietary
modification or oral agent
indicated
Severe symptoms; insulin
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an inability to properly metabolize glucose.
Navigational Note: -
Hypercalcemia
Corrected serum calcium of
>ULN - 11.5 mg/dL; >ULN - 2.9
mmol/L; Ionized calcium >ULN
- 1.5 mmol/L
Corrected serum calcium of
>11.5 - 12.5 mg/dL; >2.9 - 3.1
mmol/L; Ionized calcium >1.5
- 1.6 mmol/L; symptomatic
Corrected serum calcium of
>12.5 - 13.5 mg/dL; >3.1 - 3.4
mmol/L; Ionized calcium >1.6
- 1.8 mmol/L; hospitalization
indicated
Corrected serum calcium of
>13.5 mg/dL; >3.4 mmol/L;
Ionized calcium >1.8 mmol/L;
life-threatening consequences
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate an elevation in the concentration of calcium (corrected for albumin) in blood.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 92
Metabolism and nutrition disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Hyperglycemia
Abnormal glucose above
baseline with no medical
intervention
Change in daily management
from baseline for a diabetic;
oral antiglycemic agent
initiated; workup for diabetes
Insulin therapy initiated;
hospitalization indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate an elevation in the concentration of blood sugar. It is usually an indication of diabetes mellitus or glucose
intolerance.
Navigational Note: -
Hyperkalemia
>ULN - 5.5 mmol/L
>5.5 - 6.0 mmol/L;
intervention initiated
>6.0 - 7.0 mmol/L;
hospitalization indicated
>7.0 mmol/L; life-threatening
consequences
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate an elevation in the concentration of potassium in the blood; associated with kidney failure or sometimes
with the use of diuretic drugs.
Navigational Note: -
Hyperlipidemia
Requiring diet changes
Requiring pharmaceutical
intervention
Hospitalization; pancreatitis
Life-threatening
consequences
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate an elevation in the concentration of lipids in blood.
Navigational Note: -
Hypermagnesemia
>ULN - 3.0 mg/dL; >ULN - 1.23
mmol/L
-
>3.0 - 8.0 mg/dL; >1.23 - 3.30
mmol/L
>8.0 mg/dL; >3.30 mmol/L;
life-threatening consequences
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate an elevation in the concentration of magnesium in the blood.
Navigational Note: -
Hypernatremia
>ULN - 150 mmol/L
>150 - 155 mmol/L;
intervention initiated
>155 - 160 mmol/L;
hospitalization indicated
>160 mmol/L; life-threatening
consequences
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate an elevation in the concentration of sodium in the blood.
Navigational Note: -
Hyperphosphatemia
Laboratory finding only and
intervention not indicated
Noninvasive intervention
indicated
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated (e.g.,
dialysis)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate an elevation in the concentration of phosphate in a blood.
Navigational Note: -
Hypertriglyceridemia
150 mg/dL - 300 mg/dL; 1.71
mmol/L - 3.42 mmol/L
>300 mg/dL - 500 mg/dL;
>3.42 mmol/L - 5.7 mmol/L
>500 mg/dL - 1000 mg/dL;
>5.7 mmol/L - 11.4 mmol/L
>1000 mg/dL; >11.4 mmol/L;
life-threatening consequences
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate an elevation in the concentration of triglyceride concentration in the blood.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC
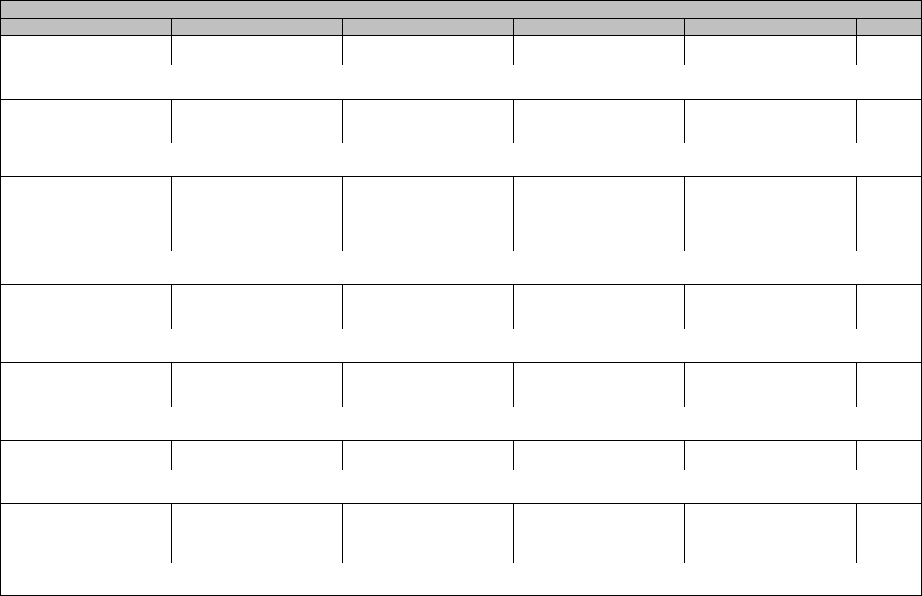
CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 93
Metabolism and nutrition disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Hyperuricemia
>ULN without physiologic
consequences
-
>ULN with physiologic
consequences
Life-threatening
consequences
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate an elevation in the concentration of uric acid.
Navigational Note: -
Hypoalbuminemia
<LLN - 3 g/dL; <LLN - 30 g/L
<3 - 2 g/dL; <30 - 20 g/L
<2 g/dL; <20 g/L
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate a low concentration of albumin in the blood.
Navigational Note: -
Hypocalcemia
Corrected serum calcium of
<LLN - 8.0 mg/dL; <LLN - 2.0
mmol/L; Ionized calcium <LLN
- 1.0 mmol/L
Corrected serum calcium of
<8.0 - 7.0 mg/dL; <2.0 - 1.75
mmol/L; Ionized calcium <1.0
- 0.9 mmol/L; symptomatic
Corrected serum calcium of
<7.0 - 6.0 mg/dL; <1.75 - 1.5
mmol/L; Ionized calcium <0.9
- 0.8 mmol/L; hospitalization
indicated
Corrected serum calcium of
<6.0 mg/dL; <1.5 mmol/L;
Ionized calcium <0.8 mmol/L;
life-threatening consequences
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate a low concentration of calcium (corrected for albumin) in the blood.
Navigational Note: -
Hypoglycemia
<LLN - 55 mg/dL; <LLN - 3.0
mmol/L
<55 - 40 mg/dL; <3.0 - 2.2
mmol/L
<40 - 30 mg/dL; <2.2 - 1.7
mmol/L
<30 mg/dL; <1.7 mmol/L; life-
threatening consequences;
seizures
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate a low concentration of glucose in the blood.
Navigational Note: -
Hypokalemia
<LLN - 3.0 mmol/L
Symptomatic with <LLN - 3.0
mmol/L; intervention
indicated
<3.0 - 2.5 mmol/L;
hospitalization indicated
<2.5 mmol/L; life-threatening
consequences
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate a low concentration of potassium in the blood.
Navigational Note: -
Hypomagnesemia
<LLN - 1.2 mg/dL; <LLN - 0.5
mmol/L
<1.2 - 0.9 mg/dL; <0.5 - 0.4
mmol/L
<0.9 - 0.7 mg/dL; <0.4 - 0.3
mmol/L
<0.7 mg/dL; <0.3 mmol/L; life-
threatening consequences
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate a low concentration of magnesium in the blood.
Navigational Note: -
Hyponatremia
<LLN - 130 mmol/L
125-129 mmol/L and
asymptomatic
125-129 mmol/L
symptomatic; 120-124
mmol/L regardless of
symptoms
<120 mmol/L; life-threatening
consequences
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate a low concentration of sodium in the blood.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 94
Metabolism and nutrition disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Hypophosphatemia
Laboratory finding only and
intervention not indicated
Oral replacement therapy
indicated
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated
Life-threatening
consequences
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate a low concentration of phosphates in the blood.
Navigational Note: -
Iron overload
-
Moderate symptoms;
intervention not indicated
Severe symptoms;
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by accumulation of iron in the tissues.
Navigational Note: -
Obesity
-
BMI 25 - 29.9 kg/m2
BMI 30 - 39.9 kg/m2
BMI >=40 kg/m2
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by having a high amount of body fat.
Navigational Note: Use term Investigations: Weight
gain
Tumor lysis syndrome
-
-
Present
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by metabolic abnormalities that result from a spontaneous or therapy-related cytolysis of tumor cells.
Navigational Note: -
Metabolism and nutrition
disorders - Other, specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 95
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Abdominal soft tissue necrosis
-
Local wound care; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
dressings or topical
medications)
Operative debridement or
other invasive intervention
indicated (e.g., tissue
reconstruction, flap, or
grafting)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the soft tissues of the abdominal wall.
Navigational Note: -
Arthralgia
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in a joint.
Navigational Note: -
Arthritis
Mild pain with inflammation,
erythema, or joint swelling
Moderate pain associated
with signs of inflammation,
erythema, or joint swelling;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe pain associated with
signs of inflammation,
erythema, or joint swelling;
irreversible joint damage;
limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation involving a joint.
Navigational Note: -
Avascular necrosis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL; elective operative
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by necrotic changes in the bone tissue due to interruption of blood supply. Most often affecting the epiphysis of the long bones, the necrotic
changes result in the collapse and the destruction of the bone structure.
Navigational Note: Use new term: Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Osteonecrosis
Back pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the back region.
Navigational Note: -
Bone pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the bones.
Navigational Note: -
Buttock pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the buttocks.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 96
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Chest wall necrosis
-
Local wound care; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
dressings or topical
medications)
Operative debridement or
other invasive intervention
indicated (e.g., tissue
reconstruction, flap, or
grafting)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the soft tissues of the chest wall including breast.
Navigational Note: -
Chest wall pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the chest wall.
Navigational Note: -
Exostosis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL; elective operative
intervention indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by non-neoplastic overgrowth of bone.
Navigational Note: -
Fibrosis deep connective
tissue
Mild induration, able to move
skin parallel to plane (sliding)
and perpendicular to skin
(pinching up)
Moderate induration, able to
slide skin, unable to pinch
skin; limiting instrumental ADL
Severe induration; unable to
slide or pinch skin; limiting
joint or orifice movement
(e.g., mouth, anus); limiting
self care ADL
Generalized; associated with
signs or symptoms of impaired
breathing or feeding
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by fibrotic degeneration of the deep connective tissues.
Navigational Note: -
Flank pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort on the lateral side of the body in the region below the ribs and above the hip.
Navigational Note: -
Generalized muscle weakness
Symptomatic; perceived by
patient but not evident on
physical exam
Symptomatic; evident on
physical exam; limiting
instrumental ADL
Limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a reduction in the strength of muscles in multiple anatomic sites.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 97
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Growth suppression
Reduction in growth velocity
by 10 - 29% ideally measured
over the period of a year
Reduction in growth velocity
by 30 - 49% ideally measured
over the period of a year or 0 -
49% reduction in growth from
the baseline growth curve
Reduction in growth velocity
of >=50% ideally measured
over the period of a year
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by stature that is smaller than normal as expected for age.
