
USFK Pam 385-2
(30 May 2007)
Guide To Safe Driving
In Korea
(English)
USFK Pam 385-2
FOREWORD
The information contained in this pamphlet is largely based on the “Manual for Safe Driving”
prepared by the Korean Road Traffic Safety Authority. Regulatory requirements contained
herein are from the Korean Road Traffic Law and DOD and USFK directives.
There must be a logical explanation why driving in Korea is more difficult than in the U.S. At
first glance, you can clearly see that there are many vehicles and too few roads to handle the
traffic in an orderly manner. This situation may be the reason taxis and other vehicles drive
aggressively, weaving in and out of traffic. Buses and heavy trucks are required to use the
extreme right lanes or designated bus lanes but very often wander into the other lanes.
In addition, experience is a factor that affects driving in Korea. Other nationalities such as
Americans have been driving for many years. As a result, they have developed and learned
safe habits when around motor vehicles. In Korea, the motor vehicle growth was sudden,
therefore Koreans have not developed the safe habits found in the U.S. or other nations.
On every road in Korea, you can expect to find people. On expressways, extra caution is
required around road construction sites. Maintenance workers are prone to step into the path of
traffic and drivers must be prepared to stop immediately. Also watch out for workers when
going through tunnels and toll gates.
There are many pedestrians in Korea. Traditionally, they feel that they have as much right to
the use of roads as vehicles, and therefore expect vehicles to yield to them. This behavior
creates a real hazard for you as a driver. It is wise to reduce speed when driving around
pedestrians, especially children. Many Korean children have a preconceived notion that by
raising their arms a vehicle will stop to allow them to cross the street. Watch out for them and
be prepared to stop. Pedestrians also become confused while crossing roads, often stopping
suddenly and then moving into the paths of moving vehicles. A common occurrence is for
pedestrians to run or walk into traffic lanes from the front or rear of halted or parked vehicles
and other blind spots.
Although much of Korea is using motor vehicles as a means of transportation, there are still
some people who rely on other more economical means of transportation. Even more
unpredictable and hazardous are bicycles and motorcycles. They are usually overloaded and
unstable. Slow down and give them lots of room, as the operators are noted for weaving into
the paths of passing vehicles and passing on the right.
Other hazards on Korea roadways are created by nature. Two of the more notable ones are
potholes, created by the winter freezing and thawing process, and flooding. Slow down and
avoid potholes if you can. Potholes damage tires, oil pans, or even entire cars.
Driving in Korea is truly a challenge. Relax, be calm, be alert, and drive defensively!

*USFK Pam 385-2
HEADQUARTERS
UNITED STATES FORCES KOREA
UNIT #15237
APO AP 96205-5237
USFK Pamphlet XX May 2007
No. 385-2
Safety
GUIDE TO SAFE DRIVING IN KOREA
INTERIM CHANGES. Interim changes to this pamphlet are not official unless authenticated by
the Adjutant General. Users will destroy interim changes on their expiration date unless sooner
superseded or rescinded.
CONTENTS
SECTION
PARAGRAPH PAGE
I GENERAL
Purpose…………………………………………………….. 1 1
Scope……………………………………………………….. 2 1
II DRIVING RULES
Traffic Signals and Directions……………………………. 3 1
Traffic Lanes……………………………………………….. 4 2
Right-of-Way………………………………………………. 5 4
Speed Limits……………………………………………….. 6 5
Passing…………………………………………………….. 7 7
Driving through Intersection………………………………. 8 8
Vehicle Lights………………………………………………. 9 8
Driver Responsibilities…………………………………….. 10 9
Parking……………………………………………………… 11 10
Passenger and Cargo Limitations……………………….. 12 11
III SPECIAL PROVISIONS FOR EXPRESSWAY DRIVING
Rules for Travel……………………………………………. 13 12
Vehicle Breakdown………………………………………... 14 13
Driver Responsibilities on the Expressway……………... 15 13
____________________
*This pamphlet supersedes USFK Pam 385-2, 24 February 2003.

USFK Pam 385-2
PARAGRAPH
PAGE
IV TRAFFIC ACCIDENTS
Procedures…………………………………………………… 16 14
Special Provisions for Punishment………………………… 17 15
V ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS FOR MILITARY VEHICLES
Vehicle Movement…………………………………………… 18 16
Highway Condition Codes………………………………….. 19 17
Maximum USFK Vehicle Speed Limits……………………. 20 17
Traffic Point System…………………………………………. 21 17
Motorcycle, Moped and Bicycle Safety
Rules and Devices………………………………………… 22 17
2 APPENDIXES
A. Korean Road Traffic Signs……………………………………………………………. A-1
B. Useful English Korean Translations………………………………………………….. B-1
ii