Navigational Note: -
Head soft tissue necrosis
-
Local wound care; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
dressings or topical
medications)
Operative debridement or
other invasive intervention
indicated (e.g., tissue
reconstruction, flap, or
grafting)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the soft tissues of the head.
Navigational Note: -
Joint effusion
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL; invasive
intervention indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by excessive fluid in a joint, usually as a result of joint inflammation.
Navigational Note: -
Joint range of motion
decreased
<=25% loss of ROM (range of
motion); decreased ROM
limiting athletic activity
>25 - 50% decrease in ROM;
limiting instrumental ADL
>50% decrease in ROM;
limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease in joint flexibility of any joint.
Navigational Note: -
Joint range of motion
decreased cervical spine
Mild restriction of rotation or
flexion between 60 - 70
degrees
Rotation <60 degrees to right
or left; <60 degrees of flexion
Ankylosed/fused over
multiple segments with no C-
spine rotation
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease in flexibility of a cervical spine joint.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 98
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Joint range of motion
decreased lumbar spine
Stiffness; difficulty bending to
the floor to pick up a very light
object but able to do athletic
activity
Pain with range of motion
(ROM) in lumbar spine;
requires a reaching aid to pick
up a very light object from the
floor
<50% lumbar spine flexion;
associated with symptoms of
ankylosis or fused over
multiple segments with no L-
spine flexion (e.g., unable to
reach to floor to pick up a very
light object)
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease in flexibility of a lumbar spine joint.
Navigational Note: -
Kyphosis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate accentuation;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe accentuation;
operative intervention
indicated; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal increase in the curvature of the thoracic portion of the spine.
Navigational Note: -
Lordosis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate accentuation;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe accentuation;
operative intervention
indicated; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal increase in the curvature of the lumbar portion of the spine.
Navigational Note: -
Muscle cramp
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by marked cramping sensation originating from a muscle or group of muscles.
Navigational Note: Synonym: Muscle spasm
Muscle weakness lower limb
Symptomatic; perceived by
patient but not evident on
physical exam
Symptomatic; evident on
physical exam; limiting
instrumental ADL
Limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a reduction in the strength of the lower limb muscles.
Navigational Note: -
Muscle weakness trunk
Symptomatic; perceived by
patient but not evident on
physical exam
Symptomatic; evident on
physical exam; limiting
instrumental ADL
Limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a reduction in the strength of the trunk muscles.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 99
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Muscle weakness upper limb
Symptomatic; perceived by
patient but not evident on
physical exam
Symptomatic; evident on
physical exam; limiting
instrumental ADL
Limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a reduction in the strength of the upper limb muscles.
Navigational Note: -
Musculoskeletal deformity
Cosmetically and functionally
insignificant hypoplasia
Deformity, hypoplasia, or
asymmetry able to be
remediated by prosthesis
(e.g., shoe insert) or covered
by clothing
Significant deformity,
hypoplasia, or asymmetry,
unable to be remediated by
prosthesis or covered by
clothing; limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a malformation of the musculoskeletal system.
Navigational Note: -
Myalgia
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by marked discomfort sensation originating from a muscle or group of muscles.
Navigational Note: -
Myositis
Mild pain
Moderate pain associated
with weakness; pain limiting
instrumental ADL
Pain associated with severe
weakness; limiting self care
ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation involving the skeletal muscles.
Navigational Note: -
Neck pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the neck area.
Navigational Note: -
Neck soft tissue necrosis
-
Local wound care; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
dressings or topical
medications)
Operative debridement or
other invasive intervention
indicated (e.g., tissue
reconstruction, flap, or
grafting)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the soft tissues of the neck.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 100
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Osteonecrosis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
analgesics or
bisphosphonates); limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL; elective operative
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by necrotic changes in the bone tissue due to interruption of blood supply. Most often affecting the epiphysis of the long bones, the necrotic
changes result in the collapse and the destruction of the bone structure.
Navigational Note: -
Osteonecrosis of jaw
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
topical agents); limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL; elective operative
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the bone of the mandible.
Navigational Note: -
Osteoporosis
Adult: Radiologic evidence of
osteoporosis or Bone Mineral
Density (BMD) t-score -1 to -
2.5 (osteopenia);
Pediatric: Radiologic evidence
of low BMD with z score of <=
-2.0 and no history of
significant fractures
Adult: BMD t-score < -2.5; loss
of height <2 cm; therapy to
improve BMD indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL;
Pediatric: Low BMD (z-score
<= -2.0) and significant
fracture history (defined as a
long bone fracture of the
lower extremity, vertebral
compression, 2 or more long
bone fractures of the upper
extremities); therapy to
improve BMD indicated
Adult: Loss of height >=2 cm;
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL;
Pediatric: Limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by reduced bone mass, with a decrease in cortical thickness and in the number and size of the trabeculae of cancellous bone (but normal chemical
composition), resulting in increased fracture incidence.
Navigational Note: -
Pain in extremity
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the upper or lower extremities.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 101
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Pelvic soft tissue necrosis
-
Local wound care; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
dressings or topical
medications)
Operative debridement or
other invasive intervention
indicated (e.g., tissue
reconstruction, flap, or
grafting)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the soft tissues of the pelvis.
Navigational Note: -
Rhabdomyolysis
Asymptomatic, intervention
not indicated; laboratory
findings only
Non-urgent intervention
indicated
Symptomatic, urgent
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; dialysis
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the breakdown of muscle tissue resulting in the release of muscle fiber contents into the bloodstream.
Navigational Note: -
Rotator cuff injury
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an injury of the rotator cuff.
Navigational Note: -
Scoliosis
<20 degrees; clinically
undetectable
>20 - 45 degrees; visible by
forward flexion; limiting
instrumental ADL
>45 degrees; scapular
prominence in forward
flexion; operative intervention
indicated; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a malformed, lateral curvature of the spine.
Navigational Note: -
Soft tissue necrosis lower limb
-
Local wound care; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
dressings or topical
medications)
Operative debridement or
other invasive intervention
indicated (e.g., tissue
reconstruction, flap, or
grafting)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the soft tissues of the lower extremity.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 102
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Soft tissue necrosis upper limb
-
Local wound care; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
dressings or topical
medications)
Operative debridement or
other invasive intervention
indicated (e.g., tissue
reconstruction, flap, or
grafting)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the soft tissues of the upper extremity.
Navigational Note: -
Superficial soft tissue fibrosis
Mild induration, able to move
skin parallel to plane (sliding)
and perpendicular to skin
(pinching up)
Moderate induration, able to
slide skin, unable to pinch
skin; limiting instrumental ADL
Severe induration; unable to
slide or pinch skin; limiting
joint or orifice movement
(e.g., mouth, anus); limiting
self care ADL
Generalized; associated with
signs or symptoms of impaired
breathing or feeding
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by fibrotic degeneration of the superficial soft tissues.
Navigational Note: -
Trismus
Decreased ROM (range of
motion) without impaired
eating
Decreased ROM requiring
small bites, soft foods or
purees
Decreased ROM with inability
to adequately aliment or
hydrate orally
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by lack of ability to open the mouth fully due to a decrease in the range of motion of the muscles of mastication.
Navigational Note: -
Unequal limb length
Mild length discrepancy <2 cm
Moderate length discrepancy
2 - 5 cm; shoe lift indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe length discrepancy >5
cm; limiting self care ADL;
operative intervention
indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a discrepancy between the lengths of the lower or upper extremities.
Navigational Note: -
Musculoskeletal and
connective tissue disorder -
Other, specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 103
Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified (incl cysts and polyps)
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Leukemia secondary to
oncology chemotherapy
-
-
-
Present
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by leukemia arising as a result of the mutagenic effect of chemotherapy agents.
Navigational Note: -
Myelodysplastic syndrome
-
-
-
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by insufficiently healthy hematapoietic cell production by the bone marrow.
Navigational Note: -
Skin papilloma
Asymptomatic; intervention
not indicated
Intervention initiated
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by the presence of one or more warts.
Navigational Note: -
Treatment related secondary
malignancy
-
-
Non life-threatening
secondary malignancy
Acute life-threatening
secondary malignancy; blast
crisis in leukemia
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by development of a malignancy most probably as a result of treatment for a previously existing malignancy.
Navigational Note: -
Tumor hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding in a tumor.
Navigational Note: -
Tumor pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort from a neoplasm that may be pressing on a nerve, blocking blood vessels, inflamed or fractured from
metastasis.
Navigational Note: -
Neoplasms benign, malignant
and unspecified (incl cysts and
polyps) - Other, specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 104
Nervous system disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Abducens nerve disorder
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by dysfunction of the abducens nerve (sixth cranial nerve).
Navigational Note: -
Accessory nerve disorder
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by dysfunction of the accessory nerve (eleventh cranial nerve).
Navigational Note: -
Acoustic nerve disorder NOS
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by dysfunction of the acoustic nerve (eighth cranial nerve).
Navigational Note: -
Akathisia
Mild restlessness or increased
motor activity
Moderate restlessness or
increased motor activity;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe restlessness or
increased motor activity;
limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an uncomfortable feeling of inner restlessness and inability to stay still; this is a side effect of some psychotropic drugs.
Navigational Note: -
Amnesia
Mild; transient memory loss
Moderate; short term
memory loss; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe; long term memory
loss; limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by systematic and extensive loss of memory.
Navigational Note: -
Anosmia
Present
-
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a change in the sense of smell.
Navigational Note: Also consider Olfactory nerve disorder
Aphonia
-
-
Voicelessness; unable to
speak
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by the inability to speak. It may result from injuries to the vocal cords or may be functional (psychogenic).
Navigational Note: -
Arachnoiditis
Mild symptoms
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation of the arachnoid membrane and adjacent subarachnoid space.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 105
Nervous system disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Ataxia
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL; mechanical
assistance indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by lack of coordination of muscle movements resulting in the impairment or inability to perform voluntary activities.
Navigational Note: -
Brachial plexopathy
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by regional paresthesia of the brachial plexus, marked discomfort and muscle weakness, and limited movement in the arm or hand.
Navigational Note: -
Central nervous system
necrosis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
corticosteroids indicated
Severe symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the brain and/or spinal cord.
Navigational Note: -
Cerebrospinal fluid leakage
Post-craniotomy:
asymptomatic; Post-lumbar
puncture: transient headache;
postural care indicated
Post-craniotomy: moderate
symptoms; medical
intervention indicated; Post-
lumbar puncture: persistent
moderate symptoms; blood
patch indicated
Severe symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by loss of cerebrospinal fluid into the surrounding tissues.
Navigational Note: -
Cognitive disturbance
Mild cognitive disability; not
interfering with
work/school/life
performance; specialized
educational services/devices
not indicated
Moderate cognitive disability;
interfering with
work/school/life performance
but capable of independent
living; specialized resources
on part time basis indicated
Severe cognitive disability;
significant impairment of
work/school/life performance
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a conspicuous change in cognitive function.