USFK Pam 385-2
SECTION I. GENERAL
1. PURPOSE. This pamphlet provides essential information for USFK personnel operating
motor vehicles in the Republic of Korea (ROK).
2. SCOPE. This pamphlet applies to all USFK personnel operating motor vehicles in the ROK.
SECTION II. DRIVING RULES
3. TRAFFIC SIGNALS AND DIRECTIONS.
a. Drivers must obey traffic signals and directions.
(1) Drivers must obey signal lights, traffic signs, and directions given by a traffic police
officer or assistant traffic controller.
(2) When a police officer is directing traffic, drivers should follow the hand signals or the
flashlight signal by the police officer even if they are contradictory to traffic signals. Manual
control by the police takes priority.
b. Traffic signal lights and their meaning.
(1) Red signal--
(a) Vehicles must come to a complete stop before reaching the stop
line, pedestrian crosswalk, or intersection.
(b) A vehicle may turn right, provided it will not interfere with a
pedestrian or right-of way vehicle.
(2) Yellow signal--A driver must come to a complete stop before reaching the stop line,
a pedestrian crosswalk, or an intersection. If a driver is already in the intersection, he or she
must proceed as quickly as possible when safe.
(3) Green signal--Driver may either go straight ahead or turn right. No left turn may be
made unless otherwise directed.
(4) Green arrow signal--Driver may go in the direction of the green indicator.
(5) Lane direction and control signals--when lane direction control signals are placed
over separate lanes of a street or highway, vehicular traffic may travel in any lane over which a
green signal is lighted but will not enter or travel in any lane where a red signal is displayed.

USFK Pam 385-2
(6) Reversible Lane Signals--Within certain areas of major cities, the overhead X and
downward arrow signal devices are used where the direction of heavy traffic volume changes
during certain peak hours of the day. These signals override the lane marks/centerline on the
pavement.
(a) Red X Light--Vehicles will not use the lane shown with red X signal.
(b) Green Downward Arrow--Vehicles may proceed in the lane shown with green arrow
light.
(7) Flashing red (stop signal). Drivers of vehicles must stop at the marked stop line.
If there is no line, a stop must be made before entering the crosswalk on the near side of the
intersection, or at the point nearest the intersecting roadway where the driver has a view of
approaching traffic on the intersecting roadway. The right to proceed is subject to the rules
applicable after making a stop.
(8) Flashing yellow (caution signal). Drivers of vehicles may proceed through the
intersection while exercising due caution.
4. TRAFFIC LANES.
a. When traffic lanes are marked, drivers must stay in the lane for the type of vehicle is
permitted. Drivers may not drive over the lane divider line.
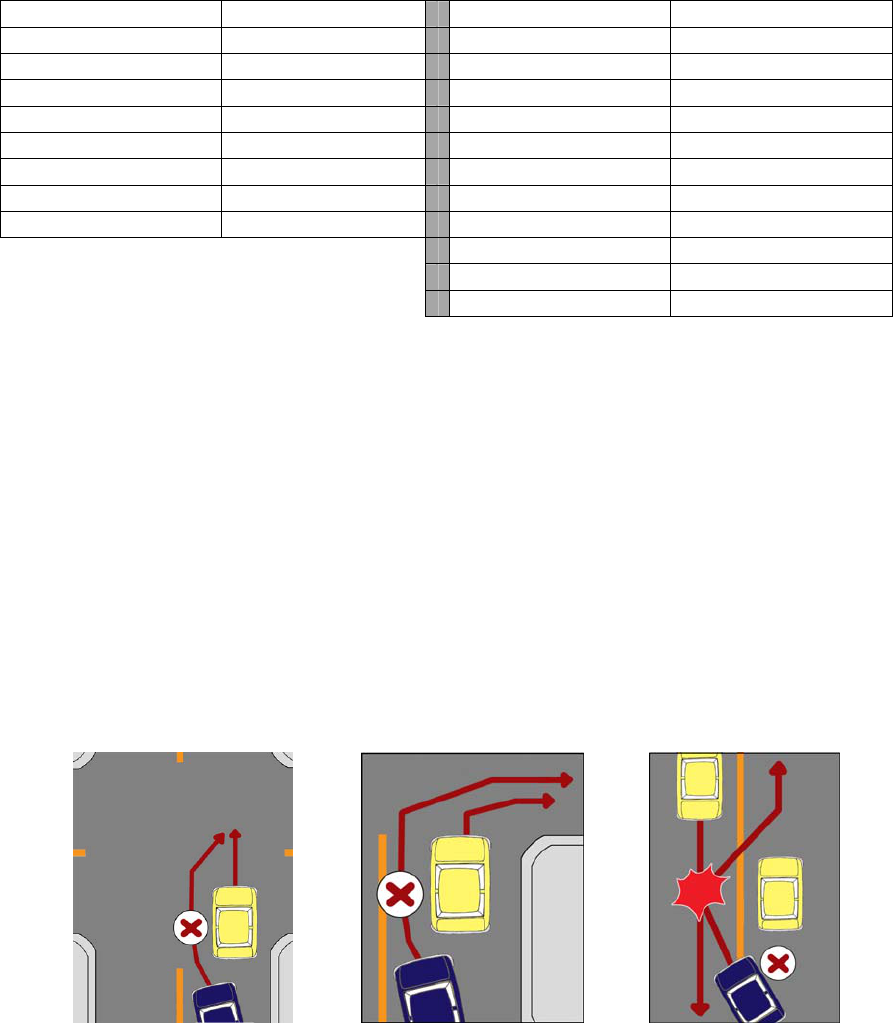
b. Examples of improper driving involving traffic lane markings are--
(1) Violation of lane usage.
(2) Straddling the lane divider line.
(3) Zigzagging over the lane divider.
(4) Changing lanes suddenly.
(5) Squeeze play.
(6) Continuously crossing many lanes.
(7) Changing lanes where prohibited. Yellow dotted or solid lines are centerlines.
Vehicles may not cross the solid lines. Where solid and dotted lines are shown together, a
vehicle on the side of dotted lines may cross the lines to pass. White dotted or solid lines are
lane dividers. A vehicle may not cross a solid lane divider to change lanes.
2