Navigational Note: -
Concentration impairment
Mild inattention or decreased
level of concentration
Moderate impairment in
attention or decreased level
of concentration; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe impairment in
attention or decreased level
of concentration; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a deterioration in the ability to concentrate.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC
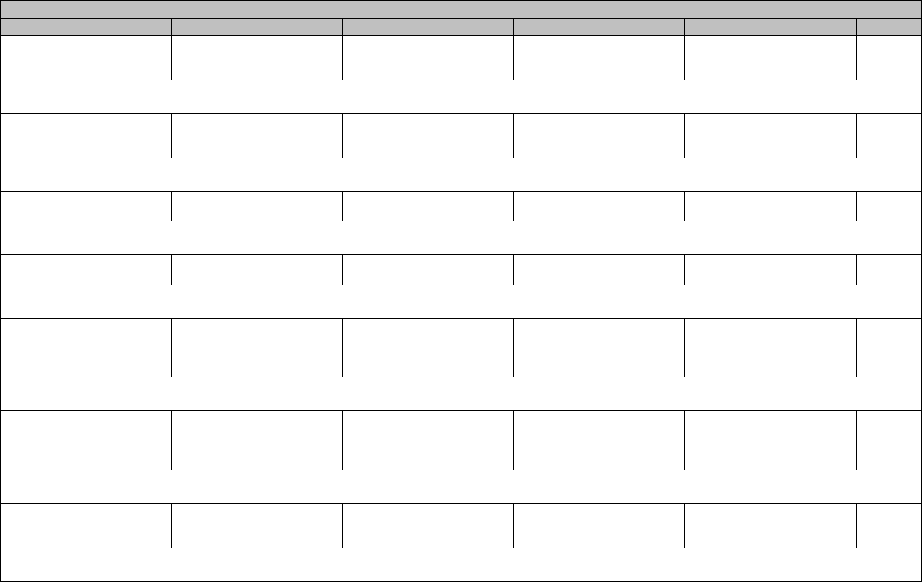
CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 106
Nervous system disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Depressed level of
consciousness
Decreased level of alertness
Sedation; slow response to
stimuli; limiting instrumental
ADL
Difficult to arouse
Life-threatening
consequences; coma; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease in ability to perceive and respond.
Navigational Note: -
Dizziness
Mild unsteadiness or
sensation of movement
Moderate unsteadiness or
sensation of movement;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe unsteadiness or
sensation of movement;
limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a disturbing sensation of lightheadedness, unsteadiness, giddiness, spinning or rocking.
Navigational Note: -
Dysarthria
Mild slurred speech
Moderate impairment of
articulation or slurred speech
Severe impairment of
articulation or slurred speech
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by slow and slurred speech resulting from an inability to coordinate the muscles used in speech.
Navigational Note: -
Dysesthesia
Mild sensory alteration
Moderate sensory alteration;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe sensory alteration;
limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by distortion of sensory perception, resulting in an abnormal and unpleasant sensation.
Navigational Note: -
Dysgeusia
Altered taste but no change in
diet
Altered taste with change in
diet (e.g., oral supplements);
noxious or unpleasant taste;
loss of taste
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by abnormal sensual experience with the taste of foodstuffs; it can be related to a decrease in the sense of smell.
Navigational Note: -
Dysphasia
Awareness of receptive or
expressive characteristics; not
impairing ability to
communicate
Moderate receptive or
expressive characteristics;
impairing ability to
communicate spontaneously
Severe receptive or expressive
characteristics; impairing
ability to read, write or
communicate intelligibly
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by impairment of verbal communication skills, often resulting from brain damage.
Navigational Note: -
Edema cerebral
-
-
New onset; worsening from
baseline
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by swelling due to an excessive accumulation of fluid in the brain.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 107
Nervous system disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Encephalopathy
Mild symptoms
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a pathologic process involving the brain.
Navigational Note: -
Extrapyramidal disorder
Mild involuntary movements
Moderate involuntary
movements; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe involuntary
movements or torticollis;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by abnormal, repetitive, involuntary muscle movements, frenzied speech and extreme restlessness.
Navigational Note: Synonym: Restless legs
Facial muscle weakness
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a reduction in the strength of the facial muscles.
Navigational Note: -
Facial nerve disorder
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by dysfunction of the facial nerve (seventh cranial nerve).
Navigational Note: -
Glossopharyngeal nerve
disorder
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by dysfunction of the glossopharyngeal nerve (ninth cranial nerve).
Navigational Note: -
Guillain-Barre syndrome
Mild symptoms
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated;
intubation
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the body's immune system attacking the peripheral nervous system causing ascending paralysis.
Navigational Note: -
Headache
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in various parts of the head, not confined to the area of distribution of any nerve.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 108
Nervous system disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Hydrocephalus
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention not indicated
Severe symptoms or
neurological deficit;
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal increase of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain.
Navigational Note: -
Hypersomnia
Mild increased need for sleep
Moderate increased need for
sleep
Severe increased need for
sleep
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by characterized by excessive sleepiness during the daytime.
Navigational Note: -
Hypoglossal nerve disorder
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by dysfunction of the hypoglossal nerve (twelfth cranial nerve).
Navigational Note: -
Intracranial hemorrhage
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Ventriculostomy, ICP
monitoring, intraventricular
thrombolysis, or invasive
intervention indicated;
hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the cranium.
Navigational Note: -
Ischemia cerebrovascular
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease or absence of blood supply to the brain caused by obstruction (thrombosis or embolism) of an artery resulting in neurological
damage.
Navigational Note: Prior to using this term consider Nervous system disorder: TIA or Stroke
Lethargy
Mild symptoms; reduced
alertness and awareness
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease in consciousness characterized by mental and physical inertness.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 109
Nervous system disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Leukoencephalopathy
Asymptomatic; small focal
T2/FLAIR hyperintensities;
involving periventricular white
matter or <1/3 of susceptible
areas of cerebrum +/- mild
increase in subarachnoid
space (SAS) and/or mild
ventriculomegaly
Moderate symptoms; focal
T2/FLAIR hyperintensities,
involving periventricular white
matter extending into
centrum semiovale or
involving 1/3 to 2/3 of
susceptible areas of cerebrum
+/- moderate increase in SAS
and/or moderate
ventriculomegaly
Severe symptoms; extensive
T2/FLAIR hyperintensities,
involving periventricular white
matter involving 2/3 or more
of susceptible areas of
cerebrum +/- moderate to
severe increase in SAS and/or
moderate to severe
ventriculomegaly
Life-threatening
consequences; extensive
T2/FLAIR hyperintensities,
involving periventricular white
matter involving most of
susceptible areas of cerebrum
+/- moderate to severe
increase in SAS and/or
moderate to severe
ventriculomegaly
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by diffuse reactive astrocytosis with multiple areas of necrotic foci without inflammation.
Navigational Note: -
Memory impairment
Mild memory impairment
Moderate memory
impairment; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe memory impairment;
limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a deterioration in memory function.
Navigational Note: -
Meningismus
Mild symptoms
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by neck stiffness, headache, and photophobia resulting from irritation of the cerebral meninges.
Navigational Note: -
Movements involuntary
Mild symptoms
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by uncontrolled and purposeless movements.
Navigational Note: -
Muscle weakness left-sided
Symptomatic; perceived by
patient but not evident on
physical exam
Symptomatic; evident on
physical exam; limiting
instrumental ADL
Limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a reduction in the strength of the muscles on the left side of the body.
Navigational Note: -
Muscle weakness right-sided
Symptomatic; perceived by
patient but not evident on
physical exam
Symptomatic; evident on
physical exam; limiting
instrumental ADL
Limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a reduction in the strength of the muscles on the right side of the body.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 110
Nervous system disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Myasthenia gravis
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by weakness and rapid fatigue of any of the skeletal muscles.
Navigational Note: -
Neuralgia
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by intense painful sensation along a nerve or group of nerves.
Navigational Note: -
Nystagmus
-
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by involuntary movements of the eyeballs.
Navigational Note: -
Oculomotor nerve disorder
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by dysfunction of the oculomotor nerve (third cranial nerve).
Navigational Note: -
Olfactory nerve disorder
-
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by dysfunction of the olfactory nerve (first cranial nerve).
Navigational Note: -
Paresthesia
Mild symptoms
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by functional disturbances of sensory neurons resulting in abnormal cutaneous sensations of tingling, numbness, pressure, cold, and/or warmth.
Navigational Note: -
Peripheral motor neuropathy
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by damage or dysfunction of the peripheral motor nerves.
Navigational Note: Also consider Nervous system disroders: Peripheral sensory neuropathy
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 111
Nervous system disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Peripheral sensory
neuropathy
Asymptomatic
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by damage or dysfunction of the peripheral sensory nerves.
Navigational Note: -
Phantom pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort related to a limb or an organ that is removed from or is not physically part of the body.
Navigational Note: -
Presyncope
-
Present (e.g., near fainting)
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an episode of lightheadedness and dizziness which may precede an episode of syncope.
Navigational Note: -
Pyramidal tract syndrome
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by dysfunction of the corticospinal (pyramidal) tracts of the spinal cord. Symptoms include an increase in the muscle tone in the lower extremities,
hyperreflexia, positive Babinski and a decrease in fine motor coordination.
Navigational Note: -
Radiculitis
Mild symptoms
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation involving a nerve root. Patients experience marked discomfort radiating along a nerve path because of spinal pressure on the
connecting nerve root.
Navigational Note: -
Recurrent laryngeal nerve
palsy
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms
Severe symptoms; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
thyroplasty, vocal cord
injection)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by paralysis of the recurrent laryngeal nerve.
Navigational Note: -
Reversible posterior
leukoencephalopathy
syndrome
-
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by headaches, mental status changes, visual disturbances, and/or seizures associated with imaging findings of posterior leukoencephalopathy. It
has been observed in association with hypertensive encephalopathy, eclampsia, and immunosuppressive and cytotoxic drug treatment. It is an acute or subacute reversible condition.
Also known as posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES).
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 112
Nervous system disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Seizure
Brief partial seizure and no
loss of consciousness
Brief generalized seizure
New onset seizures (partial or
generalized); multiple seizures
despite medical intervention
Life-threatening
consequences; prolonged
repetitive seizures
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sudden, involuntary skeletal muscular contractions of cerebral or brain stem origin.
Navigational Note: -
Somnolence
Mild but more than usual
drowsiness or sleepiness
Moderate sedation; limiting
instrumental ADL
Obtundation or stupor
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by characterized by excessive sleepiness and drowsiness.
Navigational Note: -
Spasticity
Mild or slight increase in
muscle tone
Moderate increase in muscle
tone and increase in
resistance through range of
motion
Severe increase in muscle
tone and increase in
resistance through range of
motion
Life-threatening
consequences; unable to
move active or passive range
of motion
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by increased involuntary muscle tone that affects the regions interfering with voluntary movement. It results in gait, movement, and speech
disturbances.
Navigational Note: -
Spinal cord compression
-
-
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by pressure on the spinal cord.
Navigational Note: -
Stroke
Incidental radiographic
findings only
Mild to moderate neurologic
deficit; limiting instrumental
ADL
Severe neurologic deficit;
limiting self care ADL;
hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease or absence of blood supply to the brain caused by obstruction (thrombosis or embolism) of an artery resulting in neurological
damage.
Navigational Note: -
Syncope
-
-
Fainting; orthostatic collapse
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by spontaneous loss of consciousness caused by insufficient blood supply to the brain.
Navigational Note: -
Tendon reflex decreased
Ankle reflex reduced
Ankle reflex absent; other
reflexes reduced
Absence of all reflexes
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by less than normal deep tendon reflexes.
Navigational Note: Also consider Nervous system disorders: Peripheral motor neuropathy or Peripheral sensory neuropathy
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 113
Nervous system disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Transient ischemic attacks
Mild neurologic deficit with or
without imaging confirmation
Moderate neurologic deficit
with or without imaging
confirmation
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a brief attack (less than 24 hours) of cerebral dysfunction of vascular origin, with no persistent neurological deficit.
Navigational Note: If >24 hours, Consider Nervous system disorders: Stroke
Tremor
Mild symptoms
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by the uncontrolled shaking movement of the whole body or individual parts.
Navigational Note: -
Trigeminal nerve disorder
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by dysfunction of the trigeminal nerve (fifth cranial nerve).
Navigational Note: -
Trochlear nerve disorder
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by dysfunction of the trochlear nerve (fourth cranial nerve).
Navigational Note: -
Vagus nerve disorder
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by dysfunction of the vagus nerve (tenth cranial nerve).
Navigational Note: -
Vasovagal reaction
-
-
Present
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sudden drop of the blood pressure, bradycardia, and peripheral vasodilation that may lead to loss of consciousness. It results from an increase
in the stimulation of the vagus nerve.
Navigational Note: -
Nervous system disorders -
Other, specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 114
Pregnancy, puerperium and perinatal conditions
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Fetal growth retardation
-
<10% percentile of weight for
gestational age
<5% percentile of weight for
gestational age
<1% percentile of weight for
gestational age
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by inhibition of fetal growth resulting in the inability of the fetus to achieve its potential weight.
Navigational Note: -
Pregnancy loss
-
-
-
Fetal loss at any gestational
age
-
Definition: Death in utero.
Navigational Note: -
Premature delivery
Delivery of a liveborn infant at
>34 to 37 weeks gestation
Delivery of a liveborn infant at
>28 to 34 weeks gestation
Delivery of a liveborn infant at
24 to 28 weeks gestation
Delivery of a liveborn infant at
24 weeks of gestation or less
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by delivery of a viable infant before the normal end of gestation. Typically, viability is achievable between the twentieth and thirty-seventh week of
gestation.
Navigational Note: -
Pregnancy, puerperium and
perinatal conditions - Other,
specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 115
Psychiatric disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Agitation
Mild mood alteration
Moderate mood alteration
Severe agitation;
hospitalization not indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a state of restlessness associated with unpleasant feelings of irritability and tension.
Navigational Note: -
Anorgasmia
Inability to achieve orgasm
not adversely affecting
relationship
Inability to achieve orgasm
adversely affecting
relationship
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an inability to achieve orgasm.
Navigational Note: -
Anxiety
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL; hospitalization
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by apprehension of danger and dread accompanied by restlessness, tension, tachycardia, and dyspnea unattached to a clearly identifiable stimulus.
Navigational Note: -
Confusion
Mild disorientation
Moderate disorientation;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe disorientation; limiting
self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a lack of clear and orderly thought and behavior.
Navigational Note: -
Delayed orgasm
Delay in achieving orgasm not
adversely affecting
relationship
Delay in achieving orgasm
adversely affecting
relationship
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by sexual dysfunction characterized by a delay in climax.
Navigational Note: -
Delirium
Mild acute confusional state
Moderate and acute
confusional state; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe and acute confusional
state; limiting self care ADL;
urgent intervention indicated;
new onset
Life-threatening
consequences, threats of
harm to self or others; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the acute and sudden development of confusion, illusions, movement changes, inattentiveness, agitation, and hallucinations. Usually, it is a
reversible condition.
Navigational Note: -
Delusions
-
Moderate delusional
symptoms
Severe delusional symptoms;
hospitalization not indicated;
new onset
Life-threatening
consequences, threats of
harm to self or others;
hospitalization indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by false personal beliefs held contrary to reality, despite contradictory evidence and common sense.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 116
Psychiatric disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Depression
Mild depressive symptoms
Moderate depressive
symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe depressive symptoms;
limiting self care ADL;
hospitalization not indicated
Life-threatening
consequences, threats of
harm to self or others;
hospitalization indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by melancholic feelings of grief or unhappiness.
Navigational Note: -
Euphoria
Mild mood elevation
Moderate mood elevation
Severe mood elevation (e.g.,
hypomania)
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an exaggerated feeling of well-being which is disproportionate to events and stimuli.
Navigational Note: -
Hallucinations
Mild hallucinations (e.g.,
perceptual distortions)
Moderate hallucinations
Severe hallucinations;
hospitalization not indicated
Life-threatening
consequences, threats of
harm to self or others;
hospitalization indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a false sensory perception in the absence of an external stimulus.
Navigational Note: -
Insomnia
Mild difficulty falling asleep,
staying asleep or waking up
early
Moderate difficulty falling
asleep, staying asleep or
waking up early
Severe difficulty in falling
asleep, staying asleep or
waking up early
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by difficulty in falling asleep and/or remaining asleep.
Navigational Note: -
Irritability
Mild; easily consolable
Moderate; limiting
instrumental ADL; increased
attention indicated
Severe abnormal or excessive
response; limiting self care
ADL; inconsolable; medical or
psychiatric intervention
indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal responsiveness to stimuli or physiological arousal; may be in response to pain, fright, a drug, an emotional situation or a medical
condition.
Navigational Note: -
Libido decreased
Decrease in sexual interest
not adversely affecting
relationship
Decrease in sexual interest
adversely affecting
relationship
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease in sexual desire.
Navigational Note: -
Libido increased
Present
-
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an increase in sexual desire.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 117
Psychiatric disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Mania
Mild manic symptoms (e.g.,
elevated mood, rapid
thoughts, rapid speech,
decreased need for sleep)
Moderate manic symptoms
(e.g., relationship and work
difficulties; poor hygiene)
Severe manic symptoms (e.g.,
hypomania; major sexual or
financial indiscretions);
hospitalization not indicated;
new onset
Life-threatening
consequences, threats of
harm to self or others;
hospitalization indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by excitement of psychotic proportions manifested by mental and physical hyperactivity, disorganization of behavior and elevation of mood.
Navigational Note: -
Personality change
Mild personality change
Moderate personality change
Severe personality change;
hospitalization not indicated
Life-threatening
consequences, threats of
harm to self or others;
hospitalization indicated
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a conspicuous change in a person's behavior and thinking.
Navigational Note: -
Psychosis
Mild psychotic symptoms
Moderate psychotic
symptoms (e.g., disorganized
speech; impaired reality
testing)
Severe psychotic symptoms
(e.g., paranoid, extreme
disorganization);
hospitalization not indicated;
new onset
Life-threatening
consequences, threats of
harm to self or others;
hospitalization indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by personality change, impaired functioning, and loss of touch with reality. It may be a manifestation of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder or brain
tumor.
Navigational Note: -
Restlessness
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an inability to rest, relax or be still.
Navigational Note: -
Suicidal ideation
Increased thoughts of death
but no wish to kill oneself
Suicidal ideation with no
specific plan or intent
Specific plan to commit
suicide without serious intent
to die which may not require
hospitalization
Specific plan to commit
suicide with serious intent to
die which requires
hospitalization
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by thoughts of taking one's own life.
Navigational Note: -
Suicide attempt
-
-
Suicide attempt or gesture
without intent to die
Suicide attempt with intent to
die which requires
hospitalization
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by self-inflicted harm in an attempt to end one's own life.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 118
Psychiatric disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Psychiatric disorders - Other,
specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; limiting self care
ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; hospitalization
or urgent intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 119
Renal and urinary disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Acute kidney injury
-
-
Hospitalization indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; dialysis
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the acute loss of renal function (within 2 weeks) and is traditionally classified as pre-renal (low blood flow into kidney), renal (kidney damage)
and post-renal causes (ureteral or bladder outflow obstruction).
Navigational Note: Also consider Investigations: Creatinine increased
Bladder perforation
-
Invasive intervention not
indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; organ failure;
urgent operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a rupture in the bladder wall.
Navigational Note: -
Bladder spasm
Intervention not indicated
Antispasmodics indicated
Hospitalization indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sudden and involuntary contraction of the bladder wall.
Navigational Note: -
Chronic kidney disease
eGFR (estimated Glomerular
Filtration Rate) or CrCl
(creatinine clearance) <LLN -
60 ml/min/1.73 m2 or
proteinuria 2+ present; urine
protein/creatinine >0.5
eGFR or CrCl 59 - 30
ml/min/1.73 m2
eGFR or CrCl 29 - 15
ml/min/1.73 m2
eGFR or CrCl <15 ml/min/1.73
m2; dialysis or renal
transplant indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by gradual and usually permanent loss of kidney function resulting in renal failure.
Navigational Note: -
Cystitis noninfective
Microscopic hematuria;
minimal increase in
frequency, urgency, dysuria,
or nocturia; new onset of
incontinence
Moderate hematuria;
moderate increase in
frequency, urgency, dysuria,
nocturia or incontinence;
urinary catheter placement or
bladder irrigation indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Gross hematuria; transfusion,
IV medications, or
hospitalization indicated;
elective invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent invasive
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation of the bladder which is not caused by an infection of the urinary tract.
Navigational Note: -
Dysuria
Present
-
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by painful urination.
Navigational Note: If associated with an infection, report the infection. For grades higher than Grade 1, consider Renal and urinary disorders: Bladder spasm or Cystitis noninfective;
Infections and infestations: Urinary tract infection.
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 120
Renal and urinary disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Glucosuria
Present
-
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate glucose in the urine.
Navigational Note: -
Hematuria
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; urinary catheter
or bladder irrigation indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Gross hematuria; transfusion,
IV medications, or
hospitalization indicated;
elective invasive intervention
indicated; limiting self care
ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent invasive
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate blood in the urine.
Navigational Note: -
Hemoglobinuria
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
-
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate the presence of free hemoglobin in the urine.
Navigational Note: Report underlying AE if > Grade 1
Nephrotic syndrome
-
-
Not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by symptoms that include severe edema, proteinuria, and hypoalbuminemia; it is indicative of renal dysfunction.
Navigational Note: -
Proteinuria
1+ proteinuria; urinary protein
≥ULN - <1.0 g/24 hrs
Adult: 2+ and 3+ proteinuria;
urinary protein 1.0 - <3.5 g/24
hrs;
Pediatric: Urine P/C
(Protein/Creatinine) ratio 0.5 -
1.9
Adult: Urinary protein >=3.5
g/24 hrs; 4+ proteinuria;
Pediatric: Urine P/C
(Protein/Creatinine) ratio >1.9
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate the presence of excessive protein in the urine. It is predominantly albumin, but also globulin.
Navigational Note: 24-hour urine collection takes precedence over dipstick
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 121
Renal and urinary disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Renal calculi
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; occasional use of
nonprescription analgesics
indicated
Symptomatic; oral antiemetics
indicated; around the clock
nonprescription analgesics or
any oral narcotic analgesics
indicated
Hospitalization indicated; IV
intervention (e.g., analgesics,
antiemetics); elective invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent invasive
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the formation of crystals/kidney stones in the pelvis of the kidney.
Navigational Note: -
Renal colic
Mild pain not interfering with
activity; nonprescription
medication indicated
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL;
prescription medication
indicated
Hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by paroxysmal and severe flank marked discomfort radiating to the inguinal area. Often, the cause is the passage of crystals/kidney stones.