USFK Pam 385-2
c. Changing of lanes--
(1) Drivers must use directional signal at least 30 meters prior to turning (100 meters on
the expressway).
(2) Drivers must not change directions where prohibited by traffic signs.
(3) Changing lanes is prohibited when--
(a) There is insufficient distance to do so safely.
(b) Within 70 meters from the stop line at an intersection.
d. Bus lane.
(1) The bus lane (in cities) has been
established to limit traffic. It is marked by a blue line
and it designates a lane to be used only by scheduled
buses during rush hours. Supplemental signs
normally show the time when no vehicles other than
buses will travel in the lane. At intersections the bus
lane will have a broken or dash lines, vehicles other
than buses may enter this bus lane to make a right
turn or to immediately exit the main street.
(2) Median (center) bus lane in Seoul is
marked in red and it designates a lane to be used
only by buses 24 hours a day. Do not use this lane
for any reason. Drivers can only make U-turns at intersections where designated signs
are posted.
(3) Bus lanes on the expressway (between Seoul to Shintanjin expressway only) have
been designated to be used only by buses and 9-passenger vans having (at least 6
passengers) on weekends and holidays. It also is marked by a blue line.
Day Seoul Shintanjin Time
Saturday Both directions 0900 - 2100
Shintanjin to Seoul 0900 - 2300 Sunday and Holiday
Seoul to Shintanjin 0900 -2100
e. Unprotected left turns.
(1) An unprotected left turn is allowed only where the pertinent sign is installed.
(2) An unprotected left turn is allowed when your signal is green and when there is
sufficient clearance between you and the opposing traffic. In case of traffic conflict, however,
the responsibility for signaling falls onto left-turning vehicles.
f. A vehicle must travel over the lane designated by type of vehicle.
The example given below is a road with 3 lanes (one-way).
3

USFK Pam 385-2
1st Lane Sedans, station wagons, 1.5 ton and
below pickup trucks and vehicles of
similar design and function.
2nd lane Sedans, station wagons, 1.5 ton and
over pickup trucks, trucks, and buses.
3 Lanes
(One-way)
3rd lane Motorcycles, bicycles, carts, and trucks
towing trailers or other construction
trucks.
5. RIGHT-OF-WAY.
a. When an authorized emergency vehicle approaches, sounding a siren and/or showing a
flashing light, all traffic is required to yield the right-of-way by moving as far to the right side of
the road as possible and stopping until the emergency vehicle has passed. Don't stop in an
intersection.
b. Right-of-way laws define who has the right of way. NEVER INSIST ON TAKING THE
RIGHT-OF-WAY. Wait until it is yielded to you. All drivers have a moral and legal responsibility
to avoid a collision. Courtesy and cooperation among drivers helps prevent accidents and
makes driving more pleasant.
c. At intersections without STOP or YIELD signs or traffic signals--
(1) The first vehicle in the intersection should be allowed to go ahead.
(2) If two drivers reach an intersection from different streets at the same time, the driver
of the vehicle on the left must give the right-of-way to the vehicle on the right.
(3) When you see a vehicle crossing or beginning to cross the road you are driving on,
slow down, prepare to stop, and let it go ahead.
4

USFK Pam 385-2
d. Yield the right-of-way to faster moving vehicles. Regardless of the speed at which you
are traveling, you must not obstruct another driver so he cannot pass. When driving on a
roadway wide enough for more than one line of vehicles in your direction of travel, you must
move out of the left hand lane when another vehicle is close behind you and trying to pass.
Vehicles which must move at slower speeds must travel in the lane farthest to the right or in a
lane marked for them by signs.
e. Right-of-way is defined by road condition.
(1) On a narrow inclined road, the descending vehicle has right-of-way. Ascending
vehicle must pull over to the right.
(2) On a narrow road, a vehicle with passengers or cargo has the right-of-way.
Unloaded vehicle must pull over the right.
6. SPEED LIMITS. Speed limits in this paragraph do not apply to official USFK vehicles. (See
section V for official USFK vehicle speed limits.) Speed limits established by the law must be
observed. Often the speed limit is set by individual traffic signs. When these signs are used,
the speed limit indicated must be observed.
a. Speed reduction during inclement weather. Vehicle operator should reduce speed by 20
to 50 percent when driving in snow, fog, ice, or rain.
b. Speed and force of impact. (Pictorial comparison)
5

USFK Pam 385-2
c. Speed limit for local roads and expressways.
Type of Road Speed Limit Type of Vehicle
One to two lanes 60 Km/Hr (37M/Hr)
Ordinary/small
passenger vehicles,
vans, buses
Ordinary Road
More than two
lanes
80 Km/Hr (50 M/Hr) Ordinary/small
passenger vehicles,
vans, buses
Urban expressways
Exclusive
motorway
Maximum:
90 Km/Hr (56 M/Hr)
Minimum:
30 Km/Hr (19 M/Hr)
Ordinary/small
passenger vehicles,
vans, buses, cargo
vehicles,
Two or more lanes Maximum: 100 Km/Hr
(62 M/Hr)
Minimum: 50 Km/Hr
(31 M/Hr)
Ordinary/small
passenger vehicles,
vans, buses.
* Maximum speed limit
for trucks, construction
vehicles, and special
types of vehicle is 80
Km/Hr.
Single lane Maximum: 80Km/Hr
(50M/hr)
Minimum: 40Km/Hr
(25 M/Hr)
Ordinary/small
passenger vehicles, van,
buses, cargo vehicle,
construction vehicle,
special types of vehicle
Expressways
(All Except for the
Chungbu
Expressway)
Chungbu
Expressway #10
(Seoul-Daejon)
Chungang
Expressway #55
(Chunchon-Daegu)
Maximum: 110 Km/Hr
(66 M/Hr)
Minimum: 60 Km/Hr
(37 M/Hr)
Ordinary/small
passenger vehicles,
vans, buses, and cargo
vehicle.
* Maximum speed limit
for trucks, construction
vehicles, and special
types of vehicles is 90
Km/Hr.
6
USFK Pam 385-2
d. METRIC SYSTEM. The metric system is used in Korea. Speed limit or distance is shown in
meters or kilometers rather than miles or feet. For a quick mental conversion, multiply
kilometers by .6 for approximate miles, or multiply miles by 1.6 for approximate kilometers (e.g.,
40 km x .6 = 24 miles, or 30 miles x 1.6 = 48 kilometers). The chart below shows approximate
equivalents of common measurements used in driving.
FEET METERS
MILES KILOMETERS
1 0.3048 1 1.6093
10 3 10 16
15 4.6 15 24
100 30 19 30
200 61 25 40
300 91 31 50
400 122 37 60
500 152 43 70
50 80
55 88
62 100
7. PASSING.
a. Method of passing.
(1) To alert vehicles ahead, driver must indicate in advance the intention to pass.
(2) Driver must pass to the left of a vehicle traveling in the same direction. Safe passing
must be accomplished after insuring adequate clearance and the speed of vehicles in front of, to
the rear of, and on-coming traffic.
b. Places where passing is prohibited.
(1) On or near the top of steep grades.
(2) On curves.
7

USFK Pam 385-2
(3) Descending lane on a steep incline.
(4) Inside a tunnel.
(5) Intersections.
(6) Where prohibited by traffic signs.
8. DRIVING THROUGH INTERSECTIONS.
a. Method of entering.
(1) Vehicles turning right must first move slowly to the lane nearest the right hand curb.
(2) Vehicles turning left must do so from the left hand edge of the
lane closest to the centerline and from the center point of the intersection.
(3) Vehicles turning or going straight must move slowly to the
appropriate lane at least 70 meters prior to the white line at the
intersection.
b. Pedestrians. Pedestrians have the right-of -way at intersections
and marked pedestrian crosswalks.
(1) Drivers will yield to pedestrians crossing at green crossing
signals.
(2) Drivers will yield to pedestrians crossing the road at or near intersections where
traffic is not being controlled.
c. Extreme caution must be employed when entering into intersections after a traffic signal
has changed from red to green.
9. VEHICLE LIGHTS.
a. Requirements.
(1) Vehicles must have headlights, clearance lights, taillights, and license plate light lit
when driving at night. (Night is defined as a half hour after sunset until a half hour before
sunrise.)
(2) When objects cannot be seen within 100 meters during the day due to inclement
weather, lights must be turned on the same as if driving at night. When driving through fog, it is
best to use low beams.
8