Navigational Note: -
Renal hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Analgesics and hematocrit
monitoring indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the kidney.
Navigational Note: -
Urinary fistula
-
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent invasive
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between any part of the urinary system and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Urinary frequency
Present
Limiting instrumental ADL;
medical management
indicated
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by urination at short intervals.
Navigational Note: -
Urinary incontinence
Occasional (e.g., with
coughing, sneezing, etc.), pads
not indicated
Spontaneous; pads indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Intervention indicated (e.g.,
clamp, collagen injections);
operative intervention
indicated; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by inability to control the flow of urine from the bladder.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 122
Renal and urinary disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Urinary retention
Urinary, suprapubic or
intermittent catheter
placement not indicated; able
to void with some residual
Placement of urinary,
suprapubic or intermittent
catheter placement indicated;
medication indicated
Elective invasive intervention
indicated; substantial loss of
affected kidney function or
mass
Life-threatening
consequences; organ failure;
urgent operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by accumulation of urine within the bladder because of the inability to urinate.
Navigational Note: -
Urinary tract obstruction
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic but no
hydronephrosis, sepsis, or
renal dysfunction; urethral
dilation, urinary or suprapubic
catheter indicated
Altered organ function (e.g.,
hydronephrosis or renal
dysfunction); invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by blockage of the normal flow of contents of the urinary tract.
Navigational Note: -
Urinary tract pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the urinary tract.
Navigational Note: -
Urinary urgency
Present
Limiting instrumental ADL;
medical management
indicated
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sudden compelling urge to urinate.
Navigational Note: -
Urine discoloration
Present
-
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a change in the color of the urine.
Navigational Note: -
Renal and urinary disorders -
Other, specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 123
Reproductive system and breast disorders
CTCAE Term
Grade 1
Grade 2
Grade 3
Grade 4
Grade 5
Amenorrhea
-
Present
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by the abnormal absence of menses for at least three consecutive menstrual cycles.
Navigational Note: -
Azoospermia
-
Absence of sperm in ejaculate
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate complete absence of spermatozoa in the semen.
Navigational Note: -
Breast atrophy
Minimal asymmetry; minimal
atrophy
Moderate asymmetry;
moderate atrophy
Asymmetry >1/3 of breast
volume; severe atrophy
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by underdevelopment of the breast.
Navigational Note: -
Breast pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the breast region.
Navigational Note: -
Dysmenorrhea
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by abnormally painful abdominal cramps during menses.
Navigational Note: -
Dyspareunia
Mild discomfort or pain
associated with vaginal
penetration; discomfort
relieved with use of vaginal
lubricants or estrogen
Moderate discomfort or pain
associated with vaginal
penetration; discomfort or
pain partially relieved with
use of vaginal lubricants or
estrogen
Severe discomfort or pain
associated with vaginal
penetration; discomfort or
pain unrelieved by vaginal
lubricants or estrogen
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by painful or difficult coitus.
Navigational Note: -
Ejaculation disorder
Diminished ejaculation
Anejaculation or retrograde
ejaculation
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by problems related to ejaculation. This category includes premature, delayed, retrograde and painful ejaculation.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 124
Reproductive system and breast disorders
CTCAE Term
Grade 1
Grade 2
Grade 3
Grade 4
Grade 5
Erectile dysfunction
Decrease in erectile function
(frequency or rigidity of
erections) but intervention
not indicated (e.g., medication
or use of mechanical device,
penile pump)
Decrease in erectile function
(frequency/rigidity of
erections), erectile
intervention indicated, (e.g.,
medication or mechanical
devices such as penile pump)
Decrease in erectile function
(frequency/rigidity of
erections) but erectile
intervention not helpful (e.g.,
medication or mechanical
devices such as penile pump);
placement of a permanent
penile prosthesis indicated
(not previously present)
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by the persistent or recurrent inability to achieve or to maintain an erection during sexual activity.
Navigational Note: -
Fallopian tube obstruction
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; elective
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by blockage of the normal flow of the contents in the fallopian tube.
Navigational Note: -
Feminization acquired
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by the development of secondary female sex characteristics in males due to extrinsic factors.
Navigational Note: -
Genital edema
Mild swelling or obscuration
of anatomic architecture on
close inspection
Readily apparent obscuration
of anatomic architecture;
obliteration of skin folds;
readily apparent deviation
from normal anatomic
contour
Lymphorrhea; gross deviation
from normal anatomic
contour; limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by swelling due to an excessive accumulation of fluid in the genitals.
Navigational Note: -
Gynecomastia
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic (e.g., pain or
psychosocial impact)
Severe symptoms; elective
operative intervention
indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by excessive development of the breasts in males.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 125
Reproductive system and breast disorders
CTCAE Term
Grade 1
Grade 2
Grade 3
Grade 4
Grade 5
Hematosalpinx
Minimal bleeding identified
on imaging study or
laparoscopy; intervention not
indicated
Moderate bleeding; medical
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the presence of blood in a fallopian tube.
Navigational Note: -
Irregular menstruation
Intermittent/irregular menses
for no more than 3
consecutive menstrual cycles
Intermittent/irregular menses
for more than 3 consecutive
menstrual cycles
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a change in cycle or duration of menses from baseline.
Navigational Note: Also consider Reproductive system and breast disorders: Premature menopause, Amenorrhea.
Lactation disorder
Mild changes in lactation, not
significantly affecting
production or expression of
breast milk
Changes in lactation,
significantly affecting breast
production or expression of
breast milk
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by disturbances of milk secretion. It is not necessarily related to pregnancy that is observed in females and can be observed in males.
Navigational Note: -
Menorrhagia
Mild; iron supplements
indicated
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
hormones)
Severe; transfusion indicated;
operative intervention
indicated (e.g., hysterectomy)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by abnormally heavy vaginal bleeding during menses.
Navigational Note: -
Nipple deformity
Asymptomatic; asymmetry
with slight retraction and/or
thickening of the nipple
areolar complex
Symptomatic; asymmetry of
nipple areolar complex with
moderate retraction and/or
thickening of the nipple
areolar complex
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a malformation of the nipple.
Navigational Note: -
Oligospermia
Sperm concentration > 0 to <
15 million/ml
-
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease in the number of spermatozoa in the semen.
Navigational Note: -
Ovarian hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the ovary.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 126
Reproductive system and breast disorders
CTCAE Term
Grade 1
Grade 2
Grade 3
Grade 4
Grade 5
Ovarian rupture
Asymptomatic clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic and intervention
not indicated
Transfusion; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by tearing or disruption of the ovarian tissue.
Navigational Note: -
Ovulation pain
-
Present
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in one side of the abdomen between menstrual cycles, around the time of the discharge of the ovum from the
ovarian follicle.
Navigational Note: -
Pelvic floor muscle weakness
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic, not interfering
with bladder, bowel, or
vaginal function; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a reduction in the strength of the muscles of the pelvic floor.
Navigational Note: -
Pelvic pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the pelvis.
Navigational Note: -
Penile pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the penis.
Navigational Note: -
Perineal pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the area between the genital organs and the anus.
Navigational Note: -
Premature menopause
-
Present
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by premature ovarian failure. Symptoms may include hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, and a decrease in sex drive. Laboratory findings
include elevated luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH.)
Navigational Note: -
Prostatic hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the prostate gland.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 127
Reproductive system and breast disorders
CTCAE Term
Grade 1
Grade 2
Grade 3
Grade 4
Grade 5
Prostatic obstruction
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; elective
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by compression of the urethra secondary to enlargement of the prostate gland. This results in voiding difficulties (straining to void, slow urine
stream, and incomplete emptying of the bladder).
Navigational Note: -
Prostatic pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the prostate gland.
Navigational Note: -
Scrotal pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the scrotal area.
Navigational Note: -
Spermatic cord hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the spermatic cord.
Navigational Note: -
Spermatic cord obstruction
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; elective
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by blockage of the normal flow of the contents of the spermatic cord.
Navigational Note: -
Testicular disorder
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic but not
interfering with sexual
function; intervention not
indicated; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; interfering
with sexual function; limiting
self care ADL; intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by abnormal function or appearance of the testis.
Navigational Note: Also consider Reproductive system and breast disorders: Genital edema or other AE terms in the Renal and urinary disorders SOC or Reproductive system and breast
disorders SOC.
Testicular hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the testis.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 128
Reproductive system and breast disorders
CTCAE Term
Grade 1
Grade 2
Grade 3
Grade 4
Grade 5
Testicular pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the testis.
Navigational Note: -
Uterine fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the uterus and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Uterine hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the uterus.
Navigational Note: -
Uterine obstruction
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; elective
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by blockage of the uterine outlet.
Navigational Note: -
Uterine pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the uterus.
Navigational Note: -
Vaginal discharge
Mild vaginal discharge
(greater than baseline for
patient)
Moderate to heavy vaginal
discharge; use of perineal pad
or tampon indicated
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by vaginal secretions. Mucus produced by the cervical glands is discharged from the vagina naturally, especially during the childbearing years.
Navigational Note: -
Vaginal dryness
Mild vaginal dryness not
interfering with sexual
function
Moderate vaginal dryness
interfering with sexual
function or causing frequent
discomfort
Severe vaginal dryness
resulting in dyspareunia or
severe discomfort
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an uncomfortable feeling of itching and burning in the vagina.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 129
Reproductive system and breast disorders
CTCAE Term
Grade 1
Grade 2
Grade 3
Grade 4
Grade 5
Vaginal fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the vagina and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Vaginal hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the vagina.
Navigational Note: -
Vaginal inflammation
Mild discomfort or pain,
edema, or redness
Moderate discomfort or pain,
edema, or redness; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe discomfort or pain,
edema, or redness; limiting
self care ADL; small areas of
mucosal ulceration
Life-threatening
consequences; widespread
areas of mucosal ulceration;
urgent intervention indicated
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation involving the vagina. Symptoms may include redness, edema, marked discomfort and an increase in vaginal discharge.
Navigational Note: -
Vaginal obstruction
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; elective
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by blockage of vaginal canal.
Navigational Note: -
Vaginal pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the vagina.
Navigational Note: -
Vaginal perforation
-
Invasive intervention not
indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a rupture in the vaginal wall.
Navigational Note: -
Vaginal stricture
Asymptomatic; mild vaginal
shortening or narrowing
Vaginal narrowing and/or
shortening not interfering
with physical examination
Vaginal narrowing and/or
shortening interfering with
the use of tampons, sexual
activity or physical
examination
-
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a narrowing of the vaginal canal.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 130
Reproductive system and breast disorders
CTCAE Term
Grade 1
Grade 2
Grade 3
Grade 4
Grade 5
Reproductive system and
breast disorders - Other,
specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 131
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Adult respiratory distress
syndrome
-
-
Present with radiologic
findings; intubation not
indicated
Life-threatening respiratory or
hemodynamic compromise;
intubation or urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by progressive and life-threatening pulmonary distress in the absence of an underlying pulmonary condition, usually following major trauma or
surgery.
Navigational Note: -
Allergic rhinitis
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an inflammation of the nasal mucous membranes caused by an IgE-mediated response to external allergens. The inflammation may also involve
the mucous membranes of the sinuses, eyes, middle ear, and pharynx. Symptoms include sneezing, nasal congestion, rhinorrhea and itching.