USFK Pam 385-2
b. Use of low beams.
(1) When traveling through a high density traffic area at night, low beams must be
continuously used.
(2) When encountering on-coming traffic at night, dim the headlights to prevent other
drivers from being blinded.
(3) When a vehicle is stopped or parked on the roadway at night, parking lights or
clearance lights must be on.
10. DRIVER RESPONSIBILITIES.
a. Splashing. When driving in wet areas, drivers must not splash mud or water on
pedestrians.
b. Protection of children and the blind. When an unaccompanied child or a blind person
with a white cane is walking on the road, the vehicle must come to a complete stop.
c. Protection of pedestrians at crosswalks. When a pedestrian is in a crosswalk, vehicles
must stop completely. Slow down and prepare to stop when approaching a stopped or parked
vehicle near a crosswalk. Pedestrians may be crossing in front of the stopped or parked
vehicle.
d. Do not pass or overtake a school bus or shuttle bus when buses are being used to
receive or deliver passengers, as indicated by flashing lights or directed observation. Vehicles
traveling in either direction of a stopped school bus/shuttle bus must stop.
e. Driver attendance. When leaving a vehicle, drivers must make sure that the motor is
turned off, the parking brake is set, and the vehicle is locked so that it cannot be driven by
another person.
f. Use of horns. The use of horns is prohibited in designated areas within major cities.
9
USFK Pam 385-2
g. Safety restraint usage.
(1) All occupants of Government-owned vehicles, privately owned vehicles used for
official business, or any vehicle operated on a Federal installation, will wear manufacturer-
installed restraint systems.
(2) All USFK personnel will wear manufacturer-installed restraint systems at all times
while driving or riding in a POV, both on and off any USFK installation.
(3) Individuals will not ride in seats from which manufacturer-installed occupant restraint
systems have been removed or rendered inoperative.
(4) Drivers are responsible to have front and rear seat passengers wear seat belts.
h. Alcohol and drugs. Driving while under the influence of drugs or alcohol is prohibited.
The legal limit of intoxication is 0.5mg (0.05%) or more of alcohol per 1ml of blood.
i. Distractions. Operators of vehicles must pay strict attention while driving. As such,
vehicle operators must not wear commercial headsets/headphones or earplug radios. Drivers
must also not eat or smoke while driving.
j. Use of cellular phones while operating any motor vehicle, on or off military installations is
restricted. The restriction is that; cellular phones may only be used with “hands free“devices.
Earphones versions of hand free devices are prohibited.
11. PARKING.
a. Illegal parking significantly contributes to congestion and impedes the traffic flow on and
off military installation. All persons who have registered a vehicle are responsible for the proper
use of that vehicle, including parking. Accordingly, any individual whose registered vehicle has
accumulated more than two DD Form 1408 (Armed Forces Traffic Ticket) for parking violations
during a 60-day period may have his/her driving privileges suspended for a period of up to six
months at the discretion of the installation commander. The USFK standard for parking
offenses is cited below.
b. Prohibited parking. Except when necessary to avoid conflict with other traffic or to
comply with law or the direction of law enforcement personnel or an official traffic control device,
no person will park a vehicle--
(1) On a sidewalk.
(2) In a crosswalk.
(3) In front of driveways.
10
USFK Pam 385-2
(4) On a bridge or other elevated structure upon a roadway.
(5) Within a highway tunnel.
(6) On railroad or streetcar tracks.
(7) At any place narrow enough to make passing difficult, dangerous, or impossible.
(8) On a roadway or shoulder within 100 feet (30 meters) of the crest of a hill.
(9) Beside another vehicle parked parallel to the curb or on a roadway shoulder.
(10) Where official signs prohibit parking, when the curbing is painted yellow, or when
the roadway is marked in yellow or white.
(11) Within 20 feet (6 meters) of a fire hydrant, crosswalk, bus stop or intersection.
(12) Within 20 feet (6 meters) of a driveway to any fire station or similar emergency
facility, on the side of the street opposite the entrance to any fire station or similar emergency
facility, or within 75 feet (23 meters) of the entrance.
(13) Within 30 feet (9 meters) of the approach to any flashing signal, stop sign, yield
sign, or traffic control signal located at the side of the roadway.
(14) On a grassed or seeded area on U.S. military installations unless directed by
proper authority.
(15) Stop, park, or leave a vehicle attended or unattended where it is prohibited. In any
event, an unobstructed width of the highway opposite a vehicle must be left for the free passage
of other vehicles, and a clear view of the stopped vehicle must be available from a distance of
200 feet (60 meters) in each direction. Exceptions apply to vehicle operators who cannot
accomplish this action due to injury or due to the disabled condition of the vehicle.
12. PASSENGER AND CARGO LIMITATIONS.
a. Passenger limitation. The number of passengers will not exceed the designated seating
capacity.
b. Cargo limitation.
(1) Do not exceed manufacturer’s recommended cargo weight limitation of the vehicle.
(2) Contents of the cargo should not extend beyond one tenth of the vehicle length.
11

USFK Pam 385-2
(3) Width of cargo should not block or impair the rearview mirror.
c. Warning signs for cargo that exceeds the length limit.
(1) Daylight. A red cloth, 30cm x 50cm or larger, must be affixed to the farthest
protruding edge.
(2) Night time. A light or reflector must be fastened to the farthest protruding edge.
SECTION III. SPECIAL PROVISIONS FOR EXPESSWAY DRIVING
13. RULES FOR TRAVEL.
a. Right-of-way.
(1) An emergency vehicle has the right-of-way.
(2) A vehicle already on the expressway has the right-of-way.
b. Passing.
(1) When passing, drivers must turn on the directional signal, and then pass safely
using the left lane (passing lane). Upon completion of passing, he must return to the traveling
lane using the right turn signal.
(2) The following illustration depicts the use of directional signals when passing. When
passing on the expressway, directional signals are used to indicate a change, either to enter the
passing lane or the traveling lane. When in the passing lane, the directional signal must be
turned off.
12

USFK Pam 385-2
c. Yielding. Vehicles on expressways should yield to vehicles entering onto the expressway
by adjusting speed to permit entering vehicles to merge into traffic safely.
14. VEHICLE BREAKDOWN.
a. When a vehicle is disabled and unable to travel on the expressway, move the vehicle to
the right side of the roadway and place a triangular warning sign 100 meters or more behind the
vehicle. Turn on the vehicle’s hazard lights (flashers) to provide additional visibility. Flashers
may also be used by other motorists to warn of emergency conditions (accident on or near the
roadway, disabled vehicle, etc.).
b. At night, red flares or flashing
lights must be placed at least 200 meters
behind the disabled vehicle to provide
visibility within 500 meters from both
directions.
15. DRIVERS RESPONSIBILITIES ON THE EXPRESSWAY.
a. Drivers will ensure their passengers wear installed seatbelts.
b. Warning devices must be carried at all times including a red reflective
triangular warning sign or a flashing light. (Exception: Vehicles carrying flammable or explosive
materials will not use or carry flares.)
c. If you travel on weekends or holidays, respect the bus lane. See paragraph 4d, bus lane,
for further information.
13
USFK Pam 385-2
d. Don’t drive along the side or shoulder of the expressway and be aware of stalled and
emergency vehicles in this area.
e. Slow down when going in and out of a tunnel because your vision needs to adjust to the
change in lighting.
f. The safe distance between you and the vehicle in front of you is 100 meters (or two or
three seconds).
g. When you are in need of help from a Korean and you cannot communicate, use
Appendix B of this pamphlet to point out the message you wish to convey.
SECTION IV. TRAFFIC ACCIDENTS
16. PROCEDURES.
a. Driver responsibilities.
(1) Stop immediately.
(2) Aid the injured and take other necessary emergency measures.
(3) Report the following information to the nearest police officer:
(a) Location, time, and date of accident.
(b) Degree of injuries, to include fatalities.
(c) Type and degree of property damage.
(d) Other necessary information.
(4) Document the scene with photographs if possible. Recommend carrying a disposal
(instant) camera or cell phone camera.
b. A police officer may order drivers to do the following:
(1) Aid the injured.
(2) Remain at the scene of the accident if needed to prevent traffic hazards.
(3) Take other measures necessary for maintenance of traffic safety.
c. Drivers leaving the scene of the accident without taking necessary actions will be subject
to severe punishment.
14

USFK Pam 385-2
d. If you encounter language problems with Koreans involved, show your USFK FL 1EK
(HQ USFK SOFA card) or appendix B of this pamphlet, and point out items that you desire to
express.
17. SPECIAL PROVISIONS FOR PUNISHMENT.
a. If the driver is at fault in an accident resulting in injuries or property damage, he or she
may be relieved from criminal punishment if the driver and victim agree to resolve the case
between themselves.
NOTE: An open-ended comprehensive insurance policy (bodily injuries and property damage)
will be considered as an agreement. U.S. Military vehicle operators will not agree to resolve a
vehicle accident with another party. All Government owned vehicles involved in an accident will
be reported to the Korean National Police or Military Police.
b. The following cases are still punishable regardless of an agreement:
(1) Fatal Accident.
(2) Deserting the accident scene without taking necessary actions.
(3) Concealing the victim and then fleeing.
(4) An accident resulting in injuries, by committing one or more of the following
violations:
(a) Violating a traffic signal,
entering a no-entry zone, or running a
stop sign.
(b) Exceeding speed limit
by 20 kilometers per hour.
(c) Unsafe or illegal
passing.
(d) Crossing the centerline.
(e) Driving without a driver’s
license.
(f) Violating railroad crossing
procedures.
(g) Driving while under the
influence of alcohol or drugs.
15

USFK Pam 385-2
(h) Disregarding drivers’ duties to protect pedestrians at crosswalks.
(i) Trespassing on the separated sidewalk or improper crossing.
(j) Negligence of duties to protect passengers from falling off the vehicles.
SECTION V. ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS FOR MILITARY VEHICLES
18. VEHICLE MOVEMENT.
a. Road clearances. When there is any question of road clearance, or in the absence of a
sign indicating measured clearance (width and height), the driver will stop the vehicle and
determine if there is sufficient clearance for the vehicle and its load before attempting to
negotiate an underpass, highway, or bridge.
b. Toll booths. All drivers of military vehicles will come to a complete stop at all toll booths
upon entry and exit from expressways and toll roads.
c. Eating, drinking, or smoking. Drivers of military vehicles will not eat, drink, or smoke
while operating a vehicle.
16

USFK Pam 385-2
19. HIGHWAY CONDITION CODES.
Highway conditions are color coded as follows:
a. Green - road conditions are normal.
b. Amber - only vehicles essential for official business will be allowed to exit the installation.
c. Red - only vehicles on emergency missions are authorized to exit the installation. An
emergency mission is one which meets one or more of the following:
(1) Protection of life and property.
(2) Emergency road repair crews or communication repair crews.
(3) Military police missions.
(4) Transportation regulating missions.
d. Black – road is not passable.
NOTE: Information on current road conditions can be obtained at http://www.usfk.mil
.
20. MAXIMUM USFK VEHICLE SPEED LIMITS. (USFK Reg 190-1)*
(Included in Driver’s Test)
* Vehicle operators will not drive at a speed greater than is reasonable or prudent under the
road and weather conditions and with regard to the actual and potential hazards. The maximum
speed limits are shown below. Military vehicles operators will not exceed maximum speed limits.
a. When passing a marching unit-- 10 MPH/16 KPH
b. On military installations--
(1) Residential Areas 15 MPH/24 KPH
(2) School Zones (when yellow flashing light on) 15 MPH/24 KPH
(3) Parking Area 5 MPH/8 KPH
c. Off-Military Installations--
(1) Within a city, community, or built-up area 35 MPH/56 KPH
(2) Outside a city, community, or built-up area 40 MPH/64 KPH
17