Navigational Note: -
Apnea
-
-
Present; medical intervention
indicated
Life-threatening respiratory or
hemodynamic compromise;
intubation or urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by cessation of breathing.
Navigational Note: -
Aspiration
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Altered eating habits;
coughing or choking episodes
after eating or swallowing;
medical intervention indicated
(e.g., suction or oxygen)
Dyspnea and pneumonia
symptoms (e.g., aspiration
pneumonia); hospitalization
indicated; unable to aliment
orally
Life-threatening respiratory or
hemodynamic compromise;
intubation or urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inhalation of solids or liquids into the lungs.
Navigational Note: -
Atelectasis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic (e.g., dyspnea,
cough); medical intervention
indicated (e.g., chest
physiotherapy, suctioning);
bronchoscopic suctioning
Supplemental oxygen
indicated; hospitalization or
elective operative
intervention indicated (e.g.,
stent, laser)
Life-threatening respiratory or
hemodynamic compromise;
intubation or urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the collapse of part or the entire lung.
Navigational Note: -
Bronchial fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the bronchus and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 132
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Bronchial obstruction
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic (e.g., mild
wheezing); endoscopic
evaluation indicated;
radiographic evidence of
atelectasis/lobar collapse;
medical management
indicated (e.g., steroids,
bronchodilators)
Shortness of breath with
stridor; endoscopic
intervention indicated (e.g.,
laser, stent placement)
Life-threatening respiratory or
hemodynamic compromise;
intubation or urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by blockage of a bronchus passage, most often by bronchial secretions and exudates.
Navigational Note: -
Bronchial stricture
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic (e.g., rhonchi or
wheezing) but without
respiratory distress; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
steroids, bronchodilators)
Shortness of breath with
stridor; endoscopic
intervention indicated (e.g.,
laser, stent placement)
Life-threatening respiratory or
hemodynamic compromise;
intubation or urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a narrowing of the bronchial tube.
Navigational Note: -
Bronchopleural fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Hospitalization; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between a bronchus and the pleural cavity.
Navigational Note: -
Bronchopulmonary
hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms; invasive
intervention not indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; intubation or
urgent intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the bronchial wall and/or lung parenchyma.
Navigational Note: -
Bronchospasm
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Limiting self care ADL;
supplemental oxygen
indicated
Life-threatening respiratory or
hemodynamic compromise;
intubation or urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sudden contraction of the smooth muscles of the bronchial wall.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 133
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Chylothorax
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
fat-restricted diet);
thoracentesis or tube
drainage indicated
Severe symptoms; elective
operative intervention
indicated
Life-threatening respiratory or
hemodynamic compromise;
intubation or urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by milky pleural effusion (abnormal collection of fluid) resulting from accumulation of lymph fluid in the pleural cavity.
Navigational Note: -
Cough
Mild symptoms;
nonprescription intervention
indicated
Moderate symptoms, medical
intervention indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by sudden, often repetitive, spasmodic contraction of the thoracic cavity, resulting in violent release of air from the lungs and usually accompanied
by a distinctive sound.
Navigational Note: -
Dyspnea
Shortness of breath with
moderate exertion
Shortness of breath with
minimal exertion; limiting
instrumental ADL
Shortness of breath at rest;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an uncomfortable sensation of difficulty breathing.
Navigational Note: -
Epistaxis
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
nasal packing, cauterization;
topical vasoconstrictors)
Transfusion; invasive
intervention indicated (e.g.,
hemostasis of bleeding site)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the nose.
Navigational Note: -
Hiccups
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; interfering
with sleep; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by repeated gulp sounds that result from an involuntary opening and closing of the glottis. This is attributed to a spasm of the diaphragm.
Navigational Note: -
Hoarseness
Mild or intermittent voice
change; fully understandable;
self-resolves
Moderate or persistent voice
changes; may require
occasional repetition but
understandable on telephone;
medical evaluation indicated
Severe voice changes
including predominantly
whispered speech
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by harsh and raspy voice arising from or spreading to the larynx.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 134
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Hypoxia
-
Decreased oxygen saturation
with exercise (e.g., pulse
oximeter <88%); intermittent
supplemental oxygen
Decreased oxygen saturation
at rest (e.g., pulse oximeter
<88% or PaO2 <=55 mm Hg)
Life-threatening airway
compromise; urgent
intervention indicated (e.g.,
tracheotomy or intubation)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease in the level of oxygen in the body.
Navigational Note: -
Laryngeal edema
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
dexamethasone, epinephrine,
antihistamines)
Stridor; respiratory distress;
hospitalization indicated
Life-threatening airway
compromise; urgent
intervention indicated (e.g.,
tracheotomy or intubation)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by swelling due to an excessive accumulation of fluid in the larynx.
Navigational Note: -
Laryngeal fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the larynx and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Laryngeal hemorrhage
Mild cough or trace
hemoptysis; laryngoscopic
findings
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated (e.g.,
tracheotomy or intubation)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the larynx.
Navigational Note: -
Laryngeal inflammation
Mild sore throat; raspy voice
Moderate sore throat;
analgesics indicated
Severe throat pain;
endoscopic intervention
indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an inflammation involving the larynx.
Navigational Note: -
Laryngeal mucositis
Endoscopic findings only; mild
discomfort with normal intake
Moderate pain, analgesics
indicated; altered oral intake;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe pain; severely altered
eating/swallowing; medical
intervention indicated
Life-threatening airway
compromise; urgent
intervention indicated (e.g.,
tracheotomy or intubation)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by ulceration or inflammation involving the mucous membrane of the larynx.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 135
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Laryngeal obstruction
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic (e.g., noisy
airway breathing), no
respiratory distress; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
steroids); limiting
instrumental ADL
Limiting self care ADL; stridor;
endoscopic intervention
indicated (e.g., stent, laser)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by blockage of the laryngeal airway.
Navigational Note: -
Laryngeal stenosis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic (e.g., noisy
airway breathing), no
respiratory distress; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
steroids); limiting
instrumental ADL
Limiting self care ADL; stridor;
endoscopic intervention
indicated (e.g., stent, laser)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a narrowing of the laryngeal airway.
Navigational Note: -
Laryngopharyngeal
dysesthesia
Mild symptoms; no anxiety;
intervention not indicated
Moderate symptoms; mild
anxiety, but no dyspnea; short
duration of observation
and/or anxiolytic indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; dyspnea
and swallowing difficulty;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an uncomfortable persistent sensation in the area of the laryngopharynx.
Navigational Note: -
Laryngospasm
-
Transient episode;
intervention not indicated
Recurrent episodes;
noninvasive intervention
indicated (e.g., breathing
technique, pressure point
massage)
Persistent or severe episodes
associated with syncope;
urgent intervention indicated
(e.g., fiberoptic laryngoscopy,
intubation, botox injection)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by paroxysmal spasmodic muscular contraction of the vocal cords.
Navigational Note: -
Mediastinal hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated; radiologic
evidence only
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the mediastinum.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 136
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Nasal congestion
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
Associated with bloody nasal
discharge or epistaxis
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by obstruction of the nasal passage due to mucosal edema.
Navigational Note: -
Oropharyngeal pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; altered oral
intake; non-narcotics
initiated; topical analgesics
initiated
Severe pain; severely altered
eating/swallowing; narcotics
initiated; requires parenteral
nutrition
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the oropharynx.
Navigational Note: -
Pharyngeal fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the pharynx and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Pharyngeal hemorrhage
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms;
intervention indicated
Transfusion indicated;
invasive intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; intubation or
urgent intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the pharynx.
Navigational Note: -
Pharyngeal mucositis
Endoscopic findings only;
minimal symptoms with
normal oral intake; mild pain
but analgesics not indicated
Moderate pain, analgesics
indicated; altered oral intake;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe pain; unable to
adequately aliment or hydrate
orally; limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by ulceration or inflammation involving the mucous membrane of the pharynx.
Navigational Note: -
Pharyngeal necrosis
-
-
Inability to aliment adequately
by GI tract; invasive
intervention indicated; tube
feeding or TPN indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the pharynx.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 137
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Pharyngeal stenosis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic (e.g., noisy
airway breathing), no
respiratory distress; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
steroids); limiting
instrumental ADL
Limiting self care ADL; stridor;
endoscopic intervention
indicated (e.g., stent, laser)
Life-threatening airway
compromise; urgent
intervention indicated (e.g.,
tracheotomy or intubation)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a narrowing of the pharyngeal airway.
Navigational Note: -
Pharyngolaryngeal pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the pharyngolaryngeal region.
Navigational Note: -
Pleural effusion
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; intervention
indicated (e.g., diuretics or
therapeutic thoracentesis)
Symptomatic with respiratory
distress and hypoxia;
operative intervention
including chest tube or
pleurodesis indicated
Life-threatening respiratory or
hemodynamic compromise;
intubation or urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an increase in amounts of fluid within the pleural cavity. Symptoms include shortness of breath, cough and marked chest discomfort.
Navigational Note: -
Pleural hemorrhage
Asymptomatic; mild
hemorrhage confirmed by
thoracentesis
Symptomatic or associated
with pneumothorax; chest
tube drainage indicated
>1000 ml of blood evacuated;
persistent bleeding (150-200
ml/hr for 2 - 4 hr); persistent
transfusion indicated; elective
operative intervention
indicated; hospitalization
Life-threatening
consequences; intubation or
urgent intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the pleural cavity.
Navigational Note: -
Pleuritic pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the pleura.
Navigational Note: -
Pneumonitis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL; oxygen indicated
Life-threatening respiratory
compromise; urgent
intervention indicated (e.g.,
tracheotomy or intubation)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation focally or diffusely affecting the lung parenchyma.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 138
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Pneumothorax
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; intervention
indicated
Sclerosis and/or operative
intervention indicated;
hospitalization indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by abnormal presence of air in the pleural cavity resulting in the collapse of the lung.
Navigational Note: -
Postnasal drip
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by excessive mucous secretion in the back of the nasal cavity or throat, causing sore throat and/or coughing.
Navigational Note: -
Productive cough
Occasional/minimal
production of sputum with
cough
Moderate sputum production;
limiting instrumental ADL
Persistent or copious
production of sputum; limiting
self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by expectorated secretions upon coughing.
Navigational Note: -
Pulmonary edema
Radiologic findings only;
minimal dyspnea on exertion
Moderate dyspnea on
exertion; medical intervention
indicated; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe dyspnea or dyspnea at
rest; oxygen indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening respiratory
compromise; urgent
intervention or intubation
with ventilatory support
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by accumulation of fluid in the lung tissues that causes a disturbance of the gas exchange that may lead to respiratory failure.
Navigational Note: -
Pulmonary fibrosis
Radiologic pulmonary fibrosis
<25% of lung volume
associated with hypoxia
Evidence of pulmonary
hypertension; radiographic
pulmonary fibrosis 25 - 50%
associated with hypoxia
Severe hypoxia; evidence of
right-sided heart failure;
radiographic pulmonary
fibrosis >50 - 75%
Life-threatening
consequences (e.g.,
hemodynamic/pulmonary
complications); intubation
with ventilatory support
indicated; radiographic
pulmonary fibrosis >75% with
severe honeycombing
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the replacement of the lung tissue by connective tissue, leading to progressive dyspnea, respiratory failure or right heart failure.