18
USFK Pam 385-2
d. On expressways and toll roads--
(1) For sedan type military vehicles, the minimum speed will be as posted same as
speed limits shown on page 6, speed limit by expressway.
(2) Tactical vehicle (excluding M880/M890/M998/M1000 series
)-- 40MPH/64KPH
(3) All other military vehicles are considered cargo vehicles and speed limit for these
types of vehicles is 50 MPH/80KPH regardless of the time of day.
* Official Government Vehicle.
21. TRAFFIC POINT SYSTEM.
a. Individuals whose driving privileges are suspended or revoked, to include those
individuals with an accumulation of 12 traffic points within 12 consecutive months or 18 traffic
points within 24 consecutive months, will be notified in writing through official channels.
Revocation based on traffic points will be for a minimum of six months. The unit’s Master Driver
will certify that the remedial driving has been completed and report this information to the Unit
Commander.
b. Points assessed against an individual will remain in effect for point accumulation for a
consecutive 24-month period or until separation from the service. This does not include cases
involving immediate reenlistment, change of component, military retirement, or continuation of
SOFA registration as a civilian employee of the U.S. Armed Forces in the ROK. Extension of
tours by civilian and military personnel does not constitute separation from the service or
termination.
c. Military members must attend remedial driver’s training upon the accumulation of six or
more traffic points in six months.
22. MOTORCYCLE AND BICYCLE SAFETY RULES AND DEVICES.
a. Personnel who operate motorcycles/mopeds (regardless of engine size) on a public
street or highway must be licensed IAW USFK Reg 190-1 paragraph 7c.
b. While operating any of above modes of travel, safety must be exercised at all
times. Compliance with ROK motorcycle standards are mandatory, see USFK Reg
190-1, Appendix D (19), Special Rules for Motorcycles.
c. Motorcycles will not be operated on Korean expressways or prohibited highways.
d. Local Installation/Base Commanders may have additional Safety Polices that
have further restrictions. All motorcycles/mopeds regardless of size of Cubic Centimeters (CCs)
must be registered at the Area Vehicle Registration Office.
e. Bicycle Safety: Whether in uniform or not a bicycle safety helmet will be worn at all
times along with a reflective vest. When crossing through a crosswalk, it is a good
practice to walk the bike across to the other side.

USFK Pam 385-2
Users are invited to send comments and suggested improvements on DA Form 2028
(Recommended Changes to Publications and Blank Forms) to the Commander, USFK
(FKSF), Unit #15237, APO AP 96205-5237. This publication is available electronically at:
http://www-hr.korea.army.mil.
FOR THE COMMANDER:
OFFICIAL:
DAVID P. VALCOURT
Lieutenant General, USA
Chief of Staff
F. W. MORRIS
Assistant Adjutant General
DISTRIBUTION:
Electronic Media Only
19

USFK Pam 385-2
APPENDIX A
KOREAN ROAD TRAFFIC SIGNS
교통안전표지일람표
WARNING
SIGNS
주의
표지
101
Cross Intersection
+자형교차로
101-1
T-Intersection
T 자형교차로
102-2
Y-Intersection
Y 자형교차로
101-3
Right Side Road
ㅏ자형교차로
101-4
Left Side Road
ㅓ자형교차로
102
Priority Road
우선도로
103
Right Merge
우합류도로
103-1
Left Merge
좌합류도로
104
Traffiic Circle
회전형교차로
105
Railroad
Crossing
철도건널목
106
Right Curve
우로굽은도로
106-1
Left Curve
좌로굽은도로
107
Right Double
Curve
우로이중굽은도로
107-1
Left Double
Curve
좌로이중굽은도로
108
Two-way Traffic
2 방향통행
109
Upgrade
오르막경사
109-1
Downgrade
내리막경사
110
Road Width
Reduced
노폭감소
110-1
Road Width
Reduced-Right
우차선감소
A-1

USFK Pam 385-2
110-2
Road Width
Reduced-Left
좌차선감소
111
Keep Right
우측방통행
112
May Travel
Either Lane
양측방통행
113
Divided Road
Begins
분리도로시작
113-1
Divided Road
Ends
분리도로끝
114
Traffic
Signal Ahead
신호기
115
Slippery Road
미끄러운도로
116
Wharf/
River Bank
강변도로
117
Bumpy Road
노면요철
117-1
Speed Bump
Ahead
과속방지턱
118
Falling Rocks
낙석도로
119
Loose Gravel/Mud
돌,흙탕물튀는도로
120
Pedestrian
Crossing
횡단보도
121
Children
Protection
어린이보호
122
Bicyclist Ahead
자전거
123
Road Under-
construction
도로공사중
124
Low-flying Aircraft
비행기
125
Cross Wind
횡풍
126
Tunnel Ahead
터널
127
Wild Animal
Protection
야생동물보호
128
Danger
위험
PROHIBITARY
규제
표지
201
Road Closed
통행금지
202
No Entry for
Passenger Cars
승용자동차
통행금지
203
No Entry for
Cargo Vehicles
화물자동차
통행금지
A-2

USFK Pam 385-2
204
No Entry for
Buses
승합자동차
통행금지
205
No Entry for
Motercycles
2 륜자동차
통행금지
206
No Entry for
Passenger
Cars/Motorcycles
승용자동차, 2 륜
자동차 통행금지
206-1
No Tractors
/Cultivators
트랙터및경운기
통행금지
207
No Entry for
Animal Drawn
Vehicles
우마차통행금지
208
No Entry for
Hand Carts
손수레 통행금지
209
No Entry for
Bicycles
자전거 통행금지
210
Do Not Enter
진입금지
210-1
No Through
Traffic
직진금지
211
No Right Turn
우회전금지
211-1
No Left Turn
좌회전금지
212
No Crossing
횡단금지
212-1
No U-Turn
횡단회전금지
213
Do Not Pass
앞지르기금지
214
No Parking or
Stopping
주정차금지
215
No Parking
주차금지
216
Weight Limit
중량제한
217
Height Limit
높이제한
218
Width Limit
폭제한
219
Distance Limit
차간거리제한
220
Maximum Speed
Limit
최고속도제한
221
Minimum Speed
Limit
최저속도제한
223
Slow Down
서행
224
Stop
일시정지
225
Yield
양보
A-3

USFK Pam 385-2
226
Pedestrian
Crossing
Prohibited
보행자횡단금지
226-1
No Pedestrian
Walking
보행자보행금지
227
No Entry for Vehicle
Carrying
Dangerous Material
위험물적재
차량통행금지
MANDATORY
SIGNS
지시
표지
301
Road Reserved
for Motor vehicles
자동차 전용도로
302
Road Reserved
for Bicycles
자전거 전용도로
302-1
For Bicycles
And Pedestrian
자전거 및 보행자
겸용도로
303
Traffic Circle
회전교차로
304
Direction of
Travel
직행
305
Right Turn
우회전
305-1
Left Turn
좌회전
306
Straight or
Right Turn
직행 및 우회전
306-1
Straight of
Left Turn
직행 및 좌회전
307
Right or
Left Turn
좌우회전
308
U-Turn
횡단회전
309
May Travel
Either Direction
양측방통행
310
Keep Right
우측면통행
310-1
Keep Left
좌측면통행
310-2
Proceeding
Direction
진행방향별
통행구분
310-3
Bypass
우회로
312
Use Snow tires
or Chains
스노우 타이어
또는 체인사용
313
Safety Zone
안전지대
314
Parking Permitted
주차허용
314-1
Parking for
Bicycle
자전거 주차장
315
Road Reserved
for Pedestrians
보행자 전용도로
A-4

USFK Pam 385-2
316
Pedestrian
Crossing
횡단보도
317
Children Protection
아동 보호
318
Bicycle Crossing
자전거 횡단도
319
One-way Traffic
일방통행
319-1
One-way Traffic
일방통행
319-2
One-way Traffic
일방통행
320
Unprotected Left
Turn
비보호좌회전
321
Regular Services
Bus Only
버스전용차로
322
HOV Lane
다인승차량
전용차로
A-5

USFK Pam 385-2
APPENDIX B
DRIVER’S ASSISTANCE REQUEST
USEFUL SENTENCES (CHECK) KOREAN
1. Please help me. ( ) 좀 도와주십시요
2. Please notify the military ( ) 저의 사고를 헌병에게
police of my accident. 알려 주십시오.
3. Personnel have been injured ( ) 부상당한 사람이 있어
and need medical aid. 구급조치가 필요합니다.
4. We need assistance from U.S. ( ) 미군 요원의 도움이
military personnel. 필요합니다.
5. Which direction is ____? ( ) ___ 이 어느방향입니까?
6. Where is gasoline station? ( ) 주유소는 어디에 있습니까?
7. We need water. ( ) 물이 필요합니다.
8. We need gasoline/diesel. ( ) 휘발유/디젤이 필요합니다.
9. Maintenance assistance is required. ( ) 차량 정비에 도움이 필요합니다.
10. We have a minor maintenance ( ) 정비상 약간의 문제가
problem but will leave soon. 있습니다만 곧 떠나겠습니다.
11. We need a tow truck from U.S. forces. ( ) 미군 부대의 견인차가
필요합니다.
12. Please help me call this number ____. ( ) ____로 전화할 수 있도록
도와주십시오.
13. Where is a telephone? ( ) 전화는 어디에 있습니까?
14. May I use your telephone? ( ) 전화 좀 쓸 수 있겠습니까?
15. How much do I owe you? ( ) 얼마를 드리면 되겠습니까?
16. My name is _____ ( ) 저의 이름은 _____
17. My car will not operate. ( ) 저의 차가 고장 났습니다.
18. May I park here? ( ) 여기에 주차해도 되겠습니까?
19. How can I contact you later? ( ) 제가 이 다음에 연락 할수
Please write a note for me. 있도록 연락처를 적어 주십시오.
20. Thank you very much for your help. ( ) 도움 주셔서 대단히 감사합니다.
(Gamsa Hammnida)
B-1