Navigational Note: -
Pulmonary fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the lung and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 139
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Pulmonary hypertension
Minimal dyspnea; findings on
physical exam or other
evaluation
Moderate dyspnea, cough;
requiring evaluation by
cardiac catheterization and
medical intervention
Severe symptoms, associated
with hypoxia, right heart
failure; oxygen indicated
Life-threatening airway
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated (e.g.,
tracheotomy or intubation)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an increase in pressure within the pulmonary circulation due to lung or heart disorder.
Navigational Note: -
Respiratory failure
-
-
-
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention, intubation, or
ventilatory support indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by impaired gas exchange by the respiratory system resulting in hypoxia and a decrease in oxygenation of the tissues that may be associated with
an increase in arterial levels of carbon dioxide.
Navigational Note: -
Retinoic acid syndrome
Fluid retention; <3 kg of
weight gain; intervention with
fluid restriction and/or
diuretics indicated
Moderate signs or symptoms;
steroids indicated
Severe symptoms;
hospitalization indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; ventilatory
support indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by weight gain, dyspnea, pleural and pericardial effusions, leukocytosis and/or renal failure originally described in patients treated with all-trans
retinoic acid.
Navigational Note: -
Rhinorrhea
Present
-
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by excessive mucous secretions draining from the nose.
Navigational Note: -
Sinus disorder
Asymptomatic mucosal
crusting; blood-tinged
secretions
Symptomatic stenosis or
edema/narrowing interfering
with airflow; limiting
instrumental ADL
Stenosis with significant nasal
obstruction; limiting self care
ADL
Necrosis of soft tissue or
bone; urgent operative
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by involvement of the paranasal sinuses.
Navigational Note: -
Sinus pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the face, between the eyes, or upper teeth originating from the sinuses.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 140
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Sleep apnea
Snoring and nocturnal sleep
arousal without apneic
periods
Moderate apnea and oxygen
desaturation; excessive
daytime sleepiness; medical
evaluation indicated; limiting
instrumental ADL
Oxygen desaturation;
associated with pulmonary
hypertension; medical
intervention indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Cardiovascular or
neuropsychiatric symptoms;
urgent operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by cessation of breathing for short periods during sleep.
Navigational Note: -
Sneezing
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by the involuntary expulsion of air from the nose.
Navigational Note: -
Sore throat
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL; limiting ability to
swallow
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by marked discomfort in the throat.
Navigational Note: -
Stridor
-
-
Respiratory distress limiting
self care ADL; medical
intervention indicated
Life-threatening airway
compromise; urgent
intervention indicated (e.g.,
tracheotomy or intubation)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a high pitched breathing sound due to laryngeal or upper airway obstruction.
Navigational Note: -
Tracheal fistula
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic, invasive
intervention not indicated
Invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the trachea and another organ or anatomic site.
Navigational Note: -
Tracheal mucositis
Endoscopic findings only;
minimal hemoptysis, pain, or
respiratory symptoms
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe pain; hemorrhage or
respiratory symptoms;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an inflammation or ulceration involving the mucous membrane of the trachea.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 141
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Tracheal stenosis
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic (e.g., noisy
airway breathing), no
respiratory distress; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
steroids); limiting
instrumental ADL
Stridor or respiratory distress
limiting self care ADL; invasive
intervention indicated (e.g.,
stent, laser)
Life-threatening airway
compromise; urgent
intervention indicated (e.g.,
tracheotomy or intubation)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a narrowing of the trachea.
Navigational Note: -
Voice alteration
Mild or intermittent change
from normal voice
Moderate or persistent
change from normal voice;
still understandable
Severe voice changes
including predominantly
whispered speech; may
require frequent repetition or
face-to-face contact for
understandability; may
require assistive technology
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a change in the sound and/or speed of the voice.
Navigational Note: -
Wheezing
Detectable airway noise with
minimal symptoms
Moderate symptoms; medical
intervention indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Severe respiratory symptoms
limiting self care ADL; oxygen
therapy or hospitalization
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a high-pitched, whistling sound during breathing. It results from the narrowing or obstruction of the respiratory airways.
Navigational Note: -
Respiratory, thoracic and
mediastinal disorders - Other,
specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 142
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Alopecia
Hair loss of <50% of normal
for that individual that is not
obvious from a distance but
only on close inspection; a
different hair style may be
required to cover the hair loss
but it does not require a wig
or hair piece to camouflage
Hair loss of >=50% normal for
that individual that is readily
apparent to others; a wig or
hair piece is necessary if the
patient desires to completely
camouflage the hair loss;
associated with psychosocial
impact
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease in density of hair compared to normal for a given individual at a given age and body location.
Navigational Note: -
Body odor
Mild odor; physician
intervention not indicated;
self care interventions
Pronounced odor;
psychosocial impact; patient
seeks medical intervention
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal body smell resulting from the growth of bacteria on the body.
Navigational Note: -
Bullous dermatitis
Asymptomatic; blisters
covering <10% BSA
Blisters covering 10 - 30%
BSA; painful blisters; limiting
instrumental ADL
Blisters covering >30% BSA;
limiting self care ADL
Blisters covering >30% BSA;
associated with fluid or
electrolyte abnormalities; ICU
care or burn unit indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation of the skin characterized by the presence of bullae which are filled with fluid.
Navigational Note: If infectious, consider Infections and infestations: Rash pustular or other site-specific Infections and infestations term.
Dry skin
Covering <10% BSA and no
associated erythema or
pruritus
Covering 10 - 30% BSA and
associated with erythema or
pruritus; limiting instrumental
ADL
Covering >30% BSA and
associated with pruritus;
limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by flaky and dull skin; the pores are generally fine, the texture is a papery thin texture.
Navigational Note: -
Eczema
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; additional medical
intervention over baseline not
indicated
Moderate; topical or oral
intervention indicated;
additional medical
intervention over baseline
indicated
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; IV intervention
indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by skin which becomes itchy, red, inflamed, crusty, thick, scaly, and/or forms blisters.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 143
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Erythema multiforme
Target lesions covering <10%
BSA and not associated with
skin tenderness
Target lesions covering 10 -
30% BSA and associated with
skin tenderness
Target lesions covering >30%
BSA and associated with oral
or genital erosions
Target lesions covering >30%
BSA; associated with fluid or
electrolyte abnormalities; ICU
care or burn unit indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by target lesions (a pink-red ring around a pale center).
Navigational Note: -
Erythroderma
-
Erythema covering >90% BSA
without associated symptoms;
limiting instrumental ADL
Erythema covering >90% BSA
with associated symptoms
(e.g., pruritus or tenderness);
limiting self care ADL
Erythema covering >90% BSA
with associated fluid or
electrolyte abnormalities; ICU
care or burn unit indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by generalized inflammatory erythema and exfoliation. The inflammatory process involves > 90% of the body surface area.
Navigational Note: -
Fat atrophy
Covering <10% BSA and
asymptomatic
Covering 10 - 30% BSA and
associated with erythema or
tenderness; limiting
instrumental ADL
Covering >30% BSA;
associated with erythema or
tenderness; limiting self-care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by shrinking of adipose tissue.
Navigational Note: -
Hair color changes
Present
-
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by change in hair color or loss of normal pigmentation.
Navigational Note: -
Hair texture abnormal
Present
-
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a change in the way the hair feels.
Navigational Note: -
Hirsutism
In women, increase in length,
thickness or density of hair in
a male distribution that the
patient is able to camouflage
by periodic shaving, bleaching,
or removal of hair
In women, increase in length,
thickness or density of hair in
a male distribution that
requires daily shaving or
consistent destructive means
of hair removal to
camouflage; associated with
psychosocial impact
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by the presence of excess hair growth in women in anatomic sites where growth is considered to be a secondary male characteristic and under
androgen control (beard, moustache, chest, abdomen).
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 144
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Hyperhidrosis
Limited to one site (palms,
soles, or axillae); self care
interventions
Involving >1 site; patient seeks
medical intervention;
associated with psychosocial
impact
Associated with
electrolyte/hemodynamic
imbalance
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by excessive sweating.
Navigational Note: Synonym: Night sweats,
diaphoresis
Hyperkeratosis
Present
-
Limiting self-care ADLs
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a thickening of the outer layer of the skin.
Navigational Note: -
Hypertrichosis
Increase in length, thickness
or density of hair that the
patient is either able to
camouflage by periodic
shaving or removal of hairs or
is not concerned enough
about the overgrowth to use
any form of hair removal
Increase in length, thickness
or density of hair at least on
the usual exposed areas of the
body [face (not limited to
beard/moustache area)
plus/minus arms] that
requires frequent shaving or
use of destructive means of
hair removal to camouflage;
associated with psychosocial
impact
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by hair density or length beyond the accepted limits of normal in a particular body region, for a particular age or race.
Navigational Note: -
Hypohidrosis
-
Symptomatic; limiting
instrumental ADL
Increase in body temperature;
limiting self care ADL
Heat stroke
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by reduced sweating.
Navigational Note: -
Lipohypertrophy
Asymptomatic and covering
<10% BSA
Covering 10 - 30% BSA and
associated tenderness;
limiting instrumental ADL
Covering >30% BSA and
associated tenderness and
narcotics or NSAIDs indicated;
lipohypertrophy; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by hypertrophy of the subcutaneous adipose tissue at the site of multiple subcutaneous injections of insulin.
Navigational Note: -
Nail changes
Present
-
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a change in the nails.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 145
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Nail discoloration
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only
-
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a change in the color of the nail plate.
Navigational Note: -
Nail loss
Asymptomatic separation of
the nail bed from the nail
plate or nail loss
Symptomatic separation of
the nail bed from the nail
plate or nail loss; limiting
instrumental ADL
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by loss of all or a portion of the nail.
Navigational Note: -
Nail ridging
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
-
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by vertical or horizontal ridges on the nails.
Navigational Note: -
Pain of skin
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the skin.
Navigational Note: -
Palmar-plantar
erythrodysesthesia syndrome
Minimal skin changes or
dermatitis (e.g., erythema,
edema, or hyperkeratosis)
without pain
Skin changes (e.g., peeling,
blisters, bleeding, fissures,
edema, or hyperkeratosis)
with pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe skin changes (e.g.,
peeling, blisters, bleeding,
fissures, edema, or
hyperkeratosis) with pain;
limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by redness, marked discomfort, swelling, and tingling in the palms of the hands or the soles of the feet. Also known as Hand-Foot Syndrome.
Navigational Note: -
Photosensitivity
Painless erythema and
erythema covering <10% BSA
Tender erythema covering 10
- 30% BSA
Erythema covering >30% BSA
and erythema with blistering;
photosensitivity; oral
corticosteroid therapy
indicated; pain control
indicated (e.g., narcotics or
NSAIDs)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an increase in sensitivity of the skin to light.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 146
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Pruritus
Mild or localized; topical
intervention indicated
Widespread and intermittent;
skin changes from scratching
(e.g., edema, papulation,
excoriations, lichenification,
oozing/crusts); oral
intervention indicated;
limiting instrumental ADL
Widespread and constant;
limiting self care ADL or sleep;
systemic corticosteroid or
immunosuppressive therapy
indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an intense itching sensation.
Navigational Note: -
Purpura
Combined area of lesions
covering <10% BSA
Combined area of lesions
covering 10 - 30% BSA;
bleeding with trauma
Combined area of lesions
covering >30% BSA;
spontaneous bleeding
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by hemorrhagic areas of the skin and mucous membrane. Newer lesions appear reddish in color. Older lesions are usually a darker purple color and
eventually become a brownish-yellow color.
Navigational Note: -
Rash acneiform
Papules and/or pustules
covering <10% BSA, which
may or may not be associated
with symptoms of pruritus or
tenderness
Papules and/or pustules
covering 10 - 30% BSA, which
may or may not be associated
with symptoms of pruritus or
tenderness; associated with
psychosocial impact; limiting
instrumental ADL; papules
and/or pustules covering >
30% BSA with or without mild
symptoms
Papules and/or pustules
covering >30% BSA with
moderate or severe
symptoms; limiting self-care
ADL; associated with local
superinfection with oral
antibiotics indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; papules and/or
pustules covering any % BSA,
which may or may not be
associated with symptoms of
pruritus or tenderness and are
associated with extensive
superinfection with IV
antibiotics indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an eruption of papules and pustules, typically appearing in face, scalp, upper chest and back.
Navigational Note: -
Rash maculo-papular
Macules/papules covering
<10% BSA with or without
symptoms (e.g., pruritus,
burning, tightness)
Macules/papules covering 10 -
30% BSA with or without
symptoms (e.g., pruritus,
burning, tightness); limiting
instrumental ADL; rash
covering > 30% BSA with or
without mild symptoms
Macules/papules covering
>30% BSA with moderate or
severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by the presence of macules (flat) and papules (elevated). Also known as morbillform rash, it is one of the most common cutaneous adverse events,
frequently affecting the upper trunk, spreading centripetally and associated with pruritis.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 147
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Scalp pain
Mild pain
Moderate pain; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe pain; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the skin covering the top and the back of the head.
Navigational Note: -
Skin atrophy
Covering <10% BSA;
associated with
telangiectasias or changes in
skin color
Covering 10 - 30% BSA;
associated with striae or
adnexal structure loss
Covering >30% BSA;
associated with ulceration
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by the degeneration and thinning of the epidermis and dermis.
Navigational Note: -
Skin hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation covering
<10% BSA; no psychosocial
impact
Hyperpigmentation covering
>10% BSA; associated
psychosocial impact
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by darkening of the skin due to excessive melanin deposition.
Navigational Note: -
Skin hypopigmentation
Hypopigmentation or
depigmentation covering
<10% BSA; no psychosocial
impact
Hypopigmentation or
depigmentation covering
>10% BSA; associated
psychosocial impact
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by loss of skin pigment (e.g., vitiligo).
Navigational Note: -
Skin induration
Mild induration, able to move
skin parallel to plane (sliding)
and perpendicular to skin
(pinching up)
Moderate induration, able to
slide skin, unable to pinch
skin; limiting instrumental ADL
Severe induration; unable to
slide or pinch skin; limiting
joint or orifice movement
(e.g., mouth, anus); limiting
self care ADL
Generalized; associated with
signs or symptoms of impaired
breathing or feeding
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by an area of hardness in the skin.
Navigational Note: -
Skin ulceration
Combined area of ulcers <1
cm; nonblanchable erythema
of intact skin with associated
warmth or edema
Combined area of ulcers 1 - 2
cm; partial thickness skin loss
involving skin or
subcutaneous fat
Combined area of ulcers >2
cm; full-thickness skin loss
involving damage to or
necrosis of subcutaneous
tissue that may extend down
to fascia
Any size ulcer with extensive
destruction, tissue necrosis, or
damage to muscle, bone, or
supporting structures with or
without full thickness skin loss
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a circumscribed, erosive lesion on the skin.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 148
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
-
-
Skin sloughing covering <10%
BSA with associated signs
(e.g., erythema, purpura,
epidermal detachment, and
mucous membrane
detachment)
Skin sloughing covering 10 -
30% BSA with associated signs
(e.g., erythema, purpura,
epidermal detachment and
mucous membrane
detachment)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by less than 10% total body skin area separation of dermis. The syndrome is thought to be a hypersensitivity complex affecting the skin and the
mucous membranes.
Navigational Note: -
Subcutaneous emphysema
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by air in the subcutaneous tissue.
Navigational Note: -
Telangiectasia
Telangiectasias covering <10%
BSA
Telangiectasias covering
>=10% BSA; associated with
psychosocial impact
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by local dilatation of small vessels resulting in red discoloration of the skin or mucous membranes.
Navigational Note: -
Toxic epidermal necrolysis
-
-
-
Skin sloughing covering >=30%
BSA with associated
symptoms (e.g., erythema,
purpura, or epidermal
detachment)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by greater than 30% total body skin area separation of dermis. The syndrome is thought to be a hypersensitivity complex affecting the skin and the
mucous membranes.
Navigational Note: -
Urticaria
Urticarial lesions covering
<10% BSA; topical
intervention indicated
Urticarial lesions covering 10 -
30% BSA; oral intervention
indicated
Urticarial lesions covering
>30% BSA; IV intervention
indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an itchy skin eruption characterized by wheals with pale interiors and well-defined red margins.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 149
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Skin and subcutaneous tissue
disorders - Other, specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 150
Social circumstances
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Social circumstances - Other,
specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 151
Surgical and medical procedures
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Surgical and medical
procedures - Other, specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 152
Vascular disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Arterial thromboembolism
-
-
Urgent intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; hemodynamic
or neurologic instability; organ
damage; loss of extremity(ies)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by occlusion of an arterial vessel by a blood clot that develops in an artery.
Navigational Note: Consider Nervous system disorders: TIA or Stroke for CNS-related events or Cardiac disorders: Myocardial infarction
Capillary leak syndrome
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms;
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by leakage of intravascular fluids into the extravascular space. This syndrome is observed in patients who demonstrate a state of generalized leaky
capillaries following shock syndromes, low-flow states, ischemia-reperfusion injuries, toxemias, medications, or poisoning. It can lead to generalized edema and multiple organ failure.
Navigational Note: -
Flushing
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Symptomatic, associated with
hypotension and/or
tachycardia; limiting self care
ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by episodic reddening of the skin, especially face, neck, or chest.
Navigational Note: -
Hematoma
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Minimally invasive evacuation
or aspiration indicated
Transfusion; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a localized collection of blood, usually clotted, in an organ, space, or tissue, due to a break in the wall of a blood vessel.
Navigational Note: -
Hot flashes
Mild symptoms; intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by an uncomfortable and temporary sensation of intense body warmth, flushing, sometimes accompanied by sweating upon cooling.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 153
Vascular disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Hypertension
Adult: Systolic BP 120 - 139
mm Hg or diastolic BP 80 - 89
mm Hg;
Pediatric: Systolic/diastolic BP
>90th percentile but< 95th
percentile;
Adolescent: BP ≥120/80 even
if < 95th percentile
Adult: Systolic BP 140 - 159
mm Hg or diastolic BP 90 - 99
mm Hg if previously WNL;
change in baseline medical
intervention indicated;
recurrent or persistent (>=24
hrs); symptomatic increase by
>20 mm Hg (diastolic) or to
>140/90 mm Hg;
monotherapy indicated
initiated;
Pediatric and adolescent:
Recurrent or persistent (>=24
hrs) BP >ULN; monotherapy
indicated; systolic and /or
diastolic BP between the 95th
percentile and 5 mmHg above
the 99th percentile;
Adolescent: Systolic between
130-139 or diastolic between
80-89 even if < 95th percentile
Adult: Systolic BP >=160 mm
Hg or diastolic BP >=100 mm
Hg; medical intervention
indicated; more than one drug
or more intensive therapy
than previously used
indicated;
Pediatric and adolescent:
Systolic and/or diastolic > 5
mmHg above the 99th
percentile
Adult and Pediatric: Life-
threatening consequences
(e.g., malignant hypertension,
transient or permanent
neurologic deficit,
hypertensive crisis); urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a pathological increase in blood pressure.
Navigational Note: -
Hypotension
Asymptomatic, intervention
not indicated
Non-urgent medical
intervention indicated
Medical intervention
indicated; hospitalization
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences and urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by a blood pressure that is below the normal expected for an individual in a given environment.
Navigational Note: -
Lymph leakage
-
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by the loss of lymph fluid into the surrounding tissue or body cavity.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 154
Vascular disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Lymphedema
Trace thickening or faint
discoloration
Marked discoloration;
leathery skin texture; papillary
formation; limiting
instrumental ADL
Severe symptoms; limiting self
care ADL
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by excessive fluid collection in tissues that causes swelling.
Navigational Note: -
Lymphocele
Asymptomatic; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms; invasive
intervention indicated
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a cystic lesion containing lymph.
Navigational Note: -
Peripheral ischemia
-
Brief (<24 hrs) episode of
ischemia managed medically
and without permanent
deficit
Prolonged (>=24 hrs) or
recurring symptoms and/or
invasive intervention
indicated
Life-threatening
consequences; evidence of
end organ damage; urgent
operative intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by impaired circulation to an extremity.
Navigational Note: -
Phlebitis
-
Present
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation of the wall of a vein.
Navigational Note: -
Superficial thrombophlebitis
-
Present
-
-
-
Definition: A disorder characterized by a blood clot and inflammation involving a superficial vein of the extremities.
Navigational Note: -
Superior vena cava syndrome
Asymptomatic; incidental
finding of SVC thrombosis
Symptomatic; medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
anticoagulation, radiation or
chemotherapy)
Severe symptoms; multi-
modality intervention
indicated (e.g.,
anticoagulation,
chemotherapy, radiation,
stenting)
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent multi-
modality intervention
indicated (e.g., lysis,
thrombectomy, surgery)
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by obstruction of the blood flow in the superior vena cava. Signs and symptoms include swelling and cyanosis of the face, neck, and upper arms,
cough, orthopnea and headache.
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC

CTCAE v5.0 – November 27, 2017 Page 155
Vascular disorders
CTCAE Term Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Thromboembolic event
Medical intervention not
indicated (e.g., superficial
thrombosis)
Medical intervention
indicated
Urgent medical intervention
indicated (e.g., pulmonary
embolism or intracardiac
thrombus)
Life-threatening
consequences with
hemodynamic or neurologic
instability
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by occlusion of a vessel by a thrombus that has migrated from a distal site via the blood stream.
Navigational Note: Consider Nervous system disorders: TIA or Stroke for CNS-related events. Use Vascular disorders: Arterial thromboembolism for arterial thrombi.
Vasculitis
Asymptomatic, intervention
not indicated
Moderate symptoms, medical
intervention indicated
Severe symptoms, medical
intervention indicated (e.g.,
steroids)
Life-threatening
consequences; evidence of
peripheral or visceral
ischemia; urgent intervention
indicated
Death
Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation involving the wall of a vessel.
Navigational Note: -
Vascular disorders - Other,
specify
Asymptomatic or mild
symptoms; clinical or
diagnostic observations only;
intervention not indicated
Moderate; minimal, local or
noninvasive intervention
indicated; limiting age-
appropriate instrumental ADL
Severe or medically significant
but not immediately life-
threatening; hospitalization or
prolongation of existing
hospitalization indicated;
limiting self care ADL
Life-threatening
consequences; urgent
intervention indicated
Death
Definition: -
Navigational Note: -
Back to TOC
